Dose-Dependent Analysis of Image Quality in Pediatric Head CT Scans Across Different Scanners to Optimize Clinical Protocols Using Phantom-Based Assessment
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Quantitative characterization of the dose–image-quality relationship across different CT systems using a Catphan phantom, and
- (2)
- Validation of these relationships using actual pediatric head CT data collected from eight hospitals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Study Population and Data Collection
2.3. CT Systems and Phantom Experiments
2.4. Image Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. CT Values
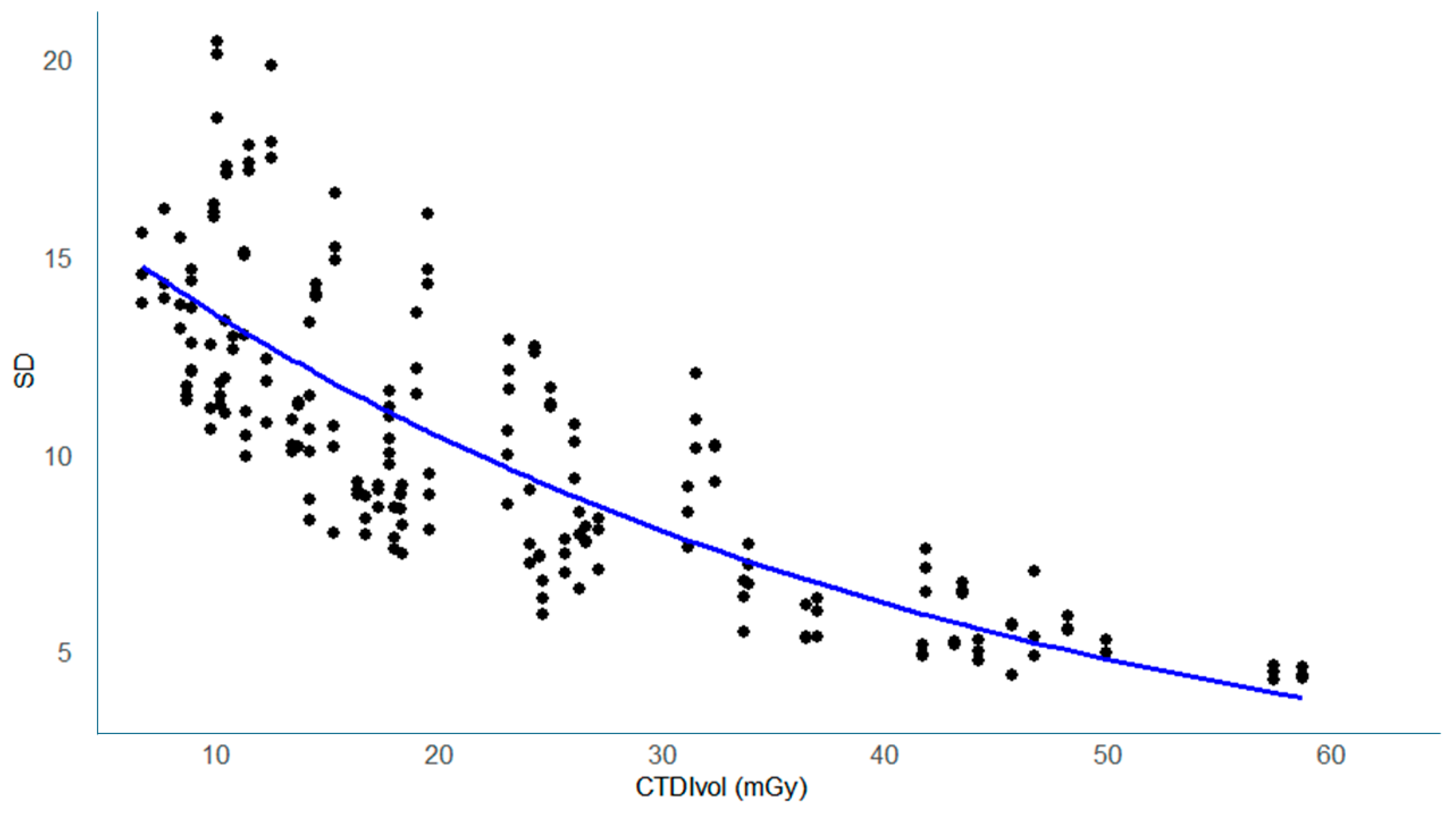
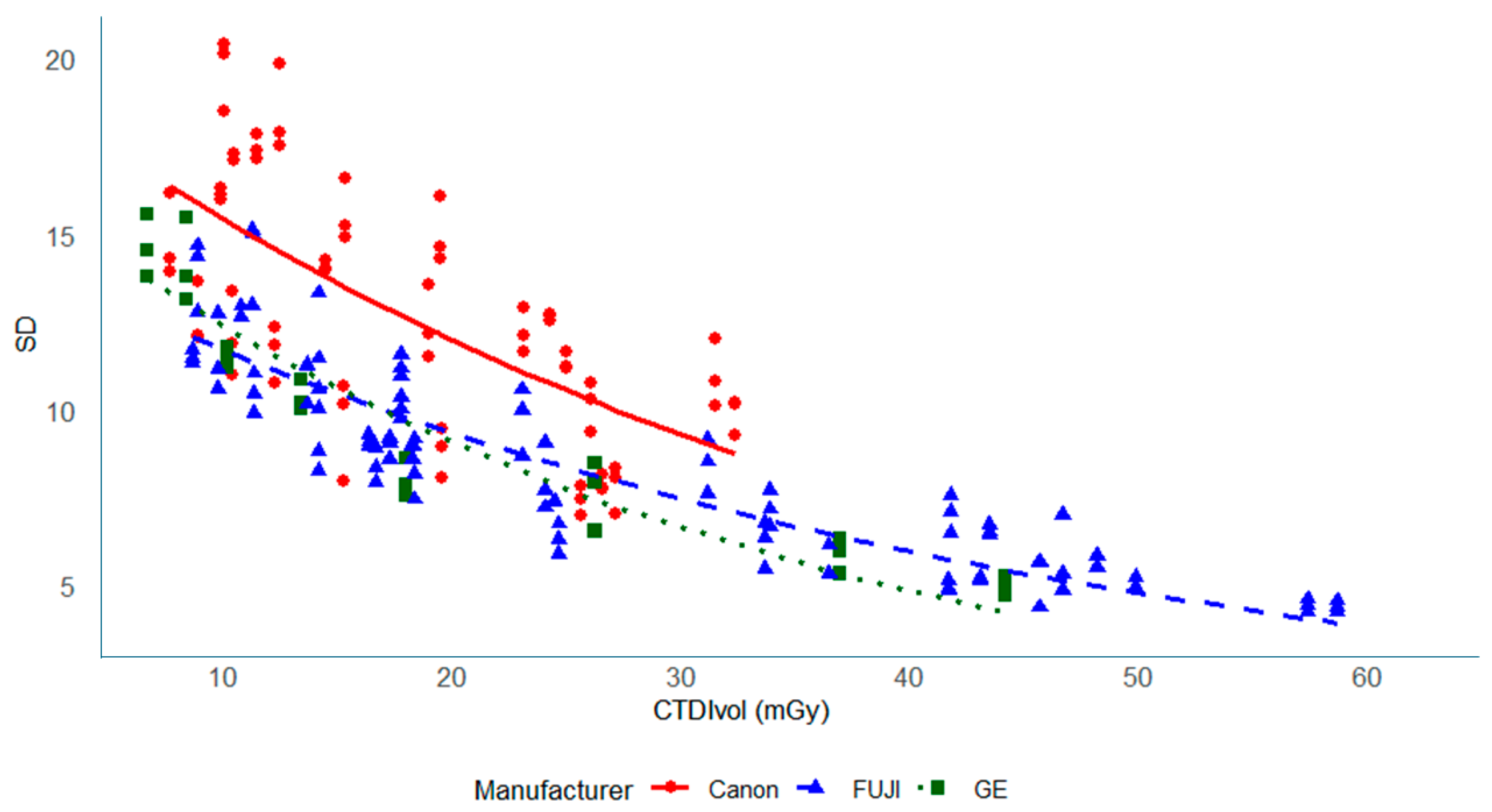
3.2. Noise (SD) Values
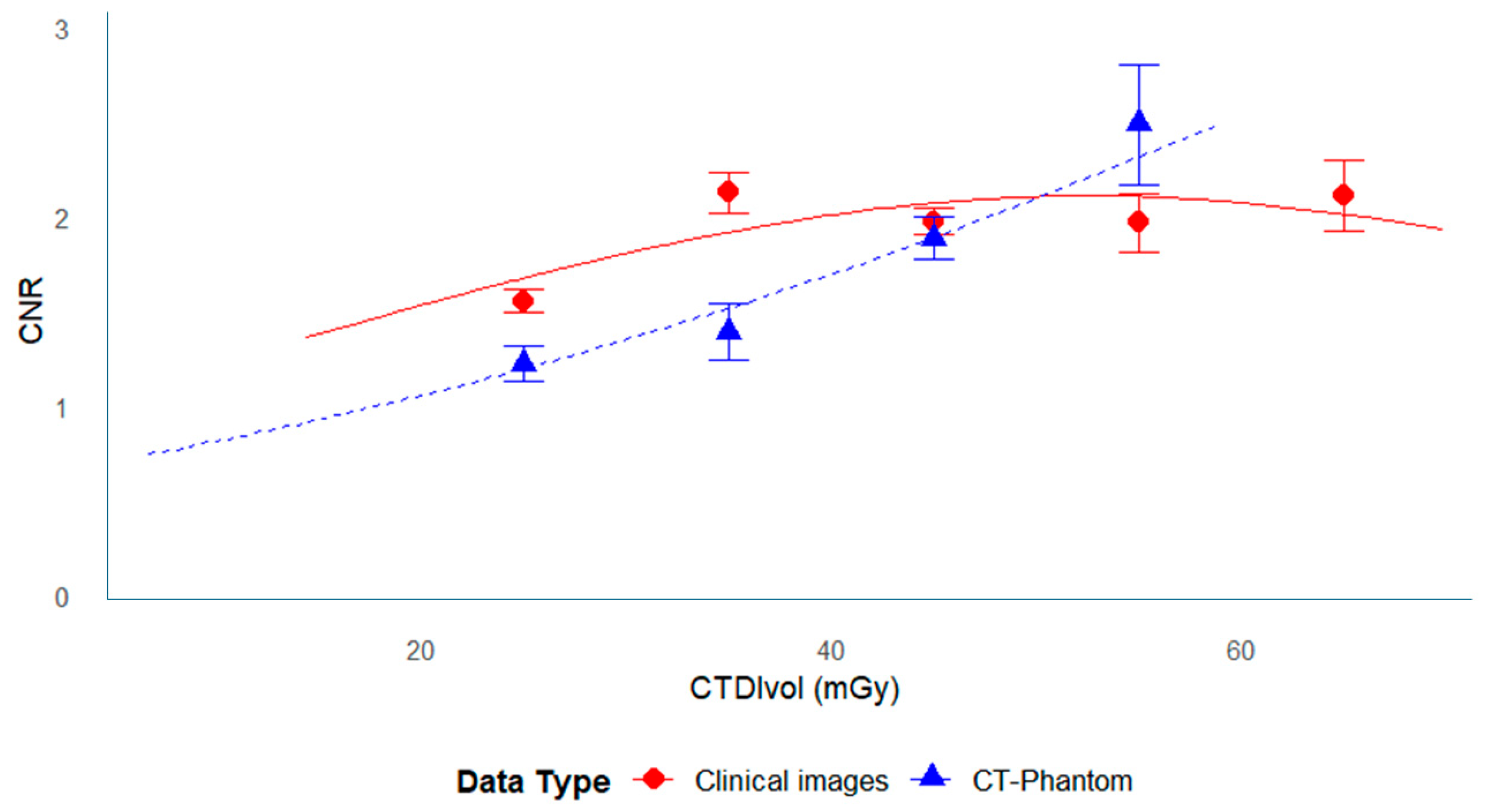
3.3. Relationship Between CNR and Dose
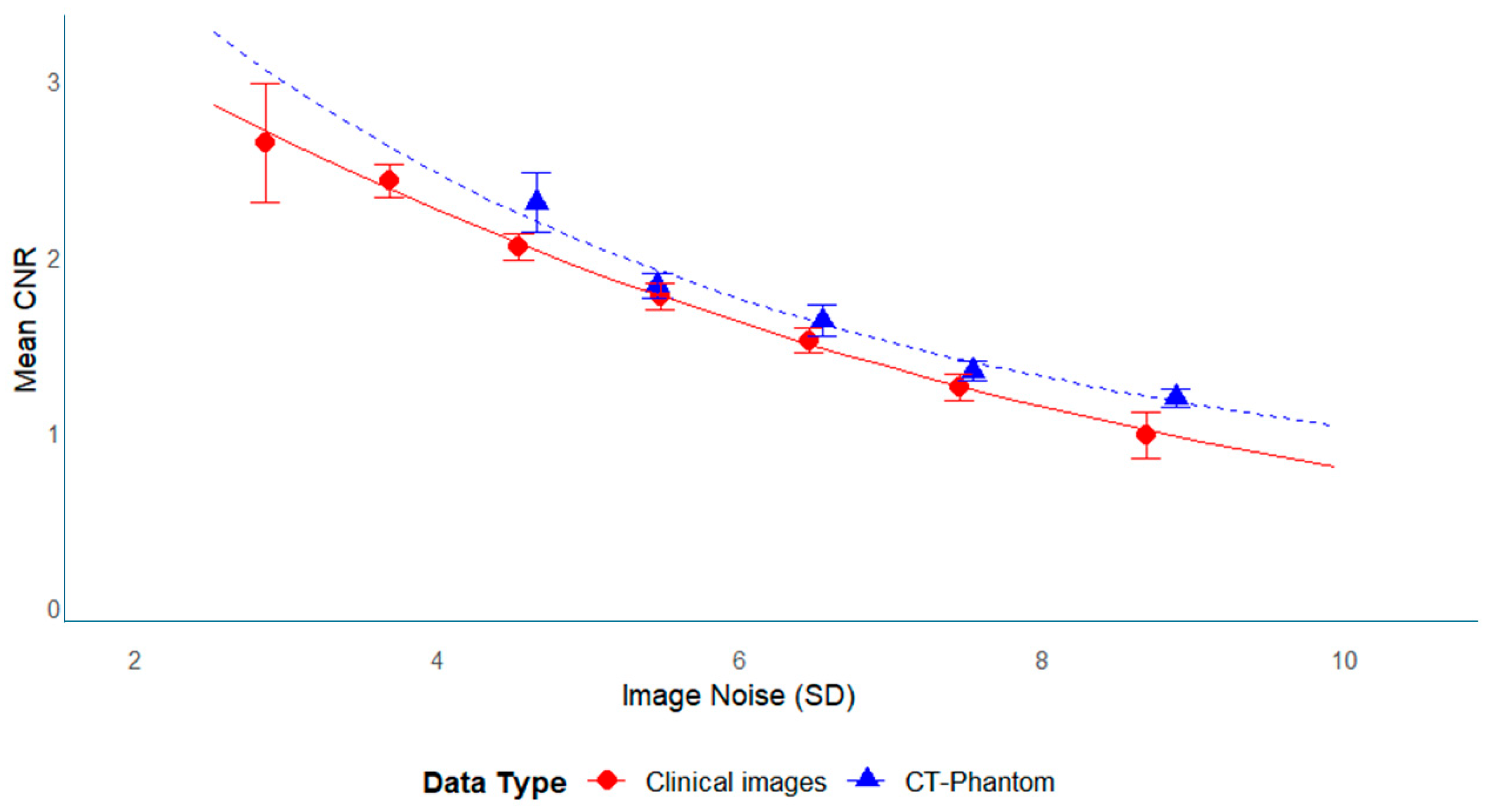
3.4. Relationship Between CNR and SD
3.5. FOM
3.5.1. Statistical Equivalence Assessment
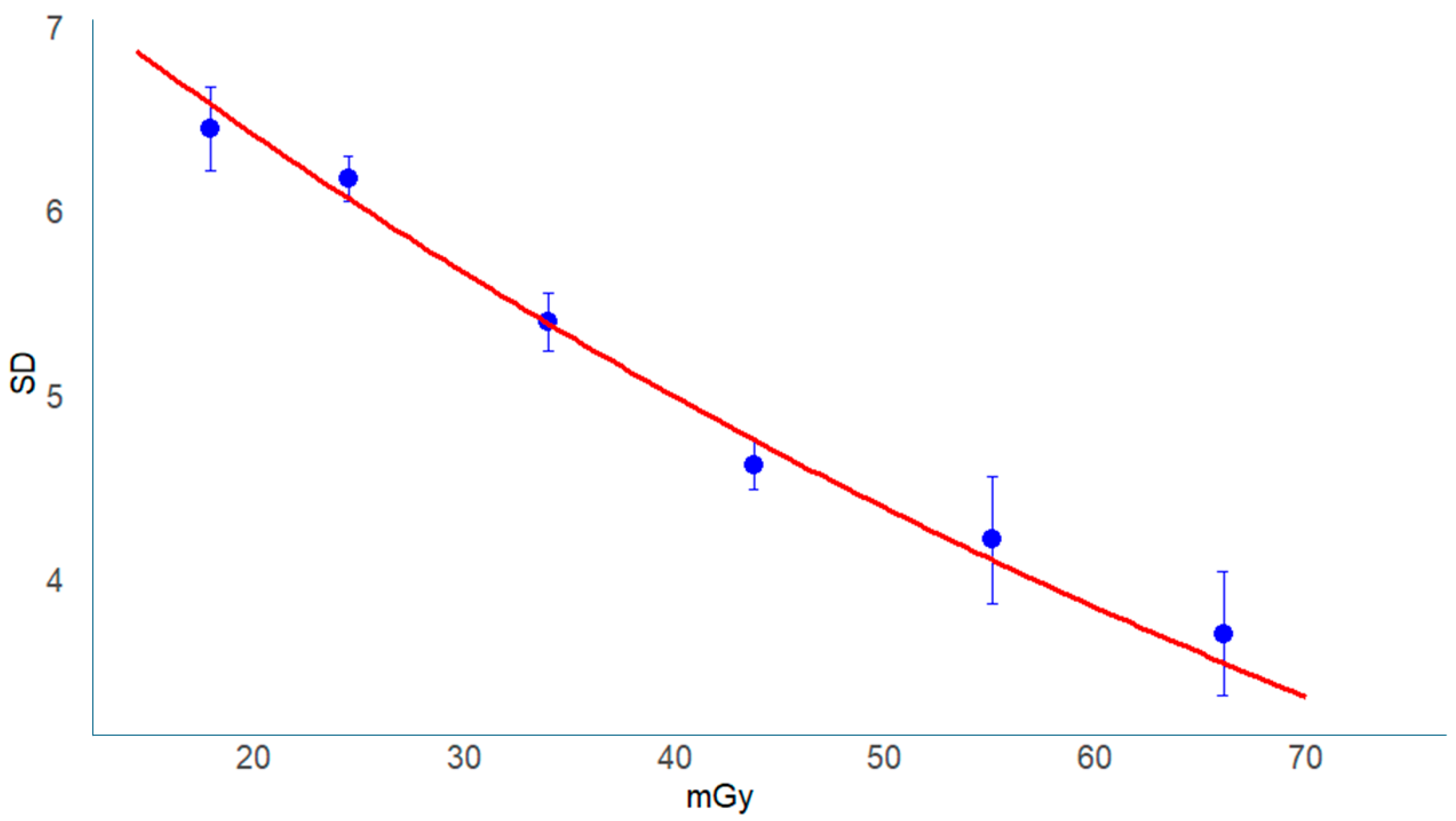
3.5.2. Modeling the Relationship Between FOM and CTDIvol
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| AEC | Automatic exposure control |
| CNR | Contrast-to-noise ratio |
| CTDIvol | Volume CT dose index |
| DLR | Deep learning reconstruction |
| DRL | Diagnostic reference level |
| FOM | Figure of merit |
| HU | Hounsfield unit |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
References
- Faul, M.; Wald, M.M.; Wu, L.; Coronado, V.G. Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths 2002–2006, 1st ed.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Li, R.; Schwebel, D.C.; Zhu, M.; Hu, G. Traumatic brain injury mortality among U.S. children and adolescents ages 0–19 years, 1999–2017. J. Safety Res. 2020, 72, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. Computed Tomography—An Increasing Source of Radiation Exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2277–2284. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra072149 (accessed on 29 May 2023). [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, M.; Byrnes, G.; Cardis, E.; Bernier, M.-O.; Blettner, M.; Dabin, J.; Engels, H.; Istad, T.S.; Johansen, C.; Kaijser, M.; et al. Brain cancer after radiation exposure from CT examinations of children and young adults: Results from the EPI-CT cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch de Basea, M.; Thierry-Chef, I.; Harbron, R.; Hauptmann, M.; Byrnes, G.; Bernier, M.O.; Le Cornet, L.; Dabin, J.; Ferro, G.; Istad, T.S.; et al. Risk of hematological malignancies from CT radiation exposure in children, adolescents and young adults. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 3111–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICRP Publication 154. Optimisation of Radiological Protection in Digital Radiology Techniques for Medical Imaging. Ann. ICRP 2024, 53, 1–106. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP Publication 102. Managing Patient Dose in Multi-Detector Computed Tomography (MDCT). Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- ICRP Publication 135. Diagnostic Reference Levels in Medical Imaging. Ann. ICRP 2017, 46, 1–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, T.; Miyazaki, O.; Kitamura, M.; Ono, K.; Kai, M. Quantitative Analysis of the Clinical Reasons Influencing the Frequency of Pediatric Head CT Examinations: A Single-Center Observation Study. Tomography 2023, 9, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicchi, F.; Faggioni, L.; Bastiani, L.; Molinaro, S.; Puglioli, M.; Caramella, D.; Bartolozzi, C. Optimizing the balance between radiation dose and image quality in pediatric head CT: Findings before and after intensive radiologic staff training. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowich, A.; Shendler, G.; Ben-Sira, L.; Shiran, S.I. Pediatric low-dose head CT: Image quality improvement using iterative model reconstruction. Neuroradiol. J. 2023, 36, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spampinato, M.V.; Stalcup, S.; Matheus, M.G.; Byington, K.; Tipnis, S. Radiation dose and image quality in pediatric head CT. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 182, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppermann, N.; Holmes, J.F.; Dayan, P.S.; Hoyle, J.D.; Atabaki, S.M.; Holubkov, R.; Nadel, F.M.; Monroe, D.; Stanley, R.M.; Borgialli, D.A.; et al. Identification of children at very low risk of clinically important brain injuries after head trauma: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2009, 374, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leva, E.; Do, M.-T.; Grieco, R.; Petrova, A. Computed tomography utilization in the management of children with mild head trauma. Children 2023, 10, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etani, R.; Yoshitake, T.; Kai, M. Estimating organ doses from pediatric cerebral computed tomography using the WAZA-ARI web-based calculator. J. Radiat. Prot. Res. 2021, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Radiation Exposure Research Information Network (J-RIME). Japan Diagnostic Reference Levels 2020. Available online: https://j-rime.qst.go.jp/report/JapanDRL2020_jp.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Santos, J.; Batista, M.d.C.; Foley, S.; Paulo, G.; McEntee, M.F.; Rainford, L. Paediatric CT optimisation utilising Catphan® 600 and age-specific anthropomorphic phantoms. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 162, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Phantom Laboratory. CTP500/515 Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.phantomlab.com/ (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Ichikawa, K. Image Quality and Radiation Dose Assessment of X-Ray CT, 2nd ed.; Ohmsha: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; pp. 102–125. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, K. CTmeasure. Available online: http://www.jsct-tech.org/ (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Zarb, F.; McEntee, M.F.; Rainford, L. A multi-phased study of optimisation methodologies and radiation dose savings for head CT examinations. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 163, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kalra, M.K.; Shenoy-Bhangle, A.S.; Saini, A.; Gervais, D.A.; Westra, S.J.; Thrall, J.H. Radiation dose reduction with hybrid iterative recon-struction for pediatric CT. Radiology 2012, 263, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M. Relationship between radiation dose and image quality in X-ray CT imaging. Med. Imaging Technol. 2017, 35, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyoshi, K.; Oomura, T.; Chino, S.; Goto, M.; Muramatsu, S.; Honma, K. X-ray energy in CT: From basics to clinical applications. Nippon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi 2022, 78, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugie, H. Age-related changes in CT values of cerebral white and gray matter in normal newborns and infants. Brain Dev. 1981, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T. The role of plain CT in pediatric head region: Clinical technique course. Jpn. J. Comput. Tomogr. Technol. 2019, 7, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Koide, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Okada, K.; Shimode, K.; Tsunematsu, T.; Komatsu, A. Age-related changes in cerebral white matter as seen from CT values. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi 1989, 26, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pula, M.; Kucharczyk, E.; Zdanowicz, A.; Guzinski, M. Image quality improvement in deep learning image reconstruction of head computed tomography examination. Tomography 2023, 9, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Cho, H.-H.; Lee, S.M.; You, S.K. Adaptation of deep learning image reconstruction for pediatric head CT: A focus on the image quality. J. Korean Soc. Radiol. 2023, 84, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, I.; Rundo, L.; Codari, M.; Di Leo, G.; Salvatore, C.; Interlenghi, M.; Gallivanone, F.; Cozzi, A.; D’Amico, N.C.; Sardanelli, F. AI applications to medical images: From machine learning to deep learning. Phys. Medica 2021, 83, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, E.; Borg, M. Optimisation of a paediatric CT brain protocol: A figure-of-merit approach. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 182, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, S.; Miura, N.; Sato, K. Possibility of low-dose imaging in head CT using model-based iterative reconstruction: Comparison with normal-dose imaging. J. Jpn. Soc. CT Technol. 2022, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miéville, F.A.; Gudinchet, F.; Brunelle, F.; Bochud, F.O.; Verdun, F.R. Iterative reconstruction methods in two different mdct scanners: Physical metrics and 4-alternative forced-choice detectability experiments–a phantom approach. Phys. Medica 2013, 29, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, Z.; Ramanauskas, F.; Cain, T.M.; Johnston, P.N. Assessment of paediatric CT dose indicators for the purpose of optimisation. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 85, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, C.; Alessio, A.M.; Otto, R.K.; Iyer, R.S.; Philips, G.S.; Swanson, J.O.; Thapa, M.M. Pediatric CT: Strategies to lower radiation dose. Am. J. Roentgenol. (AJR) 2013, 200, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, A.; Aramvith, S. Transformers in medical imaging: A review of current trends, challenges, and future directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 35471–35495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, A.; Aramvith, S. AI-driven quantitative imaging and clinical translation: Current landscape and emerging applications. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2024, 45, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

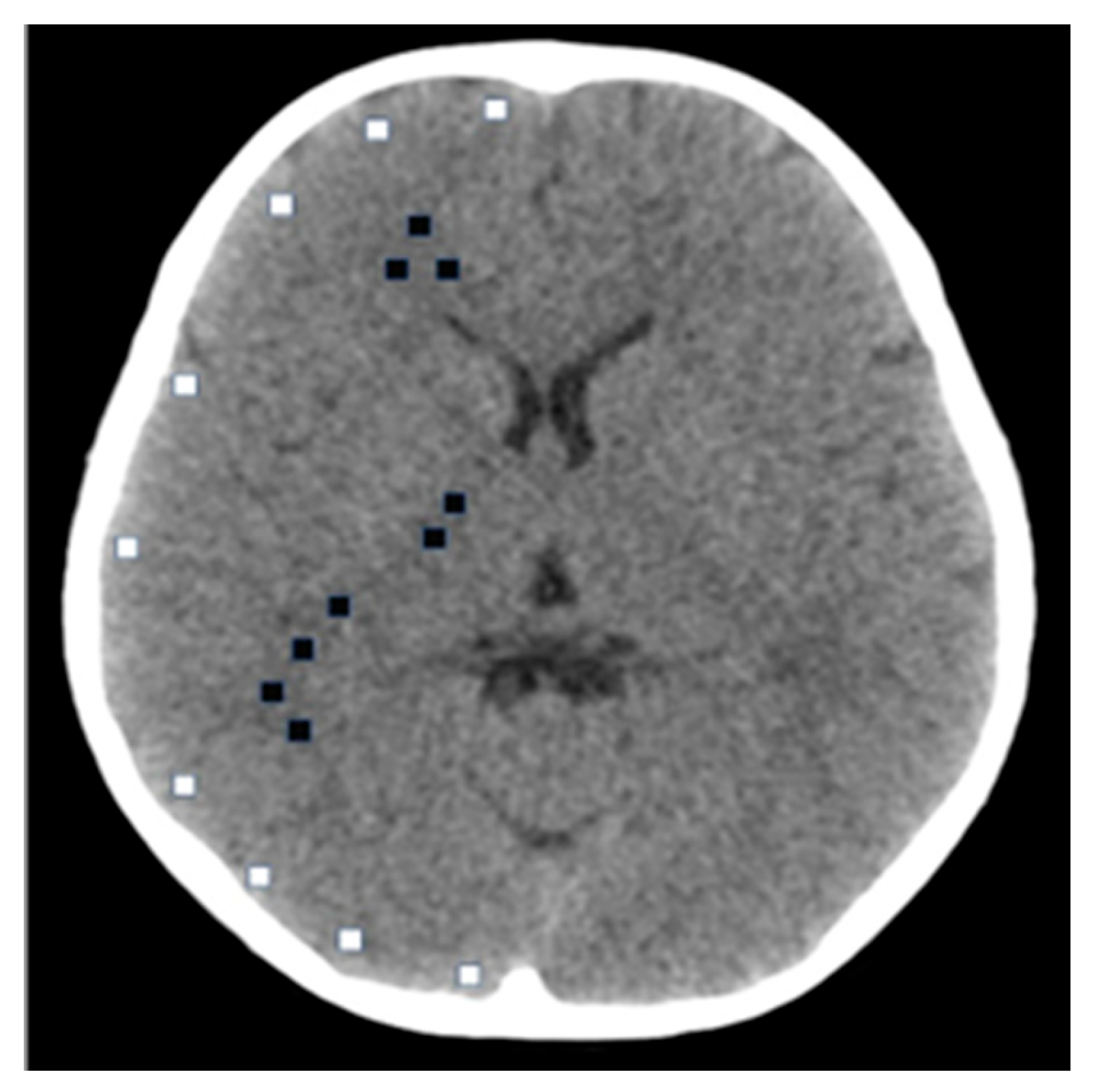

| Hospital Name | Manufacturer | Model Type | Detector Row Count | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Canon (Toshiba) (a) | Aquilion PRIME | 80 | 19 |
| B | Canon (Toshiba) | Aquilion Prime SP | 80 | 15 |
| C | Canon (Toshiba) | Aquilion Prime SP | 80 | 9 |
| D | FUJI (HITACHI) (b) | Supria Grande | 64 | 7 |
| E | FUJI (HITACHI) | SCENARIA | 64 | 16 |
| F | FUJI (HITACHI) | Supria Optica | 64 | 6 |
| G | FUJI (HITACHI) | Supria | 16 | 5 |
| H | GE | Revolution EVO | 256 | 13 |
| (a) | ||||||
| Manufacturer | Hospital Name | Tube Voltage (kV) | Upper Tube Current (mA) | Shooting Time (s) | Slice Thickness (mm) | Helical Pitch |
| Canon | A | 120 | 250 | 0.5 | 5 | 0.637 |
| Canon | B | 120 | 350 | 0.5 | 5 | 0.637 |
| Canon | C | 120 | 270 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.637 |
| FUJI | D | 120 | 250 | 0.75 | 5 | 0.5781 |
| FUJI | E | 120 | 360 | 1 | 5 | 0.813 |
| FUJI | F | 120 | 200 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.5938 |
| FUJI | G | 120 | 180 | 1 | 5 | 0.8125 |
| GE | H | 120 | 520 | 0.5 | 5 | 0.984 |
| (b) | ||||||
| Manufacturer | Hospital Name | Set SD | Helical Pitch | Image Reconstruction | Dose-Reduction Strategy | |
| Canon | A | 2.5 | 0.637 | None | Yes (reduced mA limit) | |
| Canon | B | 3 | 0.637 | None | No | |
| Canon | C | 2.5 | 0.637 | None | No | |
| FUJI | D | 4 | 0.5781 | Smooth (level 3) | Yes (reduced SD target) | |
| FUJI | E | 3.8 | 0.813 | Smooth (level 2) | No | |
| FUJI | F | 3.8 | 0.5938 | None | No | |
| FUJI | G | 4 | 0.8125 | None | No | |
| GE | H | 2.8 | 0.984 | None | No | |
| (a) | |||
| Manufacturer | Hospital | CTDIvol (mGy) Mean (95% CI) | CT Value (HU) Mean (95% CI) |
| Canon | A | 17.08(11.43–22.73) | 60.8(60.02–61.59) |
| B | 18.61(12.47–24.75) | 61.54(60.98–62.10) | |
| C | 19.5(13.91–25.09) | 62.89(61.93–63.85) | |
| FUJI | D | 31.42(21.14–41.71) | 60.63(59.92–61.55) |
| E | 28.28(15.05–41.5) | 58.26(57.34–59.19) | |
| F | 25.51(14.06–36.97) | 59.35(57.77–60.94) | |
| G | 26.13(16.41–35.85) | 60.89(58.81–62.97) | |
| GE | H | 19.71(8.6–30.83) | 59.75(58.31–61.19) |
| (b) | |||
| Manufacturer | Hospital | CTDIvol (mGy) Mean (95% CI) | CT Value (HU) Mean (95% CI) |
| Canon | A | 23.11 (21.68–24.54) | 33.32 (32.61–34.04) |
| B | 37.78 (24.43–51.12) | 35.12 (33.88–36.36) | |
| C | 30.98 (25.54–36.41) | 44.07 (40.59–47.55) | |
| FUJI | D | 26.86 (20.75–32.96) | 39.55 (37.86–41.24) |
| E | 42.44 (38.71–46.18) | 37.53 (36.59–38.47) | |
| F | 30.78 (27.42–34.15) | 39.63 (39.05–40.21) | |
| G | 35.46 (19.72–51.2) | 36.6 (35.43–37.76) | |
| GE | H | 42.18 (39.97–44.39) | 32.95 (31.86–34.03) |
| CNR | ||
|---|---|---|
| SD Value | Clinical Data | Phantom Data |
| 1 | 3.612 | 4.512 |
| 2 | 3.106 | 3.648 |
| 3 | 2.658 | 2.985 |
| 4 | 2.266 | 2.473 |
| 5 | 1.923 | 2.074 |
| 6 | 1.625 | 1.76 |
| 7 | 1.367 | 1.513 |
| 8 | 1.145 | 1.316 |
| 9 | 0.955 | 1.158 |
| 10 | 0.793 | 1.033 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuwahara, H.; Ojima, M.; Kawamura, T.; Saitou, D.; Andou, K.; Ariga, E.; Hasegawa, K.; Kai, M. Dose-Dependent Analysis of Image Quality in Pediatric Head CT Scans Across Different Scanners to Optimize Clinical Protocols Using Phantom-Based Assessment. Tomography 2025, 11, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110119
Kuwahara H, Ojima M, Kawamura T, Saitou D, Andou K, Ariga E, Hasegawa K, Kai M. Dose-Dependent Analysis of Image Quality in Pediatric Head CT Scans Across Different Scanners to Optimize Clinical Protocols Using Phantom-Based Assessment. Tomography. 2025; 11(11):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110119
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuwahara, Hiroshi, Mitsuaki Ojima, Tsuneko Kawamura, Daisuke Saitou, Kazunari Andou, Eiji Ariga, Kotaro Hasegawa, and Michiaki Kai. 2025. "Dose-Dependent Analysis of Image Quality in Pediatric Head CT Scans Across Different Scanners to Optimize Clinical Protocols Using Phantom-Based Assessment" Tomography 11, no. 11: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110119
APA StyleKuwahara, H., Ojima, M., Kawamura, T., Saitou, D., Andou, K., Ariga, E., Hasegawa, K., & Kai, M. (2025). Dose-Dependent Analysis of Image Quality in Pediatric Head CT Scans Across Different Scanners to Optimize Clinical Protocols Using Phantom-Based Assessment. Tomography, 11(11), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110119





