Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Involved in Acute Mesenteric Ischemia
Abstract
Highlights
- ✓
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a complex disease with major complications in systemic vascularization.
- ✓
- Affecting the vascularization of the small intestine, diabetes can lead to acute mesenteric ischemia.
Abstract
Introduction
Discussions
Arterial embolism
Arterial thrombosis
Nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia (NOMI)
Venous thrombosis
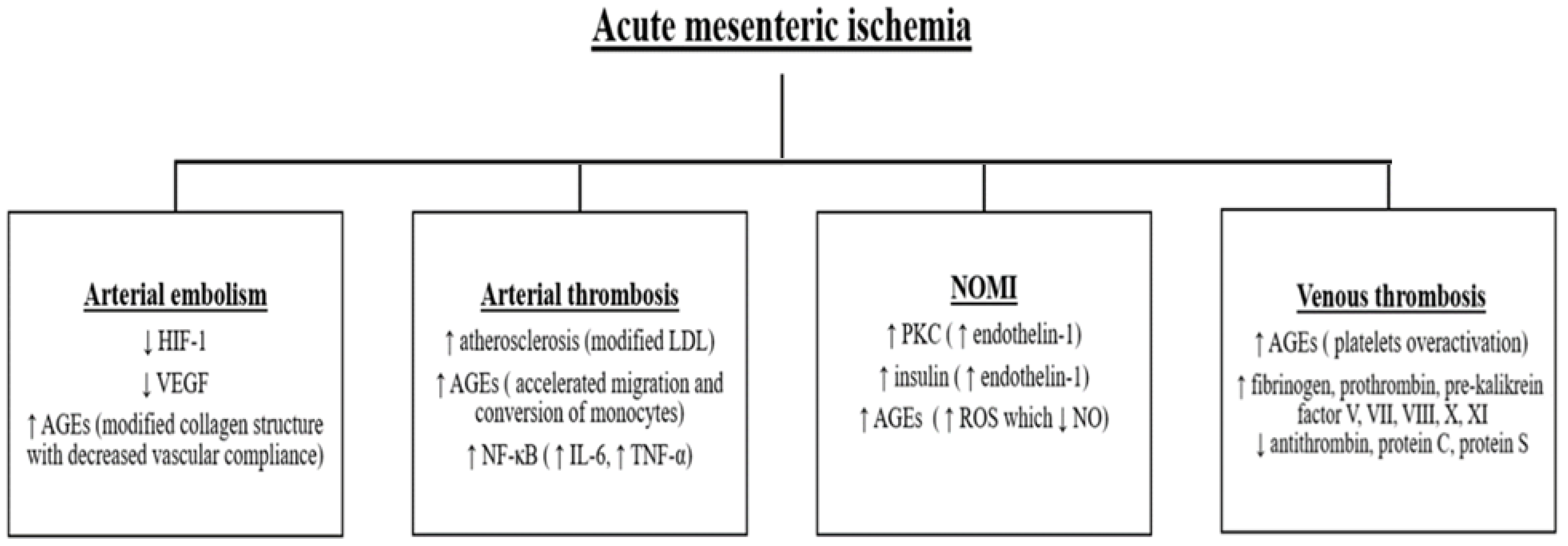
Acute mesenteric infarction outcome in diabetic patients
Conclusions
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest disclosure
Abbreviations
| AMI: | acute mesenteric ischemia |
| T2DM: | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
References
- Lam, A.A.; Lepe, A.; Wild, S.H.; Jackson, C. Diabetes comorbidities in low- and middle-income countries: An umbrella review. J Glob Health. 2021, 11, 04040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Toh, M.P.; Ko, Y. Cost-of-illness studies of diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014, 105, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.W.; Wu, C.S.; Chen, P.C.; Wei, Y.C.; Hsu, L.Y.; Wang, S.H. Risk of acute mesenteric ischemia in patients with diabetes: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Atherosclerosis. 2020, 296, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Kaleya, R.N.; Sammartano, R.J. Pathophysiology of mesenteric ischemia. Surg Clin North Am. 1992, 72, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gragossian, A.; Shaydakov, M.E.; Dacquel, P. Mesenteric Artery Ischemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 8 August 2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kassahun, W.T.; Schulz, T.; Richter, O.; Hauss, J. Unchanged high mortality rates from acute occlusive intestinal ischemia: six year review. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2008, 393, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlke, M.H.; Asshoff, L.; Popp, F.C.; et al. Mesenteric ischemia--outcome after surgical therapy in 83 patients. Dig Surg. 2008, 25, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, B.M.; Khan, Z.; Abu-Fadel, M.S.; et al. Endovascular treatment of mesenteric ischemia. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011, 78, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, S.; Surani, S.R. Guidelines for Perioperative Management of the Diabetic Patient. Surg Res Pract. 2015, 2015, 284063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Gorman, J.; Hoffman, S.N.; Zhang, L.; Boscarino, J.A. Perioperative hyperglycemia is associated with postoperative neurocognitive disorders after cardiac surgery. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014, 10, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Li, X.; Jin, X.; An, P.; Fang, Y.; Mu, Y. Postoperative adverse events in patients with diabetes undergoing orthopedic and general surgery. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019, 98, e15089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkeviciute-Ulinskiene, D.; Kaceniene, A.; Dulskas, A.; Patasius, A.; Zabuliene, L.; Smailyte, G. Increased Mortality Risk in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Lithuania. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020, 17, 6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.; et al. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheleme, T.; Mamo, G.; Melaku, T.; Sahilu, T. Prevalence, Patterns and Predictors of Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus at a Large Referral Hospital in Ethiopia: A Prospective Observational Study. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020, 13, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ageely, H. Long-term diabetes-related severe complications among individuals with T2DM in Jazan, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Acute Disease 2019, 8, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fu, C.; Wang, W.; Xu, B. Prevalence of chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in outpatients - a cross-sectional hospital based survey in urban China. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2010, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, M.J. Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2008, 26, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithian, K.; Hurel, S. Microvascular complications: pathophysiology and management. Clin Med (Lond). 2010, 10, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, W.A.; Lau, L.L.; Rodenberg, T.J.; Edmonds, H.J.; Burger, C.D. Acute mesenteric ischemia: a clinical review. Arch Intern Med. 2004, 164, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, M.; Kashuk, J.; Moore, E.E.; et al. Acute mesenteric ischemia: guidelines of the World Society of Emergency Surgery. World J Emerg Surg. 2017, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Chen, S.; Cao, H.; Wang, W.; Gao, Q. Review: Acute superior mesenteric artery embolism: A vascular emergency cannot be ignored by physicians. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019, 98, e14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boley, S.J.; Feinstein, F.R.; Sammartano, R.; Brandt, L.J.; Sprayregen, S. New concepts in the management of emboli of the superior mesenteric artery. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1981, 153, 561–569. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.S.; Kim, J.D.; Kim, H.C.; et al. Percutaneous Aspiration Embolectomy Using Guiding Catheter for the Superior Mesenteric Artery Embolism. Korean J Radiol. 2015, 16, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raizada, A.; Apte, N.; Pham, S. Q Fever Endocarditis Presenting with Superior Mesenteric Artery Embolism and Renal Infarction. Tex Heart Inst J. 2016, 43, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.A.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995, 92, 5510–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziello, J.E.; Jovin, I.S.; Huang, Y. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 regulatory pathway and its potential for therapeutic intervention in malignancy and ischemia. Yale J Biol Med. 2007, 80, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Catrina, S.B.; Okamoto, K.; Pereira, T.; Brismar, K.; Poellinger, L. Hyperglycemia regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein stability and function. Diabetes. 2004, 53, 3226–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howangyin, K.Y.; Silvestre, J.S. Diabetes mellitus and ischemic diseases: molecular mechanisms of vascular repair dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014, 34, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, C.F.; Pereira, P. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and the loss of the cellular response to hypoxia in diabetes. Diabetologia. 2011, 54, 1946–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.G.; Bailey, A.J. Glycation of collagen: the basis of its central role in the late complications of ageing and diabetes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1996, 28, 1297–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Bali, A.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic complications. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkrief, L.; Corcos, O.; Bruno, O.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for intestinal resection in patients with superior mesenteric vein thrombosis. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.A. Management of acute mesenteric ischemia. Arch Surg. 1999, 134, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastoraki, A.; Mastoraki, S.; Tziava, E.; et al. Mesenteric ischemia: Pathogenesis and challenging diagnostic and therapeutic modalities. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2016, 7, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, G.D. Common risk factors for both arterial and venous thrombosis. Br J Haematol. 2008, 140, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; et al. Diabetes Mellitus Promotes the Development of Atherosclerosis: The Role of NLRP3. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 900254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraya, T.Y.; Leibson, C.L.; Palumbo, P.J.; et al. Coronary atherosclerosis in diabetes mellitus: a population-based autopsy study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002, 40, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooradian, A.D. Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2009, 5, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerhill, V.I.; Grechko, A.V.; Yet, S.F.; Sobenin, I.A.; Orekhov, A.N. The Atherogenic Role of Circulating Modified Lipids in Atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.; Grechko, A.V.; Poggio, P.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Alfieri, V.; Orekhov, A.N. The Diabetes Mellitus-Atherosclerosis Connection: The Role of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism and Chronic Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berneis, K.K.; Krauss, R.M. Metabolic origins and clinical significance of LDL heterogeneity. J Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1363–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Uribarri, J. Advanced glycation end products (AGE) and diabetes: cause, effect, or both? Curr Diab Rep. 2014, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brănescu, C.; Serban, D.; Dascălu, A.M.; Oprescu, S.M.; Savlovschi, C. Interleukin 6 and lipopolysaccharide binding protein - markers of inflammation in acute appendicitis. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2013, 108, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Socea, B.; Silaghi, A.; Rebegea, L.F.; et al. Diabetes mellitus: interdisciplinary medical, surgical and psychological therapeutic approach. J Mind Med Sci. 2023, 10, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakami, N. Mechanism of Development of Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease in Diabetes Mellitus. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018, 25, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, S.V.; Kulkarni, Y.A. NF-κβ: A Potential Target in the Management of Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Front Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschoff, A.J.; Stuber, G.; Becker, B.W.; et al. Evaluation of acute mesenteric ischemia: accuracy of biphasic mesenteric multi-detector CT angiography. Abdom Imaging. 2009, 34, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, G.; Raspanti, C.; Licari, L.; et al. Non-Occlusive Mesenteric Ischemia (NOMI) in Parkinson's disease: case report. G Chir. 2017, 38, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascalu, A.M.; Tudosie, M.S.; Smarandache, G.C.; Serban, D. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic upon the ophthalmological clinical practice. Rom J Leg Med. 2020, 28, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalani, M. The importance of endothelin-1 for microvascular dysfunction in diabetes. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Evcimen, N.; King, G.L. The role of protein kinase C activation and the vascular complications of diabetes. Pharmacol Res. 2007, 55, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.E.; Dickens, M.; Tavare, J.M.; Roth, R.A. Overexpression of protein kinase C isoenzymes alpha, beta, I.; gamma, and epsilon in cells overexpressing the insulin receptor. Effects on receptor phosphorylation and signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993, 268, 6338–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Inoguchi, T.; Kern, T.S.; et al. Characterization of the mechanism for the chronic activation of diacylglycerol-protein kinase C pathway in diabetes and hypergalactosemia. Diabetes. 1994, 43, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, P.; King, G.L. Activation of protein kinase C isoforms and its impact on diabetic complications. Circ Res. 2010, 106, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Takahara, N.; Gabriele, A.; et al. Induction of endothelin-1 expression by glucose: an effect of protein kinase C activation. Diabetes. 2000, 49, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, S.B.; Williams, I.L.; Shah, A.M.; Kearney, M.T. Pathophysiological implications of insulin resistance on vascular endothelial function. Diabet Med. 2003, 20, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seligman, B.G.; Biolo, A.; Polanczyk, C.A.; Gross, J.L.; Clausell, N. Increased plasma levels of endothelin 1 and von Willebrand factor in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia. Diabetes Care. 2000, 23, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.B.; Cusco, J.A.; Roddy, M.A.; Johnstone, M.T.; Creager, M.A. Impaired nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996, 27, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev. 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme, P.; Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.N.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of ROS production and oxidative stress in diabetes. Biochem J. 2016, 473, 4527–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masha, A.; Dinatale, S.; Allasia, S.; Martina, V. Role of the decreased nitric oxide bioavailability in the vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.; Armstrong, P. Plasma biomarkers for early diagnosis of acute intestinal ischemia. Semin Vasc Surg. 2014, 27, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoots, I.G.; Koffeman, G.I.; Legemate, D.A.; Levi, M.; van Gulik, T.M. Systematic review of survival after acute mesenteric ischaemia according to disease aetiology. Br J Surg. 2004, 91, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, D.D., Jr. Pathophysiology of venous thrombosis. Phlebology. 2015, 30, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Kroll, A.; Goldberg, R.J.; Emery, C.; Spencer, F.A. Venous thromboembolism in patients with diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2012, 125, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clenciu, D.; Cojan, T.S.T.; Dijmarescu, A.L.; et al. Diabetic Retinopathy in Relation with eGDR Value in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Revista de Chimie (Rev. Chim.) 2019, 70, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busnatu, S.S.; Salmen, T.; Pana, M.A.; et al. The Role of Fructose as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor: An Update. Metabolites. 2022, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Rojas, A.; Palomo, I. Role of multiligand/RAGE axis in platelet activation. Thromb Res. 2014, 133, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.A.; Eybrechts, K.L.; Mocking, A.I.; Kroner, C.; Akkerman, J.W. IRS-1 mediates inhibition of Ca2+ mobilization by insulin via the inhibitory G-protein Gi. J Biol Chem. 2004, 279, 3254–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.A.; Mocking, A.I.; Feijge, M.A.; Gorter, G.; van Haeften, T.W.; et al. Platelet inhibition by insulin is absent in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006, 26, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Weber, N.C.; Cohn, D.M.; et al. Effects of Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus on Coagulation and Hemostasis. J Clin Med. 2021, 10, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembde, A.S. A study of plasma fibrinogen level in type-2 diabetes mellitus and its relation to glycemic control. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2012, 28, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, A.R.; Wolska, N.; Vara, D.; Mailer, R.K.; Schröder, K.; Pula, G. Diabetes and Thrombosis: A Central Role for Vascular Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, M.; Stoian, A.P.; Rizzo, M.; et al. The Role of Endothelium in COVID-19. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkleij, C.J.; Bruijn, R.E.; Meesters, E.W.; Gerdes, V.E.; Meijers, J.C.; Marx, P.F. The hemostatic system in patients with type 2 diabetes with and without cardiovascular disease. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2011, 17, E57–E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasescu, D.; Moisin, A.; Fleaca, R.; et al. Modern therapeutic options in diabetic foot ulcer. J Mind Med Sci. 2022, 9, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, D.; Tribus, L.C.; Vancea, G.; et al. Acute Mesenteric Ischemia in COVID-19 Patients. J Clin Med. 2021, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiridou, E.; Makris, D.; Chatzipantazi, V.; et al. Diabetes and hemoglobin a1c as risk factors for nosocomial infections in critically ill patients. Crit Care Res Pract. 2013, 2013, 279479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomposelli, J.J.; Baxter, J.K., 3rd; Babineau, T.J.; et al. Early postoperative glucose control predicts nosocomial infection rate in diabetic patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1998, 22, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinsley, J.S. Association between hyperglycemia and increased hospital mortality in a heterogeneous population of critically ill patients. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003, 78, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2024 by the authors. 2024 Andreea Pușcașu, Florin Bobîrcă, Alexandra Bolocan, Ion Daniel, Octavian Andronic, Dan Nicolae Păduraru
Share and Cite
Pușcașu, A.; Bobîrcă, F.; Bolocan, A.; Daniel, I.; Andronic, O.; Păduraru, D.N. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Involved in Acute Mesenteric Ischemia. J. Mind Med. Sci. 2024, 11, 291-298. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1519
Pușcașu A, Bobîrcă F, Bolocan A, Daniel I, Andronic O, Păduraru DN. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Involved in Acute Mesenteric Ischemia. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2024; 11(2):291-298. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1519
Chicago/Turabian StylePușcașu, Andreea, Florin Bobîrcă, Alexandra Bolocan, Ion Daniel, Octavian Andronic, and Dan Nicolae Păduraru. 2024. "Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Involved in Acute Mesenteric Ischemia" Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences 11, no. 2: 291-298. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1519
APA StylePușcașu, A., Bobîrcă, F., Bolocan, A., Daniel, I., Andronic, O., & Păduraru, D. N. (2024). Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Involved in Acute Mesenteric Ischemia. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences, 11(2), 291-298. https://doi.org/10.22543/2392-7674.1519


