Comparing Radiation Dose of Cerebral Angiography Using Conventional and High kV Techniques: A Retrospective Study on Intracranial Aneurysm Patients and a Phantom Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Consideration
2.2. Sample Size Calculation and Participant Selection
2.3. Cerebral Angiographic Protocol
2.4. Collection of Cerebral Angiographic Exposure Parameters and Patient Radiation Dose
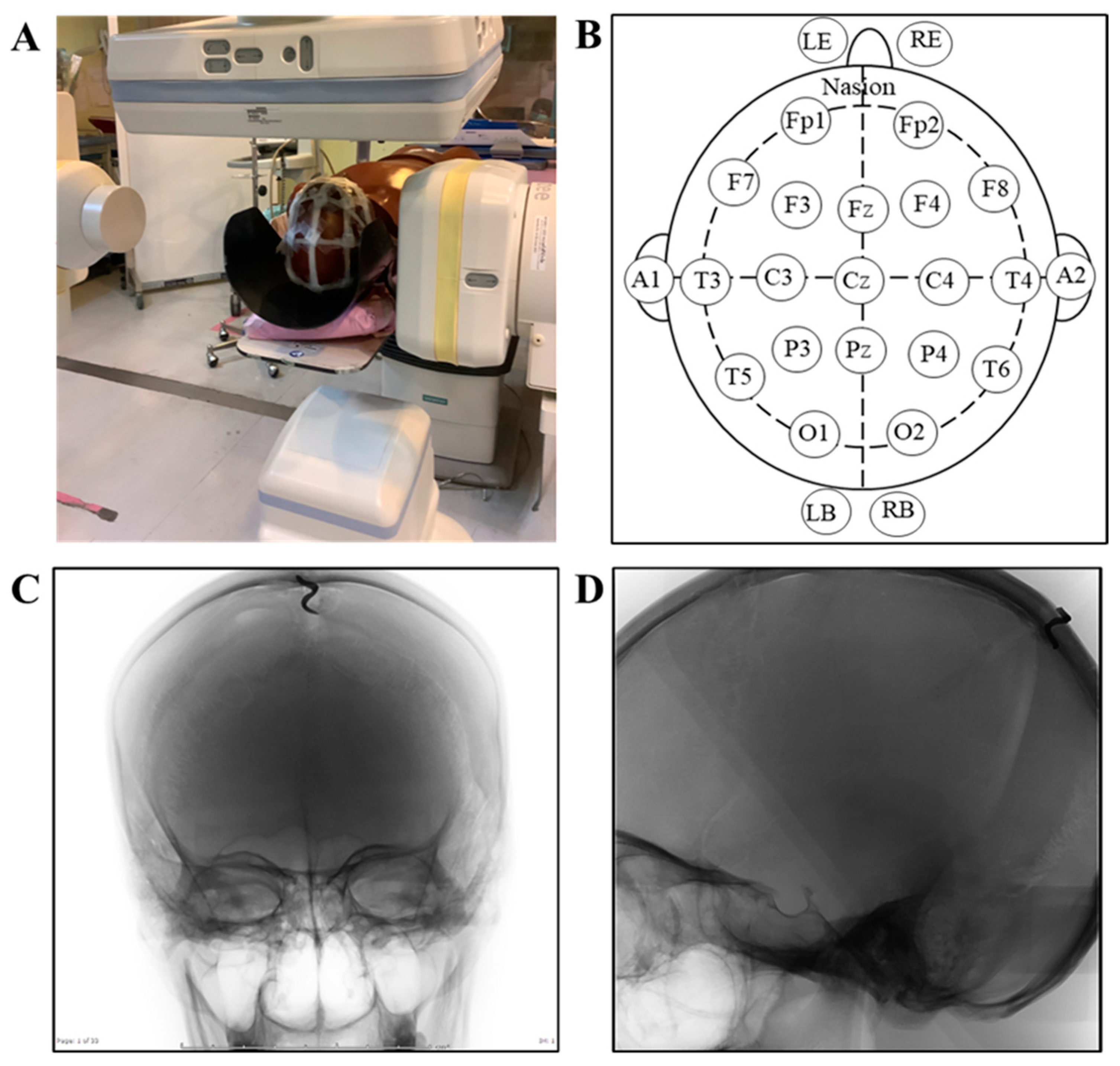
2.5. Phantom Study Protocol and Setting
2.6. Evaluation of Phantom Radiation Dose
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of the High kV Technique on Cerebral Angiographic Exposure Parameters
3.2. Effects of the High kV Technique on Patient Radiation Dose
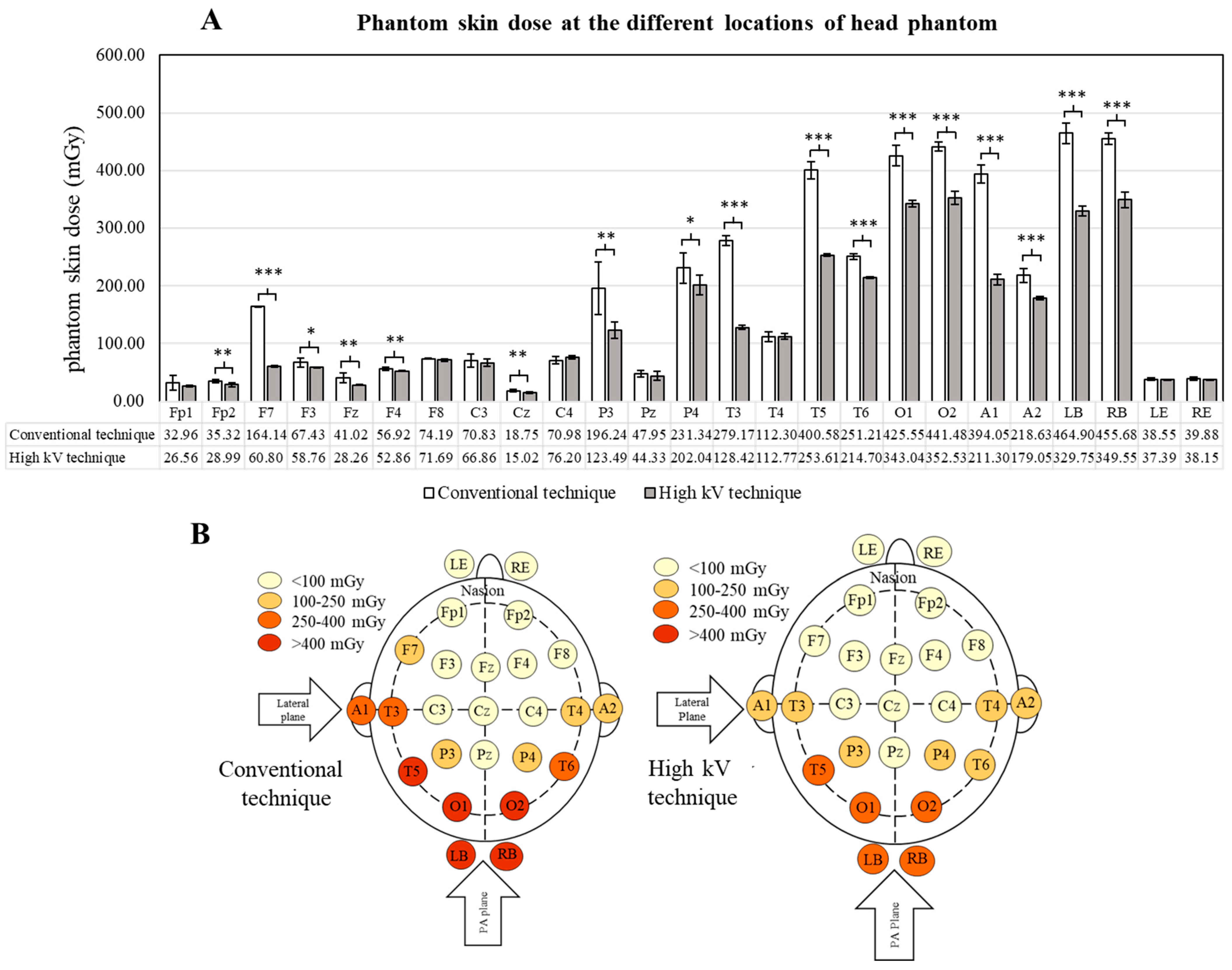
3.3. Effects of the High kV Technique on Phantom Skin Dose
3.4. Effects of the High kV Technique on Dose Report from the DAP Meter
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, C.O.; Rymer, M.M. Hemorrhagic Stroke: Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Mo Med. 2011, 108, 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Rymer, M.M. Hemorrhagic Stroke: Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Mo Med. 2011, 108, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, A.J.; Kerr, R.S.C.; Birks, J.; Ramzi, N.; Yarnold, J.; Sneade, M.; Rischmiller, J. ISAT Collaborators Risk of Recurrent Subarachnoid Haemorrhage, Death, or Dependence and Standardised Mortality Ratios after Clipping or Coiling of an Intracranial Aneurysm in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT): Long-Term Follow-Up. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, Z.; Tu, J.; Ning, X.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms in the Population at High Risk for Aneurysm in the Rural Areas of Tianjin. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 853054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacein-Bey, L.; Provenzale, J.M. Current Imaging Assessment and Treatment of Intracranial Aneurysms. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, A.-L.; Isokangas, J.-M.; Karttunen, A.; Siniluoto, T.; Nieminen, M.T. A Comparison of Radiation Exposure between Diagnostic CTA and DSA Examinations of Cerebral and Cervicocerebral Vessels. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 2038–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, N.; Fujimichi, Y. Classification of Radiation Effects for Dose Limitation Purposes: History, Current Situation and Future Prospects. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.J.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.W. Analysis of Radiation Doses and Dose Reduction Strategies During Cerebral Digital Subtraction Angiography. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, H.J.; Kim, B.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; Choi, J.H.; Shin, Y.S.; Choi, Y.; Shin, N.-Y.; Jang, J.; Ahn, K.-J. Low-Dose Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography for Evaluating Intracranial Aneurysms: Analysis of Image Quality and Radiation Dose. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Wyse, E.; Pearl, M.S. Analysis of Radiation Doses Incurred during Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography after the Implementation of Dose Reduction Strategies. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Park, M.K.; Jung, D.E.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, B.M. Radiation Dose Reduction without Compromise to Image Quality by Alterations of Filtration and Focal Spot Size in Cerebral Angiography. Korean J. Radiol. 2017, 18, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkong, W.; Kirisattayakul, W.; Pattum, P.; Kianprasit, J.; Prabsattroo, T.; Punikhom, P.; Karawek, R.; Kitkhuandee, A.; Duangthongphon, P.; Awikunprasert, P. Analysis of Patient Radiation Dose and Angiographic Techniques during Intracranial Aneurysmal Diagnosis: A 5-Year Experience of Interventional Neuroradiology Unit in Srinagarind Hospital. JAMS 2020, 51, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Tsapaki, V. Radiation Dose Optimization in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology: Current Issues and Future Perspectives. Phys. Med. 2020, 79, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ercole, L.; Thyrion, F.Z.; Bocchiola, M.; Mantovani, L.; Klersy, C. Proposed Local Diagnostic Reference Levels in Angiography and Interventional Neuroradiology and a Preliminary Analysis According to the Complexity of the Procedures. Phys. Med. 2012, 28, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, M.S.; Torok, C.; Wang, J.; Wyse, E.; Mahesh, M.; Gailloud, P. Practical Techniques for Reducing Radiation Exposure during Cerebral Angiography Procedures. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2015, 7, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Han, S.; Kim, B.J.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, T.I.; Lee, D.H. Low-Dose Fluoroscopy Protocol for Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography. Neurointervention 2020, 15, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.; Hogg, P.; Ma, W.K.; Szczepura, K. Fact or Fiction: An Analysis of the 10 KVp ‘Rule’ in Computed Radiography. Radiography 2013, 19, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagnostic Radiology Physics; Non-Serial Publications; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2014; ISBN 978-92-0-131010-1.
- Huda, W.; Abrahams, R.B. Radiographic Techniques, Contrast, and Noise in X-ray Imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W126–W131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonnessen, B.H.; Pounds, L. Radiation Physics. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 6S–8S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, M.; Henzler, T.; Nance, J.W.; Haubenreisser, H.; Meyer, M.; Sudarski, S.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Neff, K.W.; Hagelstein, C. Radiation Dose Comparison Between 70 KVp and 100 KVp With Spectral Beam Shaping for Non-Contrast-Enhanced Pediatric Chest Computed Tomography: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVey, G.; Sandborg, M.; Dance, D.R.; Alm Carlsson, G. A Study and Optimization of Lumbar Spine X-ray Imaging Systems. Br. J. Radiol. 2003, 76, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sun, S.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, G.; Liu, J. The Research of Influence of Different Additional Filtration to Image Quality and Radiation Dose in the Whole Brain DSA. Chin. J. Radiol. 2016, 50, 691–694. [Google Scholar]
- Wunderle, K.A.; Rakowski, J.T.; Dong, F.F. Approaches to Interventional Fluoroscopic Dose Curves. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 17, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C. The Importance of Radiation Quality for Optimisation in Radiology. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2007, 3, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.A.; Akleyev, A.V.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Hendry, J.H.; Kleiman, N.J.; Macvittie, T.J.; Aleman, B.M.; Edgar, A.B.; Mabuchi, K.; Muirhead, C.R.; et al. ICRP Publication 118: ICRP Statement on Tissue Reactions and Early and Late Effects of Radiation in Normal Tissues and Organs--Threshold Doses for Tissue Reactions in a Radiation Protection Context. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 1–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, P.L.; Caldas, L.V.E. Angular dependence of Tl and Osl responses of Al2O3:C commercial detectors in standard beta radiation beams. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 113, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, T.; Hayashi, H.; Takegami, K.; Okino, H.; Kimoto, N.; Maehata, I.; Kobayashi, I. Fundamental Study of NanoDot OSL Dosimeters for Entrance Skin Dose Measurement in Diagnostic X-Ray Examinations. J. Radiat. Prot. Res. 2016, 41, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Technique | Protocol | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluoroscopy | PA kV, mA | 65 kV, 137.1–141.3 mA | |
| Lateral kV, mA | 65 kV, 97.9–98 mA | ||
| Time | PA plane | 2 min | |
| Lateral plane | 1 min | ||
| 2DA | Field size | PA/Lat | 32/25 cm |
| SID | PA/Lat | 102/94 cm | |
| Projection | RICA | PA view (11° cephalad) Lateral view | |
| LICA | |||
| VA | |||
| Frame rate and acquisition time | Mask | 4 f/s 1 s | |
| Arterial phase | 4 f/s 4 s | ||
| Capillary phase | 2 f/s 4 s | ||
| Venous phase | 1 f/s 5 s | ||
| 3DRA | Field size | PA plane | 42 cm |
| SID | PA plane | 120 cm | |
| Rotational arc | RICA | 200 degrees | |
| LICA | |||
| VA | |||
| kV, mAs | 71 kV, 2.25–2.46 | ||
| Number of frames/rotations | 133 f/rotation | ||
| Rotational time | 5 s | ||
| Angiographic Exposure Parameters | Conventional Technique Mean ± SD (Median) | High kV Technique Mean ± SD (Median) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| kV | 2DA PA | 77.28 ± 2.85 (77.00) | 87.75 ± 2.70 (90.00) | <0.001 b |
| 2DA Lateral | 72.52 ± 1.56 (73.00) | 79.59 ± 1.12 (79.00) | <0.001 b | |
| 3DRA Pre-contrast | 70.00 ± 0.00 (70.00) | 70.02 ± 0.13 (70.00) | 0.317 b | |
| RA Post-contrast | 70.00 ± 0.00 (70.00) | 70.00 ± 0.00 (70.00) | 1.000 b | |
| mAs | 2DA PA | 19.91 ± 0.70 (19.89) | 12.03 ± 1.37 (11.91) | <0.001 b |
| 2DA Lateral | 16.07 ± 3.25 (16.55) | 14.98 ± 1.54 (14.98) | 0.020 a | |
| 3DRA Pre-contrast | 2.04 ± 0.34 (2.03) | 2.13 ± 0.30 (2.13) | 0.117 a | |
| 3DRA Post-contrast | 2.03 ± 0.34 (2.02) | 2.09 ± 0.30 (2.09) | 0.305 a | |
| Cu Filter thickness (mm) | 2DA PA | 0.00 ± 0.00 (0.00) | 0.05 ± 0.06 (0.00) | <0.001 b |
| 2DA Lateral | 0.02 ± 0.05 (0.00) | 0.27 ± 0.05 (0.30) | <0.001 b | |
| 2DA acquisition time (s) | 14.49 ± 2.73 (15.00) | 13.31 ± 2.02 (13.00) | 0.005 b | |
| Total number of angiographic images | 993.87 ± 13.64 (994.00) | 986.52 ± 10.37 (986.00) | 0.001 a | |
| Fluoroscopic time (min) | 4.31 ± 4.25 (3.28) | 3.30 ± 1.19 (3.03) | 0.062 b | |
| Radiation Dose | Conventional Technique | High kV Technique | Percentage Reduction | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
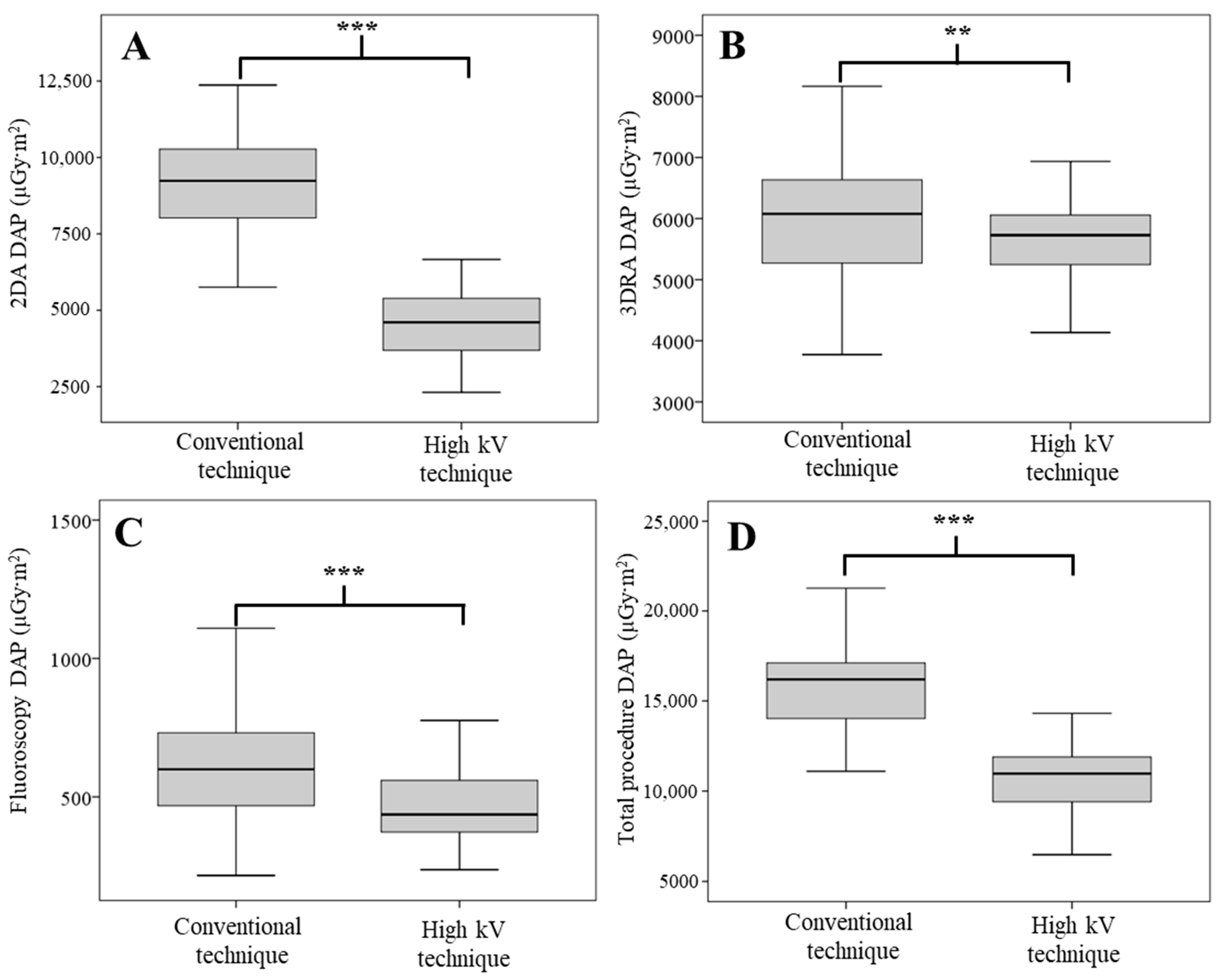
| 2DA DAP (µGy·m2) | 12,456.97 ± 77.09 | 6571.80 ± 48.55 | −47.24 | <0.001 |
| 3DRA DAP (µGy·m2) | 7768.97 ± 74.58 | 7738.23 ± 148.40 | −0.40 | 0.765 |
| Fluoroscopic DAP (µGy·m2) | 977.70 ± 24.17 | 997.48 ± 6.87 | 2.02 | 0.244 |
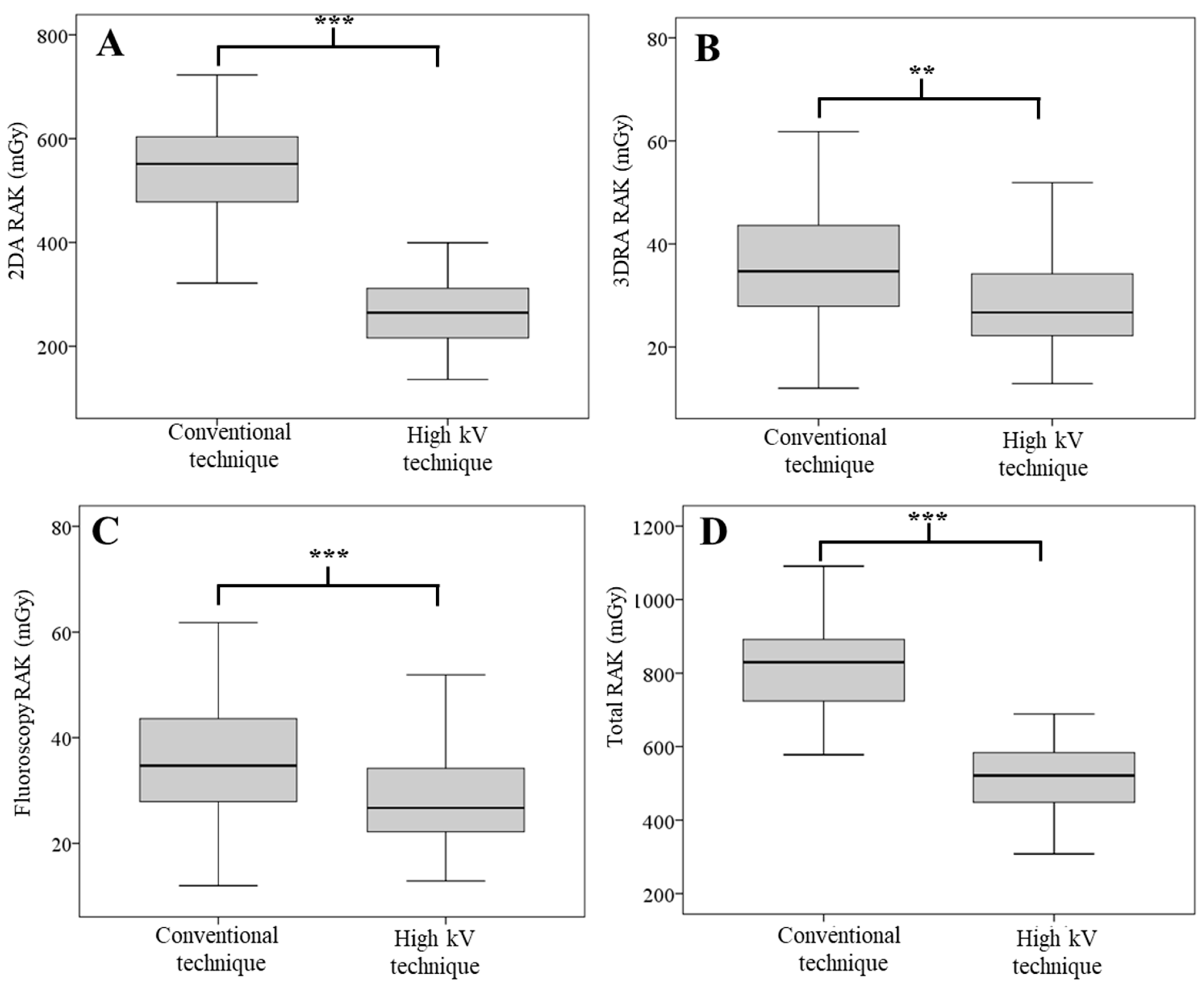
| 2DA RAK (mGy) | 668.07 ± 2.90 | 340.57 ± 13.83 | −49.02 | <0.001 |
| 3DRA RAK (mGy) | 307.93 ± 2.95 | 308.67 ± 3.21 | 0.24 | 0.786 |
| Fluoroscopic RAK | 48.40 ± 1.05 | 48.67 ± 1.44 | 0.55 | 0.809 |
| Total DAP (µGy·m2) | 21,203.63 ± 126.28 | 15,307.52 ± 132.83 | −27.81 | <0.001 |
| Total RAK (mGy) | 1024.40 ± 4.37 | 697.90 ± 15.42 | −31.87 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirisattayakul, W.; Pattum, P.; Munkong, W.; Prabsattroo, T.; Khottapat, C.; Chomkhunthod, T.; Pungkun, V. Comparing Radiation Dose of Cerebral Angiography Using Conventional and High kV Techniques: A Retrospective Study on Intracranial Aneurysm Patients and a Phantom Study. Tomography 2023, 9, 621-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020050
Kirisattayakul W, Pattum P, Munkong W, Prabsattroo T, Khottapat C, Chomkhunthod T, Pungkun V. Comparing Radiation Dose of Cerebral Angiography Using Conventional and High kV Techniques: A Retrospective Study on Intracranial Aneurysm Patients and a Phantom Study. Tomography. 2023; 9(2):621-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirisattayakul, Woranan, Panuwat Pattum, Waranon Munkong, Thawatchai Prabsattroo, Chonnatcha Khottapat, Tanyalak Chomkhunthod, and Vithit Pungkun. 2023. "Comparing Radiation Dose of Cerebral Angiography Using Conventional and High kV Techniques: A Retrospective Study on Intracranial Aneurysm Patients and a Phantom Study" Tomography 9, no. 2: 621-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020050
APA StyleKirisattayakul, W., Pattum, P., Munkong, W., Prabsattroo, T., Khottapat, C., Chomkhunthod, T., & Pungkun, V. (2023). Comparing Radiation Dose of Cerebral Angiography Using Conventional and High kV Techniques: A Retrospective Study on Intracranial Aneurysm Patients and a Phantom Study. Tomography, 9(2), 621-632. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9020050







