Respiratory Motion Mitigation and Repeatability of Two Diffusion-Weighted MRI Methods Applied to a Murine Model of Spontaneous Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. GEM Model of Pancreatic Cancer
2.2. In Vivo MRI and Test-Retest Study
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
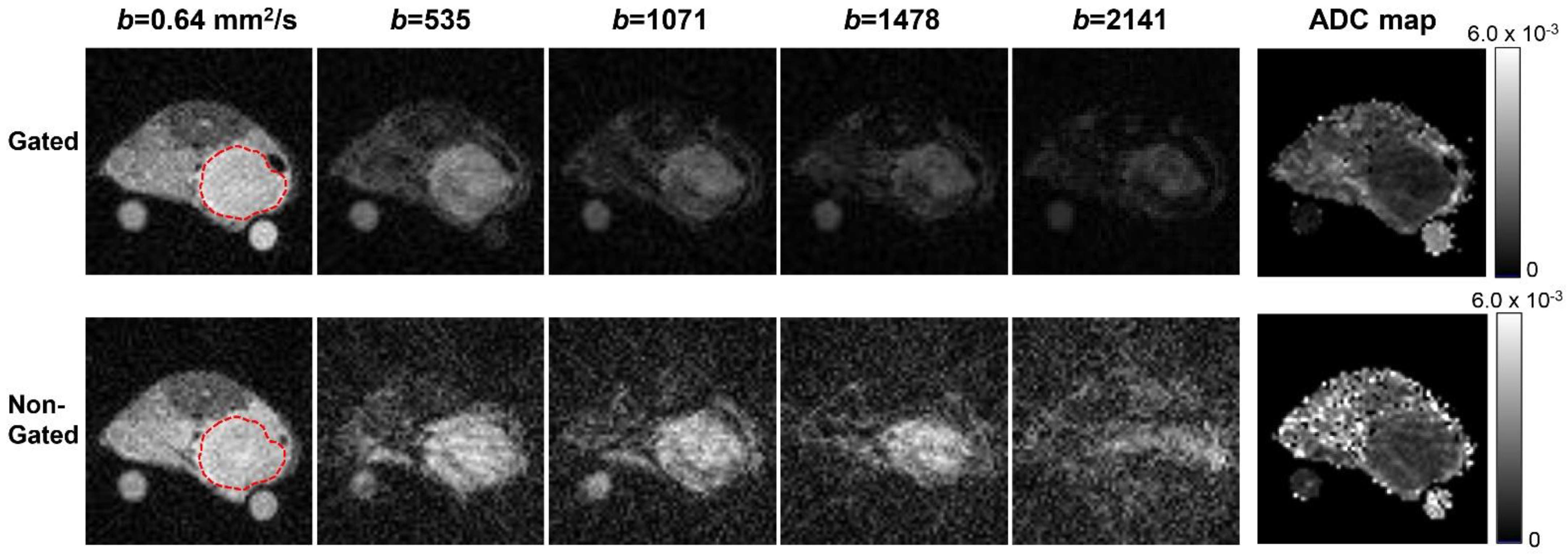
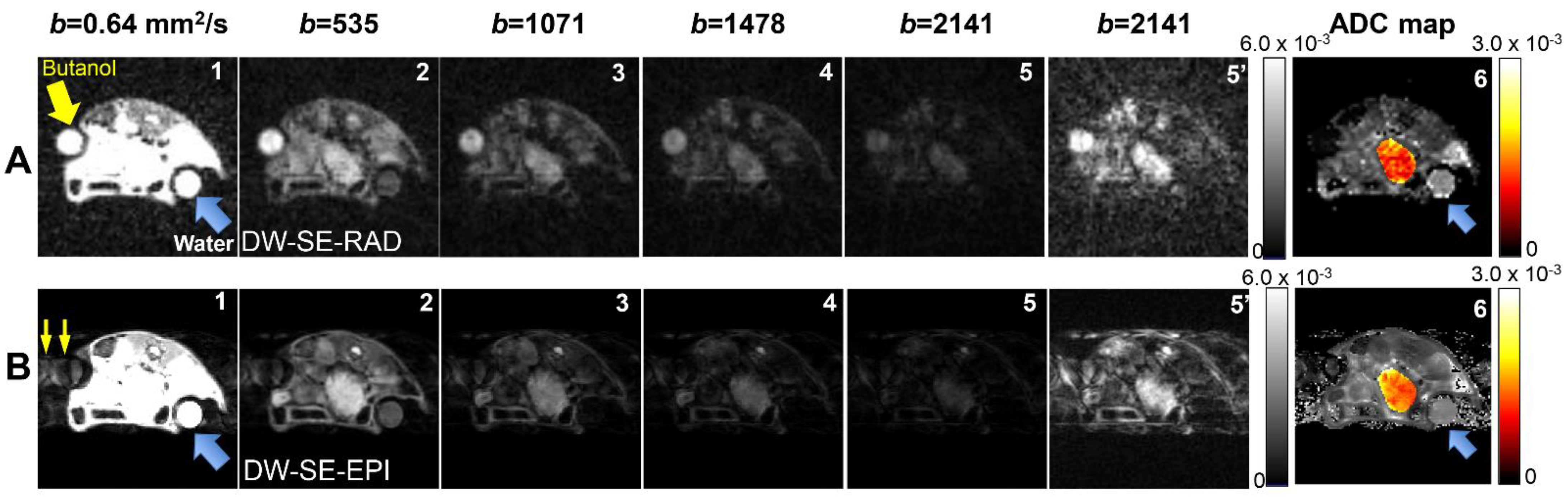
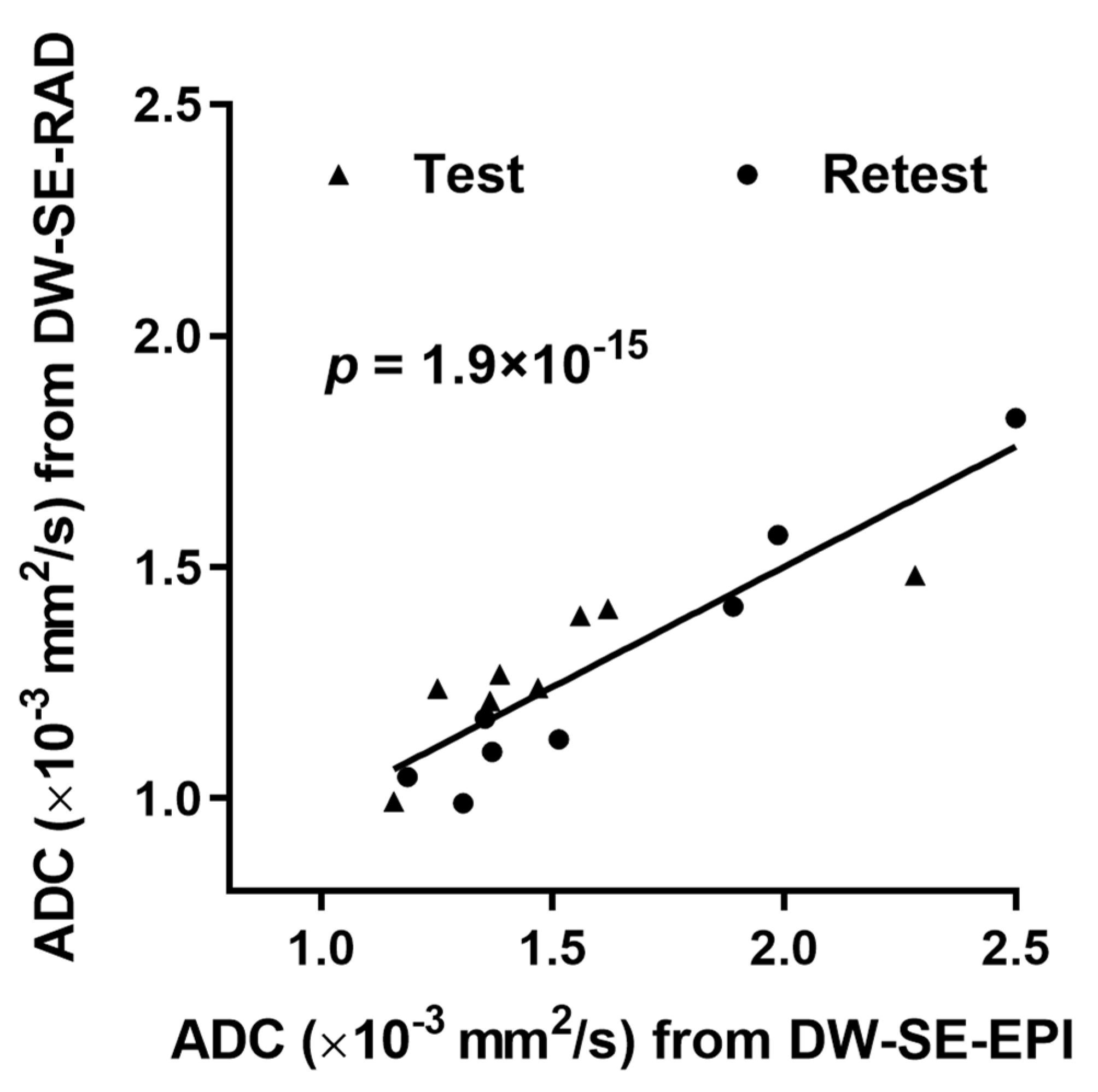
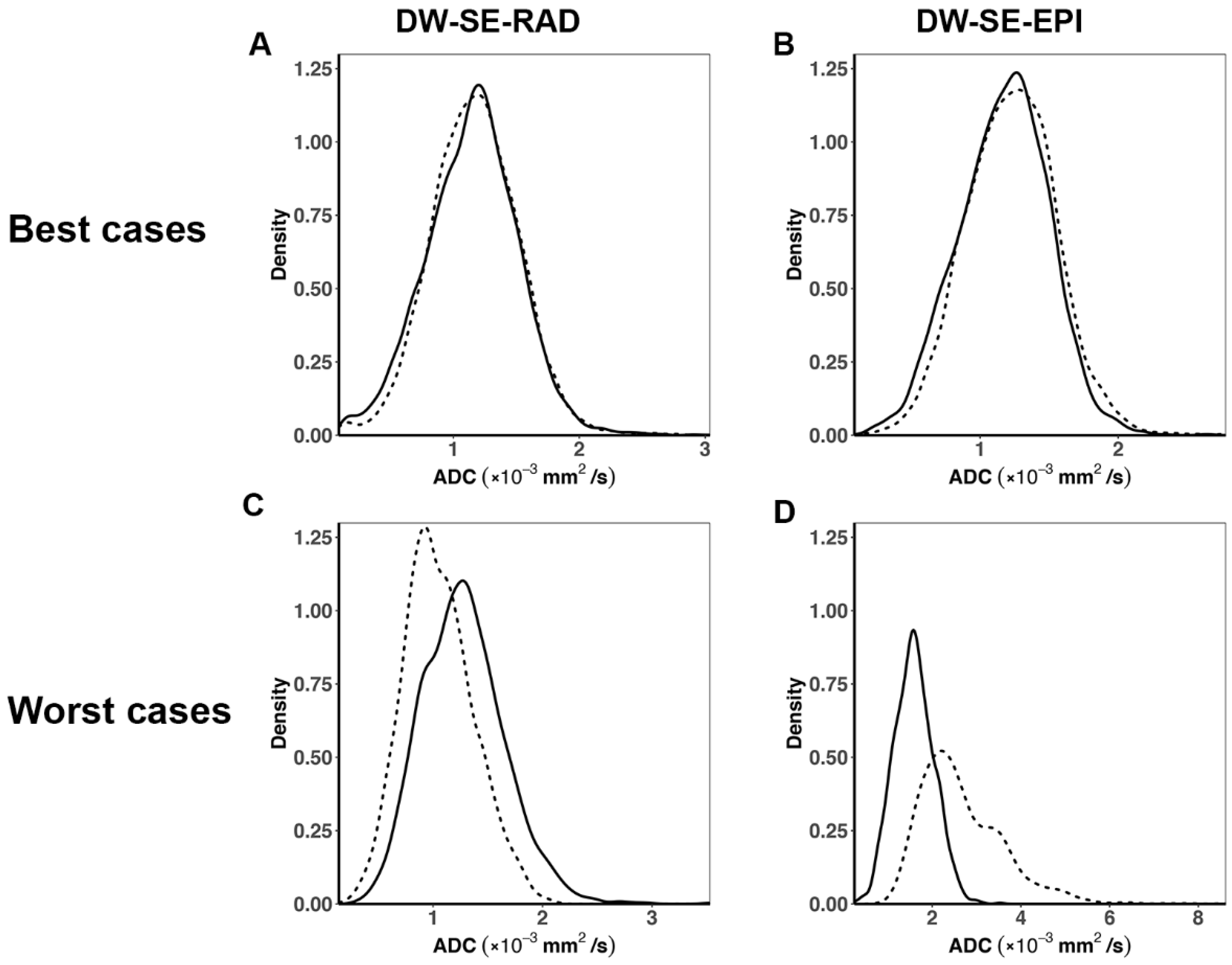
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC or D | apparent diffusion coefficient |
| CVWS | within-subject coefficient of variation |
| DWI | diffusion-weighted MRI |
| DW-SE-EPI | diffusion-weighted 4-shot spin-echo echo planar imaging protocol |
| DW-SE-RAD | diffusion-weighted radially sampled spin-echo protocol |
| GEM | genetically engineered mouse |
| PDAC | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| probability density function | |
| RC | repeatability coefficient |
| SDws | within-subject standard deviation |
References
- Hingorani, S.R.; Petricoin, E.F., III; Maitra, A.; Rajapakse, V.; King, C.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Ross, S.; Conrads, T.P.; Veenstra, T.D.; Hitt, B.A.; et al. Preinvasive and invasive ductal pancreatic cancer and its early detection in the mouse. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardeesy, N.; Cheng, K.H.; Berger, J.H.; Chu, G.C.; Pahler, J.; Olson, P.; Hezel, A.F.; Horner, J.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Hanahan, D.; et al. Smad4 is dispensable for normal pancreas development yet critical in progression and tumor biology of pancreas cancer. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3130–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frese, K.K.; Neesse, A.; Cook, N.; Bapiro, T.E.; Lolkema, M.P.; Jodrell, D.I.; Tuveson, D.A. Nab-paclitaxel potentiates gemcitabine activity by reducing cytidine deaminase levels in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobetz, M.A.; Chan, D.S.; Neesse, A.; Bapiro, T.E.; Cook, N.; Frese, K.K.; Feig, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Caldwell, M.E.; Zecchini, H.I.; et al. Hyaluronan impairs vascular function and drug delivery in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, M.H.; Ruth, T.Y.; Engle, D.D.; Ding, N.; Atkins, A.R.; Tiriac, H.; Collisson, E.A.; Connor, F.; Van Dyke, T.; Kozlov, S.; et al. Vitamin D Receptor-Mediated Stromal Reprogramming Suppresses Pancreatitis and Enhances Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Cell 2014, 159, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo, A.; Wang, L.C.S.; Scholler, J.; Monslow, J.; Avery, D.; Newick, K.; O’Brien, S.; Evans, R.A.; Bajor, D.J.; Clendenin, C.; et al. Tumor-Promoting Desmoplasia Is Disrupted by Depleting FAP-Expressing Stromal Cells. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2800–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beatty, G.L.; Chiorean, E.G.; Fishman, M.P.; Saboury, B.; Teitelbaum, U.R.; Sun, W.; Huhn, R.D.; Song, W.; Li, D.; Sharp, L.L.; et al. CD40 agonists alter tumor stroma and show efficacy against pancreatic carcinoma in mice and humans. Science 2011, 331, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Pickup, S.; Clendenin, C.; Blouw, B.; Choi, H.; Kang, D.; Rosen, M.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Zhou, R. Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI Detects Responses to Stroma-directed Therapy in Mouse Models of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2314–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, N.S.; McDonald, C.R.; Farid, N.; Kuperman, J.; Karow, D.; Schenker-Ahmed, N.M.; Bartsch, H.; Rakow-Penner, R.; Holland, D.; Shabaik, A.; et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in cancer: Physical foundations and applications of restriction spectrum imaging. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4638–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Bihan, D. Apparent diffusion coefficient and beyond: What diffusion MR imaging can tell us about tissue structure. Radiology 2013, 268, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taouli, B.; Beer, A.J.; Chenevert, T.; Collins, D.; Lehman, C.; Matos, C.; Padhani, A.R.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Shukla-Dave, A.; Sigmund, E.; et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging outside the brain: Consensus statement from an ISMRM-sponsored workshop. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, Y.; Tichler, T.; Kostenich, G.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Maier, S.E.; Cohen, J.S.; Orenstein, A.; Mardor, Y. High-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging for pretreatment prediction and early monitoring of tumor response to therapy in mice. Radiology 2004, 232, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.M.; Scurr, E.; Collins, D.; Kanber, B.; Norman, A.; Leach, M.O.; Husband, J.E. Predicting response of colorectal hepatic metastasis: Value of pretreatment apparent diffusion coefficients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbán, C.J.; Ma, B.; Malyarenko, D.; Pickles, M.D.; Heist, K.; Henry, N.L.; Schott, A.F.; Neal, C.H.; Hylton, N.M.; Rehemtulla, A.; et al. Multi-site clinical evaluation of DW-MRI as a treatment response metric for breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dolde, K.; Dávid, C.; Echner, G.; Floca, R.; Hentschke, C.; Maier, F.; Niebuhr, N.; Ohmstedt, K.; Saito, N.; Alimusaj, M.; et al. 4DMRI-based analysis of inter—And intrafractional pancreas motion and deformation with different immobilization devices. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2019, 5, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.L.; Schefter, T.; Miften, M. Adaptive motion mapping in pancreatic SBRT patients using Fourier transforms. Radiol. Oncol. 2015, 115, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batista, V.; Richter, D.; Chaudhri, N.; Naumann, P.; Herfarth, K.; Jäkel, O. Significance of intra-fractional motion for pancreatic patients treated with charged particles. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferris, W.S.; Kissick, M.W.; Bayouth, J.E.; Culberson, W.S.; Smilowitz, J.B. Evaluation of radixact motion synchrony for 3D respiratory motion: Modeling accuracy and dosimetric fidelity. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 21, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bammer, R.; Keeling, S.L.; Augustin, M.; Pruessmann, K.P.; Wolf, R.; Stollberger, R.; Hartung, H.P.; Fazekas, F. Improved diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar imaging (EPI) in stroke using sensitivity encoding (SENSE). Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 46, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porter, D.A.; Heidemann, R.M. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareis, D.; Wichmann, T.; Lanz, T.; Melkus, G.; Horn, M.; Jakob, P.M. Mouse MRI using phased-array coils. NMR Biomed. 2007, 20, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribot, E.J.; Trotier, A.J.; Castets, C.R.; Dallaudière, B.; Thiaudière, E.; Franconi, J.M.; Miraux, S. Free-breathing 3D diffusion MRI for high-resolution hepatic metastasis characterization in small animals. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2016, 33, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Luci, J.J.; Tantawy, M.N.; Lee, H.; Nam, K.T.; Peterson, T.E.; Price, R.R. Detecting peritoneal dissemination of ovarian cancer in mice by DWIBS. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, A.M.; Gao, D.S.; Fan, S.J.; Qiao, Z.; Lee, F.Y.; Yang, J.; Man, K.; Wu, E.X. Liver fibrosis: An intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, H. Assessment of diffusion tensor MR imaging (DTI) in liver fibrosis with minimal confounding effect of hepatic steatosis. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.P.; Li, X.T.; Tang, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Sun, Y.S. Applicable apparent diffusion coefficient of an orthotopic mouse model of gastric cancer by improved clinical MRI diffusion weighted imaging. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, X.; Quirk, J.D.; Engelbach, J.A.; Bretthorst, G.L.; Li, S.; Shoghi, K.I.; Garbow, J.R.; Ackerman, J.J. Test-Retest Performance of a 1-Hour Multiparametric MR Image Acquisition Pipeline with Orthotopic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patient-Derived Tumor Xenografts. Tomography 2019, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bao, Q.; Liberman, G.; Solomon, E.; Frydman, L. High-resolution diffusion MRI studies of development in pregnant mice visualized by novel spatiotemporal encoding schemes. NMR Biomed. 2020, 33, e4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Cai, C.; Yang, H.; Cai, S.; Qian, J.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, K.; Chen, Z. Motion-tolerant diffusion mapping based on single-shot overlapping-echo detachment (OLED) planar imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S.D.; Zhong, J. Diffusion measurements free of motion artifacts using intermolecular dipole-dipole interactions. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, M.; Maclaren, J.; Herbst, M. Motion artifacts in MRI: A complex problem with many partial solutions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Guo, J.; Rosen, M.A.; Song, H.K. Respiratory motion-compensated radial dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE)-MRI of chest and abdominal lesions. Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 60, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dougherty, L.; Isaac, G.; Rosen, M.A.; Nunes, L.W.; Moate, P.J.; Boston, R.C.; Schnall, M.D.; Song, H.K. High frame-rate simultaneous bilateral breast DCE-MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Khasgiwala, A.; Doshi, A.M.; Ream, J.M.; Taneja, S.S.; Lepor, H. Detection of prostate cancer local recurrence following radical prostatectomy: Assessment using a continuously acquired radial golden-angle compressed sensing acquisition. Abdom. Radiol. (N. Y.) 2017, 42, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heacock, L.; Gao, Y.; Heller, S.L.; Melsaether, A.N.; Babb, J.S.; Block, T.K.; Otazo, R.; Kim, S.G.; Moy, L. Comparison of conventional DCE-MRI and a novel golden-angle radial multicoil compressed sensing method for the evaluation of breast lesion conspicuity. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Chenevert, T.L.; Jambawalikar, S.; Schwartz, L.H.; Malyarenko, D.; Huang, W.; Noworolski, S.M.; Young, R.J.; Shiroishi, M.S.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers alliance (QIBA) recommendations for improved precision of DWI and DCE-MRI derived biomarkers in multicenter oncology trials. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e101–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjølby, B.F.; Khan, A.R.; Chuhutin, A.; Pedersen, L.; Jensen, J.B.; Jakobsen, S.; Zeidler, D.; Sangill, R.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Jespersen, S.N.; et al. Fast diffusion kurtosis imaging of fibrotic mouse kidneys. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garrett-Roe, S.; Warren, W.S. Numerical studies of intermolecular multiple quantum coherences: High-resolution NMR in inhomogeneous fields and contrast enhancement in MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 2000, 146, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeman, M.; Freyer, J.P.; Sillerud, L.O. A simple method for obtaining cross-term-free images for diffusion anisotropy studies in NMR microimaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1991, 21, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, D.A.; Oshio, K. Phase errors in multi-shot echo planar imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1994, 32, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofts, P.S.; Lloyd, D.; Clark, C.A.; Barker, G.J.; Parker, G.J.M.; McConville, P.; Baldock, C.; Pope, J.M. Test liquids for quantitative MRI measurements of self-diffusion coefficient in vivo. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 43, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patlak, C.S.; Hospod, F.E.; Trowbridge, S.D.; Newman, G.C. Diffusion of radiotracers in normal and ischemic brain slices. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1998, 18, 776–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpless, N.E.; Depinho, R.A. The mighty mouse: Genetically engineered mouse models in cancer drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, S.; Holme, H.C.M.; Uecker, M. Simple auto-calibrated gradient delay estimation from few spokes using Radial Intersections (RING). Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, K.T.; Uecker, M.; Frahm, J. Undersampled radial MRI with multiple coils. Iterative image reconstruction using a total variation constraint. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 1086–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, F.; Laun, F.B.; Kuder, T.A.; Mlynarska, A.; Maier, F.; Faust, J.; Demberg, K.; Lindemann, L.; Rivkin, B.; Nagel, A.M. Temperature and concentration calibration of aqueous polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) solutions for isotropic diffusion MRI phantoms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwa, T.; Ueno, M.; Ohkawa, S.; Yoshida, T.; Doiuchi, T.; Ito, K.; Inoue, T. Advanced pancreatic cancer: The use of the apparent diffusion coefficient to predict response to chemotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 82, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, N.; Uematsu, H.; Kimura, H.; Imamura, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Murakami, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Itoh, H. Apparent diffusion coefficient in pancreatic cancer: Characterization and histopathological correlations. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whisenant, J.G.; Ayers, G.D.; Loveless, M.E.; Barnes, S.L.; Colvin, D.C.; Yankeelov, T.E. Assessing reproducibility of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging studies in a murine model of HER2+ breast cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoghi, K.I.; Badea, C.T.; Blocker, S.J.; Chenevert, T.L.; Laforest, R.; Lewis, M.T.; Luker, G.D.; Manning, H.C.; Marcus, D.S.; Mowery, Y.M.; et al. Co-Clinical Imaging Resource Program (CIRP): Bridging the Translational Divide to Advance Precision Medicine. Tomography 2020, 6, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnes, A.; Alonzi, R.; Blackledge, M.; Charles-Edwards, G.; Collins, D.J.; Cook, G.; Coutts, G.; Goh, V.; Graves, M.; Kelly, C.; et al. UK quantitative WB-DWI technical workgroup: Consensus meeting recommendations on optimisation, quality control, processing and analysis of quantitative whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging for cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouard, T.P.; Theilmann, R.J.; Altbach, M.I.; Gmitro, A.F. High-resolution diffusion imaging with DIFRAD-FSE (diffusion-weighted radial acquisition of data with fast spin-echo) MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.N.; Huang, T.Y.; Lin, F.H.; Chuang, T.C.; Chen, N.K.; Chung, H.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Kwong, K.K. PROPELLER EPI: An MRI technique suitable for diffusion tensor imaging at high field strength with reduced geometric distortions. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knoll, F.; Raya, J.G.; Halloran, R.O.; Baete, S.; Sigmund, E.; Bammer, R.; Block, T.; Otazo, R.; Sodickson, D.K. A model-based reconstruction for undersampled radial spin-echo DTI with variational penalties on the diffusion tensor. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
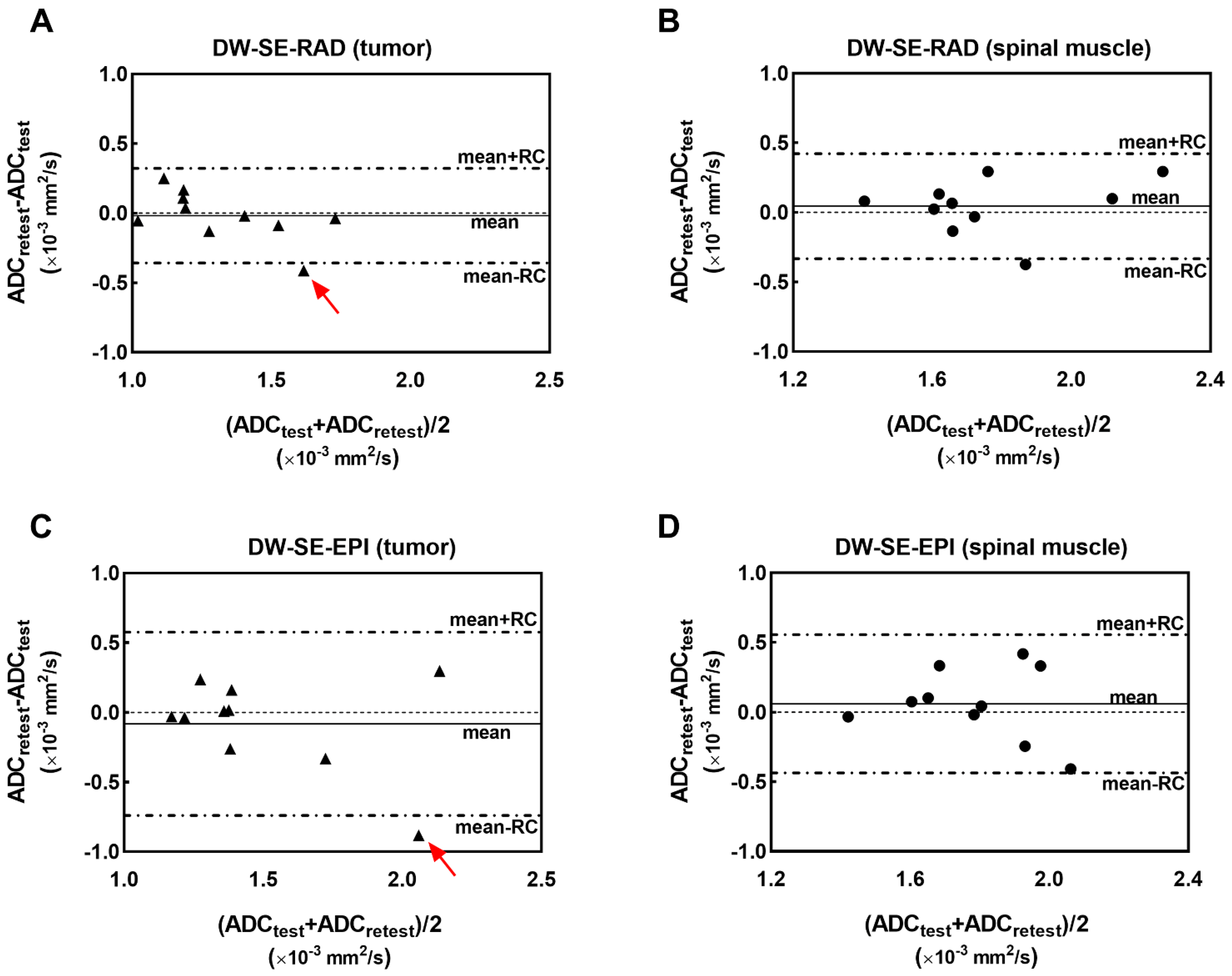
| Protocol | ADC (Mean ± SD) | ΔD (Mean ± SD) | SDws | CVWS | RC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test b | Retest b | ||||||
| Water c | DW-SE-RAD | 3.2 ± 0.29 | 3.3 ± 0.27 | −0.048 ± 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.060 | 0.53 |
| DW-SE-EPI | 2.8 ± 0.15 | 2.8 ± 0.10 | 0.069 ± 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.039 | 0.31 | |
| Muscle | DW-SE-RAD | 1.8 ± 0.29 | 1.7 ± 0.25 | 0.045 ± 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.073 | 0.38 |
| DW-SE-EPI | 1.8 ± 0.22 | 1.7 ± 0.25 | 0.060 ± 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.096 | 0.50 | |
| Tumor | DW-SE-RAD | 1.3 ± 0.19 | 1.3 ± 0.29 | −0.017 ± 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.090 | 0.34 |
| DW-SE-EPI | 1.5 ± 0.32 | 1.5 ± 0.44 | −0.082 ± 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.66 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Song, H.K.; Yang, H.; Castillo, V.; Chen, J.; Clendenin, C.; Rosen, M.; Zhou, R.; Pickup, S. Respiratory Motion Mitigation and Repeatability of Two Diffusion-Weighted MRI Methods Applied to a Murine Model of Spontaneous Pancreatic Cancer. Tomography 2021, 7, 66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010007
Cao J, Song HK, Yang H, Castillo V, Chen J, Clendenin C, Rosen M, Zhou R, Pickup S. Respiratory Motion Mitigation and Repeatability of Two Diffusion-Weighted MRI Methods Applied to a Murine Model of Spontaneous Pancreatic Cancer. Tomography. 2021; 7(1):66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jianbo, Hee Kwon Song, Hanwen Yang, Victor Castillo, Jinbo Chen, Cynthia Clendenin, Mark Rosen, Rong Zhou, and Stephen Pickup. 2021. "Respiratory Motion Mitigation and Repeatability of Two Diffusion-Weighted MRI Methods Applied to a Murine Model of Spontaneous Pancreatic Cancer" Tomography 7, no. 1: 66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010007
APA StyleCao, J., Song, H. K., Yang, H., Castillo, V., Chen, J., Clendenin, C., Rosen, M., Zhou, R., & Pickup, S. (2021). Respiratory Motion Mitigation and Repeatability of Two Diffusion-Weighted MRI Methods Applied to a Murine Model of Spontaneous Pancreatic Cancer. Tomography, 7(1), 66-79. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography7010007






