Pediatric Meningeal Diseases: What Radiologists Need to Know
Abstract
1. Introduction
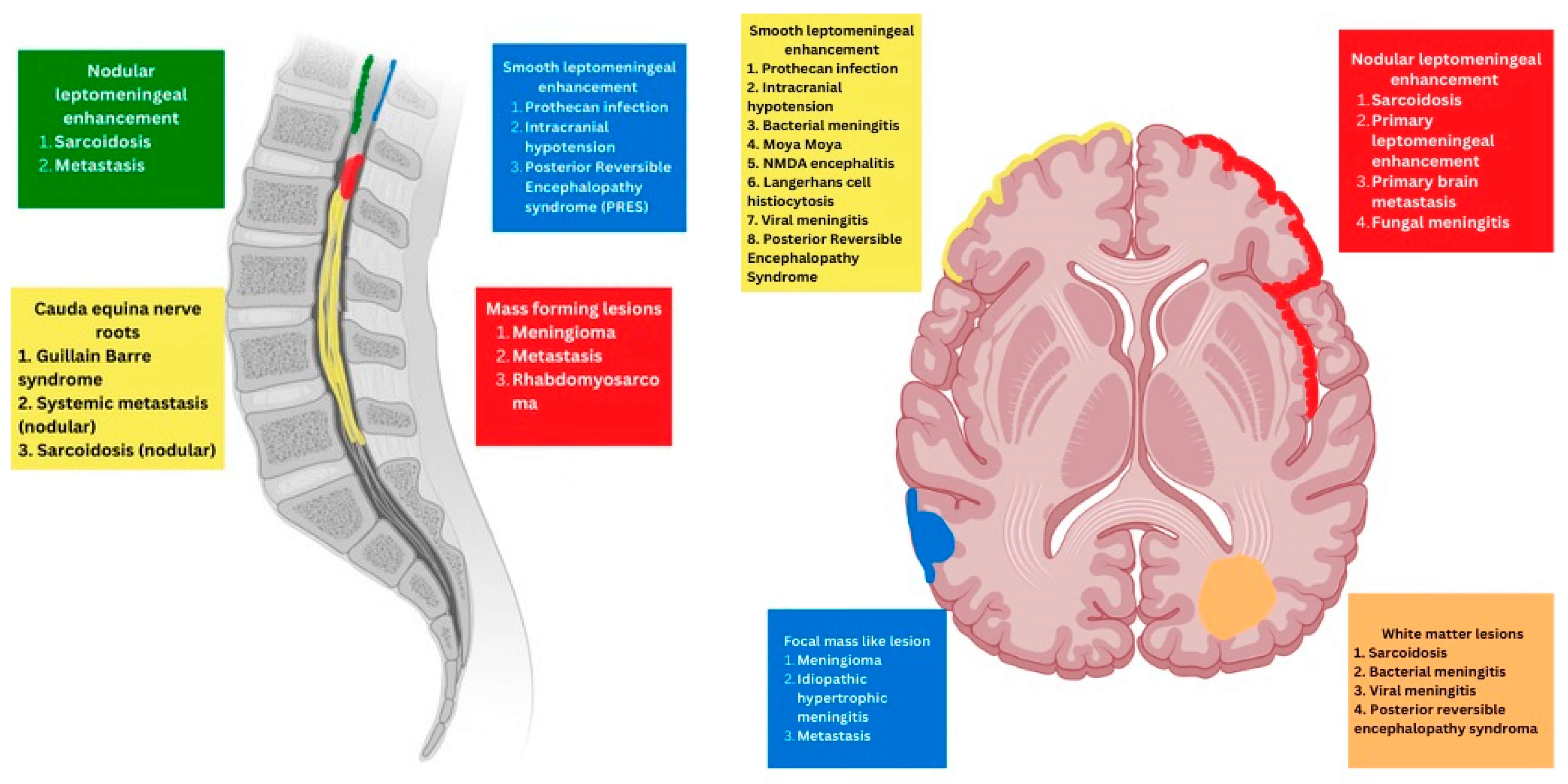
2. Imaging Based Classification of Pediatric Meningeal Diseases
- Meningeal
- Parenchymal
- Variable
3. Predominant Meningeal Features
3.1. Protothecans
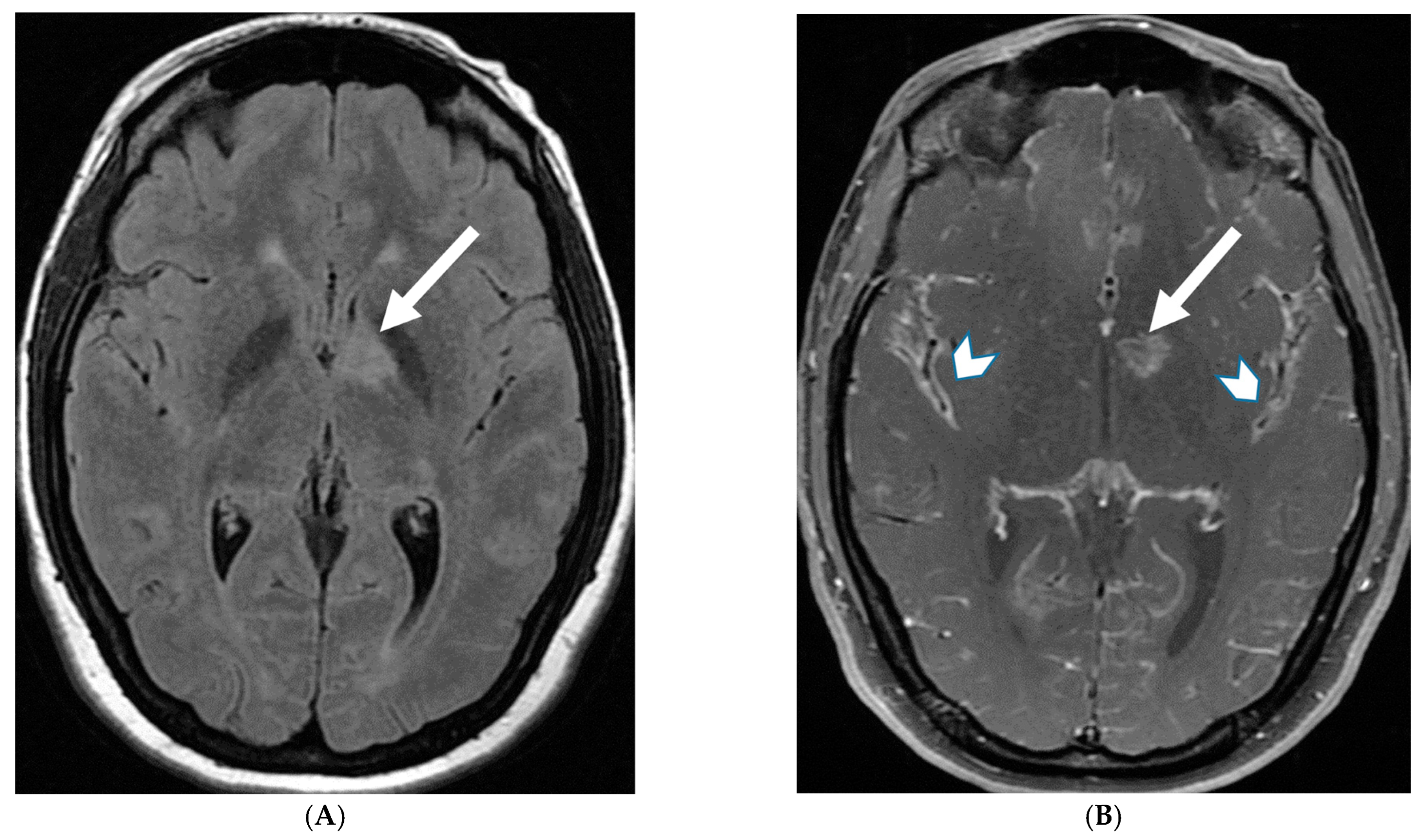
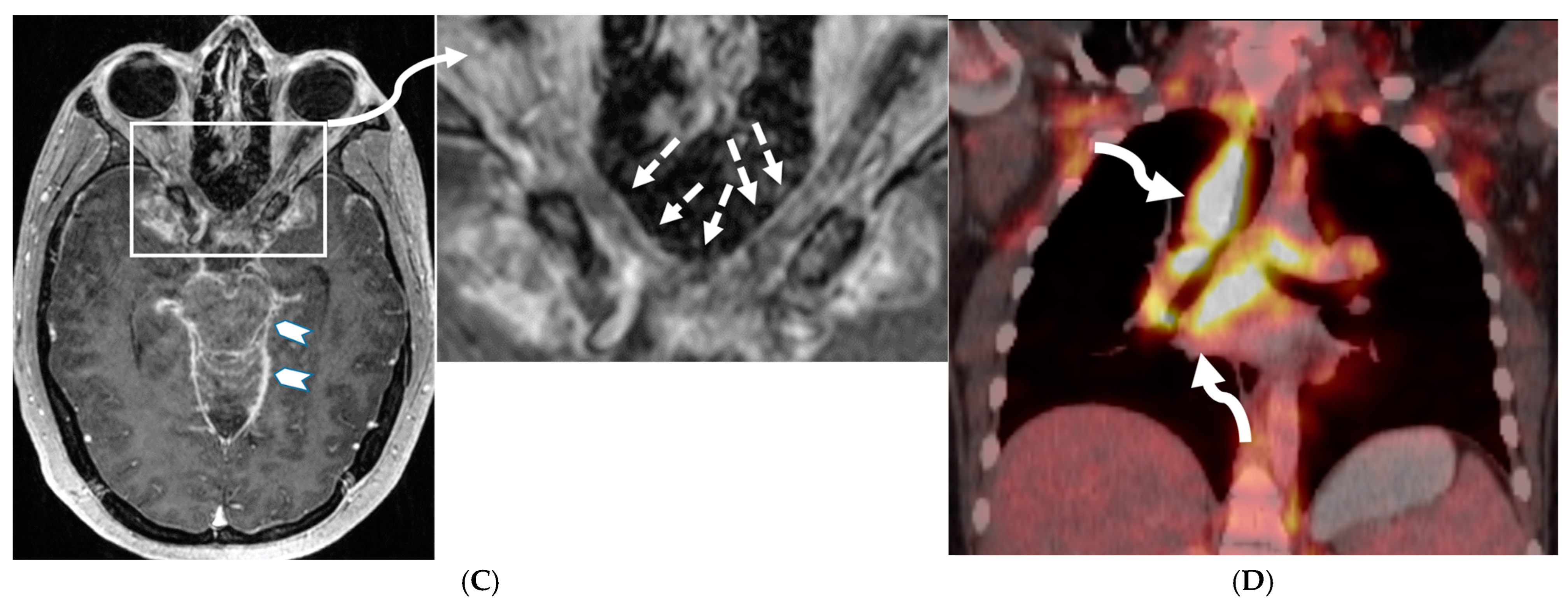
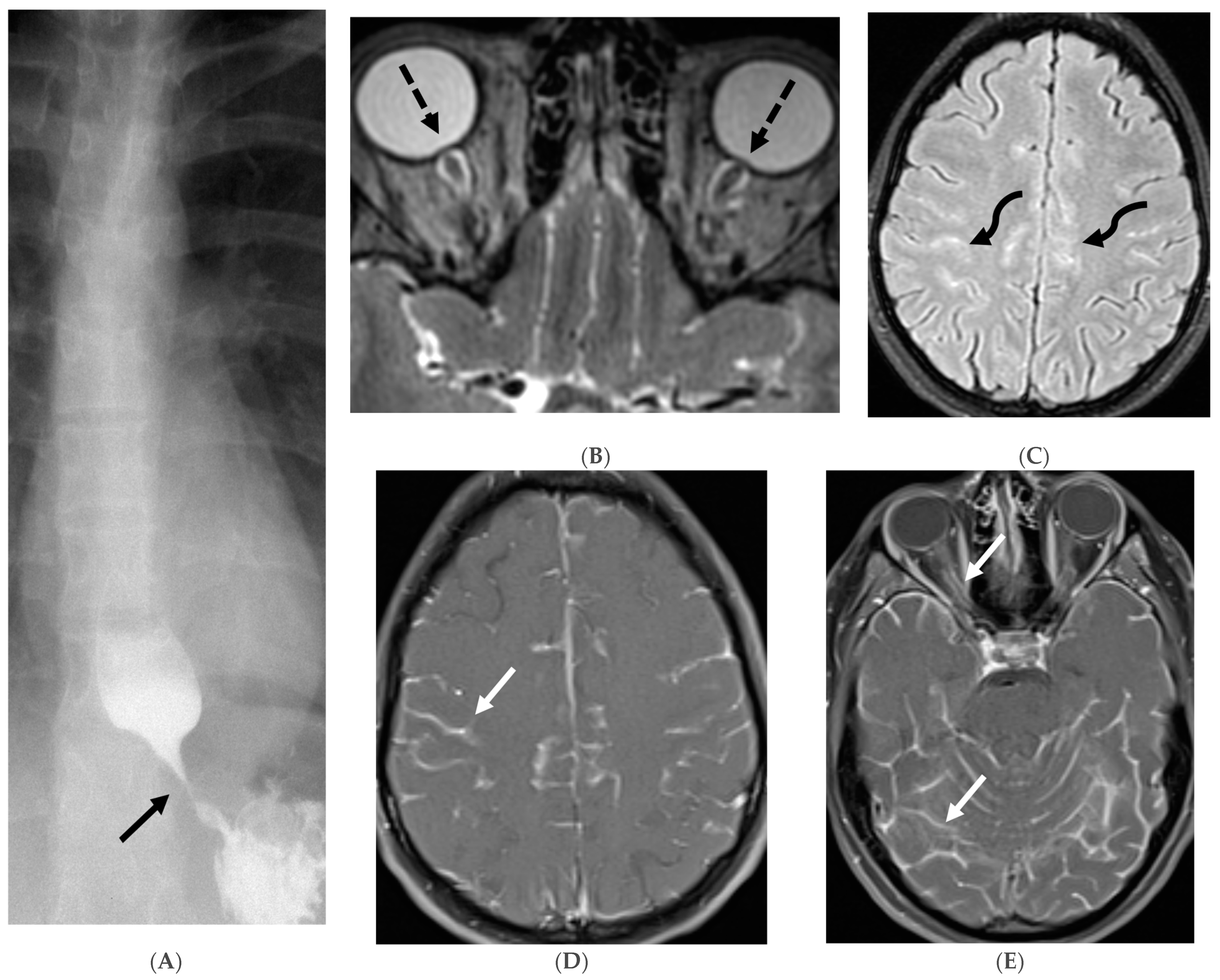
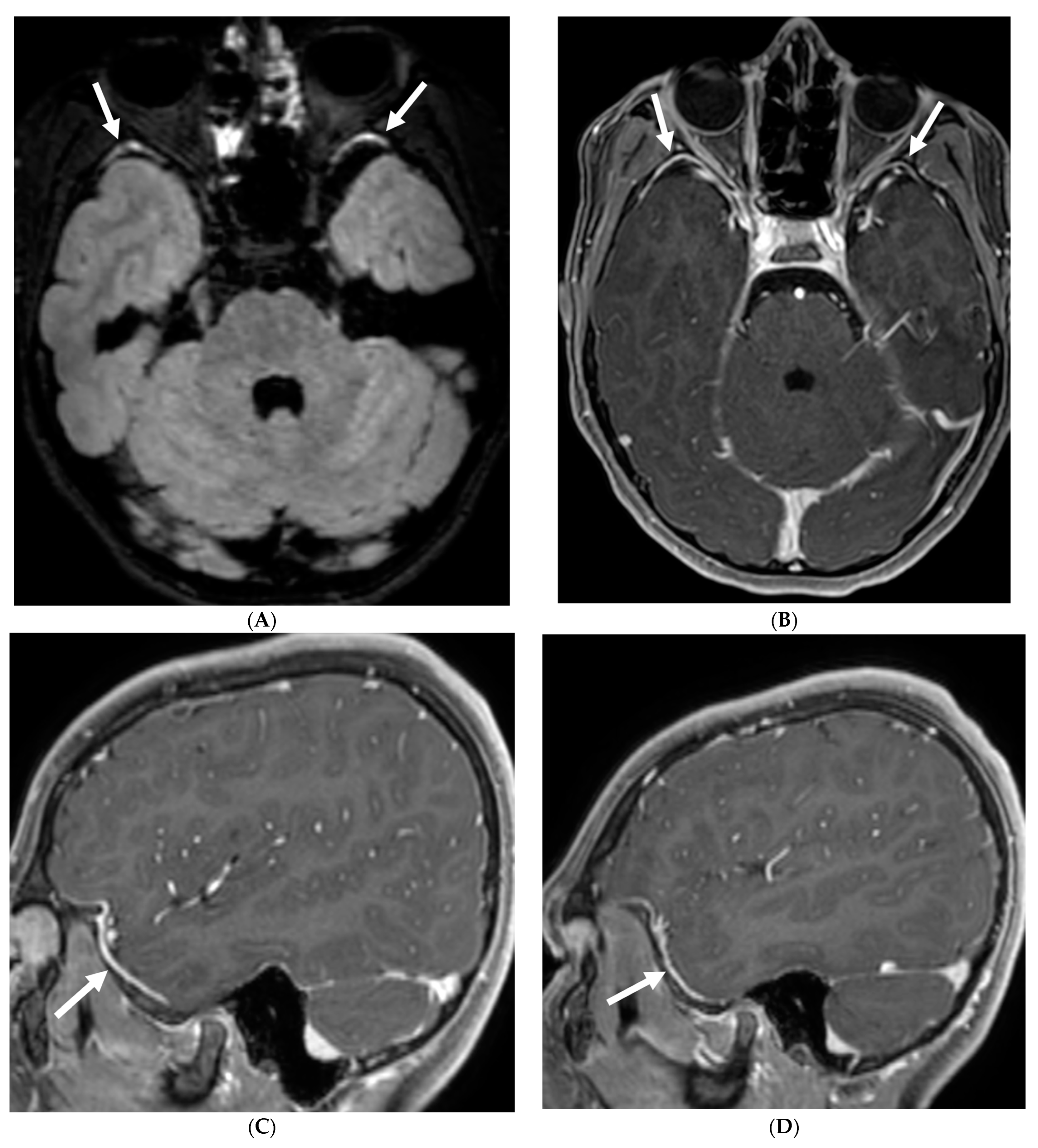
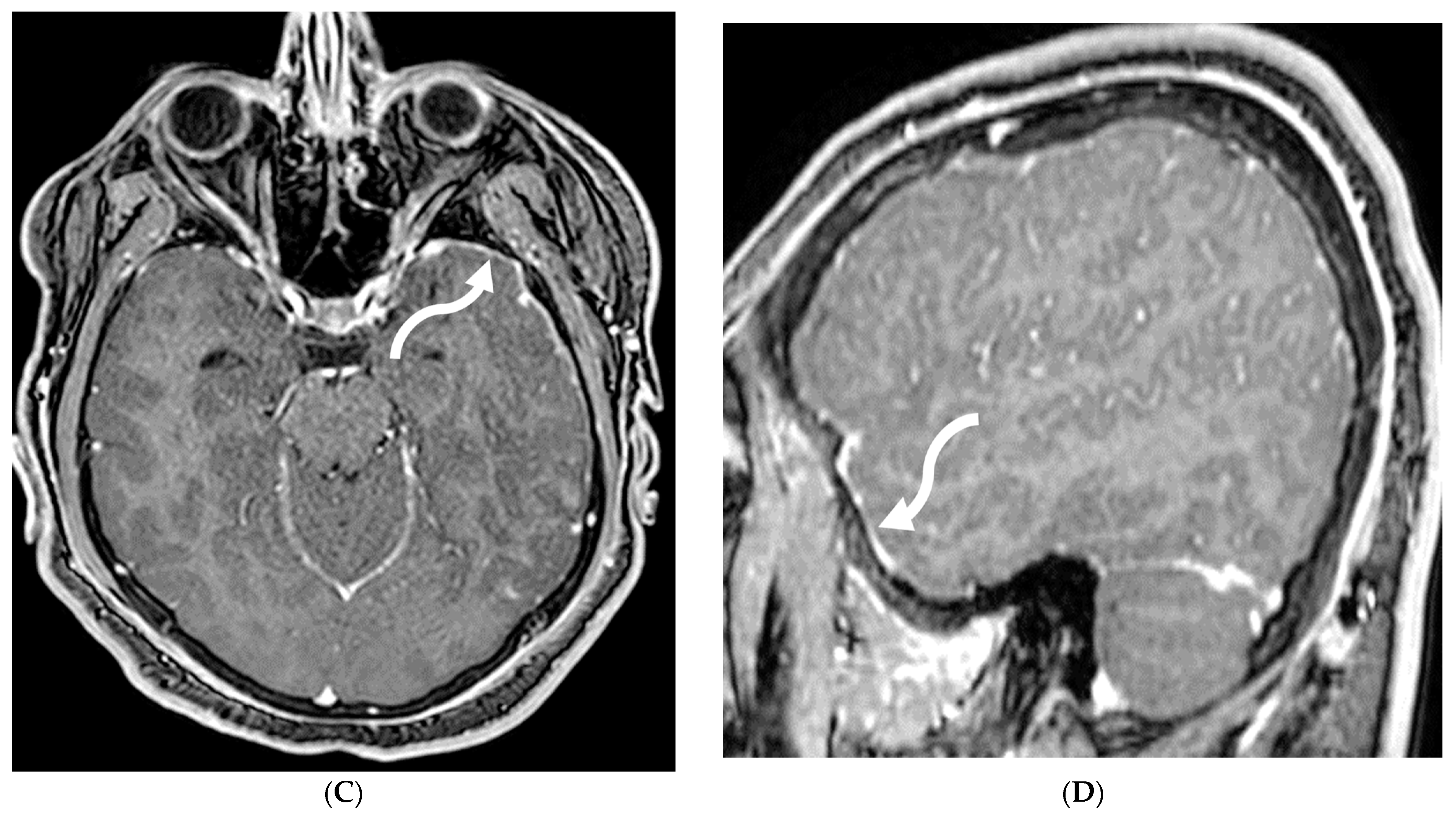
3.2. Neurosarcoidosis
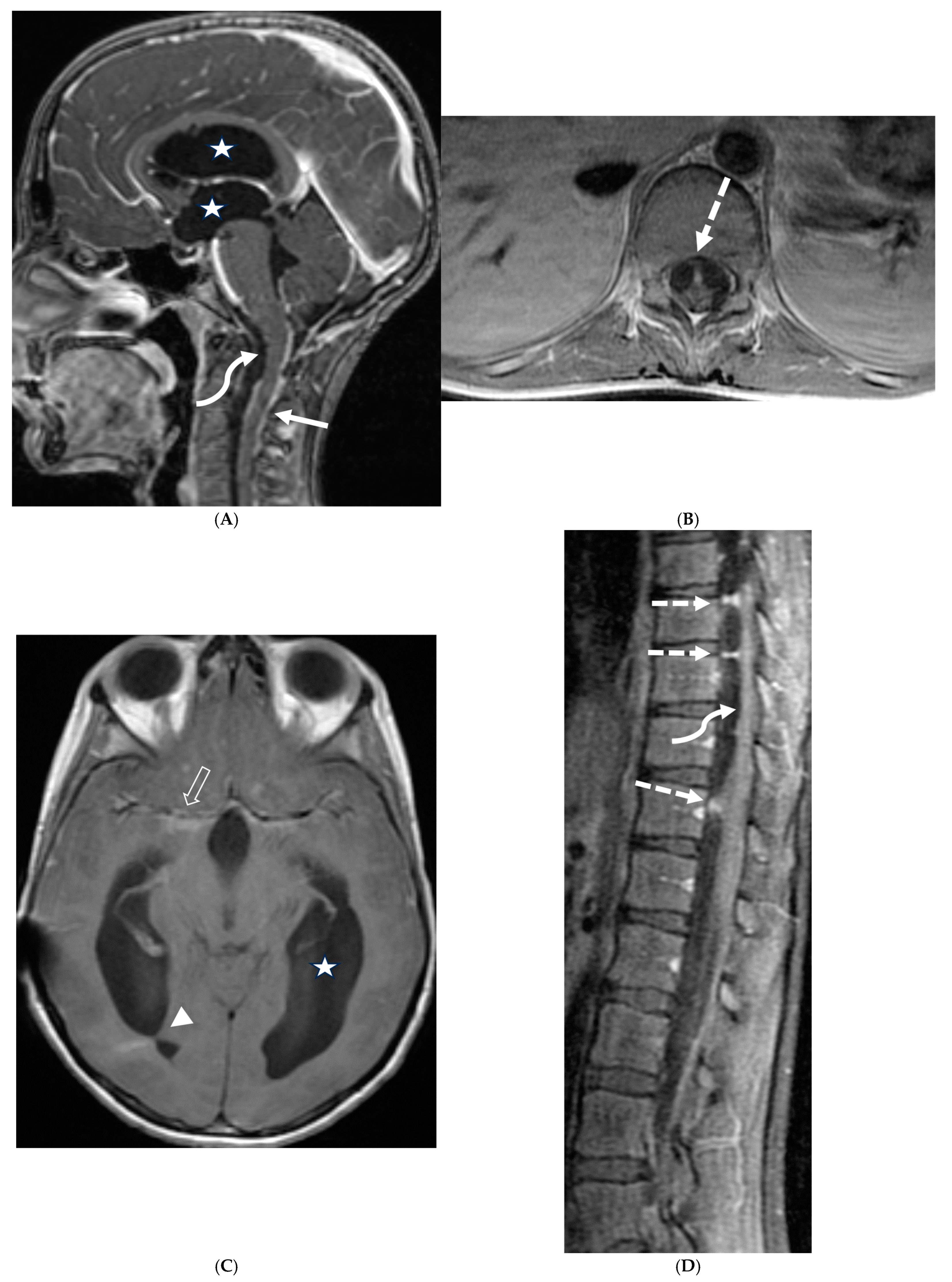
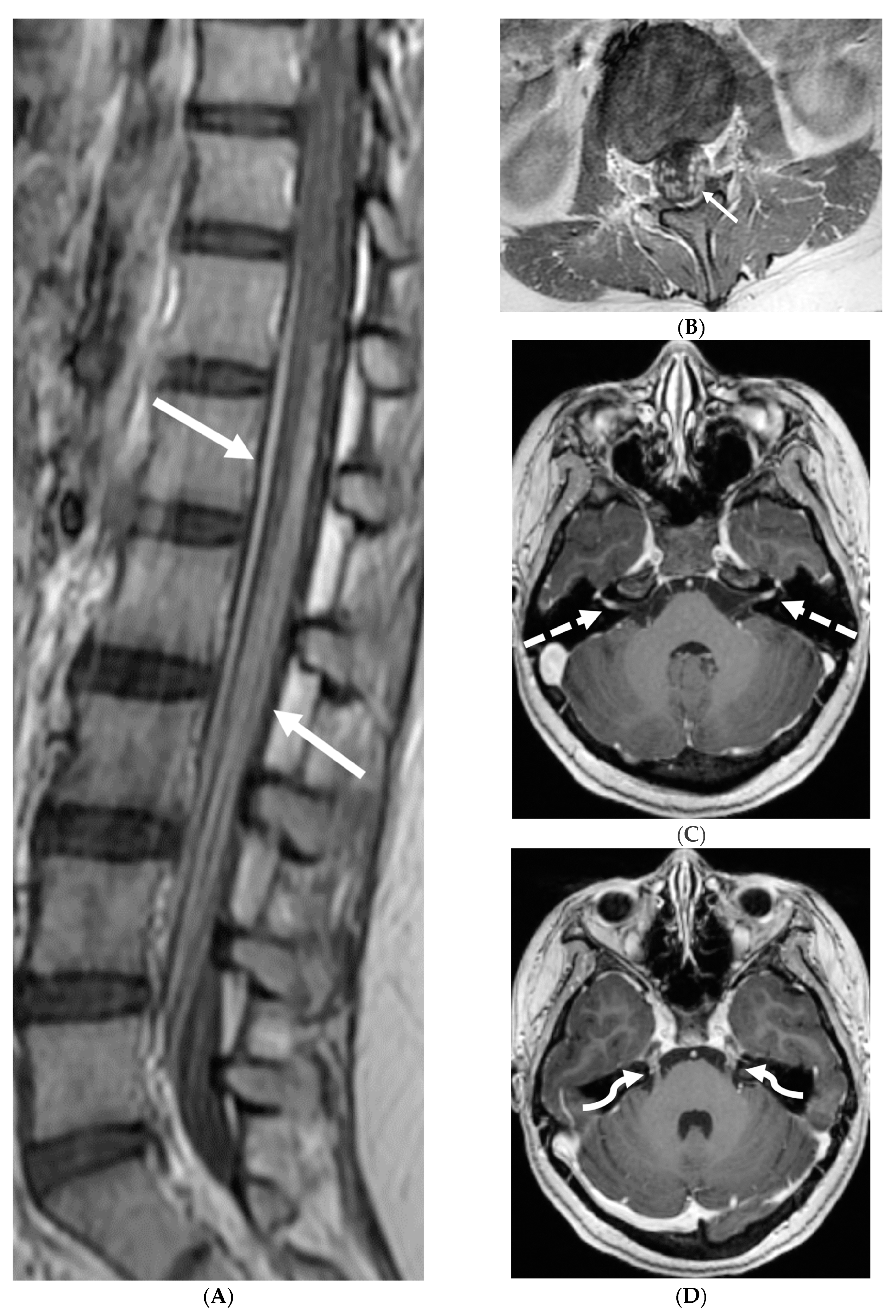
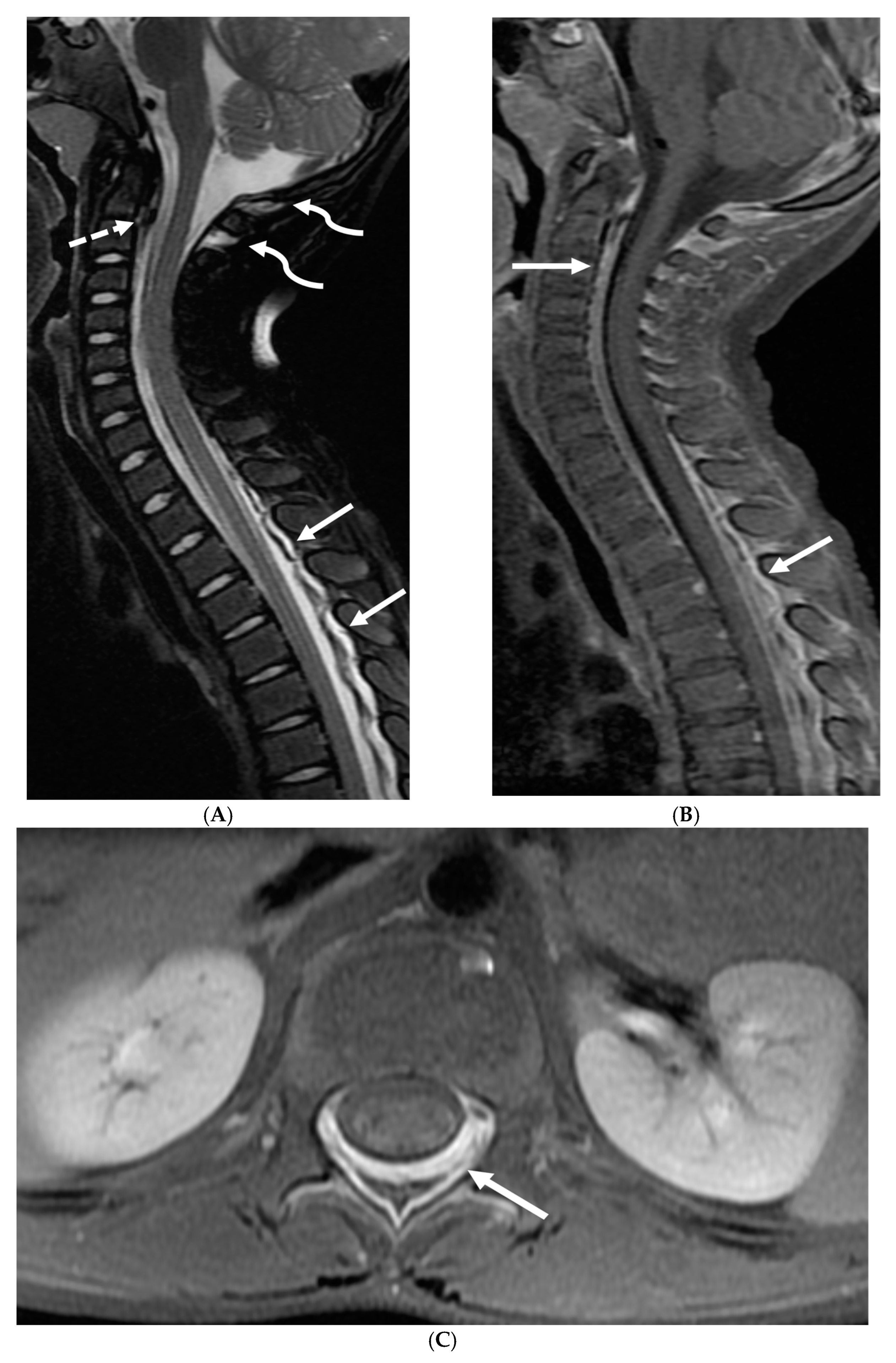
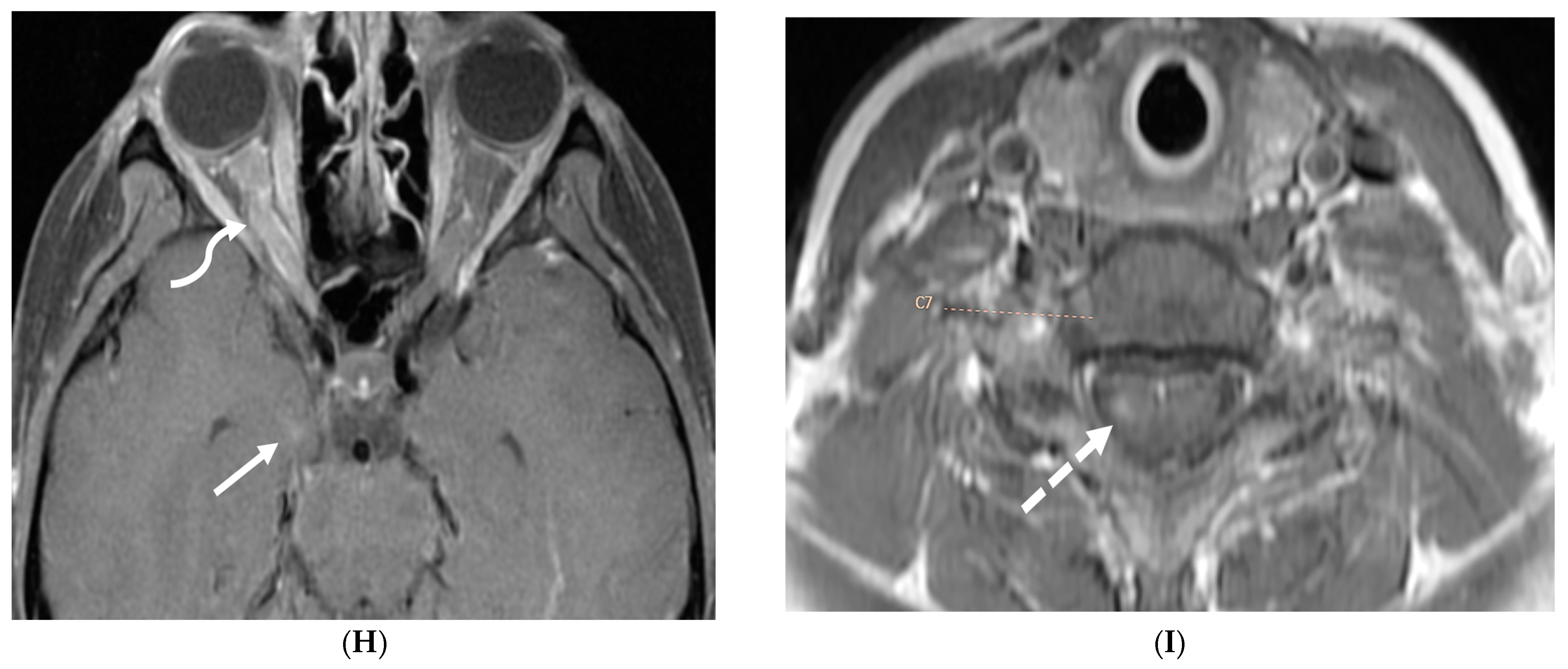
3.3. Guillain Barre Syndrome
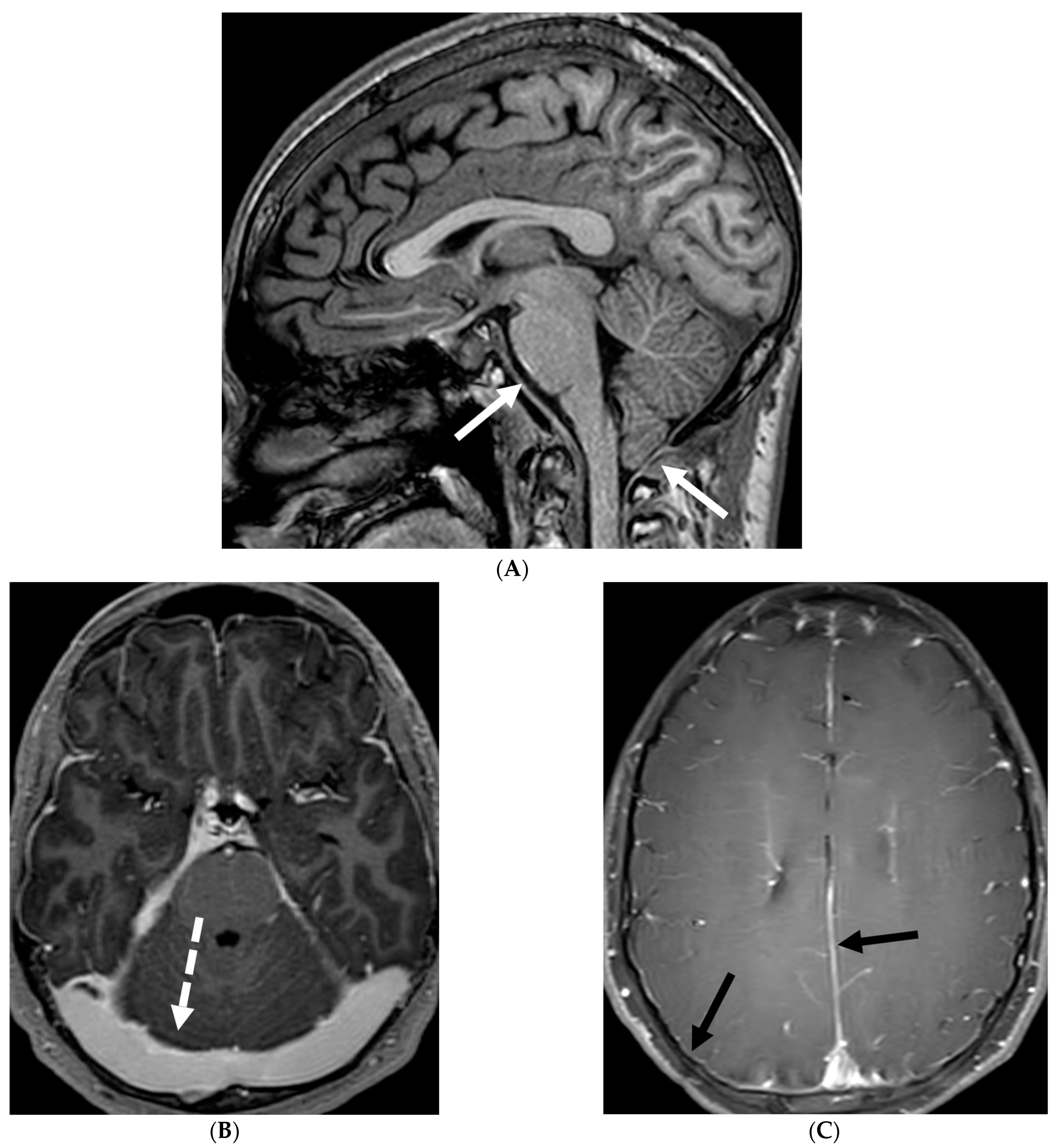
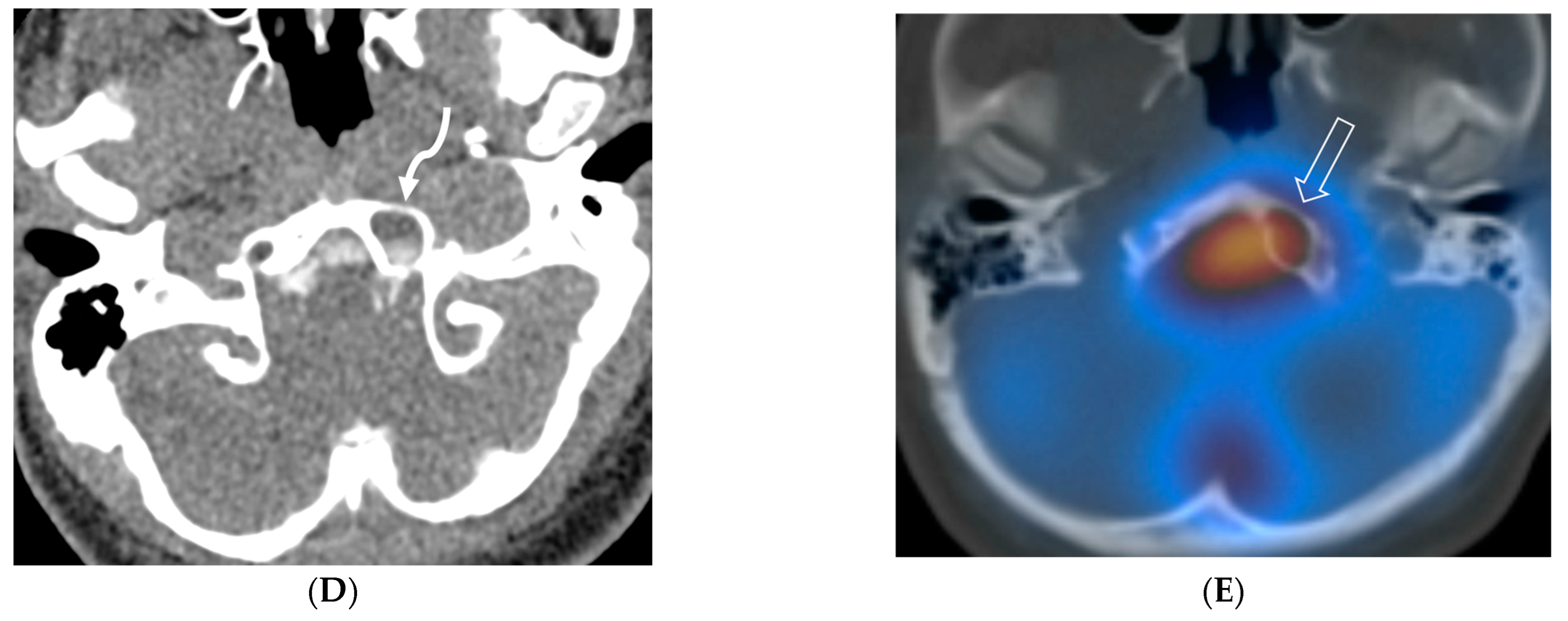
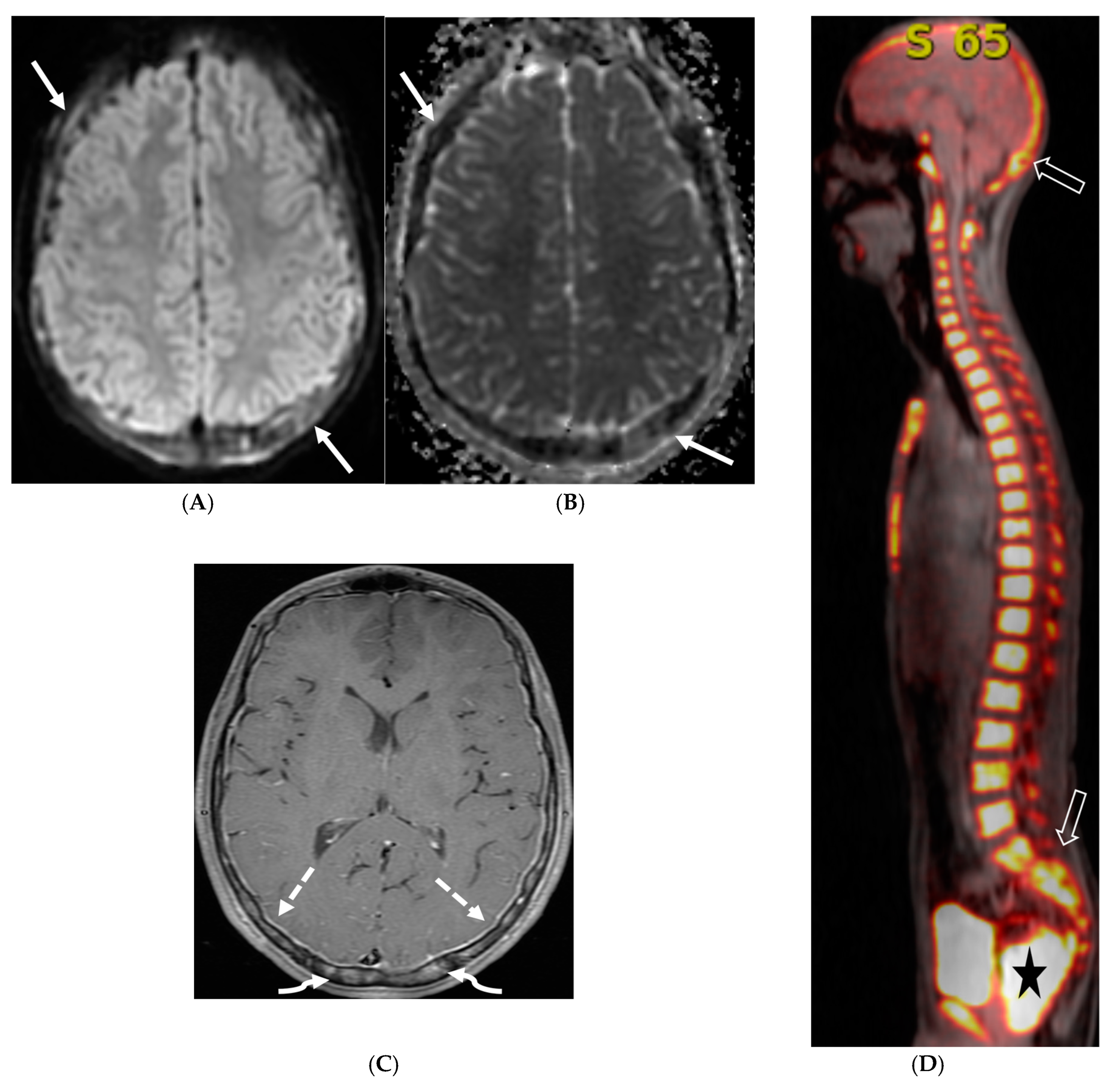
3.4. Idiopathic Hypertrophic Meningitis (IHP)
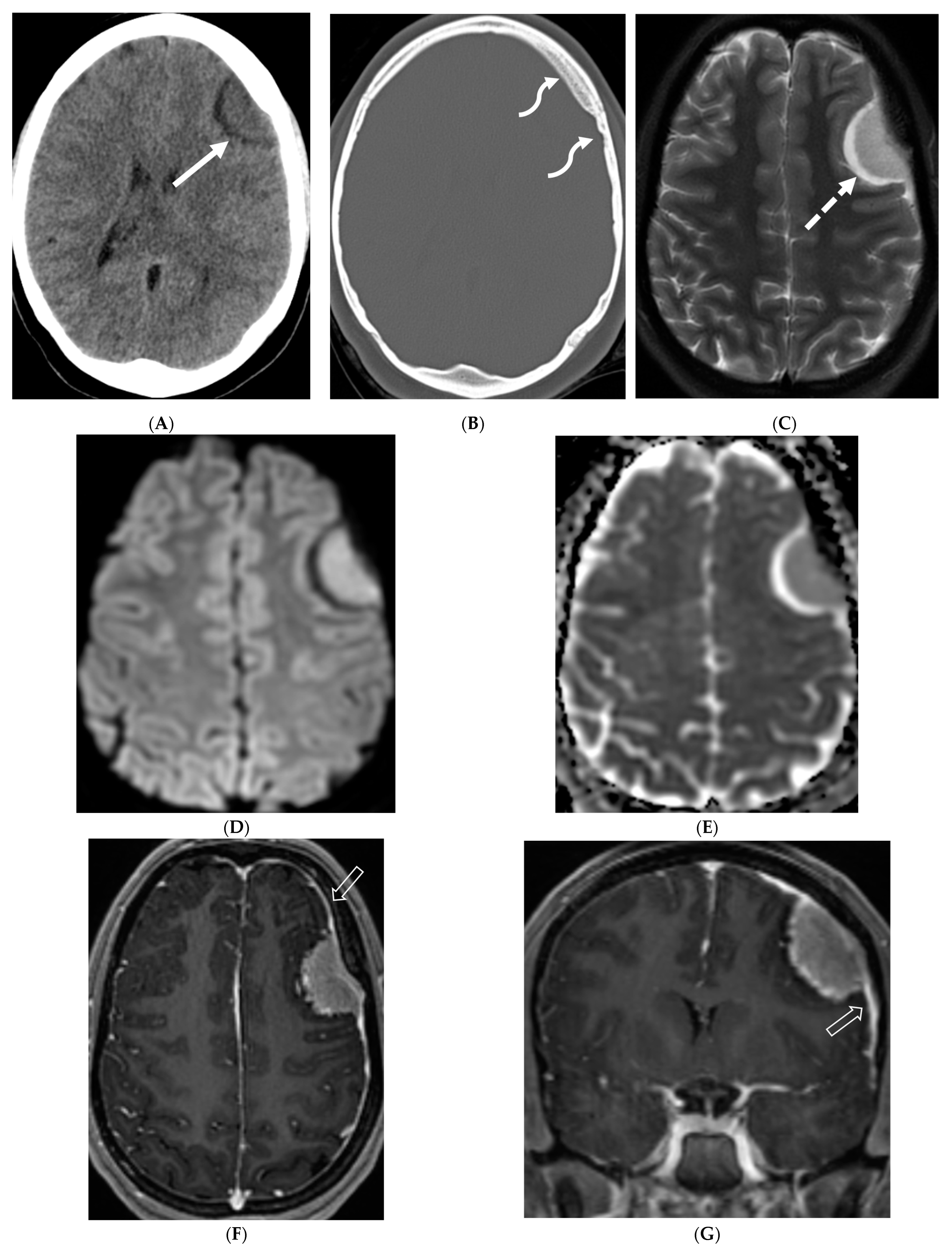
3.5. Meningioma
3.6. Glioneuronal Tumor
3.7. Primary Leptomeningeal Rhabdomyosarcoma
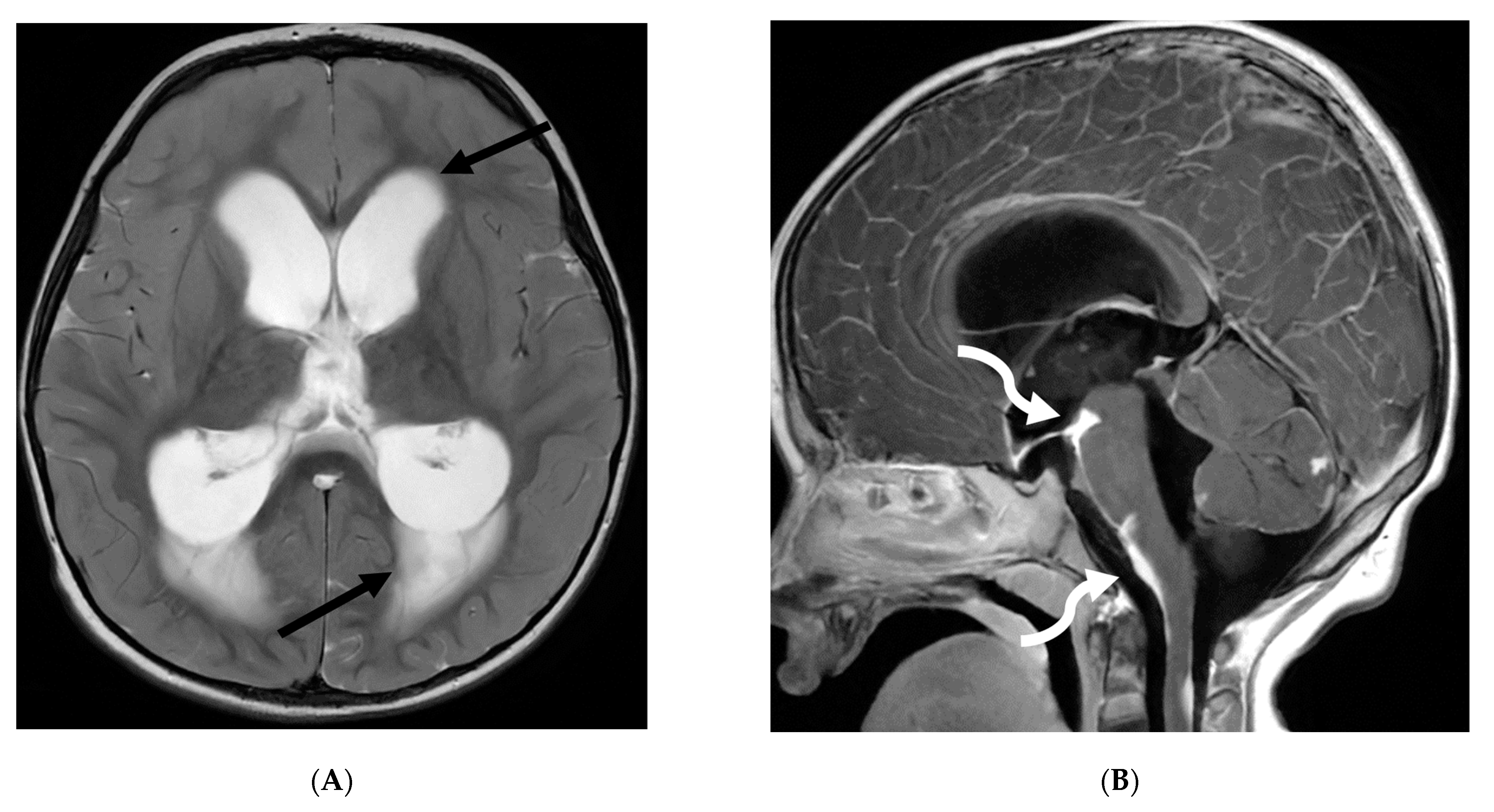
3.8. Intracranial Hypotension (IH)
3.9. Alk-Positive Histiocytosis
4. Variable Meningeal and Parenchymal Features
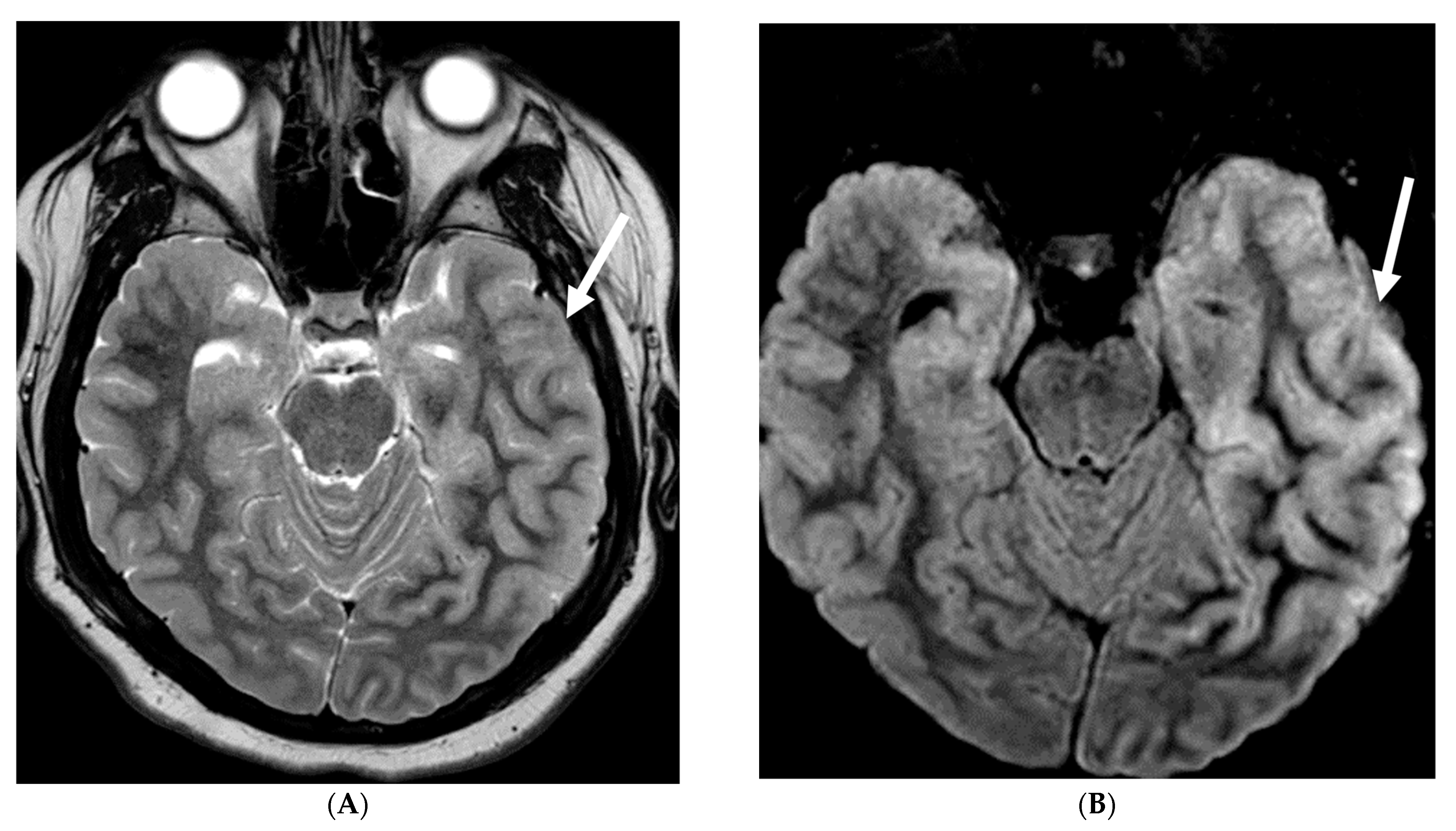
4.1. Bacterial Meningitis
4.2. Tuberculosis
4.3. Primary Brain Tumor Leptomeningeal Metastases (LM)
4.4. Systemic Meningeal Metastases (SMM)
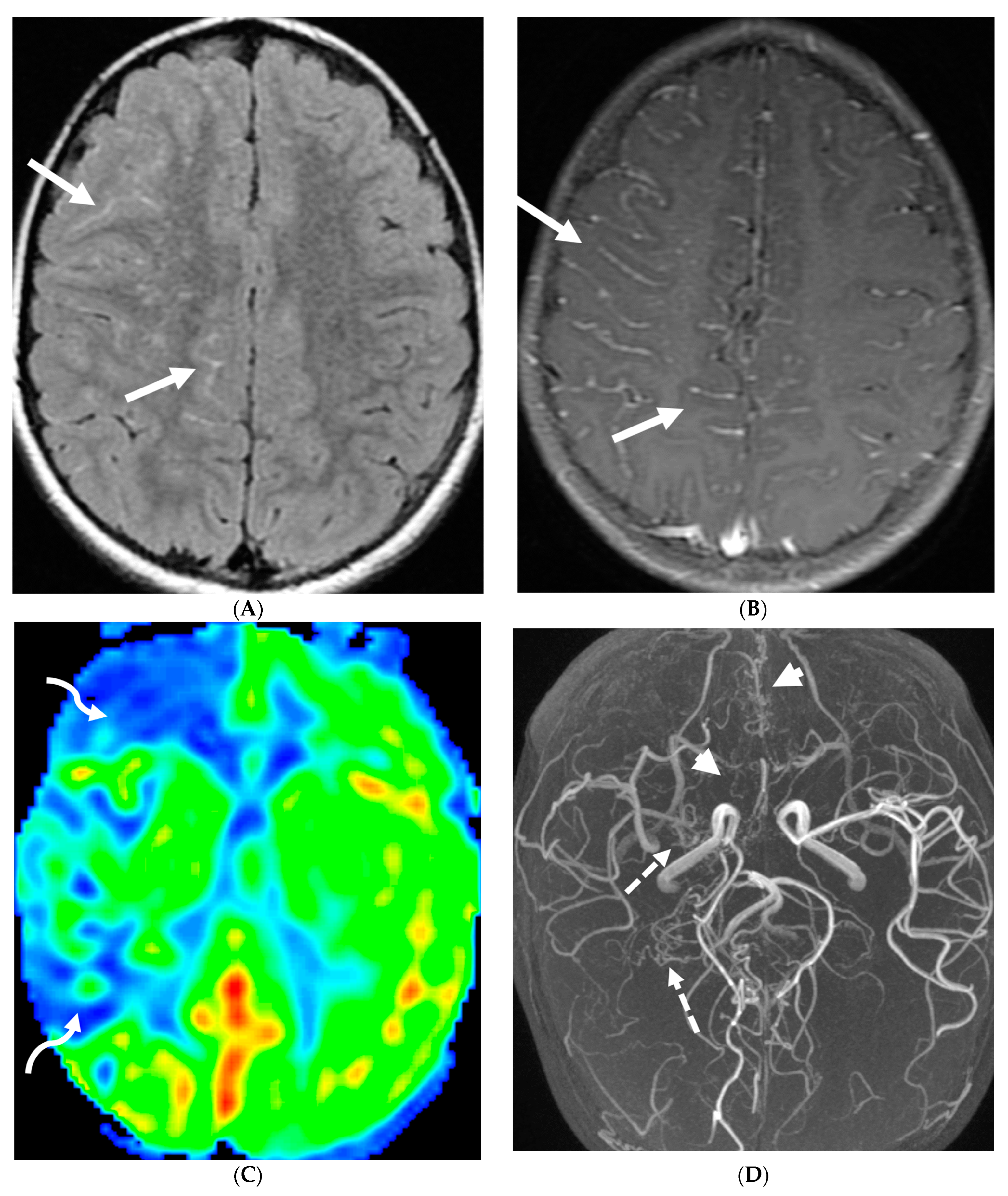
4.5. Moya Moya
5. Prominenet Parenchymal Features
5.1. Viral Meningitis
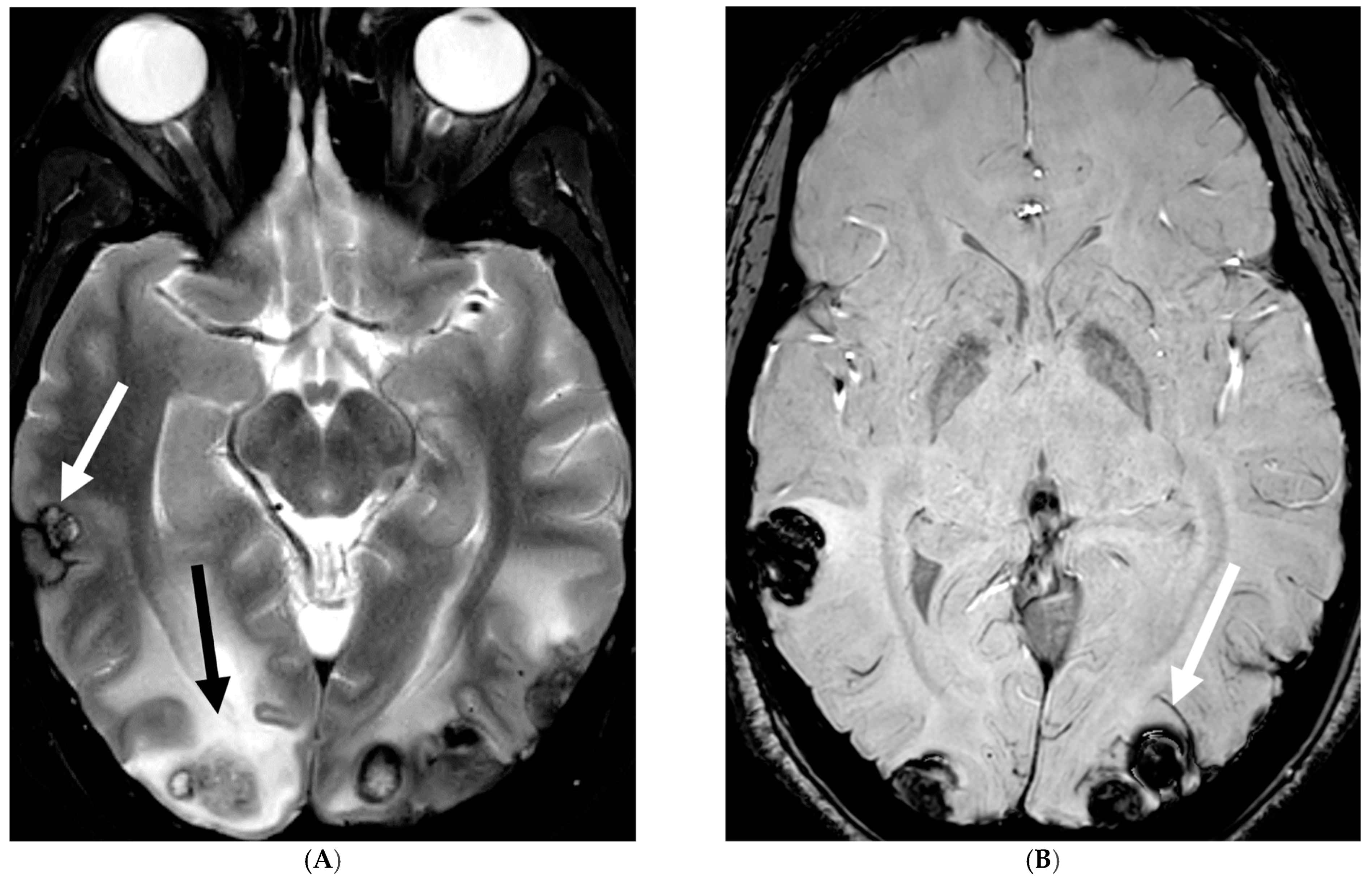
5.2. Fungal Meningitis
5.3. Anti-Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG) Demyelination
5.4. Granulomatosis Polyarteritis (GPA)
5.5. NMDA Encephalitis
5.6. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES)
5.7. Pial Angiomatosis
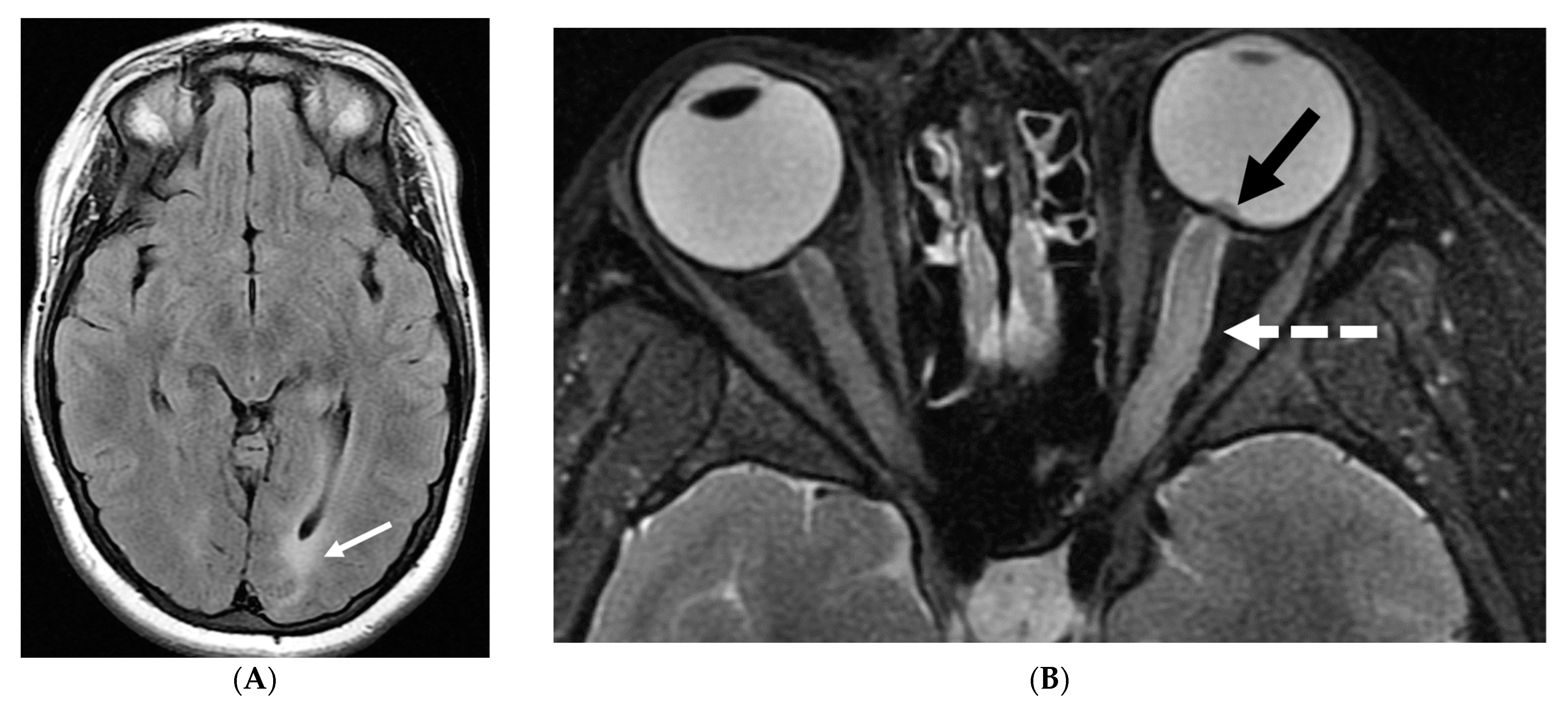
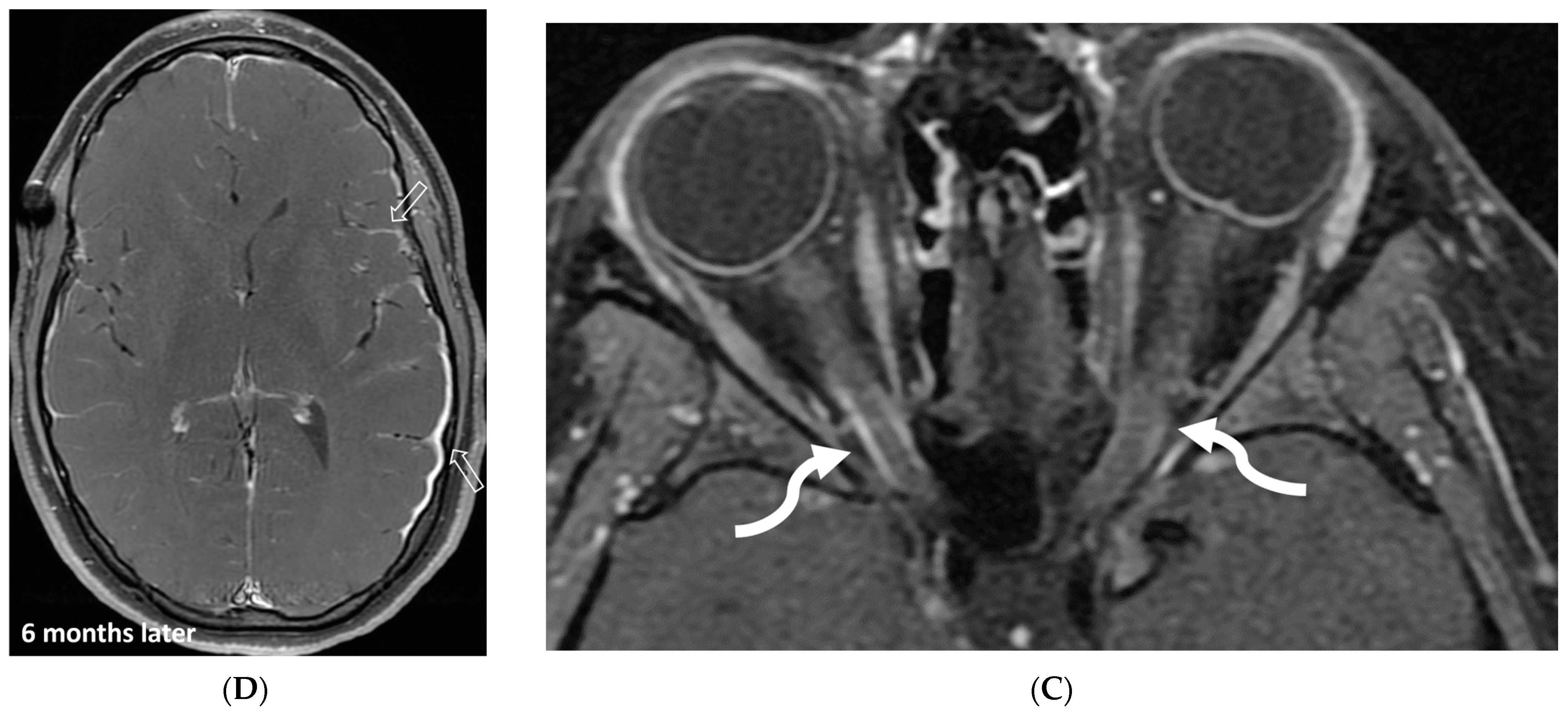
5.8. Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohan, S.; Jain, K.K.; Arabi, M.; Shah, G.V. Imaging of Meningitis and Ventriculitis. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 557–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, C.C.; Fukui, M.B.; Kanal, E.; Smirniotopoulos, J.G. MR imaging of the meninges. Part I. Normal anatomic features and nonneoplastic disease. Radiology 1996, 201, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou, G.; Goldman-Yassen, A.; Morris, M.; Dutt, M.; Philbrook, P.; Gombolay, G. Differential Diagnosis of Leptomeningeal Enhancement in the Pediatric Population (P4-4.010). Neurology 2024, 102 (Suppl. S1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrup, O.; Wanke, I.; Maschke, M. Neuroimaging of infections of the central nervous system. Semin Neurol. 2008, 28, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralik, S.; Vallejo, J.; Kukreja, M.; Salman, R.; Orman, G.; Huisman, T.; Desai, N. Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI for Detection of Meningitis in Infants. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2022, 43, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lass-Florl, C.; Mayr, A. Human Protothecosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thiele, D.; Bergmann, A. Protothecosis in human medicine. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2002, 204, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ni, F.; Xia, W. Cutaneous Protothecosis with Meningitis Due to Prototheca wickerhamii in an Immunocompetent Teenager: Case Report and Literature Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2787–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerger, T.; Sulieman, S.; Carson, V.J.; Fox, M.D. Chronic Meningitis Due to Prototheca zopfii in an Adolescent Girl. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2021, 10, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bathla, G.; Singh, A.; Policeni, B.; Agarwal, A.; Case, B. Imaging of neurosarcoidosis: Common, uncommon, and rare. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 71, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathla, G.; Watal, P.; Gupta, S.; Nagpal, P.; Mohan, S.; Moritani, T. Cerebrovascular Manifestations of Neurosarcoidosis: An Underrecognized Aspect of the Imaging Spectrum. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fritz, D.; van de Beek, D.; Brouwer, M.C. Clinical features, treatment and outcome in neurosarcoidosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jachiet, V.; Lhote, R.; Rufat, P.; Pha, M.; Haroche, J.; Crozier, S.; Dupel-Potier, C.; Psimaras, D.; Amoura, Z.; Aubart, F.C. Clinical, imaging, and histological presentations and outcomes of stroke related to sarcoidosis. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, A.; Urich, H. Sarcoidosis of the central nervous system. J. Neurol. Sci. 1969, 9, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conklin, J.; Silver, F.L.; Mikulis, D.J.; Mandell, D.M. Are acute infarcts the cause of leukoaraiosis? Brain mapping for 16 consecutive weeks. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, B.J.; Royal, W.; Gelfand, J.M.; Clifford, D.B.; Tavee, J.; Pawate, S.; Berger, J.R.; Aksamit, A.J.; Krumholz, A.; Pardo, C.A.; et al. Definition and Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Neurosarcoidosis: From the neurosarcoidosis consortium consensus group. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebel, R.; Dubaniewicz-Wybieralska, M.; Dubaniewicz, A. Overview of neurosarcoidosis: Recent advances. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shah, R.; Roberson, G.; Curé, J. Correlation of MR Imaging Findings and Clinical Manifestations in Neurosarcoidosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lexa, F.J.; Grossman, R.I. MR of sarcoidosis in the head and spine: Spectrum of manifestations and radiographic response to steroid therapy. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1994, 15, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bagnato, F.; Stern, B.J. Neurosarcoidosis: Diagnosis, therapy and biomarkers. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoforidis, G.A.; Spickler, E.M.; Recio, M.V.; Mehta, B.M. MR of CNS Sarcoidosis: Correlation of Imaging Features to Clinical Symptoms and Response to Treatment. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dumas, J.-L.; Valeyre, D.; Chapelon-Abric, C.; Belin, C.; Piette, J.-C.; Tandjaoui-Lambiotte, H.; Brauner, M.; Goldlust, D. Central Nervous System Sarcoidosis: Follow-Up at MR Imaging During Steroid Therapy. Radiology 2000, 214, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathla, G.; Freeman, C.; Moritani, T.; Song, J.; Srivastava, S.; Soni, N.; Derdeyn, C.; Mohan, S. Retrospective, dual-centre review of imaging findings in neurosarcoidosis at presentation: Prevalence and imaging sub-types. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 796.e1–796.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiò, A.; Cocito, D.; Leone, M.; Giordana, M.; Mora, G.; Mutani, R.; Piemonte, T.; Valle d’Aosta Register for Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Guillain-Barré syndrome: A prospective, population-based incidence and outcome survey. Neurology 2003, 60, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.A.C.; Rees, J.H. Clinical and Epidemiologic Features of Guillain-Barré Syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176 (Suppl. S2), S92–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, M. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barr syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27 (Suppl. S7), S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, O.; Yildirim, T.; Tokmak, N.; Tan, M. Spinal MRI Findings of Guillain-Barré Syndrome. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Winer, J.B.; Hughes, R.A.; Anderson, M.J.; Jones, D.M.; Kangro, H.; Watkins, R.P. A prospective study of acute idiopathic neuropathy. II. Antecedent events. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dimachkie, M.M.; Barohn, R.J. Guillain-Barré syndrome and variants. Neurol Clin. 2013, 31, 491–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van Doorn, P.A.; Ruts, L.; Jacobs, B.C. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulbright, R.K.; Erdum, E.; Sze, G.; Byrne, T. Cranial nerve enhancement in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1995, 16 (Suppl. S4), 923–925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yikilmaz, A.; Doganay, S.; Gumus, H.; Per, H.; Kumandas, S.; Coskun, A. Magnetic resonance imaging of childhood Guillain–Barre syndrome. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, W.M.; Park, W.K.; Park, B.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Hwang, M.S.; Chang, J.C. Guillain-Barré syndrome: MR imaging findings of the spine in eight patients. Radiology 1998, 208, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccoli, G.; Panigrahy, A.; Bailey, A.; Fitz, C. Redefining the Guillain-Barré Spectrum in Children: Neuroimaging Findings of Cranial Nerve Involvement. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Malhotra, A.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X.; Jindal, S.; Durand, D.; Makhani, N. MRI findings of optic pathway involvement in Miller Fisher syndrome in 3 pediatric patients and a review of the literature. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 39, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, E.; Sedano, M.J.; Orizaola, P.; Sánchez-Juan, P.; González-Suárez, A.; García, A.; Terán-Villagrá, N.; Ruiz-Soto, M.; Álvaro, R.L.; Berciano, M.T.; et al. Spinal nerve involvement in early Guillain–Barré syndrome: A clinico-electrophysiological, ultrasonographic and pathological study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, S.N.O.; Arumugam, T.; Yuki, N.; Rozalli, F.I.; Goh, K.-J.; Shahrizaila, N. Serial peripheral nerve ultrasound in Guillain–Barré syndrome. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosman, T.; Simonin, C.; Launay, D.; Caron, S.; Destée, A.; Defebvre, L. Idiopathic hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis treated by oral methotrexate: A case report and review of literature. Rheumatol. Int. 2008, 28, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Takahashi, H.; Wada, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Ishii, M.; Shibuya, K.; Suguro, T. Idiopathic Hypertrophic Spinal Pachymeningitis: A Case Report. J. Orthop. Surg. 2010, 18, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Virgilio, A.; de Vincentiis, M.; Inghilleri, M.; Fabrini, G.; Conte, M.; Gallo, A.; Rizzo, M.I.; Greco, A. Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis: An autoimmune IgG4-related disease. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.-K.; Cheuk, W.; Chan, K.-T.; Chan, J.K.C. IgG4-related Sclerosing Pachymeningitis: A previously unrecognized form of central nervous system involvement in IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, K.A.; Bové, R.M.; Volpicelli, E.R.; Mallery, R.M.; Stone, J.H. Relapsing course of Immunoglobulin G4-related pachymeningitis. Neurology 2012, 79, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupersmith, M.; Martin, V.; Heller, G.; Shah, A.; Mitnick, H. Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Neurology 2004, 62, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthik, S.; Bhanu, K.; Velayutham, S.; Jawahar, M. Hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2011, 14, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.P.; Flanders, A.E. Enhanced MR imaging of hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 169, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, M.; Malik, A.; Mishra, N.K.; Gaikwad, S.B. Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis: Spectrum of the disease. Neuroradiology 1997, 39, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, G.; Nair, S.; Sudhir, J.; Rao, B.R.M.; Mathew, A.; Bahuleyan, B. Childhood and adolescent meningiomas: A report of 38 cases and review of literature. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 151, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, S.; Nair, N.; Ojemann, J.G.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Avellino, A.M. Meningiomas in Children. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2008, 44, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, P.S.; Huisman, T.A.; Ahn, E.; Jordan, L.C.; Burger, P.; Cohen, K.J.; Patay, Z.; Tekes, A. Magnetic resonance imaging features of meningiomas in children and young adults: A retrospective analysis. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 39, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochat, P.; Johannesen, H.H.; Gjerris, F. Long-term follow up of children with meningiomas in Denmark: 1935 to 1984. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2004, 100 (Suppl. S2), 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenenbaum, M. Extraparenchymal Lesions in Pediatric Patients. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2017, 27, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Qiu, L.; Song, J.; Xu, D.; Sun, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Qian, J.; Yu, Z.; Peng, J. Clinical progression, pathological characteristics, and radiological findings in children with diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumors: A systematic review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 970076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferraciolli, S.F.; Tortora, M.; Godoy, L.F.d.S.; Casal, Y.R.; Lucato, L.T. Haberland Syndrome (Encephalocraniocutaneous lipomatosis) with Development of Diffuse Leptomeningeal Glioneural Tumor (DL-GNT) during Adolescence. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2024, 34, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.J.; Perry, A.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Krawitz, S.; Cohen, K.J.; Lin, D.; Mosier, S.; Lin, M.-T.; Eberhart, C.G.; Burger, P.C. Disseminated oligodendroglial-like leptomeningeal tumor of childhood: A distinctive clinicopathologic entity. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhani, D.; Mankad, K.; Chhabda, S.; Feizi, P.; Patel, R.; Sarma, A.; Pruthi, S. Diffuse Leptomeningeal Glioneuronal Tumor of Childhood. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gardiman, M.P.; Fassan, M.; Orvieto, E.; D’avella, D.; Denaro, L.; Calderone, M.; Severino, M.; Scarsello, G.; Viscardi, E.; Perilongo, G. Diffuse Leptomeningeal Glioneuronal Tumors: A New Entity? Brain Pathol. 2010, 20, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wolden, S.L.; Alektiar, K.M. Sarcomas Across the Age Spectrum. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 20, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarville, M.B.; Spunt, S.L.; Pappo, A.S. Rhabdomyosarcoma in Pediatric atients: The good, the bad, and the unusual. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korinthenberg, R.; Edel, G.; Palm, D.; Müller, K.-M.; Brandt, M.; Müller, R.-P. Primary rhabdomyosarcoma of the leptomeninx: Clinical, neuroradiological and pathological aspects. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 1984, 86, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Casas, L.E.D.L.; Dobbs, J.L.J. Primary Meningeal Rhabdomyosarcoma in a Child With Hypomelanosis of Ito. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primary Meningeal Rhabdomyosarcoma-Rahul Nikam MD, Ashrith Kandula, Tushar Chandra, MD Affiliations: Nemours/Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children, Wilmington, DE (Dr Nikam, Mr. Kandula); Nemours Children’s Hospital, Orlando, FL (Dr Chandra). Available online: https://cdn.agilitycms.com/applied-radiology/PDFs/AR_09-21_Nikam_Guerbet.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- Palta, M.; Riedel, R.F.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; Cummings, T.J.; Green, S.; Chang, Z.; Kirkpatrick, J.P. Primary Meningeal Rhabdomyosarcoma. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 312802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peterson, E.E.; Riley, B.L.; Windsor, R.B. Pediatric Intracranial Hypotension and Post-Dural Puncture Headache. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2021, 40, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievink, W.I.; Maya, M.M.; Louy, C.; Moser, F.G.; Sloninsky, L. Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension in Childhood and Adolescence. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 504–510.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, L.M.; McLean, L.A.; Heilbrun, M.E.; Salzman, K.L. Intracranial Hypotension: Improved MRI Detection With Diagnostic Intracranial Angles. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuh, E.L.; Dillon, W.P. Intracranial Hypotension and Intracranial Hypertension. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2010, 20, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, J.H.; Abrams, K.; Falcone, S.; Bhatia, R.G. Spinal Imaging Findings in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemps, P.G.; Picarsic, J.; Durham, B.H.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Hiemcke-Jiwa, L.; Bos, C.v.D.; van de Wetering, M.D.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; van Laar, J.A.M.; Verdijk, R.M.; et al. ALK-positive histiocytosis: A new clinicopathologic spectrum highlighting neurologic involvement and responses to ALK inhibition. Blood 2022, 139, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aoki, Y.; Maeda, M.; Kishi, S.; Kogue, R.; Tanaka, F.; Umino, M.; Takeoka, M.; Hanaki, R.; Hirayama, J.; Yuasa, H.; et al. Central nervous system involvement of systemic ALK-positive histiocytosis with KIF5B-ALK fusion. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 3867–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xiong, Y. Imaging features of ALK-positive histiocytosis with neurological involvement: A case report and literature review. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1333519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, H.-J.; Wang, W.-Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Yan, J.-Q.; Liu, W.-P. Multisystem ALK-positive histiocytosis: A multi-case study and literature review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.K.; Nizamani, W.M.; Ali, M.; Aneel, G.; Shahani, B.K.; Hussain, S. Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast-Enhanced FLAIR Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Diagnosis of Meningitis Correlated with CSF Analysis. ISRN Radiol. 2014, 2014, 578986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jaremko, J.L.; Moon, A.S.; Kumbla, S. Patterns of complications of neonatal and infant meningitis on MRI by organism: A 10 year review. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.S.; Khan, F.A.; Milstein, M.B.; Tolman, A.W.; Benedetti, A.; Starke, J.R.; Becerra, M.C. Treatment outcomes of childhood tuberculous meningitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, S.; Hermawan, R.; van Laarhoven, A.; Immaculata, S.; Achmad, T.H.; Ruslami, R.; Anwary, F.; Soetikno, R.D.; Ganiem, A.R.; van Crevel, R. Brain MRI findings in relation to clinical characteristics and outcome of tuberculous meningitis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krishnan, N.; Renganathan, L. Tuberculous meningitis sequelae as basal cisternal calcifications. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2016, 11, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khatri, G.D.; Krishnan, V.; Antil, N.; Saigal, G. Magnetic resonance imaging spectrum of intracranial tubercular lesions: One disease, many faces. Pol. J. Radiol. 2018, 83, e524–e535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bomanji, J.B.; Gupta, N.; Gulati, P.; Das, C.J. Imaging in Tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a017814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kralik, S.; O’Neill, D.; Kamer, A.; Rodriguez, E.; Ho, C. Radiological diagnosis of drop metastases from paediatric brain tumours using combination of 2D and 3D MRI sequences. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 902.e13–902.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.A.B.; Senerchia, A.A.; Cappellano, A.; Saba, N.; Chinelati, R.M.K.; Lederman, H. Medulloblastoma and Drop Metastasis: MRI Evaluation and Optimized Protocol. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2015, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.K.; Ditchfield, M.R.; Waters, K. Correlation of MRI and CSF cytology in the diagnosis of medulloblastoma spinal metastases. Pediatr. Radiol. 1998, 28, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisanti, C.; Carlin, C.; Banks, K.P.; Wang, D. Normal MRI Appearance and Motion-Related Phenomena of CSF. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Leeds, N.E.; Ginsberg, L.E. MR Imaging of Leptomeningeal Metastases: Comparison of Three Sequences. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 23, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porto, L.; Kieslich, M.; Bartels, M.; Schwabe, D.; Zanella, F.E.; Du Mesnil, R. Leptomeningeal metastases in pediatrics: Magnetic resonance image manifestations and correlation with cerebral spinal fluid cytology. Pediatr. Int. 2010, 52, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, M.C. A Review of Leptomeningeal Metastases in Pediatrics. J. Child Neurol. 1995, 10, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzoglou, V.; Karimi, S.; Diamond, E.L.; Lis, E.; Krol, G.; Holodny, A.I.; Young, R.J. Nonenhancing Leptomeningeal Metastases: Imaging Characteristics and Potential Causative Factors. Neurohospitalist 2016, 6, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.; Nguyen, A.; Dada, O.T.; Desai, P.D.; Ricci, J.C.; Godbole, N.B.; Pierre, K.; Lucke-Wold, B. Leptomeningeal Metastasis: A Review of the Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Methodology, and Therapeutic Landscape. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5906–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Freilich, R.J.; Krol, G.; Deangelis, L.M. Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Han, C.; Zhao, F.; Qiao, P.-G.; Wang, H.; Bao, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Yang, W.-Z.; Li, D.-S.; Duan, L. Collateral Circulation in Moyamoya Disease: A New Grading System. Stroke 2019, 50, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajmalzai, A.; Shirzai, A.; Najah, D.M. Early manifestation of Moyamoya syndrome in a 2-year-old child with Down syndrome. Radiol. Case Rep. 2021, 16, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Horie, N.; Morikawa, M.; Nozaki, A.; Hayashi, K.; Suyama, K.; Nagata, I. “Brush Sign” on Susceptibility-Weighted MR Imaging Indicates the Severity of Moyamoya Disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ohta, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kuroiwa, T. Diffuse Leptomeningeal Enhancement, “Ivy Sign,” in Magnetic Resonance Images of Moyamoya Disease in Childhood: Case report. Neurosurgery 1995, 37, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Tsuchida, C. “Ivy Sign” on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery Images in Childhood Moyamoya Disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1999, 20, 1836–1838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Z.; Han, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Bao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, L. Clinical characteristics and leptomeningeal collateral status in pediatric and adult patients with ischemic moyamoya disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Komiyama, M.; Nakajima, H.; Nishikawa, M.; Yasui, T.; Kitano, S.; Sakamoto, H. Leptomeningeal contrast enhancement in moyamoya: Its potential role in postoperative assessment of circulation through the bypass. Neuroradiology 2001, 43, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.; Eisele, P.; Ebert, A.D.; Griebe, M.; Engelhardt, B.; Szabo, K.; Hennerici, M.G.; Gass, A. Leptomeningeal contrast enhancement and blood-CSF barrier dysfunction in aseptic meningitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 2, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vossough, A.; Zimmerman, R.A.; Bilaniuk, L.T.; Schwartz, E.M. Imaging findings of neonatal herpes simplex virus type 2 encephalitis. Neuroradiology 2008, 50, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, M.; Johnson, C.E.; Sze, G. Fungal Infections of the Central Nervous System. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.W.; Kalasauskas, D.; Petraitis, V.; Petraitiene, R.; Walsh, T.J. Fungal Infections of the Central Nervous System in Children. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2017, 6, e123–e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.; Rosengart, A.; Schuetz, A.N.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Walsh, T.J. Mold infections of the central nervous system. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavito-Higuera, J.; Mullins, C.B.; Ramos-Duran, L.; Chacon, C.I.O.; Hakim, N.; Palacios, E. Fungal Infections of the Central Nervous System: A Pictorial Review. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2016, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aiken, A.H. Central Nervous System Infection. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2010, 20, 557–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Jain, K.K.; Mittal, S.K.; Kumar, S. Imaging features of central nervous system fungal infections. Neurol. India 2007, 55, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, W.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Zuo, Z.; Ma, Q.; He, S.; Jin, K. Leptomeningeal enhancement of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated encephalitis: Uncovering novel markers on contrast-enhanced fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1152235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shahriari, M.; Sotirchos, E.S.; Newsome, S.D.; Yousem, D.M. MOGAD: How It Differs From and Resembles Other Neuroinflammatory Disorders. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, J.A.; Wolf, D.S.; Keller, S.; Gombolay, G.Y. Rate of Leptomeningeal Enhancement in Pediatric Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody–Associated Encephalomyelitis. J. Child Neurol. 2021, 36, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Valencia-Sanchez, C.; Guo, Y.; Krecke, K.N.; Chen, J.J.; Redenbaugh, V.; Montalvo, M.; Elsbernd, P.M.; Tillema, J.; Lopez-Chiriboga, S.; Budhram, A.; et al. Cerebral Cortical Encephalitis in Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody-Associated Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 93, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Potentas-Policewicz, M.; Fijolek, J. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: Clinical characteristics and updates in diagnosis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1369233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fragoulis, G.E.; Lionaki, S.; Venetsanopoulou, A.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Moutsopoulos, H.M.; Tzioufas, A.G. Central nervous system involvement in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A single-center retrospective study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, X.-F.; Zhang, F.-C. Clinical analysis of nervous system involvement in ANCA-associated systemic vasculitides. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27 (Suppl. S52), S65–S69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, M.; Lai, N.; Chen, Z.; Ding, M. Central Nervous System Involvement in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: What Neurologists Need to Know. Front. Neurol. 2019, 9, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Murphy, J.M.; Gomez-Anson, B.; Gillard, J.H.; Antoun, N.M.; Cross, J.; Elliott, J.D.; Lockwood, M. Wegener Granulomatosis: MR Imaging Findings in Brain and Meninges. Radiology 1999, 213, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Soto, M.I.; Kimura, Y.; Romero-Sanchez, G.; Cienfuegos-Alvear, J.A.; Candanedo-Gonzalez, F.; Kimura-Sandoval, Y.; Sanchez-Nava, D.A.; Alonso-Ramon, I.; Hinojosa-Azaola, A. From Head to Toe: Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. RadioGraphics 2021, 41, 1973–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eran, A.; Hodes, A.; Izbudak, I. Bilateral temporal lobe disease: Looking beyond herpes encephalitis. Insights Imaging 2016, 7, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Titulaer, M.J.; McCracken, L.; Gabilondo, I.; Armangue, T.; Glaser, C.; Iizuka, T.; Honig, L.S.; Benseler, S.M.; Kawachi, I.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; et al. Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, M.-Q.; Hao, Z.-L.; Chiang, S.M.V.; Shuang, K.; Lin, M.-T.; Chi, X.-S.; Fang, J.-J.; Zhou, D.; Li, J.-M. Clinical characteristics, treatments, and outcomes of patients with anti- N -methyl- d -aspartate receptor encephalitis: A systematic review of reported cases. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 68, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabilondo, I.; Saiz, A.; Galán, L.; González, V.; Jadraque, R.; Sabater, L.; Sans, A.; Sempere, A.; Vela, A.; Villalobos, F.; et al. Analysis of relapses in anti-NMDAR encephalitis. Neurology 2011, 77, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, S.R.; Bera, K.; Waters, P.; Zuliani, L.; Maxwell, S.; Zandi, M.S.; Friese, M.A.; Galea, I.; Kullmann, D.M.; Beeson, D.; et al. N-methyl-d-aspartate antibody encephalitis: Temporal progression of clinical and paraclinical observations in a predominantly non-paraneoplastic disorder of both sexes. Brain 2010, 133 Pt 6, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kelley, B.; Patel, S.; Marin, H.; Corrigan, J.; Mitsias, P.; Griffith, B. Autoimmune Encephalitis: Pathophysiology and Imaging Review of an Overlooked Diagnosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, K.K. Isolated Leptomeningeal Enhancement in Anti-N-Methyl D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis: The Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging. J. Korean Soc. Radiol. 2022, 83, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Agarwal, A.; Kapur, G.; Altinok, D. Childhood posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Magnetic resonance imaging findings with emphasis on increased leptomeningeal FLAIR signal. Neuroradiol. J. 2015, 28, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ishikura, K.; Ikeda, M.; Hamasaki, Y.; Hataya, H.; Shishido, S.; Asanuma, H.; Nishimura, G.; Hiramoto, R.; Honda, M. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Children: Its High Prevalence and More Extensive Imaging Findings. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartynski, W.S. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome, Part 1: Fundamental Imaging and Clinical Features. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hamilton, B.E.; Nesbit, G.M. Delayed CSF Enhancement in Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 456–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aylett, S. Sturge-Weber syndrome. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2007, 10 (Suppl. S1), S55–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, C.; Pedespan, J.; Boccara, O.; Garcelon, N.; Levy, R.; Grévent, D.; Boddaert, N.; Nabbout, R. Early magnetic resonance imaging to detect presymptomatic leptomeningeal angioma in children with suspected Sturge–Weber syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.; Aylett, S.; Squier, W.; Chong, W. A Spectrum of Unusual Neuroimaging Findings in Patients with Suspected Sturge-Weber Syndrome. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jezierska, M.; Stefanowicz, J.; Romanowicz, G.; Kosiak, W.; Lange, M. Langerhans cell histiocytosis in children—A disease with many faces. Recent advances in pathogenesis, diagnostic examinations and treatment. Postepy. Dermatol. Alergol. 2018, 35, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ribeiro, B.N.d.F.; Muniz, B.C.; Marchiori, E. Langerhans cell histiocytosis with isolated meningeal involvement: Findings on magnetic resonance imaging. Radiol. Bras. 2018, 51, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pyun, J.-M.; Park, H.; Moon, K.C.; Jeon, B. Late-Onset Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis with Cerebellar Ataxia as an Initial Symptom. Case Rep. Neurol. 2016, 8, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Haroche, J.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Rollins, B.J.; Donadieu, J.; Charlotte, F.; Idbaih, A.; Vaglio, A.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Emile, J.-F.; Amoura, Z. Histiocytoses: Emerging neoplasia behind inflammation. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e113–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grois, N.; Fahrner, B.; Arceci, R.J.; Henter, J.-I.; McClain, K.; Lassmann, H.; Nanduri, V.; Prosch, H.; Prayer, D.; Histiocyte Society CNS LCH Study Group. Central Nervous System Disease in Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, 873–881.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grois, N.; Pötschger, U.; Prosch, H.; Minkov, M.; Arico, M.; Braier, J.; Henter, J.; Janka-Schaub, G.; Ladisch, S.; Ritter, J.; et al. Risk factors for diabetes insipidus in langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2006, 46, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbay, L.B.; Leite, C.d.C.; Andriola, R.S.; Pinho, P.d.C.; Lucato, L.T. Histiocytosis: A review focusing on neuroimaging findings. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2014, 72, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prayer, D.; Grois, N.; Prosch, H.; Gadner, H.; Barkovich, A.J. MR Imaging Presentation of Intracranial Disease Associated with Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grois, N.; Prosch, H.; Waldhauser, F.; Minkov, M.; Strasser, G.; Steiner, M.; Unger, E.; Prayer, D. Pineal gland abnormalities in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2004, 43, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Duverneuil, N.; Idbaih, A.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Donadieu, J.; Genereau, T.; Guillevin, R.; Chiras, J.; French Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Study Group. MRI features of neurodegenerative Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Eur. Radiol. 2006, 16, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

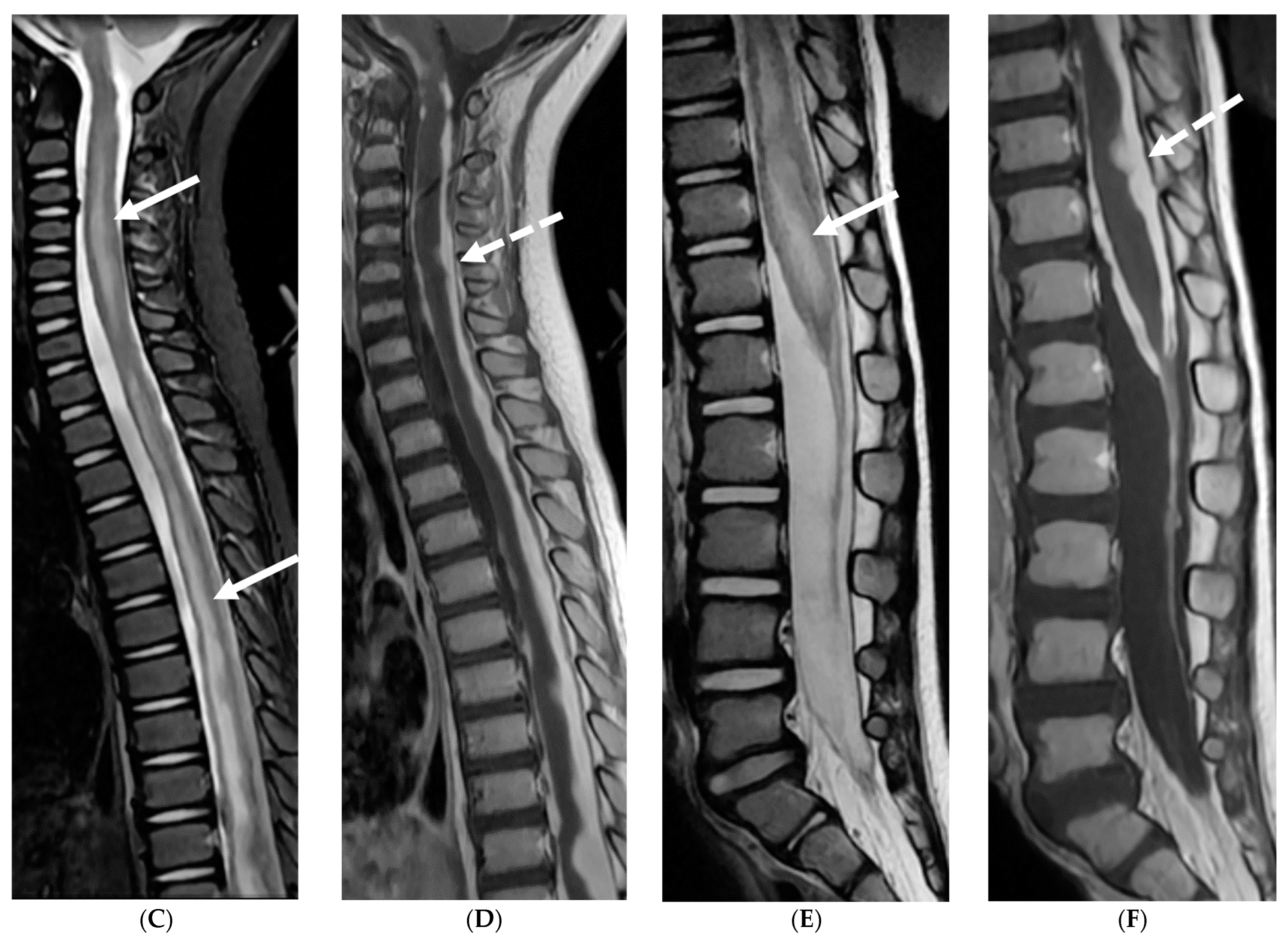
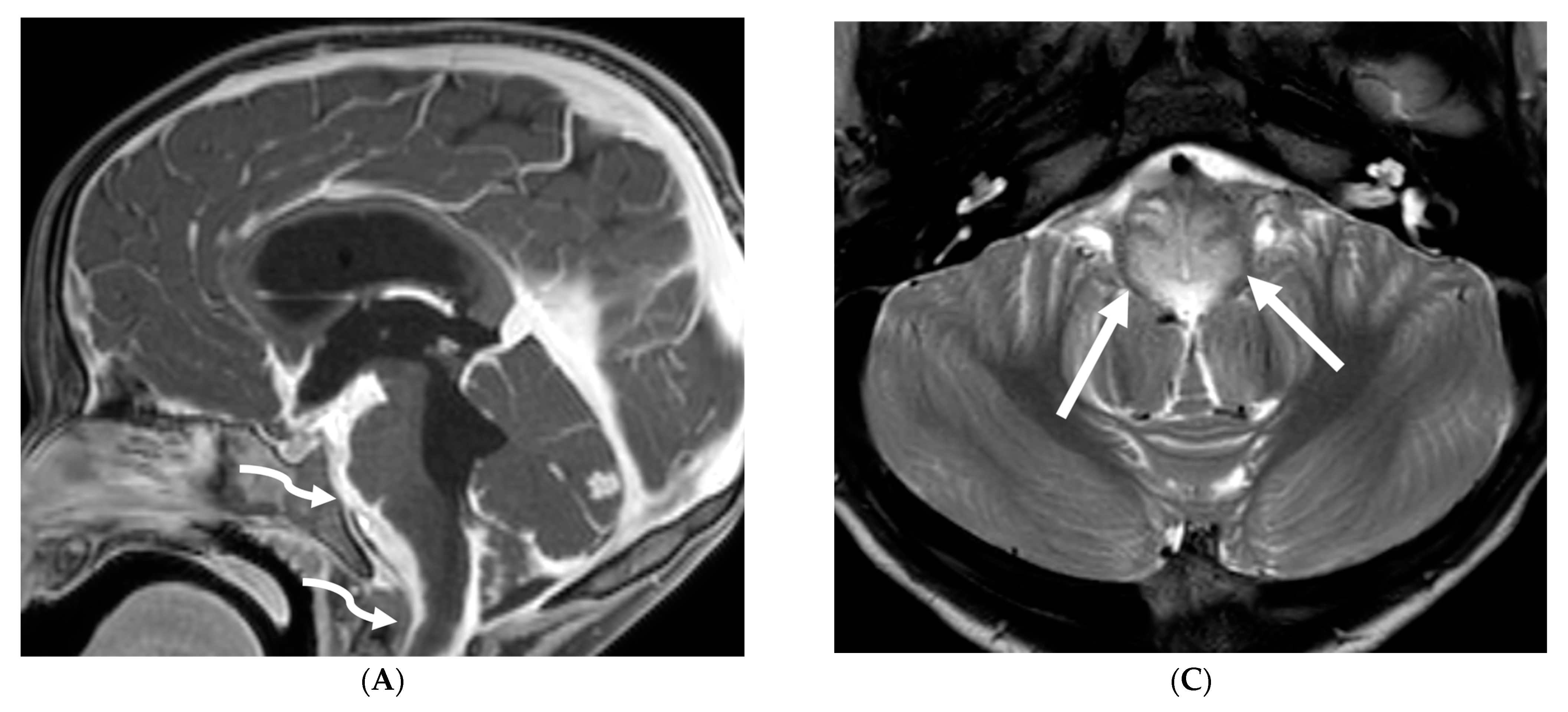



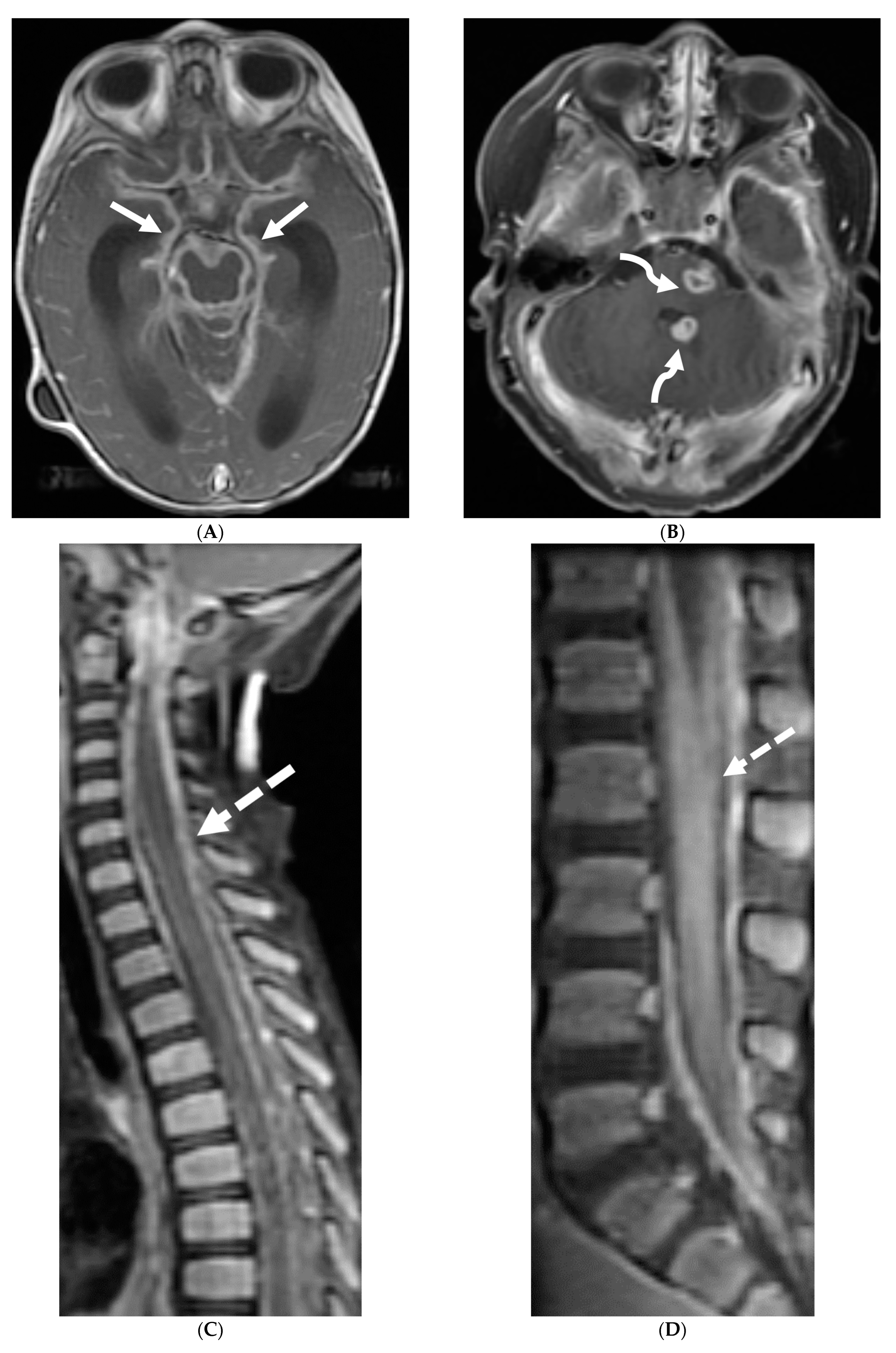
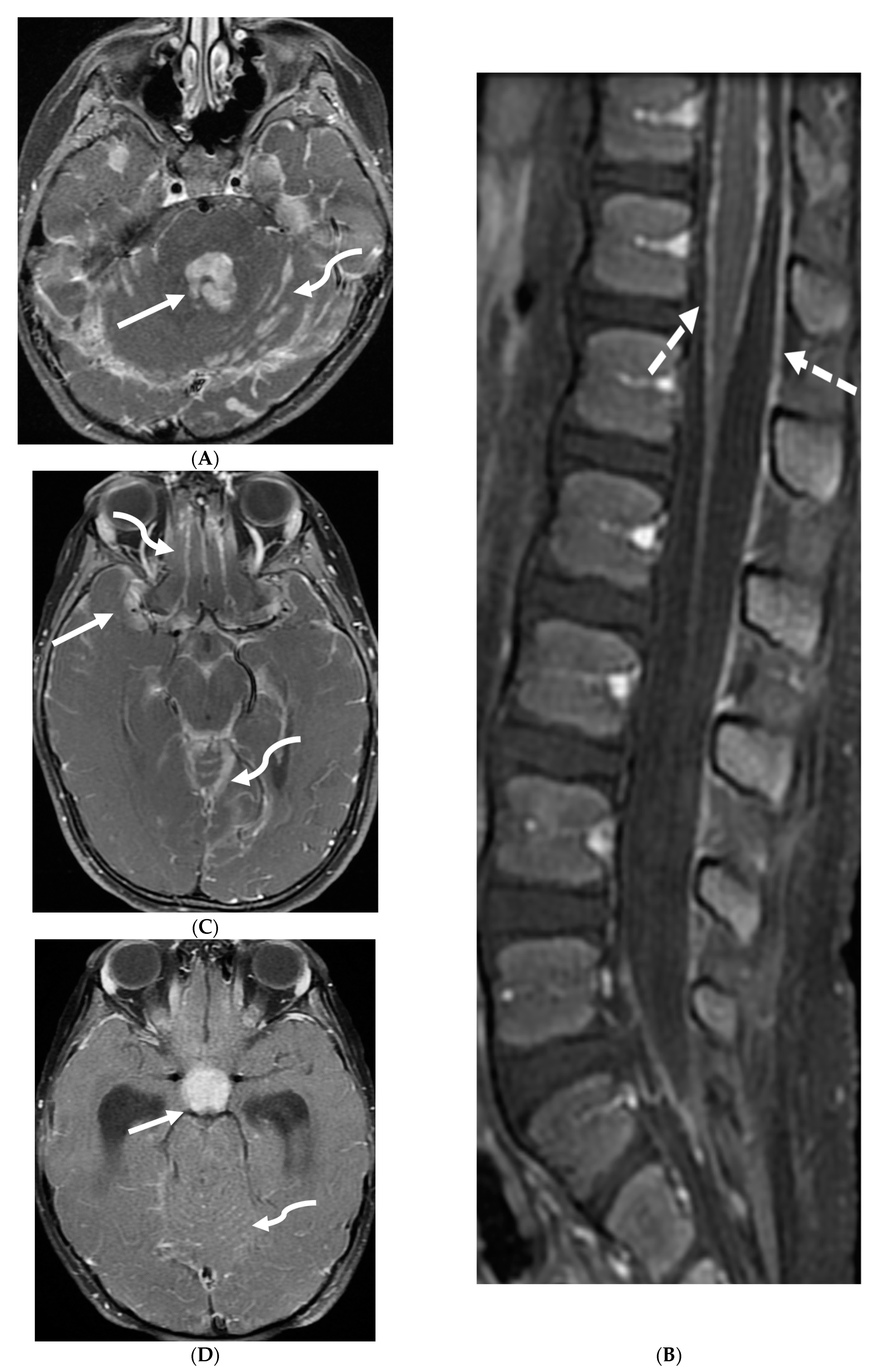

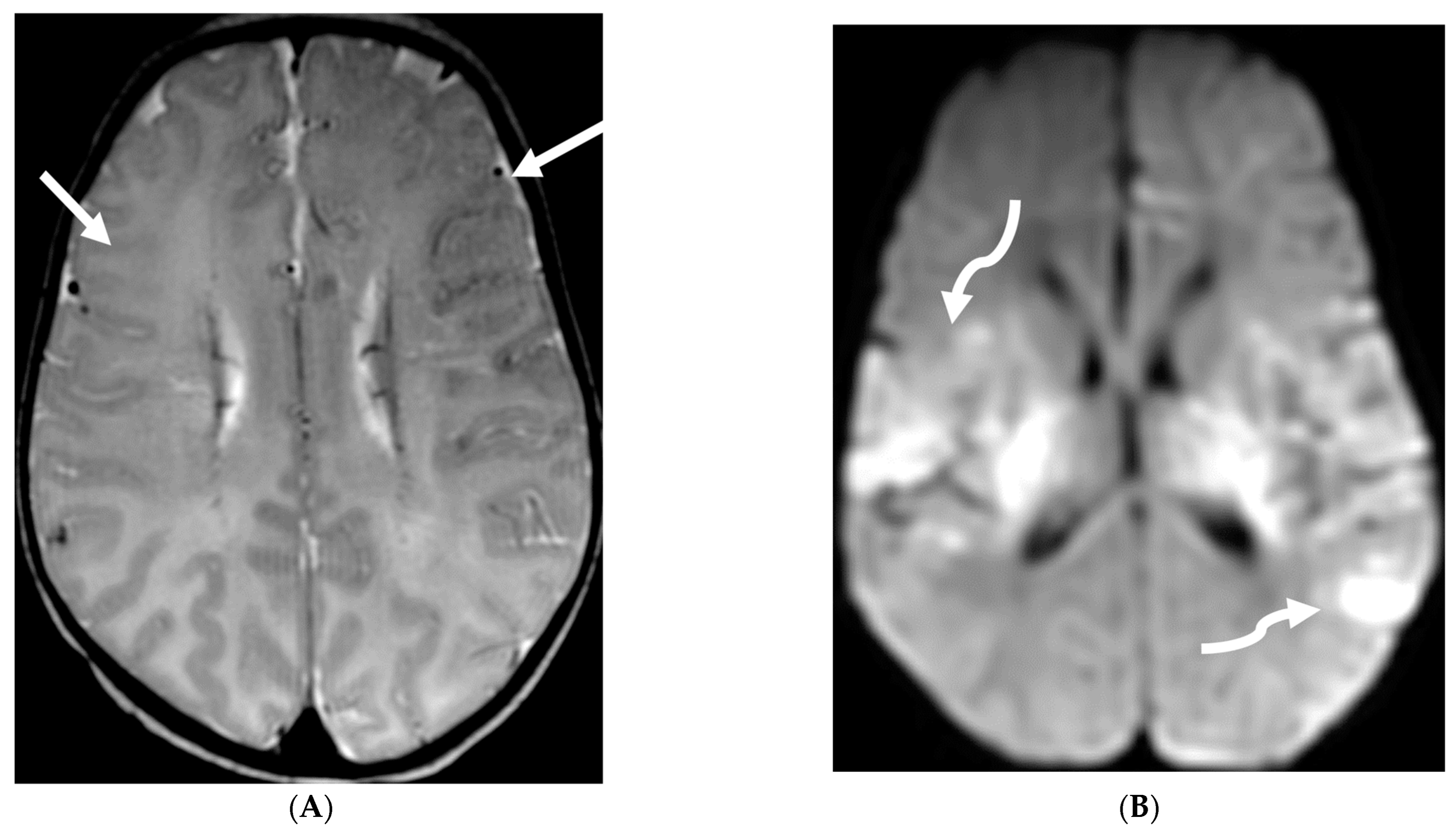
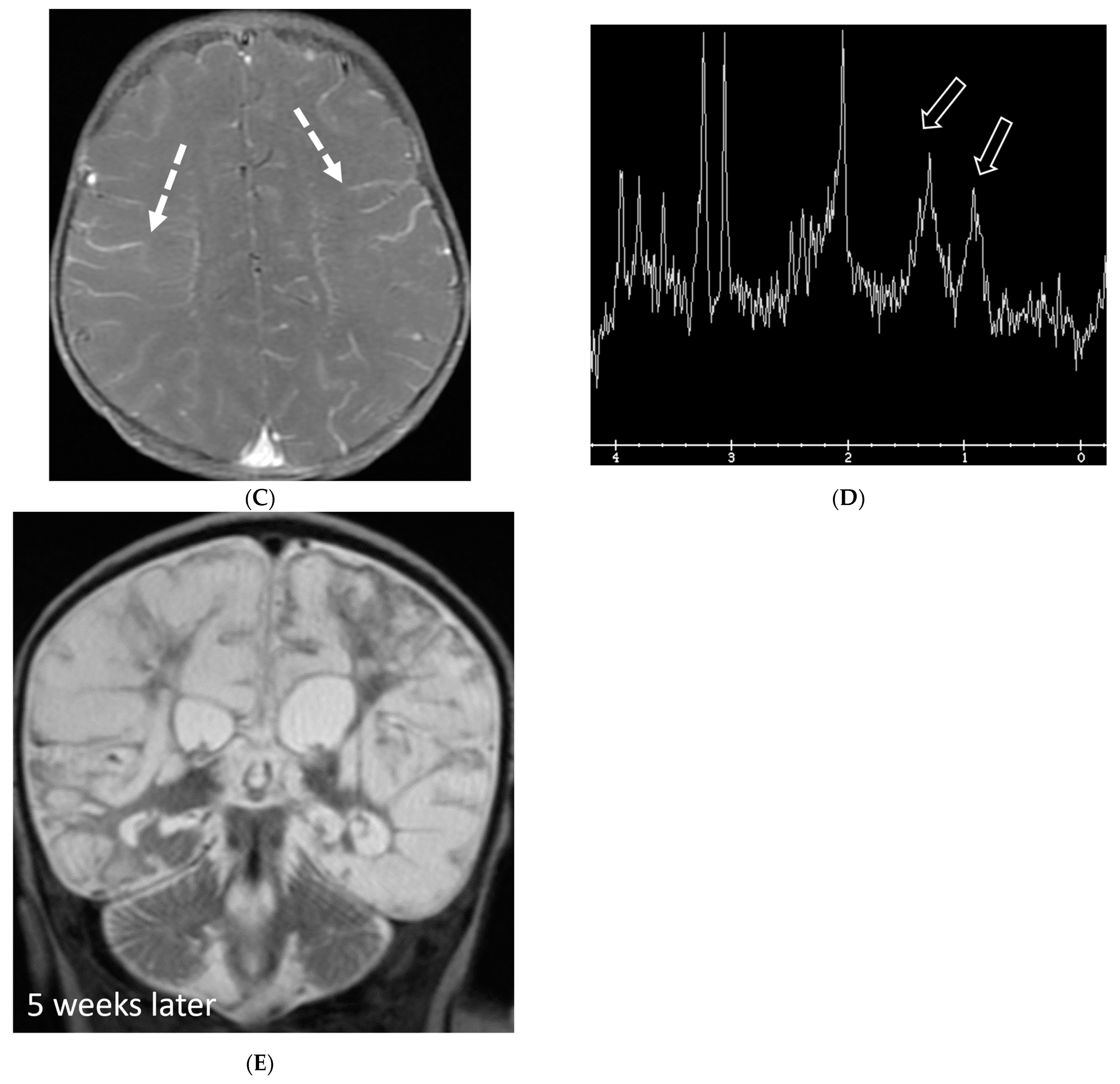

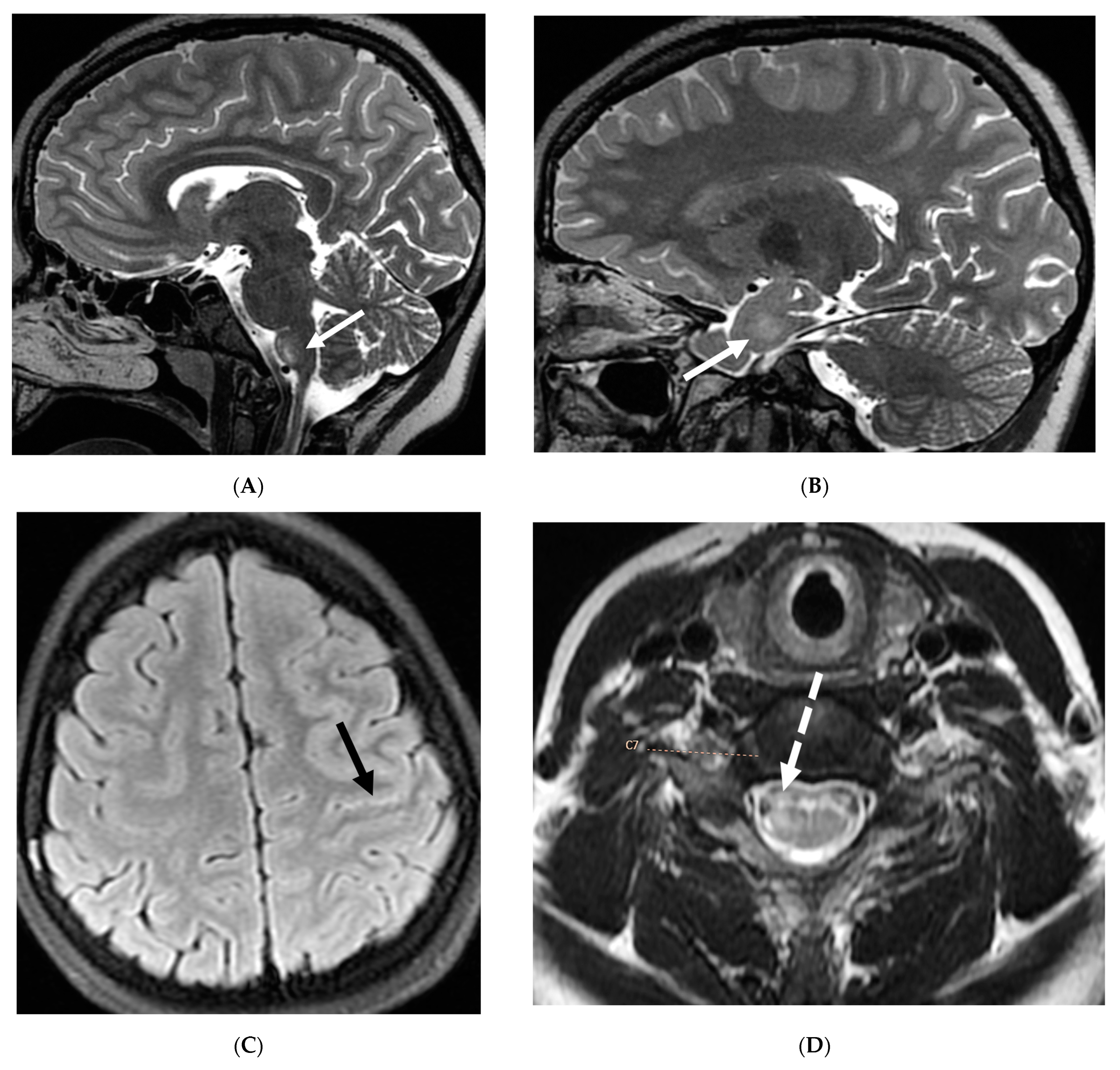
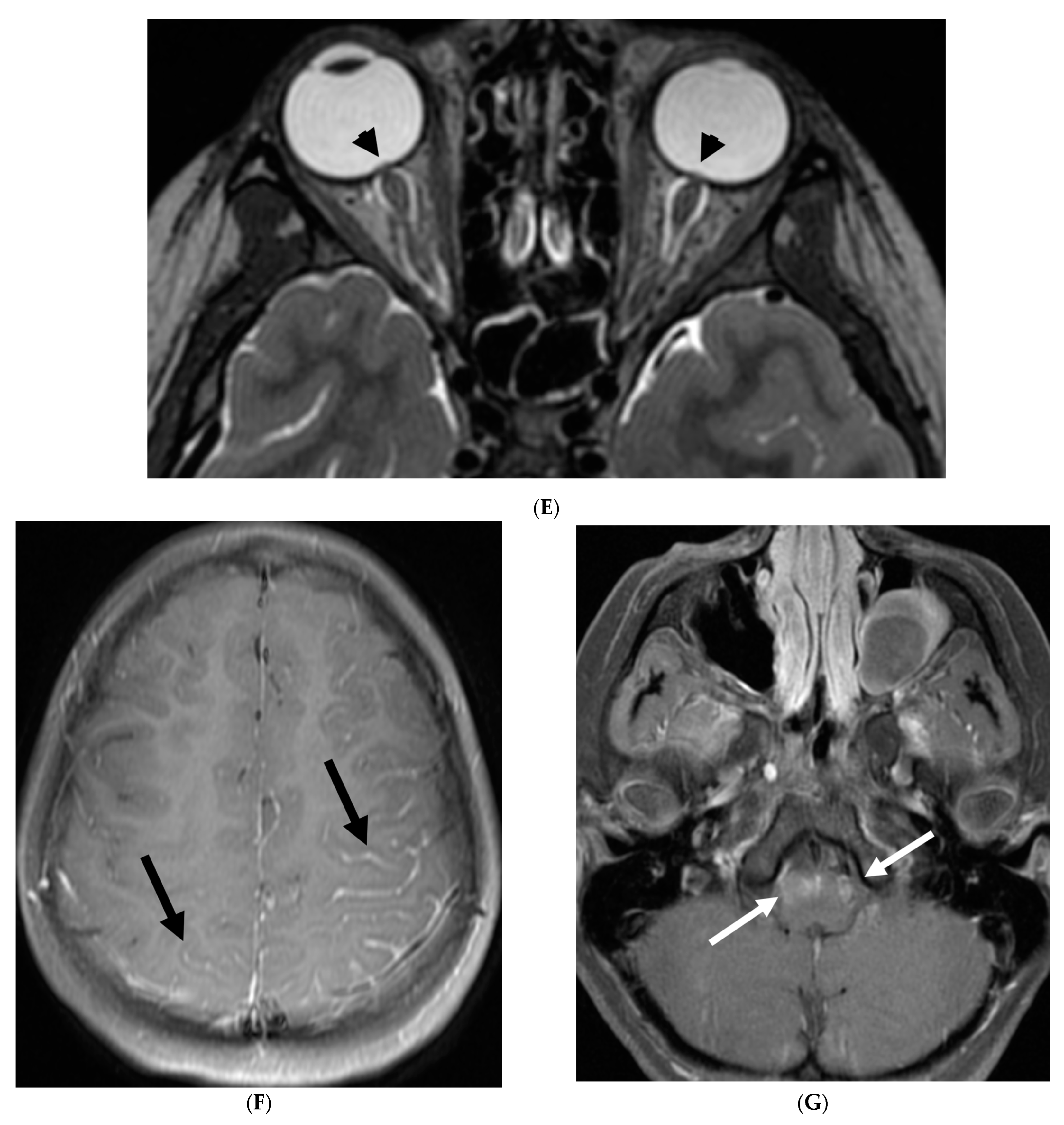
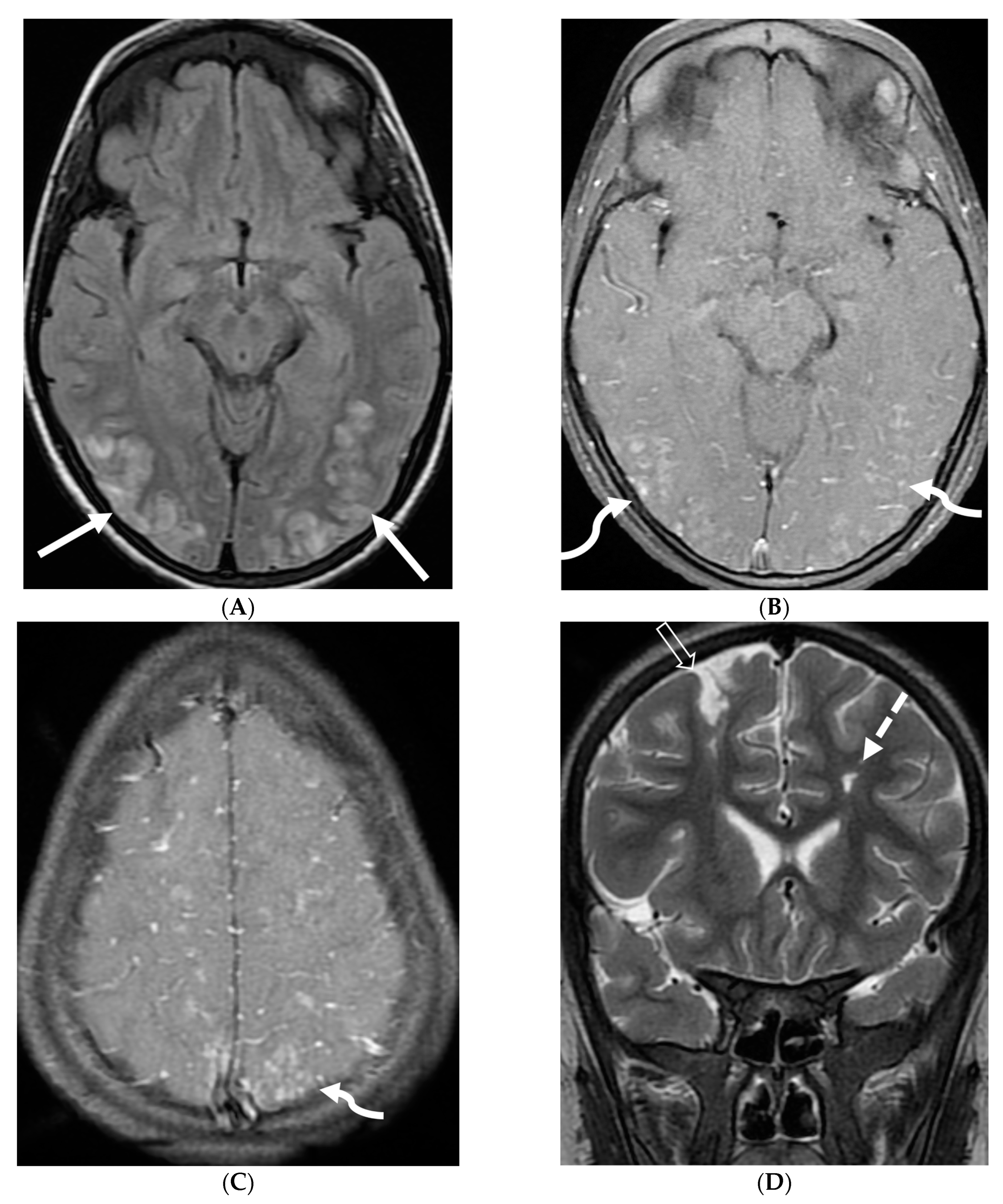
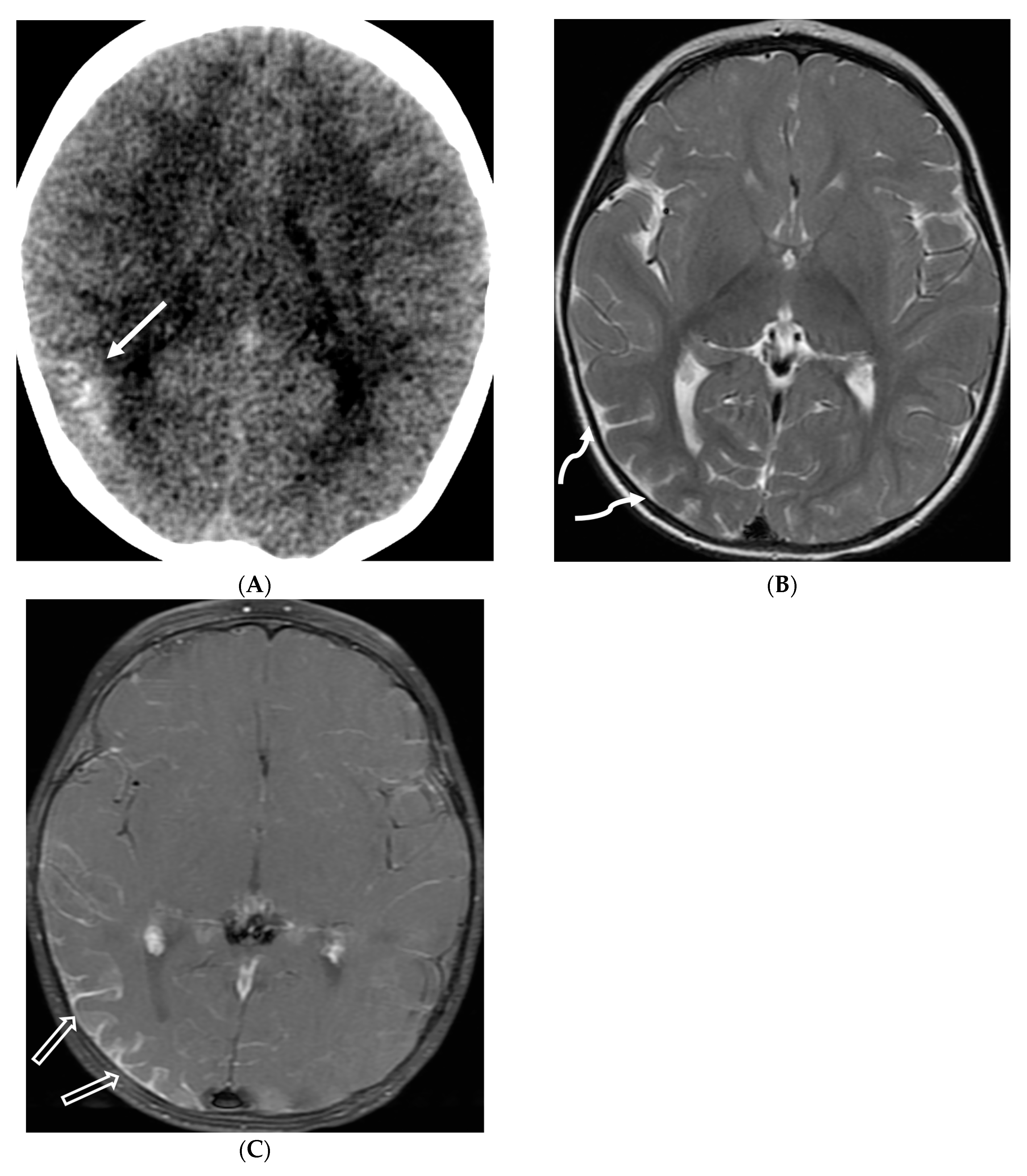
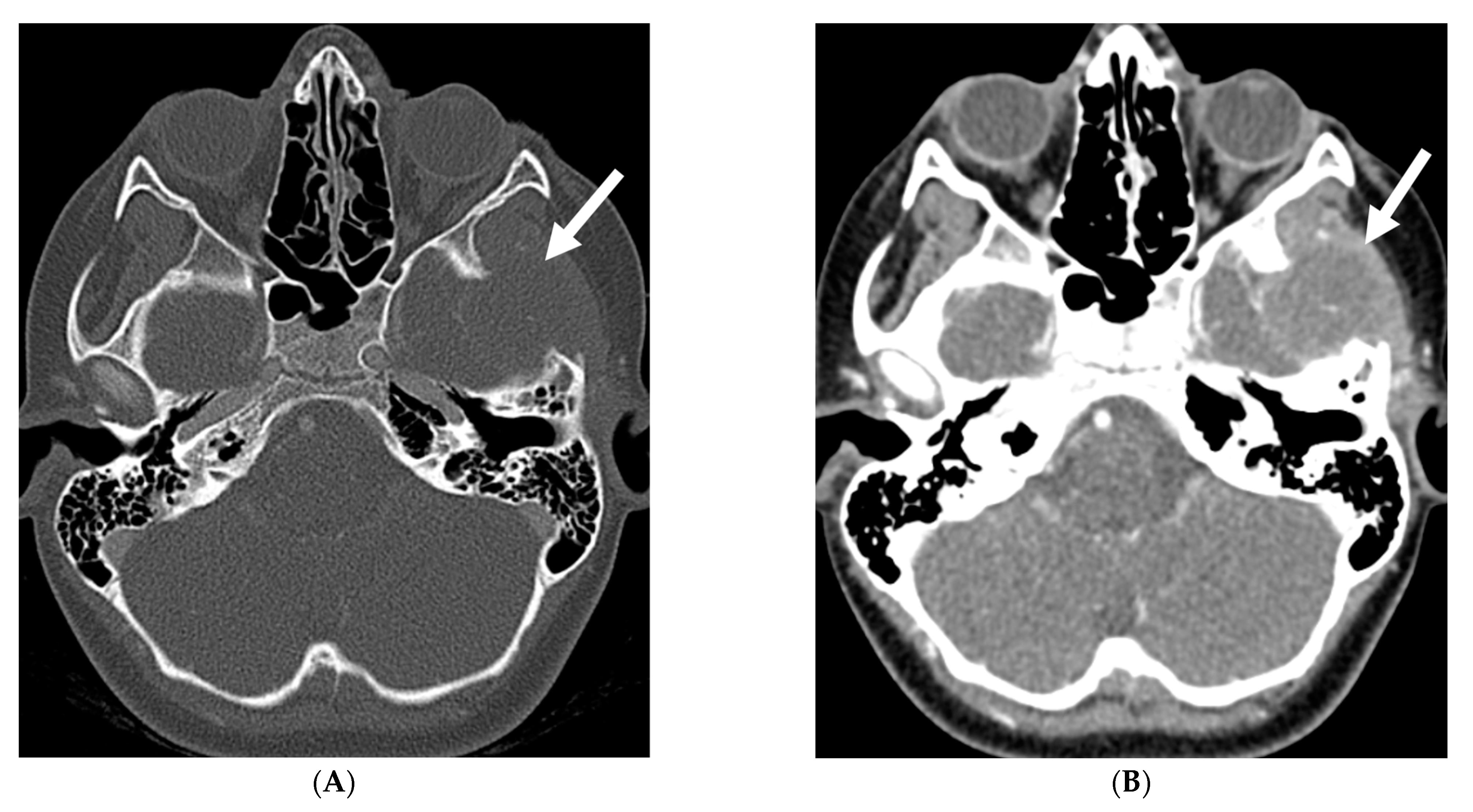

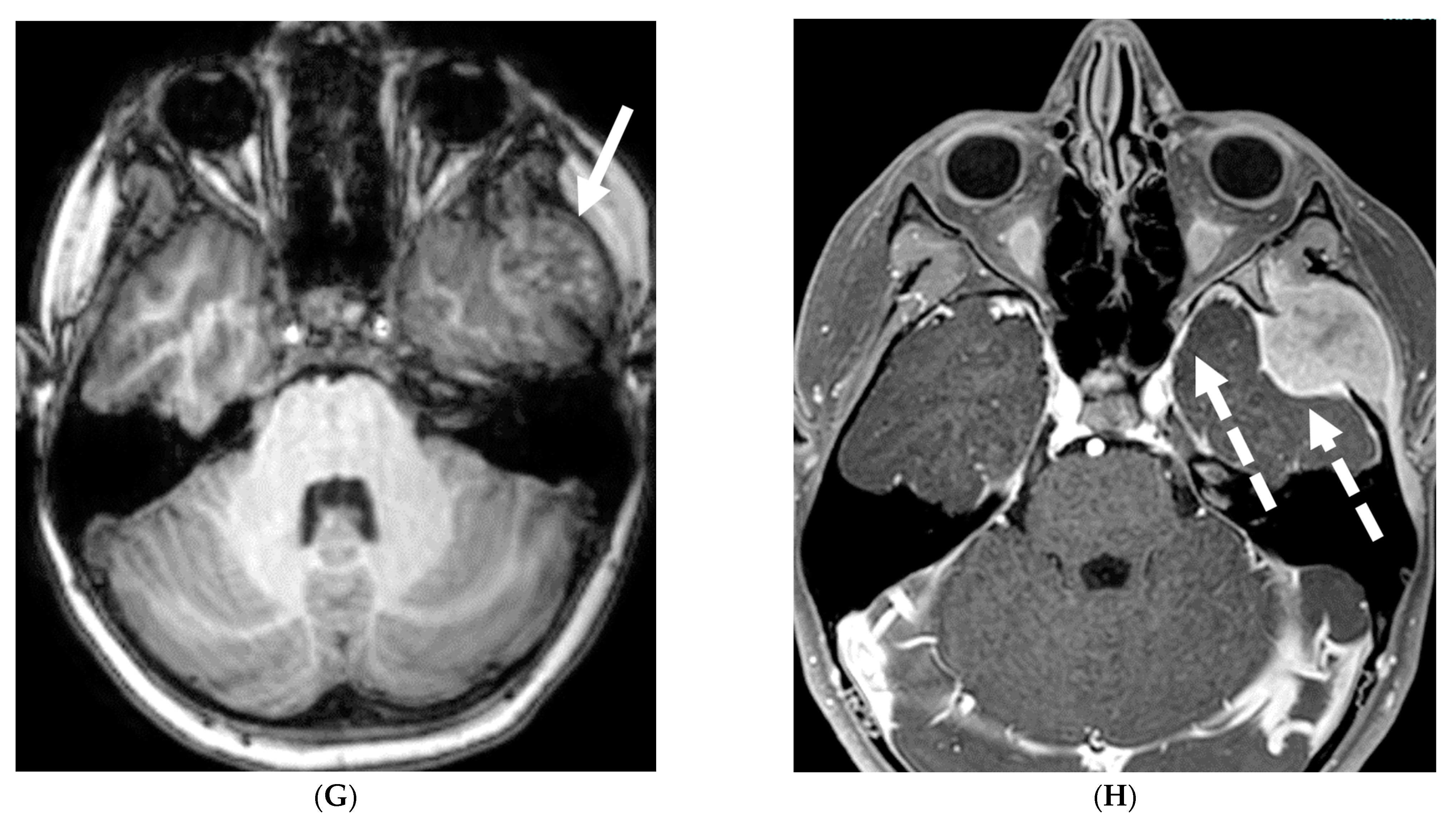
| Prominent Meningeal Features | Variable | Prominent Parenchymal Features | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infectious | Viral [Except HSV] | Group B Streptococci | HSV |
| Algae (Prototheca) | Tuberculosis | Fungal | |
| Autoimmune | Neurosarcoid | Anti-MOG Demyelination | |
| Guillian Barre Syndrome | ANCA vasculitis | ||
| Idiopathic Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis | NMDA Encephalitis | ||
| Neoplastic | Meningioma | Drop Metastasis (Primary CNS tumors) | |
| Glioneuronal tumor | Systemic Metastasis | ||
| Meningeal Rhabdomyosarcoma | |||
| Vascular | Moya Moya disease | PRES | |
| Pial Angiomatosis | |||
| Other | Intracranial hypotension | LCH | |
| ALK positive Histiocytosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, D.D.; Fenton, L.Z.; Lamture, S.; Kandula, V. Pediatric Meningeal Diseases: What Radiologists Need to Know. Tomography 2024, 10, 1970-2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10120143
Patel DD, Fenton LZ, Lamture S, Kandula V. Pediatric Meningeal Diseases: What Radiologists Need to Know. Tomography. 2024; 10(12):1970-2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10120143
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Dhrumil Deveshkumar, Laura Z. Fenton, Swastika Lamture, and Vinay Kandula. 2024. "Pediatric Meningeal Diseases: What Radiologists Need to Know" Tomography 10, no. 12: 1970-2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10120143
APA StylePatel, D. D., Fenton, L. Z., Lamture, S., & Kandula, V. (2024). Pediatric Meningeal Diseases: What Radiologists Need to Know. Tomography, 10(12), 1970-2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10120143





