Reducing Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography Imaging of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Spectral Shaping Technique with Tin Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Study Design
2.2. CT Examination
2.3. Image Reconstruction
2.4. Radiation Dose Assessment
2.5. Image Quality Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Radiation Dose
3.3. Image Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitation
4.2. Strengths and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CTDIvol | Volume computed tomography dose index |
| DLP | Dose length product |
| HU | Hounsfield unit |
| ICRP | International Commission on Radiological Protection |
| LDCT | Low-dose computed tomography |
| NDCT | Normal dose computed tomography |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
References
- Ito, M.; Chida, K.; Onodera, S.; Kojima, I.; Iikubo, M.; Kato, T.; Fujisawa, M.; Zuguchi, M. Evaluation of radiation dose and image quality for dental cone-beam computed tomography in pediatric patients. J. Radiol. Prot. 2023, 43, 031518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Haba, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, S.; Asada, Y.; Chida, K. Fetal radiation dose of four tube voltages in abdominal CT examinations during pregnancy: A phantom study. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K. Assessment of Radiation Dose in Medical Imaging and Interventional Radiology Procedures for Patient and Staff Safety. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chida, K. What are useful methods to reduce occupational radiation exposure among radiological medical workers, especially for interventional radiology personnel? Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2022, 15, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, I.I.; Khouqeer, G.A.; Ahmed, N.A.; Abuzaid, M.M.; Sulieman, A. Low-Dose Chest CT Protocols for Imaging COVID-19 Pneumonia: Technique Parameters and Radiation Dose. Life 2023, 13, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendlin, A.S.; Winkelmann, M.T.; Do, P.L.; Schwarze, V.; Peisen, F.; Almansour, H.; Bongers, M.N.; Artzner, C.P.; Weiss, J.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Simulated Radiation Dose Reduction in Whole-Body CT on a 3rd Generation Dual-Source Scanner: An Intraindividual Comparison. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C. Evaluation of Impact of Factors Affecting CT Radiation Dose for Optimizing Patient Dose Levels. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Y.; Hitachi, S.; Watanuki, M.; Chida, K. Radiation eye dose for physicians in CT fluoroscopy-guided biopsy. Tomography 2022, 8, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabiniewicz-Ziajka, D.; Szarmach, A.; Grzywińska, M.; Gać, P.; Piskunowicz, M. Redefining Radiation Metrics: Evaluating Actual Doses in Computed Tomography Scans. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.H.; Cho, S.B.; Kwon, H. Evaluating Image Quality and Radiation Dose in Low-Dose Thoraco-Abdominal CT Angiography with a Tin Filter for Patients with Aortic Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A.; Cheng, J.C.; Danielsson, A.; Morcuende, J.A. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.; Castelein, R.M.; Chu, W.C.; Danielsson, A.J.; Dobbs, M.B.; Grivas, T.B.; Gurnett, C.A.; Luk, K.D.; Moreau, A.; Newton, P.O.; et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf, F.; Gibson, A.; Dannawi, Z.; Noordeen, H. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. BMJ 2013, 346, f2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simony, A.; Hansen, E.J.; Christensen, S.B.; Carreon, L.Y.; Andersen, M.O. Incidence of cancer in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients treated 25 years previously. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3366–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, R.; Watanabe, H.; Taki, N.; Onuma, S.; Kikkawa, I.; Takeshita, K. Radiation exposure in pediatric patients with early onset scoliosis: A longitudinal single-center study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2024, 29, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Lipson, J.; Marcus, R.; Kim, K.P.; Mahesh, M.; Gould, R.; de Gonzalez, A.B.; Miglioretti, D.L. Radiation dose associated with common computed tomography examinations and the associated lifetime attributable risk of cancer. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haque, M.; Shufflebarger, H.L.; O’Brien, M.; Macagno, A. Radiation exposure during pedicle screw placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Is fluoroscopy safe? Spine 2006, 31, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzcińska, S.; Kuszewski, M.; Koszela, K. Analysis of Posture Parameters in Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis with the Use of 3D Ultrasound Diagnostics-Preliminary Results. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.K.; Young, J.H.; Lai, J.C.; Lai, K.K.; Yang, K.G.; Hung, A.L.; Chu, W.C.; Lau, A.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Cheng, J.C.; et al. Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound imaging for quantitative assessment of frontal cobb angles in patients with idiopathic scoliosis—A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2025, 26, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cool, J.; Streekstra, G.J.; Van Schuppen, J.; Stadhouder, A.; Van den Noort, J.C.; Van Royen, B.J. Estimated cumulative radiation exposure in patients treated for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RadiologyInfo.org. Patient Safety: Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams. Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) and American College of Radiology (ACR). 2025. Available online: https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/safety-xray (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP Publication 103; ICRP: Stockholm, Sweden, 2007; Volume 37, pp. 1–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ronckers, C.M.; Land, C.E.; Miller, J.S.; Stovall, M.; Lonstein, J.E.; Doody, M.M. Cancer mortality among women frequently exposed to radiographic examinations for spinal disorders. Radiat. Res. 2010, 174, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, J.F.; Boice, J.D.; Svendsen, A.L.; Frederiksen, K.; Stovall, M.; Olsen, J.H. Spontaneous abortion in a Danish population-based cohort of childhood cancer survivors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4340–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, C.; Quante, M.; Thomsen, B.; Koeszegvary, M.; Platz, U.; Ivanits, D.; Halm, H. Intraoperative radiation exposure to patients in idiopathic scoliosis surgery with freehand insertion technique of pedicle screws and comparison to navigation techniques. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettler, F.A.; Huda, W.; Yoshizumi, T.T.; Mahesh, M. Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: A catalog. Radiology 2008, 248, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, M.K.; Maher, M.M.; Toth, T.L.; Schmidt, B.; Westerman, B.L.; Morgan, H.T.; Saini, S. Techniques and applications of automatic tube current modulation for CT. Radiology 2004, 233, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, D.; Schmidt, S.; Denys, A.; Schnyder, P.; Bochud, F.O.; Verdun, F.R. Performance evaluation of CT-automatic exposure control devices. In Proceedings of the SPIE 6515, Medical Imaging 2007: Image Perception, Observer Performance, and Technology Assessment, San Diego, CA, USA, 8 March 2007; p. 65151P. [Google Scholar]
- Padole, A.; Ali Khawaja, R.D.; Kalra, M.K.; Singh, S. CT radiation dose and iterative reconstruction techniques. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W384–W392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Kalra, M.K.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Hsieh, J.; Pien, H.; Singh, S.; Gilman, M.D.; Shepard, J.-A.O. Radiation dose reduction with chest computed tomography using adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction technique: Initial experience. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2010, 34, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Bruesewitz, M.R.; James, M.; Kofler, J. CT Dose reduction and dose management tools: Overview of available options. Radiographics 2006, 26, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmendinger, T.; Hamann, A. Calcium Scoring Using tin Filter Spectral Shaping—A Demonstration of Agatston Equivalence; White Paper; Siemens Healthcare GmbH: Forchheim, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lell, M.M.; May, M.S.; Brand, M.; Eller, A.; Buder, T.; Hofmann, E.; Uder, M.; Wuest, W. Imaging the parasinus region with a third-generation dual-source CT and the effect of tin filtration on image quality and radiation dose. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubenreisser, H.; Meyer, M.; Sudarski, S.; Allmendinger, T.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Henzler, T. Unenhanced third-generation dual-source chest CT using a tin filter for spectral shaping at 100 kVp. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffilli, A.; Fiore, M.; Martikos, K.; Barile, F.; Pasini, S.; Battaglia, M.; Greggi, T.; Faldini, C. Does use of pre-operative low-dose CT-scan in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis improve accuracy in screw placement? results of a retrospective study. Spine Deform. 2021, 9, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.H.; Yu, L.; Schueler, B.A.; Nassr, A.; Guerin, J.; Milbrandt, T.A.; Larson, A.N. Radiation exposure in navigated techniques for AIS: Is there a difference between pre-operative CT and intraoperative CT? Spine Deform. 2024, 12, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.R.; Katharine, L.G.; Rainer, R. Advanced Modeled Iterative Reconstruction; White Paper; Siemens Healthcare GmbH: Forchheim, Germany, 2024; Available online: https://marketing.webassets.siemens-healthineers.com/1800000005678345/c8da9b7f6aab/Siemens-Healthineers_DI-CT_ADMIRE-Whitepaper.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Haji-Momenian, S.; Ellenbogen, A.; Khati, N.; Taffel, M.; Earls, J.; Miller, G.; Zeman, R.K. Comparing dose-length product-based and monte carlo simulation organ-based calculations of effective dose in 16- and 64-MDCT examinations using automatic tube current modulation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Klein, S.A.; Brix, G.; Fink, C.; Pilz, L.; Jafarov, H.; Hofmann, W.K.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Henzler, T. Whole-body CT for lymphoma staging: Feasibility of halving radiation dose and risk by iterative image reconstruction. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation: UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography; ICRP Publication 87; ICRP: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000; Volume 30, pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, M.S.; Salotti, J.A.; Little, M.P.; McHugh, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.P.; Howe, N.L.; Ronckers, C.M.; Rajaraman, P.; Craft, A.W.; et al. Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Communicating Radiation Risks in Paediatric Imaging: Information to Support Health Care Discussions About Benefit and Risk; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-92-4-151034-9. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/978924151034 (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Mathews, J.D.; Forsythe, A.V.; Brady, Z.; Butler, M.W.; Goergen, S.K.; Byrnes, G.B.; Giles, G.G.; Wallace, A.B.; Anderson, P.R.; Guiver, T.A.; et al. Cancer risk in 680 000 people exposed to computed tomography scans in childhood or adolescence: Data linkage study of 11 million Australians. BMJ 2013, 346, f2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglioretti, D.L.; Johnson, E.; Williams, A.; Greenlee, R.T.; Weinmann, S.; Solberg, L.I.; Feigelson, H.S.; Roblin, D.; Flynn, M.J.; Vanneman, N.; et al. The use of computed tomography in pediatrics and the associated radiation exposure and estimated cancer risk. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boice, J.D., Jr. Radiation epidemiology and recent paediatric computed tomography studies. Ann. ICRP 2015, 44, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, M.; Chida, K. Reducing the breast cancer risk and radiation dose of radiography for scoliosis in children: A phantom study. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chida, K.; Ohno, T.; Kakizaki, S.; Takegawa, M.; Yuuki, H.; Nakada, M.; Takahashi, S.; Zuguchi, M. Radiation dose to the pediatric cardiac catheterization and intervention patient. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chida, K.; Kato, M.; Kagaya, Y.; Zuguchi, M.; Saito, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Takahashi, S.; Yamada, S.; Takai, Y. Radiation Dose and Radiation Protection for Patients and Physicians During Interventional Procedure. J. Radiat. Res. 2010, 51, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. Computed tomography—An increasing source of radiation exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.; Elliston, C.; Hall, E.; Berdon, W. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Itoh, H.; Nagahara, K.; Hata, H.; Mitsui, K. Relationships of radiation dose indices with body size indices in adult body computed tomography. Tomography 2023, 9, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.-C.; Lim, C.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Jung, H.-R. A study on the correlation between patients’ physical characteristics and effective dose of liver computed tomography. Technol. Health Care 2014, 22, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, W.; Scalzetti, E.M.; Levin, G. Technique factors and image quality as functions of patient weight at abdominal CT. Radiology 2000, 217, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Duan, X.; Christner, J.A.; Leng, S.; Yu, L.; McCollough, C.H. Radiation dose reduction to the breast in thoracic CT: Comparison of bismuth shielding, organ-based tube current modulation, and use of a globally decreased tube current. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 6084–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipsic, J.; LaBounty, T.M.; Heilbron, B.; Min, J.K.; Mancini, G.B.J.; Lin, F.Y.; Taylor, C.; Dunning, A.; Earls, J.P. Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: Assessment of image noise and image quality in coronary CT angiography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Lawder, H.J.; Hara, A.; Kujak, J.; Pavlicek, W. Innovations in CT dose reduction strategy: Application of the adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction algorithm. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primak, A.N.; Ramirez Giraldo, J.C.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; McCollough, C.H. Improved dual-energy material discrimination for dual-source CT by means of additional spectral filtration. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Tanifuji, K.; Chida, K. Depth dose distribution measurements by X-ray CT: Comparison with and without tin Filter. JPN J. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 64, 1085–1092. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Noto, Y.; Endo, Y.; Ohashi, M.; Hirano, T.; Chida, K.; Watanabe, K. Usefulness of the spectral shaping dual-source computed tomography imaging technique in posterior corrective fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Task Group on Control of Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography. Managing Patient Dose in Computed Tomography. Ann. ICRP 2000, 30, 7–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, J.; International Commission on Radiation Protection. Managing Patient Dose in Multi-Detector Computed Tomography (MDCT). ICRP Publication 102. Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Optimization of the Radiological Protection of Patients Undergoing Radiography, Fluoroscopy and Computed Tomography. IAEA-TECDOC-1423. 2004. Available online: https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/te_1423_web.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Iriuchijima, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Ogura, A. Comparison of organ dose calculation using Monte Carlo simulation and in-phantom dosimetry in CT examination. JPN J. Radiol. Technol. 2018, 74, 166–171. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
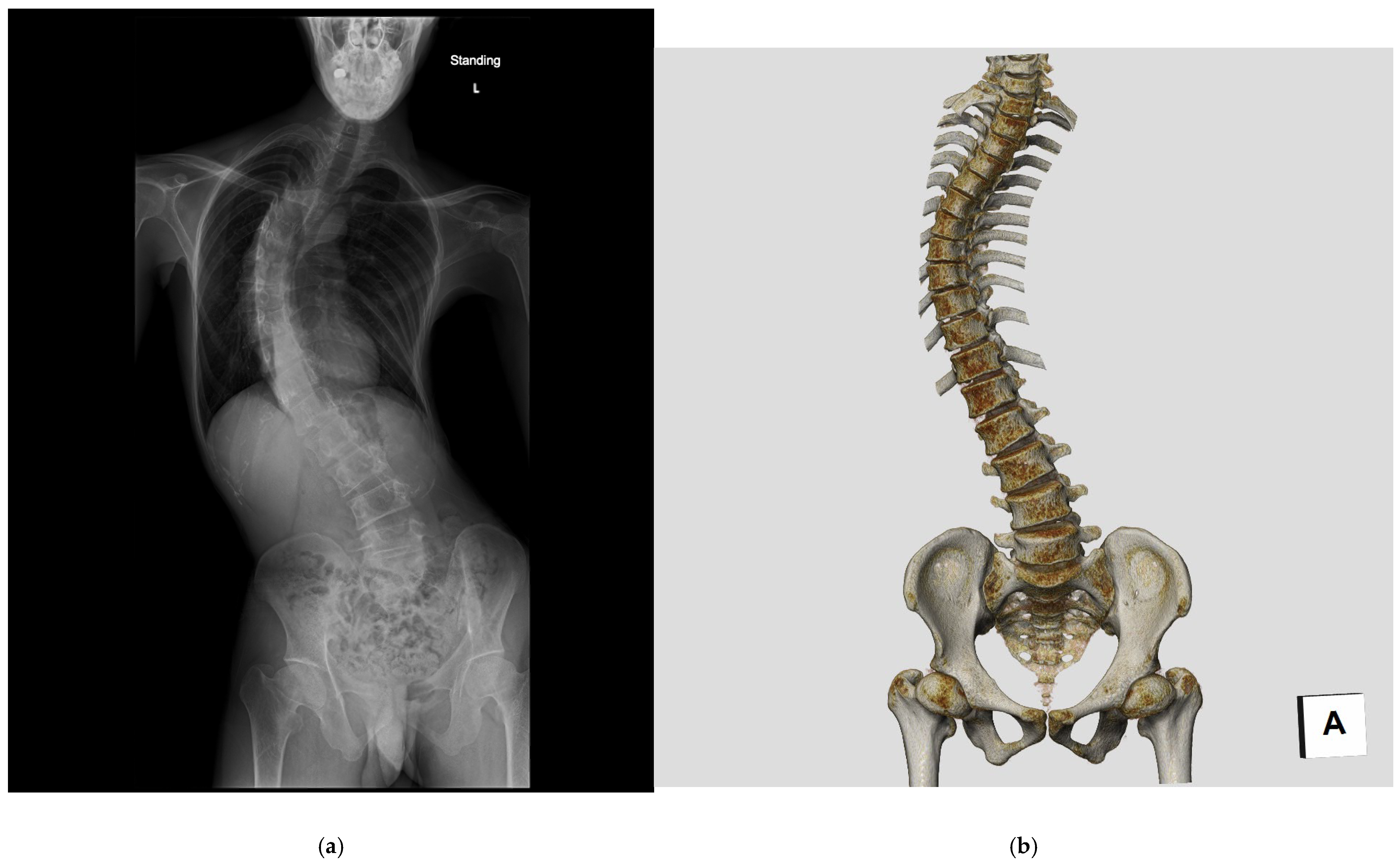



| LDCT * (n = 23) | NDCT * (n = 28) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 15.3 ± 2.1 | 15.5 ± 1.7 | 0.923 |
| Body length (cm) | 157.0 ± 5.8 | 154.9 ± 5.6 | 0.185 |
| Body weight (kg) | 46.1 ± 6.1 | 44.3 ± 5.6 | 0.302 |
| Body mass index (BMI) | 18.6 ± 1.9 | 18.4 ± 1.8 | 0.636 |
| LDCT | NDCT | Reduction Rate | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The volume CT dose index (CTDIvol) (mGy) | 0.76 ± 0.09 | 2.94 ± 0.40 | 74.1% | <0.001 |
| Dose Length Product (DLP) (mGy · cm) | 51.5 ± 7.0 | 207.1 ± 33.8 | 75.1% | <0.001 |
| Effective dose International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) 103 (mSv) | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 4.8 ± 0.7 | 77.1% | <0.001 |
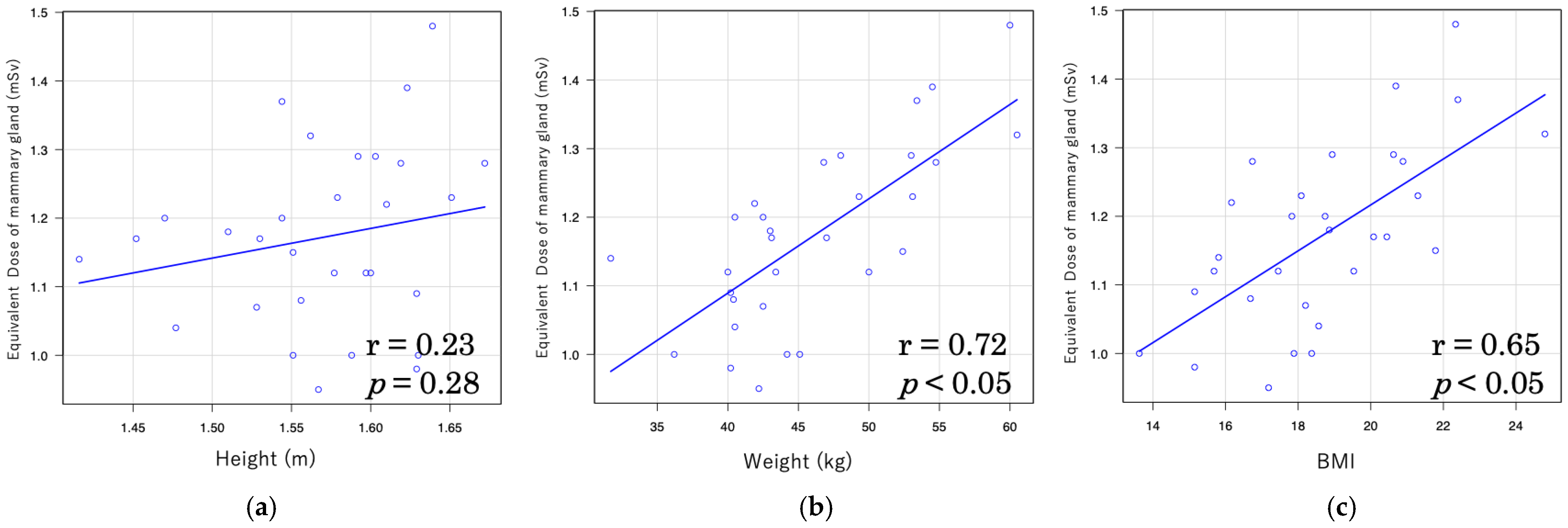
| Breast (mSv) | 1.23 ± 0.12 | 4.87 ± 0.59 | 74.7% | <0.001 |
| Uterus (mSv) | 1.15 ± 0.11 | 4.66 ± 0.49 | 74.6% | <0.001 |
| Ovary (mSv) | 1.06 ± 0.10 | 4.45 ± 0.46 | 75.2% | <0.001 |
| LDCT | NDCT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient (r) with CTDIvol | p Value | Correlation Coefficient (r) with CTDIvol | p Value | |
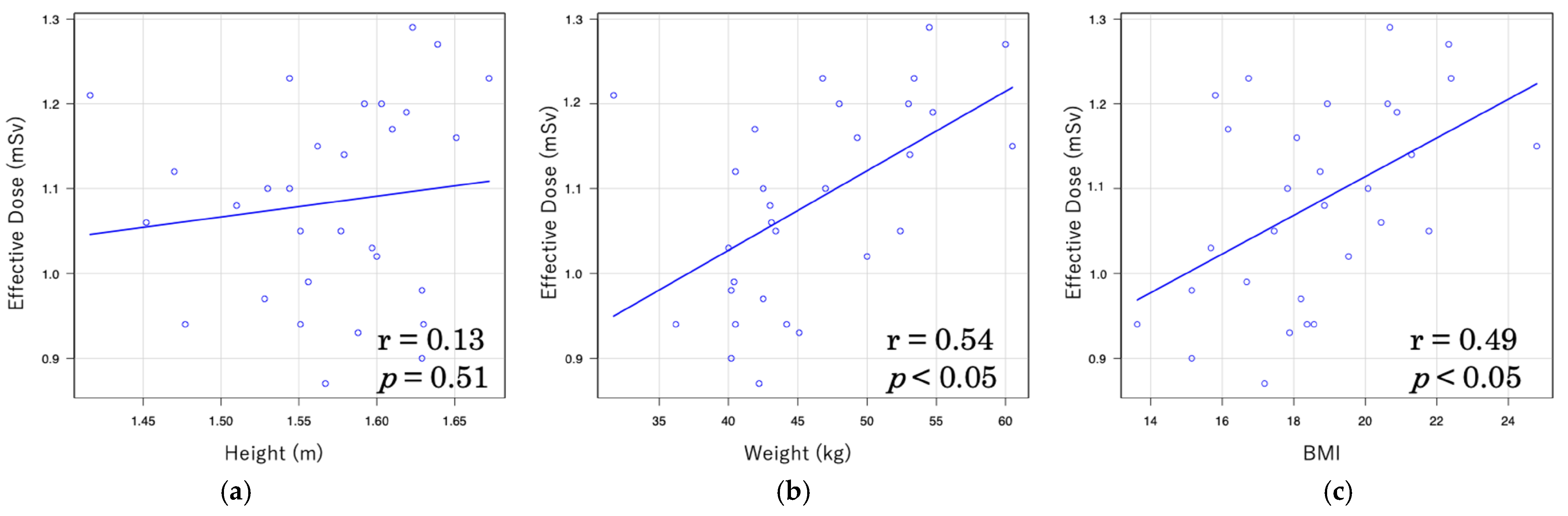
| Height | 0.371 | <0.05 | 0.083 | 0.736 |
| Weight | 0.832 | <0.001 | 0.333 | 0.164 |
| BMI | 0.694 | <0.001 | 0.375 | 0.114 |
| LDCT | NDCT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient (r) with DLP | p Value | Correlation Coefficient (r) with DLP | p Value | |
| Height | 0.489 | <0.05 | 0.333 | 0.164 |
| Weight | 0.775 | <0.001 | 0.477 | <0.05 |
| BMI | 0.574 | <0.001 | 0.33 | 0.167 |
| LDCT | NDCT | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lumber spine | 220.1 ± 24.9 | 235.7 ± 38.7 | 0.0941 |
| Liver | 63.08 ± 7.1 | 64.4 ± 3.7 | 0.65 |
| LDCT | NDCT | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lumber spine | 43.1 ± 5.4 | 70.6 ± 10.2 | <0.05 |
| Liver | 37.6 ± 4.8 | 51.3 ± 6.8 | <0.05 |
| LDCT | NDCT | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lumber spine | 5.2 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.8 | <0.05 |
| Liver | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noto, Y.; Kuramoto, T.; Watanabe, K.; Chida, K. Reducing Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography Imaging of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Spectral Shaping Technique with Tin Filter. Tomography 2025, 11, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11100110
Noto Y, Kuramoto T, Watanabe K, Chida K. Reducing Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography Imaging of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Spectral Shaping Technique with Tin Filter. Tomography. 2025; 11(10):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11100110
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoto, Yoshiyuki, Tatsuya Kuramoto, Kei Watanabe, and Koichi Chida. 2025. "Reducing Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography Imaging of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Spectral Shaping Technique with Tin Filter" Tomography 11, no. 10: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11100110
APA StyleNoto, Y., Kuramoto, T., Watanabe, K., & Chida, K. (2025). Reducing Radiation Dose in Computed Tomography Imaging of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Spectral Shaping Technique with Tin Filter. Tomography, 11(10), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11100110






