Secondary Complications in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Objective of This Work
3. Case Series
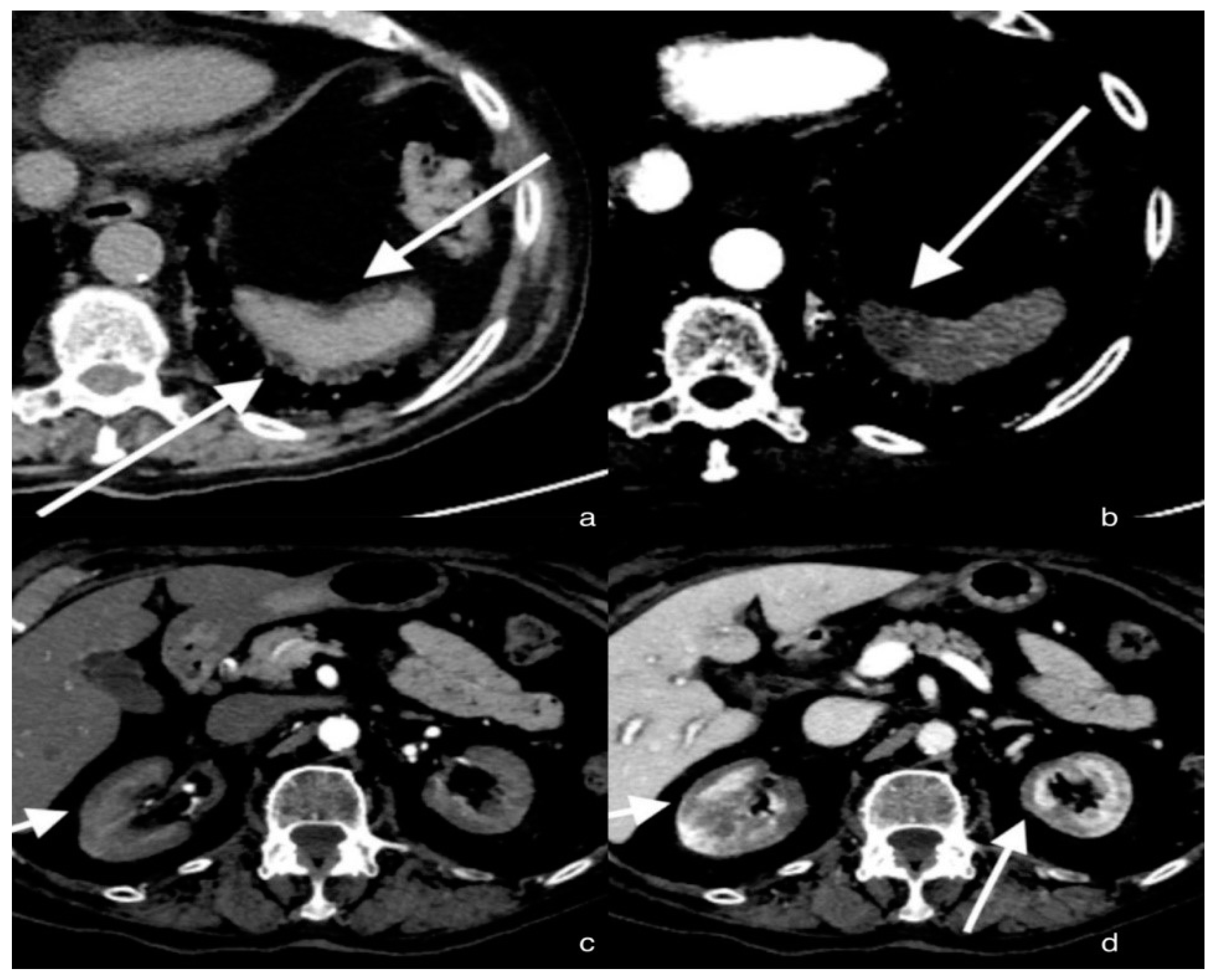
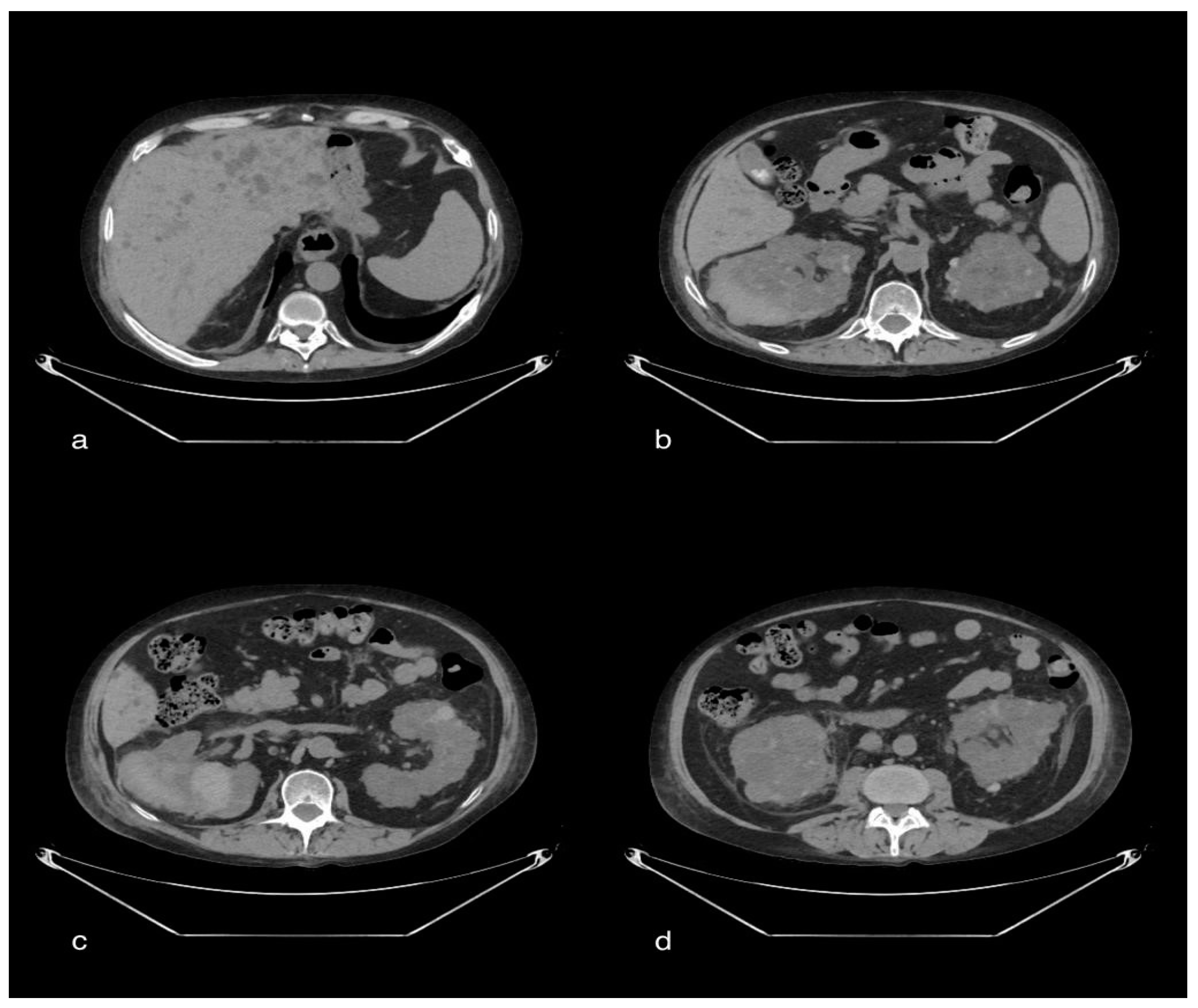
3.1. Case 1: Renal Cortical Necrosis and Splenic Infarction
3.1.1. Clinical History
3.1.2. CT Imaging Findings
3.1.3. Discussion
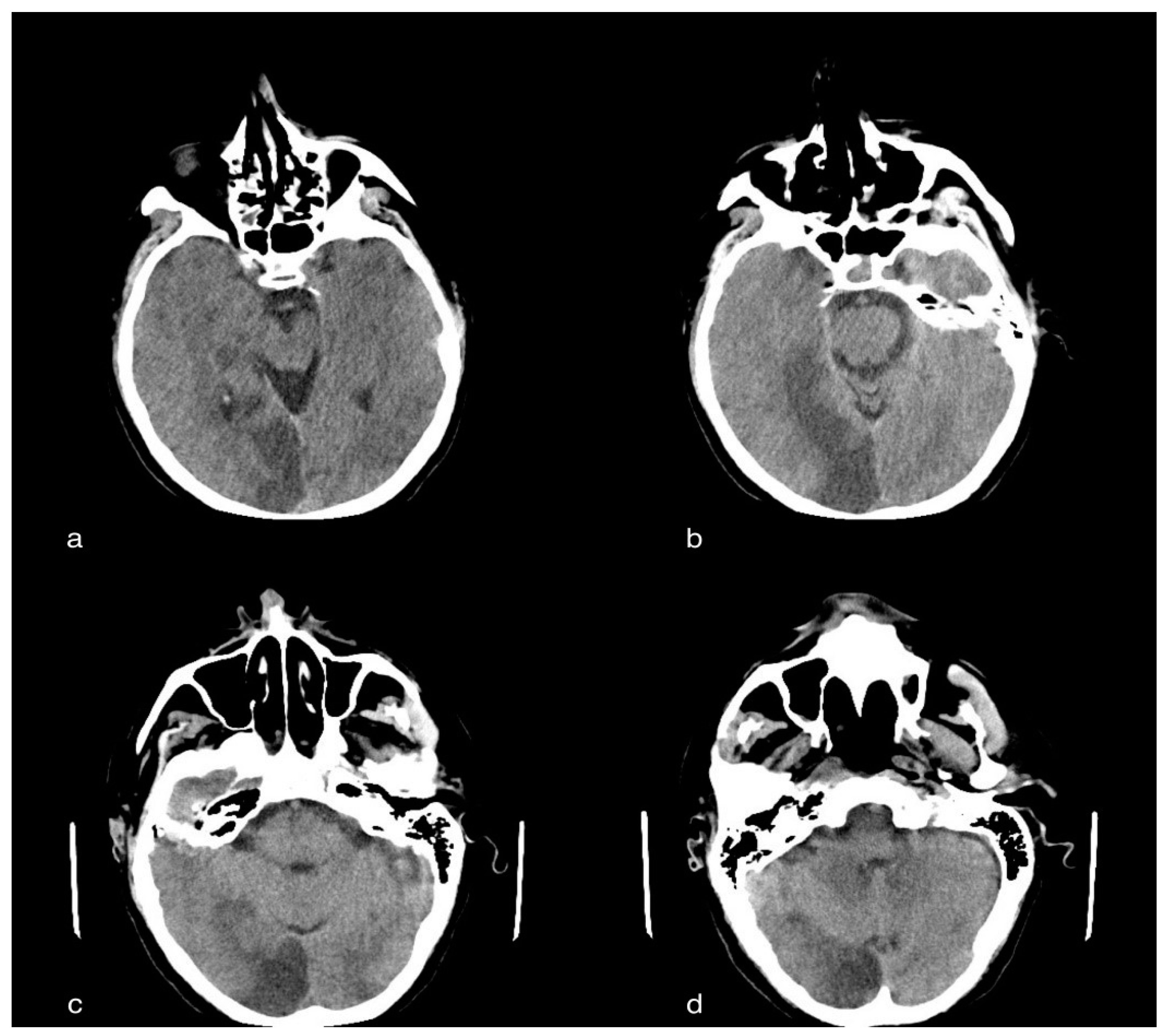
3.2. Case 2: Cerebral Ischemic Stroke
3.2.1. Clinical History
3.2.2. CT Imaging Findings
3.2.3. Discussion
- (1)
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, or of the limbs, especially on one side of the body.
- (2)
- Sudden confusion, difficulty speaking or difficulty understanding speech.
- (3)
- Sudden difficulty seeing in one or both eyes.
- (4)
- Sudden difficulty walking, dizziness, loss of balance or lack of coordination.
- (5)
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause.
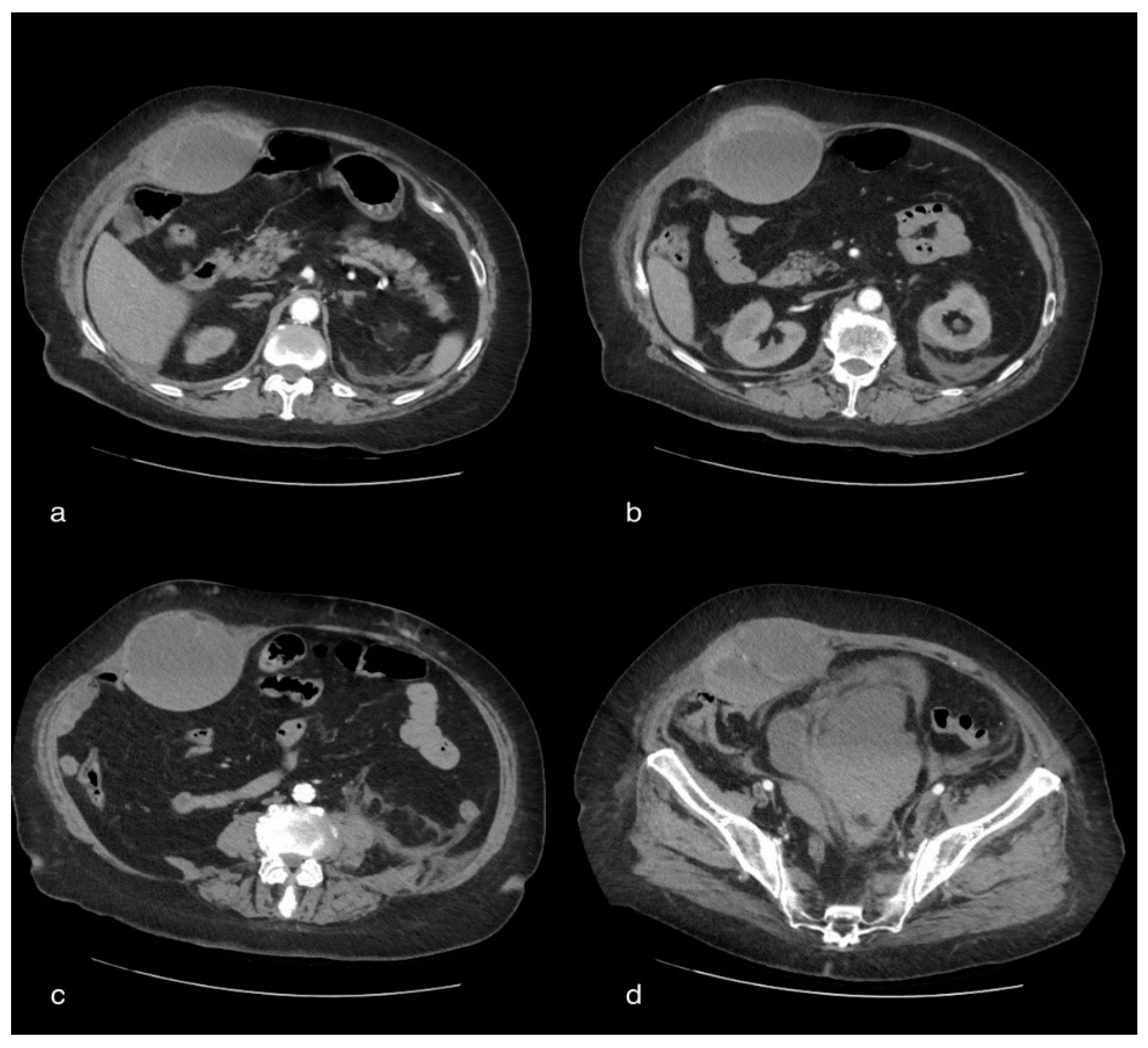
3.3. Case 3: Rectus Hematoma
3.3.1. Clinical History
3.3.2. CT Imaging Finding
3.3.3. Discussion
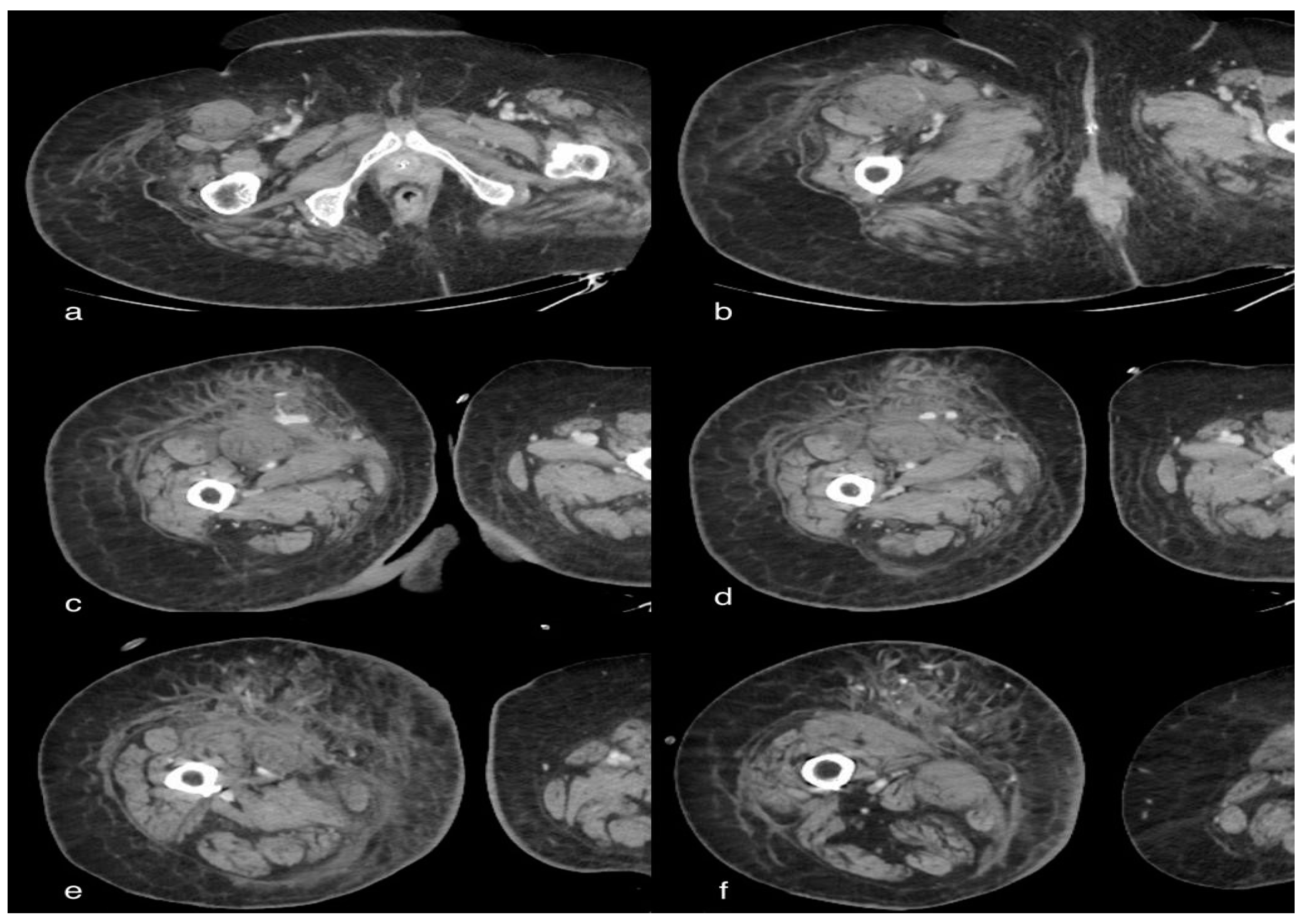
3.4. Case 4: Active Bleeding of the Right Lower Limb
3.4.1. Clinical History
3.4.2. CT Imaging Finding
3.4.3. Discussion
3.5. Case 5: Renal Hematoma
3.5.1. Clinical History
3.5.2. CT Imaging Finding
3.5.3. Discussion
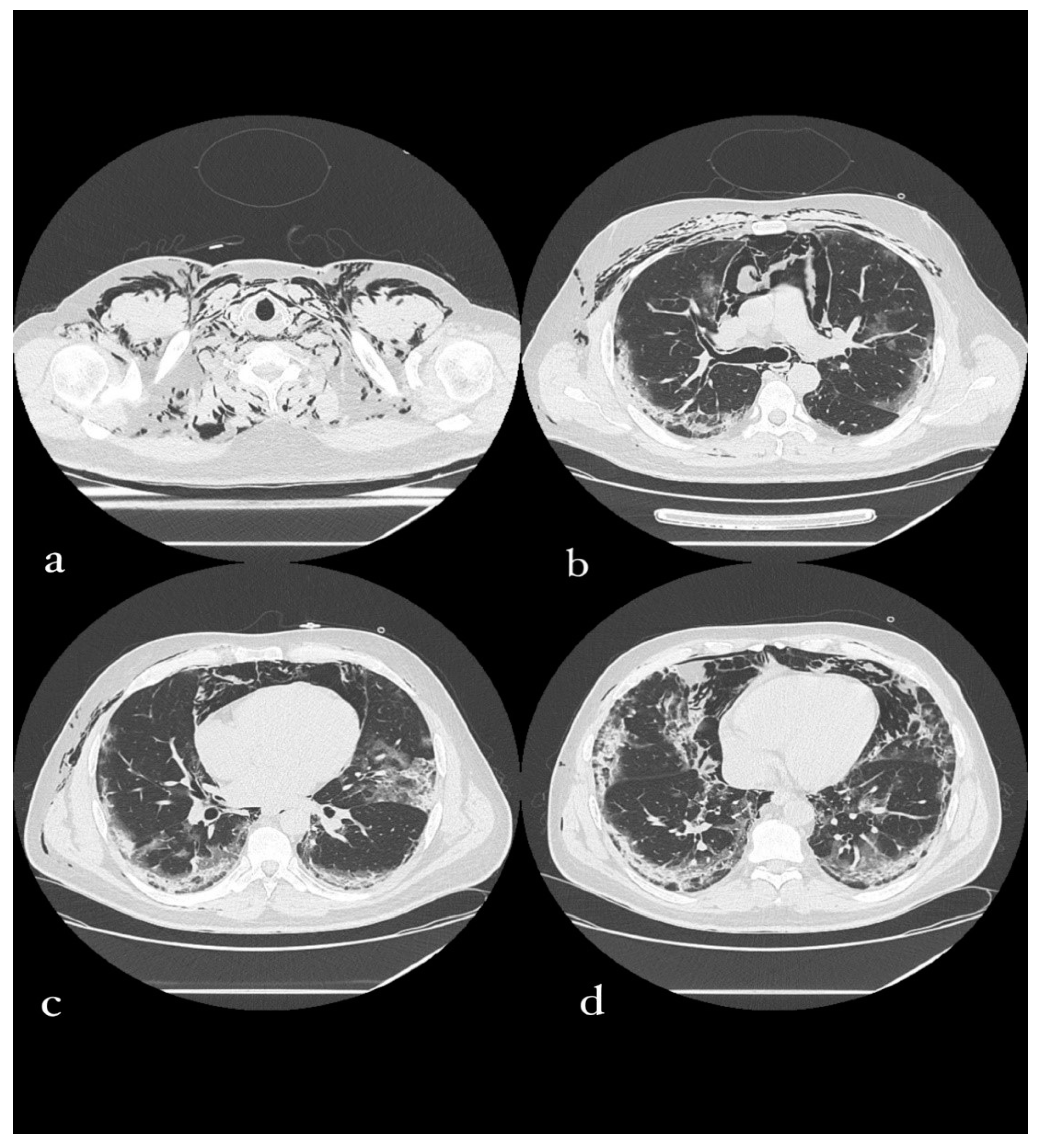
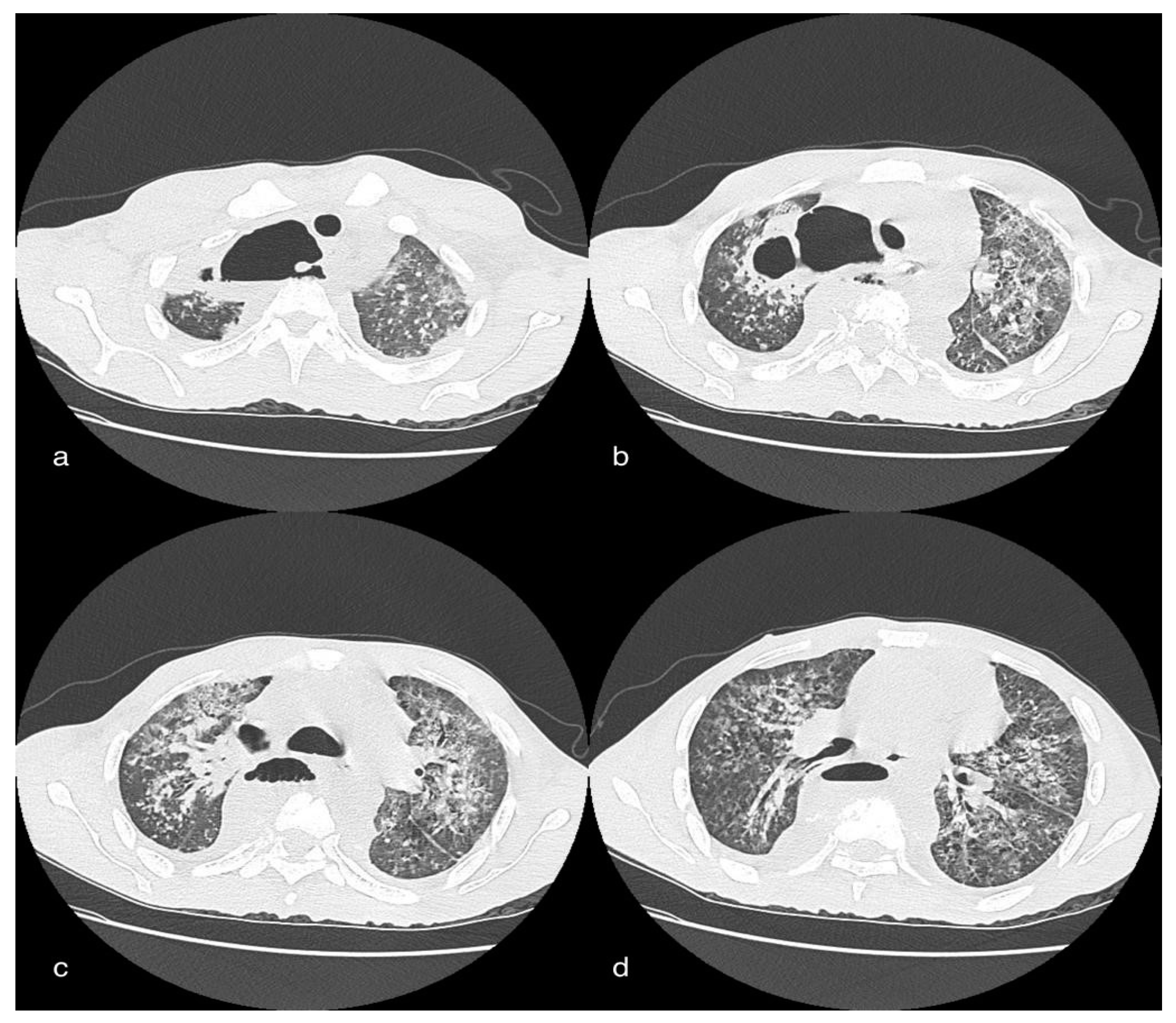
3.6. Case 6: Pneumomediastinum
3.6.1. Clinical History
3.6.2. CT Imaging Findings
3.6.3. Discussion
3.7. Case 7: Paravertebral Abscess Collection
3.7.1. Clinical History
3.7.2. Imaging Finding
3.7.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tavakoli, A.; Vahdat, K.; Keshavarz, M. Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): An Emerging Infectious Disease in the 21st Century. Iran. South Med. J. 2020, 22, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.W.; Tian, J.H.; Pei, Y.Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baratella, E.; Ruaro, B.; Marrocchio, C.; Poillucci, G.; Pigato, C.; Bozzato, A.M.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Crimi, F.; Wade, B.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Chest Digital Tomosynthesis in Patients Recovering after COVID-19 Pneumonia. Tomography 2022, 8, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, Y. Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Tools. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassi, R.; Belfiore, M.P.; Montanelli, A.; Patelli, G.; Urraro, F.; Giacobbe, G.; Fusco, R.; Granata, V.; Petrillo, A.; Sacco, P.; et al. COVID-19 pneumonia: Computer-aided quantification of healthy lung parenchyma, emphysema, ground glass and consolidation on chest computed tomography (CT). La Radiol. Med. 2021, 126, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, J.M.; Poon, L.L.; Lee, K.C.; Ng, W.F.; Lai, S.T.; Leung, C.Y.; Chu, C.M.; Hui, P.K.; Mak, K.L.; Lim, W.; et al. Lung pathology of fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet 2003, 361, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasr, T.; Holderbaum, A.M.; Chaturvedi, P.; Agarwal, K.; Kinney, J.L.; Daniels, K.; Trisno, S.L.; Ustiyan, V.; Shannon, J.M.; Wells, J.M.; et al. Disruption of a hedgehog-foxf1-rspo2 signaling axis leads to tracheomalacia and a loss of sox9+ tracheal chondrocytes. Dis. Models Mech. 2020, 14, dmm046573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyokawa, H.; Morimoto, M. Molecular crosstalk in tracheal development and its recurrence in adult tissue regeneration. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2021, 250, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratella, E.; Bussani, R.; Zanconati, F.; Marrocchio, C.; Fabiola, G.; Braga, L.; Maiocchi, S.; Berlot, G.; Volpe, M.C.; Moro, E.; et al. Radiological-pathological signatures of patients with COVID-19-related pneumomediastinum: Is there a role for the Sonic hedgehog and Wnt5a pathways? ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. CT Imaging Features of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology 2020, 295, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menter, T.; Haslbauer, J.D.; Nienhold, R.; Savic, S.; Hopfer, H.; Deigendesch, N.; Frank, S.; Turek, D.; Willi, N.; Pargger, H.; et al. Postmortem examination of COVID-19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings in lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction. Histopathology 2020, 77, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, F.A.; Kruip, M.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Arbous, M.S.; Gommers, D.; Kant, K.M.; Kaptein, F.H.J.; van Paassen, J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Huisman, M.V.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020, 191, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasim Agha, O.; Berryman, R. Acute Splenic Artery Thrombosis and Infarction Associated with COVID-19 Disease. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2020, 2020, 8880143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, D.; Soler, M.J.; Sparks, M.A.; Hiremath, S.; South, A.M.; Welling, P.A.; Swaminathan, S. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19: Emerging Evidence of a Distinct Pathophysiology. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2020, 31, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Bai, H.; Chen, X.; Gong, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2020, 18, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuysbaert, T.; Standaert, C.; De Visschere, P. Reverse Rim Sign. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2018, 102, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balcar, I.; Seltzer, S.E.; Davis, S.; Geller, S. CT patterns of splenic infarction: A clinical and experimental study. Radiology 1984, 151, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigada, M.; Bottino, N.; Tagliabue, P.; Grasselli, G.; Novembrino, C.; Chantarangkul, V.; Pesenti, A.; Peyvandi, F.; Tripodi, A. Hypercoagulability of COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit: A report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2020, 18, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.K.; Goh, C.; Leow, A.S.T.; Tambyah, P.A.; Ang, A.; Yap, E.S.; Tu, T.M.; Sharma, V.K.; Yeo, L.L.L.; Chan, B.P.L.; et al. COVID-19 and ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-summary of the literature. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 50, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntaios, G.; Michel, P.; Georgiopoulos, G.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Xiong, J.; Calleja, P.; Ostos, F.; González-Ortega, G.; Fuentes, B.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19 and Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Global COVID-19 Stroke Registry. Stroke 2020, 51, e254–e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Baskett, W.I.; Huang, W.; Shyu, D.; Myers, D.; Raju, M.; Lobanova, I.; Suri, M.F.K.; Naqvi, S.H.; French, B.R.; et al. Acute Ischemic Stroke and COVID-19: An Analysis of 27 676 Patients. Stroke 2021, 52, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deana, C.; Verriello, L.; Pauletto, G.; Corradi, F.; Forfori, F.; Cammarota, G.; Bignami, E.; Vetrugno, L.; Bove, T. Insights into neurological dysfunction of critically ill COVID-19 patients. Trends Anaesth. Crit. Care 2020, 36, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitalakumar, D.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Flora, S.J.S. Neurological Manifestations in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 2776–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Kataria, S.; Srivastava, S.; Lakhani, D.A.; Sriwastava, S. Multiple embolic stroke on magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in a COVID-19 case with persistent encephalopathy. Clin. Imaging 2021, 69, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, F.; Wu, K.L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.H.; Zhu, C.L. Prominent changes in blood coagulation of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierini, S.; Incampo, E.; Bokor, D.; Dadone, V.; Ornaghi, M.; Zanini, F.; Gentile, F.; Mancarella, S. [Coagulopathy in COVID-19: Pathophysiology]. G. Ital. Di Cardiol. 2020, 21, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudabadi, H.Z.; Hadadi, A.; Fattahi, M.R.; Kafan, S.; Ashouri, M.; Allahbeigi, R.; Hajebi, R. Rectus Sheath Hematoma in COVID-19 Patients as a Mortal Complication: A Retrospective Report. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 7436827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Sakamoto, I.; Kohzaki, S.; Uetani, M.; Mori, M.; Fujimoto, T.; Hayashi, K.; Matsuo, S. Spontaneous rectus sheath hematomas: Clinical and radiological features. Abdom. Imaging 1996, 21, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Gupta, S.; Leaf, R.K.; Wang, W.; Rosovsky, R.P.; Brenner, S.K.; Hayek, S.S.; Berlin, H.; Kapoor, R.; Shaefi, S.; et al. Thrombosis, Bleeding, and the Observational Effect of Early Therapeutic Anticoagulation on Survival in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, I.; Akoluk, A.; Douedi, S.; Upadhyaya, V.; Mazahir, U.; Costanzo, E.; Flynn, D. Life-Threatening Psoas Hematoma due to Retroperitoneal Hemorrhage in a COVID-19 Patient on Enoxaparin Treated With Arterial Embolization: A Case Report. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2020, 12, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Jayaram, S.; Kumar, D.B. Spontaneous Subcapsular Renal Haematoma: A Case Report. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2017, 11, Pd13–Pd14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Elalamy, I.; Kastritis, E.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Politou, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Gerotziafas, G.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AlZarooni, N.; AlBaroudi, A.; AlOzaibi, L.; AlZoabi, O. Splenic abscess as a possible sequela of COVID-19: A case series. Ann. Saudi Med. 2021, 41, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, S.; Gibo, S. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum and Macklin effect: Overview and appearance on computed tomography. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouritas, V.K.; Papagiannopoulos, K.; Lazaridis, G.; Baka, S.; Mpoukovinas, I.; Karavasilis, V.; Lampaki, S.; Kioumis, I.; Pitsiou, G.; Papaiwannou, A.; et al. Pneumomediastinum. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, S44–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconi, F.; Rogliani, P.; Leonardis, F.; Sarmati, L.; Fabbi, E.; De Carolis, G.; La Rocca, E.; Vanni, G.; Ambrogi, V. Incidence of pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: A single-center comparison between 1st and 2nd wave. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiraju, P.K.; Alex, N.M.; Safinaaz; Baby, N.M. Pneumomediastinum in COVID-19: A series of three cases and review of literature. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2021, 9, 2050313x211011807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooni, R.; Pandey, G.; Akbar, S. Broadening the differential: Pneumomediastinum and COVID-19 infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e237938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmanesh, A.; Raz, E.; Zan, E.; Derman, A.; Kaminetzky, M. Brain Imaging Use and Findings in COVID-19: A Single Academic Center Experience in the Epicenter of Disease in the United States. AJNR. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belfiore, M.P.; Russo, G.M.; Gallo, L.; Atripaldi, U.; Tamburrini, S.; Caliendo, V.; Impieri, L.; Del Canto, M.T.; Ciani, G.; Parrella, P.; et al. Secondary Complications in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series. Tomography 2022, 8, 1836-1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040154
Belfiore MP, Russo GM, Gallo L, Atripaldi U, Tamburrini S, Caliendo V, Impieri L, Del Canto MT, Ciani G, Parrella P, et al. Secondary Complications in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series. Tomography. 2022; 8(4):1836-1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040154
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelfiore, Maria Paola, Gaetano Maria Russo, Luigi Gallo, Umberto Atripaldi, Stefania Tamburrini, Valentina Caliendo, Luigi Impieri, Maria Teresa Del Canto, Giovanni Ciani, Pasquale Parrella, and et al. 2022. "Secondary Complications in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series" Tomography 8, no. 4: 1836-1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040154
APA StyleBelfiore, M. P., Russo, G. M., Gallo, L., Atripaldi, U., Tamburrini, S., Caliendo, V., Impieri, L., Del Canto, M. T., Ciani, G., Parrella, P., Mangoni di Santo Stefano, M. L., Salvia, A. A. H., Urraro, F., Nardone, V., Coppola, N., Reginelli, A., & Cappabianca, S. (2022). Secondary Complications in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series. Tomography, 8(4), 1836-1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8040154







