Predicting Underestimation of Invasive Cancer in Patients with Core-Needle-Biopsy-Diagnosed Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Using Deep Learning Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
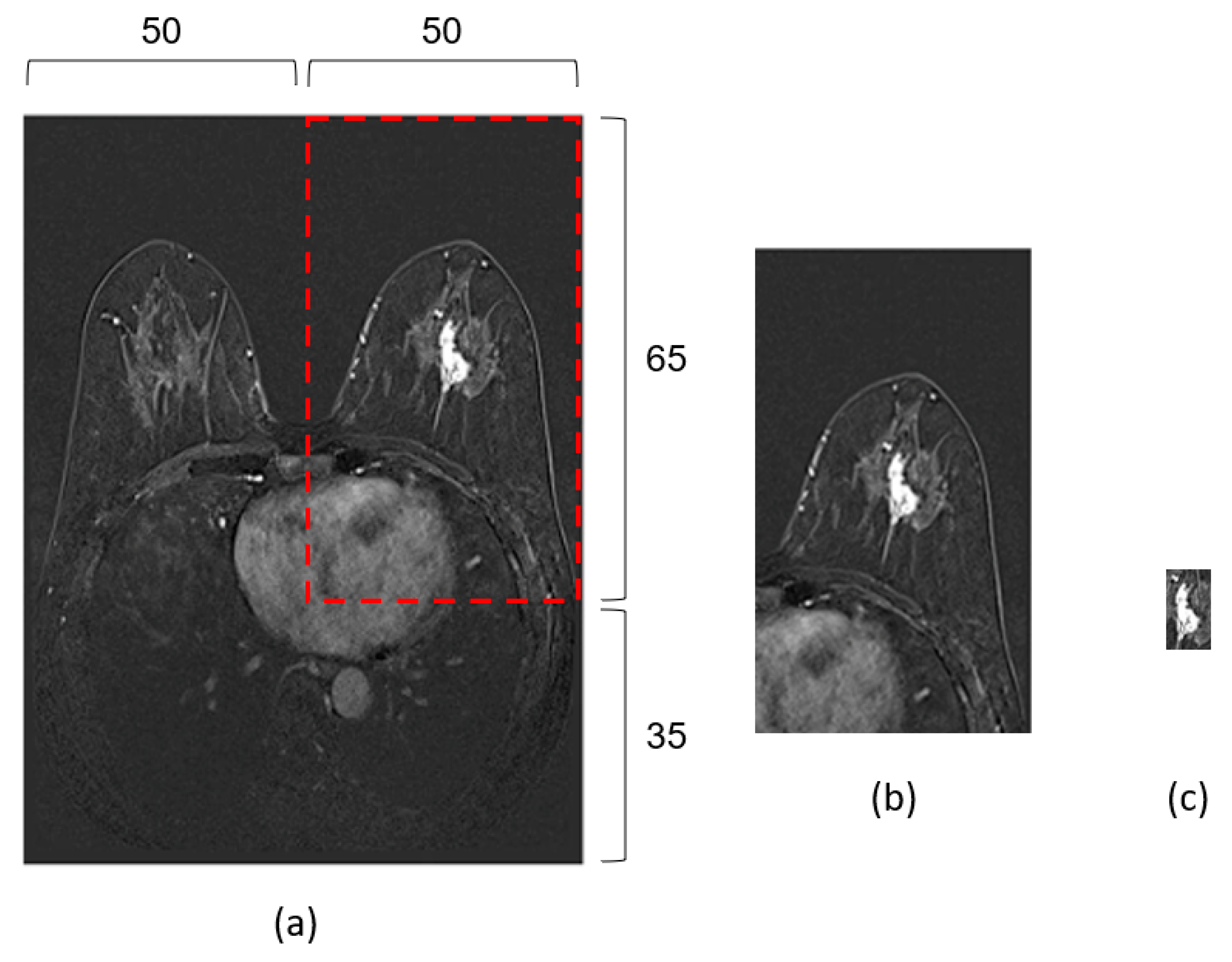
2.2. Pre-Processing
2.3. Data Preparation
2.4. Model Development
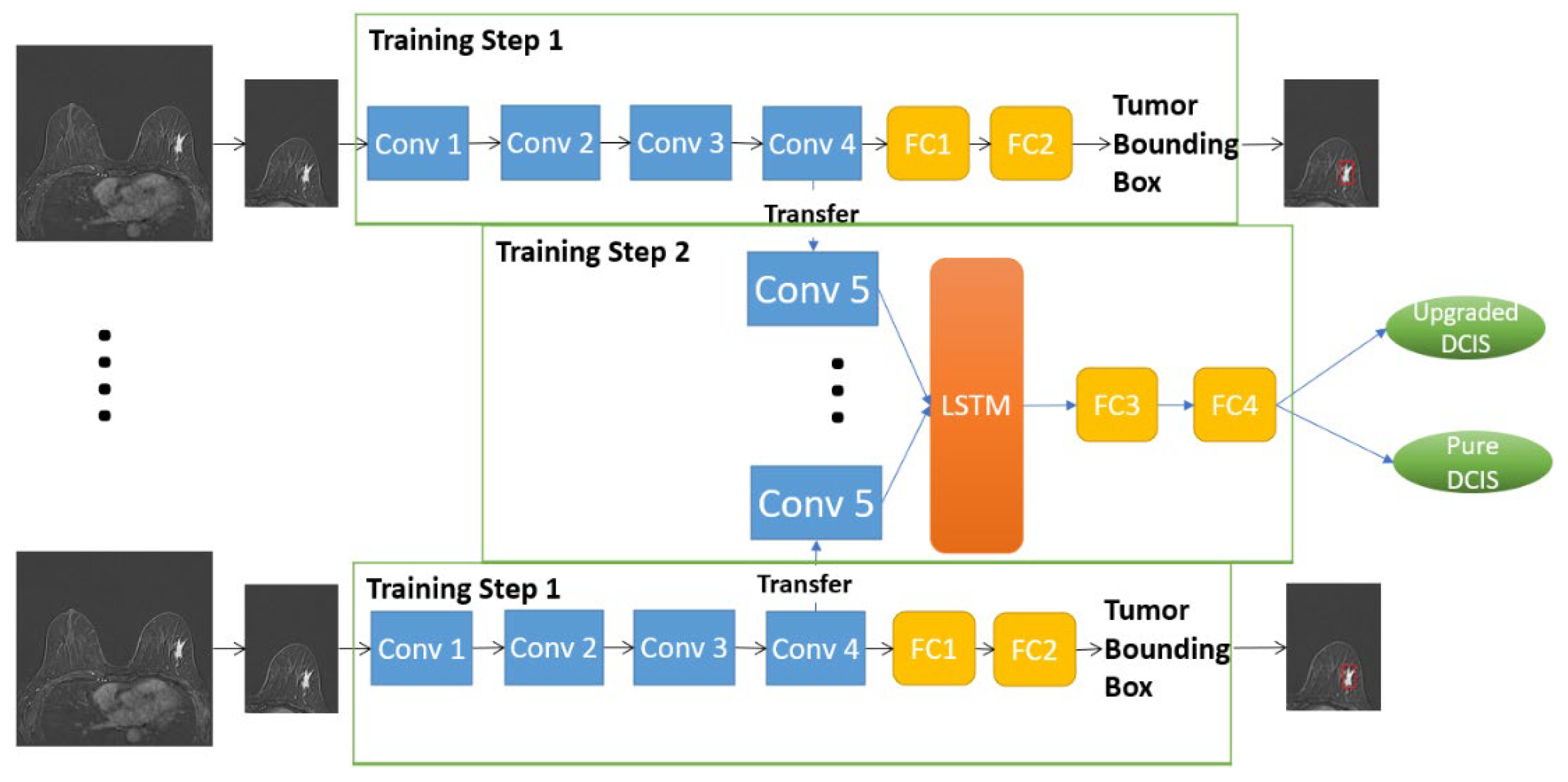
2.4.1. D-T RRCNN Model
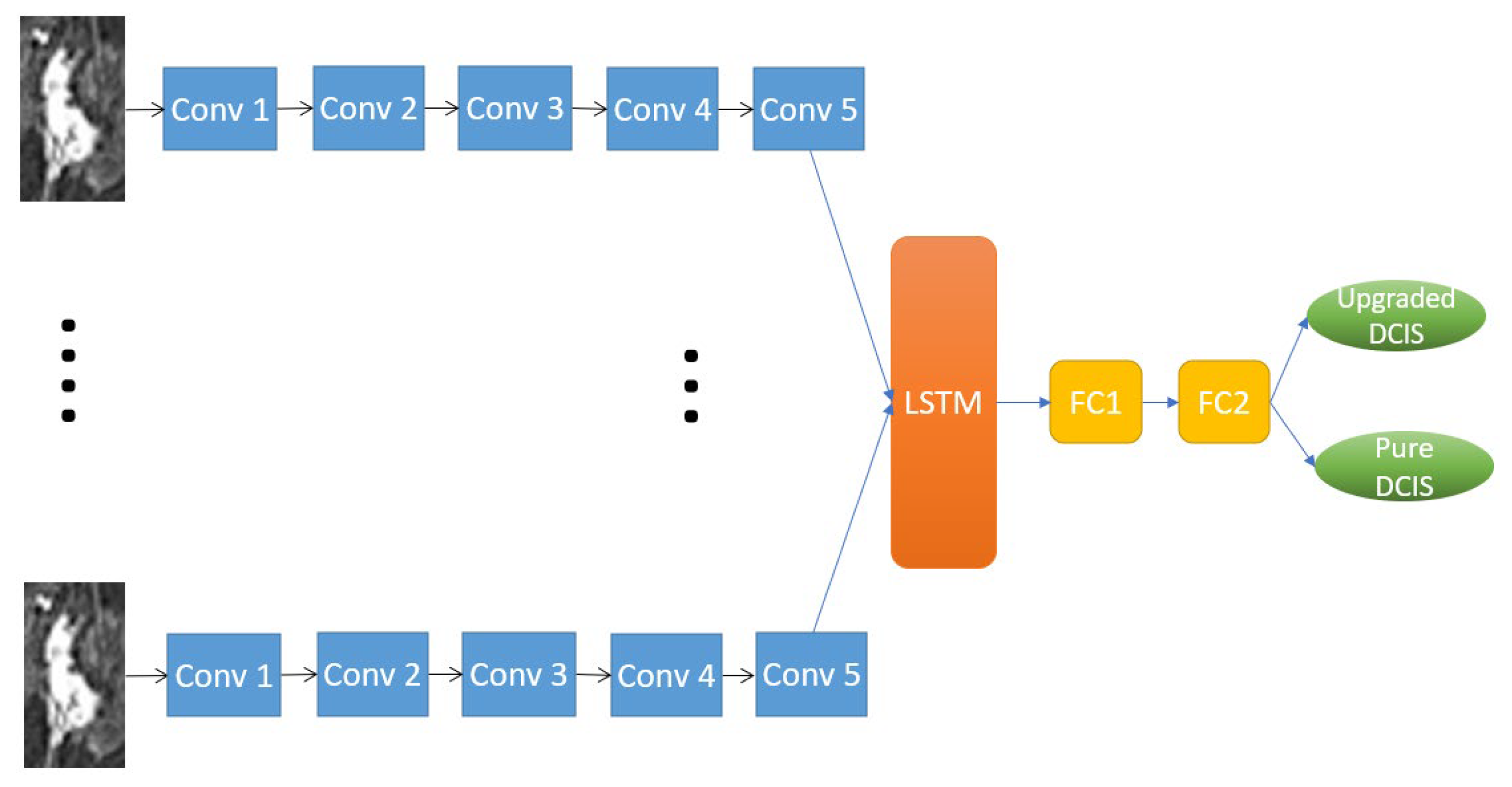
2.4.2. RRCNN with ROIs Model
2.4.3. CNN with ROIs Model
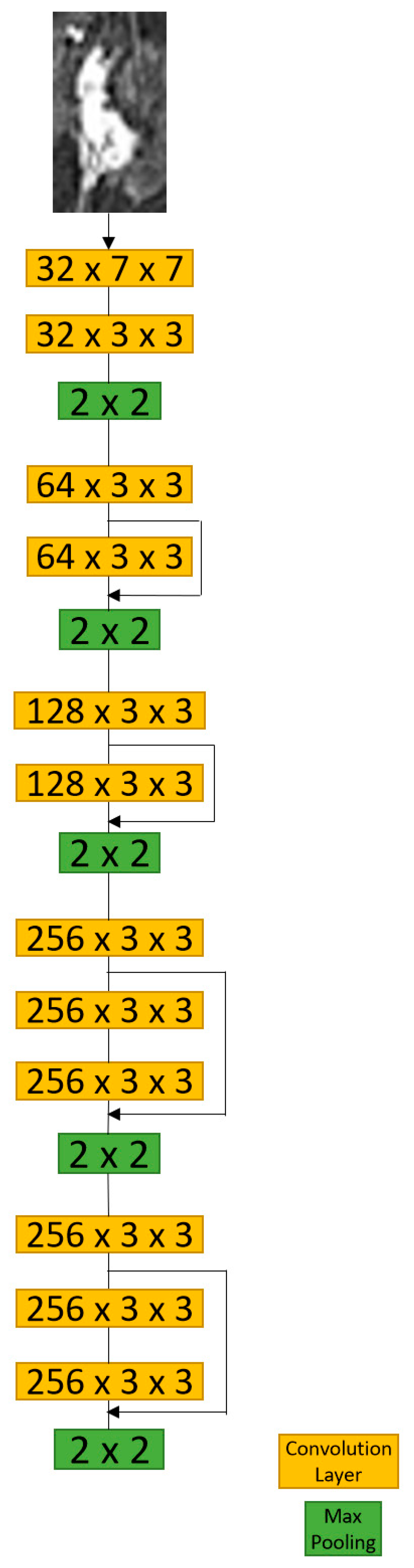
2.5. Performance Evaluation
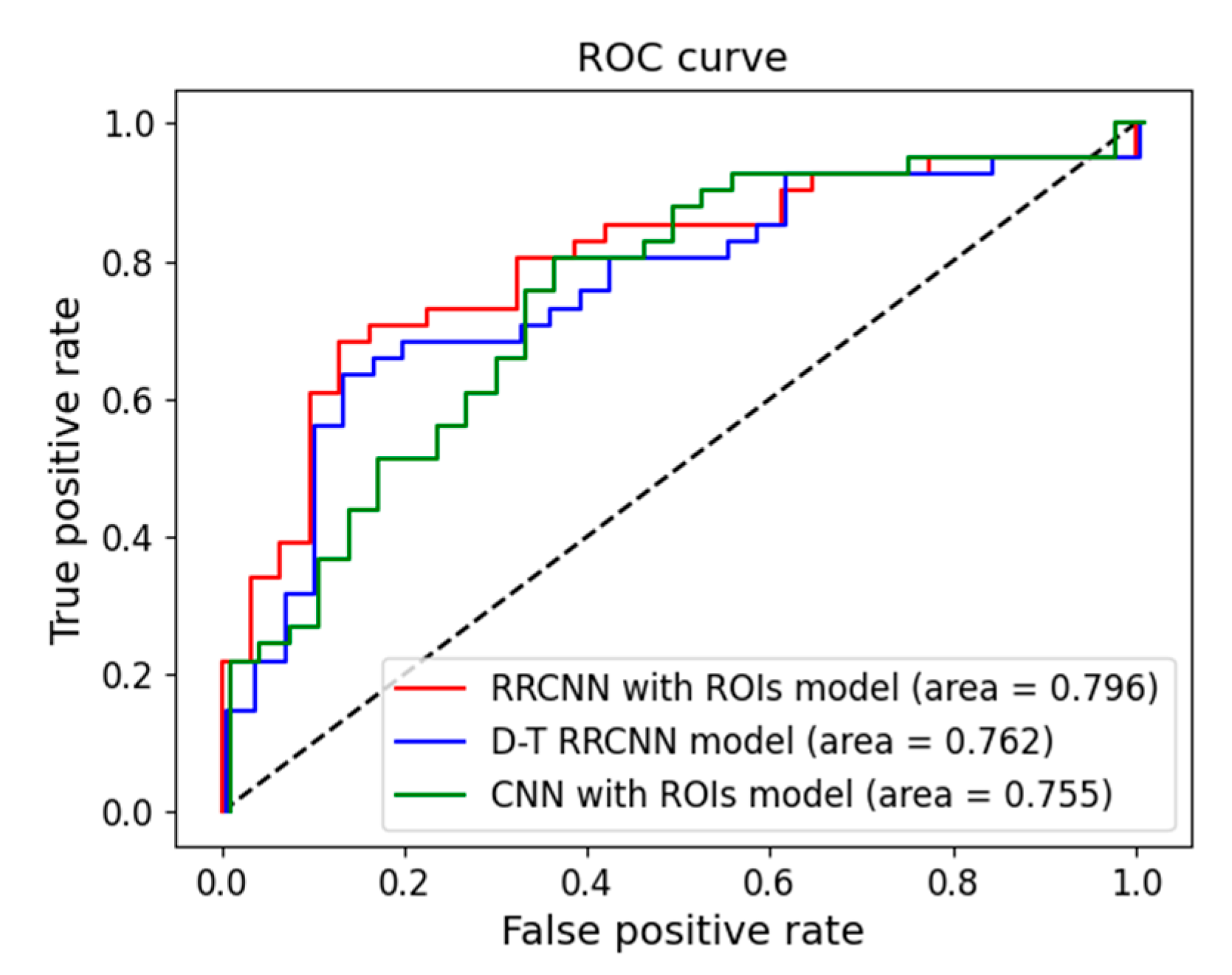
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ernster, V.L.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Barlow, W.E.; Zheng, Y.; Weaver, D.L.; Cutter, G.; Yankaskas, B.C.; Rosenberg, R.; Carney, P.A.; Kerlikowske, K.; et al. Detection of ductal carcinoma in situ in women undergoing screening mammography. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virnig, B.A.; Tuttle, T.M.; Shamliyan, T.; Kane, R.L. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: A systematic review of incidence, treatment, and outcomes. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Page, D.L.; Dupont, W.D.; Rogers, L.W.; Jensen, R.A.; Schuyler, P.A. Continued local recurrence of carcinoma 15-25 years after a diagnosis of low grade ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast treated only by biopsy. Cancer 1995, 76, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuttel, F.M.; Menezes, G.L.; van Diest, P.J.; Witkamp, A.J.; van den Bosch, M.A.; Verkooijen, H.M. Meta-analysis of the concordance of histological grade of breast cancer between core needle biopsy and surgical excision specimen. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMasters, K.M.; Chao, C.; Wong, S.L.; Martin, R.C., 3rd; Edwards, M.J. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ: A proposal. Cancer 2002, 95, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.E.; Turner, R.M.; Ciatto, S.; Marinovich, M.L.; French, J.R.; Macaskill, P.; Houssami, N. Ductal carcinoma in situ at core-needle biopsy: Meta-analysis of underestimation and predictors of invasive breast cancer. Radiology 2011, 260, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.Y.; Gweon, H.M.; Son, E.J.; Yoo, M.; Kim, J.A.; Youk, J.H. Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed at US-guided 14-gauge core-needle biopsy for breast mass: Preoperative predictors of invasive breast cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Mikhael, P.G.; Oseni, T.O.; Bahl, M. Ductal carcinoma in situ on digital mammography versus digital breast tomosynthesis: Rates and predictors of pathologic upgrade. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6089–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Park, A.Y.; Jung, H.K.; Ko, K.H.; Kim, Y.; Koh, J. The usefulness of ultrafast MRI evaluation for predicting histologic upgrade of ductal carcinoma in situ. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 136, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.T.; Cheung, Y.C.; Lo, Y.F.; Ueng, S.H.; Kuo, W.L.; Chen, S.C. MRI findings of cancers preoperatively diagnosed as pure DCIS at core needle biopsy. Acta Radiol. 2011, 52, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Yuen, S.; Akazawa, K.; Nishida, K.; Konishi, E.; Kajihara, M.; Shinkura, N.; Yamada, K. The role of breast MR imaging in pre-operative determination of invasive disease for ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed by needle biopsy. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Harowicz, M.; Zhang, J.; Saha, A.; Grimm, L.J.; Hwang, E.S.; Mazurowski, M.A. Deep learning analysis of breast MRIs for prediction of occult invasive disease in ductal carcinoma in situ. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 115, 103498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Do, L.N.; Baek, B.H.; Kim, S.K.; Yang, H.J.; Park, I.; Yoon, W. Automatic Assessment of ASPECTS Using Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Recurrent Residual Convolutional Neural Network. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Harowicz, M.R.; Saha, A.; Grimm, L.J.; Marcom, P.K.; Marks, J.R.; Hwang, E.S.; Mazurowski, M.A. Can algorithmically assessed MRI features predict which patients with a preoperative diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ are upstaged to invasive breast cancer? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamb, L.R.; Lehman, C.D.; Oseni, T.O.; Bahl, M. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) at Breast MRI: Predictors of Upgrade to Invasive Carcinoma. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, G.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Cha, J.H.; Shin, H.J.; Chae, E.Y.; Kim, H.H. The role of MRI and clinicopathologic features in predicting the invasive component of biopsy-confirmed ductal carcinoma in situ. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Mazurowski, M.A.; Grimm, L.J.; Marks, J.R.; King, L.M.; Maley, C.C.; Hwang, E.S.; Lo, J.Y. Prediction of Upstaged Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Using Forced Labeling and Domain Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Grimm, L.J.; Mazurowski, M.A.; Baker, J.A.; Marks, J.R.; King, L.M.; Maley, C.C.; Hwang, E.S.; Lo, J.Y. Prediction of Occult Invasive Disease in Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Using Deep Learning Features. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15 Pt B, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.H.; Rho, M.; Lee, M.; Kim, G.R.; Park, V.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, M.J. Prior to Breast MRI Guidelines in Korea, Where Were We? Investig. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 25, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.M.; Cho, N.; Moy, L. Breast MRI: State of the Art. Radiology 2019, 292, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Training | Validation | Testing | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure DCIS | 126 | 35 | 41 | 202 |
| Upgraded DCIS | 94 | 25 | 31 | 150 |
| Total | 220 | 60 | 72 | 352 |
| Batch Size | Learning Rate | Input Size | Size of ROI Bounding Box * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-T RRCNN | 32 | 3 × 10−6 | 128 × 128 × 3 × 20 | |
| RRCNN with ROIs | 32 | 8 × 10−7 | 64 × 64 × 3 × 20 | 20 × 30 (7 × 10~50 × 55) |
| CNN with ROIs | 128 | 10−5 | 64 × 64 × 3 | 20 × 30 (7 × 10~50 × 55) |
| Models | Validation | Testing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | Acc. (%) | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | Acc. (%) | AUC | |
| D-T RRCNN | 0.600 (0.408–0.792) | 0.828 (0.703–0.953) | 73.3 (62.1–84.5) | 0.781 (0.657–0.904) | 0.645 (0.476–0.813) | 0.804 (0.682–0.925) | 73.6 (63.4–83.8) | 0.762 (0.647–0.877) |
| RRCNN with ROIs | 0.640 (0.451–0.828) | 0.800 (0.667–0.932) | 73.3 (62.1–84.5) | 0.785 (0.663–0.907) | 0.677 (0.512–0.842) | 0.804 (0.682–0.925) | 75.0 (65.0–85.0) | 0.796 (0.688–0.904) |
| CNN with ROIs | 0.640 (0.451–0.828) | 0.828 (0.703–0.953) | 75.0 (64.1–86.0) | 0.767 (0.641–0.893) | 0.645 (0.476–0.813) | 0.756 (0.624–0.887) | 70.8 (60.3–81.3) | 0.755 (0.639–0.871) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Do, L.-N.; Lee, H.-J.; Im, C.; Park, J.H.; Lim, H.S.; Park, I. Predicting Underestimation of Invasive Cancer in Patients with Core-Needle-Biopsy-Diagnosed Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Tomography 2023, 9, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010001
Do L-N, Lee H-J, Im C, Park JH, Lim HS, Park I. Predicting Underestimation of Invasive Cancer in Patients with Core-Needle-Biopsy-Diagnosed Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Tomography. 2023; 9(1):1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleDo, Luu-Ngoc, Hyo-Jae Lee, Chaeyeong Im, Jae Hyeok Park, Hyo Soon Lim, and Ilwoo Park. 2023. "Predicting Underestimation of Invasive Cancer in Patients with Core-Needle-Biopsy-Diagnosed Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Using Deep Learning Algorithms" Tomography 9, no. 1: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010001
APA StyleDo, L.-N., Lee, H.-J., Im, C., Park, J. H., Lim, H. S., & Park, I. (2023). Predicting Underestimation of Invasive Cancer in Patients with Core-Needle-Biopsy-Diagnosed Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Using Deep Learning Algorithms. Tomography, 9(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010001






