Comparison of Incidence of Adjacent Segment Pathology between Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Treatments for Lumbosacral Junction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Surgical Procedures
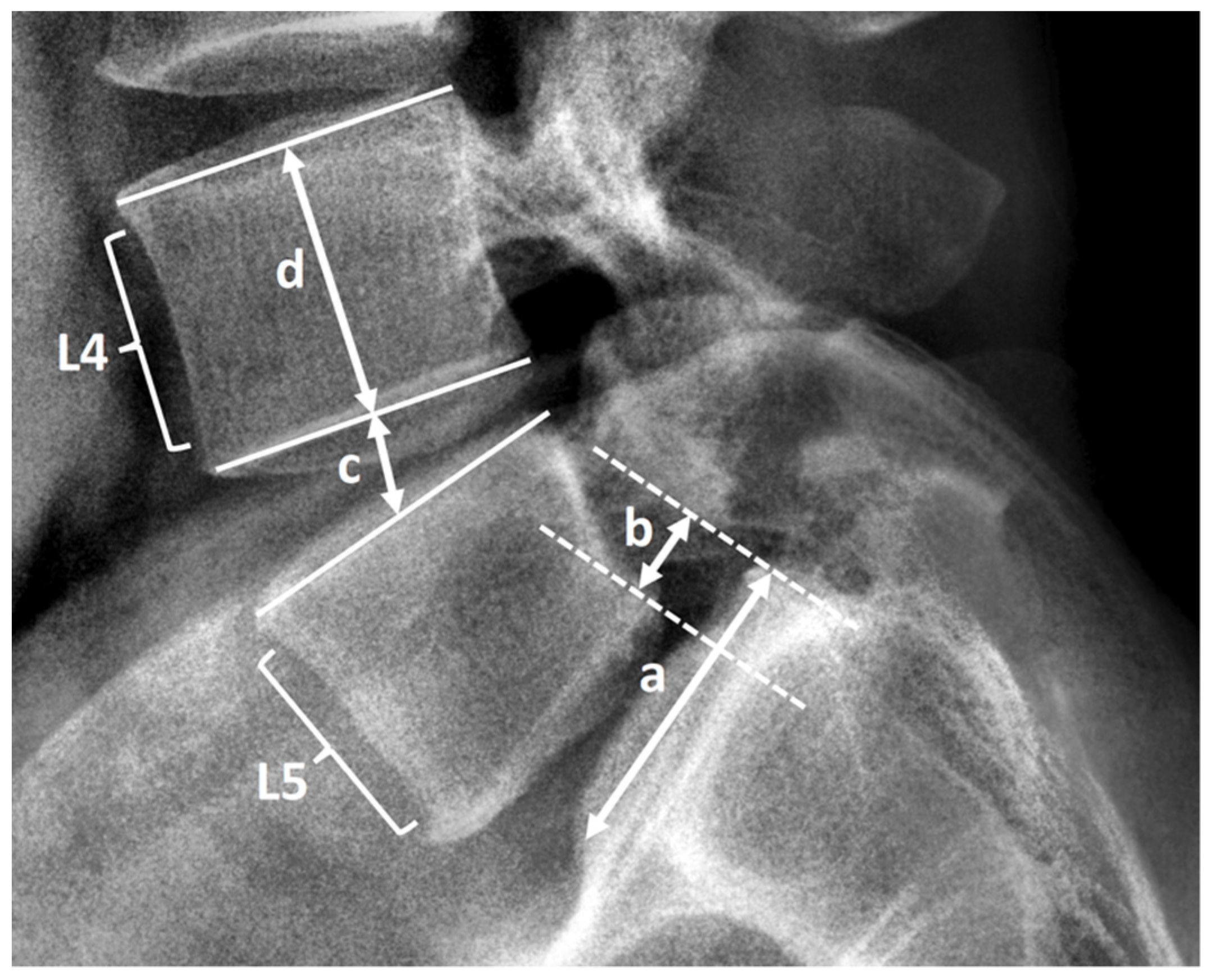
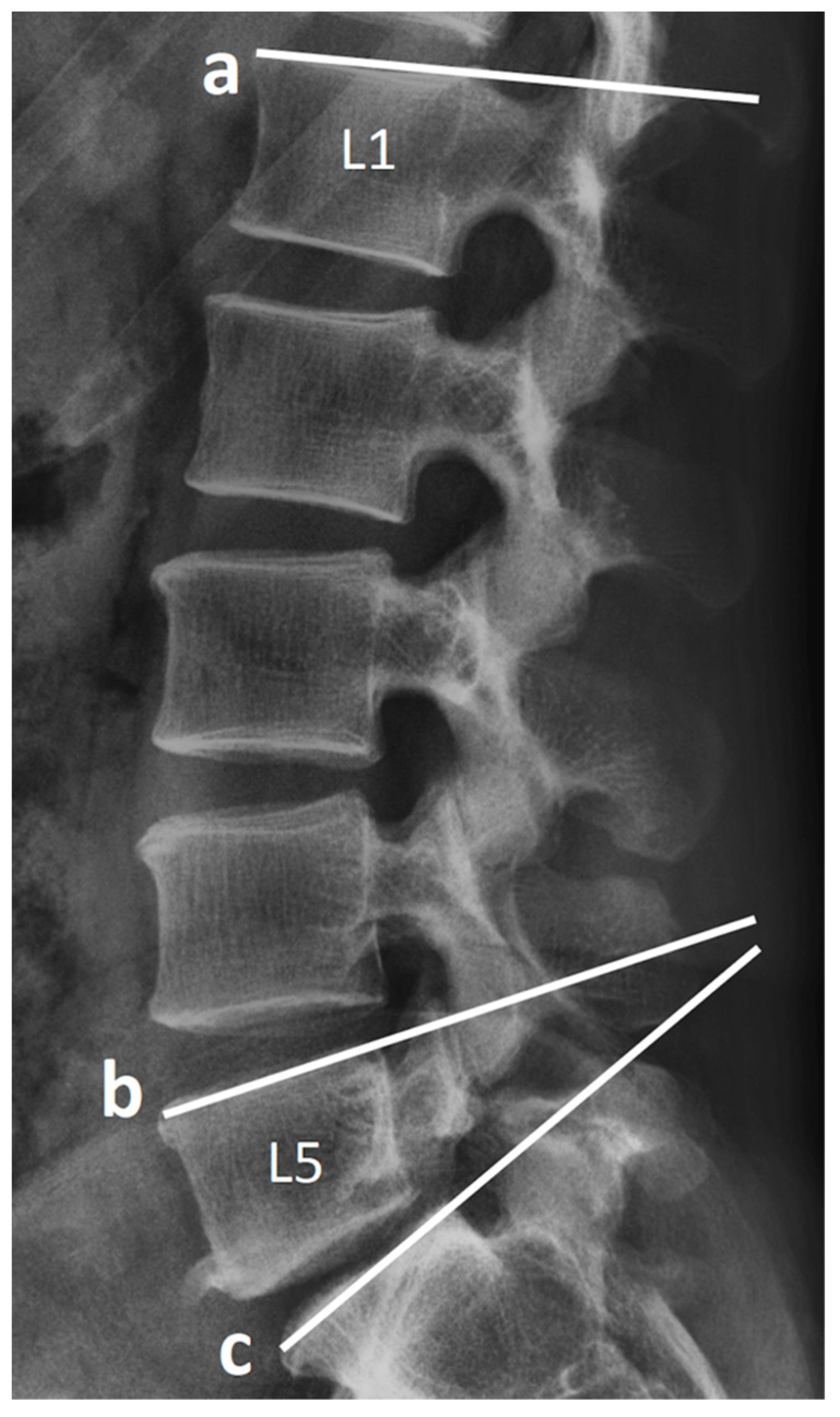
2.3. Radiological Assessment and Clinical Record
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Characteristics of Patients
3.2. RASP
3.3. CASP
4. Discussion
4.1. Lumbar Lordosis
4.2. Instability
4.3. CASP
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrey, C.; Darnis, A. Current strategies for the restoration of adequate lordosis during lumbar fusion. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Langrana, N.A. Lumbosacral spinal fusion. A biomechanical study. Spine 1984, 9, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, K.Y.; Schendel, M.J.; Lewis, J.L.; Ogilvie, J.W. Effect of immobilization and configuration on lumbar adjacent-segment biomechanics. J. Spinal Disord. 1993, 6, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riew, K.D.; Norvell, D.C.; Chapman, J.R.; Skelly, A.C.; Dettori, J.R. Introduction/Summary statement: Adjacent segment pathology. Spine 2012, 37, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Berven, S.H.; Fortin, M.; Weber, M.H. Adjacent Segment Degeneration Versus Disease After Lumbar Spine Fusion for Degenerative Pathology: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis of the Literature. Clin. Spine Surg. 2016, 29, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Hwang, C.J.; Lee, S.W.; Ahn, Y.J.; Kim, Y.T.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, M.Y. Risk factors for adjacent segment disease after lumbar fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 1637–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Yan, L.; Guo, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Hao, D. The difference in superior adjacent segment pathology after lumbar posterolateral fusion by using 2 different pedicle screw insertion techniques in 9-year minimum follow-up. Spine 2014, 39, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.M.; Deviren, V.; Tay, B.; Burch, S.; Berven, S.H. Adjacent segment disease after instrumented fusion for adult lumbar spondylolisthesis: Incidence and risk factors. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 156, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Choi, S.W. Adjacent Segment Pathology after Lumbar Spinal Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2015, 9, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, B.I.; Mirza, S.K.; Spina, N.; Spiker, W.R.; Lawrence, B.; Brodke, D.S. Trends in Lumbar Fusion Procedure Rates and Associated Hospital Costs for Degenerative Spinal Diseases in the United States, 2004 to 2015. Spine 2019, 44, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berven, S.; Wadhwa, R. Sagittal Alignment of the Lumbar Spine. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 29, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.; Garton, H.J.; Gala, V.C.; Hoff, J.T.; McGillicuddy, J.E. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: Review of the literature. Spine 2004, 29, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, C.D.; McCall, T.D.; Schmidt, M.H.; Dailey, A.T. Comparison of low back fusion techniques: Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) or posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) approaches. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2009, 2, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, J.H.; Jang, J.S.; Jung, B.; Lee, H.Y.; Choi, W.C.; Shim, C.S.; Choi, G.; Lee, S.H. The clinical characteristics and risk factors for the adjacent segment degeneration in instrumented lumbar fusion. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2008, 21, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, S.D.; Sumner, D.R. Biologic factors affecting spinal fusion and bone regeneration. Spine 1995, 20, 102S–112S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Kim, K.N.; Yi, S.; Ha, Y.; Shin, D.A.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, K.S. Comparison of Outcomes of Anterior, Posterior, and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery at a Single Lumbar Level with Degenerative Spinal Disease. World Neurosurg. 2017, 101, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.H.; Jang, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Comparison of anterior- and posterior-approach instrumented lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2007, 7, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, P.C.; Koski, T.R.; O’Shaughnessy, B.A.; Sugrue, P.; Salehi, S.; Ondra, S.; Liu, J.C. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion in comparison with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: Implications for the restoration of foraminal height, local disc angle, lumbar lordosis, and sagittal balance. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2007, 7, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.K.L.; Samartzis, D.; To, N.S.C.; Harada, G.K.; An, H.S.; Wong, A.Y.L. Demographic, Surgical, and Radiographic Risk Factors for Symptomatic Adjacent Segment Disease After Lumbar Fusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobbs, R.J.; Phan, K.; Malham, G.; Seex, K.; Rao, P.J. Lumbar interbody fusion: Techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. J. Spine Surg. 2015, 1, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiselli, G.; Wang, J.C.; Bhatia, N.N.; Hsu, W.K.; Dawson, E.G. Adjacent segment degeneration in the lumbar spine. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2004, 86, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.; Soh, J.W.; Shin, B.J. Risk factors of adjacent segment disease requiring surgery after lumbar spinal fusion: Comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion. Spine 2014, 39, E339–E345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irmola, T.M.; Hakkinen, A.; Jarvenpaa, S.; Marttinen, I.; Vihtonen, K.; Neva, M. Reoperation Rates Following Instrumented Lumbar Spine Fusion. Spine 2018, 43, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorward, I.G.; Lenke, L.G.; Bridwell, K.H.; O’Leary, P.T.; Stoker, G.E.; Pahys, J.M.; Kang, M.M.; Sides, B.A.; Koester, L.A. Transforaminal versus anterior lumbar interbody fusion in long deformity constructs: A matched cohort analysis. Spine 2013, 38, E755–E762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.J.; Lai, P.L.; Chen, L.H. Adjacent instability after instrumented lumbar fusion. Chang. Gung Med. J. 2003, 26, 792–798. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.C.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, L.H.; Shih, C.H. Reduction-fixation spinal system in spondylolisthesis. Am. J. Orthop. 1996, 25, 418–424. [Google Scholar]
- Peck, J.H.; Kavlock, K.D.; Showalter, B.L.; Ferrell, B.M.; Peck, D.G.; Dmitriev, A.E. Mechanical performance of lumbar intervertebral body fusion devices: An analysis of data submitted to the Food and Drug Administration. J. Biomech. 2018, 78, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajiboye, R.M.; Alas, H.; Mosich, G.M.; Sharma, A.; Pourtaheri, S. Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Anterior and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Comparative Studies. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, E230–E238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Ha, J.W.; Lee, Y.T.; Sung, N.Y. Cranial facet joint violations by percutaneously placed pedicle screws adjacent to a minimally invasive lumbar spinal fusion. Spine J. 2011, 11, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, R.; Park, J.G.; Mehta, A.I.; Shan, T.; Grossi, P.M.; Brown, C.R.; Richardson, W.J.; Isaacs, R.E.; Bagley, C.A.; Kuchibhatla, M.; et al. Comparison of superior-level facet joint violations during open and percutaneous pedicle screw placement. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pourtaheri, S.; Issa, K.; Lord, E.; Ajiboye, R.; Drysch, A.; Hwang, K.; Faloon, M.; Sinha, K.; Emami, A. Paraspinal Muscle Atrophy After Lumbar Spine Surgery. Orthopedics 2016, 39, e209–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| ALIF | TLIF | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 54.60 ± 15.20 | 54.25 ± 15.34 | 0.92 |
| Sex (male) * | 10 (33.33%) | 18 (45.00%) | 0.32 |
| Body weight (kg) | 63.83 ± 10.86 | 68.5 ± 12.26 | 0.10 |
| Body height (cm) | 159.5 ± 8.85 | 161.43 ± 8.95 | 0.37 |
| BMI | 25.02 ± 3.08 | 26.25 ± 3.97 | 0.16 |
| Smoking status * | 2 (6.67%) | 7 (17.50%) | 0.18 |
| BMD (T-score) | −1.37 ± 1.16 | −1.28 ± 1.39 | 0.93 |
| Follow-up (month) | 42.10 ± 22.61 | 56.20 ± 29.91 | 0.03 |
| ASA Grade 1 * | 7 (23.33%) | 7 (17.50%) | 0.90 |
| ASA Grade 2 * | 22 (73.33%) | 31 (77.50%) | |
| ASA Grade 3 * | 1 (3.33%) | 2 (5.00%) | |
| L5-S1 Spondylolisthesis * † | 26 | 29 | 0.37 |
| L5-S1 HIVD *† | 3 | 7 | |
| L5-S1 Spinal stenosis *† | 1 | 4 | |
| Preop PT (°) | 21.23 ± 7.48 | 20.41 ± 8.91 | 0.80 |
| Preop PI-LL | 10.85 ± 8.31 | 14.46 ± 12.52 | 0.39 |
| Preop LL (°) | 44.05 ± 14.51 | 38.91 ± 15.93 | 0.19 |
| Preop SL (°) | 16.98 ± 8.02 | 17.84 ± 7.17 | 0.65 |
| Preop L5–S1 disc ht (mm) | 6.99 ± 2.47 | 8.13 ± 1.85 | 0.11 |
| Preop L5–S1 slip (mm) | 5.75 ± 4.67 | 2.31 ± 4.40 | 0.03 |
| Postop PT (°) | 18.28 (5.22) | 18.94 (8.29) | 0.69 |
| Postop PI-LL | 9.56 (6.41) | 12.38 (9.92) | 0.17 |
| Postop LL (°) | 45.47 ± 13.78 | 33.17 ± 12.52 | <0.001 |
| Postop SL (°) | 20.20 ± 13.54 | 16.71 ± 6.35 | 0.16 |
| Postop L5–S1 disc ht (mm) | 12.49 ± 1.89 | 9.96 ± 1.89 | <0.001 |
| Postop L5–S1 slip (mm) | 2.15 ± 3.45 | 1.02 ± 3.14 | 0.16 |
| ALIF (n = 30) | TLIF (n = 40) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RASP at L3–4 | 16 | 19 | 0.63 |
| RASP at L4–5 | 19 | 20 | 0.27 |
| Classification of RASP at L3–4 | |||
| Disc degeneration | 13 | 12 | 0.25 |
| L3 compression fx | 1 | 0 | 0.43 |
| Listhesis | 0 | 3 | 0.25 |
| Instability | 5 | 5 | 0.73 |
| Classification of RASP at L4–5 | |||
| Disc degeneration | 11 | 15 | 0.94 |
| L4 compression fx | 1 | 1 | 1.00 |
| Listhesis | 1 | 4 | 0.38 |
| Instability | 13 | 6 | 0.008 |
| ALIF | TLIF | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level of L3–4 | |||
| Last FU − postop/postop disc ht (%) | −10 ± 8.2 | −8.2 ± 9.5 | 0.42 |
| Last FU slip (mm) * | −1.75 ± 1.16 | −1.81 ± 1.56 | 0.85 |
| Last FU angular m. (°) | 9.31 ± 3.31 | 7.52 ± 3.79 | 0.04 |
| Last FU − postop/postop L3 vertebral body ht (%) | −1.6 ± 3.3 | −0.8 ± 1.7 | 0.24 |
| Level of L4–5 | |||
| Last FU − postop/postop disk ht (%) | −8.8 ± 9.5 | −7.6 ± 9 | 0.57 |
| Last FU slip (mm) * | −1.5 ± 1.37 | −1.58 ± 1.93 | 0.85 |
| Last FU angular m. (°) | 12.03 ± 4.25 | 10.09 ± 4.89 | 0.09 |
| Last FU − postop/postop L4 vertebral body ht (%) | −1.5 ± 3.2 | −1.3 ± 3.8 | 0.78 |
| ALIF | TLIF | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-year survival rate | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| 3-year survival rate | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.75 |
| 5-year survival rate | 0.68 | 0.35 | 0.57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, P.-K.; Wu, M.-H.; Shih, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-K.; Chen, K.-H.; Pan, C.-C.; Huang, T.-J.; Lee, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Comparison of Incidence of Adjacent Segment Pathology between Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Treatments for Lumbosacral Junction. Tomography 2021, 7, 855-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040072
Wu P-K, Wu M-H, Shih C-M, Lin Y-K, Chen K-H, Pan C-C, Huang T-J, Lee C-Y, Lee C-H. Comparison of Incidence of Adjacent Segment Pathology between Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Treatments for Lumbosacral Junction. Tomography. 2021; 7(4):855-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040072
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Po-Kuan, Meng-Huang Wu, Cheng-Min Shih, Yen-Kuang Lin, Kun-Hui Chen, Chien-Chou Pan, Tsung-Jen Huang, Ching-Yu Lee, and Cheng-Hung Lee. 2021. "Comparison of Incidence of Adjacent Segment Pathology between Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Treatments for Lumbosacral Junction" Tomography 7, no. 4: 855-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040072
APA StyleWu, P.-K., Wu, M.-H., Shih, C.-M., Lin, Y.-K., Chen, K.-H., Pan, C.-C., Huang, T.-J., Lee, C.-Y., & Lee, C.-H. (2021). Comparison of Incidence of Adjacent Segment Pathology between Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Treatments for Lumbosacral Junction. Tomography, 7(4), 855-865. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7040072






