Combining Transarterial Embolization and Percutaneous Cryoablation for Early-Stage Renal Cell Carcinoma: Embolization Materials and Impacts of Tumor Size
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. TAE Technique
2.3. PCA Technique
2.4. Imaging and Laboratory Examination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Transarterial Embolization
3.3. Percutaneous Cryoablation
3.4. Laboratory Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hollingsworth, J.M.; Miller, D.C.; Daignault, S.; Hollenbeck, B.K. Rising incidence of small renal masses: A need to reassess treatment effect. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.C.; Clark, P.E.; Chang, S.S.; Karam, J.A.; Souter, L.; Uzzo, R.G. Renal Mass and Localized Renal Cancer: Evaluation, Management, and Follow-Up: AUA Guideline: Part I. J. Urol. 2021, 206, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines Version 3.2024. Kidney Cancer; The National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Jen Kintown, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- European Association of Urology. Tumour ablation. In EAU Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma; European Association of Urology: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 35–39. Available online: https://d56bochluxqnz.cloudfront.net/documents/full-guideline/EAU-Guidelines-on-Renal-Cell-Carcinoma-2024.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Kowalczyk, K.J.; Choueiri, T.K.; Hevelone, N.D.; Trinh, Q.D.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Nguyen, P.L.; Lynch, J.H.; Hu, J.C. Comparative effectiveness, costs and trends in treatment of small renal masses from 2005 to 2007. BJU Int. 2013, 112, E273–E280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junker, T.; Duus, L.; Rasmussen, B.S.B.; Azawi, N.; Lund, L.; Graumann, O.; Nørgaard, B. Quality of life and complications after nephron-sparing treatment of renal cell carcinoma stage T1-a systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2022, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, B. Cryoablation versus Partial Nephrectomy for Clinical Stage T1 Renal Masses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinek, M.; Salagierski, M.; Różański, W.; Jakóbczyk, B.; Markowski, M.; Lipiński, M.; Wilkosz, J. Comparison of the Results of Therapy for cT1 Renal Carcinoma with Nephron-Sparing Surgery (NSS) vs. Percutaneous Thermal Ablation (TA). J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Attawettayanon, W.; Rathi, N.; Wilkins, L.; Roversi, G.; Zhang, A.; Accioly, J.P.E.; Shah, S.; Munoz-Lopez, C.; et al. Comprehensive Management of Renal Masses in Solitary Kidneys. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2023, 6, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Bao, E.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.H.; Yang, L.; Zhu, P.Y. Perioperative, functional, and oncological outcomes after cryoablation or partial nephrectomy for small renal masses in solitary kidneys: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Urol. 2024, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turna, B.; Kaouk, J.H.; Frota, R.; Stein, R.J.; Kamoi, K.; Gill, I.S.; Novick, A.C. Minimally invasive nephron sparing management for renal tumors in solitary kidneys. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panumatrassamee, K.; Kaouk, J.H.; Autorino, R.; Lenis, A.T.; Laydner, H.; Isac, W.; Long, J.A.; Eyraud, R.; Kassab, A.; Khalifeh, A.; et al. Cryoablation versus minimally invasive partial nephrectomy for small renal masses in the solitary kidney: Impact of approach on functional outcomes. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, G.P.; Lee, M.C.; Crouzet, S.; Kamoi, K.; Gill, I.S. Tumour in solitary kidney: Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy vs laparoscopic cryoablation. BJU Int. 2012, 109, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Albiges, L.; Bex, A.; Comperat, E.; Grünwald, V.; Kanesvaran, R.; Kitamura, H.; McKay, R.; Porta, C.; Procopio, G.; et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 692–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Shen, S.H.; Hsu, L.N.; Chiang, P.H. Comparisons of percutaneous versus retroperitoneoscopic cryoablation for renal masses. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Lindquester, W.S.; Dhangana, R.; Medsinge, A. Percutaneous ablation of renal tumors versus surgical ablation and partial nephrectomy: Medicare trends and reimbursement cost comparison from 2010 to 2018. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, R.G.; Katz, M.; Falsarella, P.M.; Malheiros, D.T.; Fukumoto, H.; Lemos, G.C.; Teich, V.; Salvalaggio, P.R. Percutaneous cryoablation versus robot-assisted partial nephrectomy of renal T1a tumors: A single-center retrospective cost-effectiveness analysis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, M.; Friedlander, J.A.; Handel, J.; Vartanian, S.; Krishnan, A.; Wong, C.Y.; Korman, H.; Seifman, B.; Ciacci, J. Percutaneous Cryoablation vs Partial Nephrectomy: Cost Comparison of T1a Tumors. J. Endourol. 2016, 30, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Uhlig, J.; Shuch, B.M.; Uhlig, A.; Kim, H.S. Cost-effectiveness of minimally invasive partial nephrectomy and percutaneous cryoablation for cT1a renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, F.; Yamada, Y.; Ueda, T.; Nakmura, T.; Naya, Y.; Kamoi, K.; Okihara, K.; Ichijo, Y.; Miki, T.; Yamada, K.; et al. Preoperative lipiodol marking and its role on survival and complication rates of CT-guided cryoablation for small renal masses. BMC Urol. 2017, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, A.J.; Mullenbach, B.J.; Poundstone, M.M.; Gordetsky, J.B.; Underwood, E.S.; Rais-Bahrami, S. Trans-Arterial Embolization of Renal Cell Carcinoma prior to Percutaneous Ablation: Technical Aspects, Institutional Experience, and Brief Review of the Literature. Curr. Urol. 2018, 12, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, J.; Loper, T.; Hood, P.; Soule, E.; Kee-Sampson, J.; Martin, J.T. Embolization-induced Renal Tumor Shrinkage Followed by Definitive Cryoablation. Cureus 2018, 10, e3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, A.J.; Mullenbach, B.J.; Poundstone, M.M.; Gordetsky, J.B.; Underwood, E.S.; Rais-Bahrami, S. Transarterial embolization of renal cell carcinoma as an adjunctive therapy prior to cryoablation: A propensity score matching analysis. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 24, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umakoshi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Matsui, Y.; Tomita, K.; Uka, M.; Kawabata, T.; Munetomo, K.; Nagata, S.; Gobara, H.; Araki, M.; et al. Renal cryoablation combined with prior transcatheter arterial embolization in non-dialysis patients with stage 4 or 5 chronic kidney disease: A retrospective study. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2023, 41, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, Y.; Miura, H.; Hirota, T.; Ota, Y.; Yamashita, M.; Asai, S.; Fujihara, A.; Hongo, F.; Ukimura, O.; Yamada, K. Transarterial ethiodised oil marking before CT-guided renal cryoablation: Evaluation of tumour visibility in various renal cell carcinoma subtypes. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salei, A.; Raymond, M.; Savage, C.; Huang, J.; Caridi, T.M.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; Gunn, A.J. Transarterial embolization of T1b and T2a renal cell carcinoma prior to percutaneous cryoablation: A retrospective comparative study. Abdom. Radiol. 2023, 48, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobara, H.; Matsui, Y.; Uka, M.; Tomita, K.; Umakoshi, N.; Araki, M.; Sakurai, J.; Iguchi, T.; Hiraki, T. Percutaneous cryoablation combined with prior transcatheter arterial embolization for renal cell carcinomas of 3 cm or larger: A prospective study. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiwara, K.; Yoshimatsu, R.; Komoto, M.; Maeda, H.; Yamanishi, T.; Minamiguchi, H.; Karashima, T.; Inoue, K.; Awai, K.; Yamagami, T. Efficacy and safety of CT-guided cryoablation after lipiodol marking and embolization for RCC. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2022, 31, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michimoto, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kameoka, Y.; Sadaoka, S.; Miki, J.; Kishimoto, K. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization with a Mixture of Absolute Ethanol and Iodized Oil for Poorly Visualized Endophytic Renal Masses Prior to CT-Guided Percutaneous Cryoablation. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 39, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Rouvière, O. Renal artery embolization-indications, technical approaches and outcomes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.S.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, Z.B.; Zhu, K.S.; Guan, S.H.; Li, Z.R.; Shan, H. Comparison of long-term effects between intra-arterially delivered ethanol and Gelfoam for the treatment of severe arterioportal shunt in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwell, T.D.; Vlaminck, J.J.; Boorjian, S.A.; Kurup, A.N.; Callstrom, M.R.; Weisbrod, A.J.; Lohse, C.M.; Hartman, W.R.; Stockland, A.H.; Leibovich, B.C.; et al. Percutaneous cryoablation of stage T1b renal cell carcinoma: Technique considerations, safety, and local tumor control. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Enoki, K.; Kameoka, Y.; Motohashi, K.; Yanagisawa, T.; Miki, J.; Baba, A.; Sekiguchi, H.; Sadaoka, S. Image-guided percutaneous cryoablation of T1b renal cell carcinomas in patients with comorbidities. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2021, 39, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, A.J.; Joe, W.B.; Salei, A.; El Khudari, H.; Mahmoud, K.H.; Bready, E.; Keasler, E.M.; Patten, P.P.; Gordetsky, J.B.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; et al. Percutaneous Cryoablation of Stage T1b Renal Cell Carcinoma: Safety, Technical Results, and Clinical Outcomes. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Gobara, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Takaki, H.; Sato, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Yamakado, K. Radiofrequency ablation versus cryoablation for T1b renal cell carcinoma: A multi-center study. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2018, 36, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grange, R.; Tradi, F.; Izaaryene, J.; Daidj, N.; Brunelle, S.; Walz, J.; Gravis, G.; Piana, G. Computed tomography-guided percutaneous cryoablation of T1b renal tumors: Safety, functional and oncological outcomes. Int. J. Hyperth. 2019, 36, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, P.A.; Zargar, H.; Ramirez, D.; Andrade, H.S.; Akca, O.; Gao, T.; Kaouk, J.H. Cryoablation versus Partial Nephrectomy for Clinical T1b Renal Tumors: A Matched Group Comparative Analysis. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attawettayanon, W.; Kazama, A.; Yasuda, Y.; Zhang, J.J.H.; Shah, S.; Rathi, N.; Munoz-Lopez, C.; Lewis, K.; Li, J.; Beksac, A.T.; et al. Thermal Ablation Versus Partial Nephrectomy for cT1 Renal Mass in a Solitary Kidney: A Matched Cohort Comparative Analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
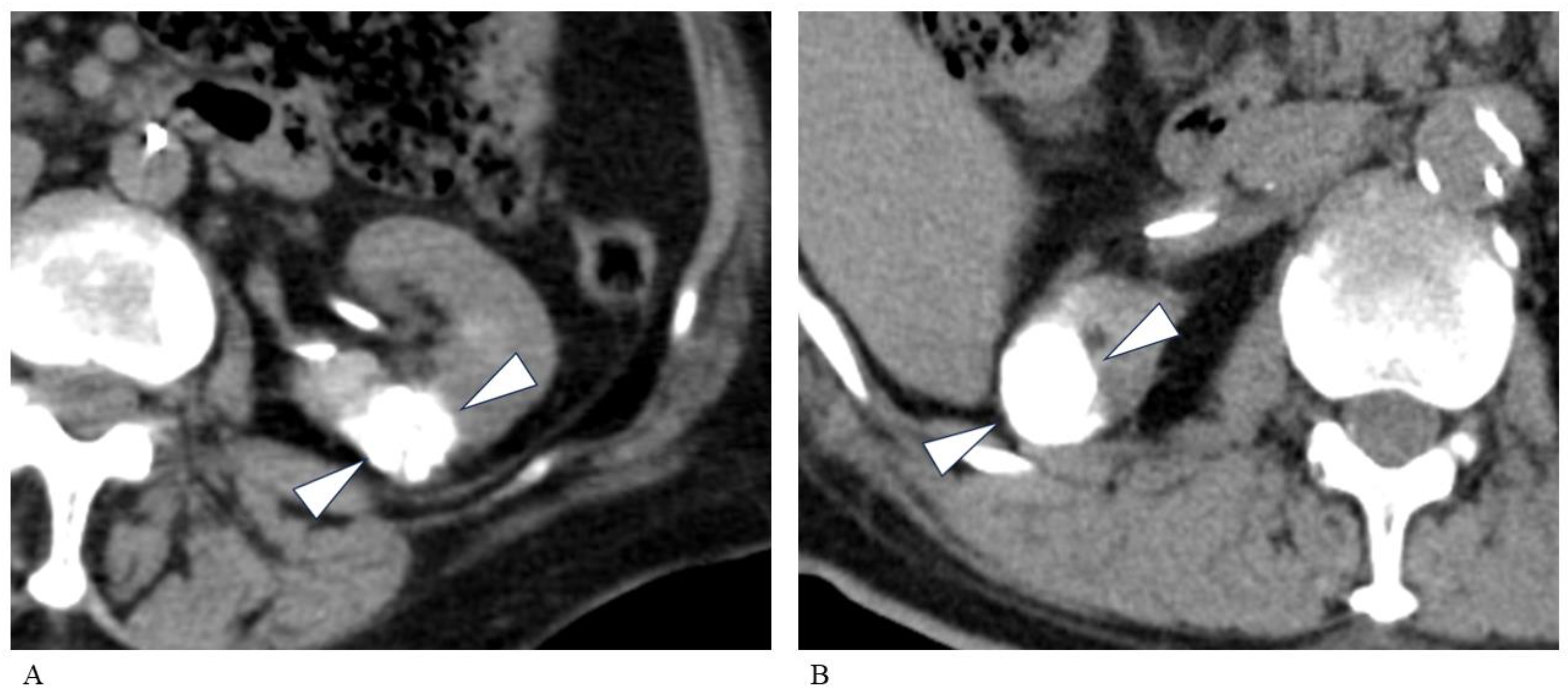
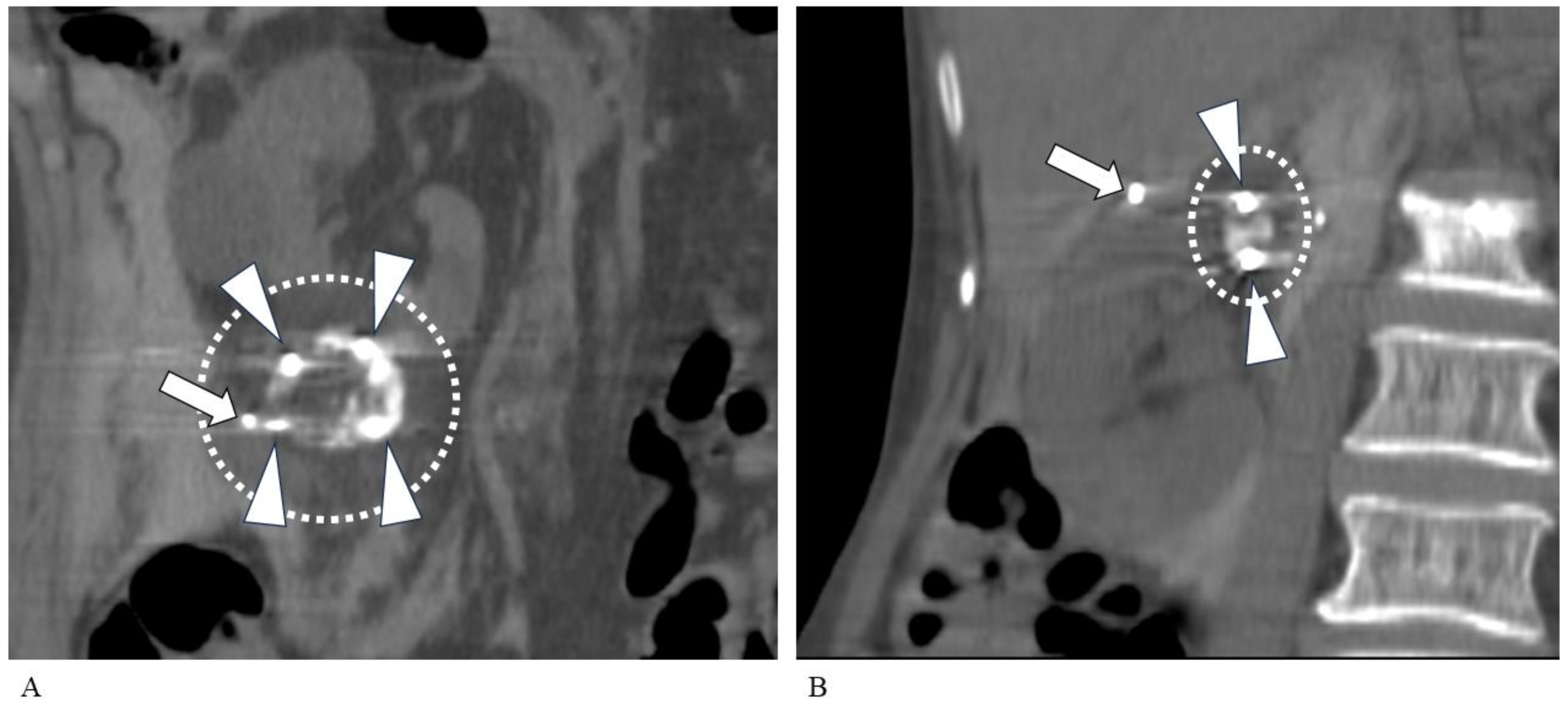

| Sex, M/F | 18/9 |
| Patient age a | 74 (16) |
| Tumor side (right/left) b | 14/14 |
| Tumor size (mm) a | 24.8 (7.2) |
| Embolization with absolute ethanol and iodized oil | 14 (F/M = 6/8) |
| Embolization with gelatin sponge and iodized oil | 13 (F/M = 3/10) |
| Total RCC (n = 28) | Absolute Ethanol and Iodized Oil (n = 15) a | Gelatin Sponge and Iodized Oil (n = 13) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor size (mm) b | 24.8 (7.2) | 23.9 (7.5) | 25.7 (7.5) | NS |
| Operative time (min) b | 71.4 (33.2) | 81.7 (39.0) | 60.4 (20.3) | NS |
| Number of patients who complained of pain during the procedure | 3 | 3 | 0 | <0.05 (0.038) |
| Iodized oil accumulation b,c | 2.1 (0.7) | 1.7 (0.6) | 2.6 (0.6) | <0.01 (0.002) |
| Vascularity (hyper/hypo) | 24/4 | 12/3 | 12/1 | NS |
| Clinical Characteristic | p Value a | |
|---|---|---|
| Operative time (min) b | 172.4 (42.0) | - |
| Tumor location (upper/middle/lower kidney) | 6/14/8 | NS |
| Hydrodissection (implemented/not implemented) | 22/6 | NS |
| Iodized oil accumulation by TAE (poor/fair/good) | 6/12/10 | NS |
| Vascularity on TAE (hyper/hypo) | 24/4 | NS |
| Embolic material (absolute ethanol/gelatin sponge) | 15/13 | NS |
| Operative Time/Options | Correlation Coefficient (ρ) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAE | Operative time | −0.09 | NS (0.64) |
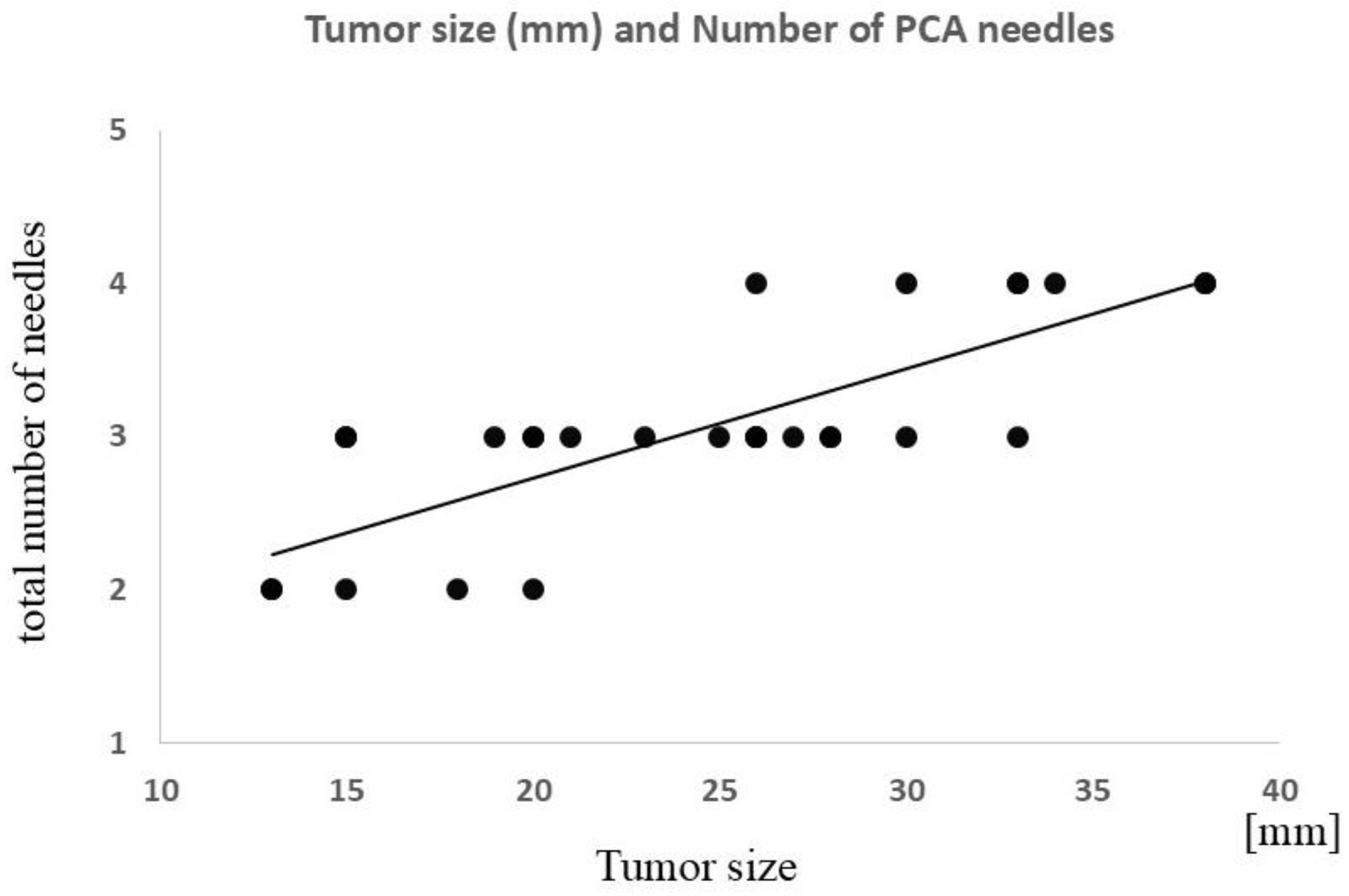
| PCA | Operative time | 0.55 | <0.01 (0.002) |
| Total number of cryoneedles | 0.78 | <0.0001 | |
| Pre-TAE | Post-PCA | Change Between Pre-TAE and Post-PCA | Absolute Ethanol and Iodized Oil | Gelatin Sponge and Iodized Oil | p Value d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/dL) (n = 26) a,b | 0.23 (0.56) | 2.69 (2.75) | 2.46 (2.65) ↑ (p < 0.0001) | 3.37 (3.32) ↑ (n = 14) | 1.40 (0.50) ↑ (n = 12) | NS |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) (n = 28) b,c | 47.2 (22.1) | 44.6 (22.8) | 2.6 (8.1) ↓ (NS, p = 0.05) | 1.8 (9.7) ↓ (n = 15) | 3.5 (5.5) ↓ (n = 13) | NS |
| Hb (g/dL) (n = 28) b,c | 13.0 (1.9) | 12.4 (2.1) | 0.6 (0.8) ↓ (p < 0.001) | 0.7 (0.9) ↓ (n = 15) | 0.4 (0.6) ↓ (n = 13) | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terauchi, M.; Yamashiro, T.; Sawamura, S.; Koyama, S.; Nakaigawa, N.; Kondo, K.; Hasumi, H.; Makiyama, K.; Utsunomiya, D. Combining Transarterial Embolization and Percutaneous Cryoablation for Early-Stage Renal Cell Carcinoma: Embolization Materials and Impacts of Tumor Size. Tomography 2024, 10, 1767-1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10110130
Terauchi M, Yamashiro T, Sawamura S, Koyama S, Nakaigawa N, Kondo K, Hasumi H, Makiyama K, Utsunomiya D. Combining Transarterial Embolization and Percutaneous Cryoablation for Early-Stage Renal Cell Carcinoma: Embolization Materials and Impacts of Tumor Size. Tomography. 2024; 10(11):1767-1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10110130
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerauchi, Miki, Tsuneo Yamashiro, Shungo Sawamura, Shingo Koyama, Noboru Nakaigawa, Keiichi Kondo, Hisashi Hasumi, Kazuhide Makiyama, and Daisuke Utsunomiya. 2024. "Combining Transarterial Embolization and Percutaneous Cryoablation for Early-Stage Renal Cell Carcinoma: Embolization Materials and Impacts of Tumor Size" Tomography 10, no. 11: 1767-1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10110130
APA StyleTerauchi, M., Yamashiro, T., Sawamura, S., Koyama, S., Nakaigawa, N., Kondo, K., Hasumi, H., Makiyama, K., & Utsunomiya, D. (2024). Combining Transarterial Embolization and Percutaneous Cryoablation for Early-Stage Renal Cell Carcinoma: Embolization Materials and Impacts of Tumor Size. Tomography, 10(11), 1767-1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10110130






