Evaluation of the Swallow-Tail Sign and Correlations of Neuromelanin Signal with Susceptibility and Relaxations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Imaging Protocols
2.3. Imaging Data Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
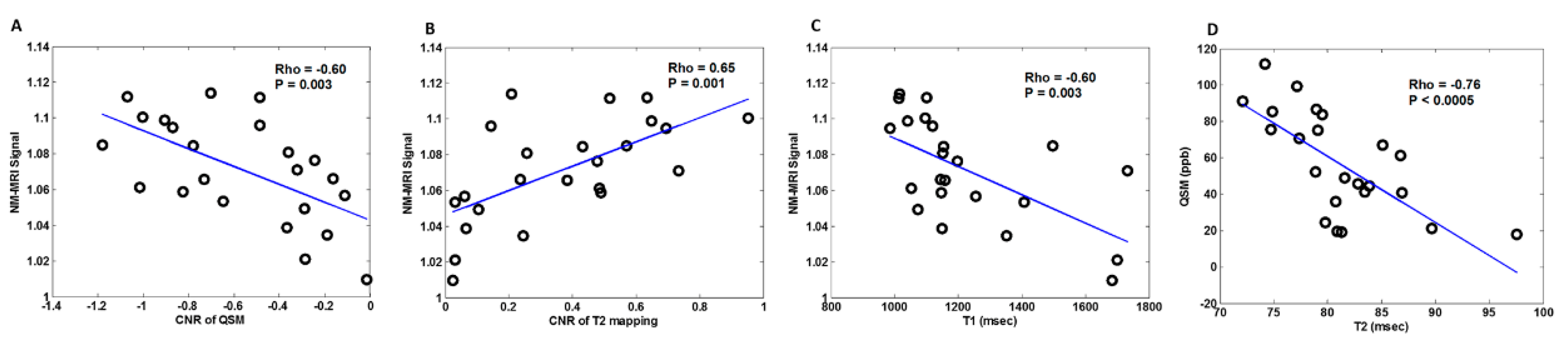
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarz, S.T.; Mougin, O.; Xing, Y.; Blazejewska, A.I.; Bajaj, N.; Auer, D.P.; Gowland, P. Parkinson’s disease related signal change in the nigrosomes 1–5 and the substantia nigra using T2* weighted 7T MRI. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 19, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.T.; Afzal, M.; Morgan, P.S.; Bajaj, N.; Gowland, P.A.; Auer, D.P. The ‘swallow tail’ appearance of the healthy nigrosome—A new accurate test of Parkinson’s disease: a case-control and retrospective cross-sectional MRI study at 3T. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, S.; Fällmar, D.; Schwarz, S.T.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Van Westen, D.; Hansson, O.; Larsson, E.-M.; Haller, S. MRI of the Swallow Tail Sign: A Useful Marker in the Diagnosis of Lewy Body Dementia? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1737–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, C.; Rauscher, A. Susceptibility weighted imaging with multiple echoes. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 31, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Lewis, M.M.; Sica, C.; He, L.; Connor, J.R.; Kong, L.; Mailman, R.B.; Huang, X. Distinct progression pattern of susceptibility MRI in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s patients. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimão, S.; Ferreira, S.; Nunes, R.G.; Lobo, P.P.; Neutel, D.; Abreu, D.; Gonçalves, N.; Campos, J.; Ferreira, J.J. Magnetic resonance correlation of iron content with neuromelanin in the substantia nigra of early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 23, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, P.; Summers, P.E.; Ferrari, E.; Zucca, F.A.; Sturini, M.; Mainardi, L.T.; Cerutti, S.; Smith, A.K.; Smith, S.A.; Zecca, L.; et al. Contrast mechanisms associated with neuromelanin-MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Shibata, E.; Tohyama, K.; Takahashi, J.; Otsuka, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Takahashi, S.; Ehara, S.; Terayama, Y.; Sakai, A. Neuromelanin magnetic resonance imaging of locus ceruleus and substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. NeuroReport 2006, 17, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haacke, E.M.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, Y.C.; Reichenbach, J.R. Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 52, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): Decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, J.; de Rochefort, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Khalidov, I.; LeDoux, J.R.; Wang, Y. Morphology enabled dipole inversion (MEDI) from a single-angle acquisition: comparison with COSMOS in human brain imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosottini, M.; Frosini, D.; Pesaresi, I.; Donatelli, G.; Cecchi, P.; Costagli, M.; Biagi, L.; Ceravolo, R.; Bonuccelli, U.; Tosetti, M. Comparison of 3T and 7T susceptibility-weighted angiography of the substantia nigra in diagnosing Parkinson disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fram, E.K.; Herfkens, R.J.; Johnson, G.; Glover, G.H.; Karis, J.P.; Shimakawa, A.; Perkins, T.G.; Pelc, N.J. Rapid calculation of T1 using variable flip angle gradient refocused imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1987, 5, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.; Velthuizen, R.; Phuphanich, S.; Hall, L.; Clarke, L.; Silbiger, M. Application of fuzzy c-means segmentation technique for tissue differentiation in MR images of a hemorrhagic glioblastoma multiforme. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1995, 13, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, P.; Summers, P.E.; Smith, A.K.; Smith, S.A.; Mainardi, L.T.; Cerutti, S.; Claassen, D.O.; Costa, A. Pool size ratio of the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease derived from two different quantitative magnetization transfer approaches. Neuroradiology 2017, 59, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.T.; Xing, Y.; Naidu, S.; Birchall, J.; Skelly, R.; Perkins, A.; Evans, J.; Sare, G.; Martin-Bastida, A.; Bajaj, N.; et al. Protocol of a single group prospective observational study on the diagnostic value of 3T susceptibility weighted MRI of nigrosome-1 in patients with parkinsonian symptoms: the N3iPD study (nigrosomal iron imaging in Parkinson’s disease). BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Lian, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, X.; et al. Combined Visualization of Nigrosome-1 and Neuromelanin in the Substantia Nigra Using 3T MRI for the Differential Diagnosis of Essential Tremor and de novo Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mok, K.; Neelavalli, J.; Cheng, Y.-C.N.; Tang, J.; Ye, Y.; Haacke, E.M. Improved MR venography using quantitative susceptibility-weighted imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 40, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Baek, S.-Y.; Kim, E.-J.; Huh, G.Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, H. MRI T2 and T2* relaxometry to visualize neuromelanin in the dorsal substantia nigra pars compacta. NeuroImage 2020, 211, 116625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, N.; Kan, H.; Ogawa, M.; Uchida, Y.; Takizawa, M.; Omori, K.; Miyati, T.; Kasai, H.; Kunitomo, H.; Shibamoto, Y. Visualization of Nigrosome 1 from the Viewpoint of Anatomic Structure. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, N.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Xu, H.; Tang, R.; Jin, Z.; Haacke, E.M.; Yan, F.; et al. Radiomic Features of the Nigrosome-1 Region of the Substantia Nigra: Using Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping to Assist the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazejewska, A.I.; Schwarz, S.T.; Pitiot, A.; Stephenson, M.C.; Lowe, J.; Bajaj, N.; Bowtell, R.W.; Auer, D.P.; Gowland, P.A. Visualization of nigrosome 1 and its loss in PD: pathoanatomical correlation and in vivo 7 T MRI. Neurology 2013, 81, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langley, J.; Huddleston, D.E.; Chen, X.; Sedlacik, J.; Zachariah, N.; Hu, X. A multicontrast approach for comprehensive imaging of substantia nigra. NeuroImage 2015, 112, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Mihara, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Tomiyama, N. Comprehensive MRI quantification of the substantia nigra pars compacta in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 109, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Baek, S.Y.; Chun, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, H. Specific visualization of neuromelanin-iron complex and ferric iron in the human post-mortem substantia nigra using MR relaxometry at 7T. NeuroImage 2018, 172, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetten, P.P.R.; Gillard, J.H.; Graves, M.J. Introduction to Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping and Susceptibility Weighted Imaging. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, H.; Cronin, M.J.; He, N.; Yan, F.; Liu, C. Longitudinal data for magnetic susceptibility of normative human brain development and aging over the lifespan. Data Brief 2018, 20, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, H.; Cronin, M.J.; He, N.; Yan, F.; Liu, C. Longitudinal atlas for normative human brain development and aging over the lifespan using quantitative susceptibility mapping. Neuroimage 2018, 171, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, G.C.; Polimeni, J.R.; Potthast, A.; Schmitt, M.; Alagappan, V.; Wald, L.L. 96-Channel receive-only head coil for 3 Tesla: design optimization and evaluation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, B.; Blau, J.N.; Biber, S.; Hoecht, P.; Tountcheva, V.; Setsompop, K.; Triantafyllou, C.; Wald, L.L. A 64-channel 3T array coil for accelerated brain MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uğurbil, K.; Auerbach, E.; Moeller, S.; Grant, A.; Wu, X.; Van De Moortele, P.-F.; Olman, C.; DelaBarre, L.; Schillak, S.; Radder, J.; et al. Brain imaging with improved acceleration and SNR at 7 Tesla obtained with 64-channel receive array. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

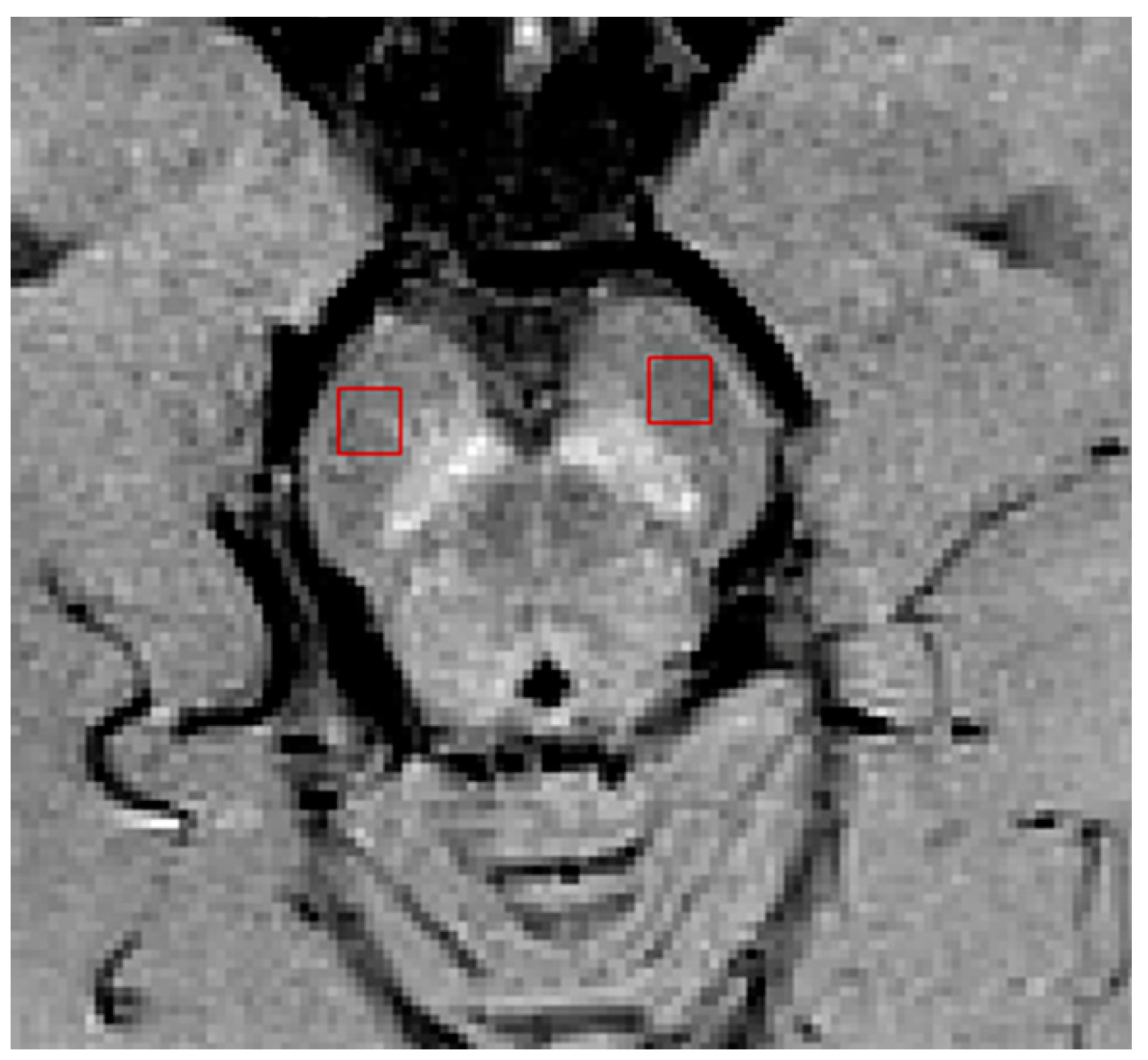
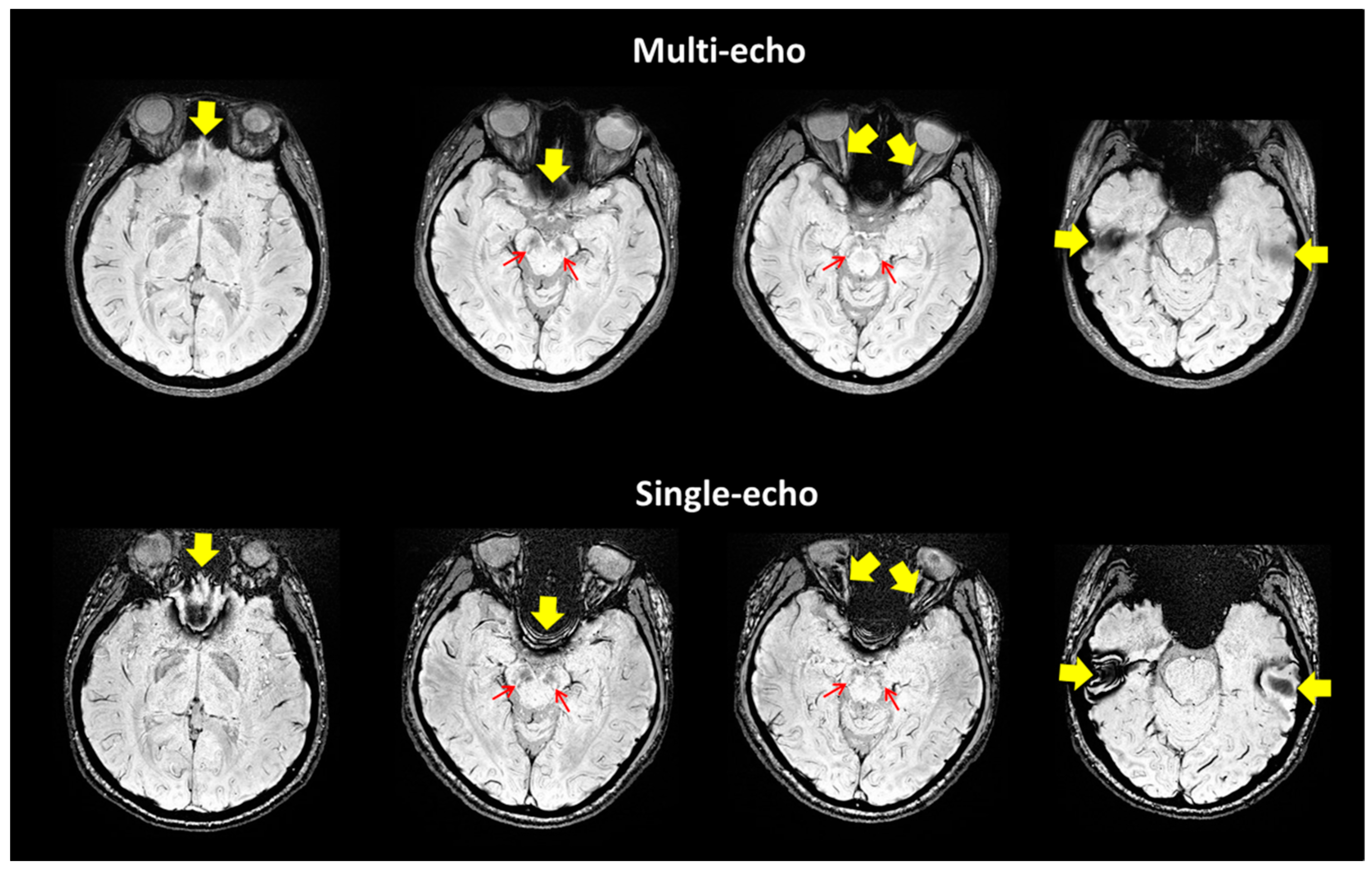
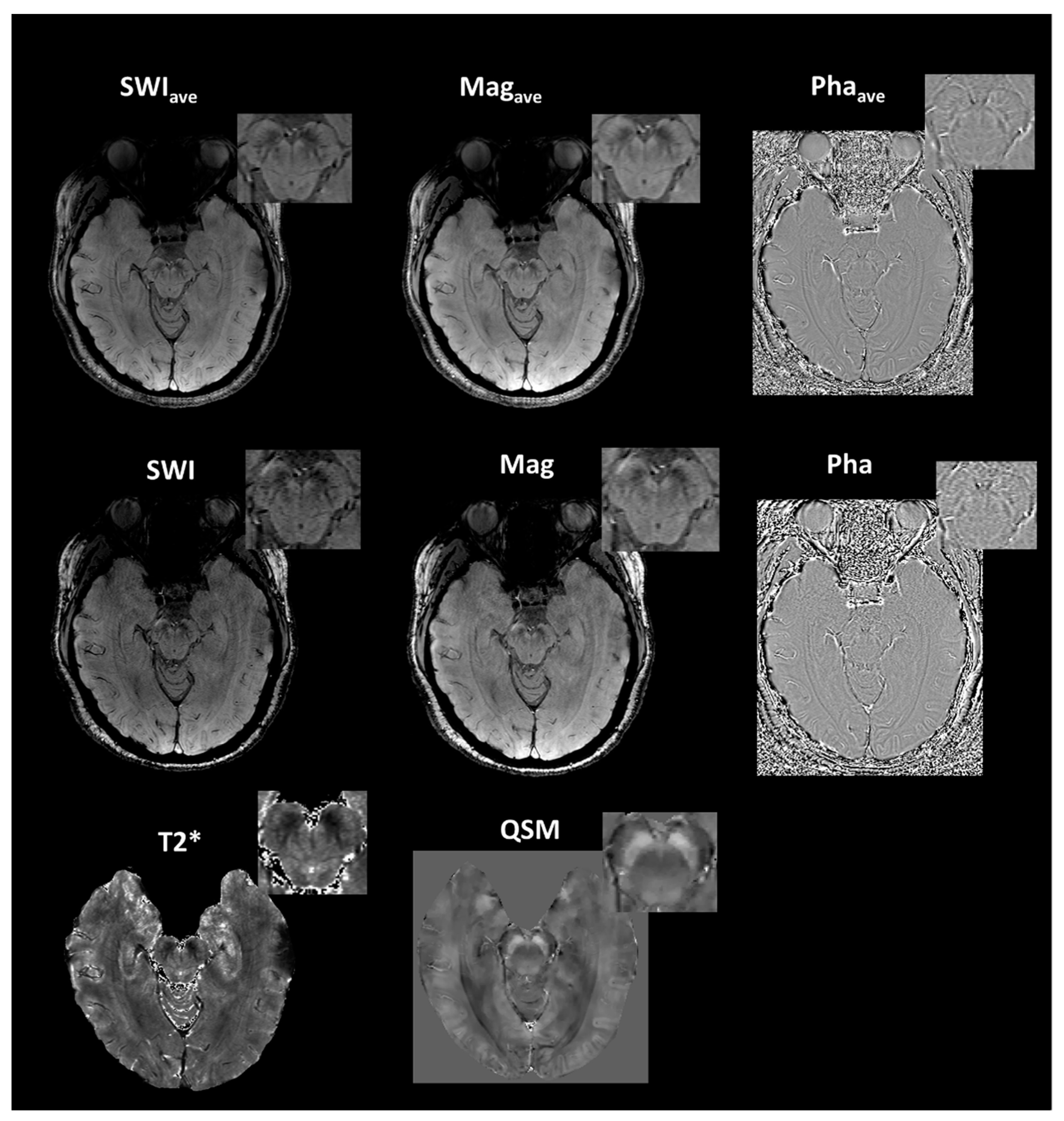
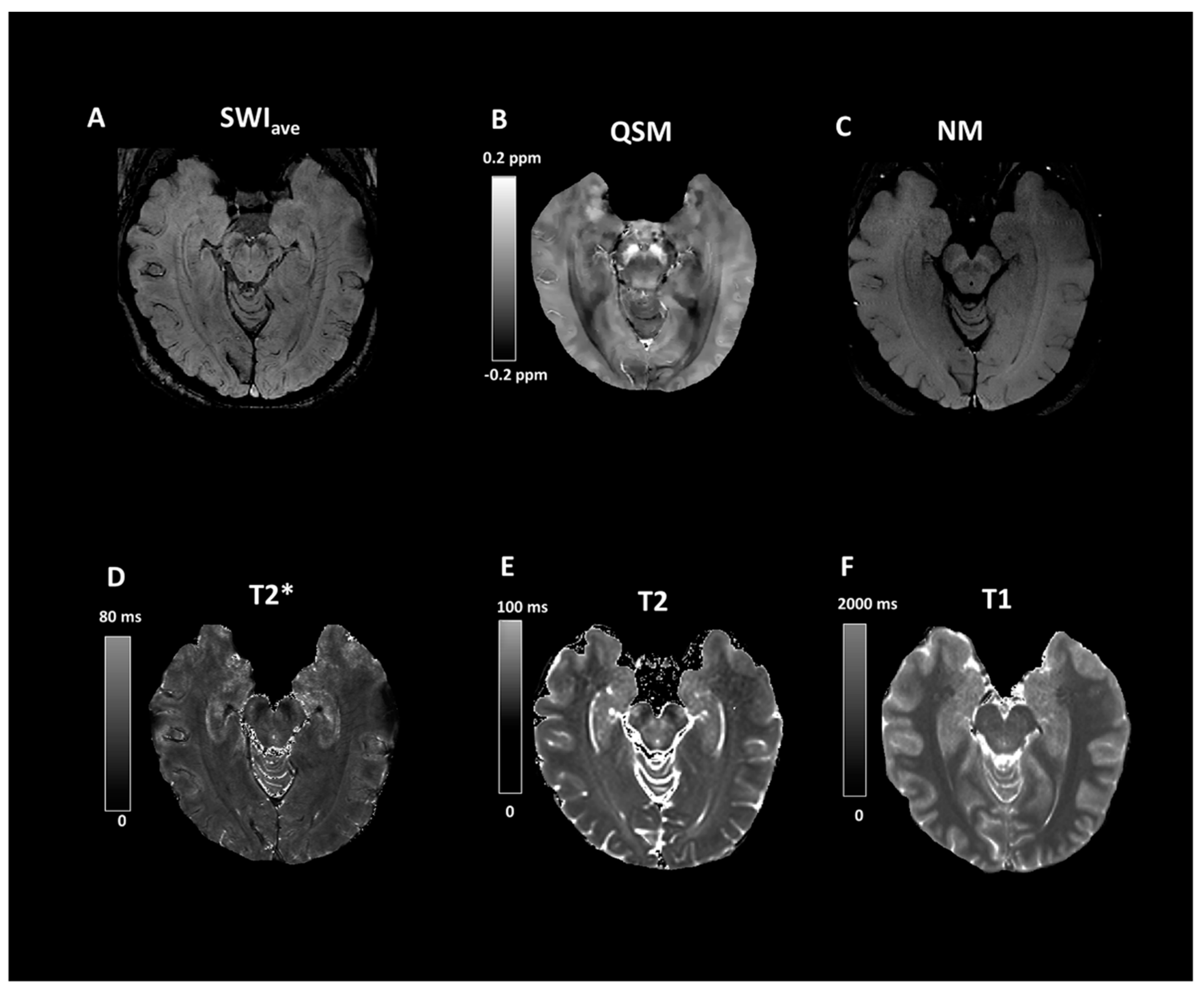
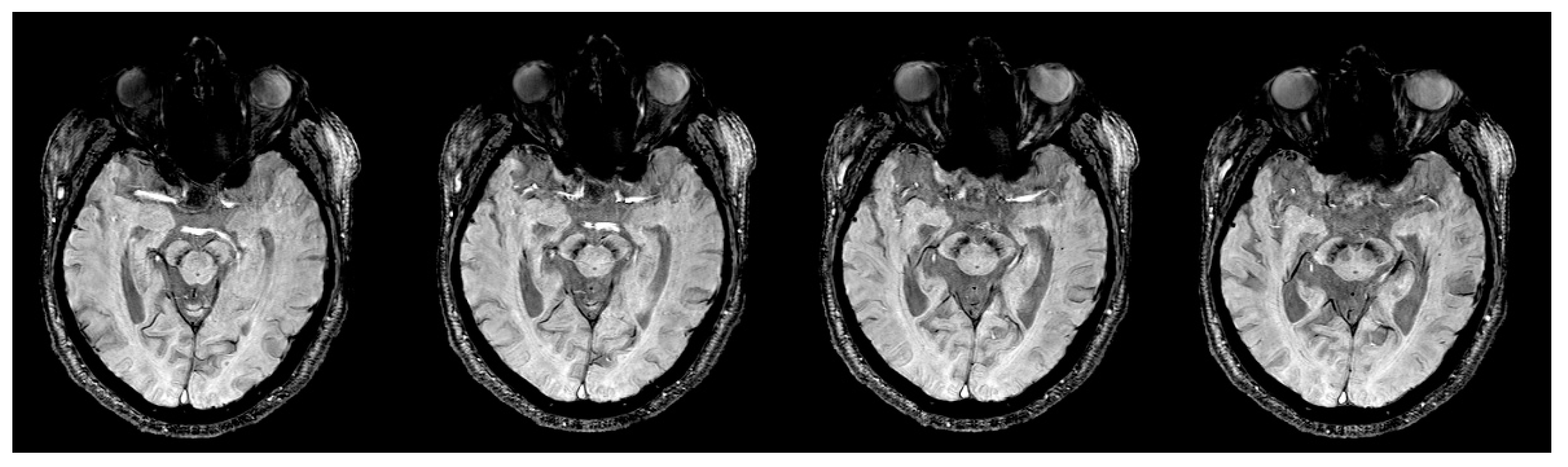
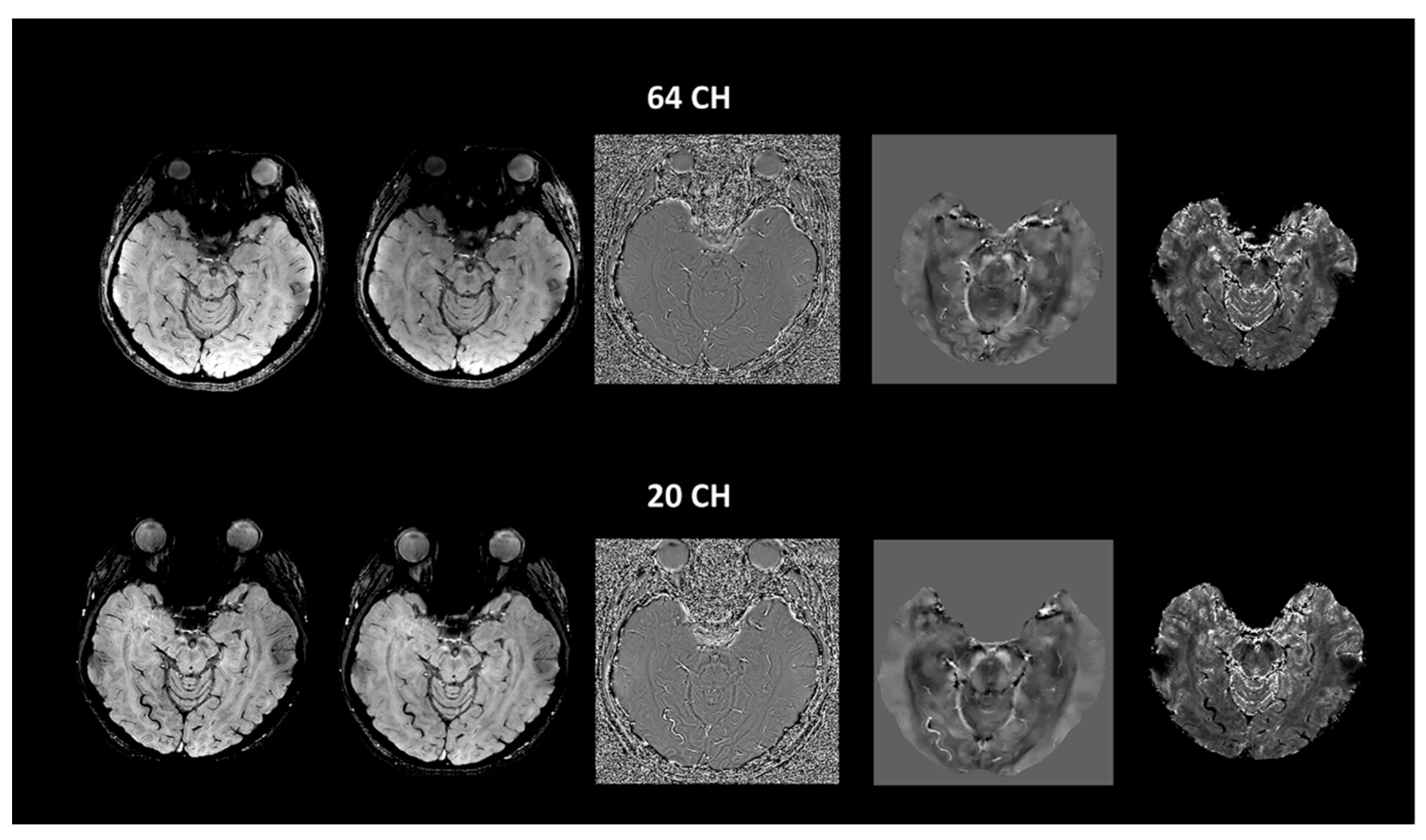
| Group (n) | Sex (n, %) | Age, Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Older adults (25) | Male (10, 40.0%) | 50.28 (12.15) years |
| Female (15, 60.0%) | ||
| Young adults (23) | Male (11, 47.8%) | 20.74 (1.21) years |
| Female (12, 52.2%) |
| SWIave | Magave | Phaave | SWI | Mag | Pha | QSM | T2* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 CH | Older | Mean (std) | 2.75 (0.22) | 2.03 (0.23) | −0.55 (0.23) | 1.99 (0.32) | 1.67 (0.29) | −0.44 (0.18) | −0.80 (0.39) | 1.80 (0.44) |
| Young | Mean (std) | 2.52 (0.28) | 1.77 (0.37) | −0.62 (0.35) | 1.67 (0.36) | 1.39 (0.34) | −0.46 (0.25) | −0.57 (0.34) | 1.47 (0.49) | |
| 20CH | Young | Mean (std) | 2.58 (0.30) | 1.82 (0.30) | −0.60 (0.24) | 1.70 (0.29) | 1.41 (0.29) | −0.47 (0.20) | −0.61 (0.32) | 1.49 (0.36) |
| QSM | T2* | Phaave | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SN1 | S0 | SN1 | S0 | SN1 | S0 | |||
| 64CH | Older | Mean (std) | 90.20 (33.01) | 136.99 (43.38) | 36.02 (5.86) | 25.26 (5.04) | −0.02 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.02) |
| Young | Mean (std) | 53.16 (29.19) | 85.52 (37.27) | 38.86 (4.49) | 28.94 (4.85) | −0.02 (0.01) | 0.03 (0.02) | |
| p-value a | <0.001 * | <0.001 * | 0.55 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.57 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, T.-W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, K.; Tso, C.-W.; Lin, H.-H.; Lai, Y.-L.L.; Hsu, F.-T.; Chung, H.-W.; Liu, H.-S. Evaluation of the Swallow-Tail Sign and Correlations of Neuromelanin Signal with Susceptibility and Relaxations. Tomography 2021, 7, 107-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7020010
Lee T-W, Chen C-Y, Chen K, Tso C-W, Lin H-H, Lai Y-LL, Hsu F-T, Chung H-W, Liu H-S. Evaluation of the Swallow-Tail Sign and Correlations of Neuromelanin Signal with Susceptibility and Relaxations. Tomography. 2021; 7(2):107-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Tzu-Wei, Cheng-Yu Chen, Kuan Chen, Chao-Wei Tso, Hui-Hsien Lin, Ying-Liang Larry Lai, Fei-Ting Hsu, Hsiao-Wen Chung, and Hua-Shan Liu. 2021. "Evaluation of the Swallow-Tail Sign and Correlations of Neuromelanin Signal with Susceptibility and Relaxations" Tomography 7, no. 2: 107-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7020010
APA StyleLee, T.-W., Chen, C.-Y., Chen, K., Tso, C.-W., Lin, H.-H., Lai, Y.-L. L., Hsu, F.-T., Chung, H.-W., & Liu, H.-S. (2021). Evaluation of the Swallow-Tail Sign and Correlations of Neuromelanin Signal with Susceptibility and Relaxations. Tomography, 7(2), 107-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7020010








