Complex-Exponential-Based Bio-Inspired Neuron Model Implementation in FPGA Using Xilinx System Generator and Vivado Design Suite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work
1.2. Outline
2. Background
2.1. Mathematical Model
2.2. MATLAB Simulation Report
- Example 1 in Figure 2 (temporal plot I and polar plot I) shows the output of the weighted sum of two neurons where are used.
- Example 2 (temporal plot II and polar plot II) all parameters of the weighted input of two neurons remain the same except is taken. This causes a change in amplitude.
- Example 3, is changed to . This changes the phase and orientation of the weighted sum.
- For example, 4 is set to 3; this dramatically changes the pattern of the weighted sum, which is shown in the polar plot iv.
3. Methodology
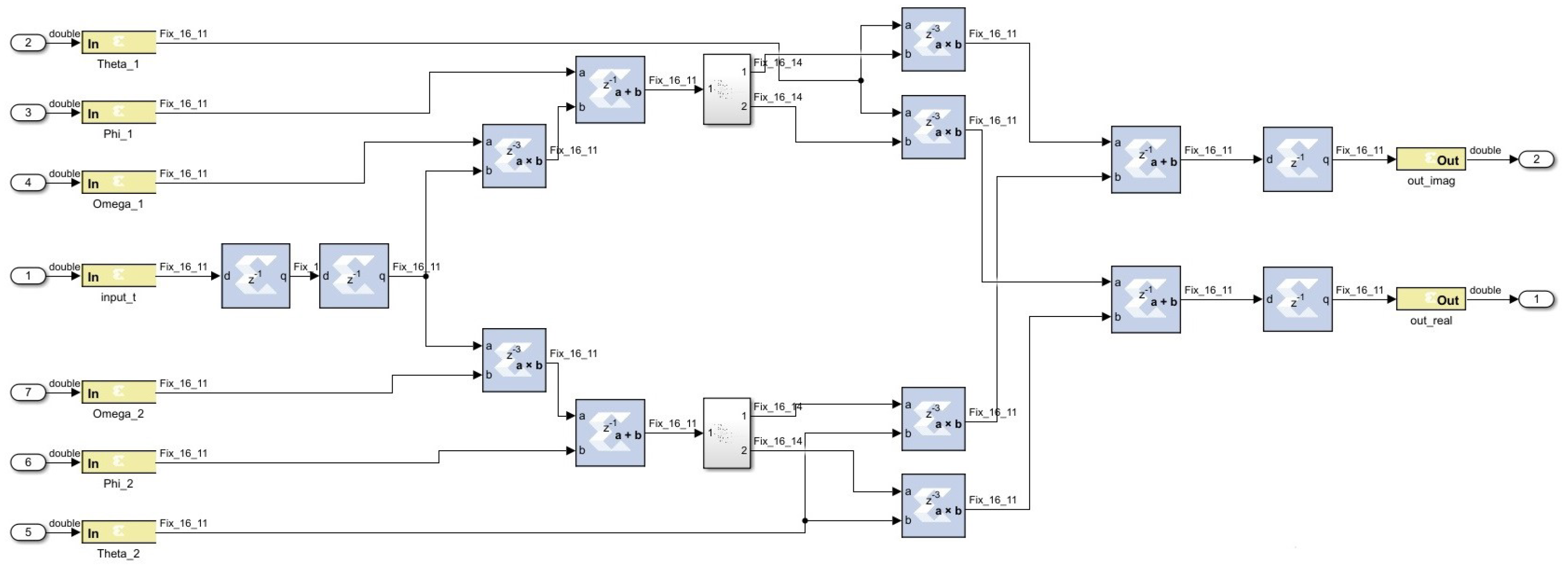
3.1. Model Design in Simulink and Vivado
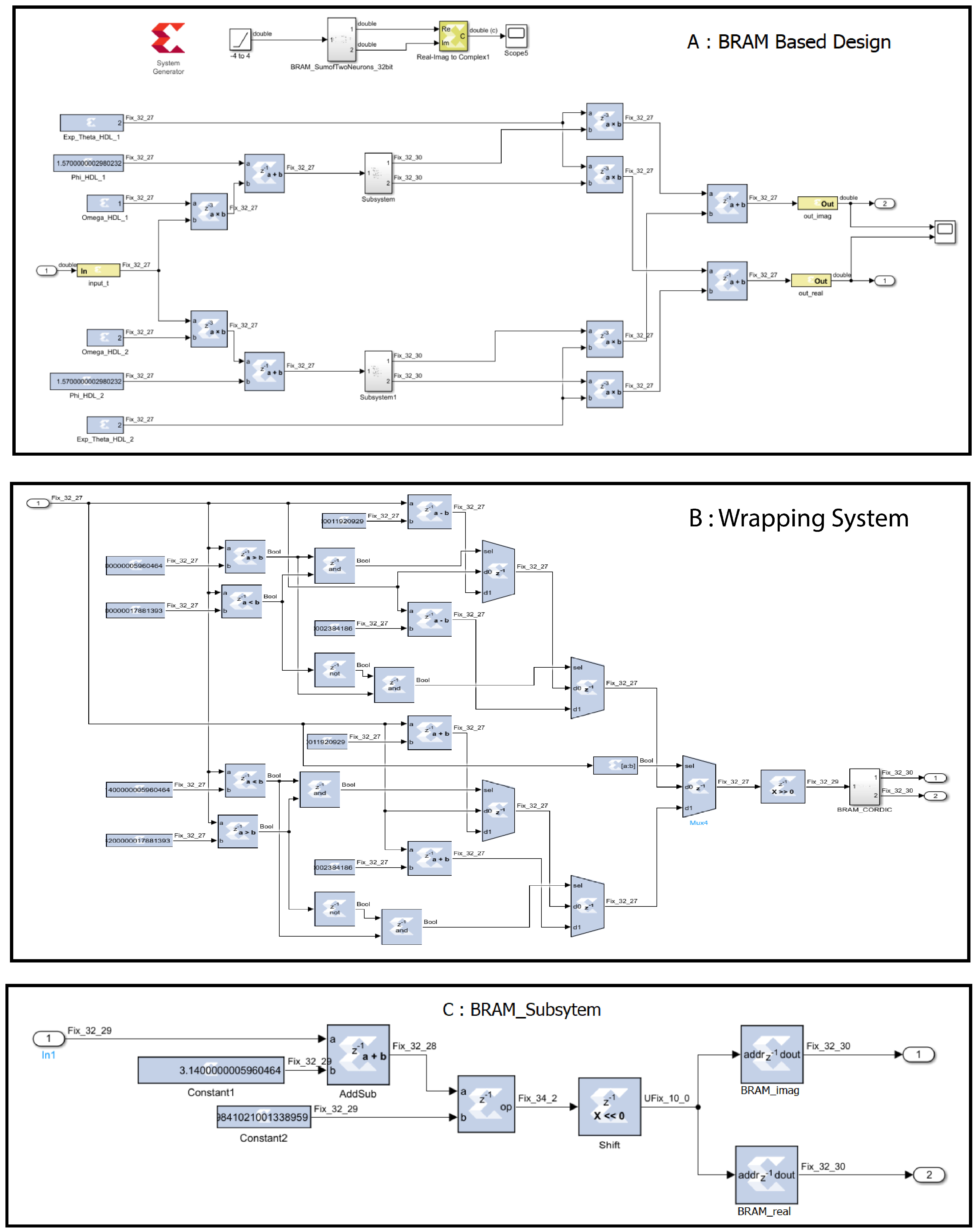
3.1.1. BRAM-Based Design (Using SysGen in MATLAB Simulink)
3.1.2. BRAM-Based Design in Vivado
3.1.3. CORDIC-Based Design (Using SysGen in MATLAB Simulink)
3.1.4. CORDIC-Based Design in Vivado
3.1.5. The Fixed-Point Implementation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Simulation Report
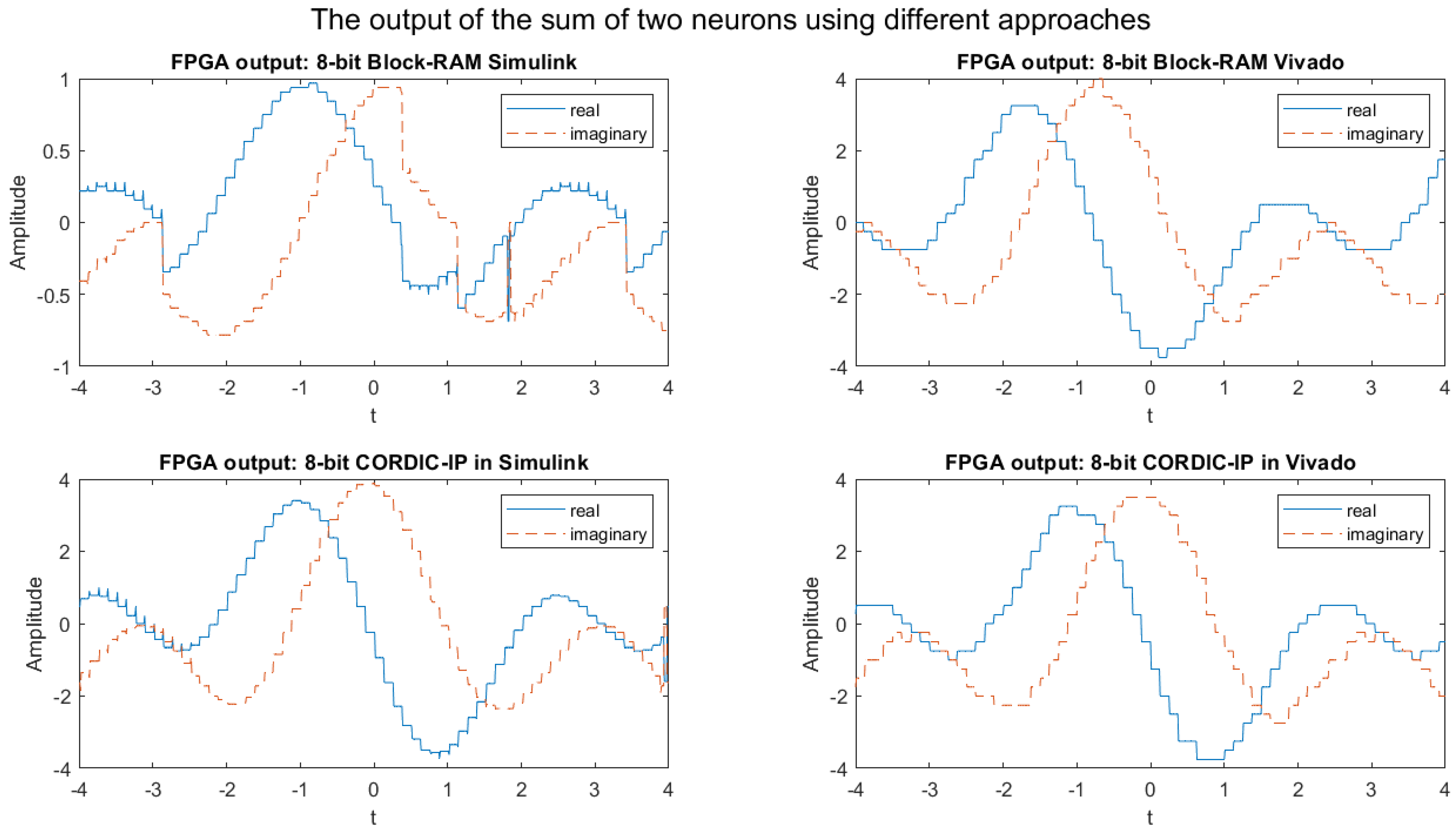
4.1.1. 8-Bit Implementation Result
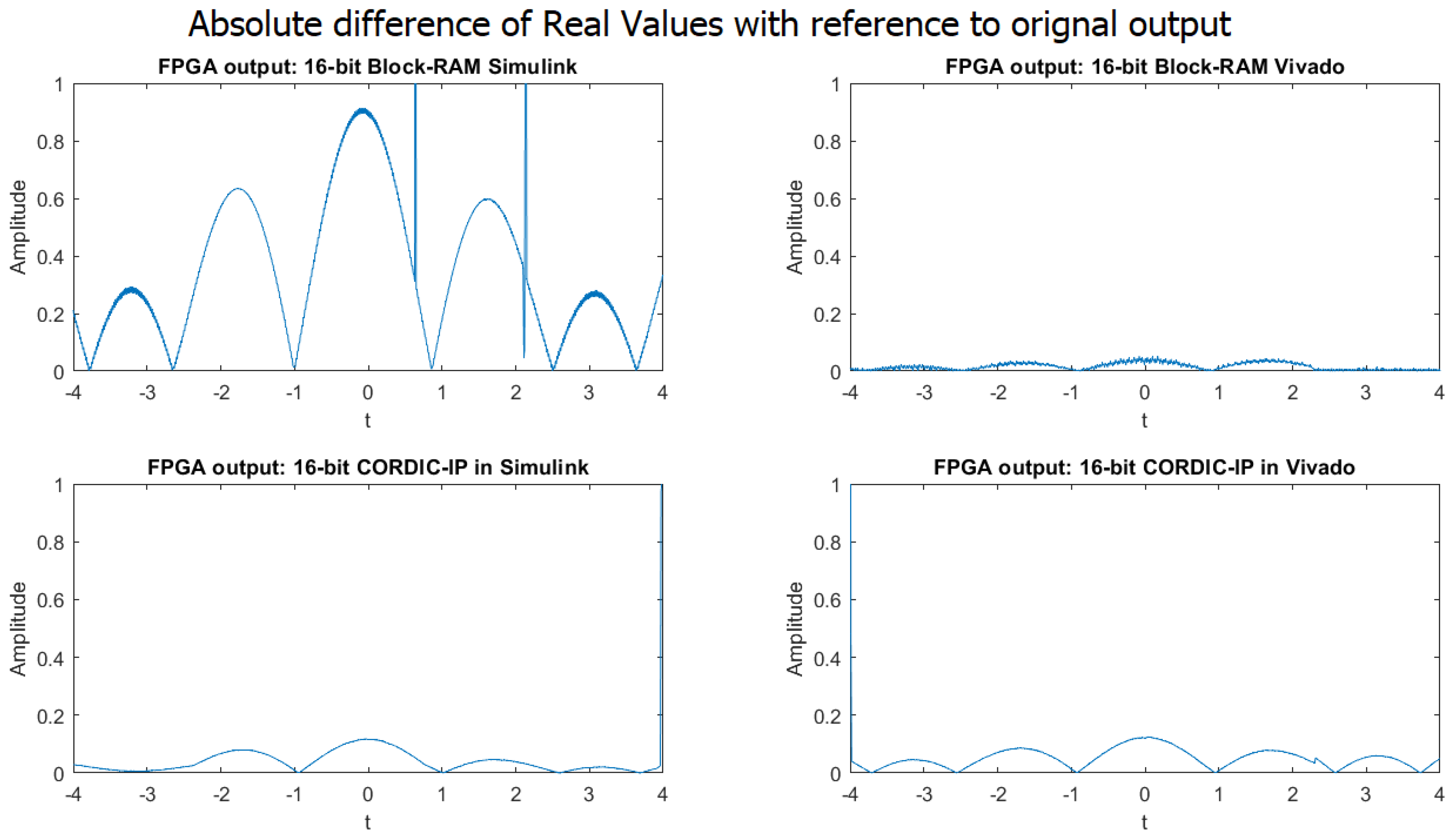
4.1.2. 16-Bit Implementation Result
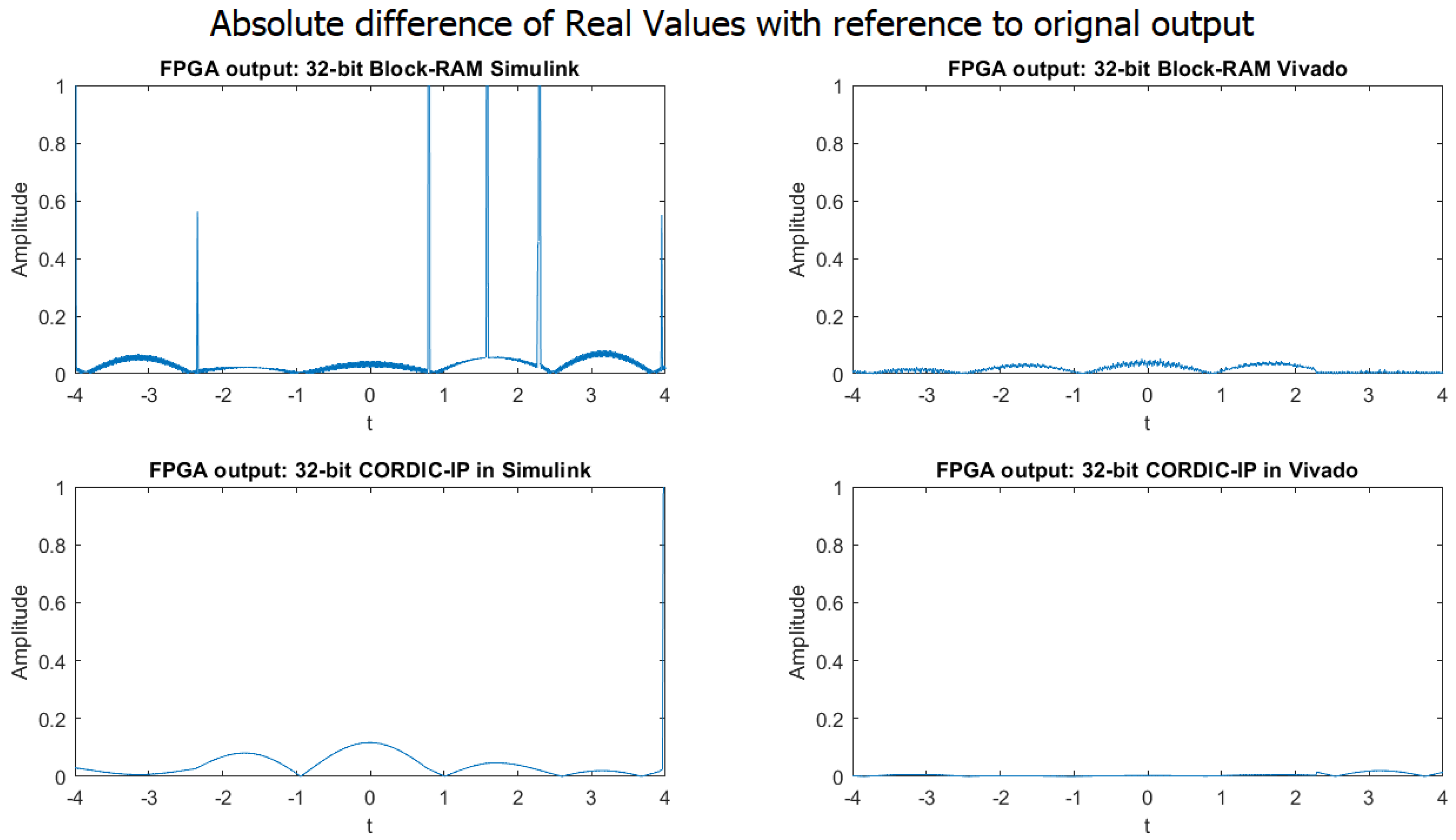
4.1.3. 32-Bit Implementation Result
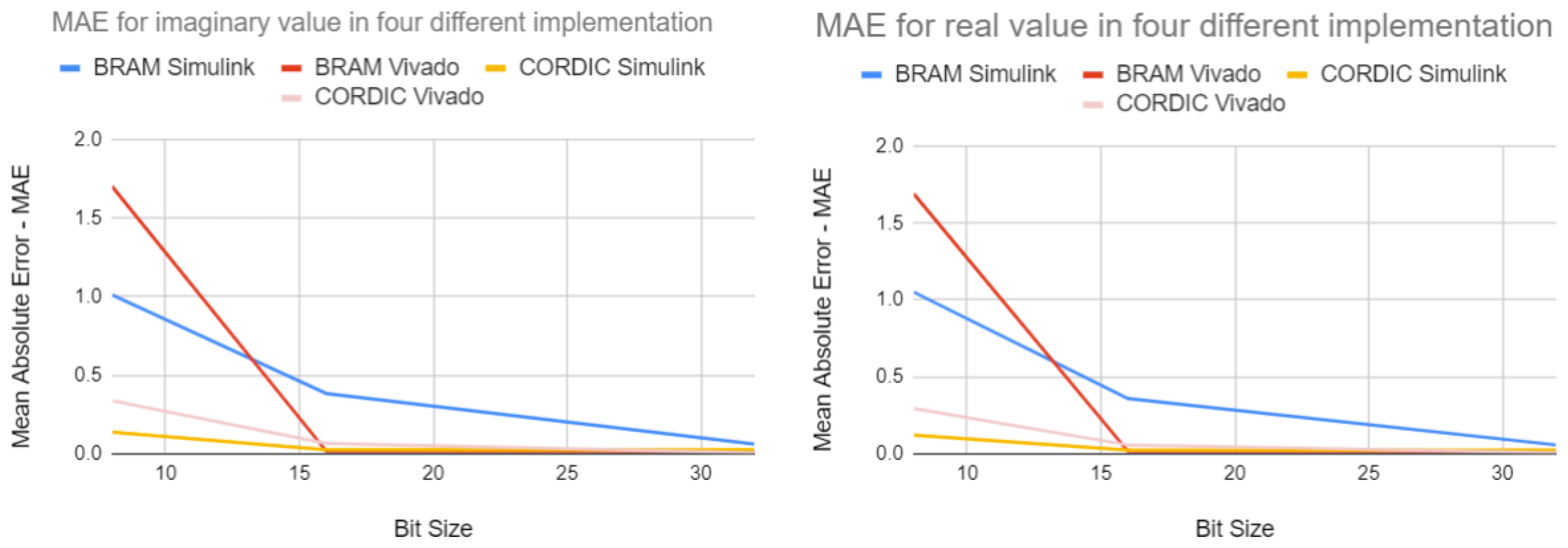
4.1.4. MAE of the Four Different Implementation Approaches
4.1.5. Discussion Summary
4.2. Hardware Implementation Report
4.2.1. WNS Report
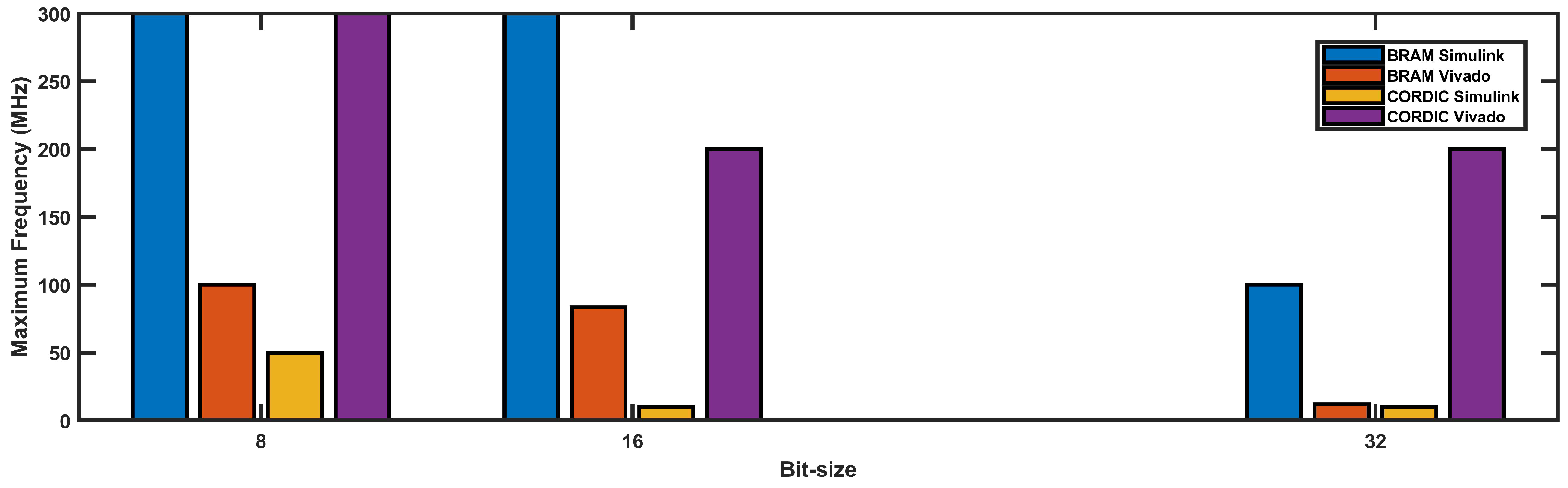
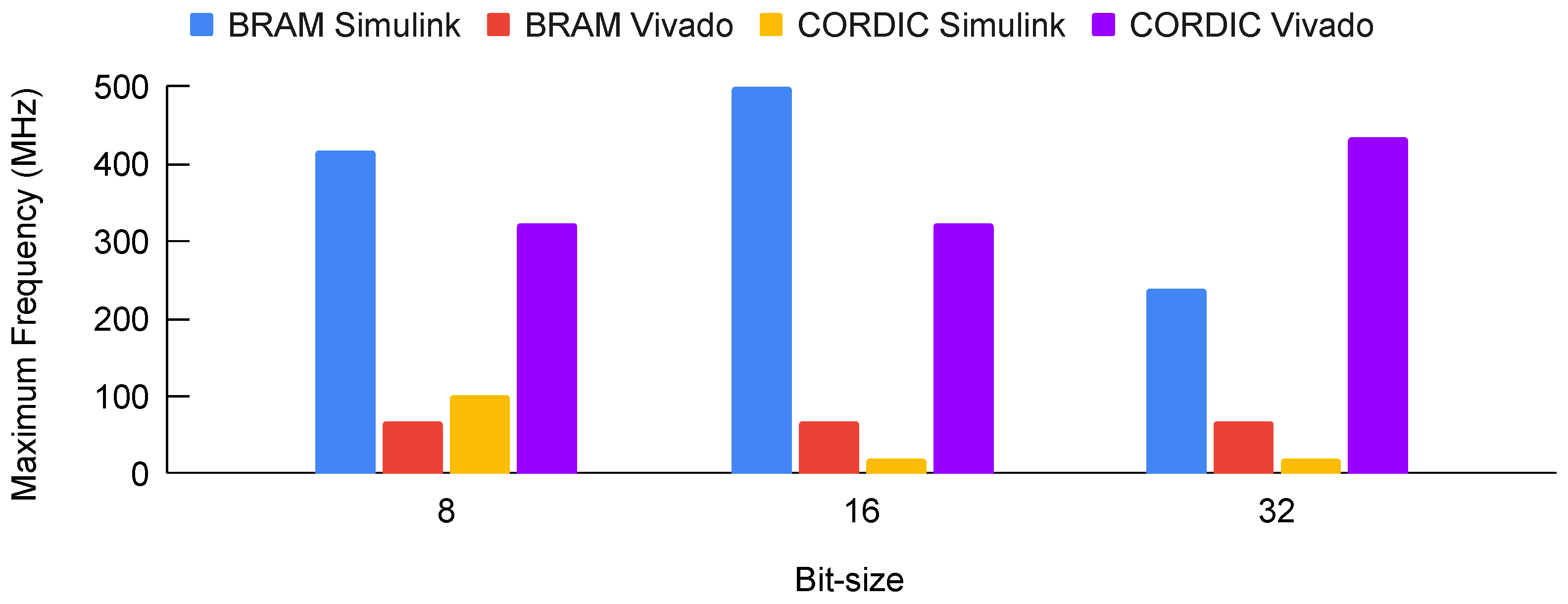
4.2.2. Max Operating Frequency
4.2.3. Resource Usages
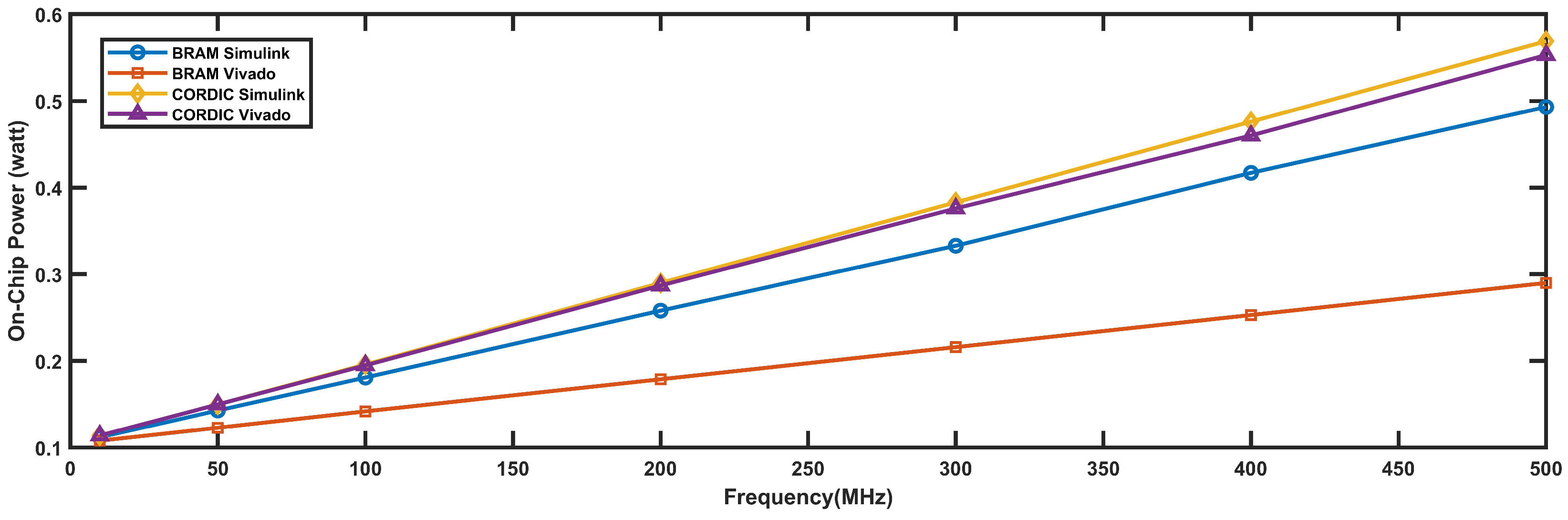
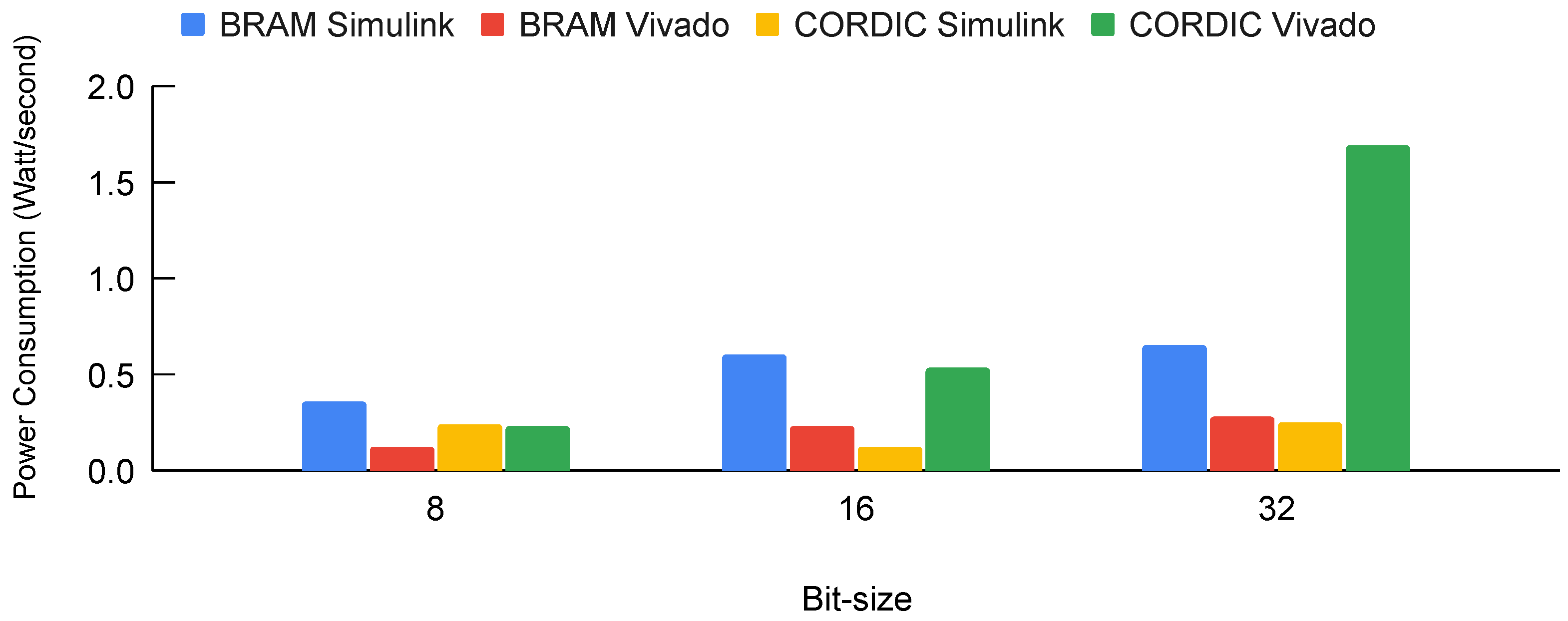
4.2.4. Power Requirement
4.2.5. Discussion Summary
4.3. Hardware Implementation Report for the Design with All the Input Variables in Use
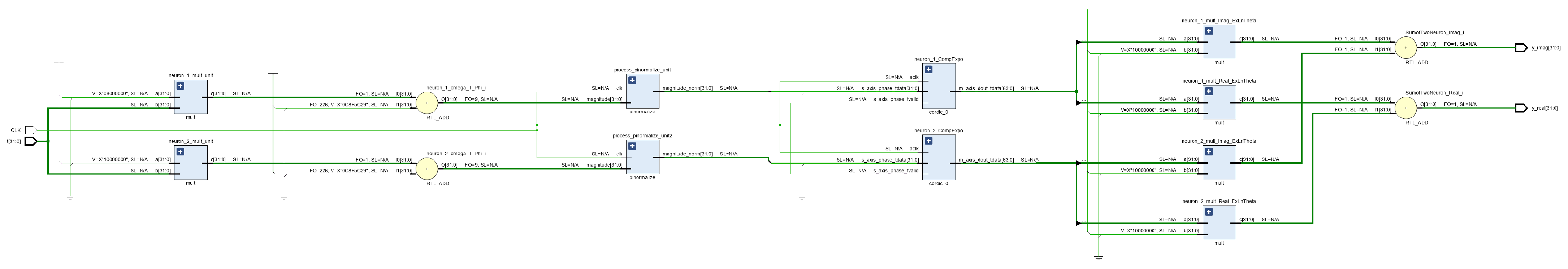
4.4. Multi-Neuron Implementation Report
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| ASIC | Application-Specific Integrated Circuit |
| DSP | Digital Signal Processor |
| HDL | Hardware Description Language |
| VHDL | VHSIC Hardware Description Language |
| LUT | Lookup Table |
| FF | Flip-Flop |
| SSN | Simultaneous Switching Noise |
| BRAM | Block RAM (Random Access Memory) |
| CORDIC | Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer |
| IO | Input/Output |
| IP | Intellectual Property |
References
- Zhang, L. Oscillation Patterns of A Complex Exponential Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Joint Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 17–20 November 2022; pp. 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Capra, M.; Bussolino, B.; Marchisio, A.; Shafique, M.; Masera, G.; Martina, M. An updated survey of efficient hardware architectures for accelerating deep convolutional neural networks. Future Internet 2020, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, D.; Kil, D.; Kim, S.h. A survey on efficient convolutional neural networks and hardware acceleration. Electronics 2022, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Spiking Neural Network Implementation on FPGA for Multiclass Classification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Systems Conference (SysCon), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–20 April 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Aizenberg, I. Complex-Valued Neural Networks with Multi-Valued Neurons; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 353. [Google Scholar]
- Aizenberg, I.; Herman, J.; Vasko, A. A Convolutional Neural Network with Multi-Valued Neurons: A Modified Learning Algorithm and Analysis of Performance. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 26–29 October 2022; pp. 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Javanshir, A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Mahmud, M.P.; Kouzani, A.Z. Advancements in Algorithms and Neuromorphic Hardware for Spiking Neural Networks. Neural Comput. 2022, 34, 1289–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, P.K.; Varshika, M.L.; Paul, A.; Isik, M.; Balaji, A.; Das, A. Implementing spiking neural networks on neuromorphic architectures: A review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.08897. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, Y. Hardware implementation of spiking neural networks on FPGA. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodamoradi, A.; Denolf, K.; Kastner, R. S2n2: A fpga accelerator for streaming spiking neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Virtual, 28 February–2 March 2021; pp. 194–205. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Mei, Z.; Shrestha, A.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Q. Encoding, model, and architecture: Systematic optimization for spiking neural network in FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, Virtual, 2–5 November 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Vyas, A.; Trivedi, G. FPGA implementation of simplified spiking neural network. In Proceedings of the 2020 27th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Glasgow, UK, 23–25 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kakani, V.; Li, X.; Cui, X.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, H. Implementation of Field-Programmable Gate Array Platform for Object Classification Tasks Using Spike-Based Backpropagated Deep Convolutional Spiking Neural Networks. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, D.; Escobar Sanabria, D.; Camargo, C. A Methodology and Open-Source Tools to Implement Convolutional Neural Networks Quantized with TensorFlow Lite on FPGAs. Electronics 2023, 12, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yantır, H.E.; Fouda, M.E.; Eltawil, A.M.; Salama, K.N. Toward the optimal design and FPGA implementation of spiking neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 3988–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseiny, A.; Jaberipur, G. Complex exponential functions: A high-precision hardware realization. Integration 2020, 73, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, R.; Menon, K.P. FPGA implementation of exponential function using cordic IP core for extended input range. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, 18–19 May 2018; pp. 597–600. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Ercegovac, M.D.; Xiao, Y. Complex function approximation using two-dimensional interpolation. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2013, 63, 2948–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malík, P. High throughput floating point exponential function implemented in FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Montpellier, France, 8–10 July 2015; pp. 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xilinx. Block RAM. 2020. Available online: https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/am007-versal-memory/Block-RAM-Introduction (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Xilinx. Introduction to System Generator. 2020. Available online: https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug948-vivado-sysgen-tutorial/Introduction-to-System-Generator (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Saidani, T.; Dia, D.; Elhamzi, W.; Atri, M.; Tourki, R. Hardware co-simulation for video processing using xilinx system generator. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 1–3 July 2009; Volume 1, pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xilinx. Introducing the Vivado IDE. 2020. Available online: https://docs.xilinx.com/r/en-US/ug910-vivado-getting-started/Introducing-the-Vivado-IDE (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Susuki, K. Myelin: A Special Membrane for Cell Communication. Nat. Educ. 2010, 3, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Neural Dynamics Analysis for A Novel Bio-inspired Logistic Spiking Neuron Model. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 January 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, H.E.; Awwal, A.A.S. Artificial neural networks using complex numbers and phase encoded weights. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, B71–B82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






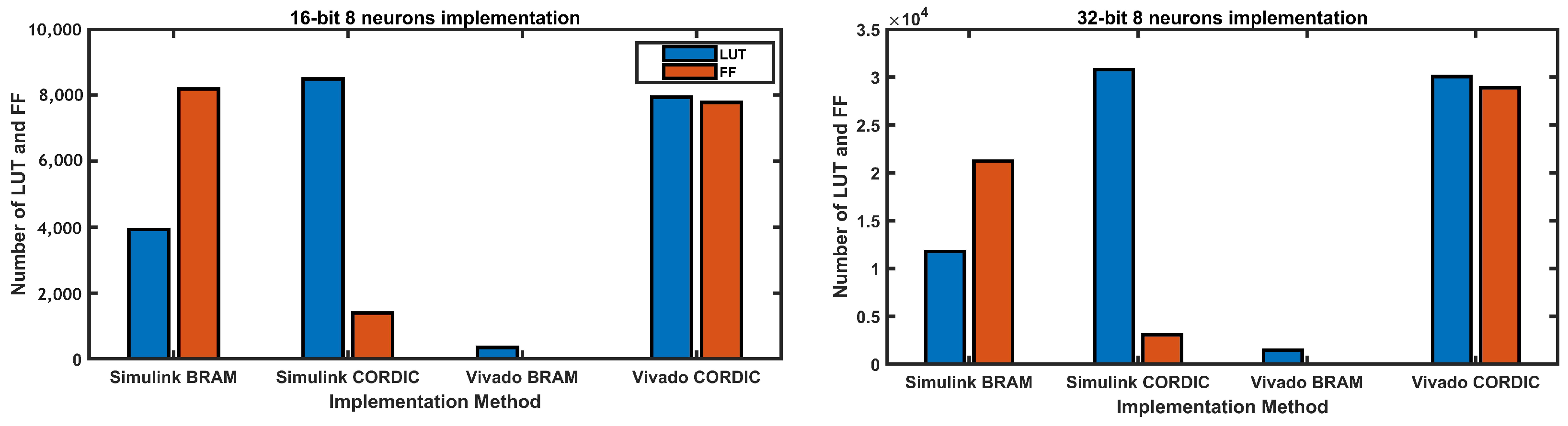
| Resource Usages | Bit Size | BRAM Simulink | BRAM Vivado | CORDIC Simulink | CORDIC Vivado |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUT usages | 8 | 286 | 41 | 612 | 548 |
| LUT usages | 16 | 965 | 202 | 2160 | 2094 |
| LUT usages | 32 | 2904 | 337 | 7660 | 7473 |
| FF usages | 8 | 514 | 0 | 196 | 516 |
| FF usages | 16 | 2190 | 0 | 412 | 1944 |
| FF usages | 32 | 5336 | 116 | 874 | 7217 |
| Resource Usages | Bit Size | BRAM Simulink | BRAM Vivado | CORDIC Simulink | CORDIC Vivado |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUT | 8 | 296 | 341 | 622 | 835 |
| LUT | 16 | 983 | 234 | 2116 | 2148 |
| LUT | 32 | 2940 | 639 | 7694 | 7777 |
| FF | 8 | 546 | 20 | 196 | 516 |
| FF | 16 | 1966 | 0 | 508 | 1944 |
| FF | 32 | 5336 | 88 | 874 | 7218 |
| BRAM | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| BRAM | 16 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| BRAM | 32 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| DSP | 8 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| DSP | 16 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| DSP | 32 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| IO | 8 | 73 | 73 | 73 | 73 |
| IO | 16 | 145 | 145 | 145 | 145 |
| IO | 32 | 289 | 289 | 289 | 289 |
| 8-Neuron Method | Max. Number of Neurons | |
|---|---|---|
| 16 Bit | 32 Bit | |
| Simulink BRAM | 64 | 16 |
| Simulink CORDIC | 32 | 8 |
| Vivado BRAM | 128 | 64 |
| Vivado CORDIC | 32 | 8 |
| 8-Neuron Method | Maximum Frequency (MHz) | |
|---|---|---|
| 16 Bit | 32 Bit | |
| Simulink BRAM | 250 | 150 |
| Simulink CORDIC | 19 | 9 |
| Vivado BRAM | 50 | 53 |
| Vivado CORDIC | 200 | 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, M.; Zhang, L.; Ng, K.T.W.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. Complex-Exponential-Based Bio-Inspired Neuron Model Implementation in FPGA Using Xilinx System Generator and Vivado Design Suite. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8080621
Ahmad M, Zhang L, Ng KTW, Chowdhury MEH. Complex-Exponential-Based Bio-Inspired Neuron Model Implementation in FPGA Using Xilinx System Generator and Vivado Design Suite. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(8):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8080621
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Maruf, Lei Zhang, Kelvin Tsun Wai Ng, and Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury. 2023. "Complex-Exponential-Based Bio-Inspired Neuron Model Implementation in FPGA Using Xilinx System Generator and Vivado Design Suite" Biomimetics 8, no. 8: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8080621
APA StyleAhmad, M., Zhang, L., Ng, K. T. W., & Chowdhury, M. E. H. (2023). Complex-Exponential-Based Bio-Inspired Neuron Model Implementation in FPGA Using Xilinx System Generator and Vivado Design Suite. Biomimetics, 8(8), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8080621








