Bile Flow Dynamics in Patients with Cholelithiasis: An Evaluation with Cine-Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Using a Spatially Selective Inversion-Recovery Pulse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
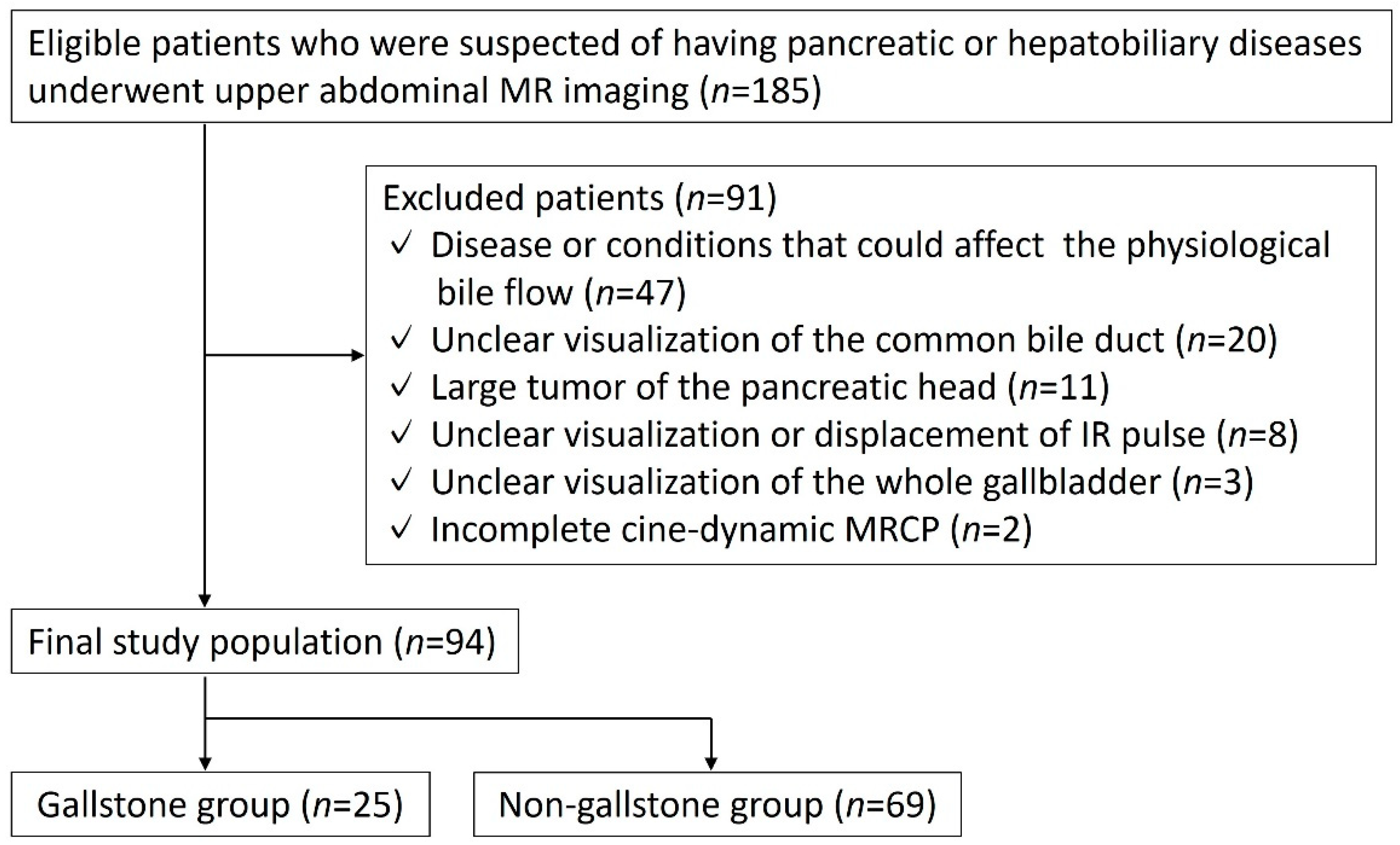
2.1. Study Population
2.2. MRI Technique
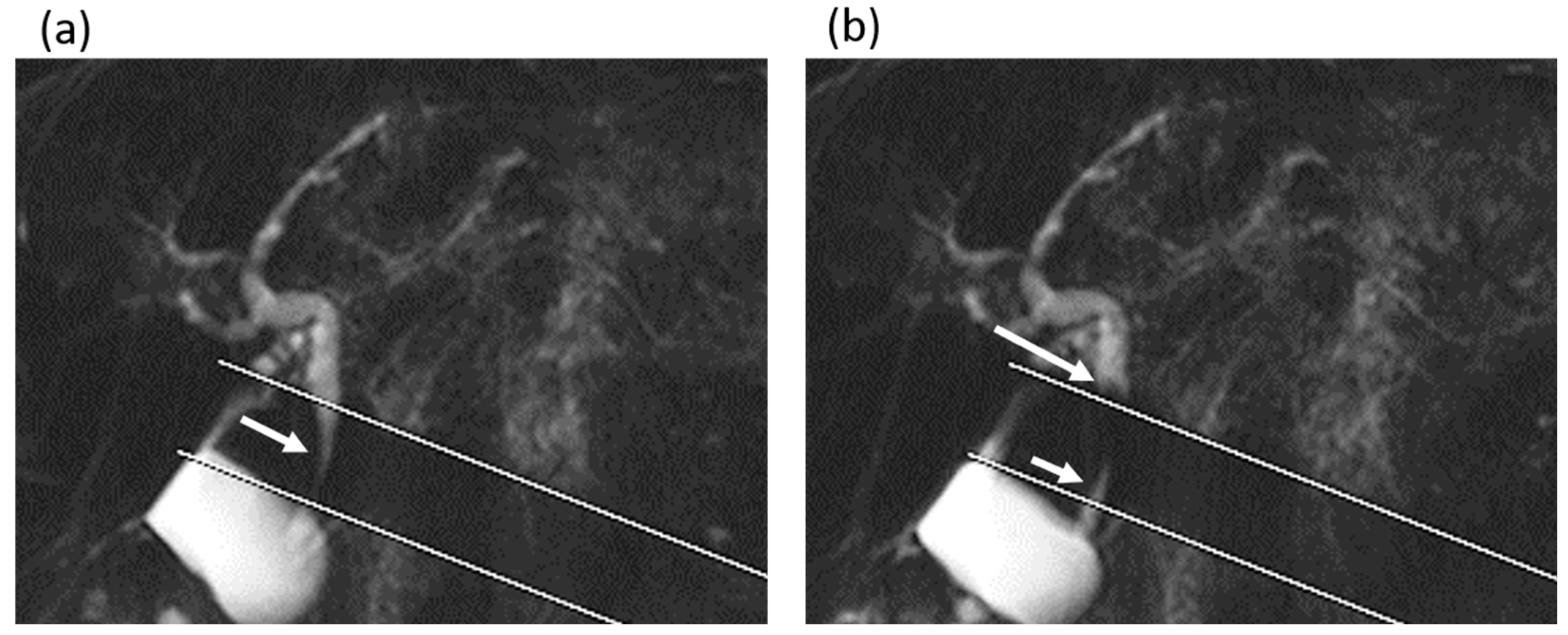
2.3. Image Evaluations
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Littlefield, A.; Lenahan, C. Cholelithiasis: Presentation and Management. J. Midwifery Women’s Health 2019, 64, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabanzadeh, D.M. Incidence of gallstone disease and complications. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 34, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, B.D.; Winters, K.L.; Edlich, R.F. Cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implant. 2005, 15, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshikhes, A.W. Asymptomatic gallstones in the laparoscopic era. J. R. Coll. Surg. Edinb. 2002, 47, 742–748. [Google Scholar]
- Cerçi, S.S.; Ozbek, F.M.; Cerçi, C.; Baykal, B.; Eroğlu, H.E.; Baykal, Z.; Yildiz, M.; Sağlam, S.; Yeşildağ, A. Gallbladder function and dynamics of bile flow in asymptomatic gallstone disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2763–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán, M.A.; Beltrán, A.A. Common bile duct pressure in patients with and without cholelithiasis: A case-control study. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2021, 28, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, H.A.; Roslyn, J.J.; Kuchenbecker, S.L.; Doty, J.E.; Denbesten, L. The role of cystic duct resistance in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstones. J. Surg. Res. 1981, 30, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, J.E.; Pitt, H.A.; Kuchenbecker, S.L.; DenBesten, L. Impaired gallbladder emptying before gallstone formation in the prairie dog. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Kanki, A.; Yamamoto, A.; Tamada, T.; Yasokawa, K.; Tanimoto, D.; Sato, T.; Higaki, A.; Noda, Y.; Yoshida, K. Assessment of physiologic bile flow in the extrahepatic bile duct with cine-dynamic MR cholangiopancreatography and a spatially selective inversion-recovery pulse. Radiology 2014, 270, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Ihara, K.; Iida, E.; Furukawa, M.; Okada, M.; Ito, K. Pancreatobiliary Flow Dynamics: Association Between Bile and Pancreatic Juice Evaluated With Cine-Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Using Spatially Selective Inversion Recovery Pulse. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotozono, H.; Tamada, T.; Kanki, A.; Yasokawa, K.; Fukunaga, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Ito, K. Influence of cholecystectomy on the flow dynamic pattern of bile in the extrahepatic bile duct: Assessment by cine-dynamic MRCP with spatially-selective IR pulse. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 74, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaim, A.; Steinke, K.; Frank, M.; Enriquez, R.; Kirsch, E.; Bongartz, G.; Steinbrich, W. Diameter of the common bile duct in the elderly patient: Measurement by ultrasound. Eur. Radiol. 1998, 8, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toouli, J. Evaluation of sphincter of Oddi function. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1989, 59, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toouli, J. Sphincter of Oddi: Function, dysfunction, and its management. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24 (Suppl. 3), S57–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housset, C.; Chrétien, Y.; Debray, D.; Chignard, N. Functions of the Gallbladder. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1549–1577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kao, C.H.; Wang, S.J.; Chen, G.H.; Yeh, S.H. Evaluation of gallbladder function by quantitative radionuclide cholescintigraphy in patients with gallbladder sludge or stones. Nucl. Med. Commun. 1994, 15, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamada, T.; Ito, K.; Yasokawa, K.; Higaki, A.; Kanki, A.; Noda, Y.; Yamamoto, A. Accumulation of Bile in the Gallbladder: Evaluation by means of Serial Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Cholangiography with Gadolinium Ethoxybenzyl Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic Acid. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 479067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Catalano, O.A.; Sahani, D.V.; Kalva, S.P.; Cushing, M.S.; Hahn, P.F.; Brown, J.J.; Edelman, R.R. MR imaging of the gallbladder: A pictorial essay. Radiogr. A Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc. 2008, 28, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S.; Rivero, H.G.; Erlikh, I.V.; Griffith, L.F.; Kondamudi, V.K. Surgical and nonsurgical management of gallstones. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 89, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.Y.; Olde Hartman, T.C.; van der Velden, J.J.; Bohnen, A.M. Is biliary pain exclusively related to gallbladder stones? A controlled prospective study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. J. R. Coll. Gen. Pract. 2004, 54, 574–579. [Google Scholar]


| Gallstone Group | Non-Gallstone Group | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 25 | 69 | - |
| Age (year) | 72 (62–77) | 71 (65–78) | 0.592 |
| Common bile duct diameter (mm) | 7 (6–8) | 6 (5–7.5) | 0.015 |
| Frequency of observation of antegrade bile flow | 8 (4–11) | 3 (0–8) | 0.011 |
| Mean secretion grade of antegrade bile flow | 0.55 (0.25–0.85) | 0.2 (0–0.4) | 0.003 |
| Frequency of observation of reverse bile flow | 3 (0–8) | 3 (0–5) | 0.729 |
| Mean secretion grade of reverse bile flow | 0.15 (0–0.5) | 0.2 (0–0.35) | 0.703 |
| SIR in in-phase images | 1.2 (0.77–1.51) | 1.62 (1.2–2.12) | 0.004 |
| SIR in opposed-phase images | 0.76 (0.65–1.2) | 1.0 (0.76–1.42) | 0.210 |
| SRR | 0.11 (–0.029–0.36) | 0.35 (0.23–0.42) | 0.004 |
| Frequency of Antegrade Bile Flow | Mean Secretion Grade of Antegrade Bile Flow | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | ||
| Gallstone group | Diameter of common bile duct | −0.164 | 0.433 | −0.099 | 0.638 |
| SIR in in-phase images | 0.194 | 0.353 | 0.192 | 0.358 | |
| SIR in opposed-phase images | 0.209 | 0.316 | 0.135 | 0.519 | |
| Non-gallstone group | Diameter of common bile duct | 0.065 | 0.593 | 0.061 | 0.619 |
| SIR in in-phase images | −0.146 | 0.232 | −0.134 | 0.273 | |
| SIR in opposed-phase images | −0.097 | 0.428 | −0.092 | 0.450 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Higashi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Ihara, K.; Iida, E.; Furukawa, M.; Ito, K. Bile Flow Dynamics in Patients with Cholelithiasis: An Evaluation with Cine-Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Using a Spatially Selective Inversion-Recovery Pulse. Tomography 2022, 8, 815-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020067
Higashi M, Tanabe M, Ihara K, Iida E, Furukawa M, Ito K. Bile Flow Dynamics in Patients with Cholelithiasis: An Evaluation with Cine-Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Using a Spatially Selective Inversion-Recovery Pulse. Tomography. 2022; 8(2):815-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020067
Chicago/Turabian StyleHigashi, Mayumi, Masahiro Tanabe, Kenichiro Ihara, Etsushi Iida, Matakazu Furukawa, and Katsuyoshi Ito. 2022. "Bile Flow Dynamics in Patients with Cholelithiasis: An Evaluation with Cine-Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Using a Spatially Selective Inversion-Recovery Pulse" Tomography 8, no. 2: 815-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020067
APA StyleHigashi, M., Tanabe, M., Ihara, K., Iida, E., Furukawa, M., & Ito, K. (2022). Bile Flow Dynamics in Patients with Cholelithiasis: An Evaluation with Cine-Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Using a Spatially Selective Inversion-Recovery Pulse. Tomography, 8(2), 815-823. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020067







