Abstract
An inverted papilloma is a medical condition in which epithelial cells placed on the surface grow in depth into the underlying supporting tissue. The case of a 68-year-old man with a 6-month history of right-sided complete nasal obstruction, who was referred to the ENT Department of our hospital, is presented. The associated symptoms were represented by repeated epistaxis, rhinorrhea and anosmia. From a clinical point of view, a polypous reddish-gray irregular mass, with cauliflower-like appearance, has been described. The formation was friable, richly vascularized, and with minor bleeding on light touch. The patient was diagnosed with inverted papilloma which was treated by endoscopic surgery. By analyzing the clinical, histochemical and immunohistochemical aspects of this case, the cause of tumor growth and its potential for malignant transformation were established. Many particularities are presented in this article: increased regional aggressiveness, its ethmoidal sinus origin, specific symptomatology, paraclinical examinations, all of which were useful in choosing a customized therapy and follow-up program.
Introduction
Inverted papilloma (IP) was first described in 1854 by Ward [1]. IP rates in the sinonasal cavity tumors range between 0.4% and 7% [2]. Incidence ranges between 0.2 and 1.5/100,000 per year [3,4,5] in the general population. Sex ratio ranges between 2 and 5 males to 1 female [2]. The vast majority of IPs occur in adults, with a mean age at diagnosis of 55 years [3,6].
IP etiology is yet unknown. Certain hypotheses have been suggested, but causality has not yet been established for the suspected factors: smoking, allergy or certain occupational exposures [4]. Recurrence and carcinomatous potential have suggested viral origin for many years. An implication of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) has been studied, but inconclusively [2]. For more than 30 years, human papilloma virus (HPV) has been suspected of playing a major role in the pathophysiology of IP, but literature data remains contradictory. The main studies and meta-analyses of recent years show HPV rates varying between 17% and 38%, with ranges from 0% to 70% in individual series [7,8,9]. HPV integration in the cell genome induces overexpression of oncoproteins E6 and E7, which deactivate cell-cycle regulators such as p16, p21, p27, p53, cyclin D1 or retinoblastoma (Rb) gene protein [10,11], of which p53 and p21 have been most widely studied. According to several reports, p53 is found in IP associated with carcinoma and not in benign IP or healthy mucosa [8,10].
IP is generally diagnosed at a late stage, 1–4 years after first onset of sinonasal symptoms [12,13]. Functional signs are non-specific, nasal obstruction, anterior, and/or posterior rhinorrhea, headache, hyposmia or anosmia, epistaxis, or facial pain. In 4–23% of cases, the lesion is asymptomatic and discovered serendipitously [12,14].
Clinical examination by endoscopic exploration of the nasal cavities finds a reddish-gray lobulated tumor, firmer than an inflammatory polyp, with a fairly characteristic “raspberry” aspect [2].
Pathologic examination is essential to diagnosis [11,15,16]. IP may coexist with an inflammatory process showing inflammatory polyps. This accounts for the false negative rates of up to 17% on biopsy reported in the literature, diagnosing inflammatory polyp [13,17], due to insufficient sampling, restricted to the polyps and not the papilloma. In case of unilateral polyp, sinonasal tumor, and IP in particular, should always be suspected; one study reported 16% incidence of IP in patients with a unilateral polyp [18].
Radiologic assessment has two main objectives: precise determination of tumor extension, and location of the tumor site. Sinus computed tomography (CT) is systematic. The aspect on CT is non-specific, with an isodense unilateral homogeneous lesion generally centered on the meatus nasi medius. Microcalcifications within the lesion are found in about 20% of cases, and guide diagnosis [19]. Bone erosion is frequent. IP may be associated with CT images, such as bone lysis, suggestive of malignancy, but biopsy is essential to guiding treatment [2,6].
Endoscopic treatment for IP was first described in 1992 by Waitz and Wigand, and by Kamel in the same year [20,21], and is now for many authors the new gold-standard [16,22,23].
Success depends on complete exposure of the tumor insertion point, allowing total resection, as most recurrences occur early, within 2 years of surgery, usually in the site of the primary lesion [8,15,16]. IP follow-up duration and modalities are not codified; many authors recommend a minimum 3–5 years [6,15,16], others for lifetime follow-up [14].
Case Presentation
We present a case of a 68-year-old man with a 6-month history of completely right-sided nasal obstruction, who was referred to the Department of Ear Nose Throat (ENT) of our hospital. Accompanying symptoms were: repeated epistaxis, rhinorrhea, anosmia.
From a clinical point of view, a polypous reddish-gray irregular mass, with cauliflower-like appearance was described. It was friable, richly vascularized, with mild bleeding after soft contact (Figure 1).
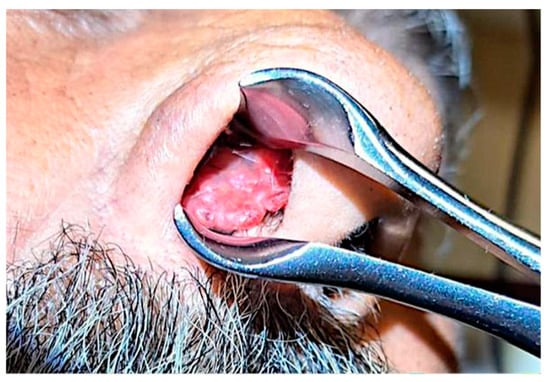
Figure 1.
Clinical aspect of the tumor.
The patient did not present headaches, visual disorders, which led us to the fact that the extension did not reach the sphenoid sinus. Also, he did not present any hearing loss, therefore the extension was not towards Eustachio's tube.
The origin of the tumor could not be established by local anesthesia fibroscopy due to very large-sized mass which exceeded the nasal orifice, not allowing us extensive and full endoscopic examination.
CT showed complete fluid and parafluid accumulation in the right maxillary sinus, with medial sinus wall resorption and antero-lateral walls osteosclerosis, extension of the inflammatory process through the right ostiomeatal complex at the ethmoid cells level as well as at the right frontal sinus level which was completely occupied; this was accompanied by discrete iodophilic right nasal polyposis and thickening of the mucosa at the right sphenoidal sinus level (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
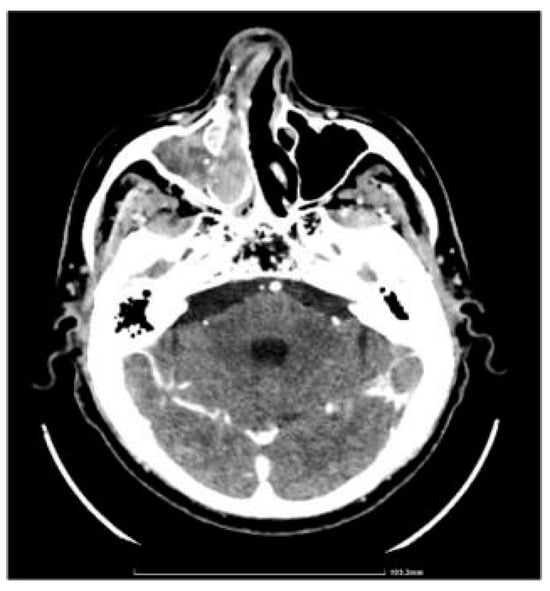
Figure 2.
CT axial section.
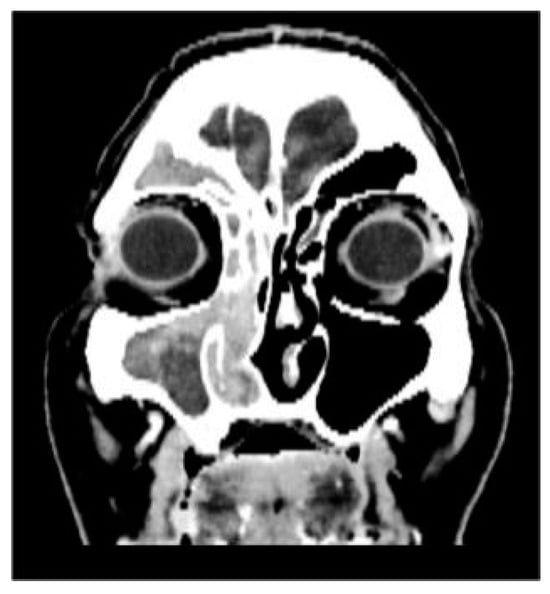
Figure 3.
CT coronal section.
Multiple biopsies ware taken under local anesthesia. The fragments were sent for histopathological (HP) examination (Figure 4).
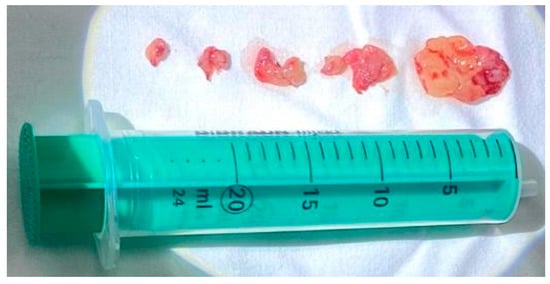
Figure 4.
Biopsy tumor fragments.
HP results reveal: all fragments of respiratory mucosa show at chorionic level, an epithelial papillary pattern proliferation, arranged endophytically. The papillae are composed of stratified squamous epithelium including multiple mucoid cysts and intraepithelial polymorpho-nuclear leukocytes. The chorion is myxoedematous, with moderate diffuse chronic inflammation with multiple eosinophils. Appearance of benign epithelial tumor was represented by Schneiderian papilloma, inverted type.
At this moment we obtained the certainty diagnosis and we prepared for the next step – the surgical treatment. We were guided by the Krouse staging, which helped us decide the most suitable surgical technique, as presented below.
- Stage T1: confined to the nasal cavity
- StageT2: involves ostiomeatal complex region, ethmoid, or medial wall of the maxillary sinus
- Stage T3: involves any wall of the maxillary sinus but medial, frontal sinus, or sphenoid sinus
- Stage T4: any extranasal or extrasinus extension or presence of a malignant neoplasm [24].
We opted for endoscopic surgical treatment with "piecemeal" type ablation of the papillomatous tumor formation at the level of the right nasal fossa, because the inverted papilloma was classified in stage 2 of the Krouse classification. We resected the tumor from its ethmoidal level (antero-posterior ethmoidectomy) to the jaw level (maxillary antrostomy); a portion of the middle nasal turbinate was also resected to the posterior insertion level where a vascular branch from the sphenopalatine artery was cauterized. Many tissue fragments were taken, including maxillary sinus and ethmoid sinus (suspected origin) bone fragments which were all sent for HP examination. Final endoscopic assessment did not reveal residual tumor remains at the right nasal fossa level (Figure 5 and Figure 6).
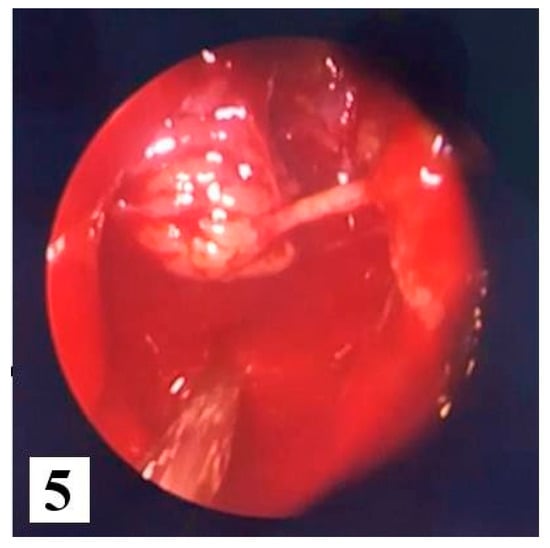
Figure 5.
Intraoperative excision of the tumor.
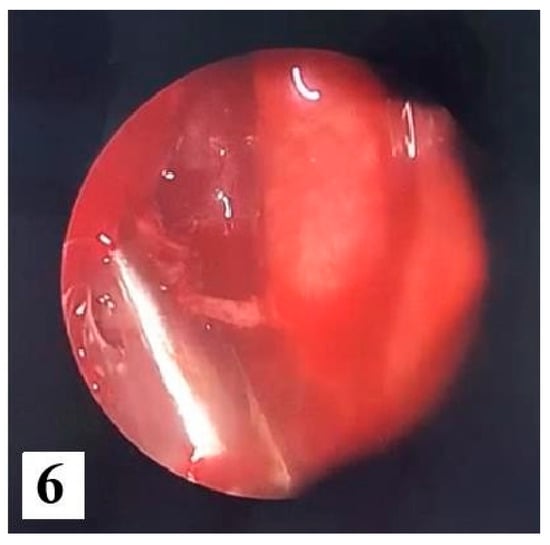
Figure 6.
Final endoscopic assessment without residual tumor.
Postoperative HP examination revealed benign epithelial tumor appearance of inverted Schneiderian papilloma type, present at the right nasal fossa level, maxillary and ethmoidal sinuses with incipient dissociation of ethmoidal bone tissue. Inverted papilloma diagnosis and origin are therefore certified (Figure 7).
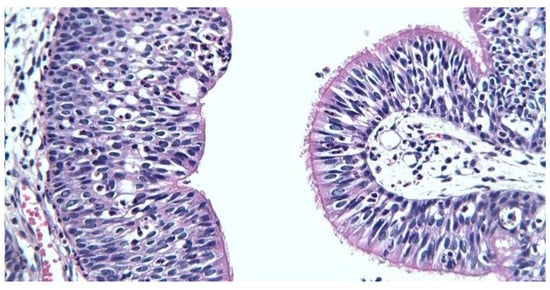
Figure 7.
Respiratory (right) and transitional (left) epithelium, x400.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed with the aim of highlighting the possible etiology of the inverted papilloma and to follow the invasive nature and possible malignant transformation. We opted for immunolabeling for Cytokeratin 5 (CK5), nuclear protein Ki-67, protein p16 and the p53 suppressor gene expression (protein). In our study, IHC results were as presented below. CK5 immunolabeling: CK5 membrane and cytoplasmic markers, positive diffuse throughout the thickness of the epithelium in the squamous areas, predominantly basal and in the intermediate layers in the transitional areas and with respiratory columnar epithelium; the mucus-secreting cells embedded in the metaplastic and surface epithelia were negative (Figure 8).
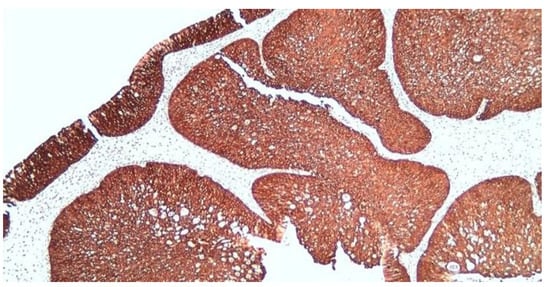
Figure 8.
Diffuse positive CK5 in squamous and transitional epithelial areas, x100.
Ki67 immunolabeling - nuclear markers, positive predominantly basally in the areas with squamous, transitional or respiratory epithelia, with an average proliferation index of approx. 10%. In the scaly areas, there was a focus of areas with a proliferation index higher than the average (25% in the hot spot), with the tendency of markings towards the intermediate layers (Figure 9).
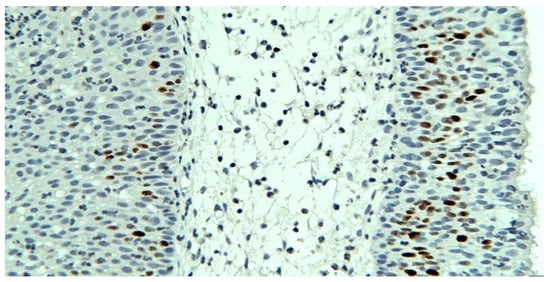
Figure 9.
Ki67 with proliferation index above average, basal and intermediate layer markings, squamous epithelium, x200.
P16 immunolabeling - nuclear and cytoplasmic markings, present throughout the epithelia, throughout the thickness, more frequent superficially; negative mucin secreting cells (Figure 10).
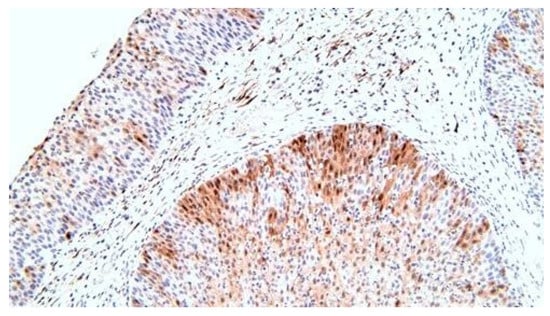
Figure 10.
p16, superior markings at the level of the squamous epithelium compared to that of the respiratory, x200.
P53 immunolabeling – nuclear positive in the basal layer of the epithelia, in less of 10% of the cells, more frequently in the case of squamous epithelia (Figure 11).
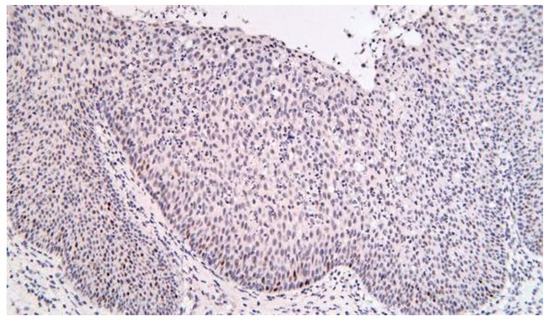
Figure 11.
p53, squamous epithelium, x200.
Patient follow-up was programed at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year and then 2 years and 3 years. At the moment, the control was carried out 1 month after the surgical intervention without noticing any signs of tumor contiguous evolution. The patient did not complain of nasal obstruction or related symptoms, nor did develop new symptoms.
Discussions
The etiology of inverted papilloma remains an unsolved problem. Several causes are suspected to contribute to its development, but none of them has yet been scientifically proven. Different mechanisms are thought to be associated: p53 gene mutation or increased degradation of normal p53 protein, both reducing the tumor-suppression action of p53. p21 mediates cell-cycle arrest in phase G1, and is induced by p53. Relations between HPV, p53 and p21 and their involvement in the oncogenesis of malignant tumors associated with IP are strongly suspected but yet to be fully elucidated [5].
The HPV is involved in the etiology of IP. However, many studies are contradictory, and levels of evidence are generally insufficient to establish a clear line of causality [2,7,9]. Thus, HPV is very probably involved in IP pathogenesis, but present data provide no certainty as to its precise role [2].
The most frequent localization of the inverted papilloma is at the ethmoidal level, a fact also demonstrated in the present case by the histopathological examination of certainty. The most common nasal sites involved by inverted papilloma, in order of descending prevalence, are: lateral nasal wall, ethmoid cells, maxillary sinus, and less often, the frontal and sphenoid sinuses and nasal septum [25].
Regardless of the surgical method chosen, the recurrence rate increases if the tumor was not completely removed. Despite achieving complete surgical removal, recurrences tend to occur. Recurrence rates of inverted papilloma, when treated surgically are as high as 71% [25,26].
There has also been speculation as to whether HPV can lead to higher recurrence rates. Lawson reported in 2008 an odds ratio (OR) of 10.2 when estimating the risk of HPV-positivity in recurrence [9]. More recently, Der Holte et al. [27] used polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) microarrays to detect HPV in 80 IP patients. First and second recurrent IPs were more HPV-positive than non-recurrent IP (60% and 65%, respectively, versus 38.8%).
Referring to IHC, in this case, the discussions regarding immunolabeling are imposed in the following way:
CK5 is a structural protein produced by epithelial cells that helps cells maintain their shape. IHC highlighted the cells that produce CK5 in the tissue sample. This type of protein is found in benign tumors as well as in malignant tumors. In the present case, we were interested in immunohistochemical staining for CK5, which revealed well-defined islands, without an invasive character.
We also opted to measure levels of the nuclear protein Ki-67 to assess how actively cells are dividing, providing insights into the growth behavior of tissues, particularly in tumors. Ki67 immunolabeling allows the distribution of proliferating cells to be evaluated in addition simply to determine the proliferation rate of cells. The Ki67 monoclonal antibody recognizes a nuclear antigen that is present in all phases of the cell growth cycle, but is absent in resting cells [28]. The resulting index helped us observe the benign or malignant character. It is more likely that tumors have a high labeling index, as in this case, where we noted the presence of a large number of dividing cells, suggesting an intermediate potential for malignancy. This aspect provided information about how the inverted papilloma will behave or respond to treatment.
The mutation of the suppressor gene p53 is considered the "guardian of the genome" and has an important risk factor for malignant transformation. This is deactivated in the case of the majority of cancer patients, which allows the unhindered development of cancer.
The p53 protein is encoded by a tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome 17, and the wild-type protein is known to be involved in the negative regulation of cell growth. It is widely accepted that alterations affecting the p53 gene are among the most common changes occurring during malignant transformation [29].
Ingle et al. [30] showed that overexpression of the p53 protein is commonly demonstrable in benign epithelial lesions of the upper respiratory tract. They concluded from their study that p53 protein may accumulate in the absence of p53 gene mutation and may correlate with epithelial proliferative activity. Schwerer et al. [31] also showed overexpression of p53 in inverted papilloma compared with normal nasal mucosa.
In the present case, p53 immunolabeling reveals a low presence of it (in less than 10% of the cells), more frequently in the case of squamous epithelia (tissue with more pronounced turnover), a fact that correlates with an increased potential for malignancy.
Also, we used immunolabeling for p16 to highlight the probable etiology of the inverted papilloma, specifically the human papillomavirus (HPV) because cells infected with this virus produce large amounts of this protein. It should also be noted that HPV-associated precancerous and cancerous tumors such as high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) and squamous cell carcinoma frequently overexpress p16 and pathologists often perform IHC for p16 to help confirm the diagnosis. Lin et al. [32] found that p16 expression usually is preserved in sinonasal IP (SIP), whereas p16 expression is more likely to be lost when the papilloma lesions undergo malignant change. A ‘hit and run’ hypothesis has previously been postulated. This theory implies that HPV may induce SIP formation, however, the non-keratinizing SIP may not be capable of harboring an HPV infection [33].
One of the peculiarities of this inverted papilloma is the possibility of malignancy.
Persistent disease is unacceptable due to the possibility of malignant transformation in squamous cell carcinoma, the incidence of which is as high as 10-15%, according to one study by Roh et al. [34]. In a literature review by von Buchwald and Bradley the risk of transformation of cases to squamous cell carcinoma was quoted as 10% with the rates of synchronous and metachronous malignancy in inverted papilloma being 7.1% and 3.6%, respectively [35]. This aspect can be prevented by a proper follow-up.
The current surgical approach remains endoscopic surgery. Therapeutic success in the case of inverted papilloma requires both complete excision of the tumor formation, with resection of the adjacent mucosa and the underlying bone and periosteum around the tumor insertion. It is extremely important, therefore, to find the origin of the inverted papilloma in order to remove it and reduce the recurrence rates.
Endoscopic treatment for IP was first described in 1992 by Waitz and Wigand, and by Kamel in the same year [20,21], and is now for many authors the new gold-standard [16,22,23]. However, endonasal endoscopic approaches are indicated only for tumors of limited extension.
Conclusions
The inverted papilloma, although it is a benign tumor, still remains a real challenge for the otorhinolaryngologist because it is characterized by strong local aggressiveness and the possibility of malignant transformation.
The etiology is not yet fully elucidated. HPV testing of patients with inverted papilloma could help in the early demystification of this pathology.
Immunohistochemistry helped not only in detecting the etiology in the present case, but especially in elucidating the tendency of malignant transformation of the presented inverted papilloma.
The treatment of choice in the case of inverted papilloma is eminently surgical. Endoscopic surgery lends itself to stages I, II, III Krouse, and for stage IV Krouse the most indicated is either external surgery or combined approach.
Success consists in the complete removal of the inverted papilloma and its point of origin.
The follow-up is extremely important both for the early detection of relapses and for the detection of the malignant transformation in these patients. Should be performed both clinically end endoscopically postoperatively for a minimum of 3 years (at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, one year, then biannually), and clinical yearly assessment for all following years.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Any aspect of the work covered in this manuscript has been conducted with the ethical approval of all relevant bodies and that such approvals are acknowledged within the manuscript. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no known conflicts of interest in the publication of this article. The manuscript was read and approved by all authors.
References
- Ward, N. A mirror of the practice of medicine and surgery in the hospitals of London: London Hospital. Lancet 1854, 2, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinos, D.; Kalamatianos, T.; Terzakis, D.; Piagkou, M.; Georgalas, C. Treatment strategies for inverted papillomas with intracranial or intraorbital involvement. J Laryngol Otol. 2021, 135, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outzen, K.E.; Grøntveld, A.; Jørgensen, K.; Clausen, P.P.; Ladefoged, C. Inverted papilloma: Incidence and late results of surgical treatment. Rhinology. 1996, 34, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buchwald, C.; Franzmann, M.B.; Tos, M. Sinonasal papillomas: A report of 82 cases in Copenhagen County, including a longitudinal epidemiological and clinical study. Laryngoscope. 1995, 105, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sham, C.L.; Woo, J.K.; van Hasselt, C.A.; Tong, M.C. Treatment results of sinonasal inverted papilloma: An 18-year study. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2009, 23, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund VJ, Stammberger H, Nicolai P; et al. European position paper on endoscopic management of tumours of the nose, paranasal sinuses and skull base. Rhinol Suppl. 2010, 22, 1–143. [Google Scholar]
- Syrjänen, K.; Syrjänen, S. Detection of human papillomavirus in sinonasal papillomas: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2013, 123, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sham, C.L.; To, K.F.; Chan, P.K.; Lee, D.L.; Tong, M.C.; van Hasselt, C.A. Prevalence of human papillomavirus, Epstein-Barr virus, p21, and p53 expression in sinonasal inverted papilloma, nasal polyp, and hypertrophied turbinate in Hong Kong patients. Head Neck. 2012, 34, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, W.; Schlecht, N.F.; Brandwein-Gensler, M. The role of the human papillomavirus in the pathogenesis of Schneiderian inverted papillomas: An analytic overview of the evidence. Head Neck Pathol. 2008, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altavilla, G.; Staffieri, A.; Busatto, G.; Canesso, A.; Giacomelli, L.; Marioni, G. Expression of p53, p16INK4A, pRb, p21WAF1/CIP1, p27KIP1, cyclin D1, Ki-67 and HPV DNA in sinonasal endophytic Schneiderian (inverted) papilloma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009, 129, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, A.; Matharu, R.; Hörmann, K.; Naim, R. Current advances in the basic research and clinical management of sinonasal inverted papilloma (review). Oncol Rep. 2007, 17, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrabec, D.P. The inverted Schneiderian papilloma: A 25-year study. Laryngoscope. 1994, 104 (5 Pt 1), 582–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, T.; Atai, E.; Schubert, M.; Glanz, H. Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: Clinical data, surgical strategy and recurrence rates. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000, 120, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minovi, A.; Kollert, M.; Draf, W.; Bockmühl, U. Inverted papilloma: Feasibility of endonasal surgery and long-term results of 87 cases. Rhinology. 2006, 44, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carta F, Blancal JP, Verillaud B; et al. Surgical management of inverted papilloma: Approaching a new standard for surgery. Head Neck. 2013, 35, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi D, Tomenzoli D, Buttà L; et al. Limitations and complications of endoscopic surgery for treatment for sinonasal inverted papilloma: A reassessment after 212 cases. Head Neck. 2011, 33, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.W.; Lee, B.J.; Jang, Y.J.; Chung, Y.S. Clinical value of office-based endoscopic incisional biopsy in diagnosis of nasal cavity masses. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritt, S.; McMains, K.C.; Kountakis, S.E. Unilateral nasal polyposis: Clinical presentation and pathology. Am J Otolaryngol. 2008, 29, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, A.K.; Roberts, C.C.; Chew, F.S. Imaging of chronic and exotic sinonasal disease: Review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007, 189 (Suppl. 6), S35–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waitz, G.; Wigand, M.E. Results of endoscopic sinus surgery for the treatment of inverted papillomas. Laryngoscope. 1992, 102, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, R.H. Conservative endoscopic surgery in inverted papilloma. Preliminary report. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992, 118, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.Y.; Koo, B.S.; Park, Y.H.; Rha, K.S. External vs endoscopic approach for inverted papilloma of the sino-nasal cavities: A retrospective study of 136 cases. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008, 128, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortuaire, G.; Arzul, E.; Darras, J.A.; Chevalier, D. Surgical management of sinonasal inverted papillomas through endoscopic approach. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 264, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krouse, J.H. Development of a staging system for inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope. 2000, 110, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krouse, J.H. Endoscopic treatment of inverted papilloma: Safety and efficacy. Am J Otolaryngol. 2001, 22, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alius, R.O.; Zainea, V.; Voiosu, C.; Ionita, I.G.; Rusescu, A.; Balalau, O.D.; Alius, C.; Pulpa, R.O.; Hainarosie, R. Nasal surgery versus pharyngeal surgery in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. J Mind Med Sci. 2022, 9, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pähler Vor der Holte, A.; Fangk, I.; Glombitza, S.; Wilkens, L.; Welkoborsky, H.J. Prognostic factors and risk factors for development and recurrence of sinonasal papillomas: Potential role of different HPV subtypes. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.J.; Banks, P.M.; O'Malley, D.P. Ki67 staining pattern as a diagnostic tool in the evaluation of lymphoproliferative disorders. Histopathology. 2006, 48, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumbuc, S.; Karakok, M.; Baglam, T.; Karatas, E.; Durucu, C.; Kibar, Y. Immunohistochemical analysis of PCNA, Ki67 and p53 in nasal polyposis and sinonasal inverted papillomas. J Int Med Res. 2007, 35, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle RR, Setzen G, Koltai PJ, Monte D, Pastore J, Jennings TA. p53 protein expression in benign lesions of the upper respiratory tract. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997, 123, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerer, M.J.; Sailer, A.; Kraft, K.; Baczako, K.; Maier, H. Differentiation-related p53 protein expression in nondysplastic sinonasal inverted papillomas. Am J Rhinol. 2001, 15, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin GC, Scheel A, Akkina S; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor, p16, cyclin D1, and p53 staining patterns for inverted papilloma. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dascalu, A.M.; Tudosie, M.S.; Smarandache, G.C.; Serban, D. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon the ophthalmological clinical practice. Rom J Leg Med. 2020, 28, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.J.; Procop, G.W.; Batra, P.S.; Citardi, M.J.; Lanza, D.C. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of inverted papilloma. Am J Rhinol. 2004, 18, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Buchwald C, Bradley PJ. Risks of malignancy in inverted papilloma of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007, 15, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).