Whole-Body Dynamics-Based Aerial Fall Trajectory Optimization and Landing Control for Humanoid Robot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
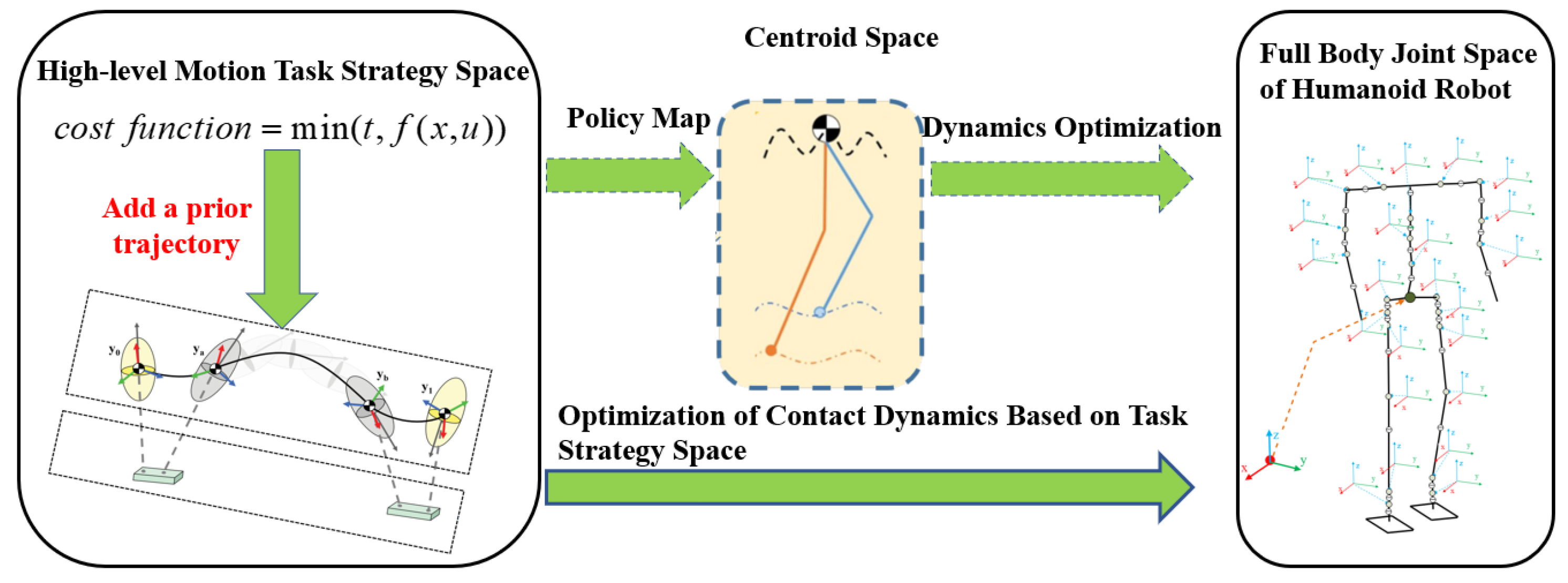
- An optimized trajectory for the robot falling from the air is generated, enabling the humanoid robot to land smoothly on the ground.
- Direct mapping is adopted from the high-level task strategy space to the joint space, bypassing the need to go through the centroid space as in previous methods.
- Simulation results show that the trajectories optimized after adding contact point information are more human-like compared to those without contact information.
2. Trajectory Optimization
2.1. Methods
2.2. Cost Function
2.3. Constraints
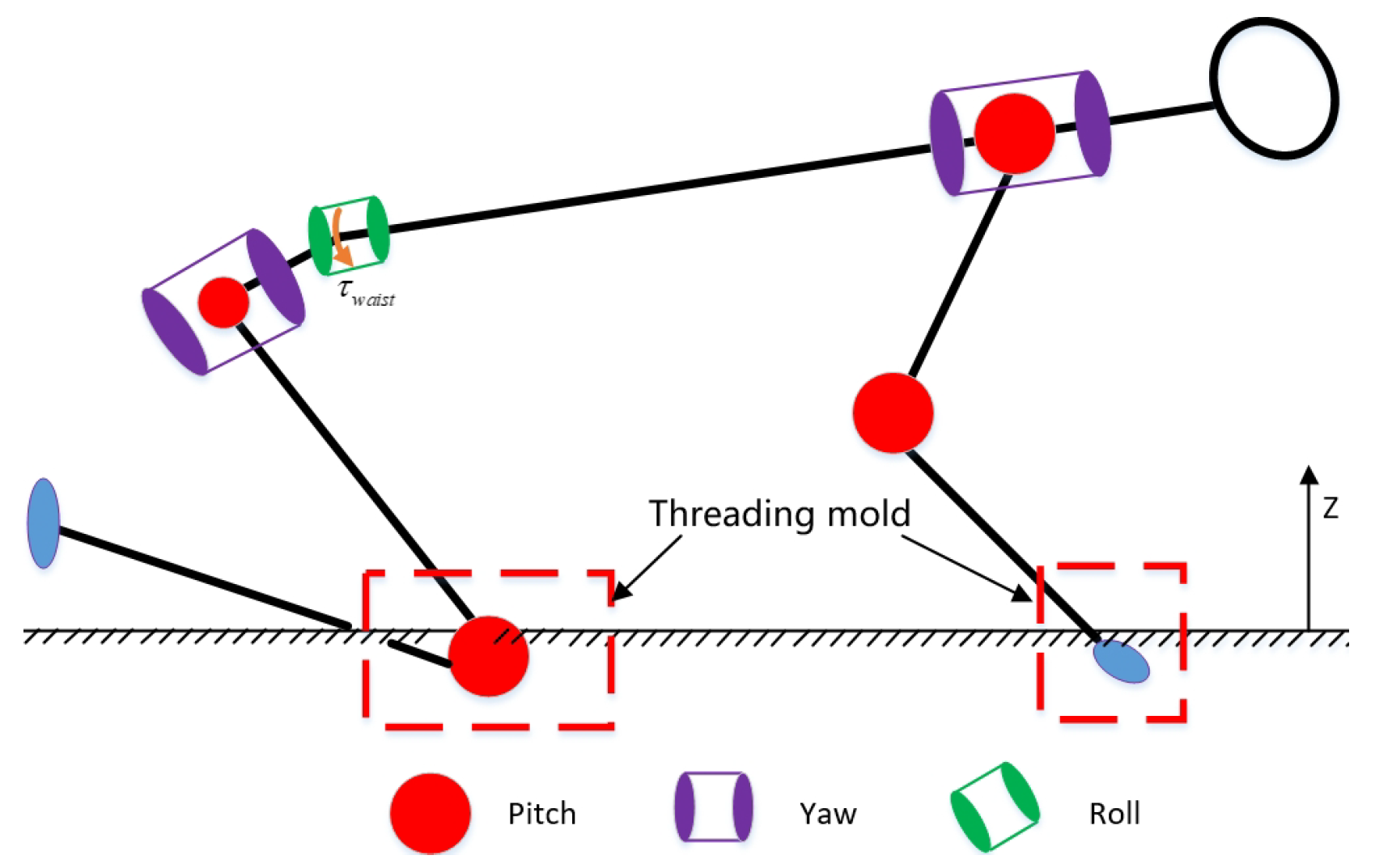
3. Controller
3.1. Air Stage Controller
3.2. Landing Controller
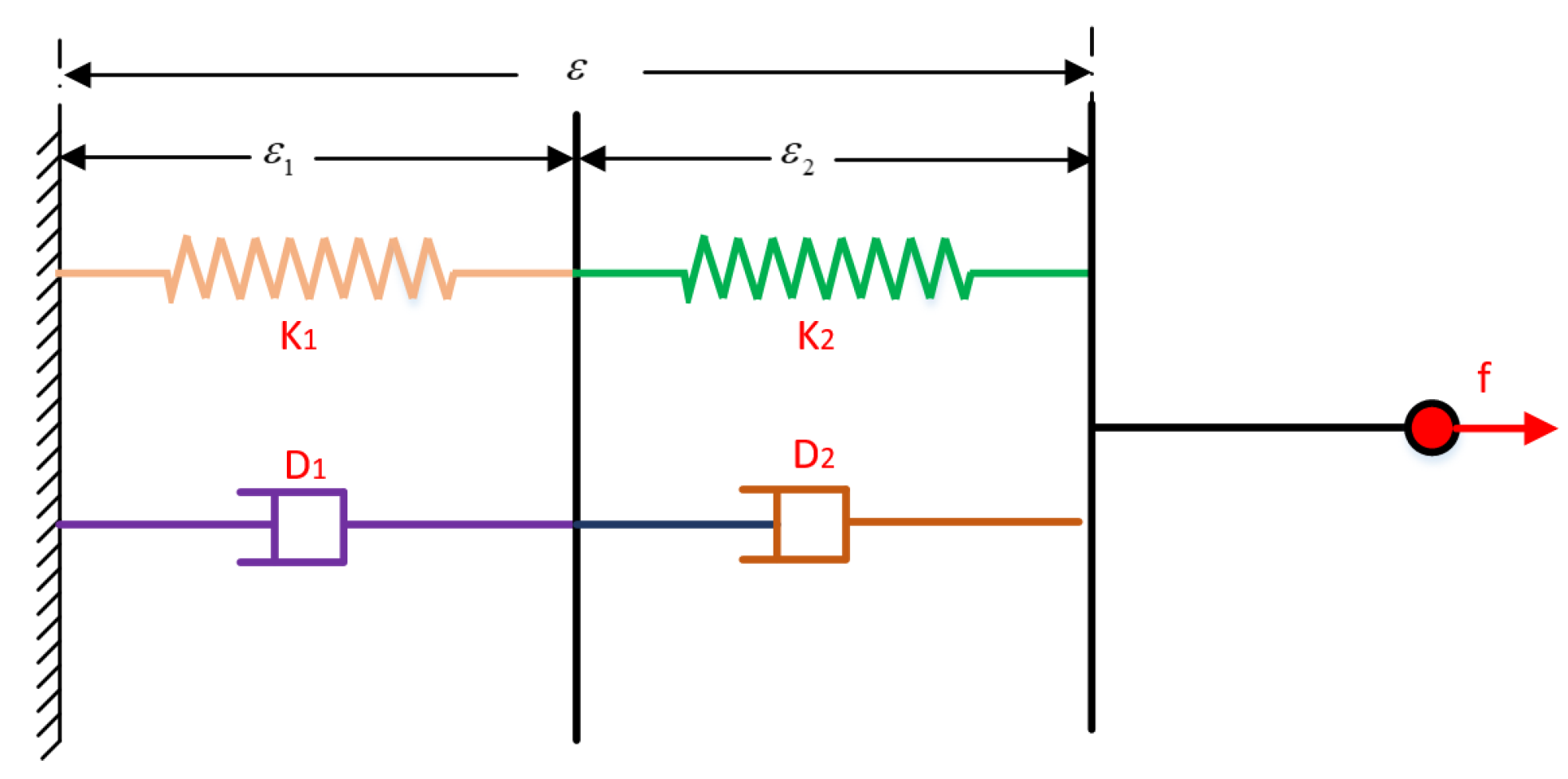
3.3. Spring–Damper Controller
4. Simulation and Experiment
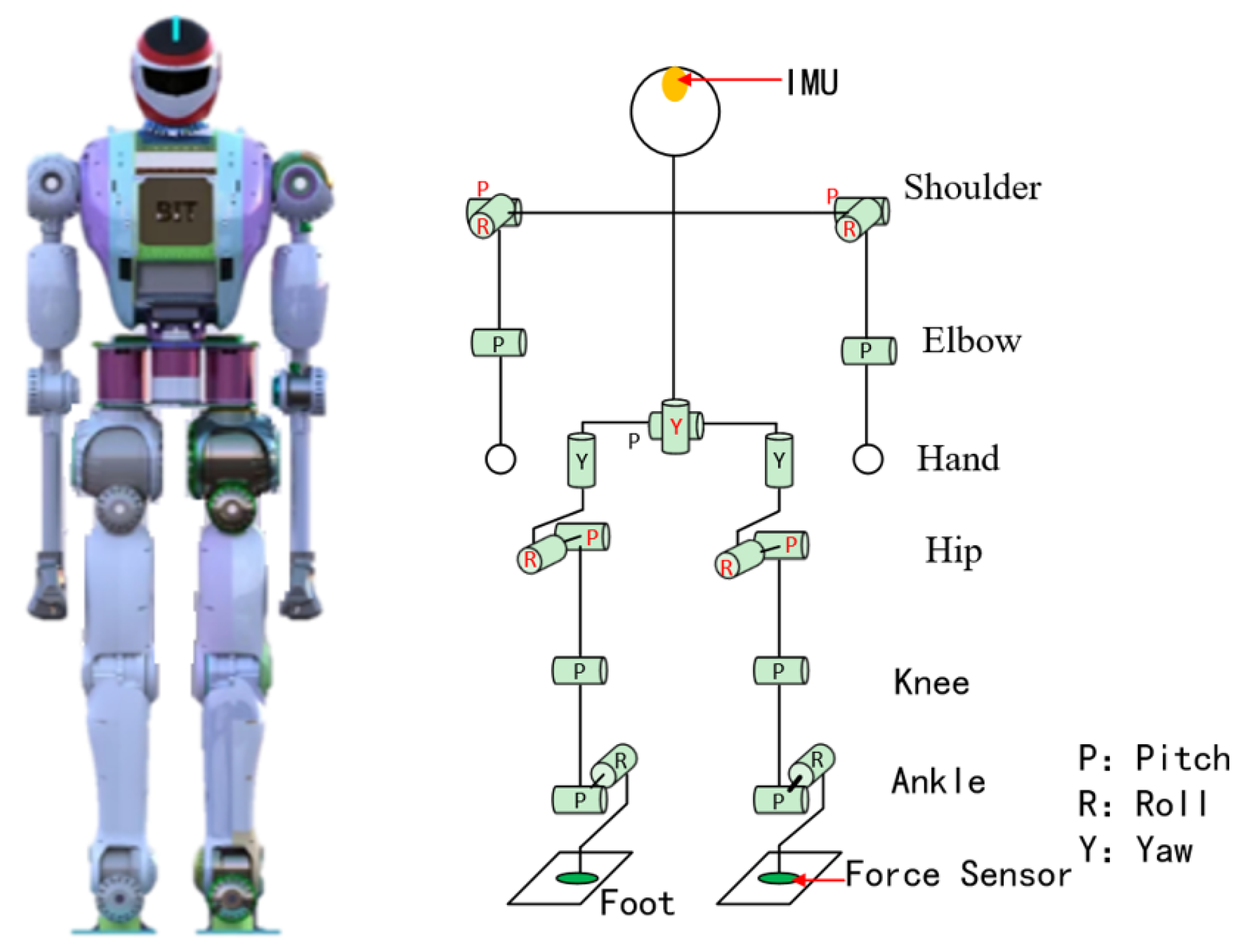
4.1. Simulation Platform
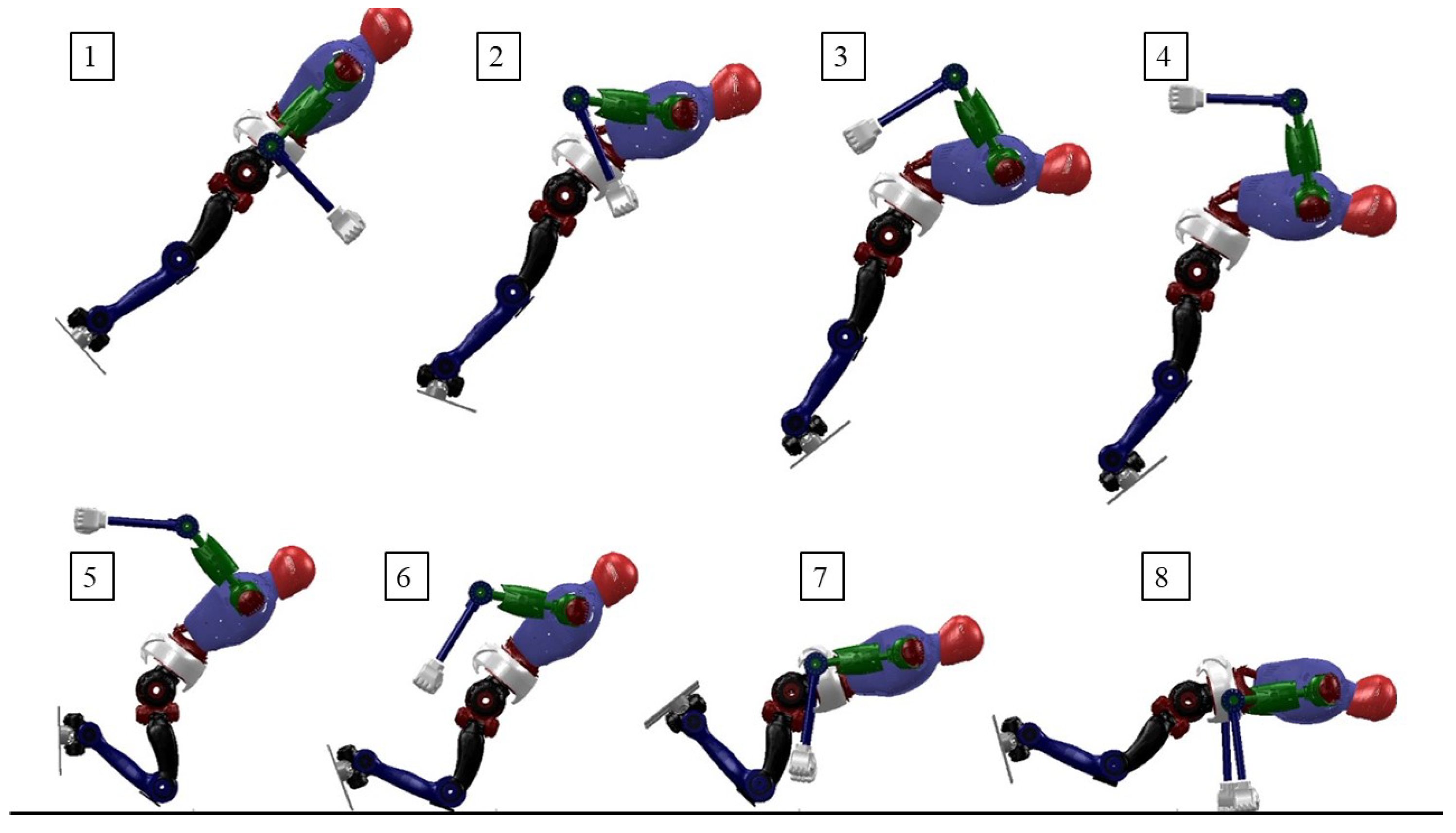
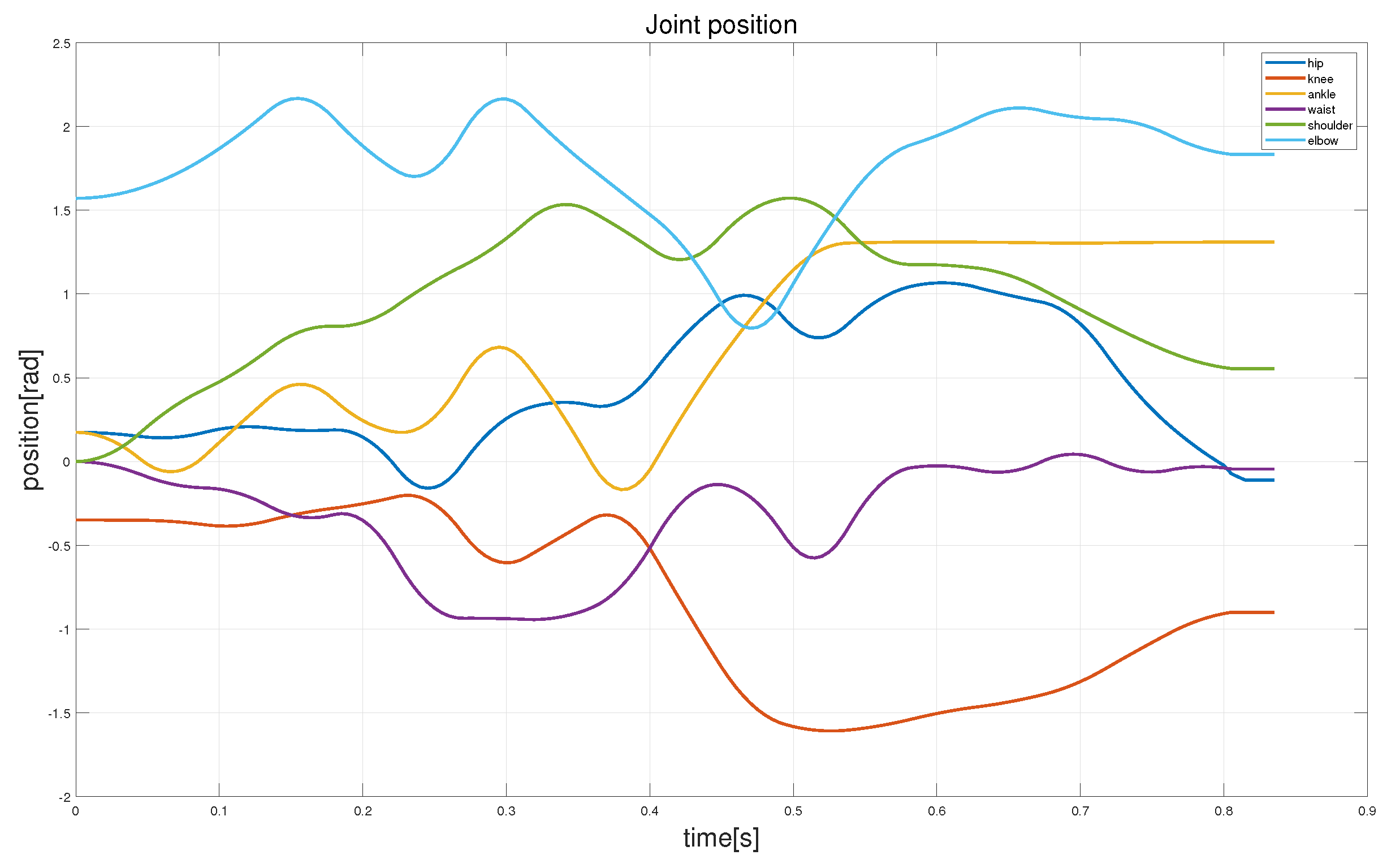
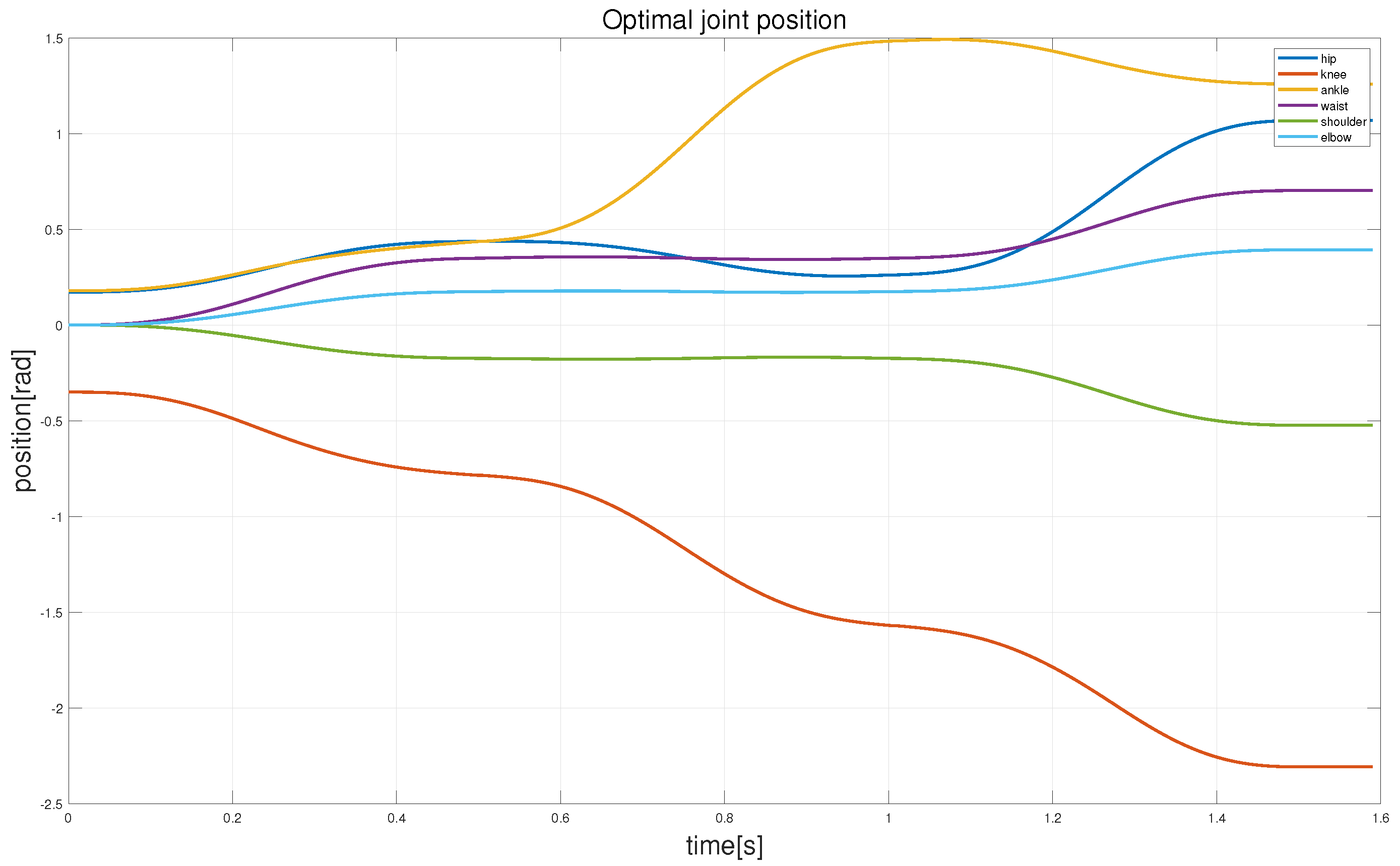
4.2. Trajectory Optimization
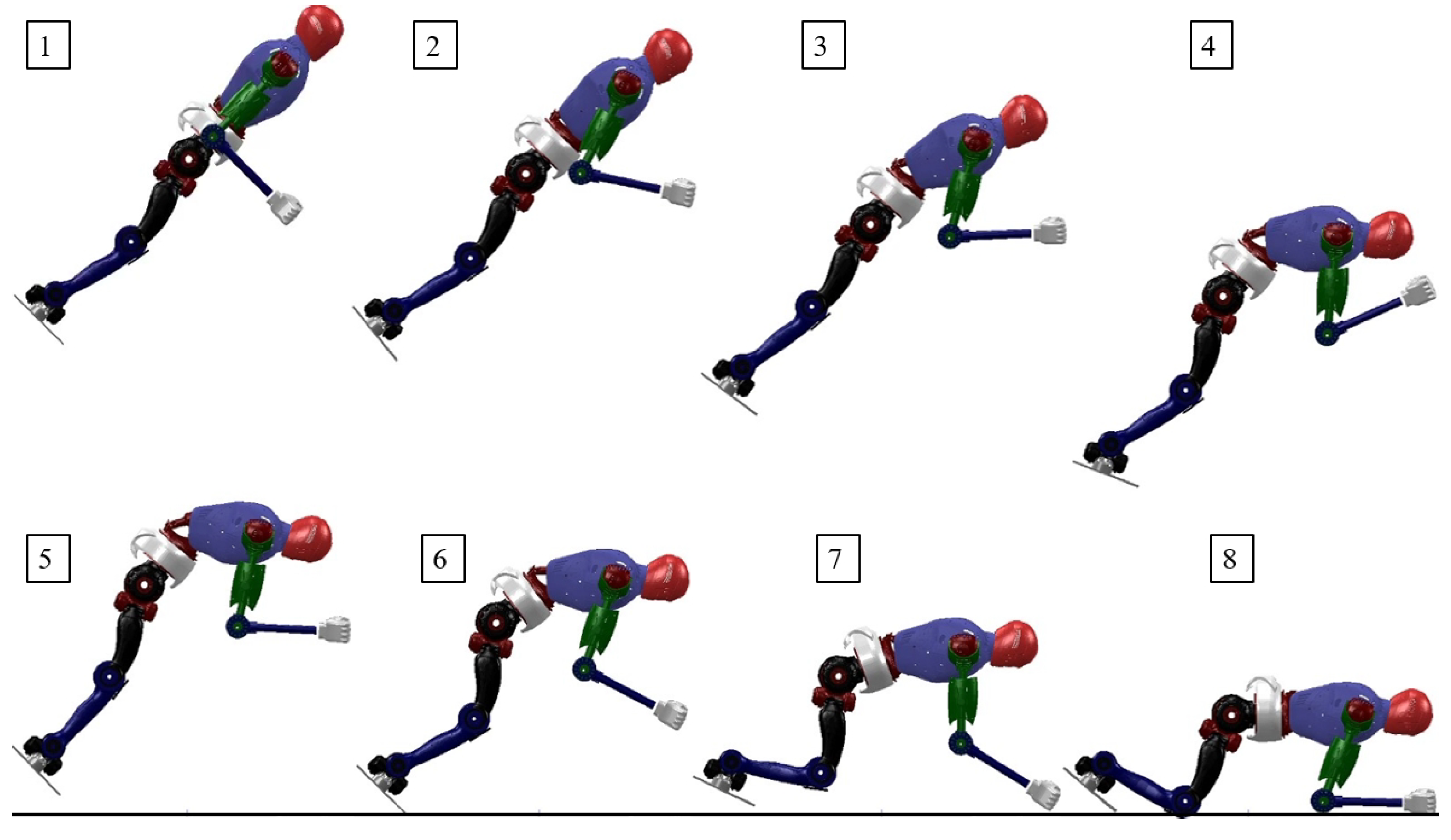
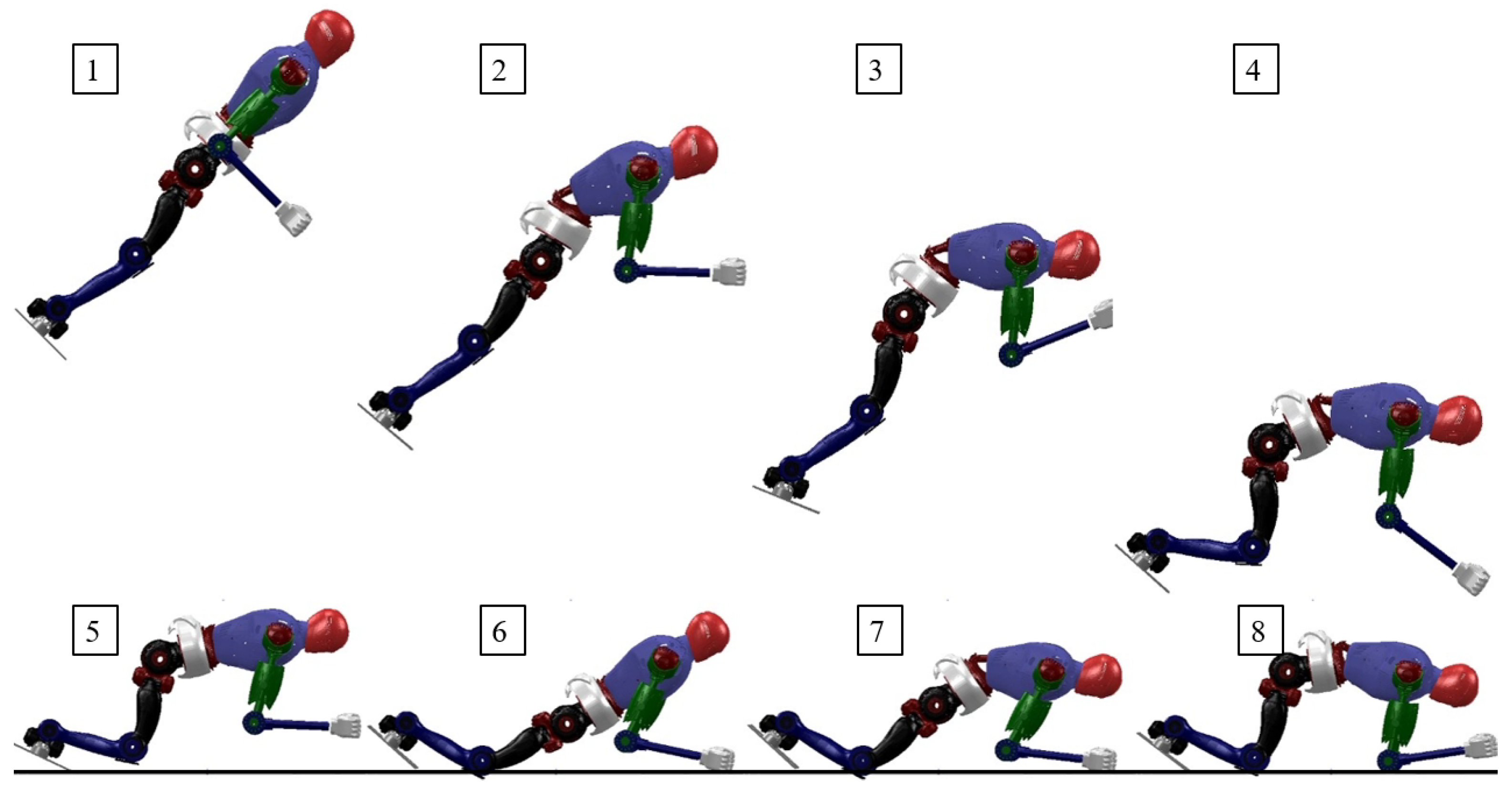
4.3. Simulation
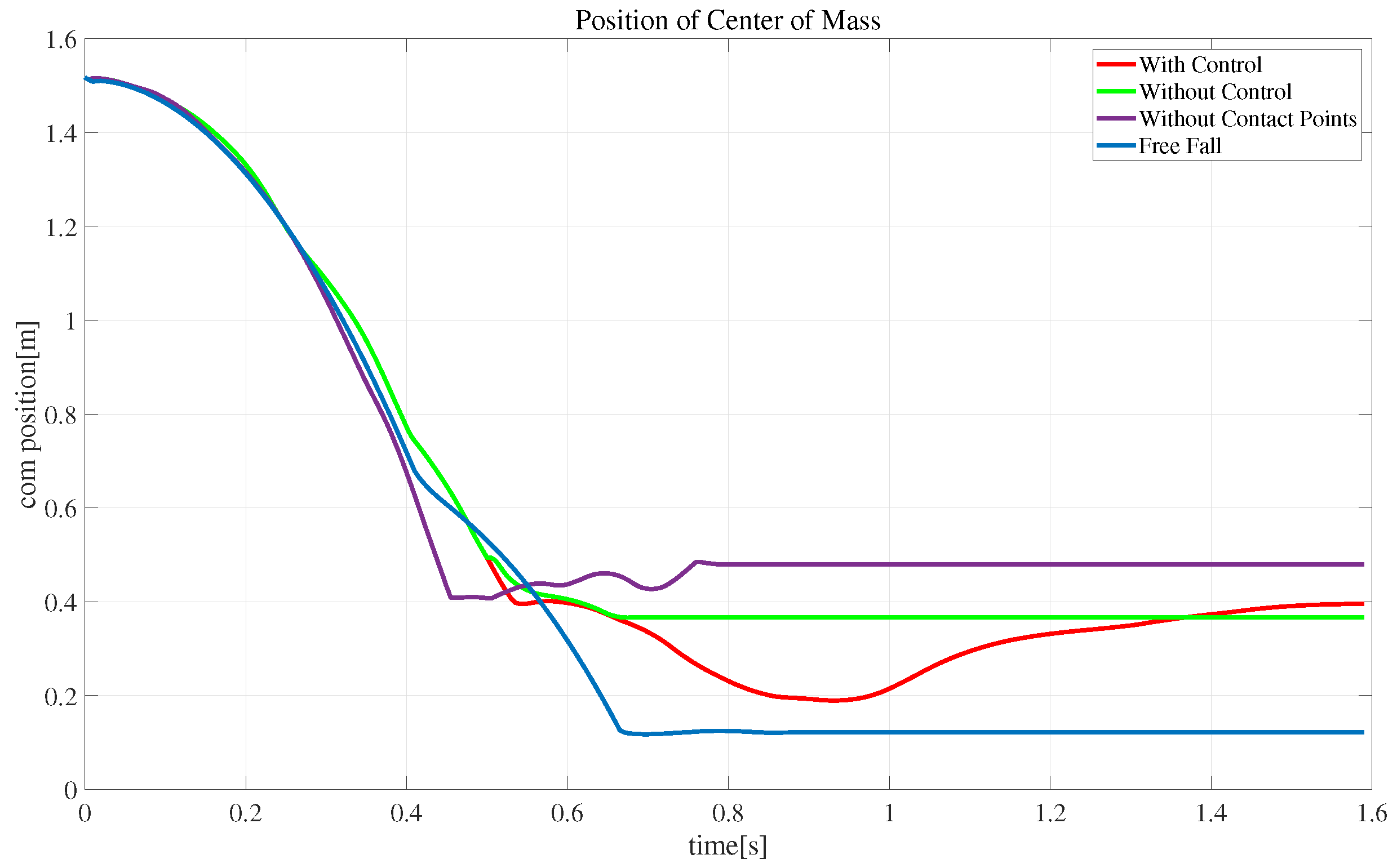
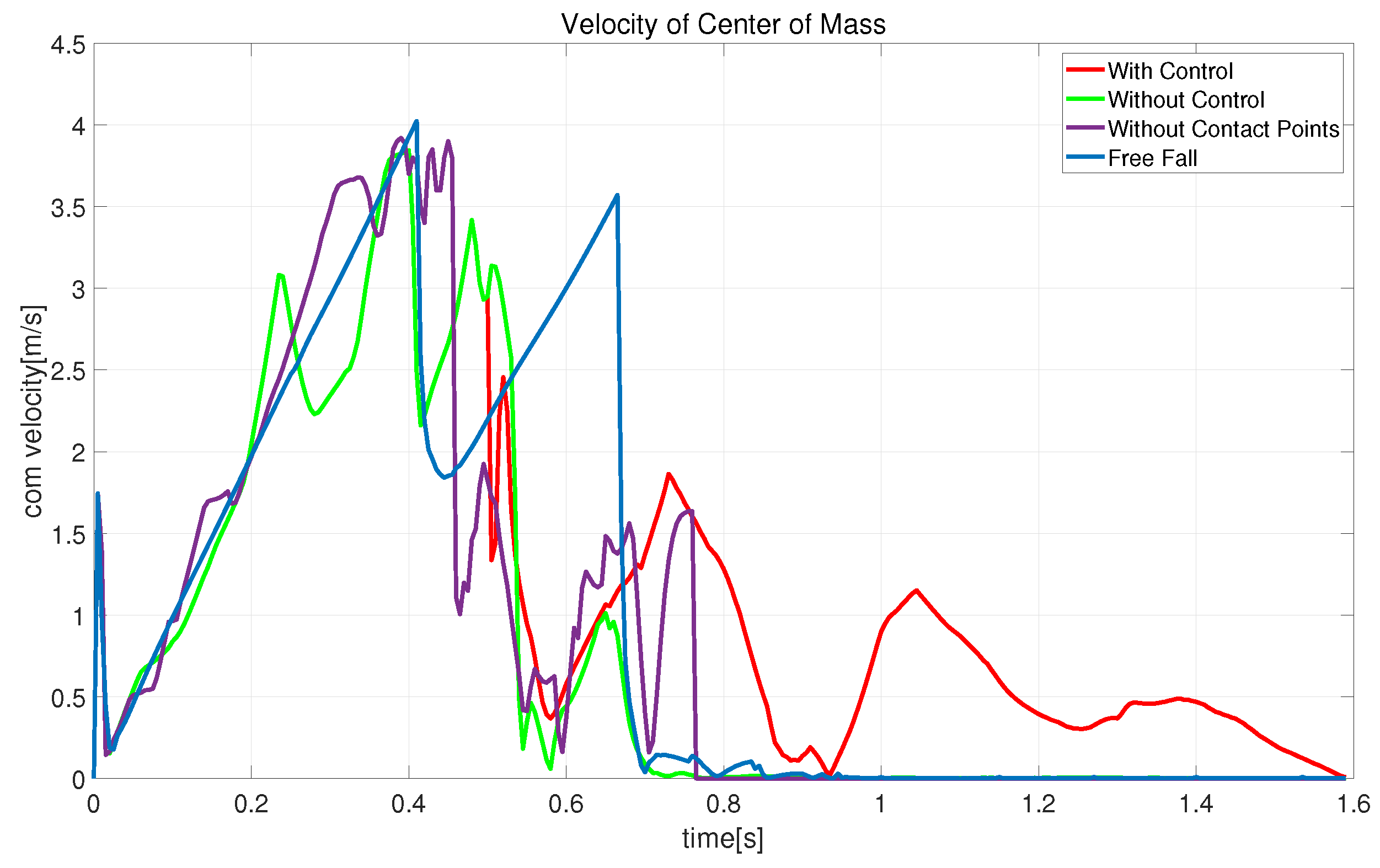
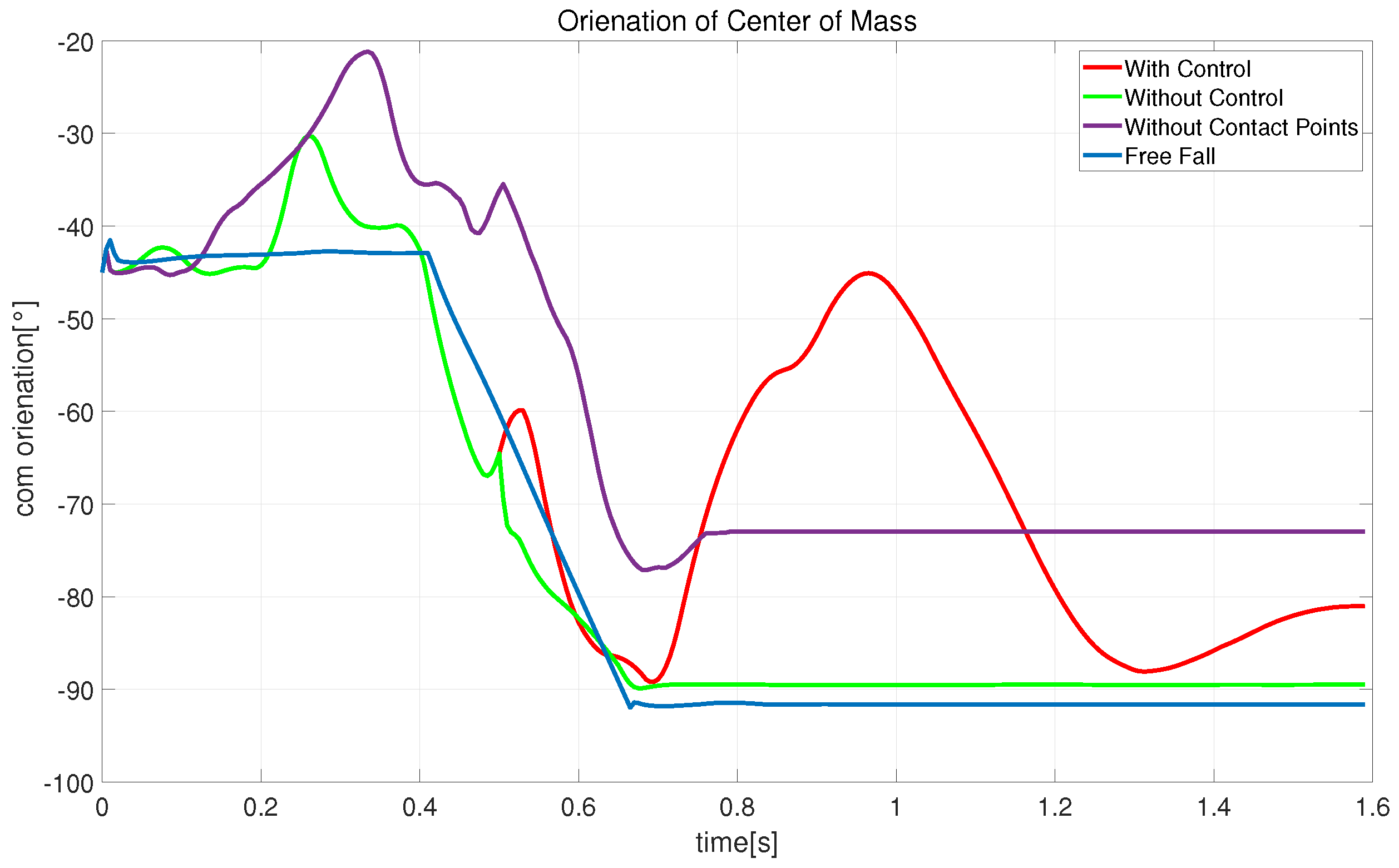
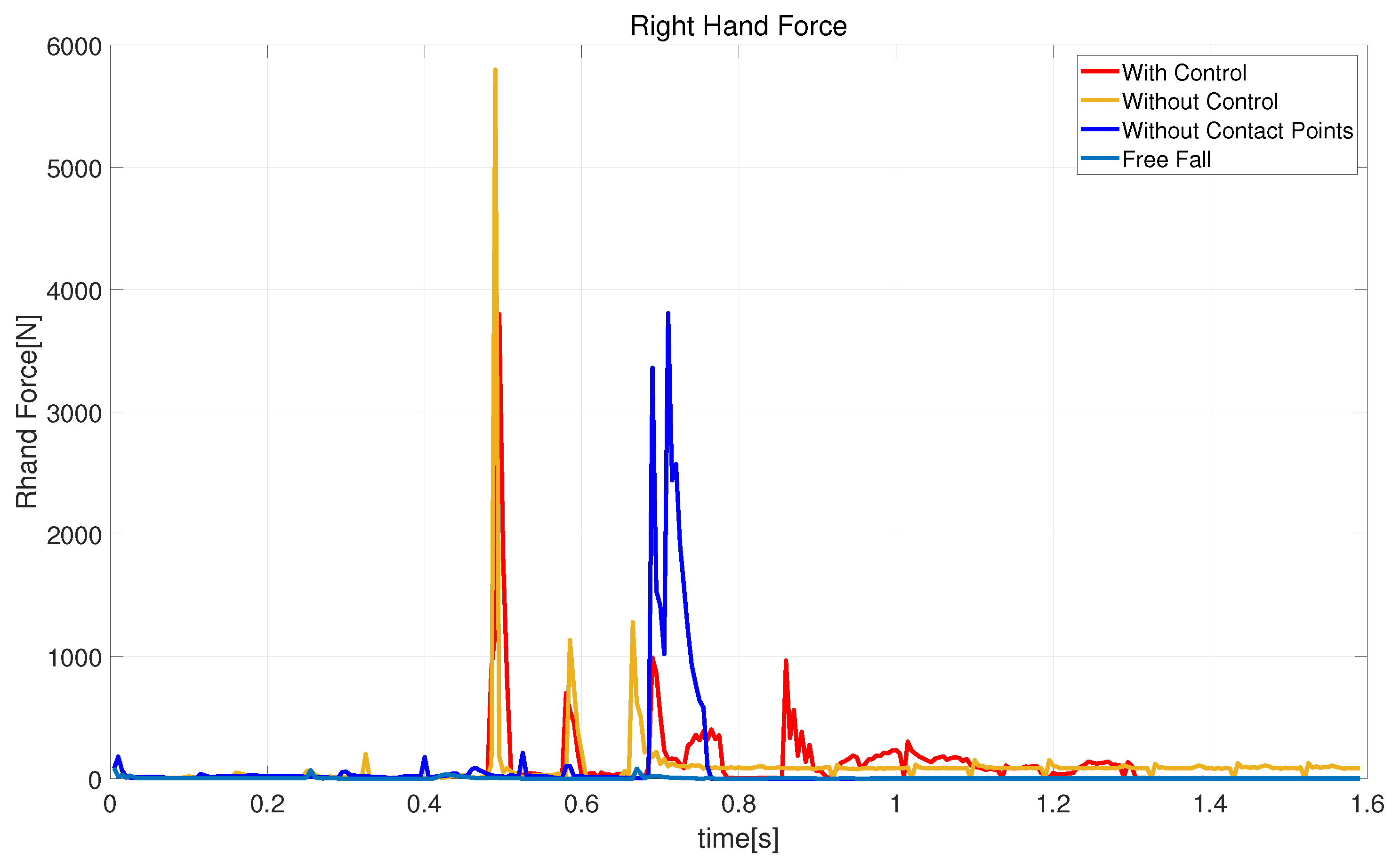
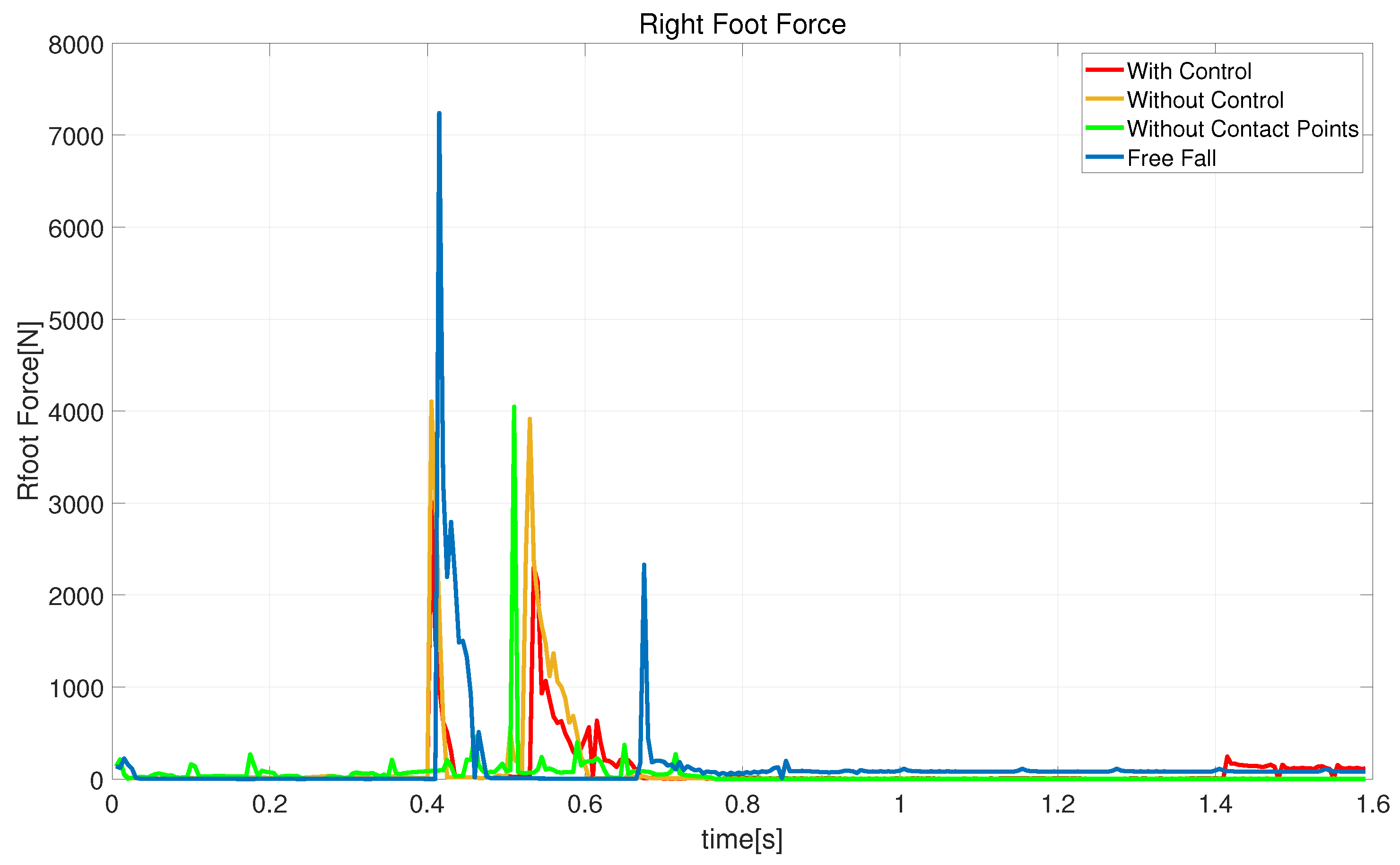
4.3.1. Simple State Variables
4.3.2. Extended State Variables
4.3.3. Extended State Variables and Control
4.3.4. Graphical Analysis
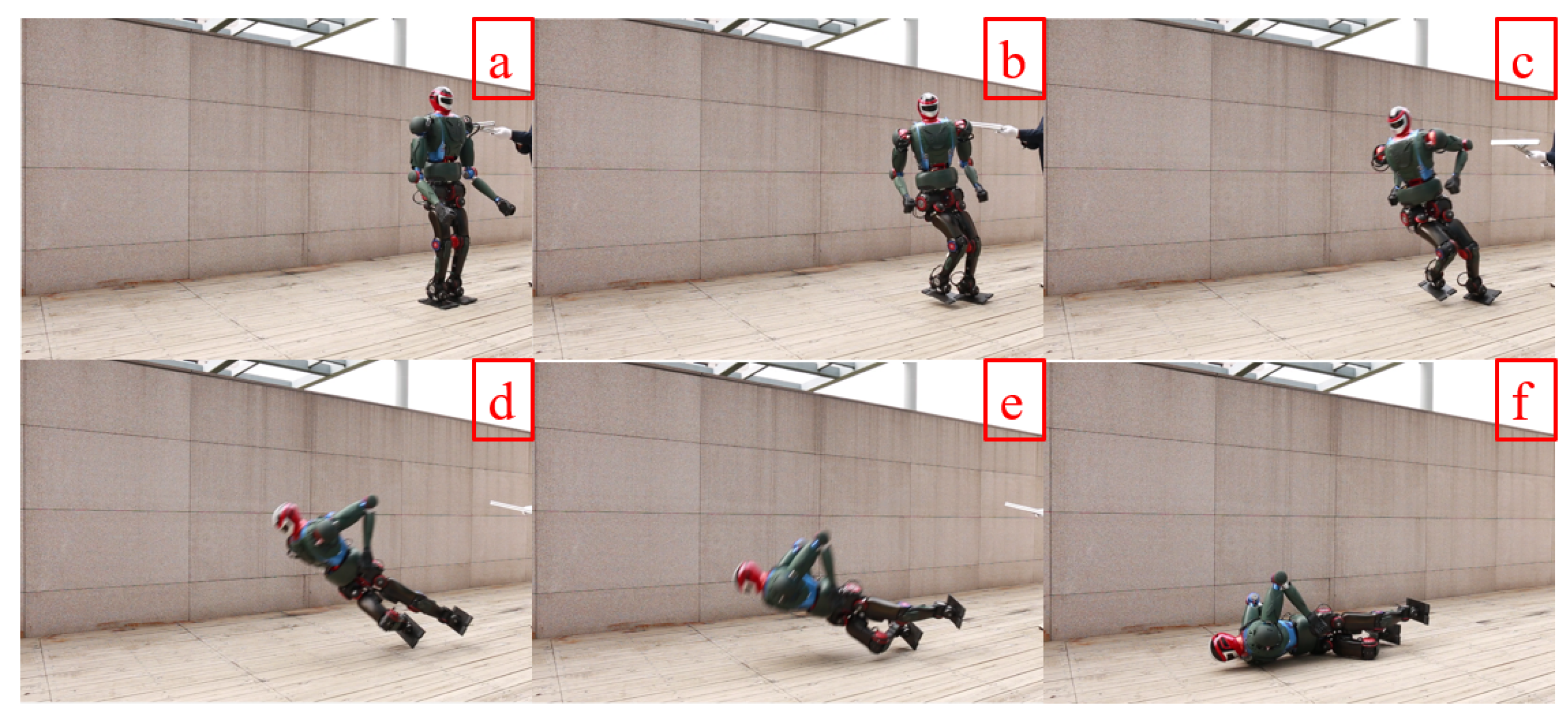
4.4. Experiment
5. Conclusions
6. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, S.; Xinjilefu, X.; Atkeson, C.G.; Kim, J. Optimization based controller design and implementation for the atlas robot in the darpa robotics challenge finals. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE-RAS 15th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 3–5 November 2015; Volume 10, pp. 1028–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Elon Musk Reveals New Optimus Robot Video! (2023 Tesla Shareholder Meetinig). Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KW3iRzXs940 (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Jeong, H.; Lee, I.; Oh, J.; Lee, K.K.; Oh, J.H. A robust walking controller based on online optimization of ankle, hip, and stepping strategies. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 1367–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Harada, K.; Kanehiro, F.; Miyamori, G.; Akachi, K. Humanoid robot HRP-3. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 2471–2478. [Google Scholar]
- Mesesan, G.; Englsberger, J.; Garofalo, G.; Ott, C.; Albu-Schffer, A. Dynamic walking on compliant and uneven terrain using dcm and passivity-based whole-body control. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE-RAS 19th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–17 October 2019; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyarmane, K.; Chappellet, K.; Vaillant, J.; Kheddar, A. Quadratic programming for multirobot and task-space force control. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, S.; Cisneros, R.; Benallegue, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Nakaoka, S.; Morisawa, M.; Kaneko, K.; Kanehiro, F. Impact acceleration of falling humanoid robot with an airbag. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE-RAS 16th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Cancun, Mexico, 15–17 November 2016; Volume 35, pp. 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Goswami, A.; Kaneko, K.; Kanehiro, F. Fall on backpack: Damage minimization of humanoid robots by falling on targeted body segments. Journal of Computational Nonlinear Dynamics. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2013, 8, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiuchi, Y.; Kamon, M.; Shimomura, N.; Yukizaki, S.; Inaba, M. Develop- ment of life-sized humanoid robot platform with robustness for falling down, long time working and error occurrence. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, K.; Kojio, Y.; Noda, S.; Sugai, F.; Inaba, M. Dynamic fall recovery motion generation on biped robot with shell protector. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 6741–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subburaman, R.; Lee, J.; Caldwell, D.G.; Tsagarakis, N.G. Online falling-over control of humanoids exploiting energy shaping and distribution methods. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 448–454. [Google Scholar]
- Braghin, F.; Henze, B.; Garzon, M.A.R. Optimal trajectory for active safe falls in humanoid robots. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE-RAS 19th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–17 October 2019; pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Del-Solar, J.; Palma-Amestoy, R.; Marchant, R.; Parra-Tsunekawa, I.; Zegers, P. Learning to fall: Designing low damage fall sequences for humanoid soccer robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2009, 57, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Liu, C.K. Multiple contact planning for minimizing damage of humanoid falls. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 2761–2767. [Google Scholar]
- Mujica, M.; Crespo, M.; Benoussaad, M.; Junco, S.; Fourquet, J.Y. Robust variable admittance control for human–robot co-manipulation of objects with unknown load. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2023, 79, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, A.S.S.; Ordys, A.; Pierscionek, B. Novel off-line self-tuning controller with guaranteed stability. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2023, 24, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Chen, T.; Zhu, H.; Fu, M.; Xu, J. Fuzzy variable impedance-based adaptive neural network control in physical human–robot interaction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2023, 237, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chignoli, M.; Kim, D.; Stanger-Jones, E.; Kim, S. The MIT humanoid robot: Design, motion planning, and control for acrobatic behaviors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE-RAS 20th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Munich, Germany, 19–21 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Huang, G.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Huang, Q. Vertical Jump of a Humanoid Robot with CoP-Guided Angular Momentum Control and Impact Absorption. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 3154–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, V.; Li, H.; Wensing, P.M.; Lin, H. Mini cheetah, the falling cat: A case study in machine learning and trajectory optimization for robot acrobatics. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 4635–4641. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, D. Online optimal landing control of the mit mini cheetah. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; An, J.; Chu, X.; Wang, S.; Wong, C.Y.; Au, K.S. Towards Safe Landing of Falling Quadruped Robots Using a 3-DoF Morphable Inertial Tail. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Norby, J.; Yim, J.K.; Johnson, A.M. Proprioception and Tail Control Enable Extreme Terrain Traversal by Quadruped Robots. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.04781. [Google Scholar]
- Roscia, F.; Focchi, M.; Del Prete, A.; Caldwell, D.G.; Semini, C. Reactive Landing Controller for Quadruped Robots. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.07748. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Valenzuela, A.; Tedrake, R. Whole-body motion planning with centroidal dynamics and full kinematics. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Madrid, Spain, 18–20 November 2014; pp. 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone, R. Robot Dynamics Algorithms; Edinburgh University: Edinburgh, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Posa, M.; Cantu, C.; Tedrake, R. A direct method for trajectory optimization of rigid bodies through contact. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, R.; Benallegue, M.; Morisawa, M.; Kanehiro, F. QP-based task-space hybrid/parallel control for multi-contact motion in a torque-controlled humanoid robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE-RAS 19th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.; Powell, M.J.; Katz, B.; Carlo, J.D.; Kim, S. Optimized jumping on the mit cheetah 3 robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7448–7454. [Google Scholar]
- Murooka, M.; Morisawa, M.; Kanehiro, F. Centroidal trajectory generation and stabilization based on preview control for humanoid multi-contact motion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 8225–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereid, A.; Ames, A.D. FROST: Fast Robot Optimization and Simulation Toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- OptimTraj—Trajectory Optimization for Matlab. Available online: https://github.com/MatthewPeterKelly/OptimTraj (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Kelly, M. An Introduction to Trajectory Optimization: How to Do Your Own Direct Collocation. SIAM Rev. 2017, 59, 849–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Dong, C.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Q. Falling Prediction based on Machine Learning for Biped Robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2021, 103, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

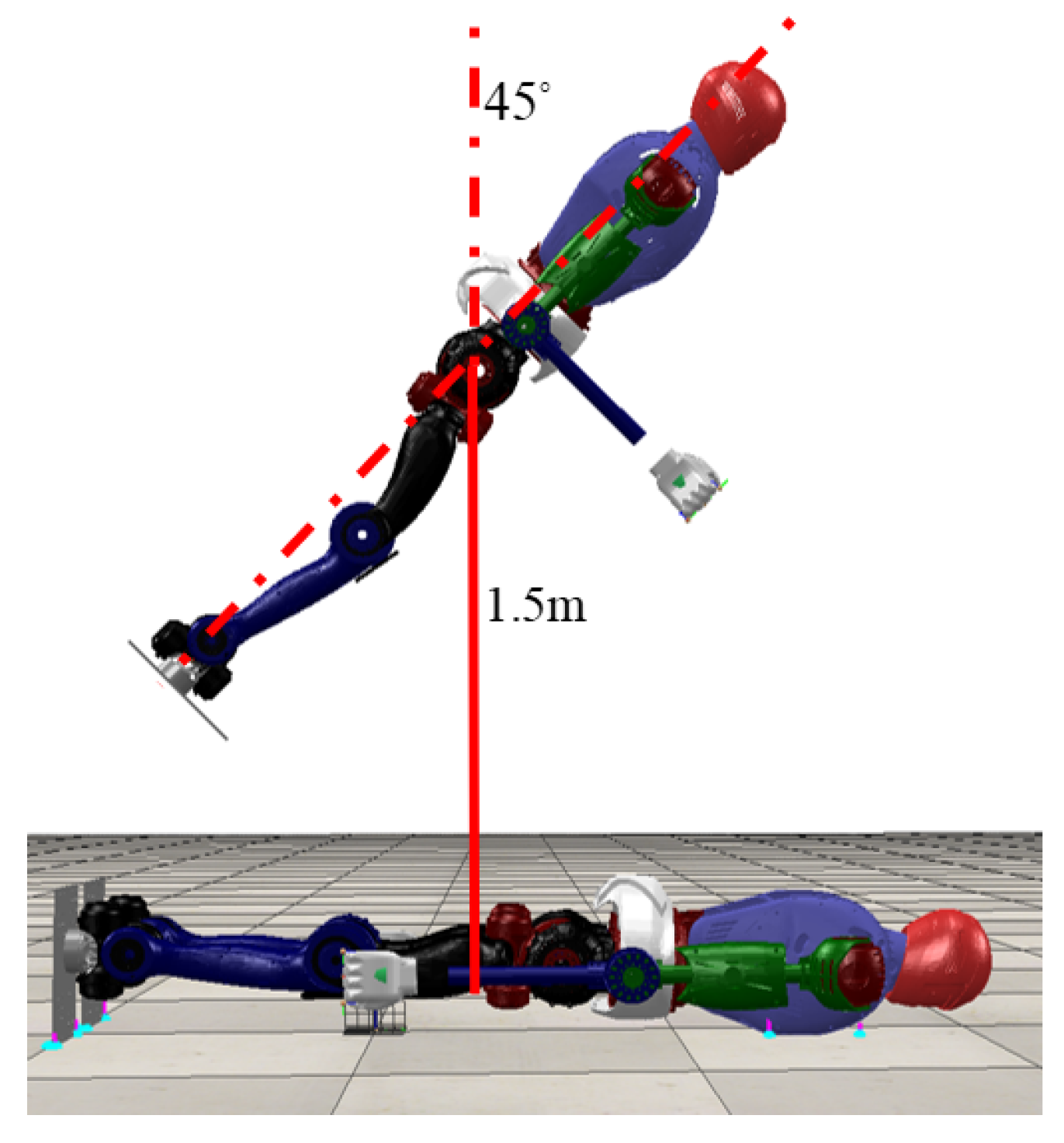
| Parameter | Size | Mass |
|---|---|---|
| Thigh | 361 (mm) | 7.36 (kg) |
| Shank | 330 (mm) | 5.12 (kg) |
| Boom | 350 (mm) | 4.15 (kg) |
| Jib | 360 (mm) | 2.3 (kg) |
| Others | ─ | 31.07 (kg) |
| Total Mass | ─ | 50 (kg) |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | diag([10 850 1760]) | 200 | |||
| 0.8 | diag([0.005 27 50]) | 1500 | |||
| 0.005 | diag([5 150 1000]) | 1800 | |||
| 0.03 | diag([0.005 52.3 65]) | Q | diag([1 1 1]) | ||
| diag([10 1000 2000]) | 0.52 | R | 0.0001 | ||
| diag([0.01 12.7 45]) | 1 | m | 50 | ||
| diag([2 100 750]) | 0.75 | ||||
| diag([0.002 10.0 25]) | 210,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, W.; Gao, J.; Cao, J.; Xin, X.; Jin, M.; Chen, X. Whole-Body Dynamics-Based Aerial Fall Trajectory Optimization and Landing Control for Humanoid Robot. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8060460
Zuo W, Gao J, Cao J, Xin X, Jin M, Chen X. Whole-Body Dynamics-Based Aerial Fall Trajectory Optimization and Landing Control for Humanoid Robot. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(6):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8060460
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Weilong, Junyao Gao, Jingwei Cao, Xilong Xin, Mingyue Jin, and Xuechao Chen. 2023. "Whole-Body Dynamics-Based Aerial Fall Trajectory Optimization and Landing Control for Humanoid Robot" Biomimetics 8, no. 6: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8060460
APA StyleZuo, W., Gao, J., Cao, J., Xin, X., Jin, M., & Chen, X. (2023). Whole-Body Dynamics-Based Aerial Fall Trajectory Optimization and Landing Control for Humanoid Robot. Biomimetics, 8(6), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8060460





