Current Concepts in Imaging Diagnosis and Screening of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Imaging Techniques
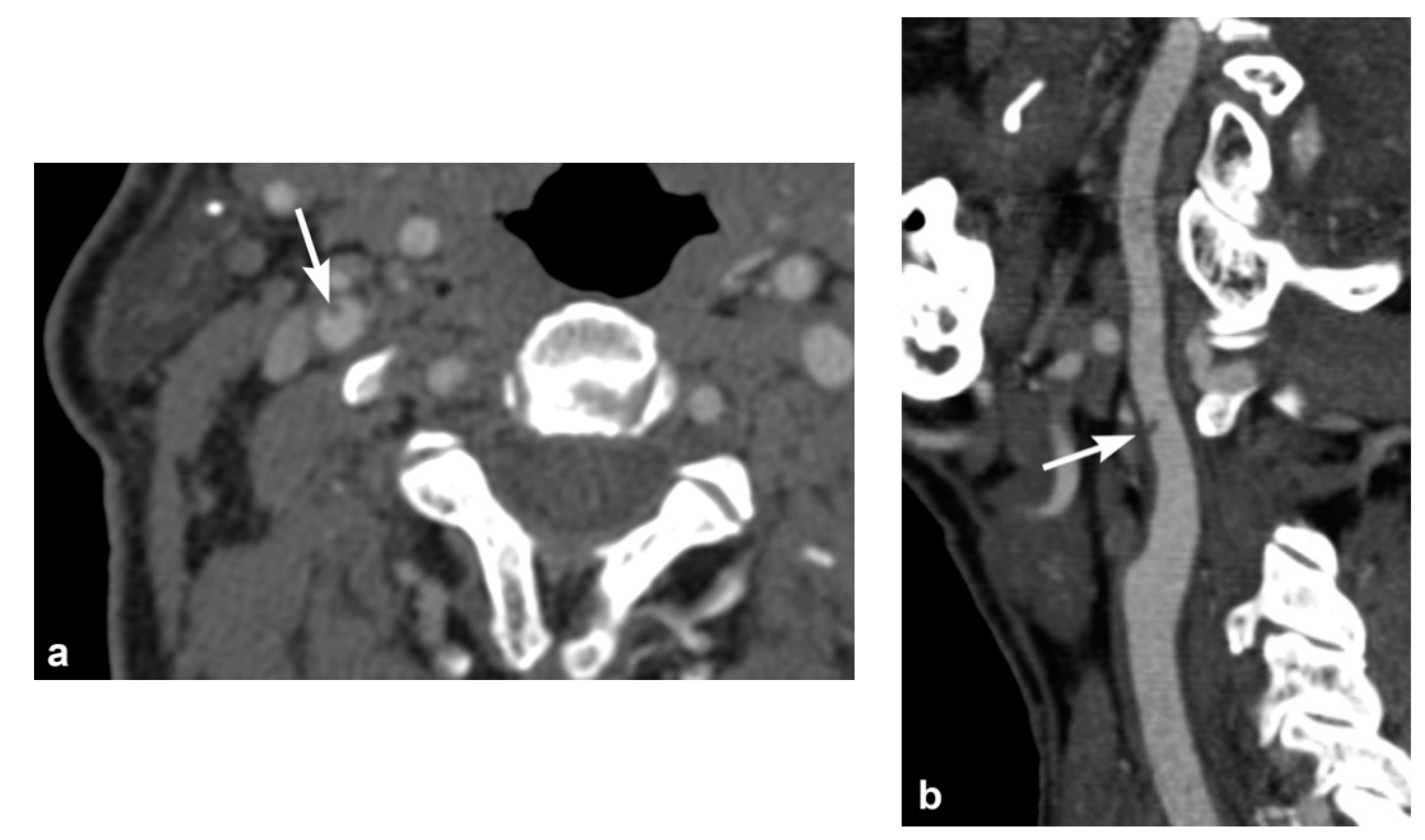
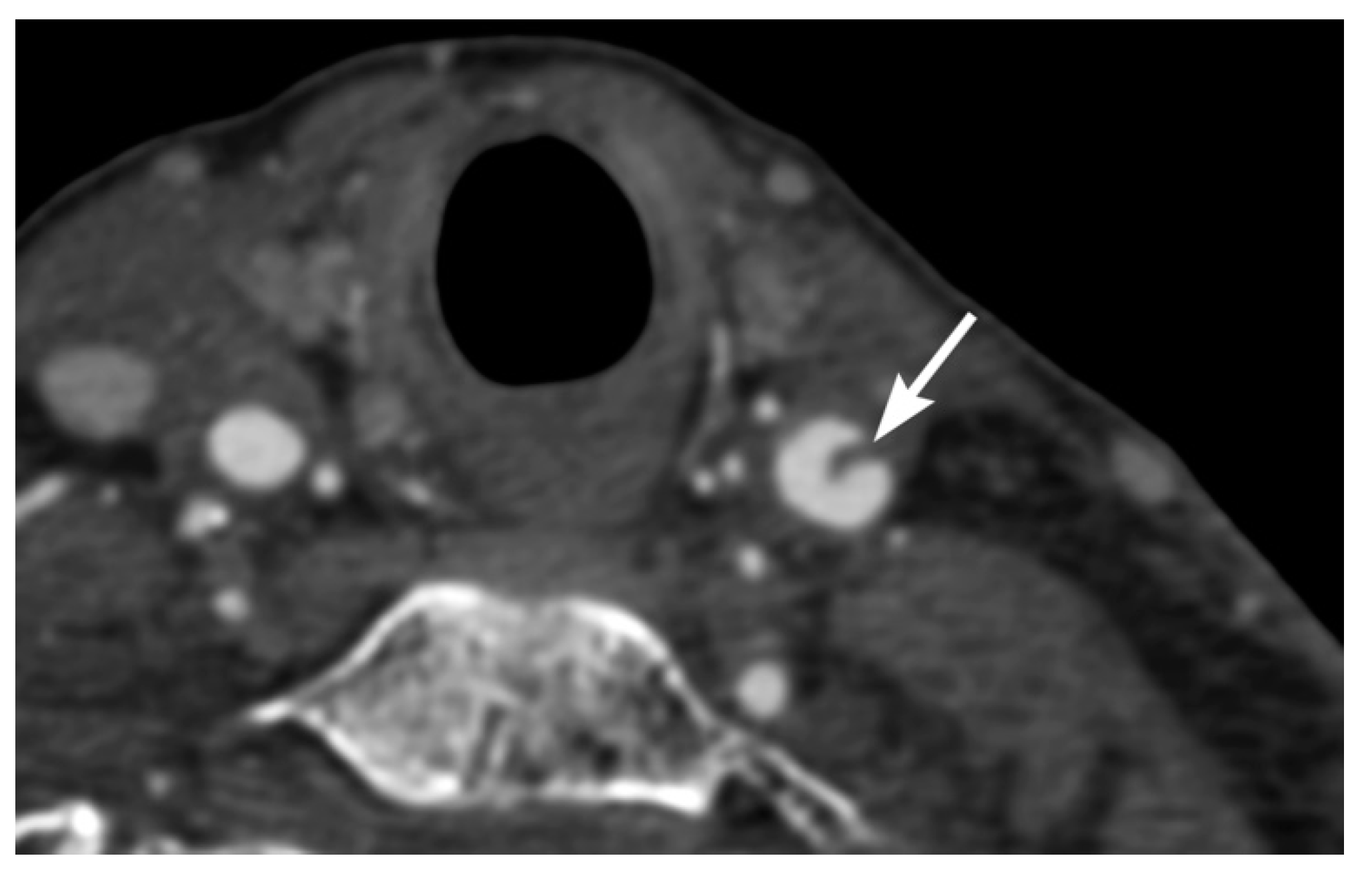
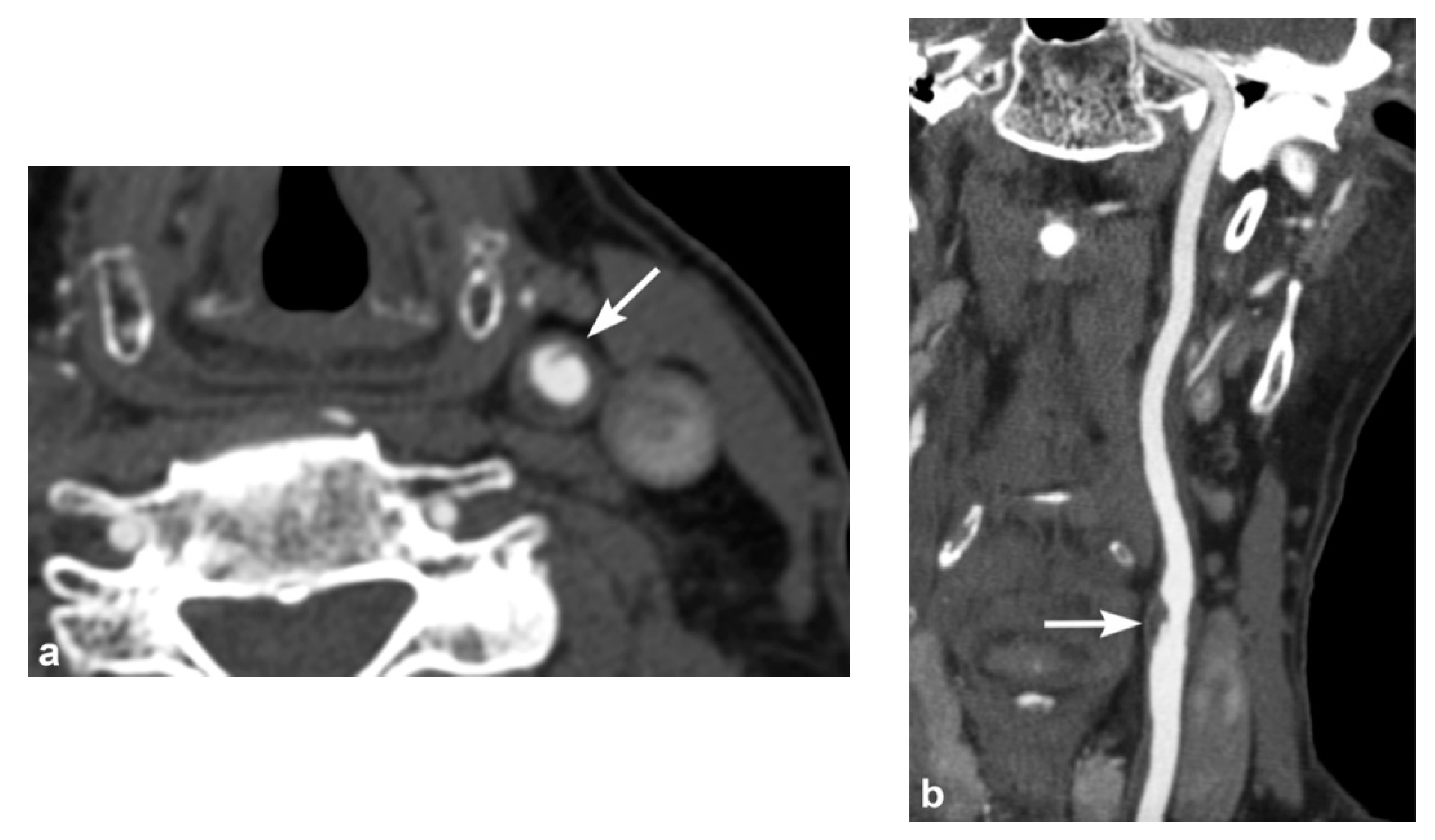
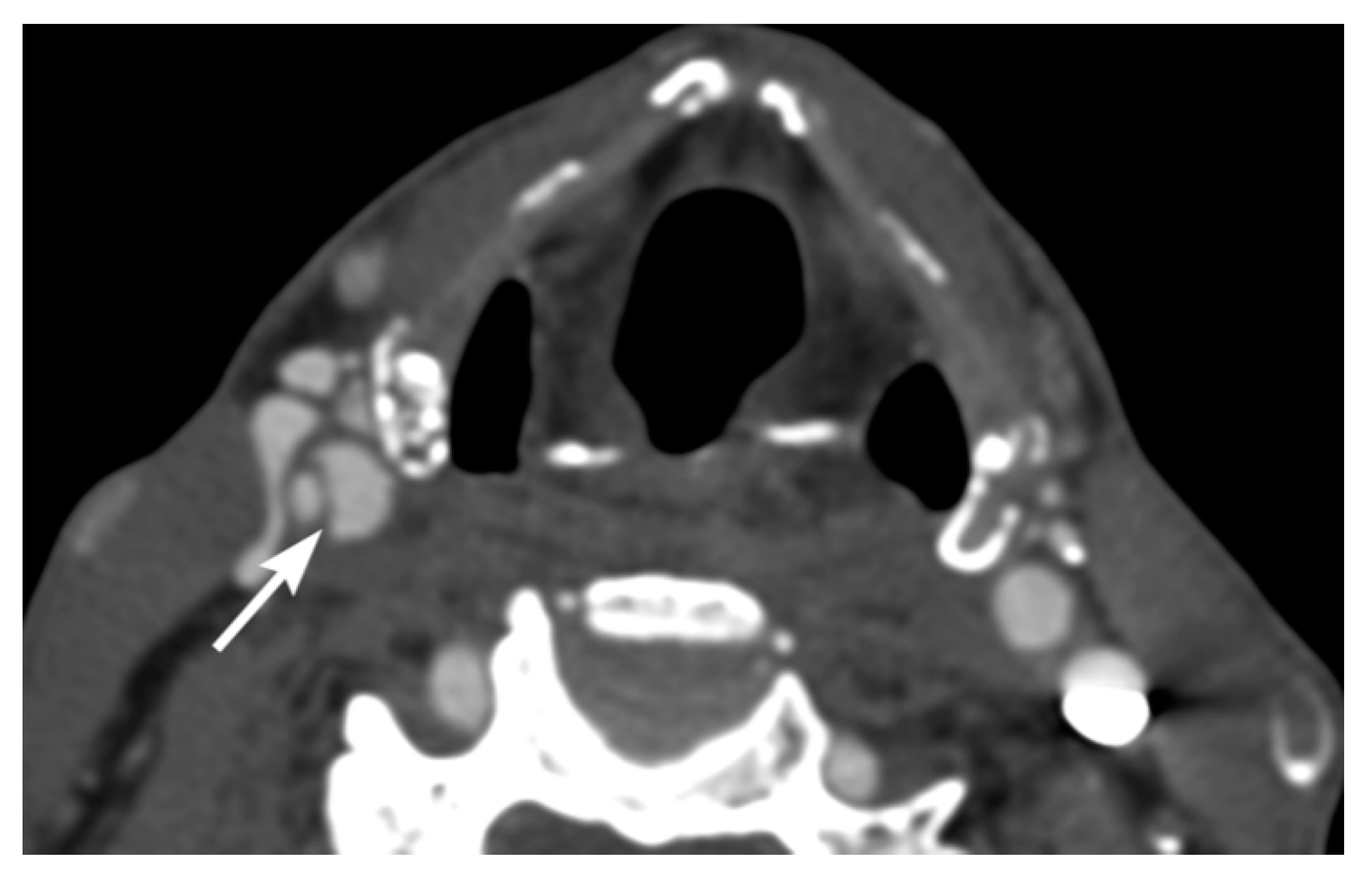
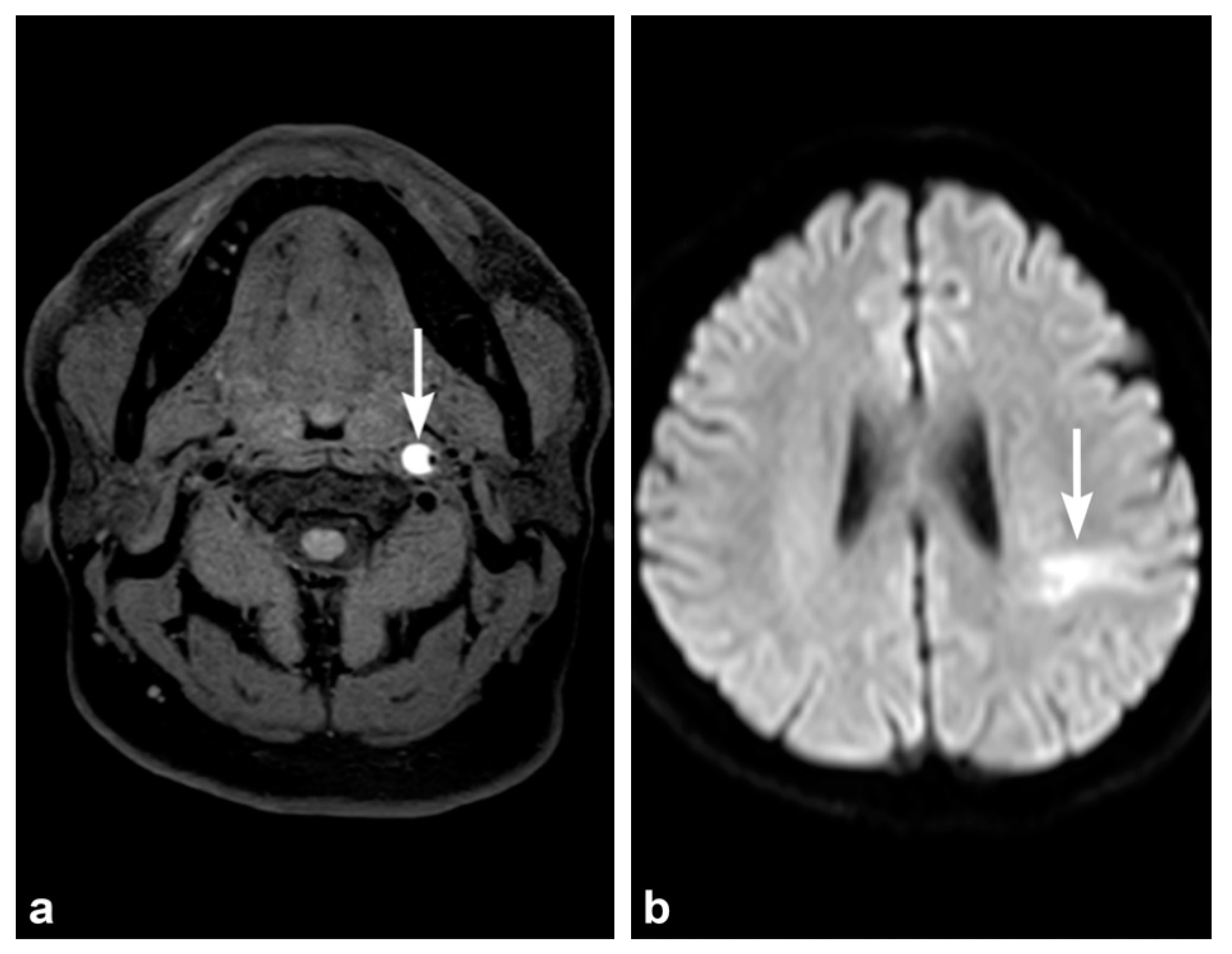
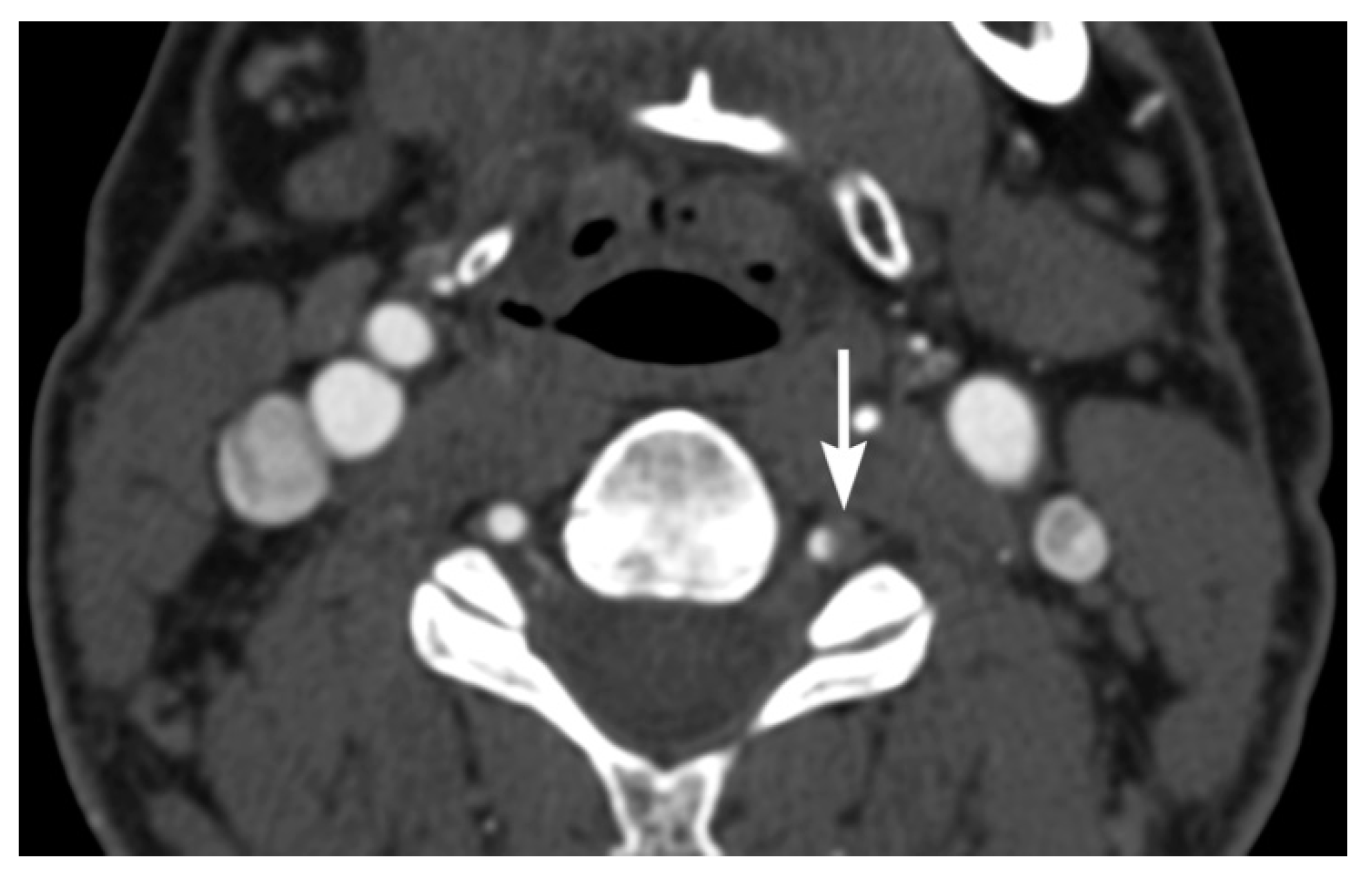
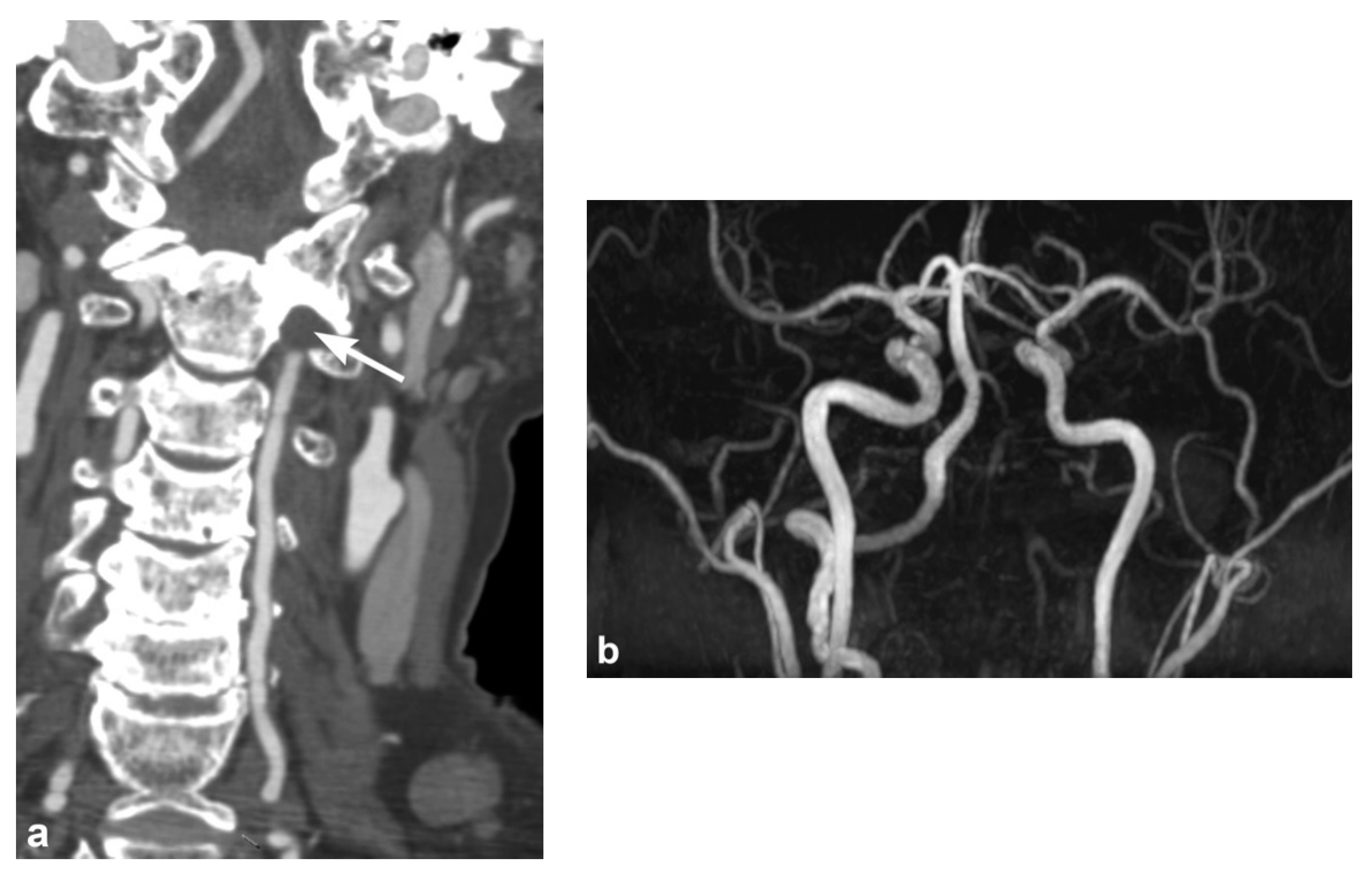
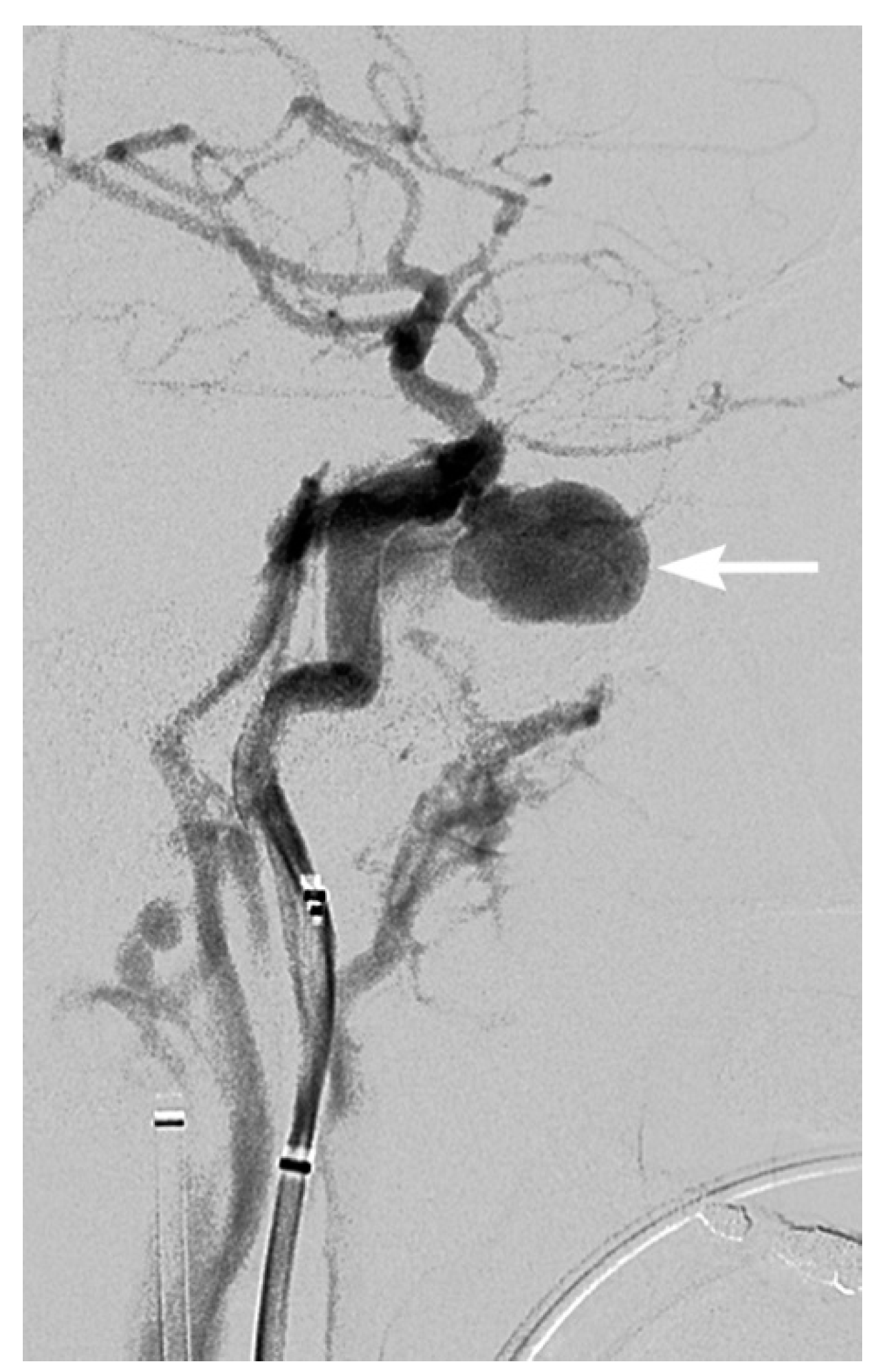
3. Imaging Findings of Arterial Injury
4. Screening for Blunt Cerebrovascular Injury
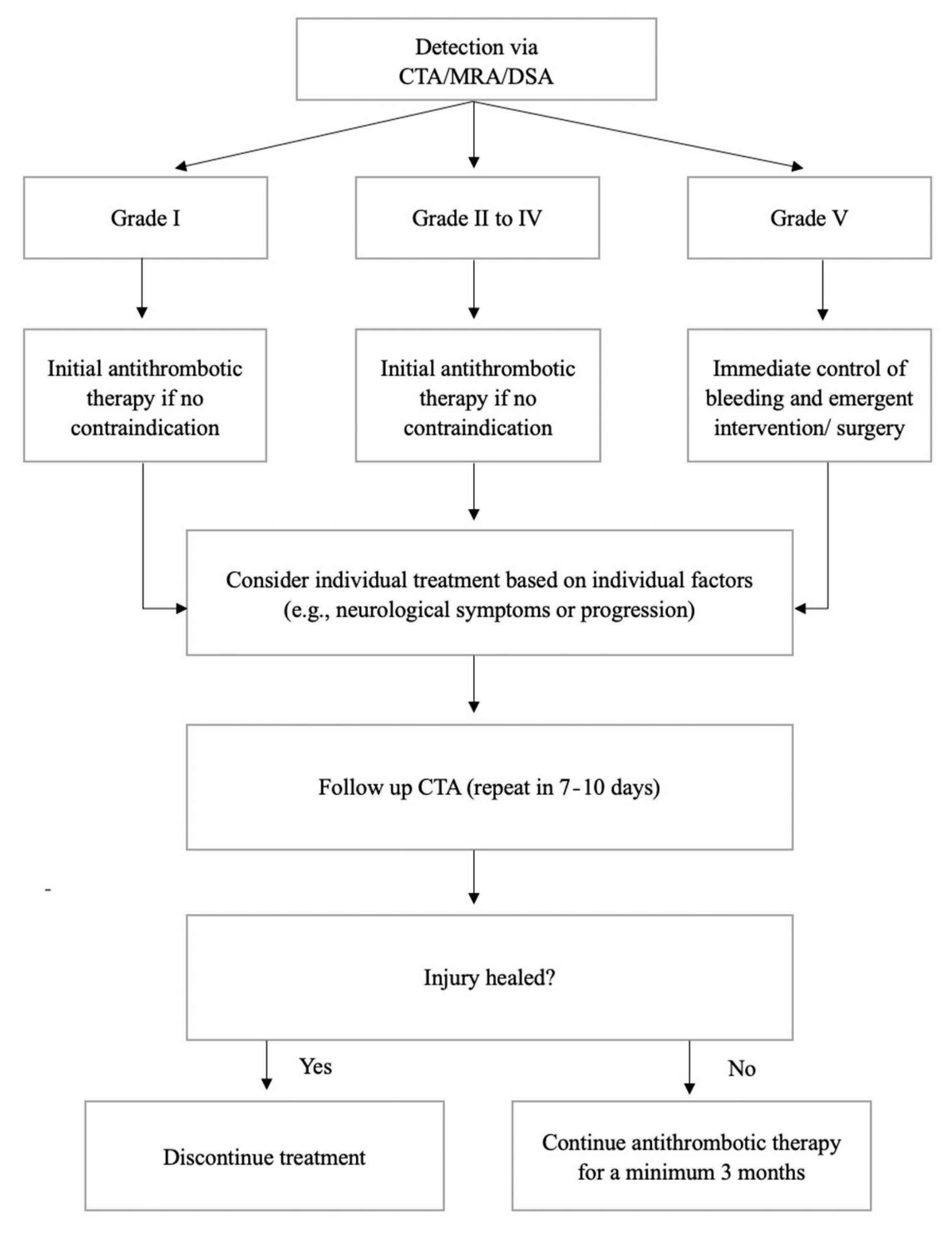
5. Treatment and Follow-Up
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anaya, C.; Munera, F.; Bloomer, C.W.; Danton, G.H.; Caban, K. Screening multidetector computed tomography angiography in the evaluation on blunt neck injuries: An evidence-based approach. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2009, 30, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biffl, W.L.; Ray, C.E., Jr.; Moore, E.E.; Franciose, R.J.; Aly, S.; Heyrosa, M.G.; Johnson, J.L.; Burch, J.M. Treatment-related outcomes from blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Importance of routine follow-up arteriography. Ann. Surg. 2002, 235, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogbill, T.H.; Moore, E.E.; Meissner, M.; Fischer, R.P.; Hoyt, D.B.; Morris, J.A.; Shackford, S.R.; Wallace, J.R.; Ross, S.E.; Ochsner, M.G.; et al. The spectrum of blunt injury to the carotid artery: A multicenter perspective. J. Trauma 1994, 37, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutman, A.M.; Vranic, J.E.; Mossa-Basha, M. Imaging and management of blunt cerebrovascular injury. Radiographics 2018, 38, 542–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berne, J.D.; Reuland, K.S.; Villarreal, D.H.; McGovern, T.M.; Rowe, S.A.; Norwood, S.H. Sixteen-Slice Multi-Detector Computed Tomographic angiography improves the accuracy of screening for blunt cerebrovascular injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2006, 60, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutze, S.; Rademacher, G.; Matthes, G.; Hosten, N.; Stengel, D. Blunt cerebrovascular injury in patients with blunt multiple trauma: Diagnostic accuracy of duplex Doppler US and early CT angiography. Radiology 2005, 237, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidereit, N.P.; Simons, R.; Nicolaou, S.; Graeb, D.; Brown, D.R.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Redekop, G.; McKevitt, E.C.; Neye-stani, A. Utility of screening for blunt vascular neck injuries with computed tomographic angiography. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2006, 60, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, R.W.; Willette, P.A.; Wood, M.J.; Wright, M.L.; Hartman, J.F. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic screening criteria for blunt cerebrovascular injuries. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2012, 214, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlew, C.C.; Biffl, W.L. Blunt cerebrovascular trauma. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2010, 16, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, V.; Trinci, M. Diagnostic Imaging in Polytrauma Patients; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Grandhi, R.; Weiner, G.M.; Agarwal, N.; Panczykowski, D.M.; Ares, W.J.; Rodriguez, J.S.; Gelfond, J.A.; Myers, J.G.; Alarcon, L.H.; Okonkwo, D.O. Limitations of multidetector computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis of blunt cerebrovascular injury. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 128, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, W.J.; Collier, B.C.; Diebel, L.N.; Dwyer, K.M.; Holevar, M.R.; Jacobs, D.G.; Kurek, S.J.; Schreiber, M.A.; Shapiro, M.L.; Vogel, T.R. Blunt cerebrovascular injury practice management guidelines: The eastern association for the surgery of trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2010, 68, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.; Wu, X.; Kalra, V.B.; Schindler, J.; Matouk, C.C.; Forman, H.P. Evaluation for blunt cerebrovascular injury: Review of the literature and a cost-Effectiveness analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brommeland, T.; Helseth, E.; Aarhus, M.; Moen, K.G.; Dyrskog, S.; Bergholt, B.; Olivecrona, Z.; Jeppesen, E. Best practice guidelines for blunt cerebrovascular injury (BCVI). J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2018, 26, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.J.; Chaubey, V.P.; Zygun, D.A.; Lorenzetti, D.; Faris, P.D.; Ball, C.G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W.; James, M.T. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomographic angiography for blunt cerebrovascular injury detection in trauma patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2013, 257, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, E.M.; Fabian, T.C.; Savage, S.A.; Zarzaur, B.L.; Botta, V.; Dutton, W.; Croce, M.A. Blunt cerebrovascular injury screening with 64-channel multidetector computed tomography: More slices finally cut it. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014, 76, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiCocco, J.M.; Emmett, K.P.; Fabian, T.C.; Zarzaur, B.L.; Williams, J.S.; Croce, M.A. Blunt cerebrovascular injury screening with 32-channel multidetector computed tomography: More slices still don’t cut it. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, B.R.; Tesoriero, R.; Kufera, J.; Sliker, C.; Laser, A.; Scalea, T.M.; Stein, D.M. Blunt cerebrovascular injury screening guidelines: What are we willing to miss? J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014, 76, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, A.L.; Muraliraj, V.; Sperry, J.L.; Minei, J.P. CTA-Based screening reduces time to diagnosis and stroke rate in blunt cervical vascular injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2009, 67, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kik, C.C.; Slooff, W.M.; Moayeri, N.; de Jong, P.A.; Muijs, S.P.J.; Oner, F.C. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography angiography (CTA) for diagnosing blunt cerebrovascular injury in trauma patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, C.; Laissy, J.P.; Raveau, V.; Amarenco, P.; Servois, V.; Bousser, M.G.; Tubiana, J.M. Carotid and vertebral artery dissections: Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography and MR imaging versus conventional angiography. Radiology 1994, 190, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, P.; Policeni, B.; Bathla, G.; Khandelwal, A.; Derdeyn, C.; Skeete, D. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Advances in screening, imaging, and management trends. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, A.P.; Peter, J.C. Carotid and vertebral artery occlusion after blunt cervical injury: The role of MR angiography in early diagnosis. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1996, 40, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobetti, F.B.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Bos-Giacobetti, M.A.; Deeley, D.M.; Albert, T.J.; Farmer, J.C.; Cotler, J.M. Vertebral artery occlusion associated with cervical spine trauma: A prospective analysis. Spine 1997, 22, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.; Flanders, A.; Thomas, C.; Millar, W. Vertebral artery injury after acute cervical spine trauma: Rate of occurrence as detected by MR angiography and assessment of clinical consequences. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1995, 164, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miller, P.R.; Fabian, T.C.; Croce, M.A.; Cagiannos, C.; Williams, J.S.; Vang, M.; Qaisi, W.G.; Felker, R.E.; Timmons, S.D. Prospective screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Analysis of diagnostic modalities and outcomes. Ann. Surg. 2002, 236, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliker, C.W. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Imaging with multidetector CT angiography. Radiographics 2008, 28, 1689–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, J.; Zisk, J.; Edelman, R.; Wallner, B.; Hartnell, G.; Stokes, K.; Longmaid, H. Central venous occlusion: MR angiography. Radiology 1993, 187, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Offner, P.J.; Brega, K.E.; Franciose, R.J.; Burch, J.M. Blunt carotid arterial injuries: Implications of a new grading scale. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1999, 47, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, D.B., Jr.; Torres-León, M.; Múnera, F. Vascular injuries of the neck and thoracic inlet: Helical CT–angiographic correlation. Radiographics 2004, 24, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staller, B.; Mùnera, F.; Sanchez, A.; Nuñez, D.B. Helical and multislice CTA following penetrating trauma to the subclavian and axillary arteries (pictorial essay). Emerg. Radiol. 2005, 11, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, A.; Kramer, U.; Bischof, F.; Schuettauf, F.; Ebner, F.; Danz, S.; Ernemann, U.; Hauser, T.-K. Feasibility of noninvasive diagnosis and treatment planning in a case series with carotid-cavernous fistula using high-resolution time-resolved MR-angiography with stochastic trajectories (TWIST) and extended parallel acquisition technique (ePAT 6) at 3T. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2015, 25, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciapetti, M.; Circelli, A.; Zagli, G.; Migliaccio, M.; Spina, R.; Alessi, A.; Acquafresca, M.; Bartolini, M.; Peris, A. Diagnosis of carotid arterial injury in major trauma using a modification of Memphis criteria. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2010, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cothren, C.C.; Moore, E.E.; Ray, C.E.; Johnson, J.L.; Moore, J.B.; Burch, J.M. Cervical spine fracture patterns mandating screening to rule out blunt cerebrovascular injury. Surgery 2007, 141, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlew, C.; Biffl, W.; Moore, E.; Barnett, C.; Johnson, J.; Bensard, D. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Redefining screening criteria in the era of noninvasive diagnosis. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Cothren, C.C.; Moore, E.E.; Kozar, R.; Cocanour, C.; Davis, J.W.; McIntyre, R.C., Jr.; West, M.A.; Moore, F.A. Western Trauma Association critical decisions in trauma: Screening for and treatment of blunt cerebrovascular injuries. J. Trauma 2009, 67, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Biffl, W.; Bokhari, F.; Brakenridge, S.; Chao, E.; Claridge, J.A.; Fraser, D.; Jawa, R.; Kasotakis, G.; Kerwin, A.; et al. Evaluation and management of blunt cerebrovascular injury: A practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 88, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddes, A.; Burlew, C.; Wagenaar, A.; Biffl, W.; Johnson, J.; Pieracci, F.; Campion, E.; Moore, E. Expanded screening criteria for blunt cerebrovascular injury: A bigger impact than anticipated. Am. J. Surg. 2016, 212, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esnault, P.; Cardinale, M.; Boret, H.; D’Aranda, E.; Montcriol, A.; Bordes, J.; Prunet, B.; Joubert, C.; Dagain, A.; Goutorbe, P.; et al. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries in severe traumatic brain injury: Incidence, risk factors, and evolution. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.M.; Davidson, A.J.; Alam, H.B.; DuBose, J.J.; Galante, J.M.; Fabian, T.C.; Savage, S.; Holcomb, J.B.; Scalea, T.M.; Rasmussen, T.E.; et al. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Outcomes from the American association for the surgery of trauma PROspective Observational Vascular Injury Treatment (PROOVIT) multicenter registry. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021, 90, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cothren, C.C.; Biffl, W.L. Treatment for blunt cerebrovascular injuries. Arch. Surg. 2009, 144, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.C.; Priola, S.M.; Mathieu, F.; Taslimi, S.; Pasarikovski, C.R.; Zeiler, F.A.; Machnowska, M.; Nathens, A.; Yang, V.X.D.; da Costa, L. Antithrombotic choice in blunt cerebrovascular injuries: Experience at a tertiary trauma center, systematic review, and meta-analysis. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021, 91, e1–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.B.; Severance, S.; Holler, E.; Menard, L.; Savage, S.; Zarzaur, B.L. Treatment of asymptomatic blunt cerebrovascular injury (BCVI): A systematic review. Trauma Surg. Acute Care Open 2021, 6, e000668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.D.; Allan, K.M.; Patel, K.U.; Hart, K.D.; Schreiber, M.A.; Azarbal, A.F.; Liem, T.K.; Mitchell, E.L.; Moneta, G.L.; Landry, G.J. The natural history of indeterminate blunt cerebrovascular injury. JAMA Surg. 2015, 150, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, A.E.; Burlew, C.C.; Biffl, W.L.; Beauchamp, K.M.; Pieracci, F.M.; Stovall, R.T.; Jurkovich, G.J.; Moore, E.E. Early repeat imaging is not warranted for high-grade blunt cerebrovascular injuries. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014, 77, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Christensen, D.; Call, L.; Vranic, J.; Colip, C.; Hippe, D.S.; Witt, C.; Bonow, R.H.; Mossa-Basha, M. Natural history of blunt cerebrovascular injury: Experience over a 10-year period at a level I trauma center. Radiology 2020, 297, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
So, T.Y.; Sawhney, A.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.X.J. Current Concepts in Imaging Diagnosis and Screening of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries. Tomography 2022, 8, 402-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010033
So TY, Sawhney A, Wang L, Wang YXJ. Current Concepts in Imaging Diagnosis and Screening of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries. Tomography. 2022; 8(1):402-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleSo, Tiffany Y., Apurva Sawhney, Lei Wang, and Yi Xiang J. Wang. 2022. "Current Concepts in Imaging Diagnosis and Screening of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries" Tomography 8, no. 1: 402-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010033
APA StyleSo, T. Y., Sawhney, A., Wang, L., & Wang, Y. X. J. (2022). Current Concepts in Imaging Diagnosis and Screening of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries. Tomography, 8(1), 402-413. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010033






