Assessment of the Bioaccumulation of Nicotine and Cotinine by the Crustacean Daphnia magna
Abstract
Introduction
Materials and Methods
- Evaluation of the toxicity of nicotine and cotinine on D. magna
- Assessment of the bioaccumulation of nicotine and cotinine by D. magna
Results
Discussions
- Evaluation of bioaccumulation of nicotine and cotinine by D. magna
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guilhermino, L.; Diamantino, T.; Silva, M.C.; Soares, A.M. Acute toxicity test with Daphnia magna: an alternative to mammals in the prescreening of chemical toxicity? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2000, 46, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, M.; De Marchi, L.; Cuccaro, A.; Pretti, C. Bioassay-based ecotoxicological investigation on marine and freshwater impact of cigarette butt littering. Environmental Pollution. 2021, 288, 117787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciucă Anghel, D.M.; Nițescu, G.V.; Tiron, A.T.; Guțu, C.M.; Baconi, D.L. Understanding the Mechanisms of Action and Effects of Drugs of Abuse. Molecules 2023, 28, 4969, Published 2023 Jun 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalaki, A.; McGivern, A.R.; Poschet, G.; Büttner, M.; Altenburger, R.; Grintzalis, K. The Effects of Single and Combined Stressors on Daphnids-Enzyme Markers of Physiology and Metabolomics Validate the Impact of Pollution. Toxics 2022, 10, 604, Published 2022 Oct 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas-Navarro, A.; Rosas-L, E.; Reyes, J.L. The heart of Daphnia magna: effects of four cardioactive drugs. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2003, 136, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corotto, F.; Ceballos, D.; Lee, A.; Vinson, L. Making the Most of the Daphnia Heart Rate Lab: Optimizing the Use of Ethanol, Nicotine & Caffeine. American Biology Teacher. 2010, 72, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Gholap, V.V.; Kosmider, L.; Halquist, M.S. A Standardized Approach to Quantitative Analysis of Nicotine in e-Liquids Based on Peak Purity Criteria Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J Anal Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 1720375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trehy, M.L.; Ye, W.; Hadwiger, M.E. Analysis of electronic cigarette cartridges, refill solutions, and smoke for nicotine and nicotine related impurities. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies. 2011, 34, 1442–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, B.; Dang, M.; Kim, J.; Talbot, P. Nicotine concentrations in electronic cigarette refill and do-it-yourself fluids. Nicotine Tob Res. 2015, 17, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meruva, N.K.; Benvenuti, M.E.; et al. Simultaneous Determination of Nicotine and Related Impurities in E-Liquids and E-Cigarettes Using UPLC-UV-MS; Waters Corporation: Milford, MA, USA, 2016; https://www.waters.com/webassets/cms/library/docs/720005802en.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, R.; Messina, S.M.; Stokes, C.; et al. Solid-phase extraction and HPLC assay of nicotine and cotinine in plasma and brain. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2002, 12, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, M.; VanNoord, T.; Greden, J.F. A high-performance liquid-chromatographic method for routine simultaneous determination of nicotine and cotinine in plasma. Clin Chem. 1988, 34, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, M.; VanNoord, T. Liquid-chromatographic determination of nicotine and cotinine in urine from passive smokers: comparison with gas chromatography with a nitrogen-specific detector. Clin Chem. 1991, 37, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccaro, P.; Altieri, I.; Rosa, M.; et al. Determination of nicotine and four metabolites in the serum of smokers by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr. 1993, 621, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rop, P.P.; Grimaldi, F.; Oddoze, C.; Viala, A. Determination of nicotine and its main metabolites in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1993, 612, 302–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.F.; Nagajothi, G.; Latha, K.S.; et al. Possible role of nicotine and cotinine on nitroxidative stress and antioxidant content in saliva of smokeless tobacco consumers. Pract Lab Med. 2018, 12, e00105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axente, R.E.; Stan, M.; Chitescu, C.L.; et al. Application of Ionic Liquids as Mobile Phase Additives for Simultaneous Analysis of Nicotine and Its Metabolite Cotinine in Human Plasma by HPLC-DAD. Molecules 2023, 28, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, D.A.; Jiang, N.S. Quantification of cotinine in plasma and saliva by liquid chromatography. Clin Chem. 1986, 32, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, G.O.; Leite, C.E.; Chatkin, J.M.; Thiesen, F.V. Cotinine as a biomarker of tobacco exposure: development of a HPLC method and comparison of matrices. J Sep Sci. 2010, 33, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichini, S.; Altieri, I.; Pacifici, R.; et al. Simultaneous determination of cotinine and trans-3′-hydroxycotinine in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1992, 577, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosheh, O.A.; Browne, D.; Rogers, T.; de Leon, J.; Dwoskin, L.P.; Crooks, P.A. A simple high performance liquid chromatographic method for the quantification of total cotinine, total 3′-hydroxycotinine and caffeine in the plasma of smokers. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2000, 23, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasceanu, A.M.; Baconi, D.L.; Ciobanu, A.M.; et al. HPTLC assay of nicotine and cotinine in biological samples. J Mind Med Sci. 2018, 5, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, M.; Burcea-Dragomiroiu, G.T.A.; Vasiliu, A.; Ginghină, O.; Nițescu, G.V.; Vlăsceanu, A.M.; Ciobanu, A.M.; Baconi, D.L. Screening method for the detection of dextromethorphan abuse by HPTLC. Farmacia. 2022, 70, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitulescu, G.M.; Draghici, C.; Olaru, O.T. New potential antitumor pyrazole derivatives: synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation. Int J Mol Sci. 2013, 14, 21805–21818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaru, O.T.; Venables, L.; VANDEVenter, M.; et al. Anticancer potential of selected Fallopia Adans species. Oncol Lett. 2015, 10, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasceanu, A.M.; Olaru, O.T.; Tuchila, C.; et al. Development of a HPLC-DAD method to evaluate the bioaccumulation of nicotine and cotinine by Daphnia magna. Toxicology Letters. 2016, 258, S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitulescu, G.; Nicorescu, I.M.; Olaru, O.T.; et al. Molecular Docking and Screening Studies of New Natural Sortase A Inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci. 2017, 18, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropesa, A.L.; Floro, A.M.; Palma, P. Toxic potential of the emerging contaminant nicotine to the aquatic ecosystem. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017, 24, 16605–16616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, M.C.; Suérez, L.A.; Lassiter, R.R. Modeling bioconcentration of nonpolar organic pollutants by fish. Environ Toxicol Chem. 1988, 7, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.C.; Suárez, L.A.; Lassiter, R.R. Modelling bioaccumulation of organic pollutants in fish with an application to PCBs in lake Ontario Salmonids. Can J Fish Aquatic Sci. 1991, 48, 318–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, J. Measurement of the bioconcentration factors of pesticides by freshwater fish and their correlation with physicochemical properties or acute toxicities. Pesticide Sci. 1981, 12, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, G.D.; DeFoe, D.L.; Bergstedt, B.V. Measuring and estimating the bioconcentration factor of chemicals in fish. J Fish Board Can. 1979, 36, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Franco, A.; Trapp, S. Methods for estimating the bioconcentration factor of ionizable organic chemicals. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2009, 28, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterhaus, S.L.; Grace, R.; Hamilton, M.C.; Yee, D. Method validation and reconnaissance of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and alkylphenols in surface waters, sediments, and mussels in an urban estuary. Environ Int. 2013, 54, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, L.C.; Schnell, S.; Hogstrand, C.; Owen, S.F.; Bury, N.R. A primary fish gill cell culture model to assess pharmaceutical uptake and efflux: evidence for passive and facilitated transport. Aquat Toxicol. 2015, 159, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordet, M.; Berlioz-Barbier, A.; Buleté, A.; et al. Quantification of emerging micropollutants in an amphipod crustacean by nanoliquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry using multiple reaction monitoring cubed mode. J Chromatogr A 2016, 1456, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashauer, R.; Hintermeister, A.; O’Connor, I.; et al. Significance of xenobiotic metabolism for bioaccumulation kinetics of organic chemicals in Gammarus pulex. Environ Sci Technol. 2012, 46, 3498–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith-Williams, M.; Carter, L.J.; Fussell, R.; et al. Uptake and depuration of pharmaceuticals in aquatic invertebrates. Environ Pollut. 2012, 165, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.H.; McEneff, G.L.; Stott, L.C.; Owen, S.F.; Bury, N.R.; Barron, L.P. Assessing the reliability of uptake and elimination kinetics modelling approaches for estimating bioconcentration factors in the freshwater invertebrate, Gammarus pulex. Sci Total Environ. 2016, 547, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.H.; Bury, N.R.; Owen, S.F.; Barron, L.P. Uptake, biotransformation and elimination of selected pharmaceuticals in a freshwater invertebrate measured using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashauer, R.; Hintermeister, A.; Potthoff, E.; Escher, B.I. Acute toxicity of organic chemicals to Gammarus pulex correlates with sensitivity of Daphnia magna across most modes of action. Aquat Toxicol. 2011, 103, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kurth, D.; Hollender, J. Biotransformation pathways of biocides and pharmaceuticals in freshwater crustaceans based on structure elucidation of metabolites using high resolution mass spectrometry. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013, 26, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösch, A.; Anliker, S.; Hollender, J. How Biotransformation Influences Toxicokinetics of Azole Fungicides in the Aquatic Invertebrate Gammarus pulex. Environ Sci Technol. 2016, 50, 7175–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, M.J. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in aquatic invertebrates: recent advances and future directions. Aquat Toxicol. 2000, 48, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretschmann, A.; Ashauer, R.; Preuss, T.G.; Spaak, P.; Escher, B.I.; Hollender, J. Toxicokinetic model describing bioconcentration and biotransformation of diazinon in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol. 2011, 45, 4995–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenaka, Y.; Eun, H.; Ishizaka, M.; Miyabara, Y. Metabolism of pyrene by aquatic crustacean, Daphnia magna. Aquat Toxicol. 2006, 80, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


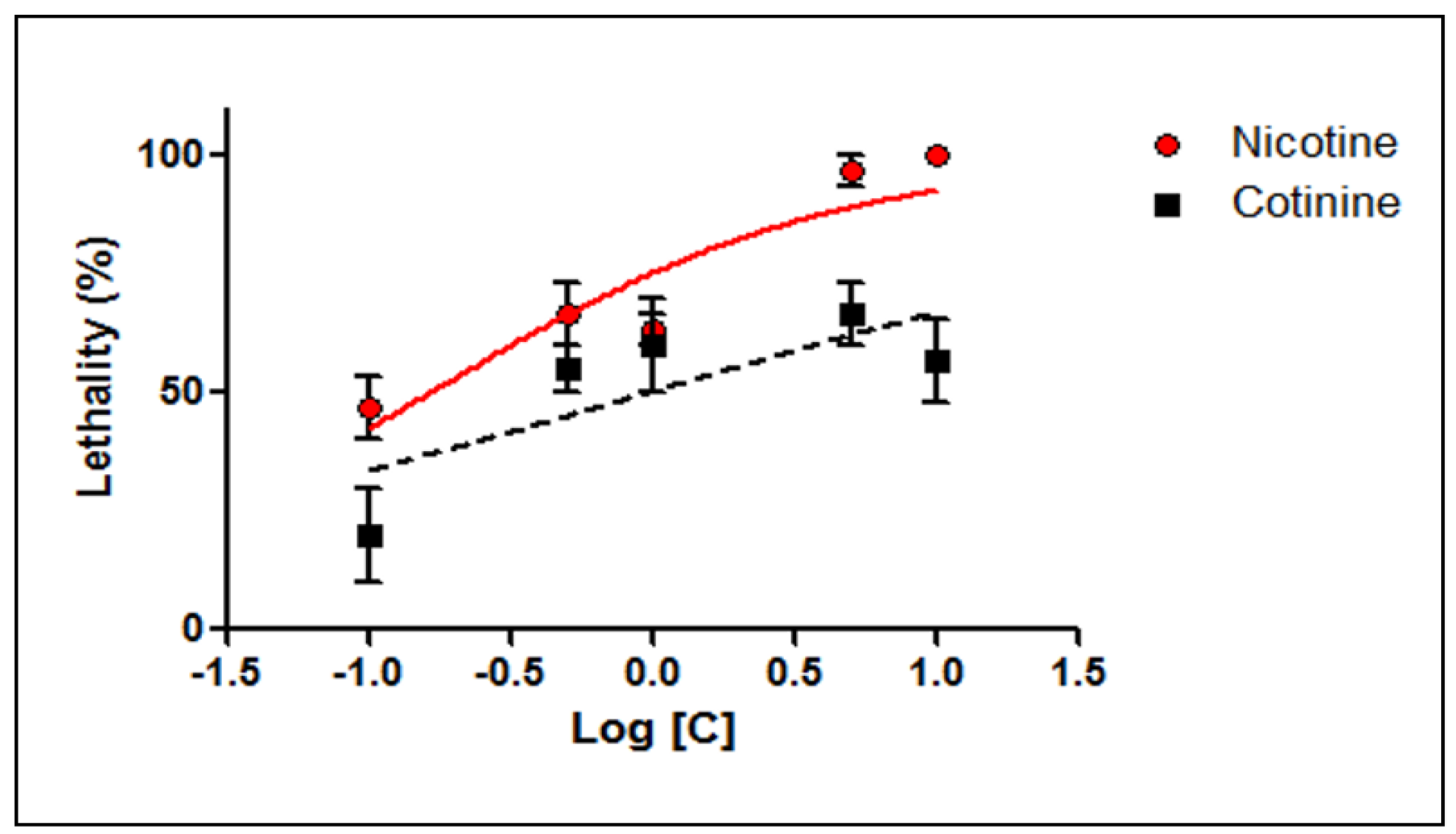
| Compound | Moment of Determination | LC50 (µM) | CI95% of LC50 (µM) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nicotine | 24 h | 2.134 | 1.204–3.781 | 0.7601 |
| 48 h | 0.163 | 0.084–0.316 | 0.7876 | |
| Cotinine | 24 h | ND | ND | ND |
| 48 h | 0.959 | 0.225–4.083 | <0.6000 | |
| ND—not determined; CI95% of LC50—95% confidence interval of LC50; r2—goodness of fit | ||||
| Sample | N | Quantity (µ/g) | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minim | Maxim | Average | ||||
| Nicotine (24 h) | 3 | 3.87 | 4.93 | 4.27 | 0.5736 | 0.3311 |
| Cotinine (24 h) | 3 | 3.47 | 4.54 | 4.17 | 0.3394 | 0.1956 |
| Nicotine in mixture, 24 h | 3 | 3.75 | 4.76 | 4.24 | 0.5056 | 0.2919 |
| Cotinine in mixture, 24 h | 3 | 2.90 | 3.33 | 3.10 | 0.2165 | 0.1250 |
| Cotinine in nicotine samples, 24 h | 3 | 1.17 | 1.44 | 1.29 | 0.1365 | 0.0788 |
| Nicotine 48 h | 3 | 1.84 | 2.34 | 2.10 | 0.2516 | 0.1453 |
| Cotinine 48 h | 3 | 3.43 | 4.01 | 3.81 | 0.3292 | 0.1900 |
| Nicotine in mixture, 48 h | 3 | 1.02 | 1.56 | 1.31 | 0.2730 | 0.1576 |
| Cotinine in mixture, 48 h | 3 | 2.58 | 3.30 | 2.92 | 0.3611 | 0.2085 |
| Cotinine in nicotine samples | 3 | 1.87 | 2.39 | 2.10 | 0.2640 | 0.1524 |
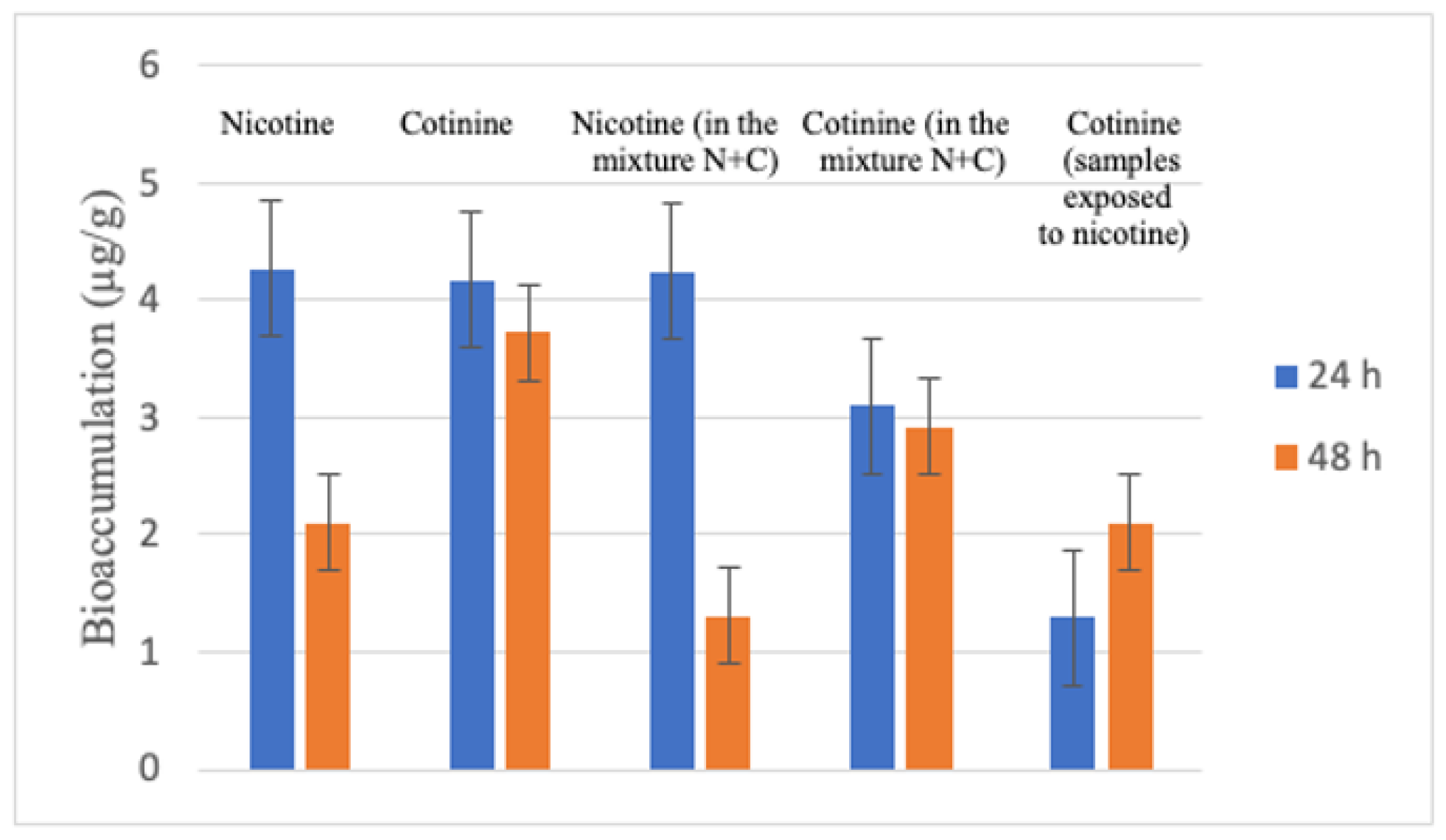
| Substance | Determined Quantity (µg/g) * | |
|---|---|---|
| Exposure 24 h | Exposure 48 h | |
| Nicotine | 4.27 +/− 0.331 | 2.10 +/− 0.145 |
| Cotinine | 4.17 +/− 0.195 | 3.72 +/− 0.190 |
| Nicotine (determined in the samples exposed to the mixture (nicotine+cotinine) | 4.24 +/− 0.291 | 1.31 +/− 0.157 |
| Cotinine (determined in the samples exposed to the mixture nicotine+cotinine) | 3.10 +/− 0.125 | 2.92 +/− 0.208 |
| Cotinine (determined in the samples exposed to nicotine) | 1.29 +/− 0.078 | 2.10 +/− 0.152 |
| * average +/− standard error | ||
© 2024 by the authors. 2008 Ana Maria Vlasceanu, Daniela Luiza Baconi, Octavian Tudorel Olaru, Daniela Grădinaru, Viorela Gabriela Nitescu.
Share and Cite
Vlasceanu, A.M.; Baconi, D.L.; Olaru, O.T.; Grădinaru, D.; Nitescu, V.G. Assessment of the Bioaccumulation of Nicotine and Cotinine by the Crustacean Daphnia magna. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2024, 11, 459-465. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1540
Vlasceanu AM, Baconi DL, Olaru OT, Grădinaru D, Nitescu VG. Assessment of the Bioaccumulation of Nicotine and Cotinine by the Crustacean Daphnia magna. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2024; 11(2):459-465. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1540
Chicago/Turabian StyleVlasceanu, Ana Maria, Daniela Luiza Baconi, Octavian Tudorel Olaru, Daniela Grădinaru, and Viorela Gabriela Nitescu. 2024. "Assessment of the Bioaccumulation of Nicotine and Cotinine by the Crustacean Daphnia magna" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 11, no. 2: 459-465. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1540
APA StyleVlasceanu, A. M., Baconi, D. L., Olaru, O. T., Grădinaru, D., & Nitescu, V. G. (2024). Assessment of the Bioaccumulation of Nicotine and Cotinine by the Crustacean Daphnia magna. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 11(2), 459-465. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1540



