Comparison of CT and Dixon MR Abdominal Adipose Tissue Quantification Using a Unified Computer-Assisted Software Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Image Acquisition
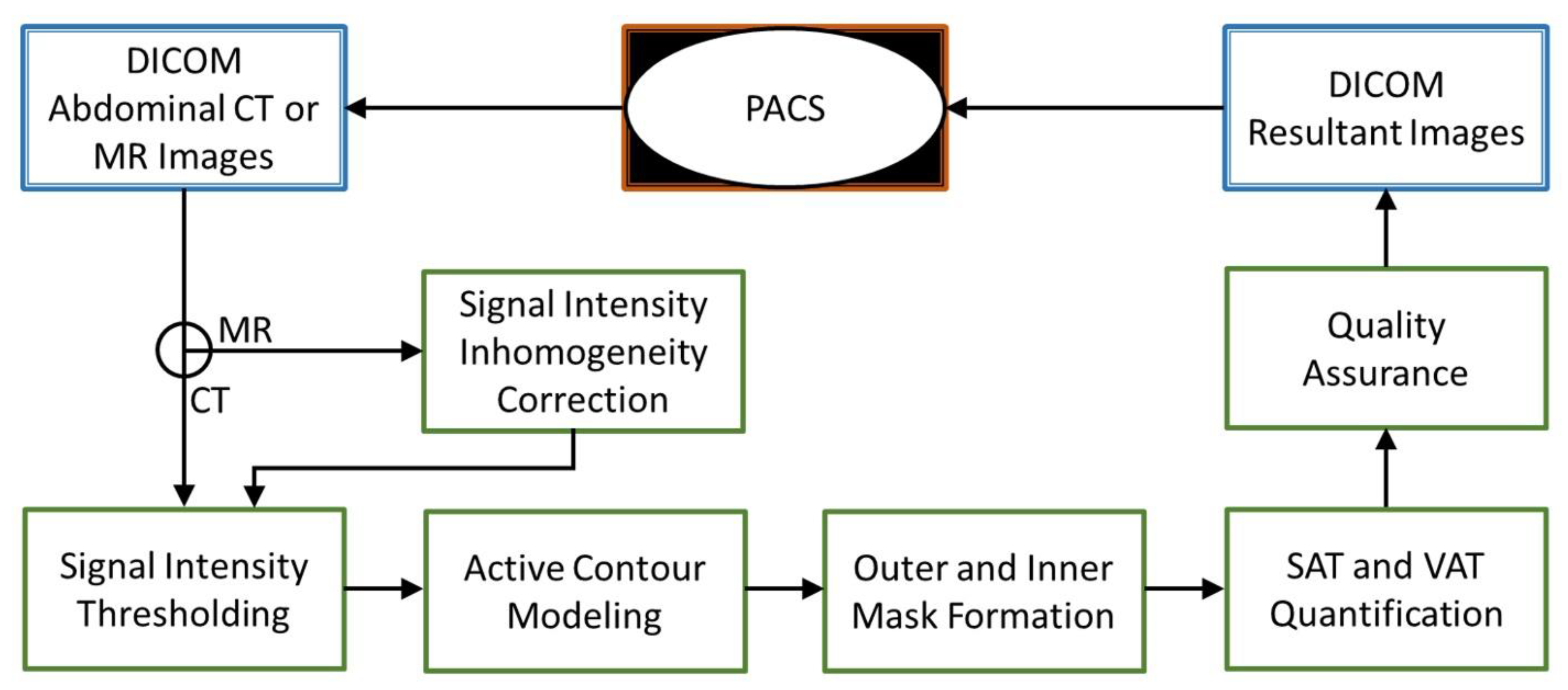
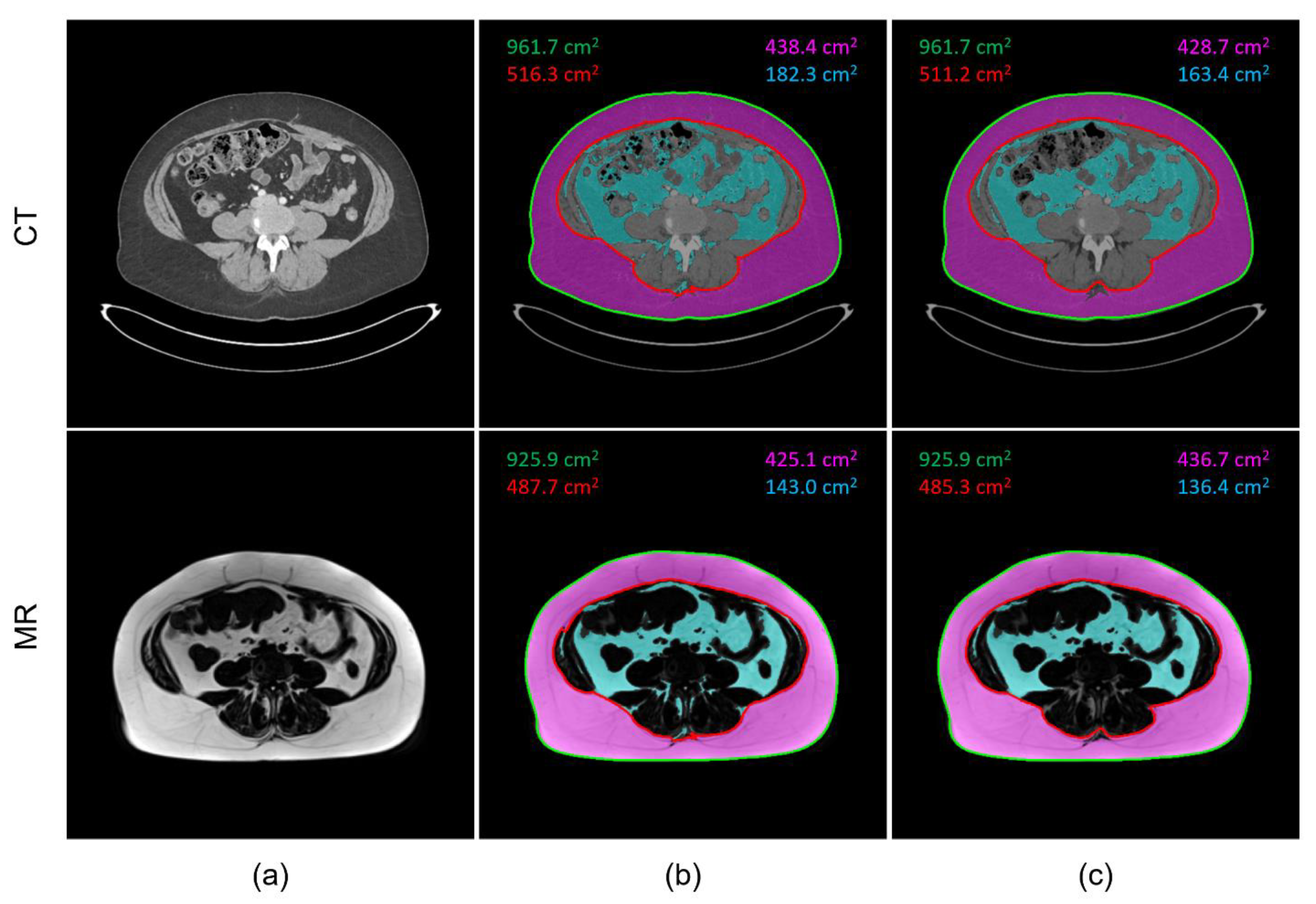
2.3. Image Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
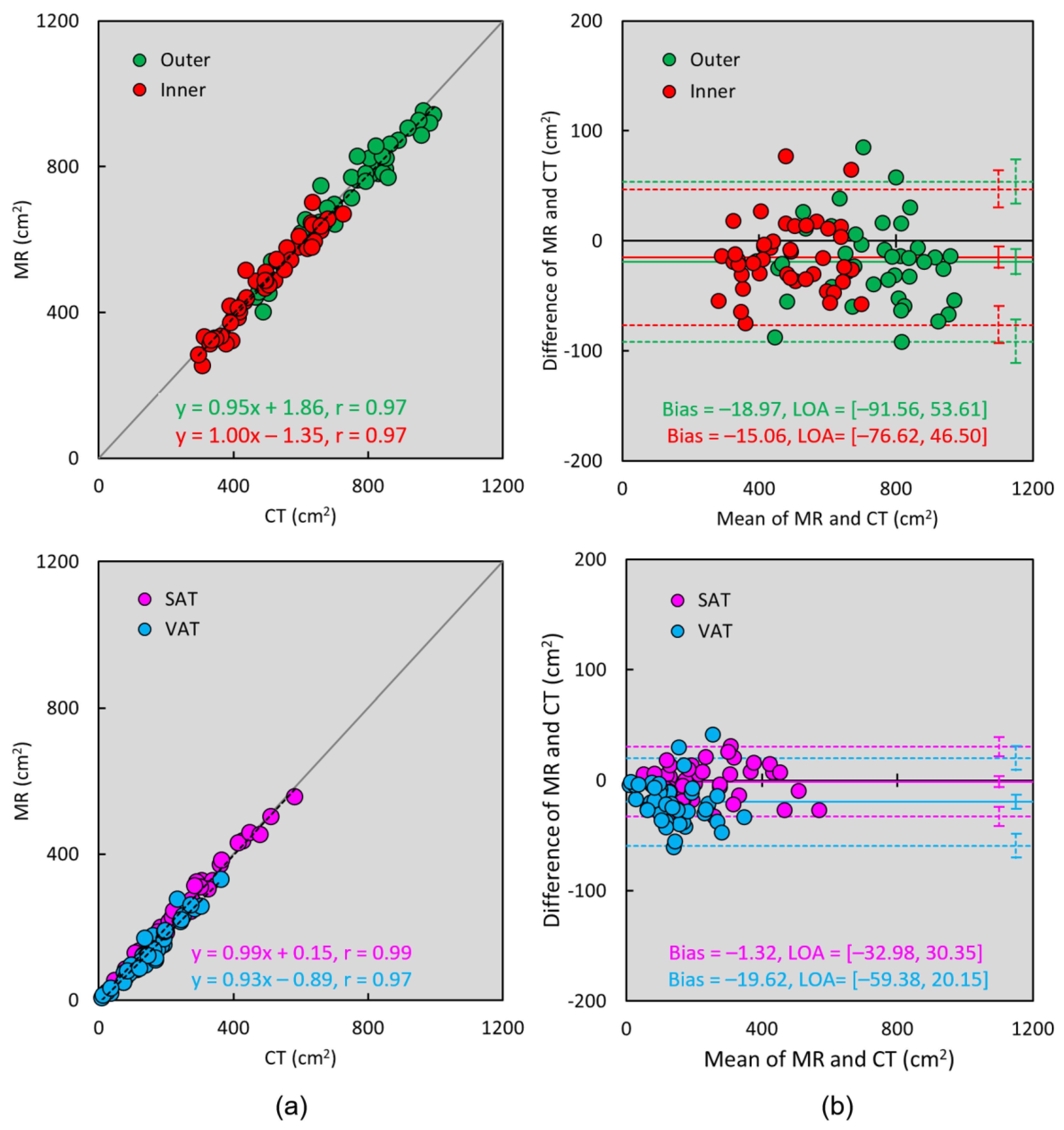
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT | computed tomography |
| DICOM | digital imaging and communications in medicine |
| HU | Hounsfield unit |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| PACS | picture archiving and communication system |
| SAT | subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| VAT | visceral adipose tissue |
References
- Després, J.-P.; Lemieux, I.; Bergeron, J.; Pibarot, P.; Mathieu, P.; LaRose, E.; Rodés-Cabau, J.; Bertrand, O.F.; Poirier, P. Abdominal Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome: Contribution to Global Cardiometabolic Risk. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.S. Body Fat Distribution and the Risk of Incident Metabolic Syndrome: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elffers, T.W.; De Mutsert, R.; Lamb, H.J.; De Roos, A.; Van Dijk, K.W.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Jukema, J.W.; Trompet, S. Body fat distribution, in particular visceral fat, is associated with cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Berg, E.; Cheng, X.; Shen, W. How to best assess abdominal obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2018, 21, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.H.; Chen, J.; Shen, W. Segmentation and quantification of adipose tissue by magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Mater. Physics, Biol. Med. 2016, 29, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, W.T. Simple proton spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 1984, 153, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J. Dixon techniques for water and fat imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 28, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.; Leger, L.; Guardo, R.; de Guise, J.; Pike, B. Adipose tissue volume measured by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography in rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 70, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidell, J.C.; Bakker, C.J.; van der Kooy, K. Imaging techniques for measuring adipose-tissue distribution--a comparison between computed tomography and 1.5-T magnetic resonance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopfenstein, B.J.; Kim, M.S.; Krisky, C.M.; Szumowski, J.; Rooney, W.D.; Purnell, J.Q. Comparison of 3 T MRI and CT for the measurement of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue in humans. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e826–e830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Massaro, J.; Fox, C.S.; Moselewski, F.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Hoffmann, U. Comparison of anthropometric, area- and volume-based assessment of abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue volumes using multi-detector computed tomography. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, M. MRI adipose tissue and muscle composition analysis—A review of automation techniques. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20180252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussman, D.L.; Yao, J.; Summers, R.M. Automated fat measurement and segmentation with intensity inhomogeneity correction. Proc. SPIE Med. Imaging 2010, 7623, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Sussman, D.L.; Summers, R.M. Fully automated adipose tissue measurement on abdominal CT. Proc. SPIE Med. Imaging Med. Imaging 2011, 7965, 79651Z–79651Z-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-Y.; Aletras, A.H.; Arai, A. Correcting surface coil intensity inhomogeneity improves quantitative analysis of cardiac magnetic resonance images. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, Paris, France, 14–17 May 2008; pp. 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.; Witkin, A.; Terzopoulos, D. Snakes: Active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1988, 1, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, R.; Thamizhvani, T.; Dhivya, A.J.A.; Joseph, J.E.; Babu, B.; Chandrasekaran, R. Active Contour Based Segmentation Techniques for Medical Image Analysis. Med. Biol. Image Anal. 2018, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Kawawa, Y.; Nagamoto, M.; Terada, H.; Kohda, E. Measurement of visceral fat/subcutaneous fat ratio by 0.3 tesla MRI. Radiat. Med. 2005, 23, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heckman, K.M.; Otemuyiwa, B.; Chenevert, T.L.; Malyarenko, D.; Derstine, B.A.; Wang, S.C.; Davenport, M.S. Validation of a DIXON-based fat quantification technique for the measurement of visceral fat using a CT-based reference standard. Abdom. Imaging 2019, 44, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waduud, M.A.; Sharaf, A.; Roy, I.; Lopez-Gonzalez, R.; Hart, A.; McGill, D.; Roditi, G.; Biddlestone, J. Validation of a semi-automated technique to accurately measure abdominal fat distribution using CT and MRI for clinical risk stratification. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, K.G.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Park, J.Y.; et al. Body Fat Assessment Method Using CT Images with Separation Mask Algorithm. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N.; Sugimoto, M.; Psutka, S.; Chen, B.; Moynagh, M.R.; Carter, R.E. Validation study of a new semi-automated software program for CT body composition analysis. Abdom. Imaging 2017, 42, 2369–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, A.M.; Coletta, A.M.; Yu, Z.H.; Rauch, G.M.; Cheung, J.P.; Court, L.E.; Klopp, A.H. Development and validation of a rapid and robust method to determine visceral adipose tissue volume using computed tomography images. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozola-Zālīte, I.; Mark, E.; Gudauskas, T.; Lyadov, V.; Olesen, S.S.; Drewes, A.; Pukitis, A.; Frokjær, J.B. Reliability and validity of the new VikingSlice software for computed tomography body composition analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Positano, V.; Gastaldelli, A.; Sironi, A.M.; Santarelli, M.F.; Lombardi, M.; Landini, L. An accurate and robust method for unsupervised assessment of abdominal fat by MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 20, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, T.-H.; Chan, W.P.; Pan, L.-C.; Lin, P.-W.; Chou, P.; Chen, C.-H. Fully automated large-scale assessment of visceral and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue by magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Murillo, H.; Peng, Q. Novel segmentation method for abdominal fat quantification by MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 34, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würslin, C.; Machann, J.; Rempp, H.; Claussen, C.; Yang, B.; Schick, F. Topography mapping of whole body adipose tissue using A fully automated and standardized procedure. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullberg, J.; Ahlström, H.; Johansson, L.; Frimmel, H. Automated and reproducible segmentation of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue from abdominal MRI. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzakis, M.; Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Reiman, T.; McCargar, L.J.; Baracos, V.E. A practical and precise approach to quantification of body composition in cancer patients using computed tomography images acquired during routine care. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 33, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjønigsen, L.J.; Harneshaug, M.; Fløtten, A.-M.; Karterud, L.K.; Petterson, K.; Skjolde, G.; Eggesbø, H.B.; Weedon-Fekjær, H.; Henriksen, H.B.; Lauritzen, P.M. Reproducibility of semiautomated body composition segmentation of abdominal computed tomography: A multiobserver study. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demerath, E.W.; Ritter, K.J.; Couch, W.; Rogers, N.L.; Moreno, G.M.; Choh, A.; Lee, M.; Remsberg, K.; Czerwinski, S.; Chumlea, W.C.; et al. Validity of a new automated software program for visceral adipose tissue estimation. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonekamp, S.; Ghosh, P.; Crawford, S.; Solga, S.F.; Horska, A.; Brancati, F.L.; Diehl, A.M.; Smith, S.; Clark, J.M. Quantitative comparison and evaluation of software packages for assessment of abdominal adipose tissue distribution by magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddalo, M.; Zorza, I.; Zubani, S.; Nocivelli, G.; Calandra, G.; Soldini, P.; Mascaro, L.; Maroldi, R. Validation of a free software for unsupervised assessment of abdominal fat in MRI. Phys. Medica 2017, 37, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udupa, J.K.; Samarasekera, S. Fuzzy Connectedness and Object Definition: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications in Image Segmentation. Graph. Model. Image Process. 1996, 58, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Hsiao, H.-F.; Yang, H.-T.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chan, W.P. Reproducibility and Repeatability of Computer Tomography-based Measurement of Abdominal Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.H.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, D.-W. Optimal CT Number Range for Adipose Tissue When Determining Lean Body Mass in Whole-Body F-18 FDG PET/CT Studies. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 46, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Yan, C.; Yang, C.; Dong, H.; Xu, S.; Li, C.; Zeng, M. Measurement of epicardial adipose tissue using non-contrast routine chest-CT: A consideration of threshold adjustment for fatty attenuation. BMC Med Imaging 2022, 22, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, F.; Mallio, C.A. Artificial intelligence and abdominal adipose tissue analysis: A literature review. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 4461–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, A.T.; Krishnaraj, A.; Quinones, M.H.; Tustison, N.J.; Epstein, S.; Fuller, D.; Jha, A.; Allman, K.L.; Shi, W. Deep Learning-based Quantification of Abdominal Subcutaneous and Visceral Fat Volume on CT Images. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, C.P.; Rosenthal, M.; Wright, B.; Kotecha, G.; Fintelmann, F.; Troschel, F.; Miskin, N.; Desai, K.; Wrobel, W.; Babic, A.; et al. Fully-Automated Analysis of Body Composition from CT in Cancer Patients Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In OR 2.0 Context-Aware Operating Theaters, Computer Assisted Robotic Endoscopy, Clinical Image-Based Procedures, and Skin Image Analysis, Proceedings of the First International Workshop, OR 2.0 2018, 5th International Workshop, CARE 2018, 7th International Workshop, CLIP 2018, Third International Workshop, ISIC 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; Stoyanov, D., Taylor, Z., Sarikaya, D., McLeod, J., Ballester, M.A.G., Codella, N.C.F., Martel, A., Maier-Hein, L., Malpani, A., Zenati, M.A., et al., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.T.; Tandon, P.; Heyland, D.K.; Furberg, H.; Premji, T.; Low, G.; Mourtzakis, M. Automated body composition analysis of clinically acquired computed tomography scans using neural networks. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3049–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koitka, S.; Kroll, L.; Malamutmann, E.; Oezcelik, A.; Nensa, F. Fully automated body composition analysis in routine CT imaging using 3D semantic segmentation convolutional neural networks. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Punyanitya, M.; Wang, Z.; Gallagher, D.; St-Onge, M.-P.; Albu, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Heshka, S. Visceral adipose tissue: Relations between single-slice areas and total volume. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demerath, E.W.; Shen, W.; Lee, M.; Choh, A.C.; Czerwinski, S.; Siervogel, R.M.; Towne, B. Approximation of total visceral adipose tissue with a single magnetic resonance image. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maislin, G.; Ahmed, M.M.; Gooneratne, N.; Thorne-Fitzgerald, M.; Kim, C.; Teff, K.; Arnardottir, E.S.; Benediktsdottir, B.; Einarsdottir, H.; Juliusson, S.; et al. Single Slice vs. Volumetric MR Assessment of Visceral Adipose Tissue: Reliability and Validity Among the Overweight and Obese. Obesity 2012, 20, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lv, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, N.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, Q.; Ren, P.; et al. The Appropriateness Criteria of Abdominal Fat Measurement at the Level of the L1-L2 Intervertebral Disc in Patients with Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sex | Male: 12 (57%); Female: 9 (43%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Max | Min | |
| Age (year) | 56 | 14 | 78 | 31 |
| Height (cm) | 169.7 | 10.6 | 190.0 | 155.0 |
| Weight (kg) | 79.1 | 14.3 | 100.0 | 51.0 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 27.5 | 4.6 | 37.9 | 18.7 |
| CT | Mean | SD | Max | Min |
| Outer (cm2) | 736.3 | 163.2 | 996.2 | 400.3 |
| Inner (cm2) | 489.3 | 121.2 | 727.2 | 297.1 |
| SAT (cm2) | 242.1 | 127.2 | 582.5 | 46.9 |
| VAT (cm2) | 149.4 | 81.2 | 363.5 | 9.5 |
| MR | Mean | SD | Max | Min |
| Outer (cm2) | 717.3 | 159.0 | 952.4 | 382.3 |
| Inner (cm2) | 474.2 | 124.8 | 701.4 | 253.6 |
| SAT (cm2) | 240.7 | 126.7 | 555.7 | 52.8 |
| VAT (cm2) | 129.8 | 77.8 | 330.4 | 5.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, L.-Y.; Ali, Z.; Bagheri, H.; Huda, F.; Redd, B.A.; Jones, E.C. Comparison of CT and Dixon MR Abdominal Adipose Tissue Quantification Using a Unified Computer-Assisted Software Framework. Tomography 2023, 9, 1041-1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030085
Hsu L-Y, Ali Z, Bagheri H, Huda F, Redd BA, Jones EC. Comparison of CT and Dixon MR Abdominal Adipose Tissue Quantification Using a Unified Computer-Assisted Software Framework. Tomography. 2023; 9(3):1041-1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030085
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Li-Yueh, Zara Ali, Hadi Bagheri, Fahimul Huda, Bernadette A. Redd, and Elizabeth C. Jones. 2023. "Comparison of CT and Dixon MR Abdominal Adipose Tissue Quantification Using a Unified Computer-Assisted Software Framework" Tomography 9, no. 3: 1041-1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030085
APA StyleHsu, L.-Y., Ali, Z., Bagheri, H., Huda, F., Redd, B. A., & Jones, E. C. (2023). Comparison of CT and Dixon MR Abdominal Adipose Tissue Quantification Using a Unified Computer-Assisted Software Framework. Tomography, 9(3), 1041-1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9030085






