Differences in PI-RADS Classification of Prostate Cancer Based on mpMRI Scans Taken 6 Weeks Apart
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. mpMRI
2.3. Biopsy
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs in Deutschland für 2019/2020; 14. Ausgabe; Robert Koch-Institut und die Gesellschaft der epideminologischen Krebsregister in Deutschland e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2023.
- EAU Guidelines; EAU Annual Congress: Madrid, Spain, 2025; ISBN 978-94-92671-29-5.
- Boyle, H.J.; Alibhai, S.; Decoster, L.; Efstathiou, E.; Fizazi, K.; Mottet, N.; Oudard, S.; Payne, H.; Prentice, M.; Puts, M.; et al. Updated recommendations of the International Society of Geriatric Oncology on prostate cancer management in older patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 116, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.U.; El-Shater Bosaily, A.; Brown, L.C.; Gabe, R.; Kaplan, R.; Parmar, M.K.; Collaco-Moraes, Y.; Ward, K.; Hindley, R.G.; Freeman, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): A paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet 2017, 389, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Rannikko, A.S.; Borghi, M.; Panebianco, V.; Mynderse, L.A.; Vaarala, M.H.; Briganti, A.; Budaus, L.; Hellawell, G.; Hindley, R.G.; et al. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy for Prostate-Cancer Diagnosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M.; et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging—Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackett, J.; Shih, J.H.; Reese, S.E.; Brender, J.R.; Harmon, S.A.; Barrett, T.; Coskun, M.; Madariaga, M.; Marko, J.; Law, Y.M.; et al. Quality of Prostate MRI: Is the PI-RADS Standard Sufficient? Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burn, P.R.; Freeman, S.J.; Andreou, A.; Burns-Cox, N.; Persad, R.; Barrett, T. A multicentre assessment of prostate MRI quality and compliance with UK and international standards. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 894.e19–894.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basar, Y.; Alis, D.; Seker, M.E.; Kartal, M.S.; Guroz, B.; Arslan, A.; Sirolu, S.; Kurtcan, S.; Denizoglu, N.; Karaarslan, E. Inter-reader agreement of the prostate imaging quality (PI-QUAL) score for basic readers in prostate MRI: A multi-center study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 165, 110923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, A.; Giganti, F.; Kasivisvanathan, V.; Giannarini, G.; Moore, C.M.; Padhani, A.R.; Panebianco, V.; Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Salomon, G.; Turkbey, B.; et al. Factors Influencing Variability in the Performance of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Ayoola, A.; Hoffman, D.; Khasgiwala, A.; Prabhu, V.; Smereka, P.; Somberg, M.; Taneja, S.S. The Learning Curve in Prostate MRI Interpretation: Self-Directed Learning Versus Continual Reader Feedback. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, W92–W100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Reyes, K.; Passoni, N.M.; Palmeri, M.L.; Kauffman, C.R.; Choudhury, K.R.; Polascik, T.J.; Gupta, R.T. Detection of prostate cancer with multiparametric MRI (mpMRI): Effect of dedicated reader education on accuracy and confidence of index and anterior cancer diagnosis. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, O.; Riedl, C.C.; Ishill, N.M.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Zhang, J.; Hricak, H. Interactive dedicated training curriculum improves accuracy in the interpretation of MR imaging of prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.S.; Neelsen, C.J.O.; Wennmann, M.; Glemser, P.A.; Hielscher, T.; Weru, V.; Gortz, M.; Schutz, V.; Stenzinger, A.; Hohenfellner, M.; et al. Same-day repeatability and Between-Sequence reproducibility of Mean ADC in PI-RADS lesions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 165, 110898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Vangel, M.G.; Tempany, C.M.; Fennessy, F.M. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Prostate: Repeatability of Volume and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadinski, M.; Medved, M.; Karademir, I.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sammet, S.; Karczmar, G.; Oto, A. Short-term reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficient estimated from diffusion-weighted MRI of the prostate. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Leest, M.; Cornel, E.; Israel, B.; Hendriks, R.; Padhani, A.R.; Hoogenboom, M.; Zamecnik, P.; Bakker, D.; Setiasti, A.Y.; Veltman, J.; et al. Head-to-head Comparison of Transrectal Ultrasound-guided Prostate Biopsy Versus Multiparametric Prostate Resonance Imaging with Subsequent Magnetic Resonance-guided Biopsy in Biopsy-naive Men with Elevated Prostate-specific Antigen: A Large Prospective Multicenter Clinical Study. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorny, M.; Kua, B.; Esler, R.; Yaxley, J.; Samaratunga, H.; Dunglison, N.; Gianduzzo, T.; Coughlin, G.; Holt, R.; Laing, B.; et al. MRI-guided in-bore biopsy for prostate cancer: What does the evidence say? A case series of 554 patients and a review of the current literature. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.; Eisenhuber, E.; Assinger, P.; Schima, R.; Susani, M.; Doblhammer, S.; Schima, W. MRI-guided in-bore biopsy of the prostate—Defining the optimal number of cores needed. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | n = 111 | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (yr), median (IQR) | 67 [62–72] | |
| PSA level (ng/mL), median (IQR) | 7.6 [5.0–10.1] | |
| <10 | 76 | 68.5 |
| ≥10 | 35 | 31.5 |
| DRE | ||
| Normal | 71 | 64.0 |
| Abnormal | 31 | 27.9 |
| No information | 9 | 8.1 |
| Prostate volume (mL), median (IQR) | 52 [37–67] | |
| PSAD (ng/mL/mL), median (IQR) | 0.14 [0.08–0.20] | |
| Number of lesions | ||
| 0 | 3 | 2.7 |
| 1 | 75 | 67.6 |
| 2 | 28 | 25.2 |
| 3 | 5 | 4.5 |
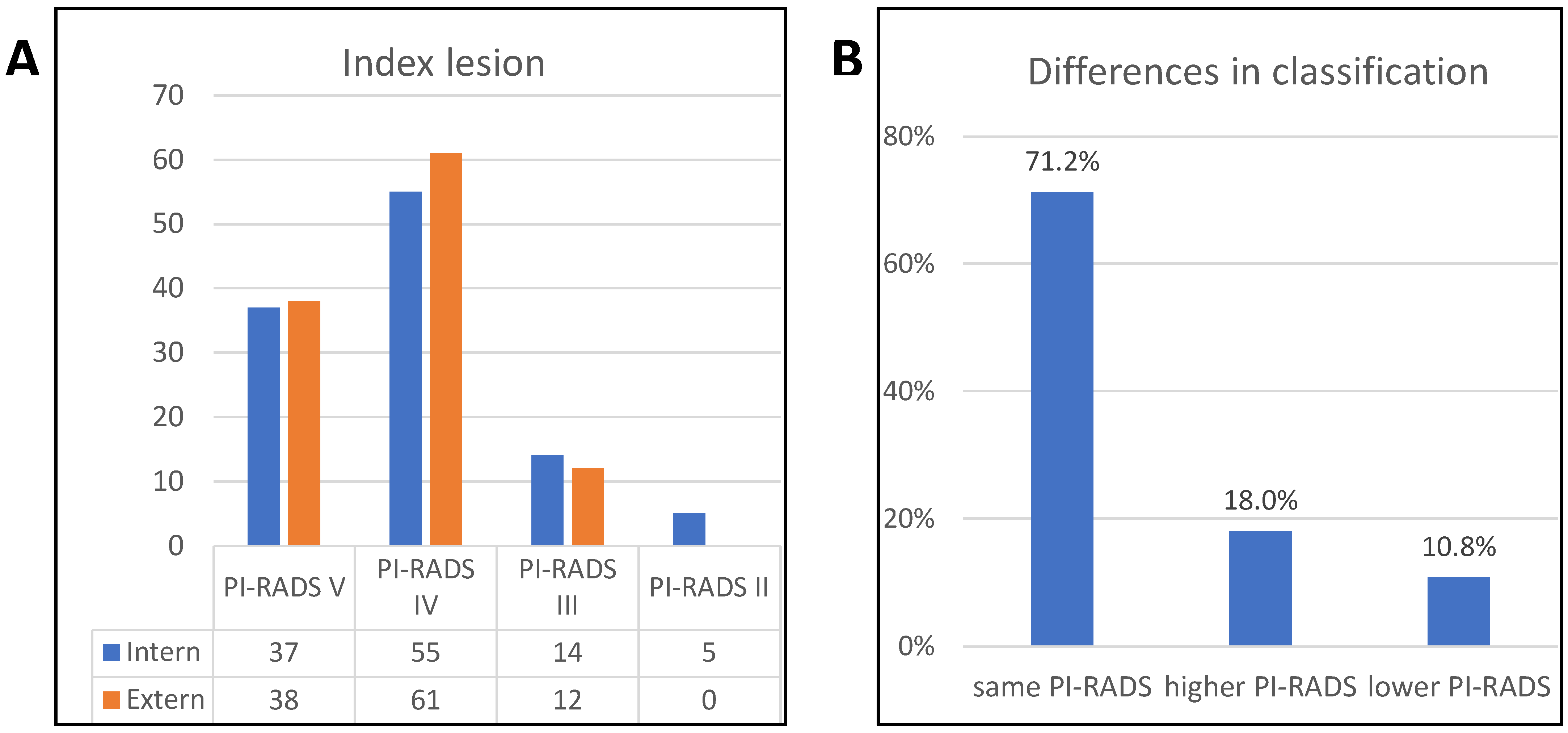
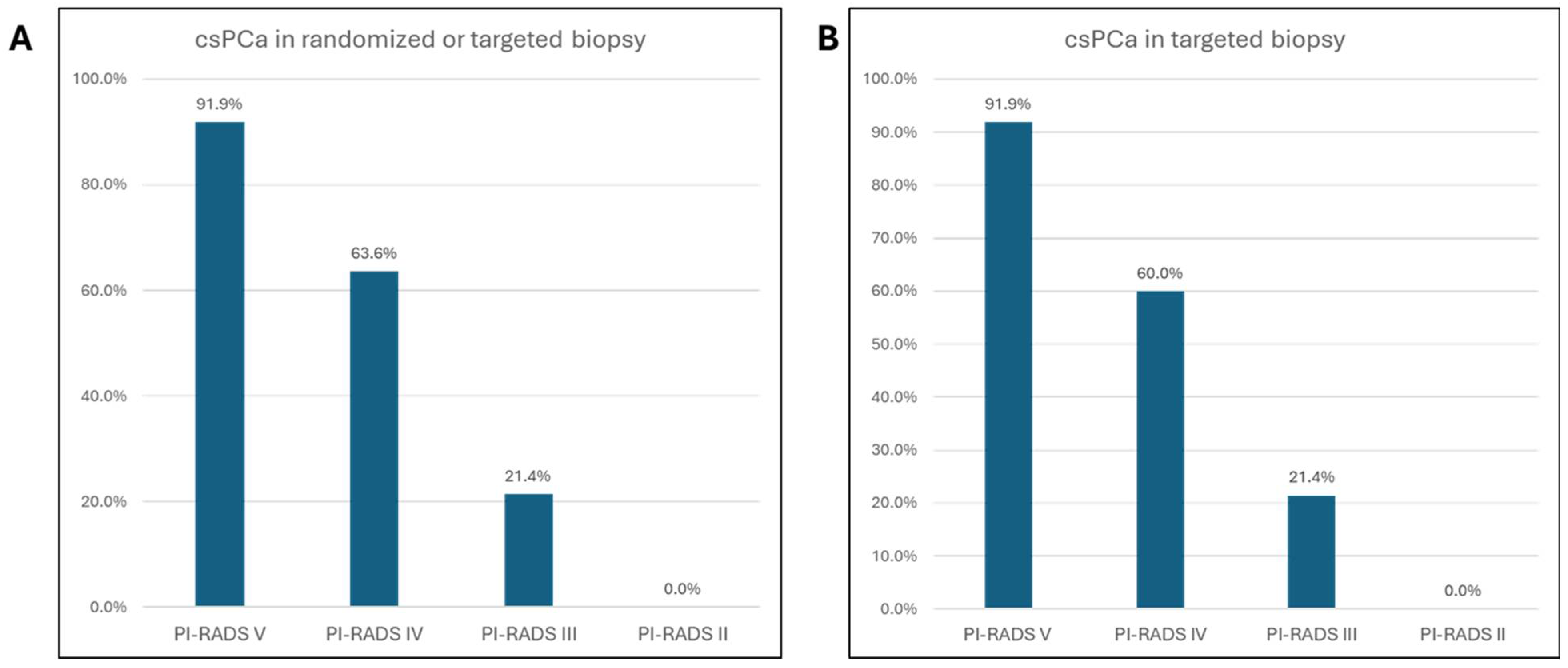
| Index lesion | ||
| PI-RADS V | 37 | 33.3 |
| PI-RADS IV | 55 | 49.5 |
| PI-RADS III | 14 | 12.6 |
| PI-RADS II | 5 | 4.5 |
| Location of index lesion | ||
| PZ | 75 | 68.8 |
| TZ | 33 | 30.3 |
| AFS | 1 | 0.9 |
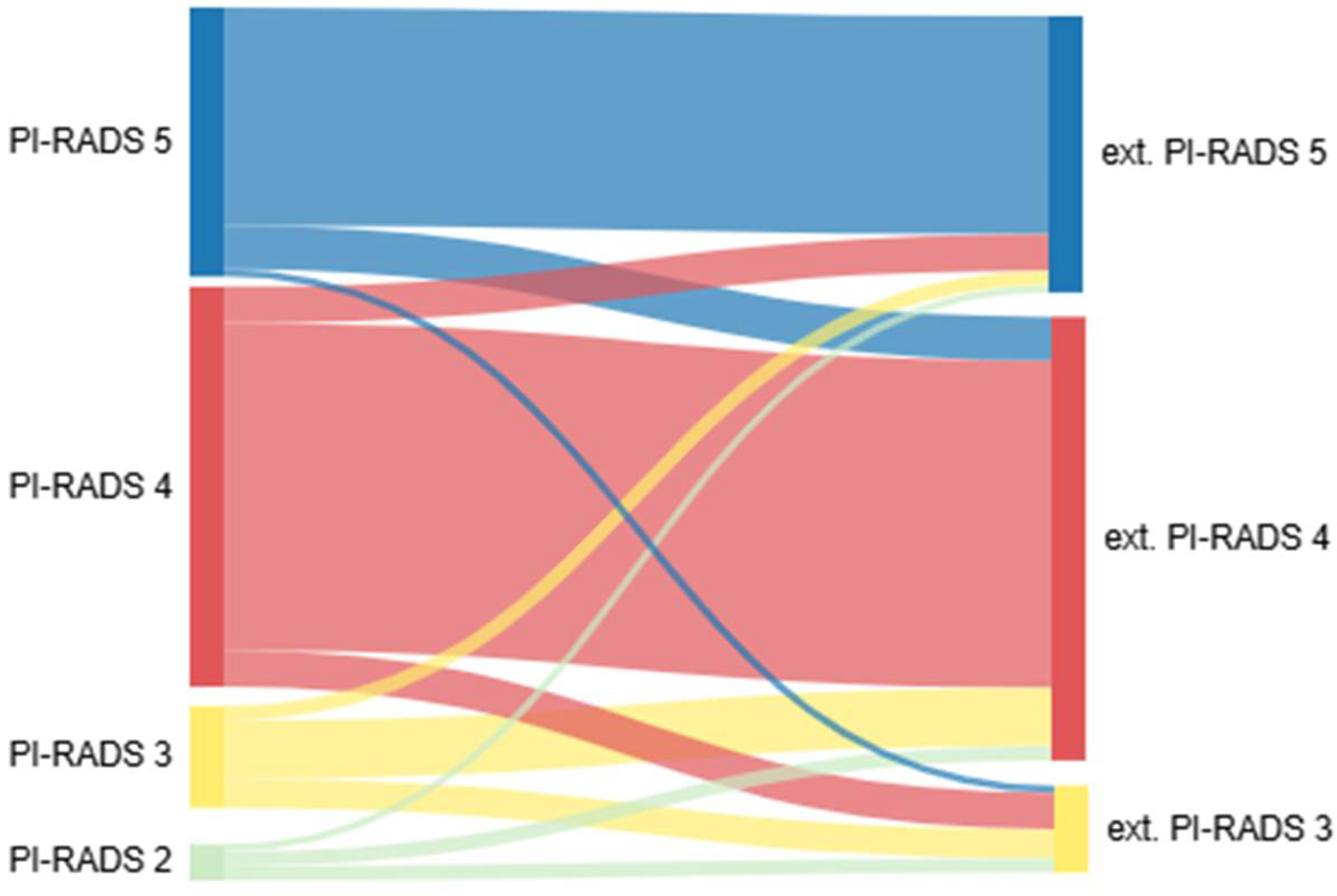
| External MRI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI-RADS II | PI-RADS III | PI-RADS IV | PI-RADS V | All | ||
| Internal MRI | PI-RADS II | 0 | 40% (2) | 40% (2) | 20% (1) | 5 |
| PI-RADS III | 0 | 28.6% (4) | 57.1% (8) | 14.3% (2) | 14 | |
| PI-RADS IV | 0 | 9.1% (5) | 81.8% (45) | 9.1% (5) | 55 | |
| PI-RADS V | 0 | 2.7% (1) | 16.2% (6) | 81.1% (30) | 37 | |
| All | 0 | 12 | 61 | 38 | ||
| Characteristics | n = 111 | % |
|---|---|---|
| No cancer/benign | 31 | 27.9 |
| HGPIN | 1 | 1.3 |
| Cancer detection rate | 77 | 69.4 |
| Grade group ≥ 2 (GS ≥ 3 + 4) | ||
| csPCA | 76 | 98.7 |
| insignPCA | 1 | 1.3 |
| Biopsy history | ||
| Biopsy naive | 89 | 80.2 |
| Previously biopsied | 22 | 19.8 |
| AS | 4 | 3.6 |
| Re-biopsy ASAP | 2 | 1.8 |
| Number of biopsies | 23 [21–25] | |
| Number of biopsies in the lesion | 7 [5.5–8.5] | |
| Number of randomized biopsies | 13 [11–15] | |
| PCA in lesion biopsies | 72 | 64.9 |
| PCA in randomized biopsies | 66 | 59.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schoch, J.; Düring, V.; Wiedmann, M.; Overhoff, D.; Dillinger, D.; Waldeck, S.; Schmelz, H.-U.; Nestler, T. Differences in PI-RADS Classification of Prostate Cancer Based on mpMRI Scans Taken 6 Weeks Apart. Tomography 2025, 11, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080092
Schoch J, Düring V, Wiedmann M, Overhoff D, Dillinger D, Waldeck S, Schmelz H-U, Nestler T. Differences in PI-RADS Classification of Prostate Cancer Based on mpMRI Scans Taken 6 Weeks Apart. Tomography. 2025; 11(8):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080092
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchoch, Justine, Viola Düring, Michael Wiedmann, Daniel Overhoff, Daniel Dillinger, Stephan Waldeck, Hans-Ulrich Schmelz, and Tim Nestler. 2025. "Differences in PI-RADS Classification of Prostate Cancer Based on mpMRI Scans Taken 6 Weeks Apart" Tomography 11, no. 8: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080092
APA StyleSchoch, J., Düring, V., Wiedmann, M., Overhoff, D., Dillinger, D., Waldeck, S., Schmelz, H.-U., & Nestler, T. (2025). Differences in PI-RADS Classification of Prostate Cancer Based on mpMRI Scans Taken 6 Weeks Apart. Tomography, 11(8), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11080092







