A Literature Review on the Relative Diagnostic Accuracy of Chest CT Scans versus RT-PCR Testing for COVID-19 Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Review Background
1.2. COVID-19: CT Imaging Manifestations
1.3. COVID-19 Pneumonia: Early versus Late Chest CT Findings
1.4. Differentiation of COVID-19 Pneumonia
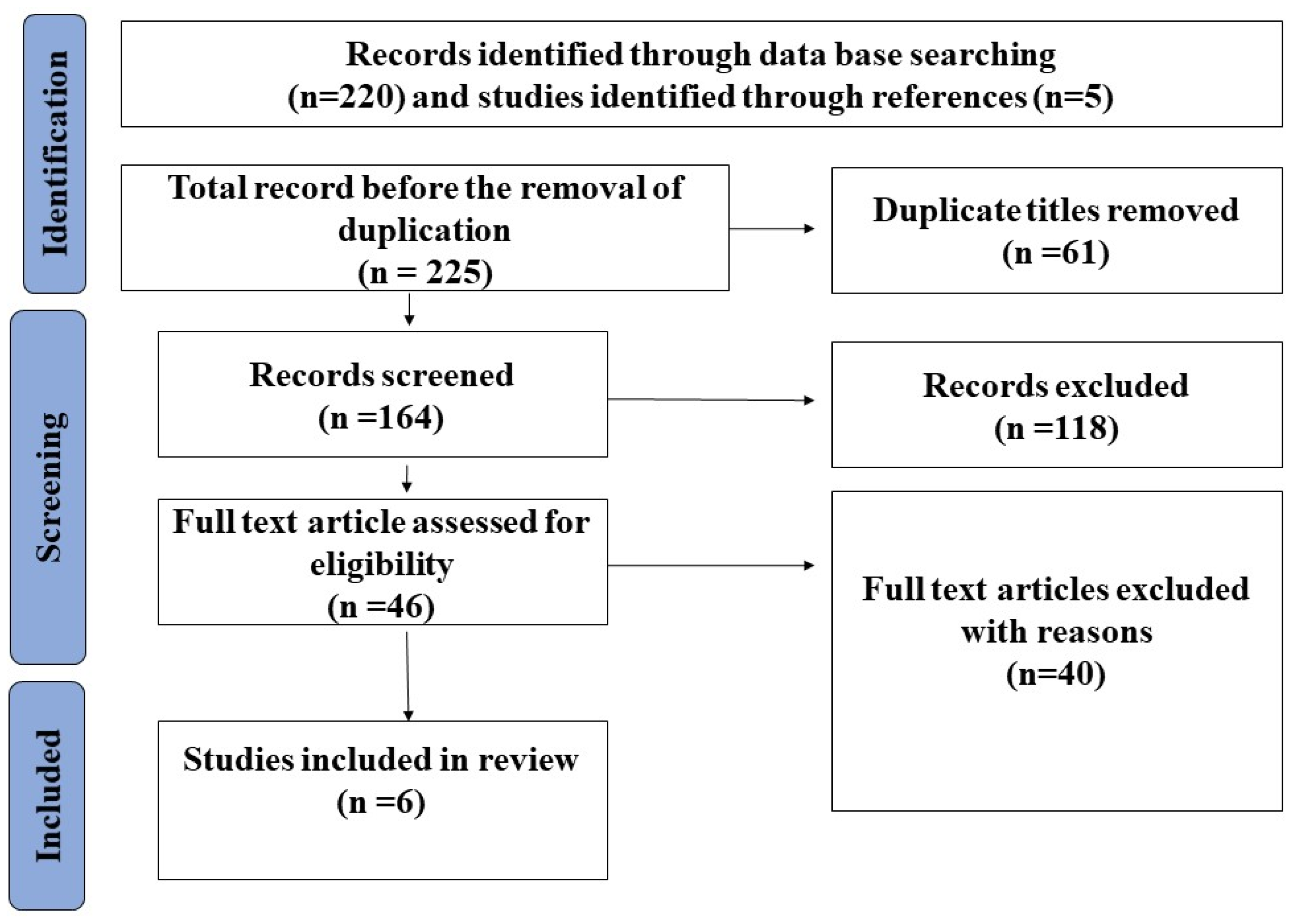
2. Methodology
2.1. Reviw Question, Keywords, and Databases
2.2. Database Search Result
3. Findings
3.1. Assessment of the Included Studies
3.2. Sensitivity and Specificity of the CT Scan Regarding the Detection of COVID-19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, F.; Deng, Y.; Li, W. Coronavirus disease 2019: What we know? J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.; Groot, R.J.d.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: The species and its viruses–a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. BioRxiv 2020, 2, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.H.; Strope, J.D.; Figg, W.D. COVID-19 clinical diagnostics and testing technology. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2020, 40, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Sirajuddin, A.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Teng, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lu, M. The role of imaging in 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19). Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4874–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, R.; Lu, R.; Han, K.; Wu, G.; Tan, W. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA 2020, 323, 1843–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.J.; Kwee, T.C.; Yakar, D.; Hope, M.D.; Kwee, R.M. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the value of chest CT in the diagnosis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Sol Scientiae, Illustra Nos. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Shi, N.; Shan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Lu, H.; Ling, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y. Emerging 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pneumonia. Radiology 2020, 295, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnano, S.; Angelini, F.; Fonsi, G.B.; Novelli, S.; Drudi, F.M. Diagnostic imaging in COVID-19 pneumonia: A literature review. J. Ultrasound 2021, 24, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljondi, R.; Alghamdi, S.J. Diagnostic value of imaging modalities for COVID-19: Scoping review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, D.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Chen, L.; Yang, R.; Li, X.; Zeng, W. Coronavirus disease 2019: Initial chest CT findings. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4398–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefeda, M.M. CT chest findings in patients infected with COVID-19: Review of literature. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2020, 51, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, M.; Donuru, A.; Balasubramanya, R.; Kapur, S. Review of the chest CT differential diagnosis of ground-glass opacities in the COVID era. Radiology 2020, 297, E289–E302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.-Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Lui, M.M.-s.; Lo, C.S.-Y.; Leung, B.; Khong, P.-L.; et al. Imaging profile of the COVID-19 infection: Radiologic findings and literature review. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; Zhang, N.; Diao, K.; Lin, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, K.; et al. Chest CT findings in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): Relationship to duration of infection. Radiology 2020, 295, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Abedi, A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Kang, S.; Tian, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Imaging manifestations and diagnostic value of chest CT of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the Xiaogan area. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) CT findings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 17, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xia, L. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of chest CT in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabsi, S.; Dhole, A.; Hozayen, S.; Chapman, S.A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, M. Temporal changes of CT findings in 90 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A longitudinal study. Radiology 2020, 296, E55–E64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kents, A.; Zotin, A.; Simonov, K. Comparative Analysis of Laboratory and Radiation Methods of Studies with the Degree of Severity of Patients with COVID-19. In Proceedings of the 2023 25th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing and its Applications (DSPA), Moscow, Russian Federation, 29–31 March 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, N.; Kansal, A.; Barneih, F.; Al-Shaltone, O.; Bonny, T.; Al-Shabi, M.; Al Shammaa, A. Multi-modal image classification of COVID-19 cases using computed tomography and X-rays scans. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2023, 17, 200160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, S.; You, F.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, J. The evolution of chest CT findings from admission to follow-up in 30 moderate to severe adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Chin. J. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 4, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwee, T.C.; Kwee, R.M. Chest CT in COVID-19: What the radiologist needs to know. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1848–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duzgun, S.A.; Durhan, G.; Demirkazik, F.B.; Akpinar, M.G.; Ariyurek, O.M. COVID-19 pneumonia: The great radiological mimicker. Insights Into Imaging 2020, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fang, X.; Bian, Y.; Lu, J. Comparison of chest CT findings between COVID-19 pneumonia and other types of viral pneumonia: A two-center retrospective study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5470–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Fu, G.; Chen, S.; Tao, J.; Qian, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, M. CT manifestations of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia and influenza virus pneumonia: A comparative study. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslambolchi, A.; Maliglig, A.; Gupta, A.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. COVID-19 or non-COVID viral pneumonia: How to differentiate based on the radiologic findings? World J. Radiol. 2020, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajlan, A.M.; Quiney, B.; Nicolaou, S.; Muller, N.L. Swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) viral infection: Radiographic and CT findings. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, J.; Lehners, N.; Egerer, G.; Kauczor, H.; Heußel, C. CT-morphological characterization of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia in immune-compromised adults. In RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der bildgebenden Verfahren; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 686–692. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzi, D.; Cavigli, E.; Moroni, C.; Smorchkova, O.; Zantonelli, G.; Pradella, S.; Miele, V. Ground-glass opacity (GGO): A review of the differential diagnosis in the era of COVID-19. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2021, 39, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Kim, T.; Cho, E. Herpes simplex virus pneumonia: High-resolution CT findings. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meline, T. Selecting studies for systemic review: Inclusion and exclusion criteria. Contemp. Issues Commun. Sci. Disord. 2006, 33, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, C.; Lv, W.; Tao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L. Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A report of 1014 cases. Radiology 2020, 296, E32–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J.; Lin, M.; Ying, L.; Pang, P.; Ji, W. Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: Comparison to RT-PCR. Radiology 2020, 296, E115–E117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.; Xu, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Fan, B.; Wang, C.; Zeng, B.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Li, H. Diagnosis of the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): rRT-PCR or CT? Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 126, 108961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, D.; Panvini, N.; Rengo, M.; Vicini, S.; Lichtner, M.; Tieghi, T.; Ippoliti, D.; Giulio, F.; Orlando, E.; Iozzino, M. Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver variability of CO-RADS in patients with suspected coronavirus disease-2019: A multireader validation study. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-L.; Luo, L.; Luo, Z.-D.; Lyu, J.-X.; Ng, M.-Y.; Shen, X.-P.; Wen, Z.J.R.m. Diagnostic performance between CT and initial real-time RT-PCR for clinically suspected 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients outside Wuhan, China. Respir. Med. 2020, 168, 105980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, S.; Bekci, T.; Çakır, İ.M.; Ekiz, M.; Yavuz, I.; Şahin, A.M. Diagnostic performance of low-dose chest CT to detect COVID-19: A Turkish population study. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 27, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyrer, S.; Heyman, B. Sampling in epidemiological research: Issues, hazards and pitfalls. BJPsych Bull. 2016, 40, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrokhi, F.; Mahmoudi-Hamidabad, A. Rethinking convenience sampling: Defining quality criteria. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2012, 2, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Sullivan, K.M.; Barker, N.D. Information bias. ActivEpi Companion Textbook: A Supplement for Use with the ActivEpi CD-ROM; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 231–281. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.L.; Factor, R.E. Understanding sources of bias in diagnostic accuracy studies. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatami, F.; Saatchi, M.; Zadeh, S.S.T.; Aghamir, Z.S.; Shabestari, A.N.; Reis, L.O.; Aghamir, S.M.K. A meta-analysis of accuracy and sensitivity of chest CT and RT-PCR in COVID-19 diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, A.; Palásti, P.; Veréb, D.; Bozsik, B.; Palkó, A.; Kincses, Z.T. The sensitivity and specificity of chest CT in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hong, H.; Yoon, S.H. Diagnostic performance of CT and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for coronavirus disease 2019: A meta-analysis. Radiology 2020, 296, E145–E155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Luo, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhou, C.; He, J.; Lyu, J.; Shen, X. CT differential diagnosis of COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 in symptomatic suspects: A practical scoring method. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirani, F.; Shayganfar, A.; Hajiahmadi, S. COVID-19 pneumonia: A pictorial review of CT findings and differential diagnosis. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.J.; Lim, S.; Choe, J.; Choi, S.-H.; Sung, H.; Do, K.-H. Radiographic and CT features of viral pneumonia. Radiographics 2018, 38, 719–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gempeler, A.; Griswold, D.P.; Rosseau, G.; Johnson, W.D.; Kaseje, N.; Kolias, A.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Rubiano, A.M. An umbrella review with meta-analysis of chest computed tomography for diagnosis of COVID-19: Considerations for trauma patient management. Frontiers in Medicine. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 907–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, C.S.; Lv, Z.B.; Yan, S.; Du, Y.N.; Chen, H.; Wei, L.G.; Xie, R.M.; Chen, B.D. Imaging features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Evaluation on thin-section CT. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.; Husson, O.; Drey, N.; Murray, I.; May, K.; Thurston, J.; Oyen, W. Ionising radiation exposure from medical imaging—A review of Patient’s (un) awareness. Radiography 2020, 26, e25–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, S. Recommendation of low-dose CT in the detection and management of COVID-2019. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4356–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Deng, L.; Song, B. The battle against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Emergency management and infection control in a radiology department. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 17, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, K.; Kato, H.; Yamashiro, T.; Izumi, T.; Takeuchi, I.; Nakajima, H.; Utsunomiya, D. COVID-19 pneumonia: Infection control protocol inside computed tomography suites. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2020, 38, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, M.; Som, A.; Mendoza, D.P.; Flores, E.J.; Li, M.D.; Shepard, J.-A.O.; Little, B.P. Detection of unsuspected coronavirus disease 2019 cases by computed tomography and retrospective implementation of the Radiological Society of North America/Society of Thoracic Radiology/American College of Radiology consensus guidelines. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 35, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, B.K.; Demirjian, N.L.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) diagnostic technologies: A country-based retrospective analysis of screening and containment procedures during the first wave of the pandemic. Clin. Imaging 2020, 67, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, D.; Sun, H.; Tang, Y. Distinguishing COVID-19 from influenza pneumonia in the early stage through CT imaging and clinical features. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 847836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.S.; Lai, J.K.; McCusker, M.W.; Irving, L.; Pascoe, D.M.; Heinze, S.B. Chest imaging findings in COVID-19-positive patients in an Australian tertiary hospital. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 66, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak, S.B.; Van Gool, I.C.; Cohen, D.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; van Paassen, J. A systematic review of pathological findings in COVID-19: A pathophysiological timeline and possible mechanisms of disease progression. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, B.; Eibschutz, L.S.; Asadollahi, S.; Gupta, A.; Akhlaghpoor, S.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. The role of imaging techniques in understanding and evaluating the long-term pulmonary effects of COVID-19. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, B.; Tonkin, J.; Devaraj, A.; Philip, K.E.; Orton, C.M.; Desai, S.R.; Shah, P.L. CT lung abnormalities after COVID-19 at 3 months and 1 year after hospital discharge. Radiology 2022, 303, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchino, M.; Rea, G.; Capitelli, L.; Lieto, R.; Bruzzese, D. Chest CT lung abnormalities 1 year after COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 2023, 308, e230535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, R.; Gomaa, A.A.K.; Ghazy, T.; Hassanein, S.A.; Ibrahem, R.A.l.; Khalifa, M.H. Predicting lung fibrosis in post-COVID-19 patients after discharge with follow-up chest CT findings. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.; Jacob, J.; George, P.M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Porter, J.C.; Allen, R.J.; Aslani, S.; Baillie, J.K.; Barratt, S.L.; Beirne, P. Residual lung abnormalities after COVID-19 hospitalization: Interim analysis of the UKILD post–COVID-19 study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sensitivity of Chest CT (95% CI) | Sensitivity of the First RT-PCR Test | Specificity of CT Scan | Specificity of RT-PCR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fang and Zhang [36] | 98% (90–100%) | 71% (56–83%) | N/R | 100% |
| Long and Xu [37] | 97.2% (N/R) | 84.6% | N/R | 100% |
| Ai and Yang [35] | 97% (95–98%) | N/R | 25% (22–30%) | 100% |
| Aslan and Bekci [40] | 90.4% (86–93.7%) | 51.6% | 64.2% (50.3–76.6%) | 100% |
| He and Luo [39] | 77% (62–91%) | 79% (66–93%) | 96% (90–100%) | 100% |
| Bellini and Panvini [38] | 61% (52–69%) | N/R | 81% (77–84%) | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Momani, H. A Literature Review on the Relative Diagnostic Accuracy of Chest CT Scans versus RT-PCR Testing for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Tomography 2024, 10, 935-948. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060071
Al-Momani H. A Literature Review on the Relative Diagnostic Accuracy of Chest CT Scans versus RT-PCR Testing for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Tomography. 2024; 10(6):935-948. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060071
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Momani, Hafez. 2024. "A Literature Review on the Relative Diagnostic Accuracy of Chest CT Scans versus RT-PCR Testing for COVID-19 Diagnosis" Tomography 10, no. 6: 935-948. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060071
APA StyleAl-Momani, H. (2024). A Literature Review on the Relative Diagnostic Accuracy of Chest CT Scans versus RT-PCR Testing for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Tomography, 10(6), 935-948. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10060071






