The Cerebellum’s Orchestra: Understanding the Functional Connectivity of Its Lobes and Deep Nuclei in Coordination and Integration of Brain Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Scanning Parameters
2.3. Pre-Processing
2.4. Selection of Regions of Interest
2.5. Statistical Analysis
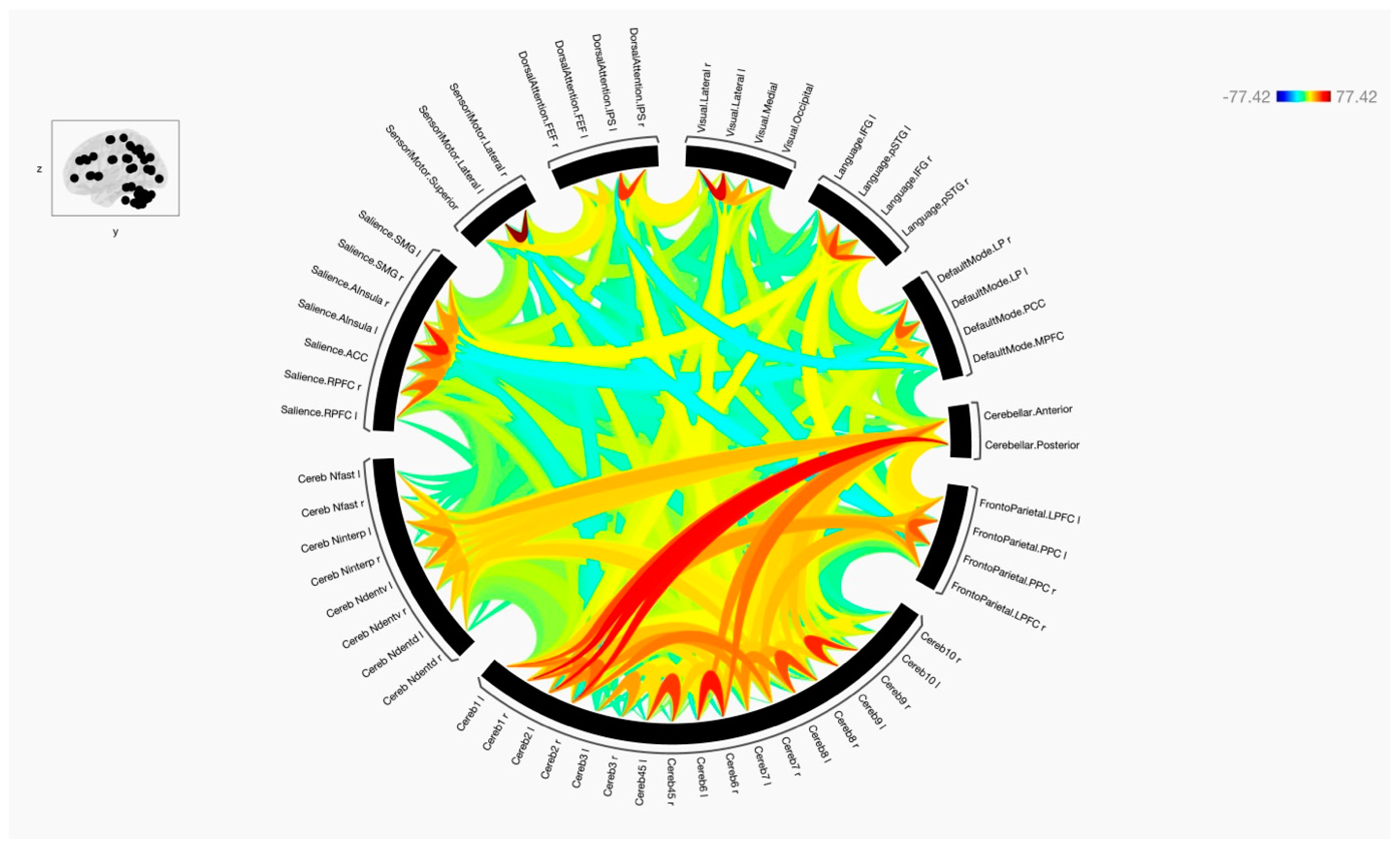
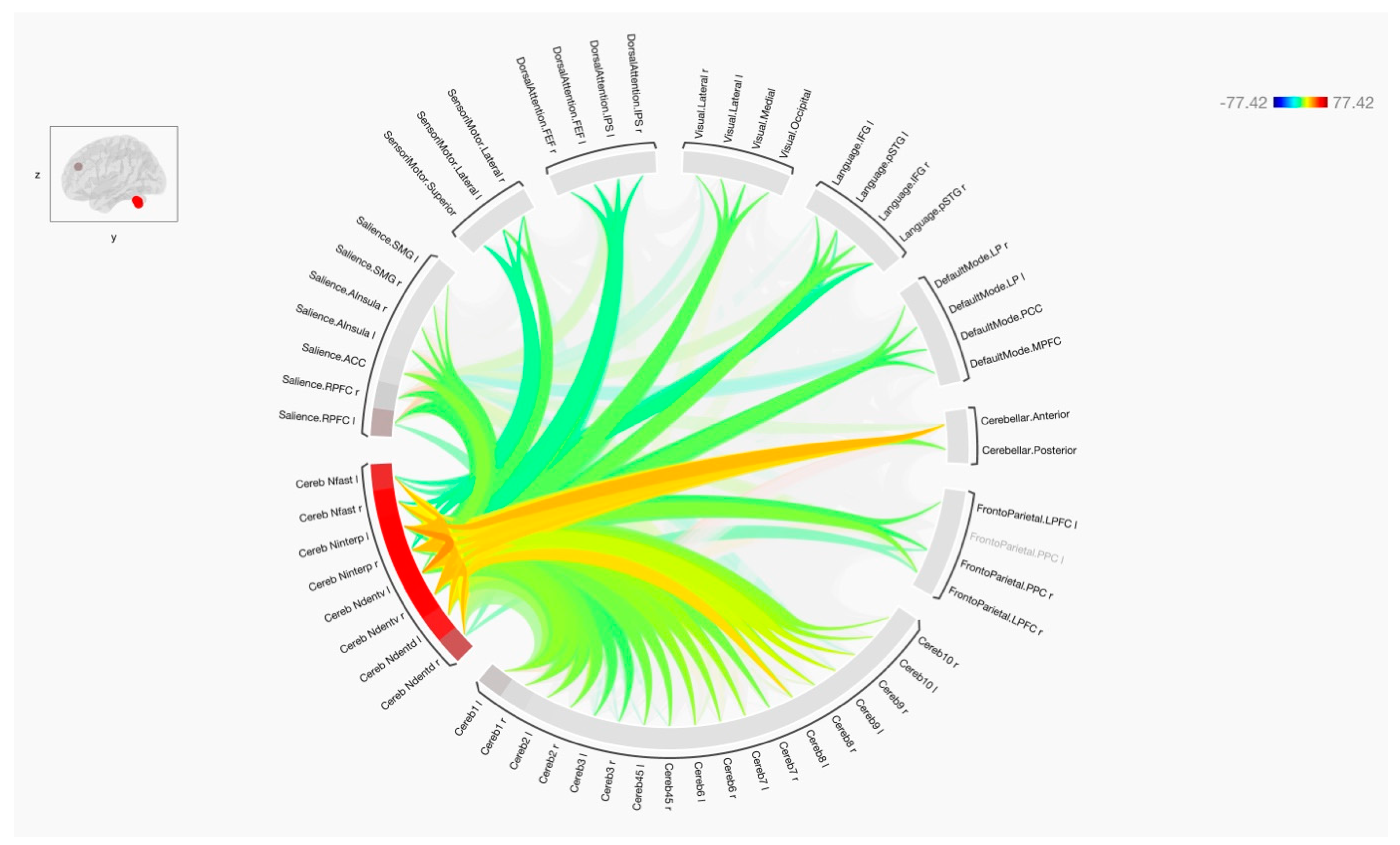
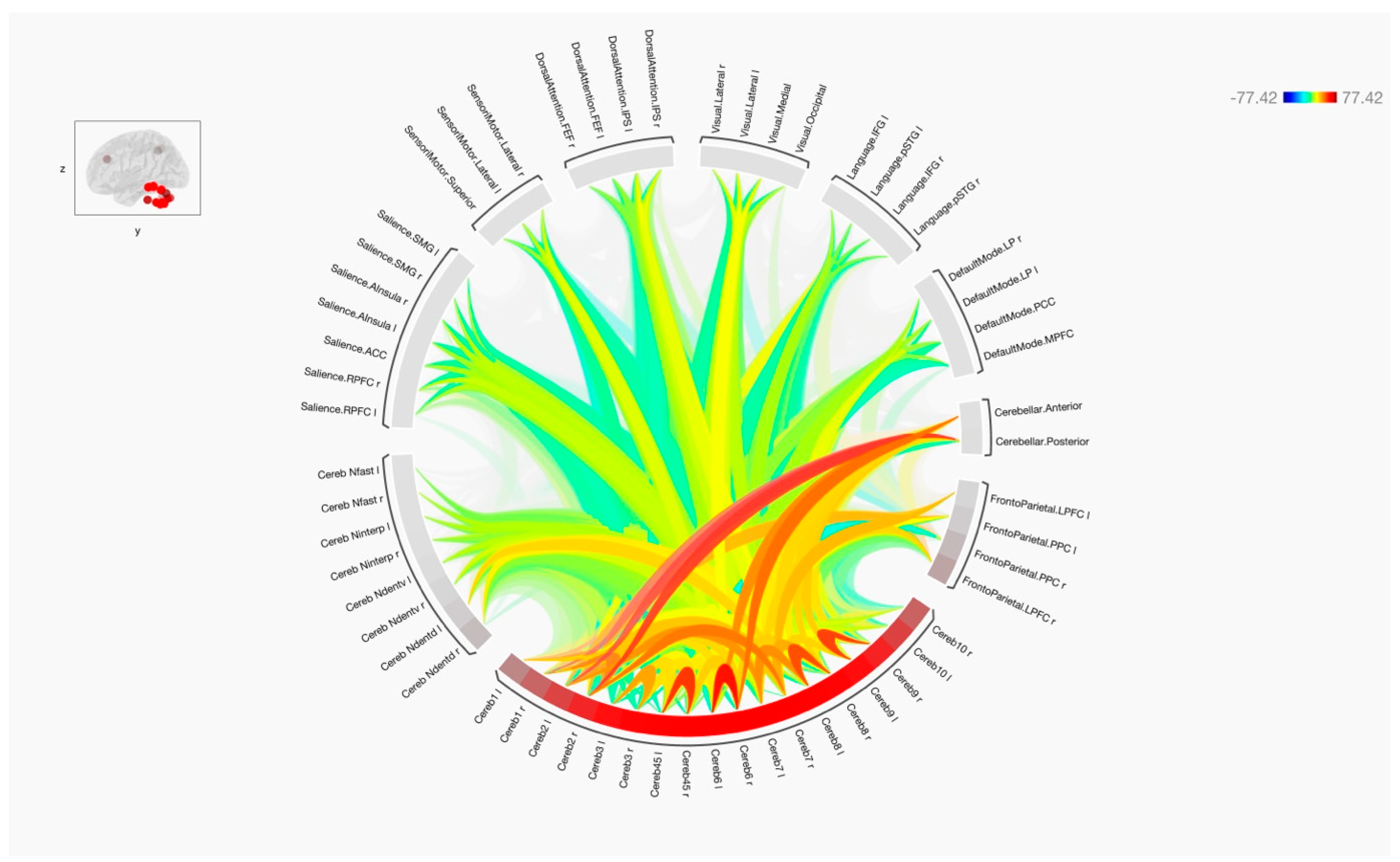
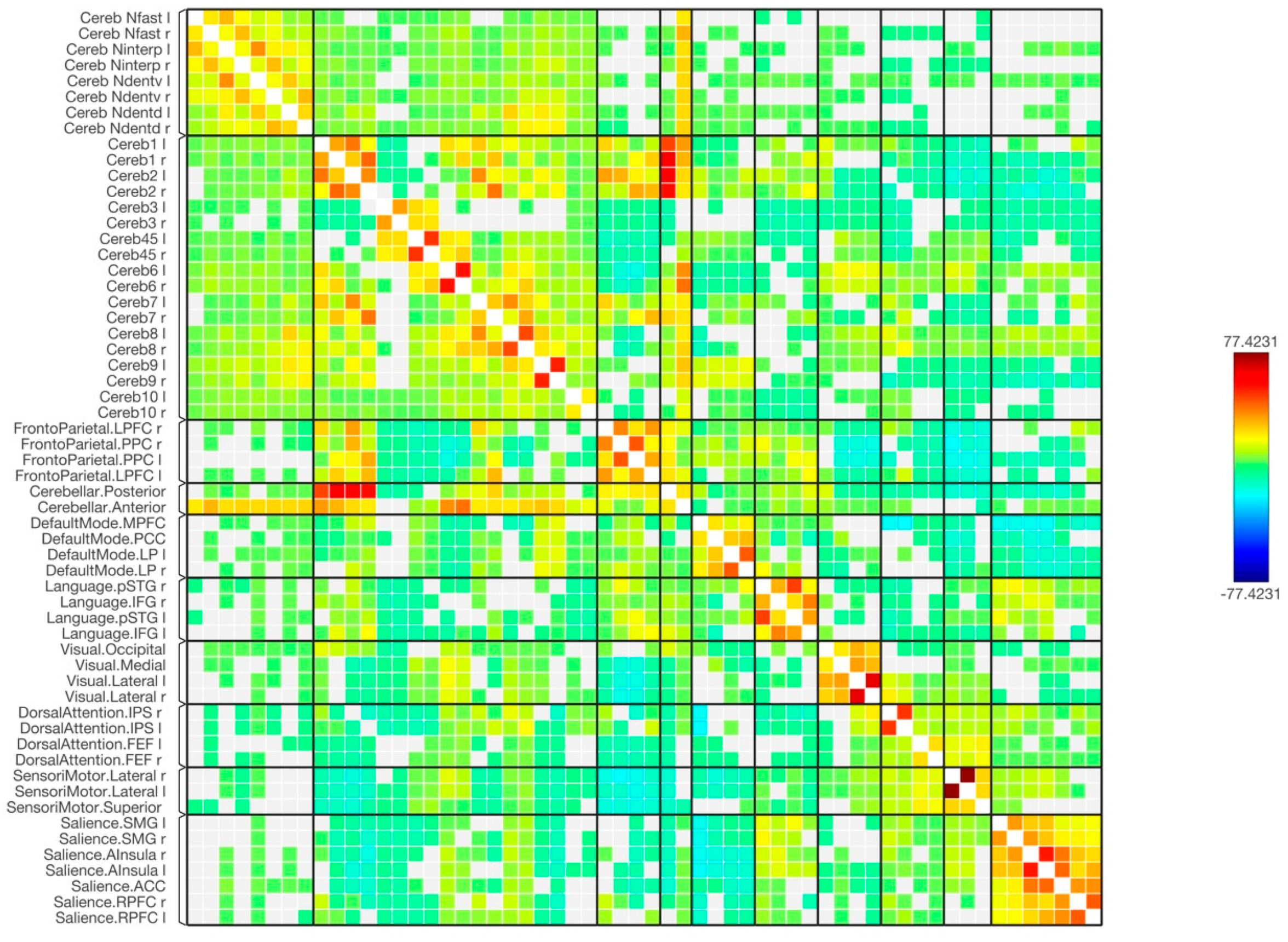
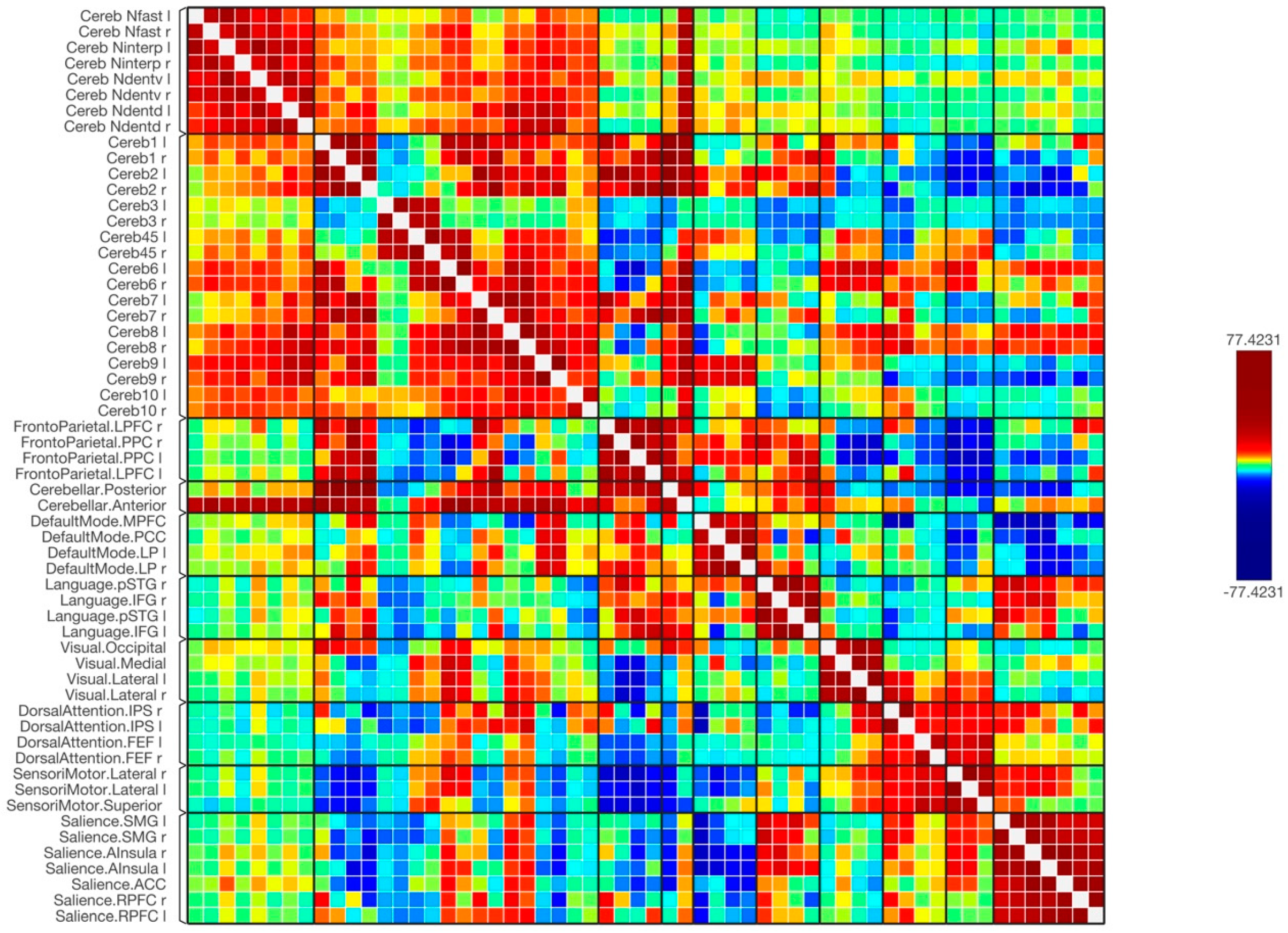
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1. Default Mode Network (DMN): | |
| MPFC: | Medial Prefrontal Cortex |
| LP (L): | Left Lateral Parietal Cortex |
| LP (R): | Right Lateral Parietal Cortex |
| PCC: Posterior Cingulate Cortex | |
| 2. SensoriMotor Network (SMN): | |
| Lateral (L): | Left Lateral Sensorimotor Cortex |
| Lateral (R): | Right Lateral Sensorimotor Cortex |
| Superior: | Superior Sensorimotor Cortex |
| 3. Visual Network (VN): | |
| Medial: | Medial Visual Cortex |
| Occipital: | Occipital Visual Cortex |
| Lateral (L): | Left Lateral Visual Cortex |
| Lateral (R): | Right Lateral Visual Cortex |
| 4. Salience Network (SN): | |
| ACC: | Anterior Cingulate Cortex |
| AInsula (L): | Left Anterior Insula |
| AInsula (R): | Right Anterior Insula |
| RPFC (L): | Left Rostral Prefrontal Cortex |
| RPFC (R): | Right Rostral Prefrontal Cortex |
| SMG (L): | Left Supramarginal Gyrus |
| SMG (R): | Right Supramarginal Gyrus |
| 5. Dorsal Attention Network (DAN): | |
| FEF (L): | Left Frontal Eye Field |
| FEF (R): | Right Frontal Eye Field |
| IPS (L): | Left Intraparietal Sulcus |
| IPS (R): | Right Intraparietal Sulcus |
| 6. FrontoParietal Network (FPN): | |
| LPFC (L): | Left Lateral Prefrontal Cortex |
| PPC (L): | Left Posterior Parietal Cortex |
| LPFC (R): | Right Lateral Prefrontal Cortex |
| PPC (R): | Right Posterior Parietal Cortex |
| 7. Language Network (LN): | |
| IFG (L): | Left Inferior Frontal Gyrus |
| IFG (R): | Right Inferior Frontal Gyrus |
| pSTG (L): | Left Posterior Superior Temporal Gyrus |
| pSTG (R): | Right Posterior Superior Temporal Gyrus |
| 8. Cerebellar Network (CN): | |
| Anterior: | Anterior Cerebellum |
| Posterior: | Posterior Cerebellum |
| Ndentv: | Dentate Nucleus Ventral |
| Ndentd: | Dentate Nucleus Dorsal |
| Ninterp: Interposed Nucleus, which can be further divided into: | |
| a. Globose Nucleus (GN) | |
| b. Emboliform Nucleus (EN) | |
| Nfast: | Fastigial Nucleus |
References
- Stoodley, C.J.; Schmahmann, J.D. Functional Topography in the Human Cerebellum: A Meta-Analysis of Neuroimaging Studies. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, J.; Seidler, R.D.; Hassevoort, K.M.; Benson, B.L.; Welsh, R.C.; Wiggins, J.L.; Jaeggi, S.M.; Buschkuehl, M.; Monk, C.S.; Jonides, J.; et al. Resting State Cortico-Cerebellar Functional Connectivity Networks: A Comparison of Anatomical and Self-Organizing Map Approaches. Front. Neuroanat. 2012, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Valera, E.M.; Schmahmann, J.D. An Fmri Study of Intra-Individual Functional Topography in the Human Cerebellum. Behav. Neurol. 2010, 23, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, C.J. The cerebellum and Cognition: Evidence from Functional Imaging Studies. Cerebellum 2012, 11, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Valera, E.M.; Schmahmann, J.D. Functional Topography of the Cerebellum for Motor and Cognitive Tasks: An Fmri Study. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, M.; Rauch, H.G.; Stein, D.J.; Brooks, S.J. The Handyman’s Brain: A Neuroimaging Meta-Analysis Describing the Similarities and Differences Between Grip Type and Pattern in Humans. Neuroimage 2014, 102, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, S.P.; Davis, N.J.; Morgan, H.M.; Bracewell, R.M. Cerebellar Contributions to Verbal Working Memory. Cerebellum 2014, 13, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Zerrin Yetkin, F.; Haughton, V.M.; Hyde, J.S. Functional Connectivity in the Motor Cortex of Resting Human Brain Using Echo-Planar Mri. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.B.; Mennes, M.; Zuo, X.N.; Gohel, S.; Kelly, C.; Smith, S.M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Adelstein, J.S.; Buckner, R.L.; Colcombe, S.; et al. Toward Discovery Science of Human Brain Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4734–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M. Control of Mental Activities by Internal Models in the Cerebellum. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlerf, J.; Wiestler, T.; Verstynen, T.; Diedrichsen, J. Big Challenges from the Little Brain—Imaging the Cerebellum. Adv. Brain Neuroimaging Top. Health Dis. Methods Appl. 2014, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedrichsen, J.; Maderwald, S.; Küper, M.; Thürling, M.; Rabe, K.; Gizewski, E.R.; Ladd, M.E.; Timmann, D. Imaging the Deep Cerebellar Nuclei: A Probabilistic Atlas and Normalization Procedure. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küper, M.; Dimitrova, A.; Thürling, M.; Maderwald, S.; Roths, J.; Elles, H.G.; Gizewski, E.R.; Ladd, M.E.; Diedrichsen, J.; Timmann, D. Evidence for a Motor and a Non-Motor Domain in the Human Dentate Nucleus—An Fmri Study. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 2612–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küper, M.; Wünnemann, M.J.; Thürling, M.; Stefanescu, R.M.; Maderwald, S.; Elles, H.G.; Göricke, S.; Ladd, M.E.; Timmann, D. Activation of the Cerebellar Cortex and the Dentate Nucleus in a Prism Adaptation Fmri Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahmadi, A.; Pardini, M.; Samson, R.; Friston, K.; Toosy, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C. The Healthy Human Cerebellum Engaging in Complex Patterns: An Fmri Study. In Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Toronto, ON, Canada, 31 May–5 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Schmahmann, J.D. Functional Topography of the Human Cerebellum. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 154, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habas, C. Functional Connectivity of the Cognitive Cerebellum. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 642225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A Functional Connectivity Toolbox for Correlated and Anticorrelated Brain Networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Holmes, A.P.; Worsley, K.J.; Poline, J.P.; Frith, C.D.; Frackowiak, R.S. Statistical Parametric Maps in Functional Imaging: A General Linear Approach. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1995, 2, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, V.D.; Wager, T.D.; Krishnan, A.; Rosch, K.S.; Seymour, K.E.; Nebel, M.B.; Mostofsky, S.H.; Nyalakanai, P.; Kiehl, K. The Impact of T1 Versus EPI Spatial Normalization Templates for Fmri Data Analyses; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K. Multimodal Image Coregistration and Partitioning—A Unified Framework. Neuroimage 1997, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, J.; Friston, K.J. Unified Segmentation. Neuroimage 2005, 26, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellmann, S.; Bludau, S.; Eickhoff, S.; Mohlberg, H.; Minnerop, M.; Amunts, K. Cytoarchitectonic Mapping of the Human Brain Cerebellar Nuclei in Stereotaxic Space and Delineation of Their Co-Activation Patterns. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickhoff, S.B.; Stephan, K.E.; Mohlberg, H.; Grefkes, C.; Fink, G.R.; Amunts, K.; Zilles, K. A New SPM Toolbox for Combining Probabilistic Cytoarchitectonic Maps and Functional Imaging Data. Neuroimage 2005, 25, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guell, X.; Schmahmann, J.D.; Gabrieli, J.D.; Ghosh, S.S. Functional Gradients of the Cerebellum. Elife 2018, 7, e36652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habas, C. Functional Imaging of the Deep Cerebellar Nuclei: A Review. Cerebellum 2010, 9, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlerf, J.E.; Verstynen, T.D.; Ivry, R.B.; Spencer, R.M. Evidence of a Novel Somatopic Map in the Human Neocerebellum during Complex Actions. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamizu, H.; Kawato, M. Brain Mechanisms for Predictive Control by Switching Internal Models: Implications for Higher-Order Cognitive Functions. Psychol. Res. PRPF 2009, 73, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, L.Q. Salience Network of the Human Brain; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Seeley, W.W. The Salience Network: A Neural System for Perceiving and Responding to Homeostatic Demands. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9878–9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, A.A. Effects of Different Smoothing on Global and Regional Resting Functional Connectivity. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedrichsen, J. A Spatially Unbiased Atlas Template of the Human Cerebellum. NeuroImage 2006, 33, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedrichsen, J.; Balsters, J.H.; Flavell, J.; Cussans, E.; Ramnani, N. A Probabilistic MR Atlas of the Human Cerebellum. NeuroImage 2009, 46, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amunts, K.; Kedo, O.; Kindler, M.; Pieperhoff, P.; Mohlberg, H.; Shah, N.J.; Habel, U.; Schneider, F.; Zilles, K. Cytoarchitectonic Mapping of the Human Amygdala, Hippocampal Region and Entorhinal Cortex: Intersubject Variability and Probability Maps. Anat. Embryol. 2005, 210, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, L.; Cerasa, A.; Liguori, M.; Gioia, M.C.; Valentino, P.; Nistico, R.; Quattrone, A.; Fera, F. Neurobiological Mechanisms Underlying Emotional Processing in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Brain J. Neurol. 2009, 132, 3380–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.; Fox, M.D. Towards a Consensus Regarding Global Signal Regression for Resting State Functional Connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 2017, 154, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Chen, G.; Xie, C.; Li, S.J. Negative Functional Connectivity and Its Dependence on the Shortest Path Length of Positive Network in the Resting-State Human Brain. Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, H. Cortical Activities Associated with Voluntary Movements and Involuntary Movements. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alahmadi, A.A.S. The Cerebellum’s Orchestra: Understanding the Functional Connectivity of Its Lobes and Deep Nuclei in Coordination and Integration of Brain Networks. Tomography 2023, 9, 883-893. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020072
Alahmadi AAS. The Cerebellum’s Orchestra: Understanding the Functional Connectivity of Its Lobes and Deep Nuclei in Coordination and Integration of Brain Networks. Tomography. 2023; 9(2):883-893. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020072
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlahmadi, Adnan A. S. 2023. "The Cerebellum’s Orchestra: Understanding the Functional Connectivity of Its Lobes and Deep Nuclei in Coordination and Integration of Brain Networks" Tomography 9, no. 2: 883-893. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020072
APA StyleAlahmadi, A. A. S. (2023). The Cerebellum’s Orchestra: Understanding the Functional Connectivity of Its Lobes and Deep Nuclei in Coordination and Integration of Brain Networks. Tomography, 9(2), 883-893. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020072




