Feasibility of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting on Aging MRI Hardware
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
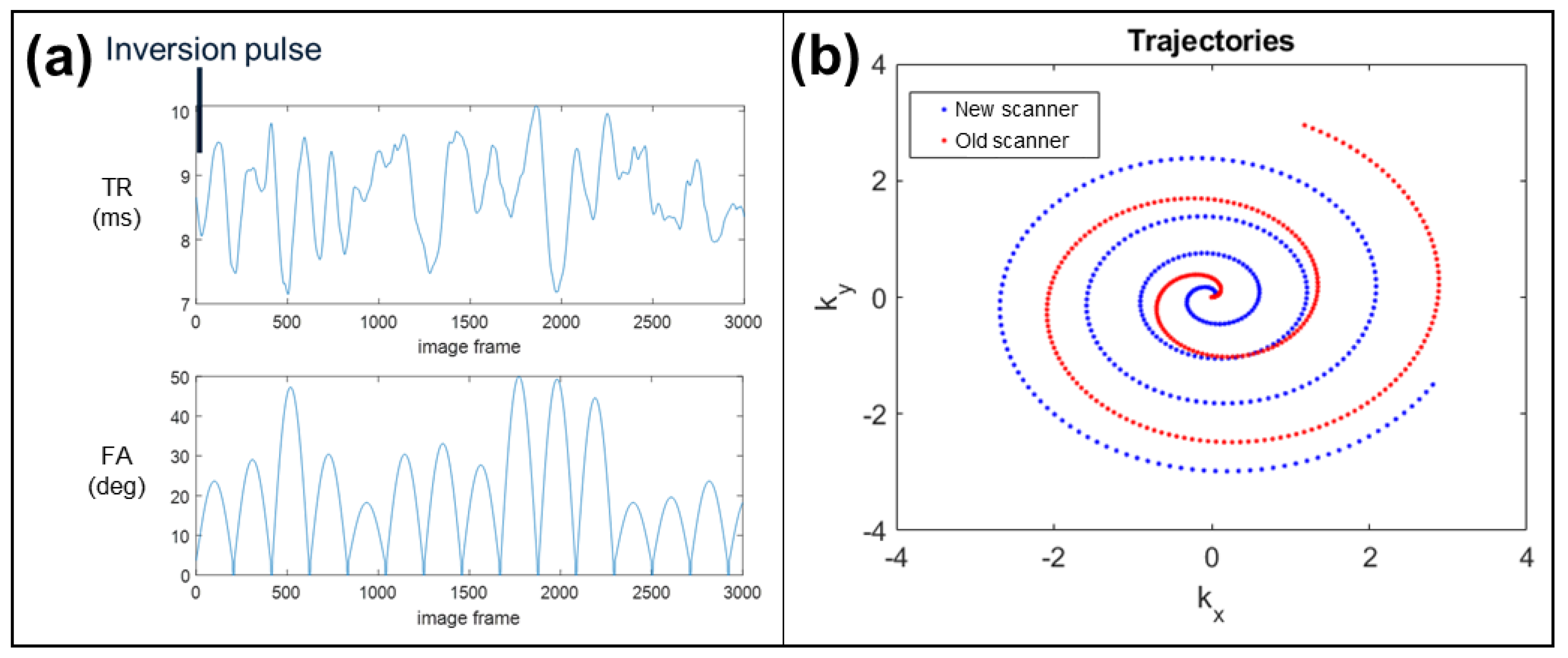
2.1. MRI Scanner Hardware
2.2. MRF Sequence
2.3. Phantom Experiments
2.4. In Vivo Experiments
3. Results
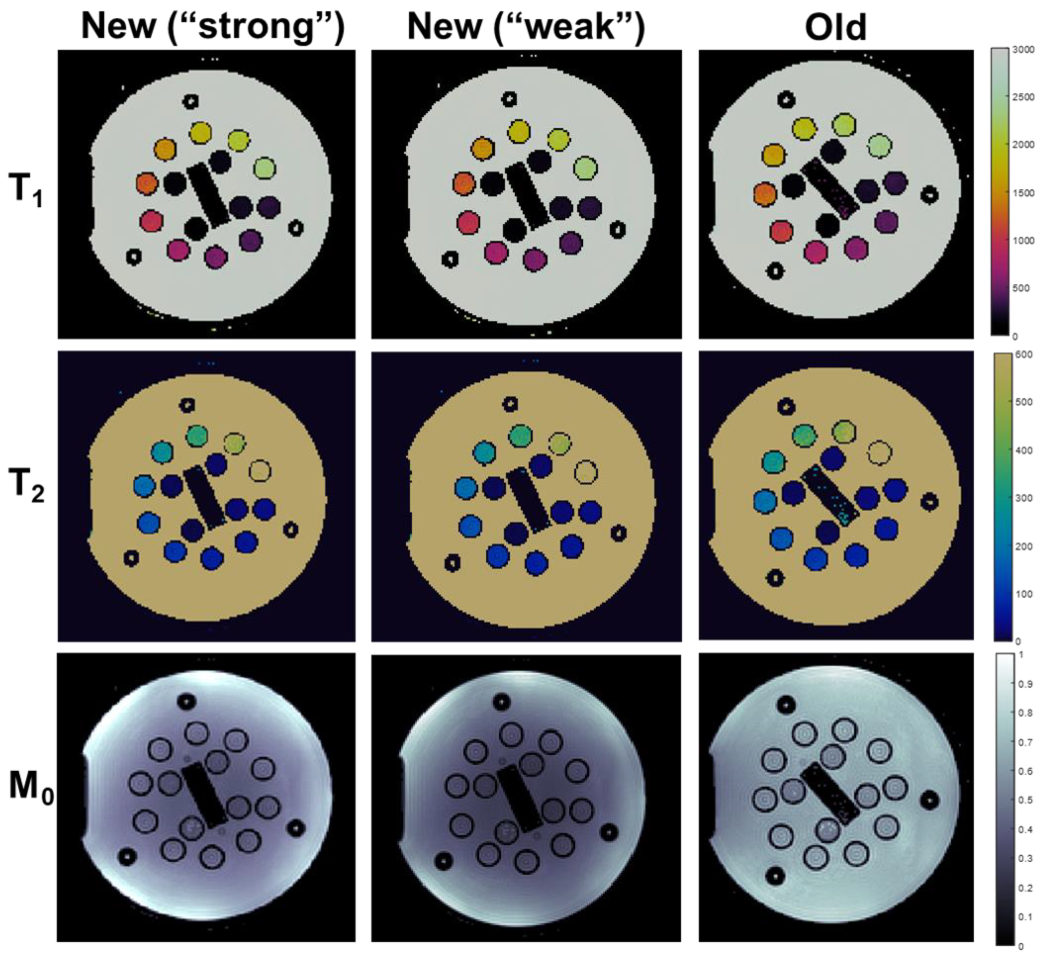
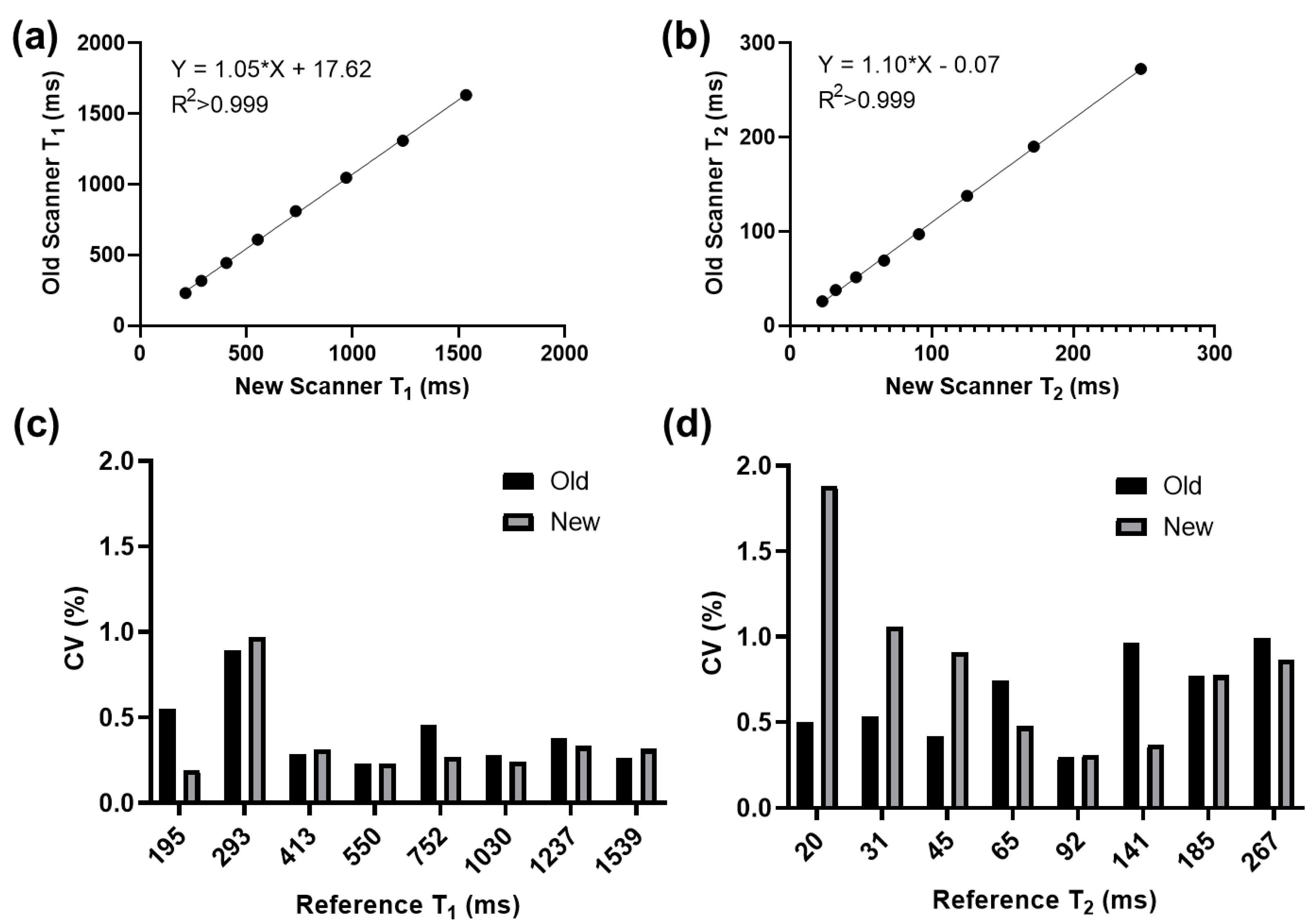
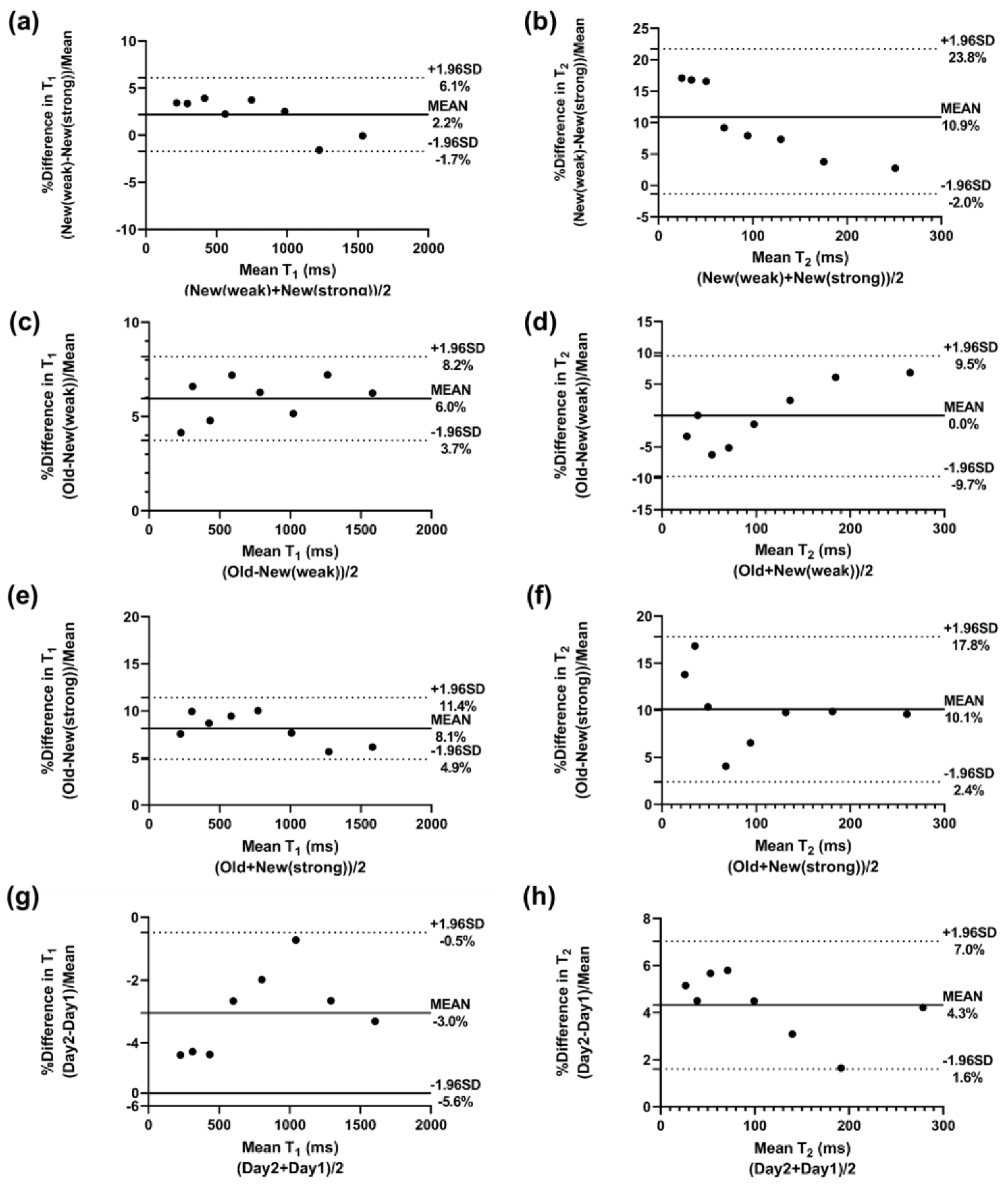
3.1. Phantom Experiments
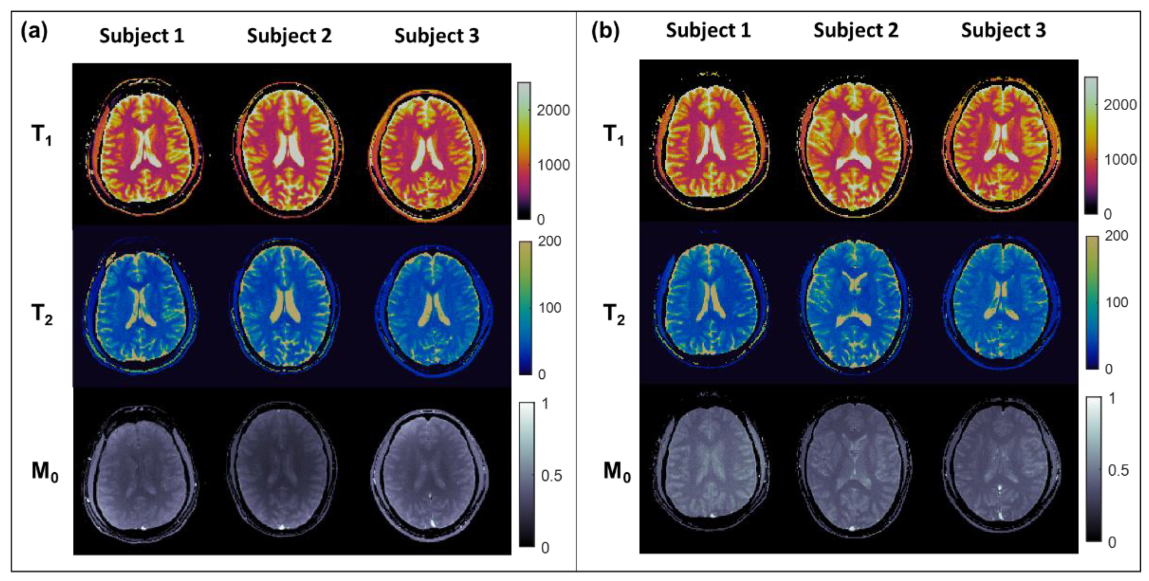
3.2. In Vivo Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hollingsworth, K.G. Reducing Acquisition Time in Clinical MRI by Data Undersampling and Compressed Sensing Reconstruction. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, R297–R322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Nguyen, C.T.; Han, F.; Wang, N.; Deng, Z.; Binesh, N.; Moser, F.G.; Christodoulou, A.G.; Li, D. Three-Dimensional Simultaneous Brain T1, T2, and ADC Mapping with MR Multitasking. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COCIR Medical Imaging Equipment Age Profile & Density—2019 Edition. Available online: https://www.cocir.org/media-centre/publications/article/cocir-medical-imaging-equipment-age-profile-density-2019-edition.html (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Average MRI Scanner Nearing Adolescence. Available online: https://www.diagnosticimaging.com/view/average-mri-scanner-nearing-adolescence (accessed on 4 September 2020).
- Wald, L.L.; McDaniel, P.C.; Witzel, T.; Stockmann, J.P.; Cooley, C.Z. Low-Cost and Portable MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, D.M.; Summers, L.H. The COVID-19 Pandemic and the $16 Trillion Virus. JAMA 2020, 324, 1495–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, B.; Carlier, P.G. MR Fingerprinting for Water T1 and Fat Fraction Quantification in Fat Infiltrated Skeletal Muscles. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hamilton, J.; Eck, B.; Griswold, M.; Seiberlich, N. Myocardial T1 and T2 Quantification and Water–Fat Separation Using Cardiac MR Fingerprinting with Rosette Trajectories at 3T and 1.5T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolstra, K.; Beenakker, J.-W.M.; Koken, P.; Webb, A.; Börnert, P. Cartesian MR Fingerprinting in the Eye at 7T Using Compressed Sensing and Matrix Completion-Based Reconstructions. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 2551–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostenson, J.; Damon, B.M.; Welch, E.B. MR Fingerprinting with Simultaneous T1, T2, and Fat Signal Fraction Estimation with Integrated B0 Correction Reduces Bias in Water T1 and T2 Estimates. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 60, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonincontri, G.; Sawiak, S.J. MR Fingerprinting with Simultaneous B1 Estimation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virtue, P.; Tamir, J.I.; Doneva, M.; Yu, S.X.; Lustig, M. Learning Contrast Synthesis from MR Fingerprinting; International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Buonincontri, G.; Biagi, L.; Retico, A.; Cecchi, P.; Cosottini, M.; Gallagher, F.A.; Gómez, P.A.; Graves, M.J.; McLean, M.A.; Riemer, F. Multi-Site Repeatability and Reproducibility of MR Fingerprinting of the Healthy Brain at 1.5 and 3.0 T. NeuroImage 2019, 195, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, K.T.; Uecker, M. Simple Method for Adaptive Gradient-Delay Compensation in Radial MRI; International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, D.; Seiberlich, N.; Gulani, V.; Griswold, M.A. MR Fingerprinting Using Fast Imaging with Steady State Precession (FISP) with Spiral Readout. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Hu, B.S.; Nishimura, D.G. Fast 3D Imaging Using Variable-Density Spiral Trajectories with Applications to Limb Perfusion. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessler, J. Michigan Image Reconstruction Toolbox. 2018. Available online: http://web.eecs.umich.edu/~fessler/code/index.html (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Walsh, D.O.; Gmitro, A.F.; Marcellin, M.W. Adaptive Reconstruction of Phased Array MR Imagery. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 43, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Coppo, S.; Chen, Y.; McGivney, D.F.; Jiang, Y.; Pahwa, S.; Gulani, V.; Griswold, M.A. Slice Profile and B1 Corrections in 2D Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyn, J.H.; Yang, Y.; Frank, J.A.; van der Veen, J.W. Simple Correction Method Fork-Space Trajectory Deviations in MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 1998, 132, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, D.; Keenan, K.E.; Stupic, K.F.; Gulani, V.; Griswold, M.A. Repeatability of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting T1 and T2 Estimates Assessed Using the ISMRM/NIST MRI System Phantom. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Spincemaille, P.; Gauthier, S.A.; Wang, Y. Rapid Whole Brain Myelin Water Content Mapping without an External Water Standard at 1.5T. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 39, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-Q.; Finsterbusch, J.; Wittkugel, O.; Saager, C.; Goebell, E.; Fitting, T.; Grzyska, U.; Zeumer, H.; Fiehler, J. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Fractional Anisotropy and T2 Relaxation Time Measurement: Does the Field Strength Matter? Clin. Neuroradiol. 2007, 17, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Terada, Y. Diffusion-Weighting Caused by Spoiler Gradients in the Fast Imaging with Steady-State Precession Sequence May Lead to Inaccurate T2 Measurements in MR Fingerprinting. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2018, 18, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilbert, T.; Xia, D.; Block, K.T.; Yu, Z.; Lattanzi, R.; Sodickson, D.K.; Kober, T.; Cloos, M.A. Magnetization Transfer in Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Körzdörfer, G.; Pfeuffer, J.; Kluge, T.; Gebhardt, M.; Hensel, B.; Meyer, C.H.; Nittka, M. Effect of Spiral Undersampling Patterns on FISP MRF Parameter Maps. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 62, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Setsompop, K.; Ye, H.; Cauley, S.F.; Wald, L.L. Maximum Likelihood Reconstruction for Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Obmann, V.C.; Lo, W.-C.; Margevicius, S.; Jiang, Y.; Schluchter, M.; Patel, I.J.; Nakamoto, D.; Badve, C.; Griswold, M.A.; et al. MR Fingerprinting and ADC Mapping for Characterization of Lesions in the Transition Zone of the Prostate Gland. Radiology 2019, 292, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Inati, S.; Sørensen, T.S.; Kellman, P.; Hansen, M.S. Distributed MRI Reconstruction Using Gadgetron-Based Cloud Computing. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell-Washburn, A.E.; Jiang, Y.; Körzdörfer, G.; Nittka, M.; Griswold, M.A. Feasibility of MR Fingerprinting Using a High-Performance 0.55 T MRI System. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 81, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, T.; Bornert, P.; Webb, A.; Koolstra, K. 3D Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting at 50 mT. In Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Virtual Meeting, 15 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cloos, M.A.; Knoll, F.; Zhao, T.; Block, K.T.; Bruno, M.; Wiggins, G.C.; Sodickson, D.K. Multiparametric Imaging with Heterogeneous Radiofrequency Fields. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Cloos, M.A.; Okada, T. A Simple Method to Estimate Gradient Delay for MRF. In Proceedings of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Virtual Meeting, 8 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
| Subject | T1 (Old) | T1 (New) | p | T2 (Old) | T2 (New) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 599 ± 22 | 639 ± 10 | 0.01 | 37.0 ± 0.4 | 35.7 ± 0.5 | <0.01 |
| 1 (retest) | 610 ± 20 | 35.5 ± 1.1 | ||||
| 1 (p) | 0.42 | 0.03 | ||||
| 2 | 626 ± 17 | 594 ± 14 | 0.01 | 36.1 ± 1.5 | 30.7 ± 1.7 | <0.01 |
| 3 | 638 ± 15 | 697 ± 16 | <0.01 | 37.6 ± 1.0 | 36.8 ± 1.3 | 0.38 |
| CV (intra) | 2.9% | 2.1% | 2.6% | 3.5% | ||
| CV (inter) | 4.8% | 5.1% | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eck, B.L.; Liu, K.; Lo, W.-c.; Jiang, Y.; Gulani, V.; Seiberlich, N. Feasibility of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting on Aging MRI Hardware. Tomography 2022, 8, 10-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010002
Eck BL, Liu K, Lo W-c, Jiang Y, Gulani V, Seiberlich N. Feasibility of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting on Aging MRI Hardware. Tomography. 2022; 8(1):10-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleEck, Brendan Lee, Kecheng Liu, Wei-ching Lo, Yun Jiang, Vikas Gulani, and Nicole Seiberlich. 2022. "Feasibility of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting on Aging MRI Hardware" Tomography 8, no. 1: 10-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010002
APA StyleEck, B. L., Liu, K., Lo, W.-c., Jiang, Y., Gulani, V., & Seiberlich, N. (2022). Feasibility of Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting on Aging MRI Hardware. Tomography, 8(1), 10-21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010002






