SmartLact8: A Bio-Inspired Robotic Breast Pump for Customized and Comfort Milk Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
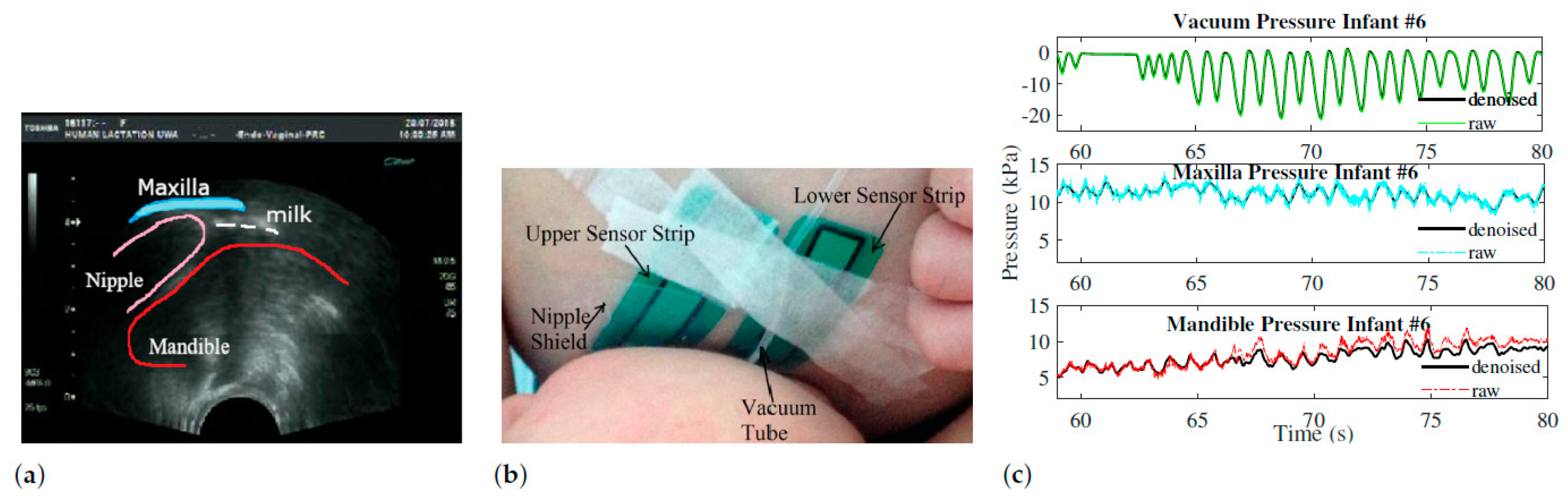
2. Preliminary Data from Clinical Study
3. Materials and Methods
- A flexible breast phantom for testing
- A vacuum pump that generates rhythmic intra-oral pressure
- Two miniature pneumatic pumps along with two solenoid valves that generate rhythmic compression pressure
- A soft robotic pad with eight pneumatic actuators for compressive-pressure mimicking
- A piezoelectric sensor pad for data capturing
- An inline pressure sensor that captures air flow rates
- Drivers and control systems for commanding the inputs and recording the output components.

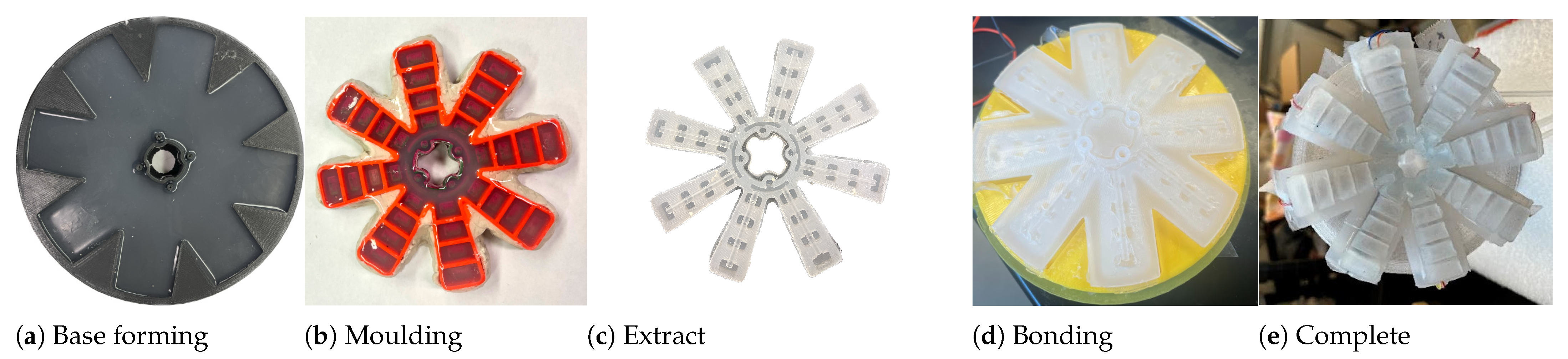
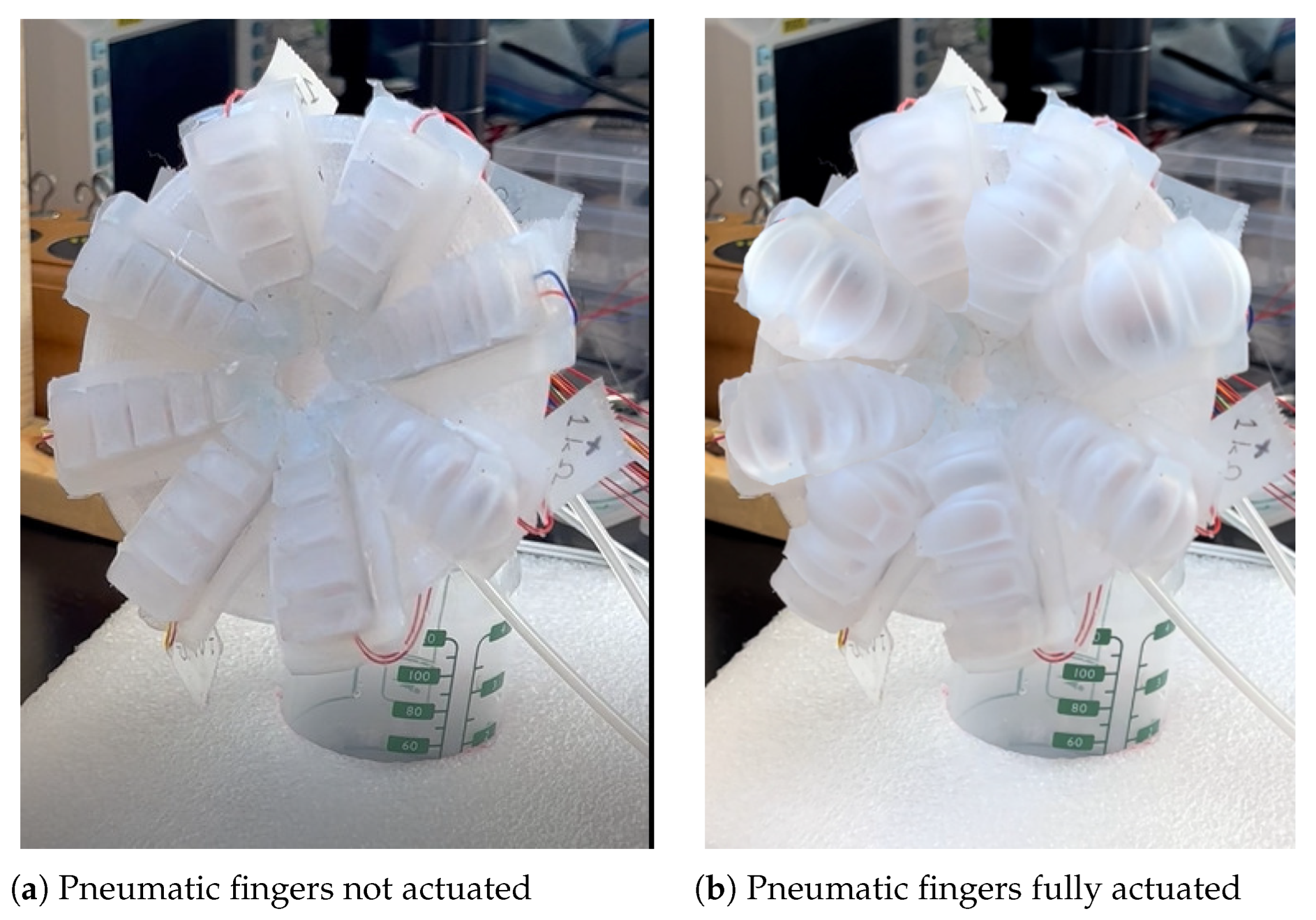
3.1. Bio-Inspired Soft Robotic Pad for Breast Pumping
Fabrication of the Soft Robotic Pad
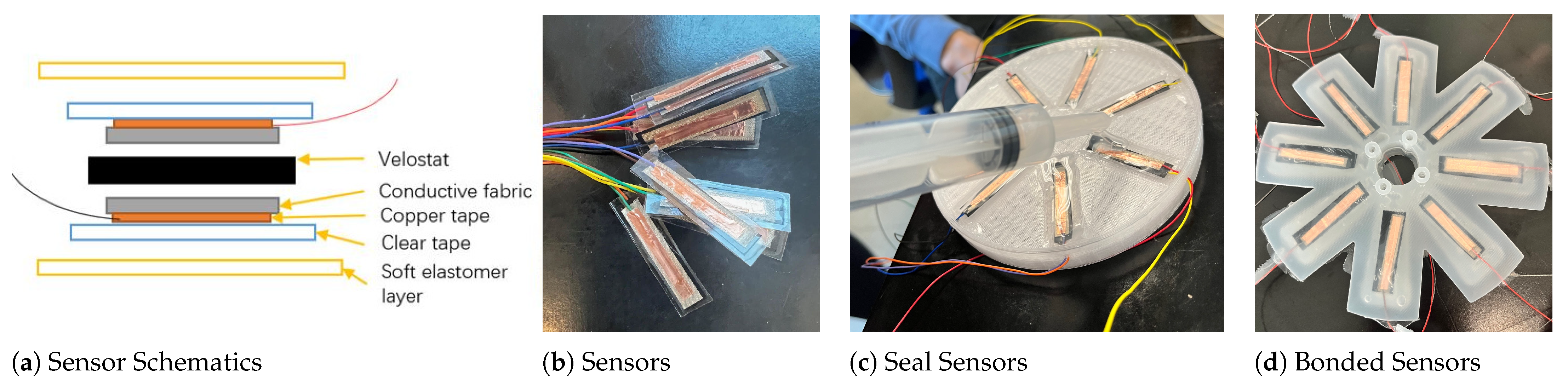
3.2. Sensor Fabrication
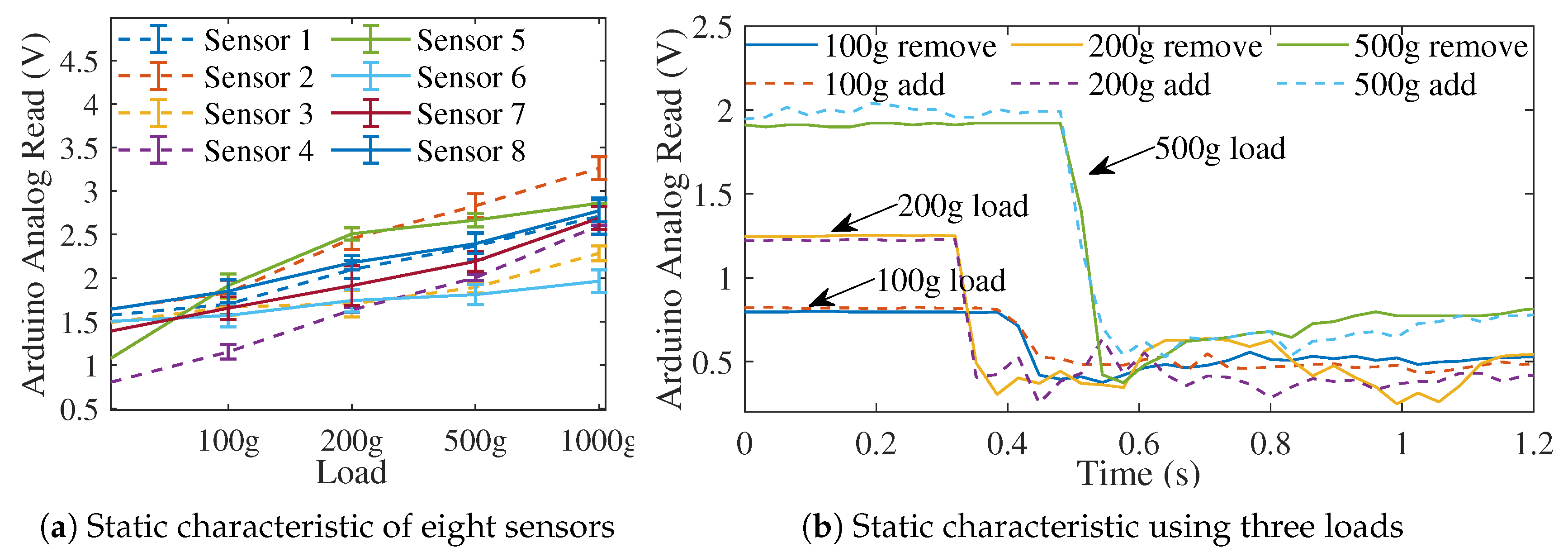
3.3. Sensor Calibration
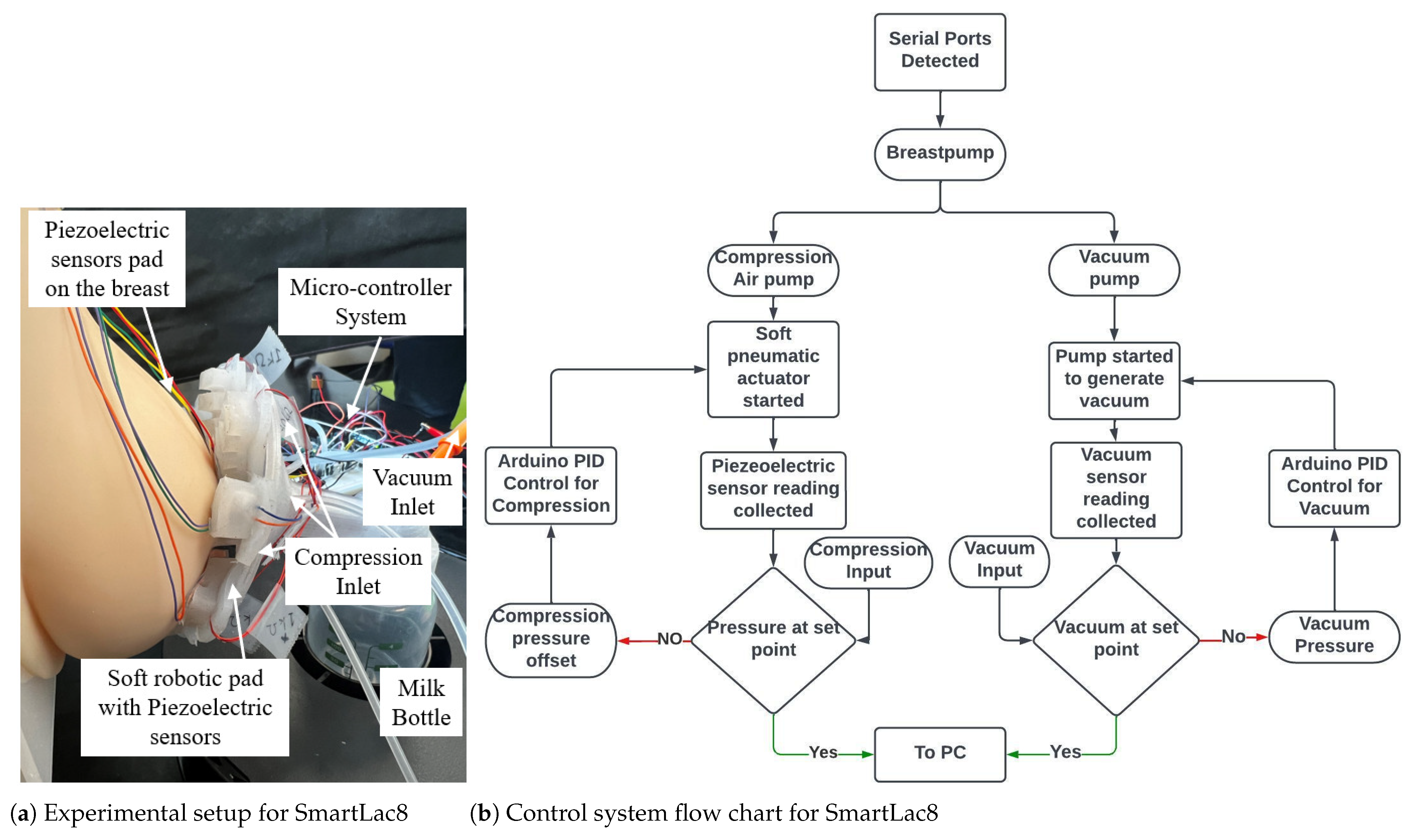
3.4. Complete Design, Control System and Experimental Setup
4. Results
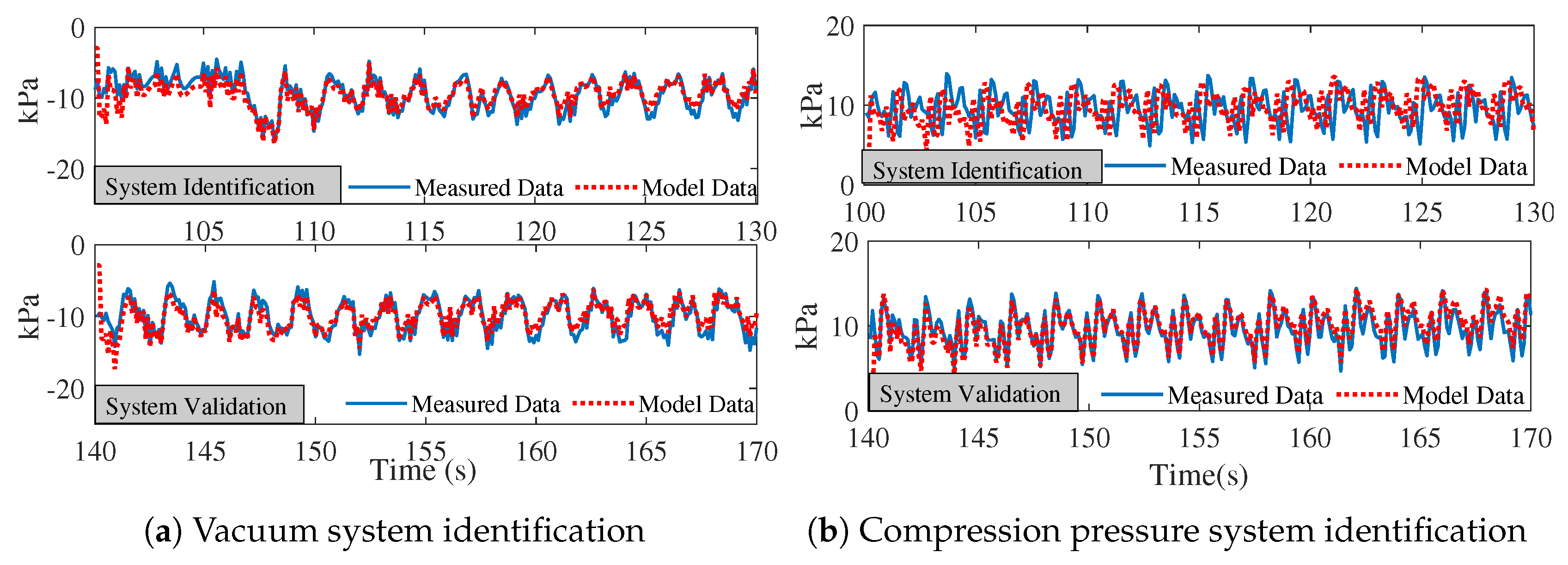
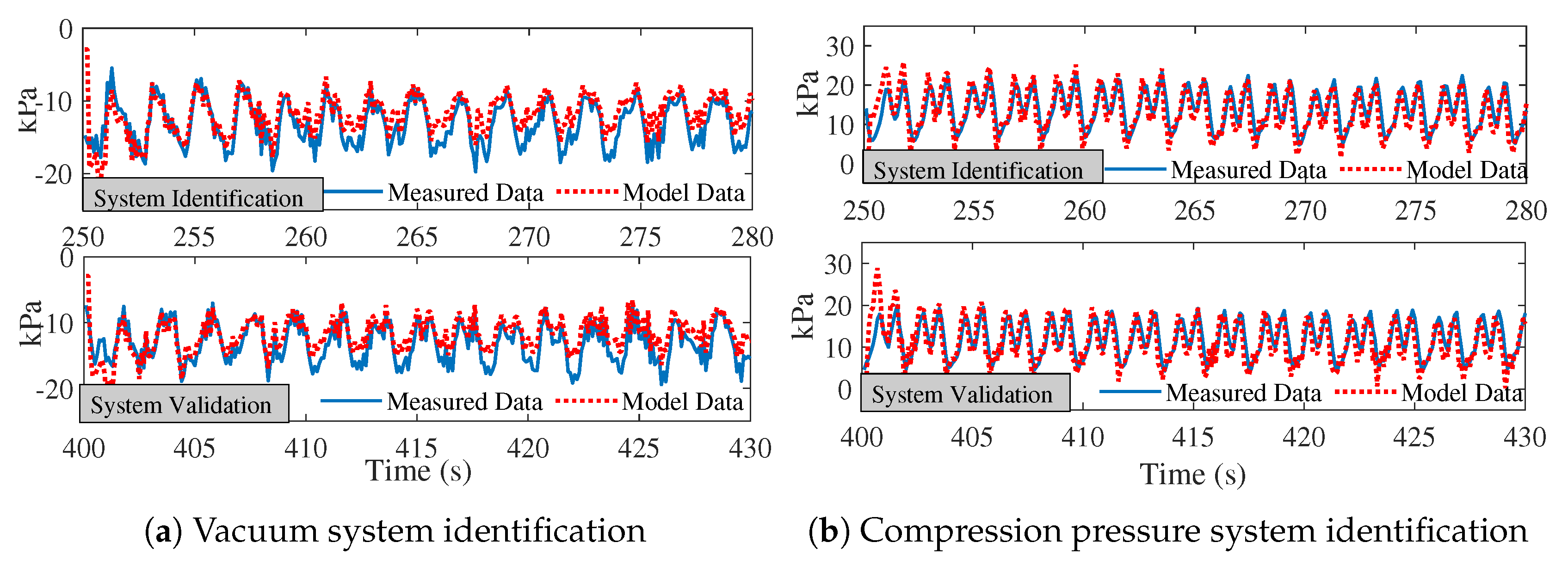
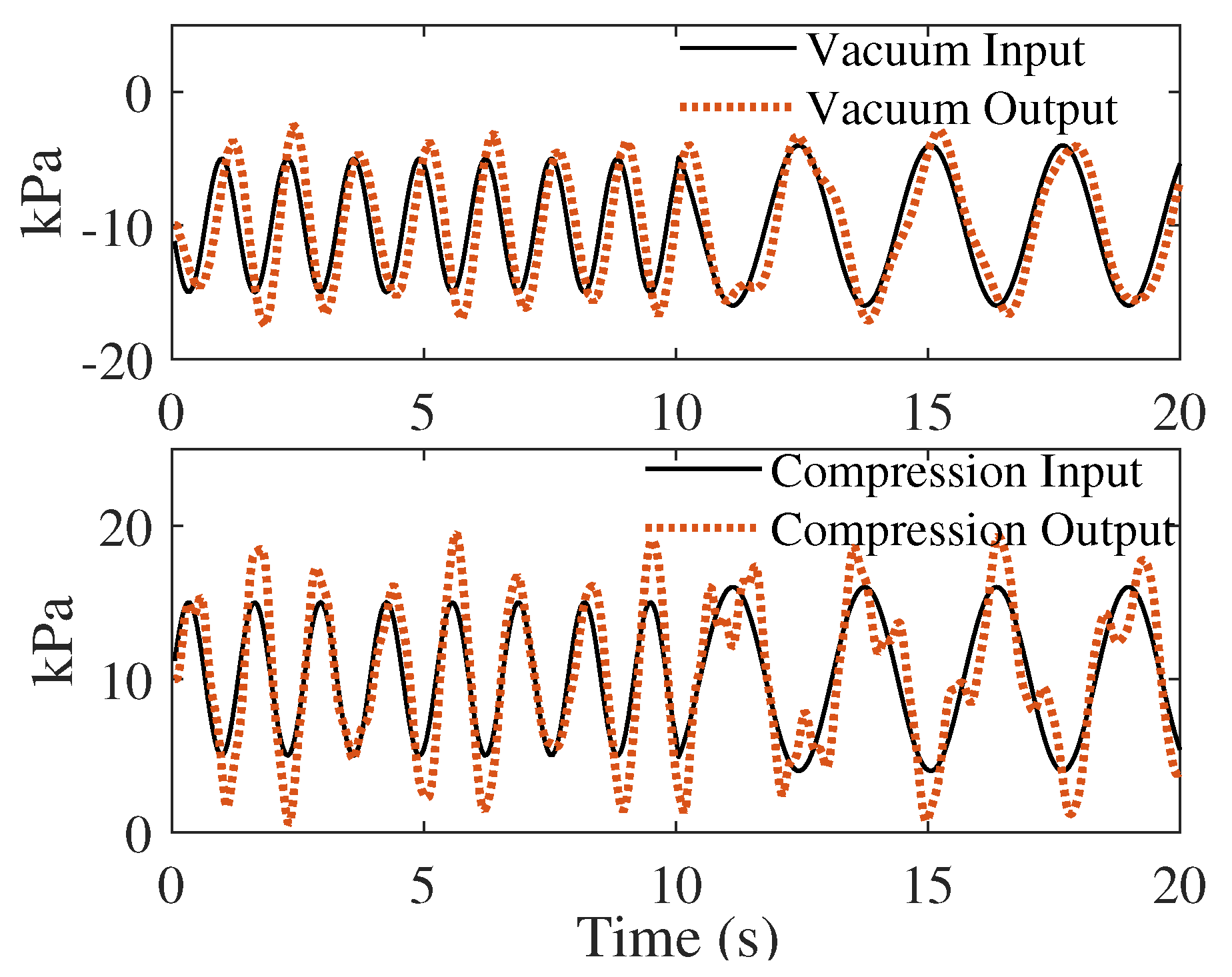
4.1. Soft Robotic Pad Actuation and Open-Loop System Identification
4.2. Closed-Loop Controller Design and System Performance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three dimensional |
| MIMO | Multiple-input multiple-output |
| PID | Proportional-integral-derivative |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| ID | Identification |
| PC | Personal computer |
References
- Schwartz, K.; D’arcy, H.J.; Gillespie, B.; Bobo, J.; Longeway, M.; Foxman, B. Factors associated with weaning in the first 3 months postpartum. J. Fam. Pract. 2002, 51, 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.A.; Binns, C.W.; Oddy, W.H.; Graham, K.I. Predictors of breastfeeding duration: Evidence from a cohort study. Pediatrics 2006, 117, e646–e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odom, E.C.; Li, R.; Scanlon, K.S.; Perrine, C.G.; Grummer-Strawn, L. Reasons for earlier than desired cessation of breastfeeding. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e726–e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuebe, A.M.; Horton, B.J.; Chetwynd, E.; Watkins, S.; Grewen, K.; Meltzer-Brody, S. Prevalence and risk factors for early, undesired weaning attributed to lactation dysfunction. J. Women’s Health 2014, 23, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, D.T.; Mitoulas, L.R.; Kent, J.C.; Larsson, M.; Hartmann, P.E. The use of ultrasound to characterize milk ejection in women using an electric breast pump. J. Hum. Lact. 2005, 21, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfield, E.C.; Richardson, M.J.; Lee, K.G.; Margetts, S. Coordination of sucking, swallowing, and breathing and oxygen saturation during early infant breast-feeding and bottle-feeding. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 60, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatalo, D.; Jiang, L.; Geddes, D.; Hassanipour, F. Nipple Deformation and Peripheral Pressure on the Areola during Breastfeeding. J. Biomech. Eng. 2020, 142, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolridge, M.W.; Baum, J.D. The regulation of human milk flow. Perinat. Nutr. 1988, 6, 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Woolridge, M.W. The ’anatomy’ of infant sucking. Midwifery 1986, 2, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, D.T.; Sakalidis, V.S.; Hepworth, A.R.; McClellan, H.L.; Kent, J.C.; Lai, C.T.; Hartmann, P.E. Tongue movement and intra-oral vacuum of term infants during breastfeeding and feeding from an experimental teat that released milk under vacuum only. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatalo, D.; Hassanipour, F. An Experimental Study on Human Milk Rheology: Behavior Changes from External Factors. Fluids 2020, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Woolridge, M.; Baum, J. An ultrasonographic study of the organisation of sucking and swallowing by newborn infants. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1986, 28, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseev, N.; Omel’ianuk, E.; Talalaeva, N. Dynamics of milk ejection reflex during continuous rhythmic stimulation of areola-nipple complex of the mammary gland. Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal Imeni IM Sechenova/Rossiiskaia Akademiia Nauk 2000, 86, 711–719. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseev, N.P.; Ilyin, V.I. The Mechanics of Breast Pumping: Compression Stimuli Increased Milk Ejection. Breastfeed. Med. 2016, 11, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, N.R.; Newton, M. Relation of the let-down reflex to the ability to breast feed. Pediatrics 1950, 5, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, H. The early failure of breast feeding: A clinical study of its causes and their prevention. Arch. Dis. Child. 1946, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, J.C.; Ramsay, D.T.; Doherty, D.; Larsson, M.; Hartmann, P.E. Response of breasts to different stimulation patterns of an electric breast pump. J. Hum. Lact. 2003, 19, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglash, A.; Malloy, M.L. Breastmilk expression and breast pump technology. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 58, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, V.I.; Alekseev, N.P.; Troschkin, M.M.; Uleziko, V.A. Comparative Assessment of Excretion of Milk from Two Breast Pumps with Different Vacuum Strength and Duration. Breastfeed. Med. 2019, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Hung, J.S.; Wang, L.Y.; Ko, M.J.; Chou, W.; Kuo, H.C.; Lin, B.S. Development of a wireless oral-feeding monitoring system for preterm infants. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 19, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lucas, R.F.; Feng, B. A Novel System to Measure Infants’ Nutritive Sucking during Breastfeeding: The Breastfeeding Diagnostic Device (BDD). IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2018, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fein, S.; Wang, C.; Loyo-Berríos, N. Maternal and breast pump factors associated with breast pump problems and injuries. J. Hum. Lact. 2014, 30, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, J.; Mitoulas, L.; Leon, R.; Cregan, M.; Mark, D.; Geddes, D.T.; Larsson, M.; Doherty, D.; Ramsay, D.; Peter, E. Importance of vacuum for breastmilk expression. Breastfeed. Med. 2008, 3, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hygeia II Medical Group, Inc. Evolve Breast Pump. U.S. Patent 21 CFR 884.5160, 18 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ag, M. Freestyle Dulexe Breast Pump. U.S. Patent 21 CFR 884.5160, 23 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Prime, D.K.; Geddes, D.T.; Spatz, D.L.; Robert, M.; Trengove, N.J.; Hartmann, P.E. Using milk flow rate to investigate milk ejection in the left and right breasts during simultaneous breast expression in women. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2009, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ag, M. Medela Symphony Breast Pump. U.S. Patent 21 CFR 884.5160, 31 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, C.; Cardenas, H.; Salvatierra, A.; Boza, C.; Montes, C.; Croxatto, H. Sucking pressure and its relationship to milk transfer during breastfeeding in humans. Reproduction 1996, 108, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, D.T.; Kent, J.C.; Mitoulas, L.R.; Hartmann, P.E. Tongue movement and intra-oral vacuum in breastfeeding infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2008, 84, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Alatalo, D.L.; Geddes, D.T.; Hassanipour, F. A Clinical Experiment on Infant Applied Pressures during Breastfeeding. In Proceedings of the ASME 2018 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 9–15 November 2018; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Teo, A.J.; Mishra, A.; Park, I.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, W.T.; Yoon, Y.J. Polymeric biomaterials for medical implants and devices. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 454–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.A. FDA Regulation of Medical Devices; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Available online: https://sgp.fas.org/crs/misc/R42130.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Zare, M.; Ghomi, E.R.; Venkatraman, P.D.; Ramakrishna, S. Silicone-based biomaterials for biomedical applications: Antimicrobial strategies and 3D printing technologies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, Y.S.; Paik, J. Characterization of silicone rubber based soft pneumatic actuators. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IEEE, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4446–4453. [Google Scholar]
- Dabling, J.G.; Filatov, A.; Wheeler, J.W. Static and cyclic performance evaluation of sensors for human interface pressure measurement. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August 2012–1 September 2012; pp. 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, J. A morphometric study of normal and abnormal fetal to childhood tongue size. Arch. Oral Biol. 1985, 30, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaïm, M. Dynamics of stochastic approximation algorithms. In Seminaire de probabilites XXXIII; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Warwick, K.; Kang, Y.H.; Mitchell, R.J. Genetic least squares for system identification. Soft Comput. 1999, 3, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| References | Pump Brand | Vacuum Pressure | Compression Pressure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast-pumping | Evolve [24] | Evolve®Hygeia II | to kPa | - |
| Freestyle [25] | Freestyle®Medela AG | to kPa | - | |
| Symphony [26,27] | Symphony®Medela AG | to kPa | - | |
| References | Infant Age | Vacuum Pressure | Compression Pressure | |
| Breast-feeding | Prieto et al. [28] | 6 Days to 7 months | to kPa | - |
| Geddes et al. [29] | 3 to 24 weeks | to 19.3317 | - | |
| Alatalo et al. [7] | 6 Days to 21 months | to kPa | 8.74 to 16.88 kPa |
| Entity | Unit | Allowance |
|---|---|---|
| Actuator number | 8 | - |
| Air chamber number on each actuator finger | 4 | − |
| Soft Robotic Pad Diameter (mm) | 100 | ± 2.5 |
| Air chamber width (mm) | 5 | ± 0.5 |
| Air chamber height (mm) | 5 | 0 ± 0.5 |
| Air chamber length (mm) | 7.5 | ± 0.5 |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 3 | ± 0.2 |
| System ID | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum | Compression | Vacuum | Compression | |
| RMSE | 2.3721 | 12.363 | 3.5607 | 5.607 |
| Goodness of Fit | 91.77% | 68.8% | 74.88% | 72.45% |
| Parameters | Vacuum Control | Compression Control |
|---|---|---|
| Proportional, P | 0.011 | 167.3 |
| Integration, I | 0.109 | 334.6 |
| Derivative, D | 0.0157 | - |
| Settling time, s | 0.72 | 0.85 |
| Overshoot | 5.65% | 7.64% |
| Steady state error | 6.85% | 10.03% |
| RMSE for Stage 1, kPa | 2.3727 | 1.6509 |
| RMSE for Stage 2, kPa | 3.6544 | 3.1405 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Lozano, M.V.; Peña, D.; Gulati, I.K.; Jiang, L. SmartLact8: A Bio-Inspired Robotic Breast Pump for Customized and Comfort Milk Expression. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020190
Li Y, Lozano MV, Peña D, Gulati IK, Jiang L. SmartLact8: A Bio-Inspired Robotic Breast Pump for Customized and Comfort Milk Expression. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(2):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020190
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuying, Marlenne Valadez Lozano, David Peña, Ish Kumar Gulati, and Lin Jiang. 2023. "SmartLact8: A Bio-Inspired Robotic Breast Pump for Customized and Comfort Milk Expression" Biomimetics 8, no. 2: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020190
APA StyleLi, Y., Lozano, M. V., Peña, D., Gulati, I. K., & Jiang, L. (2023). SmartLact8: A Bio-Inspired Robotic Breast Pump for Customized and Comfort Milk Expression. Biomimetics, 8(2), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020190






