Examination of Various Abutment Designs Behavior Depending on Load Using Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
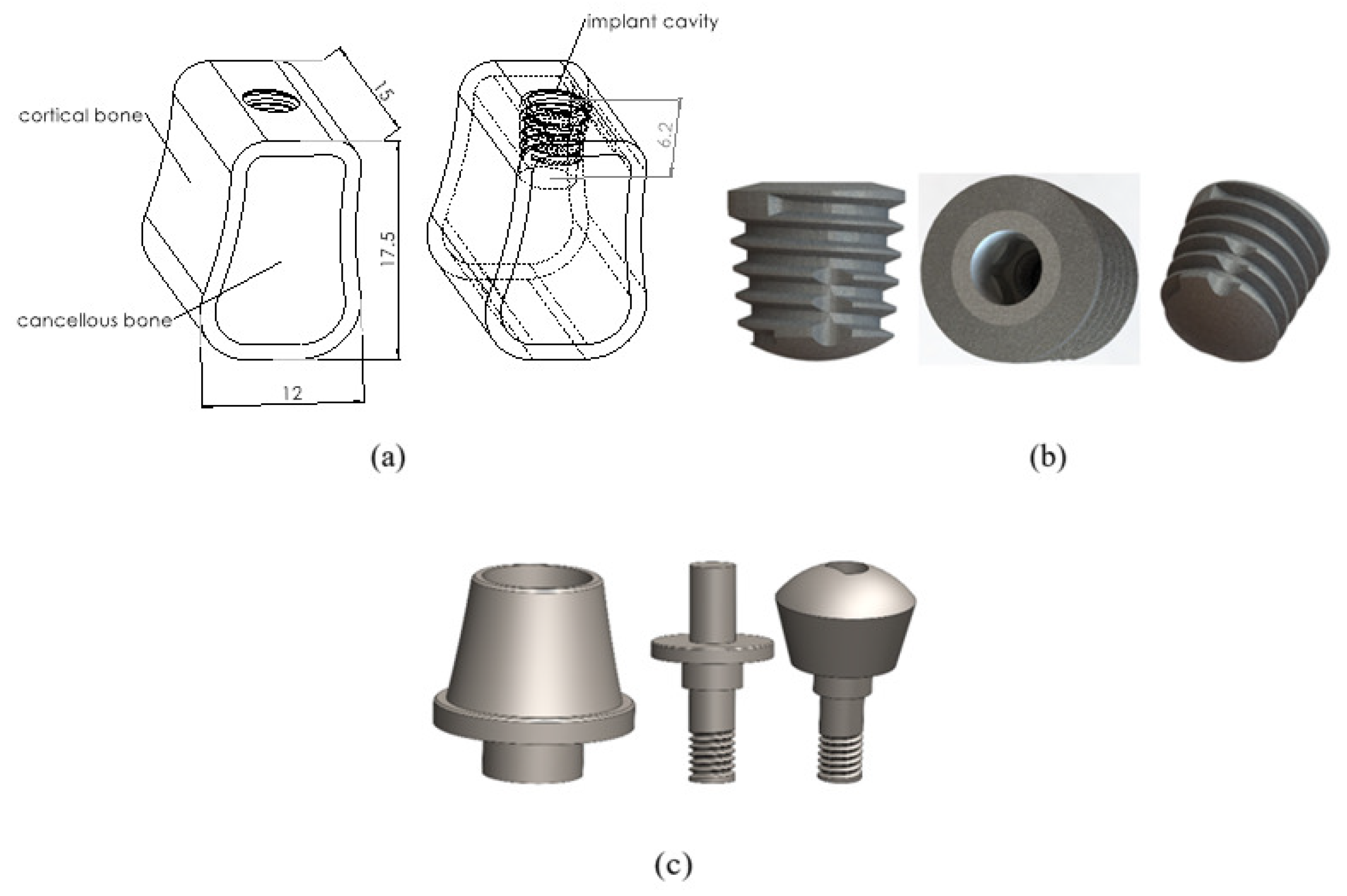
2.1. Bone Model and Material
2.2. Implant Model and Material
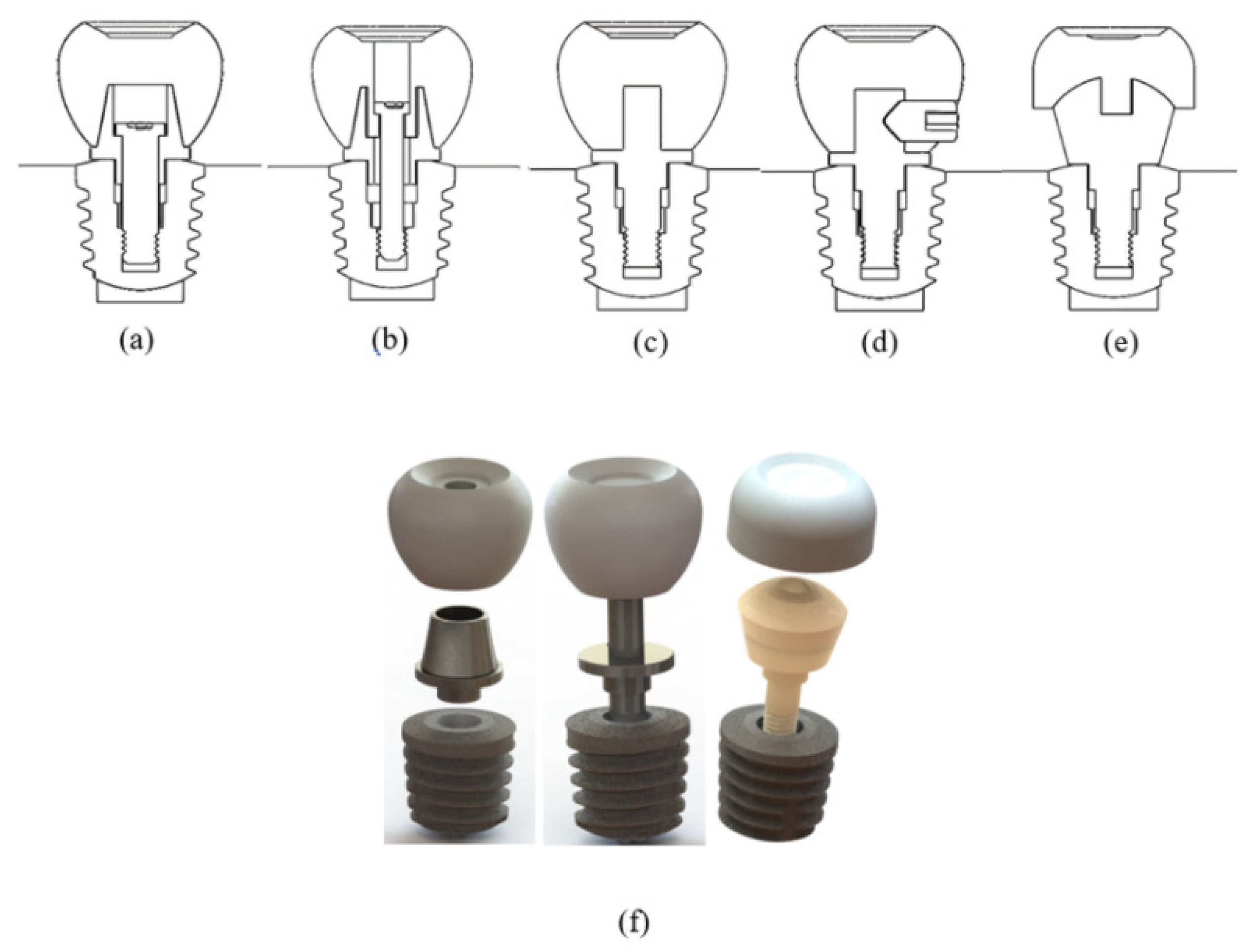
2.3. Abutment Model and Material
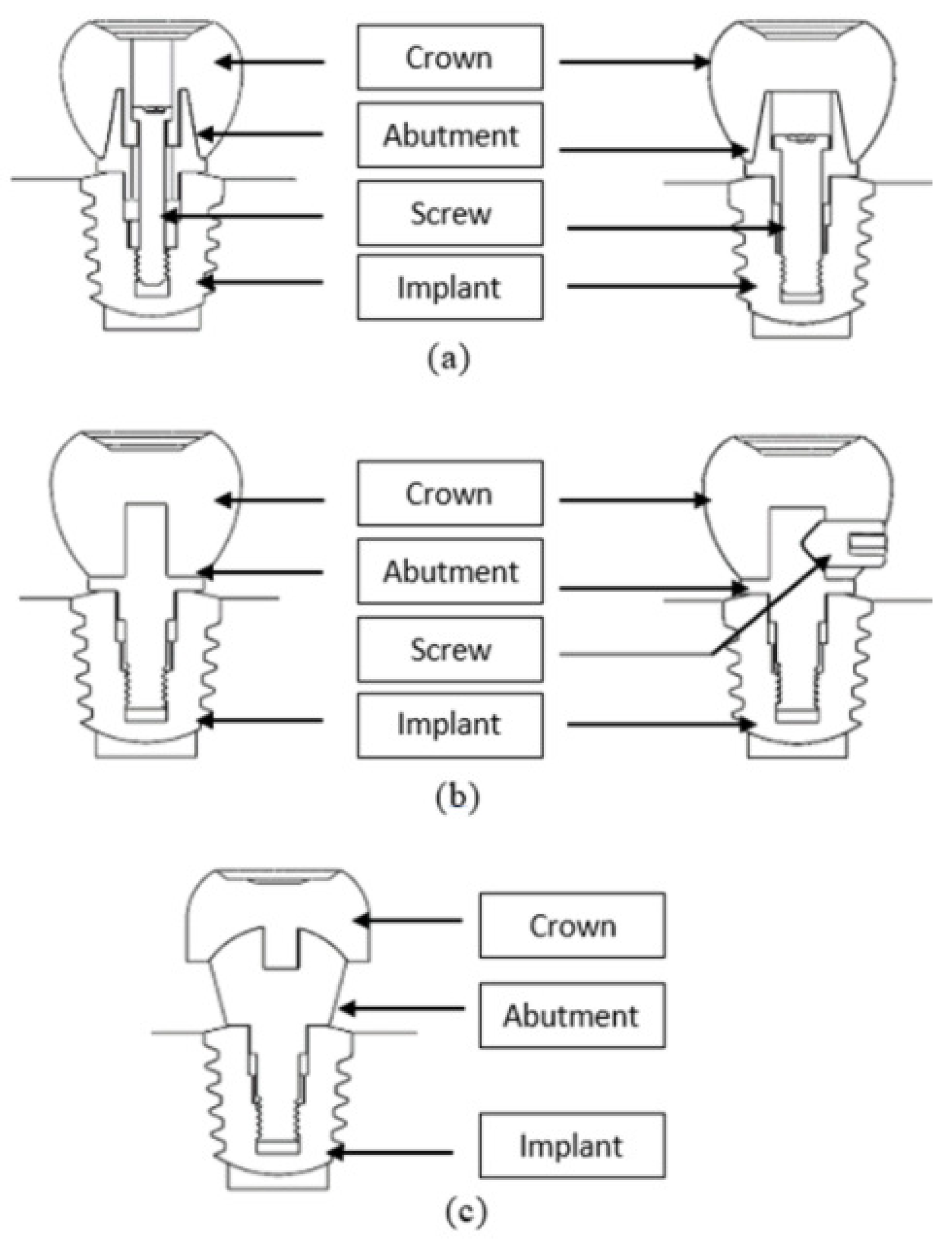
2.4. Three-Dimensional Models of Implant Systems with Different Abutment Designs
2.5. Finite Element Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
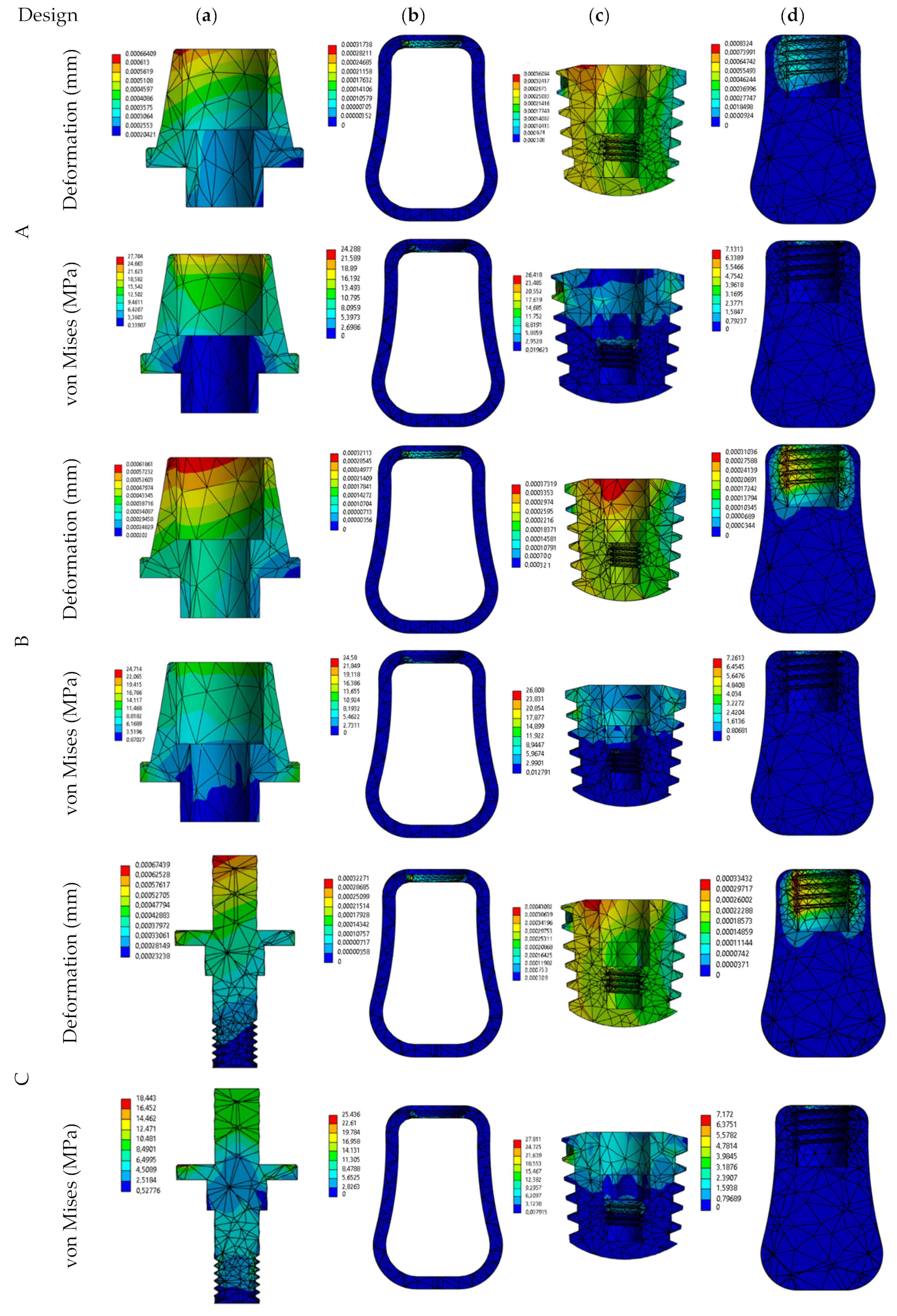
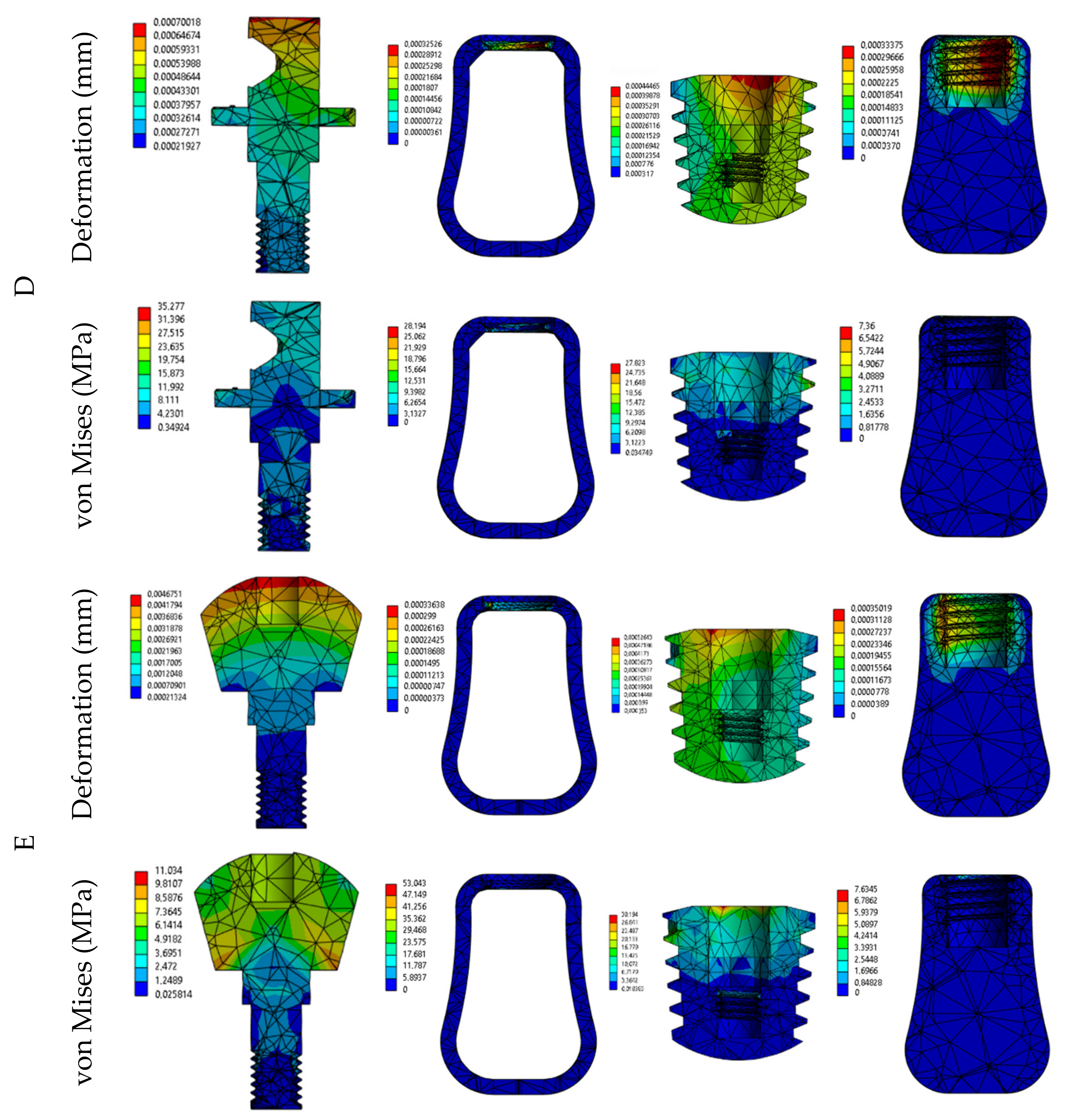
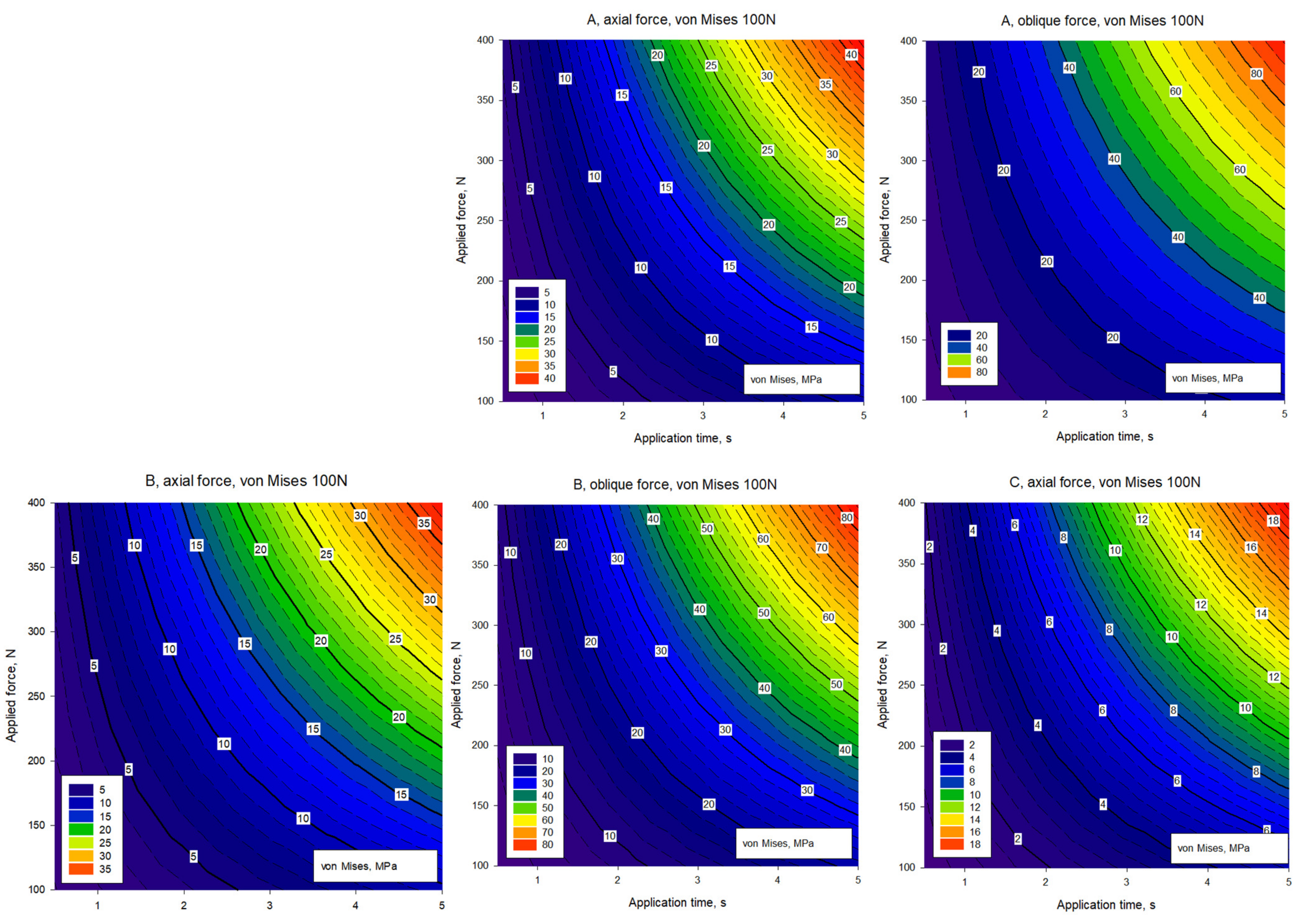
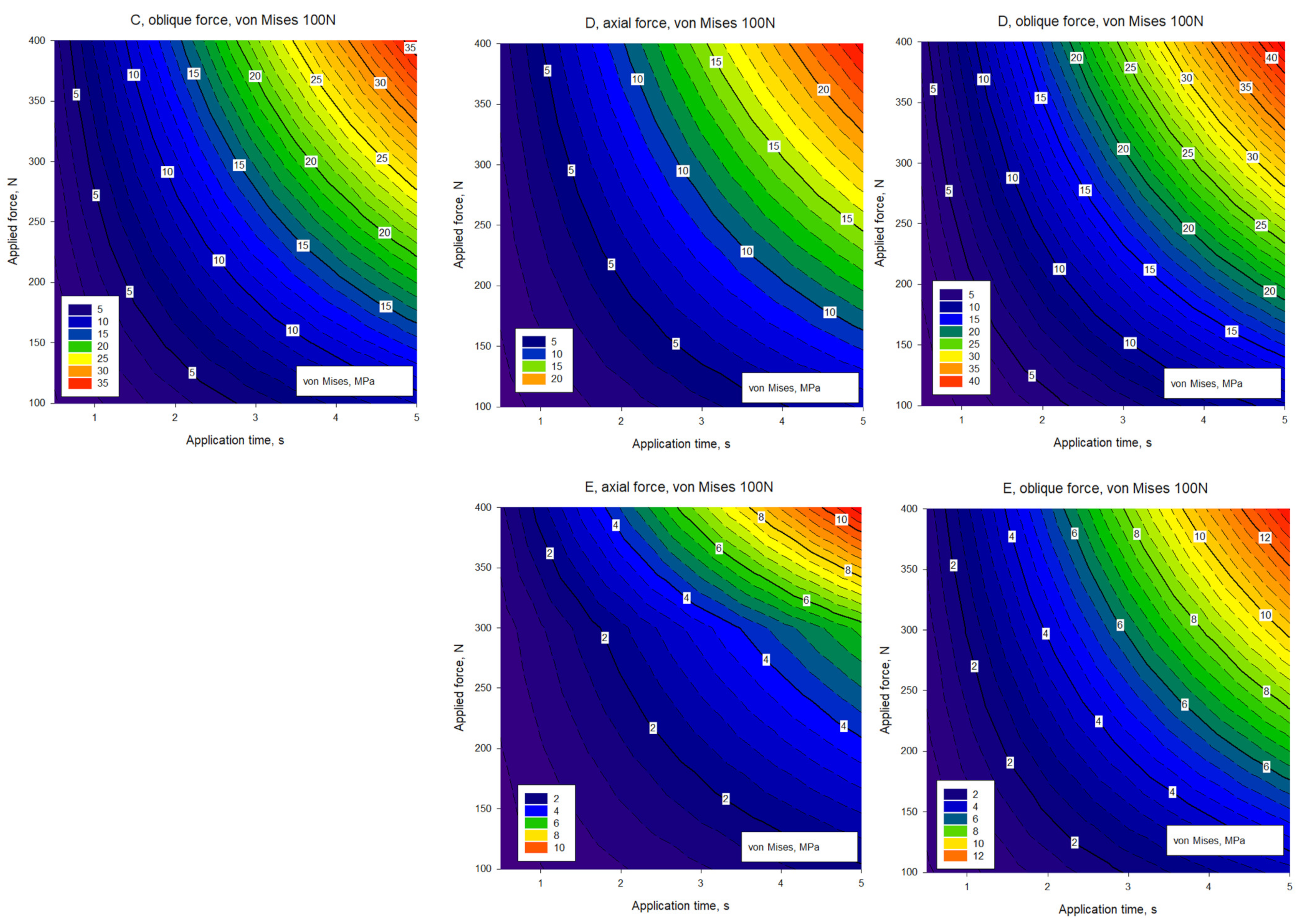
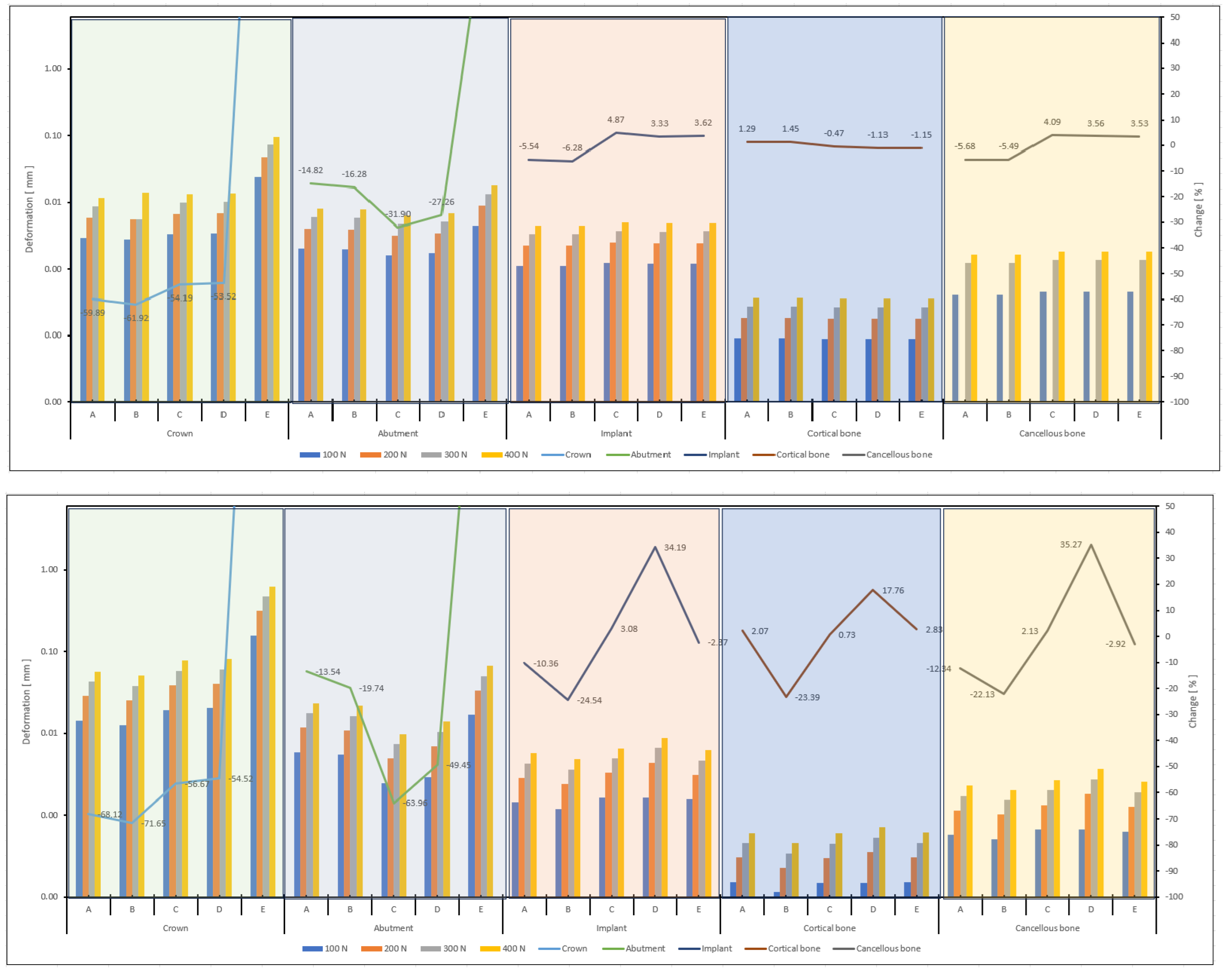
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Târtea, D.A.; Ionescu, M.; Manolea, H.O.; Mercuț, V.; Obădan, E.; Amărăscu, M.O.; Mărășescu, P.C.; Dăguci, L.; Popescu, S.M. Comparative Study of Dental Custom CAD-CAM Implant Abutments and Dental Implant Stock Abutments. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascos, R.; Celemín-Viñuela, A.; Mory-Rubiños, N.; Gómez-Polo, C.; Ortega, R.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Gómez-Polo, M. Influence of the Use of Transepithelial Abutments vs. Titanium Base Abutments on Microgap Formation at the Dental Implant–Abutment Interface: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2023, 16, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmitasari, F.; Ishida, Y.; Kurahashi, K.; Matsuda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Ichikawa, T. PEEK with Reinforced Materials and Modifications for Dental Implant Applications. Dent. J. 2017, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Yao, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, C.; Oates, T.W.; Weir, M.D.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.H. Review on Development and Dental Applications of Polyetheretherketone-Based Biomaterials and Restorations. Materials 2021, 14, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinhas, A.S.; Aroso, C.; Salazar, F.; López-Jarana, P.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Herrero-Climent, M. Review of the Mechanical Behavior of Different Implant–Abutment Connections. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, J.-K.; Caballero, C.; Rodriguez, F.; Scarano, A.; Prados-Frutos, J.C.; De Aza, P.N.; Fernandes, G.V.O.; Gehrke, S.A. Mechanical Behavior of Five Different Morse Taper Implants and Abutments with Different Conical Internal Connections and Angles: An In Vitro Experimental Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghiri, M.A.; Freag, P.; Fakhrzadeh, A.; Saghiri, A.M.; Eid, J. Current technology for identifying dental implants: A narrative review. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2021, 45, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Schmuki, P.; Von Der Mark, K.; Park, J.; Park, J. Engineering biocompatible implant surfaces Part I: Materials and surfaces. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 261–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J. Titanium alloys for dental implants: A review. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshardt, D.D.; Chappuis, V.; Buser, D. Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: Current knowledge and open questions. Periodontology 2000 2017, 73, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Thobity, A.M. Titanium Base Abutments in Implant Prosthodontics: A Literature Review. Eur. J. Dent. 2022, 16, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totou, D.; Naka, O.; Mehta, S.B.; Banerji, S. Esthetic, mechanical, and biological outcomes of various implant abutments for single-tooth replacement in the anterior region: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2021, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.K.; Sivaswamy, V. A Literature Review on Implant Abutment Types, Materials, and Fabrication Processes. J. Long. Term. Eff. Med. Implant. 2023, 33, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidambe, A.T.; Oh, J.K. Biocompatibility of Advanced Manufactured Titanium Implants—A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 8168–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, O.; Pihlajamak, H. Clinical biocompatibility of biodegradable orthopaedic implants for internal xation: A review. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar]
- Calin, M.; Gebert, A.; Cosmina Ghinea, A.; Gostin, P.F.; Abdi, S.; Mickel, C.; Eckert, J. Designing biocompatible Ti-based metallic glasses for implant applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera, F.; Menini, M.; Bagnasco, F.; Mussano, F.; Ambrogio, G.; Pesce, P. Evaluation of internal and external hexagon connections in immediately loaded full-arch rehabilitations: A within-person randomized split-mouth controlled trial with a 3-year follow-up. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciej, S.; Becker, F.G.; Cleary, M.; Kaczyński, M.; Kowalski, P.; Nowak, A. Synthesis and Biological Activity of New Thiosemicarbazone Analogues of Iron Chelators [Synteza i Aktywność Biologiczna Nowych Analogów Tiosemikarbazonowych Chelatorów Żelaza]. Ph.D. Dissertation, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Silesia in Katowice, Katowice, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, F.; Hegewald, A.; Becker, J. Impact of implant–abutment connection and positioning of the machined collar/microgap on crestal bone level changes: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Yeh, C.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Li, Y.T.; Yang, J.H.; Lin, C.P. Differences in the biomechanical behaviors of natural teeth and dental implants. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tang, C.; Yu, J.; Dai, W.; Bao, Y.; Hu, D. The effect of platform switching on stress distribution in implants and periimplant bone studied by nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Chen, J.; Han, L.; Yang, J.; Huang, W.; Wu, D. Angled abutments result in increased or decreased stress on surrounding bone of single-unit dental implants: A finite element analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2012, 34, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, T.; Tanimoto, Y.; Nemoto, K.; Aida, M. Influence of Cortical Bone Quality on Stress Distribution in Bone around Dental Implant. Dent. Mater. J. 2005, 24, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Liao, S.H.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, L. Effect of Diameter and Length on Stress Distribution of the Alveolar Crest around Immediate Loading Implants. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 11, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkir, S.E. Effect of restoration material on stress distribution on partial crowns: A 3D finite element analysis. J. Dent. Sci. 2018, 13, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazzawi, T.F.F. Relation of Crown Failure Load to Flexural Strength for Dental Polymers and a Fiber Reinforced Composite Resin. 2023. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202309.1985/v1 (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Dhatrak, P.; Shirsat, U.; Sumanth, S.; Deshmukh, V. Numerical investigation on stress intensity around Bone-Implant interface by 3-Dimensional FEA and experimental verification by optical technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 39, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevimay, M.; Turhan, F.; Kiliçarslan, M.A.; Eskitascioglu, G. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of different bone quality on stress distribution in an implant-supported crown. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 93, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidhatika, B.; Widyaya, V.T.; Nalam, P.C.; Swasono, Y.A.; Ardhani, R. Surface Modifications of High-Performance Polymer Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) to Improve Its Biological Performance in Dentistry. Polymers 2022, 14, 5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondani, J.R.; Iyer, J.; Tran, S.D. Surface Treatments of PEEK for Osseointegration to Bone. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Kuang, H.; Gong, B.; Li, Z.; Sun, H. PEEK for Oral Applications: Recent Advances in Mechanical and Adhesive Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevinç, E.H.D.; İnal, C.B.; Aydın, C. Protetik Diş Hekimliğinde Polietereterketon Materyalinin Yeri. ADO Klin. Bilim. Derg. 2022, 11, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çulhaoğlu, A.k.; Özkir, S.; Türkkal, F. Polieter eter keton (peek) ve dental kullanimi. Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekim. Fakültesi Derg. 2019, 29, 711–718. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoğlu, S.; Ozan, O. Finite element methods in dentistry. Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekim. Fakültesi Derg. 2015, 24, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Ando, H.; Unno, S.; Roy, R.R.; Kitagawa, J. Pharmacological activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 promotes triggering of the swallowing reflex in rats. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1149793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.S.; Shrivastava, V.; Dwivedi, M.K.; Shukla, O.P. 3-dimensional CFD simulation and correlation development for circular tube equipped with twisted tape. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 2662–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Chauhan, P.; Kumar, A.; Tekasakul, P. Applications of software in solar drying systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, J.; Chand, Y.B.; Mahendra, L.; Fageeh, H.N.; Fageeh, H.I.; Ibraheem, W.; Alzahrani, K.M.; Alqahtani, N.M.; Alahmari, N.M.; Almagbol, M.; et al. Evaluation of Stress Distribution during Insertion of Tapered Dental Implants in Various Osteotomy Techniques: Three-Dimensional Finite Element Study. Materials 2021, 14, 7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostertagová, E.; Ostertag, O.; Kováč, J. Methodology and Application of the Kruskal-Wallis Test. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 611, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, B.; Saneja, R.; Singh, A.; Dubey, P.K.; Bhatnagar, A. Peri-implant stress distribution assessment of various attachment systems for implant supported overdenture prosthesis by finite element analysis—A systematic review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2022, 12, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, F.R.; Bitencourt, S.B.; Rosa, C.D.D.R.D.; Vieira, A.B.; Dos Santos, D.M.; Goiato, M.C. Influence of Different Restoring Materials on Stress Distribution in Prosthesis on Implants: A Review of Finite Element Studies. Eur. J. Dent. 2023, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badalia, I.; Kumar, M.; Bansal, A.; Mehra, S.; Batra, R. Evaluation of stress patterns in bone around implants for different abutment angulations under axial and oblique loading in anterior maxillary region—A finite element analysis. Dent. J. Adv. Stud. 2020, 8, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, S.; Stegaroiu, R.; Kitamura, E.; Miyakawa, O.; Kusakari, H. Influence of implant design and bone quality on stress/strain distribution in bone around implants: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 357. [Google Scholar]
- Tonin, B.S.H.; Fu, J.; He, Y.; Ye, N.; Chew, H.P.; Fok, A. The effect of abutment material stiffness on the mechanical behavior of dental implant assemblies: A 3D finite element study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 142, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.T.; Kao, H.C.; Cheng, C.K.; Fang, H.W.; Huang, C.H.; Hsu, M.L. Mechanical performance of conical implant-abutment connections under different cyclic loading conditions. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 90, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.M.; Cheng, K.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Nizza, M.; Baur, D.A.; Jiang, X.F.; Dong, X.T. Biomechanical and Mechanostat analysis of a titanium layered porous implant for mandibular reconstruction: The effect of the topology optimization design. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 124, 112056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsiyakull, C.; Li, Q.; Sun, G.; Li, W.; Swain, M.V. Surface morphology optimization for osseointegration of coated implants. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7196–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, Y.; Tanimoto, Y.; Maruyama, N.; Nagakura, M. A review of improved fixation methods for dental implants. Part. II: Biomechanical integrity at bone–implant interface. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2015, 59, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Fraulob, M.; Haïat, G. Biomechanical behaviours of the bone–implant interface: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaney, D.F. Mechanical Properties of Implantable Biomaterials. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 1995, 12, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yao, Y.; Tang, W.; Han, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, K.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. Design of dental implants at materials level: An overview. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2020, 108, 1634–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Cortical bone | 13.7 [21,22] | 0.3 [21,22] |
| Cancellous bone | 1.37 [23,24] | 0.3 [23,24] |
| Porcelain (crown) | 65 [25,26] | 0.25 [25,26] |
| Implant, abutment, screw | 110 [21,27,28] | 0.35 [21,27,28] |
| PEEK Juvora | 5.5 [25,26] | 0.36 [25,26] |
| Group | N | Missing | Median | 25% | 75% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 42 | 6 | 11.294 | 6.076 | 21.629 |
| B | 42 | 6 | 10.079 | 5.420 | 19.303 |
| C | 42 | 6 | 5.151 | 2.770 | 9.865 |
| D | 42 | 6 | 6.492 | 3.491 | 12.433 |
| E | 42 | 6 | 2.180 | 1.118 | 4.420 |
| Comparison | Diff of Ranks | q’ | p | p < 0.050 | |
| E vs. A | 2748.000 | 6.215 | <0.001 | Yes | |
| C vs. A | 1423.000 | 3.219 | 0.005 | Yes | |
| D vs. A | 996.000 | 2.253 | 0.080 | No | |
| B vs. A | 218.000 | 0.493 | 0.967 | Not tested | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| A Deformation (µm) | Crown | 2.9 | 5.8 | 8.8 | 11,7 | 14 | 28 | 43 | 57 |
| Abutment | 2 | 4 | 5.9 | 7.9 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 23 | |
| Implant | 1.1 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | |
| Cortical bone | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.6 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| B Deformation (µm) | Crown | 2.8 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 11.1 | 13 | 25 | 38 | 51 |
| Abutment | 1.9 | 3.9 | 5.8 | 7.8 | 5 | 11 | 16 | 22 | |
| Implant | 1.1 | 2.2 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | |
| Cortical bone | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| C Deformation (µm) | Crown | 3.3 | 6.7 | 10 | 13.3 | 19 | 39 | 58 | 77 |
| Abutment | 1.6 | 3.2 | 4.7 | 6.3 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 10 | |
| Implant | 1.2 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 4.9 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
| Cortical bone | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.45 | 0.6 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.5 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| D Deformation (µm) | Crown | 3.38 | 6.76 | 10.14 | 13.52 | 20 | 41 | 61 | 81 |
| Abutment | 1.69 | 3.38 | 5.07 | 6.76 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 14 | |
| Implant | 1.21 | 2.43 | 3.64 | 4.85 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 9 | |
| Cortical bone | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.71 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.45 | 0.9 | 1.34 | 1.79 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| E Deformation (µm) | Crown | 24 | 47.9 | 71.9 | 95.9 | 157 | 313 | 470 | 626 |
| Abutment | 4.4 | 8.8 | 13.3 | 17.7 | 17 | 33 | 50 | 67 | |
| Implant | 1.2 | 2.4 | 3.6 | 4.9 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | |
| Cortical bone | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.46 | 0.61 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
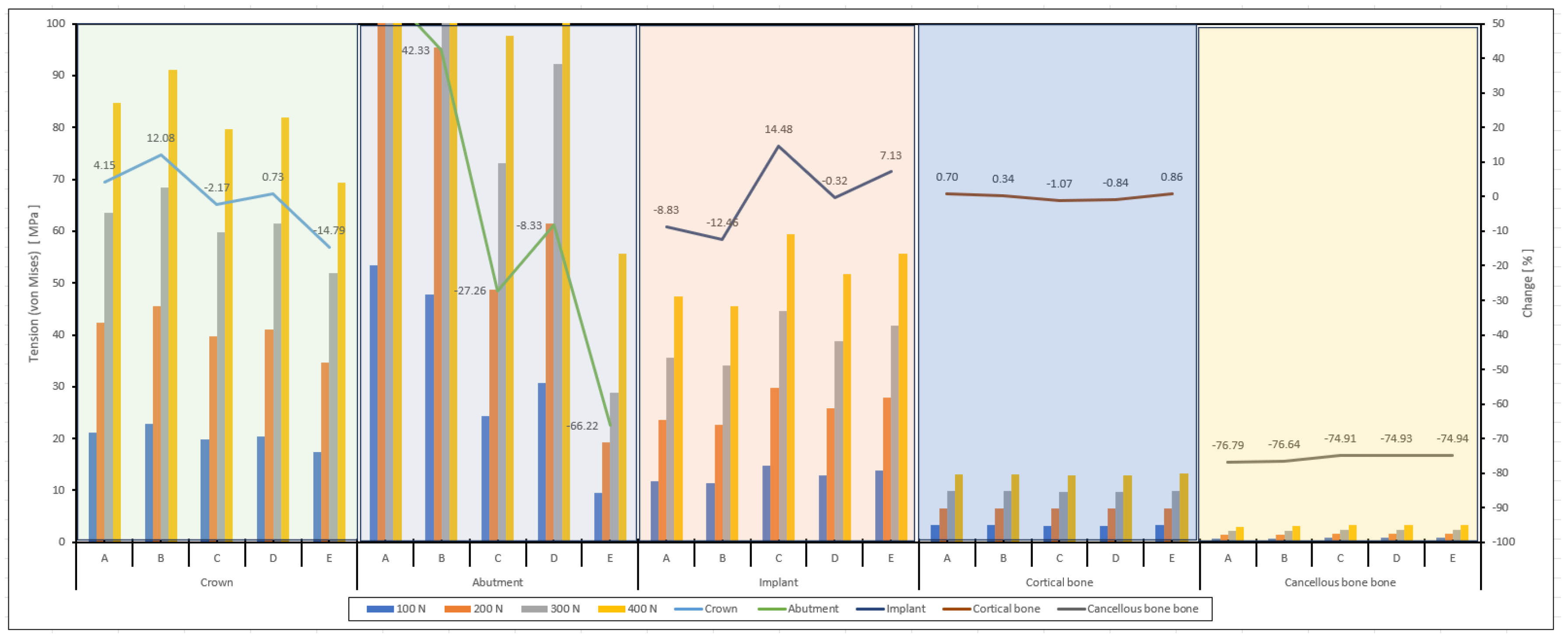
| A von Mises (MPa) | Crown | 21.1 | 42.3 | 63.5 | 84.7 | 37.6 | 75.3 | 113.0 | 150.7 |
| Abutment | 53.4 | 106.9 | 160.4 | 213.9 | 116.0 | 232.1 | 348.2 | 464.2 | |
| Implant | 11.8 | 23.6 | 35.5 | 47.3 | 18.3 | 36.6 | 54.9 | 73.2 | |
| Cortical bone | 3.2 | 6.5 | 9.8 | 13.1 | 6.0 | 12.1 | 18.1 | 24.2 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.7 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 3.5 | 4.7 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| B von Mises (MPa) | Crown | 22.7 | 45.5 | 68.3 | 91.1 | 41.8 | 83.7 | 125.5 | 167.4 |
| Abutment | 47.7 | 95.4 | 143.2 | 190.9 | 105.9 | 211.9 | 317.9 | 423.8 | |
| Implant | 11.3 | 22.7 | 34.1 | 45.4 | 17.9 | 35.8 | 53.8 | 71.7 | |
| Cortical bone | 3.2 | 6.5 | 9.8 | 13.1 | 3.9 | 7.9 | 11.8 | 15.8 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.7 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 4.1 | |
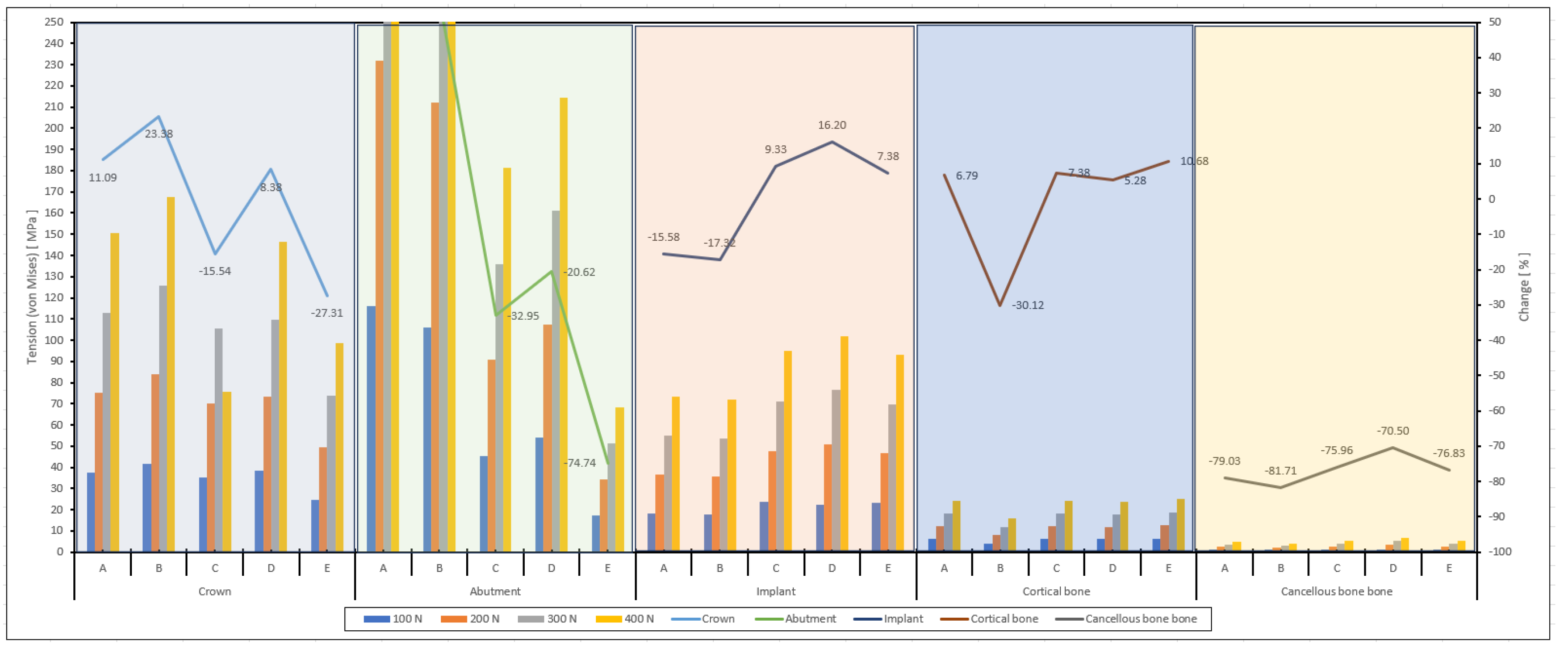
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| C von Mises (MPa) | Crown | 19.8 | 39.7 | 59.6 | 79.5 | 35.1 | 70.3 | 105.4 | 75.5 |
| Abutment | 24.3 | 48.7 | 73.1 | 97.5 | 45.3 | 90.6 | 136.0 | 181.3 | |
| Implant | 14.8 | 29.7 | 44.6 | 59.4 | 23.7 | 47.4 | 71.1 | 94.8 | |
| Cortical bone | 3.2 | 6.4 | 9.7 | 12.9 | 6.0 | 12.1 | 18.2 | 24.3 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 2.7 | 4.0 | 5.4 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| D von Mises (MPa) | Crown | 20.4 | 40.9 | 61.4 | 81.9 | 38.3 | 73.1 | 109.7 | 146.3 |
| Abutment | 30.7 | 61.4 | 92.2 | 122.9 | 54.0 | 107.2 | 160.9 | 214.5 | |
| Implant | 12.9 | 25.8 | 38.8 | 51.7 | 22.4 | 51.0 | 76.5 | 102.0 | |
| Cortical bone | 3.2 | 6.4 | 9.7 | 12.9 | 6.0 | 11.9 | 17.8 | 23.8 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 6.8 | |
| VL | VO | ||||||||
| 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | 100 N | 200 N | 300 N | 400 N | ||
| E von Mises (MPa) | Crown | 17.3 | 34.6 | 51.9 | 69.3 | 24.6 | 49.3 | 73.9 | 98.6 |
| Abutment | 9.6 | 19.2 | 28.8 | 55.6 | 17.0 | 34.1 | 51.2 | 68.3 | |
| Implant | 13.9 | 27.8 | 41.7 | 55.6 | 23.3 | 46.6 | 69.9 | 93.2 | |
| Cortical bone | 3.2 | 6.5 | 9.8 | 13.1 | 6.2 | 12.5 | 18.8 | 25.1 | |
| Cancellous bone | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 2.6 | 3.9 | 5.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yağır, M.O.; Şen, Ş.; Şen, U. Examination of Various Abutment Designs Behavior Depending on Load Using Finite Element Analysis. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080498
Yağır MO, Şen Ş, Şen U. Examination of Various Abutment Designs Behavior Depending on Load Using Finite Element Analysis. Biomimetics. 2024; 9(8):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080498
Chicago/Turabian StyleYağır, Mehmet Onur, Şaduman Şen, and Uğur Şen. 2024. "Examination of Various Abutment Designs Behavior Depending on Load Using Finite Element Analysis" Biomimetics 9, no. 8: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080498
APA StyleYağır, M. O., Şen, Ş., & Şen, U. (2024). Examination of Various Abutment Designs Behavior Depending on Load Using Finite Element Analysis. Biomimetics, 9(8), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics9080498






