Pre-Procedure Thrombocytopenia and Leukopenia Association with Risk for Infection in Image-Guided Tunneled Central Venous Catheter Placement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maki, D.G.; Kluger, D.M.; Crnich, C.J. The risk of bloodstream infection in adults with different intravascular devices: A systematic review of 200 published prospective studies. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, M.J.; Pellegrini, D.C.; Safdar, N. Attributable mortality of central line associated bloodstream infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Infection 2015, 43, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacigalupo, A.; Ballen, K.; Rizzo, D.; Giralt, S.; Lazarus, H.; Ho, V.; Apperley, J.; Slavin, S.; Pasquini, M.; Sandmaier, B.M.; et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: Working definitions. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009, 15, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Chmielewski, M.; Honda, H.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Matsuo, S.; Yuzawa, Y.; Tranaeus, A.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B. Aspects of immune dysfunction in end-stage renal disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elihu, A.; Gollin, G. Complications of implanted central venous catheters in neutropenic children. Am. Surg. 2007, 73, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoss, D.R.; Bedros, A.A.; Mesipam, A.; Criddle, J.; Smith, J.C. Severe Neutropenia at the Time of Implantable Subcutaneous Chest Port Insertion Is Not a Risk Factor for Port Removal at a Tertiary Pediatric Center. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, R.; Lorenz, J.M.; Lale, A.J.; Funaki, B.S.; Zangan, S.M. Clinical predictors of port infections within the first 30 days of placement. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 25, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skummer, P.; Kobayashi, K.; DeRaddo, J.S.; Blackburn, T.; Schoeneck, M.; Patel, J.; Jawed, M. Risk Factors for Early Port Infections in Adult Oncologic Patients. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beathard, G.A.; Urbanes, A.; Litchfield, T. The risk of bleeding with tunneled dialysis catheter placement. J. Vasc. Access. 2016, 17, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.E., Jr.; Shenoy, S.S. Patients with thrombocytopenia: Outcome of radiologic placement of central venous access devices. Radiology 1997, 204, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.J.; Rahim, S.; Davidson, J.C.; Hanks, S.E.; Tam, A.L.; Walker, T.G.; Wilkins, L.R.; Sarode, R.; Weinberg, I. Society of Interventional Radiology Consensus Guidelines for the Periprocedural Management of Thrombotic and Bleeding Risk in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Image-Guided Interventions-Part II: Recommendations: Endorsed by the Canadian Association for Interventional Radiology and the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1168–1184.e1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van de Weerdt, E.K.; Biemond, B.J.; Baake, B.; Vermin, B.; Binnekade, J.M.; van Lienden, K.P.; Vlaar, A.P.J. Central venous catheter placement in coagulopathic patients: Risk factors and incidence of bleeding complications. Transfusion 2017, 57, 2512–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van de Weerdt, E.K.; Peters, A.L.; Goudswaard, E.J.; Binnekade, J.M.; van Lienden, K.P.; Biemond, B.J.; Vlaar, A.P.J. The practice of platelet transfusion prior to central venous catheterization in presence of coagulopathy: A national survey among clinicians. Vox Sang. 2017, 112, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duszak, R., Jr.; Bilal, N.; Picus, D.; Hughes, D.R.; Xu, B.J. Central venous access: Evolving roles of radiology and other specialties nationally over two decades. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2013, 10, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, B.; Schalk, E.; Buchheidt, D.; Hasenkamp, J.; Kiehl, M.; Kiderlen, T.R.; Kochanek, M.; Koldehoff, M.; Kostrewa, P.; Classen, A.Y.; et al. Central venous catheter-related infections in hematology and oncology: 2020 updated guidelines on diagnosis, management, and prevention by the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (DGHO). Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.E.; Huber, T.S.; Lee, T.; Shenoy, S.; Yevzlin, A.S.; Abreo, K.; Allon, M.; Asif, A.; Astor, B.C.; Glickman, M.H.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Vascular Access: 2019 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, S1–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bream, P.R., Jr. Update on Insertion and Complications of Central Venous Catheters for Hemodialysis. Semin. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 33, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaul, D.B.; Scheer, B.; Rokhsar, S.; Jones, V.A.; Chan, L.S.; Boody, B.A.; Malogolowkin, M.H.; Mason, W.H. Risk factors for early infection of central venous catheters in pediatric patients. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1998, 186, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.C.; Hsu, C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chien, S.F.; Kao, H.F.; Chang, S.Y.; Hu, F.C.; Yeh, K.H. Predictors of bloodstream infection associated with permanently implantable venous port in solid cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Ni, H. Crosstalk between Platelets and Microbial Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, H.G.; Peng, J.; Ni, H.; Hou, M.; Jansen, A.J.G. Low platelet count as risk factor for infections in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia: A retrospective evaluation. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norgaard, M.; Jensen, A.O.; Engebjerg, M.C.; Farkas, D.K.; Thomsen, R.W.; Cha, S.; Zhao, S.; Sorensen, H.T. Long-term clinical outcomes of patients with primary chronic immune thrombocytopenia: A Danish population-based cohort study. Blood 2011, 117, 3514–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumtaz, H.; Williams, V.; Hauer-Jensen, M.; Rowe, M.; Henry-Tillman, R.S.; Heaton, K.; Mancino, A.T.; Muldoon, R.L.; Klimberg, V.S.; Broadwater, J.R.; et al. Central venous catheter placement in patients with disorders of hemostasis. Am. J. Surg. 2000, 180, 503–505; discussion 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, M.A.; Thakor, A.S.; Tulin-Silver, S.; Connolly, B.L.; Cahill, A.M.; Ward, T.J.; Padia, S.A.; Kohi, M.P.; Midia, M.; Chaudry, G.; et al. Adult and Pediatric Antibiotic Prophylaxis during Vascular and IR Procedures: A Society of Interventional Radiology Practice Parameter Update Endorsed by the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe and the Canadian Association for Interventional Radiology. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1483–1501.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
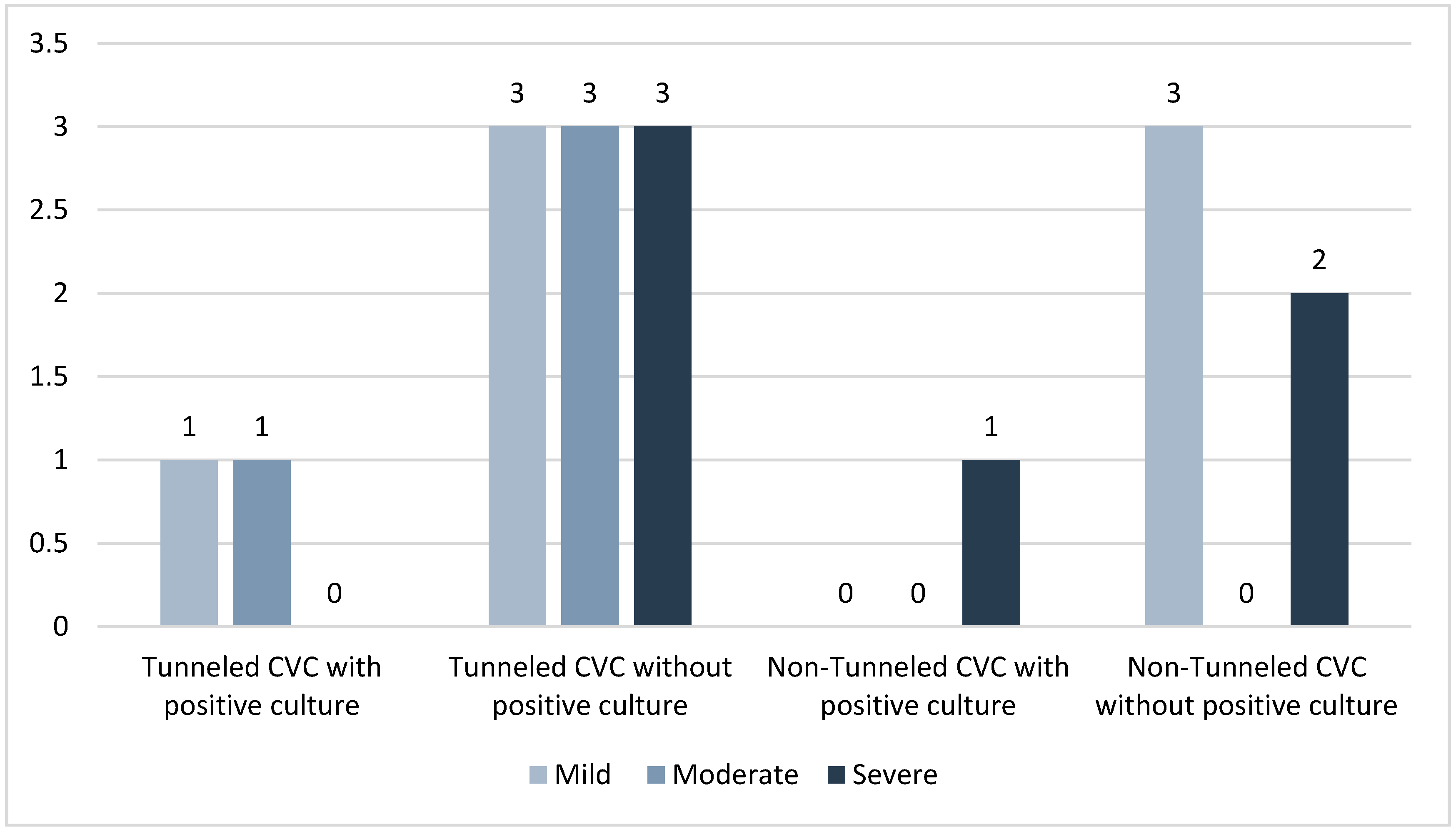
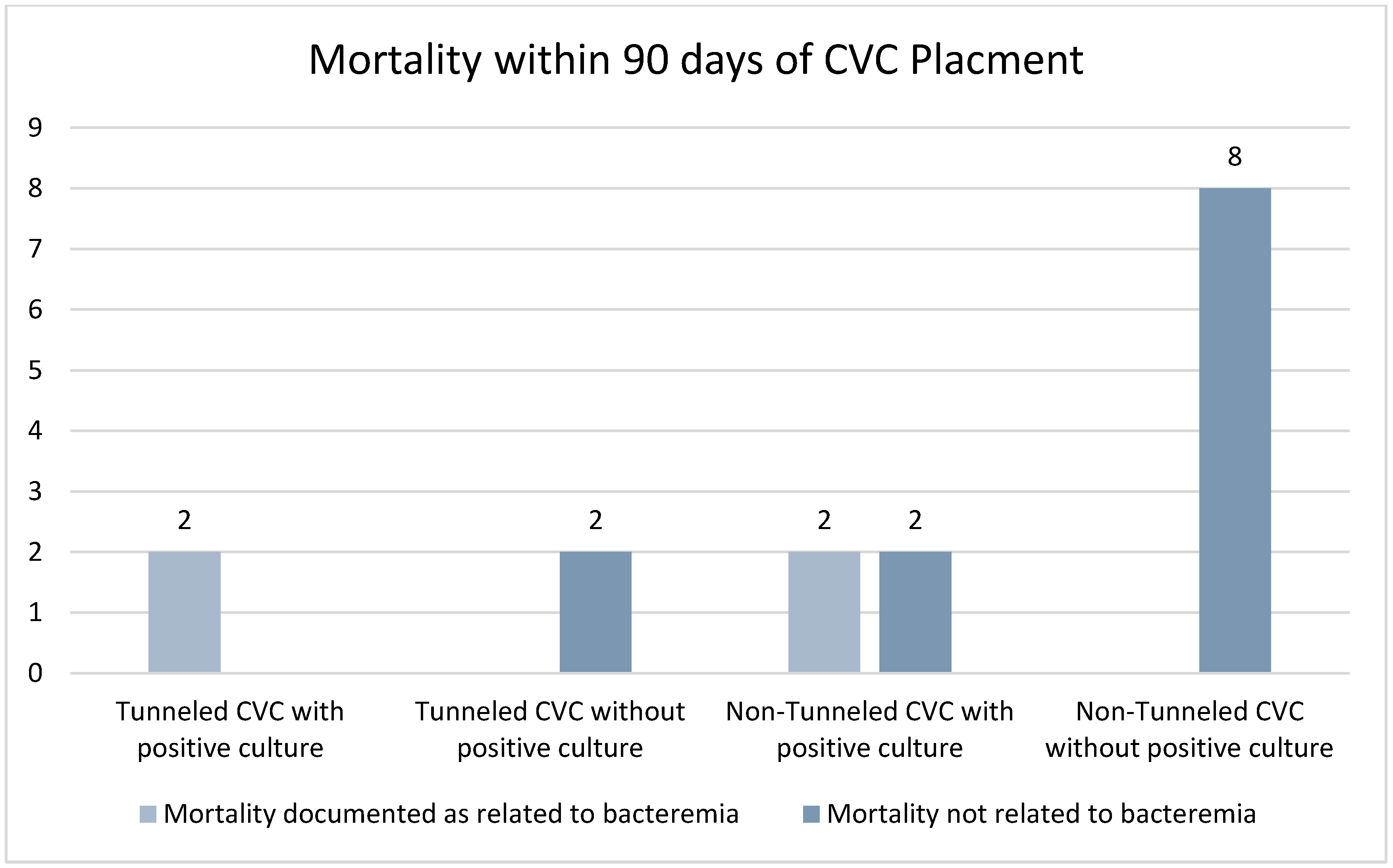
| Positive Blood Cultures n = 25 | No Positive Blood Culture n = 152 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 23–75 mean 53.3 | 17–85 mean 53.0 |
| Male | 14 (56.0%) | 93 (61.2%) |
| Female | 11 (44.0%) | 59 (38.8%) |
| Tunneled CVCs | 19 (76.0%) | 77 (50.7%) |
| Non-tunneled CVCs | 6 (24.0%) | 75 (49.3%) |
| Catheter French | 12–14.5 | 12–16 |
| Underlying Diagnosis | Hematologic (n = 15): - Leukemia (n = 7) - Lymphoma (n = 4) - Other (n = 4) Renal (n = 10): - Acute kidney injury (n = 4) - CKD/ESRD (n = 6) | Hematologic (n = 48) - Lymphoma (n = 2) - Leukemia (n = 31) - Stem cell donor (n = 7) - Other (n = 8) Renal (n = 77): - Acute kidney injury (n = 31) - CKD/ESRD (n = 46) Neuro (n = 14) - Encephalitis (n = 3) - Inflammatory polyneuropathy (n = 4) - Myositis (n = 3) - Other inflammatory disorder (n = 4) Other (n = 13): - Solid organ transplant rejection (n = 10) - Other (n = 3) |
| Reason for CVC | - Bone marrow transplant (n = 13) - Stem cell collection (n = 2) - Hemodialysis (n = 10) | - Plasmapheresis (n = 25) - Bone marrow transplant (n = 14) - Stem cell collection (n = 31) - Hemodialysis (n = 78) - Other: (n = 4) |
| Pre-Procedural Antibiotics Given | Already Receiving Antibiotics | No Antibiotics Given | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive blood cultures and tunneled CVC n= 19 | 15 (78.9%) | 3 (15.8%) | 1 (5.3%) |
| No positive blood culture and tunneled CVC n= 77 | 62 (80.5%) | 11 (14.3%) | 4 (5.2%) |
| Positive blood cultures and non-tunneled CVC n= 6 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 6 (100.0%) |
| No positive blood cultures and non-tunneled CVC n= 75 | 1 (1.3%) | 0 (0%) | 74 (98.7%) |
| Positive Blood Cultures n = 19 | No Positive Blood Culture n = 77 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC | |||
| Mean (sd) | 4.53 ± 3.08 | 9.55 ± 8.22 | p = 0.01 |
| Median | 4.05 | 7.86 | |
| Range | 0.51–12.87 | 2.25–60.11 | |
| Hemoglobin | |||
| Mean (sd) | 10.50 ± 2.17 | 10.61 ± 2.58 | p = 0.86 |
| Median | 10.20 | 10.3 | |
| Range | 22.10–44.3 | 6.5–19.0 | |
| Hematocrit | |||
| Mean (sd) | 31.85 ± 6.13 | 32.81 ± 7.98 | p = 0.62 |
| Median | 31.70 | 31.8 | |
| Range | 22.10–44.30 | 18.5–58.9 | |
| Platelets | |||
| Mean (sd) | 150 ± 84.93 | 209.54 ± 100.93 | p = 0.02 |
| Median | 181 | 197 | |
| Range | 12–270 | 32–541 |
| Patients with Positive Blood Cultures n = 6 | Patients without Positive Blood Cultures n = 75 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBC | |||
| Mean (sd) | 9.74 ± 10.27 | 23.10 ± 68.13 | p = 0.63 |
| Median | 7.61 | 11.31 | |
| Range | 1.55–29.97 | 2.44–593.52 | |
| Hemoglobin | |||
| Mean (sd) | 8.77 ± 1.6 | 11.22 ± 2.32 | p = 0.01 |
| Median | 8.35 | 11.4 | |
| Range | 7.2–11.7 | 3.94–15.9 | |
| Hematocrit | |||
| Mean (sd) | 27.33 ± 5.86 | 34.61 ± 6.76 | p = 0.01 |
| Median | 25.75 | 35.1 | |
| Range | 22.2–38.7 | 19.3–35.1 | |
| Platelets | |||
| Mean (sd) | 125.82 ± 75.05 | 212.85 ± 111.34 | p = 0.06 |
| Median | 112.5 | 197 | |
| Range | 26–247 | 6–487 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luman, A.; Quencer, K.B.; Kaufman, C. Pre-Procedure Thrombocytopenia and Leukopenia Association with Risk for Infection in Image-Guided Tunneled Central Venous Catheter Placement. Tomography 2022, 8, 627-634. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020052
Luman A, Quencer KB, Kaufman C. Pre-Procedure Thrombocytopenia and Leukopenia Association with Risk for Infection in Image-Guided Tunneled Central Venous Catheter Placement. Tomography. 2022; 8(2):627-634. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuman, Abigail, Keith B. Quencer, and Claire Kaufman. 2022. "Pre-Procedure Thrombocytopenia and Leukopenia Association with Risk for Infection in Image-Guided Tunneled Central Venous Catheter Placement" Tomography 8, no. 2: 627-634. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020052
APA StyleLuman, A., Quencer, K. B., & Kaufman, C. (2022). Pre-Procedure Thrombocytopenia and Leukopenia Association with Risk for Infection in Image-Guided Tunneled Central Venous Catheter Placement. Tomography, 8(2), 627-634. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8020052





