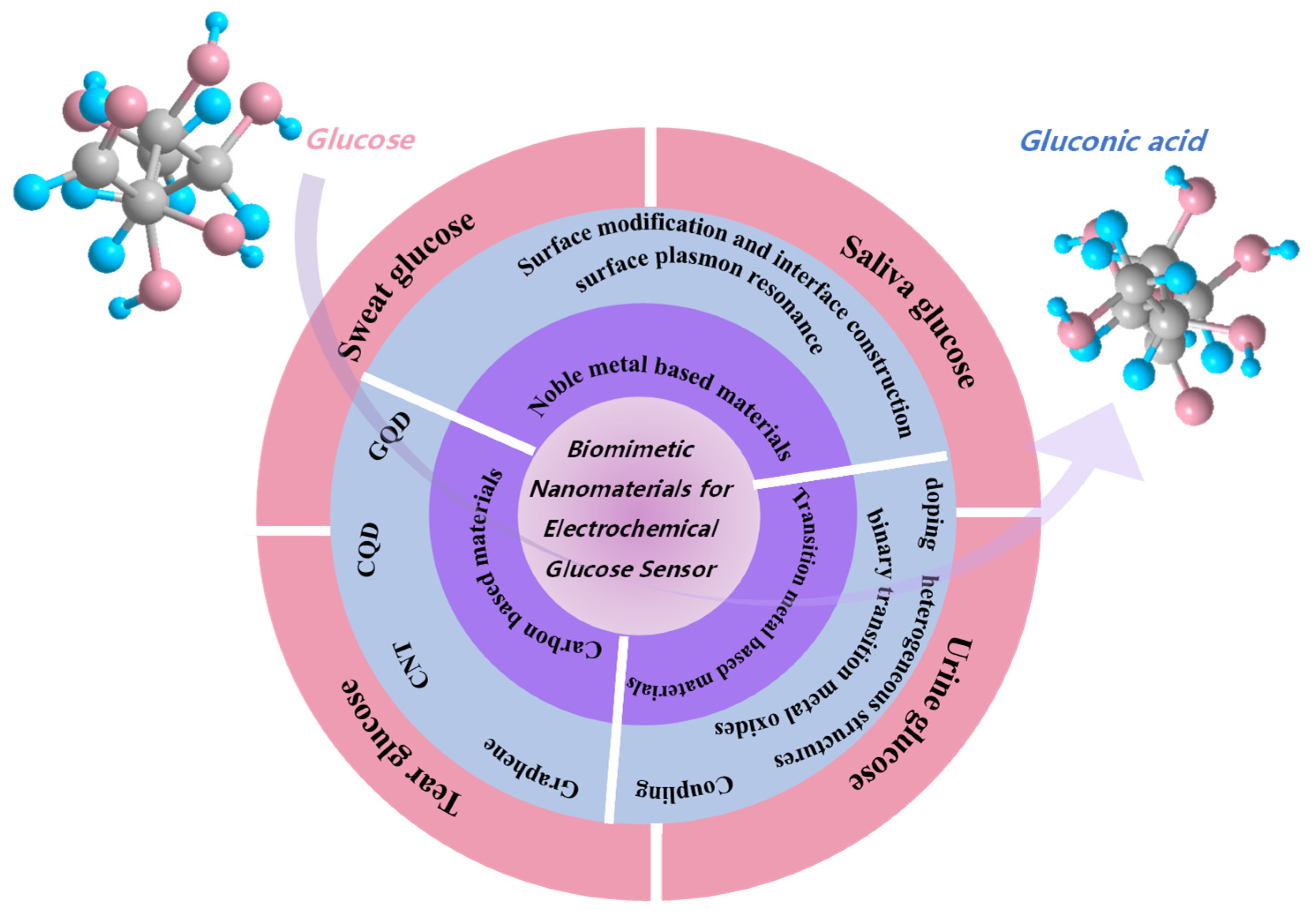
Research Progress on Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Glucose Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biomimetic Nanomaterials
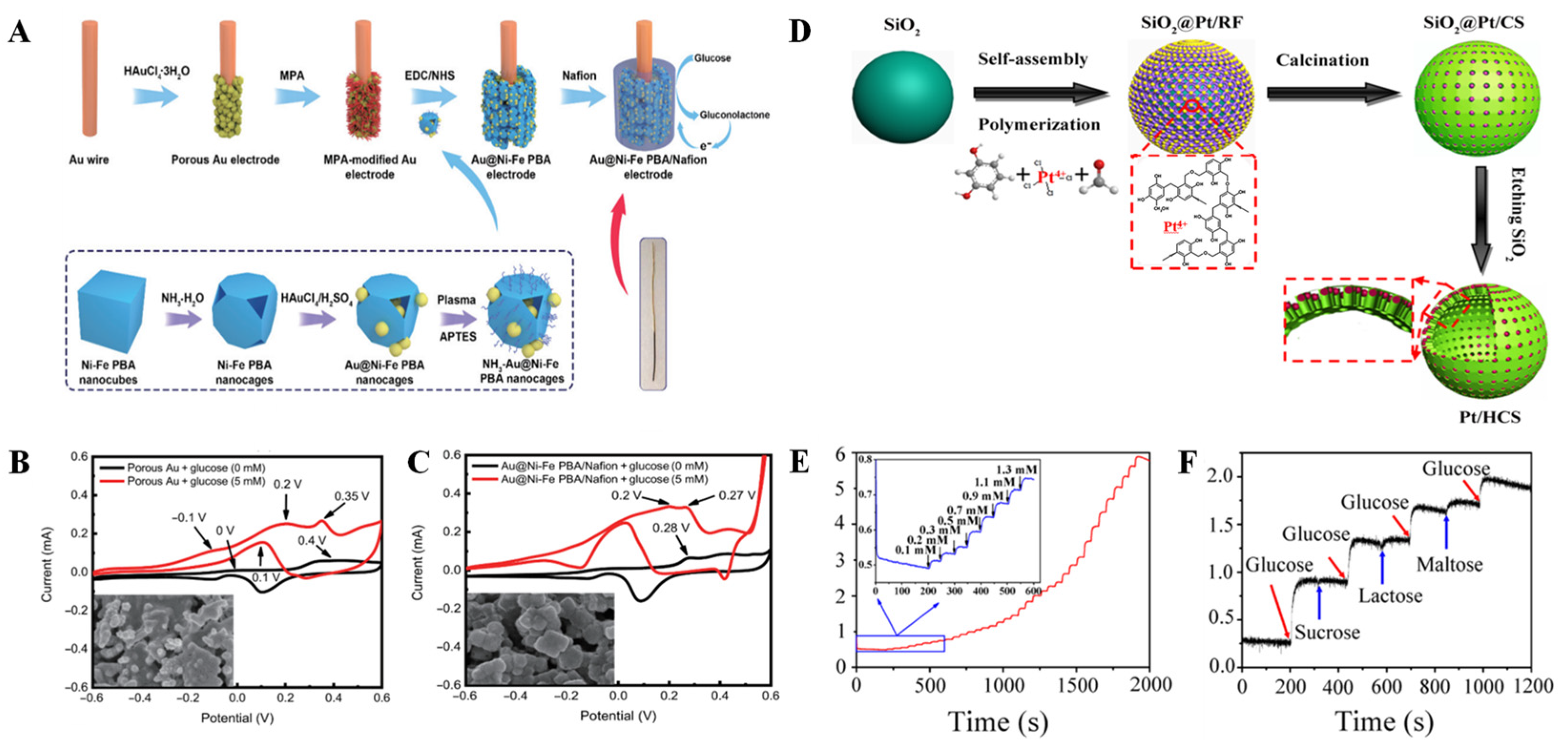
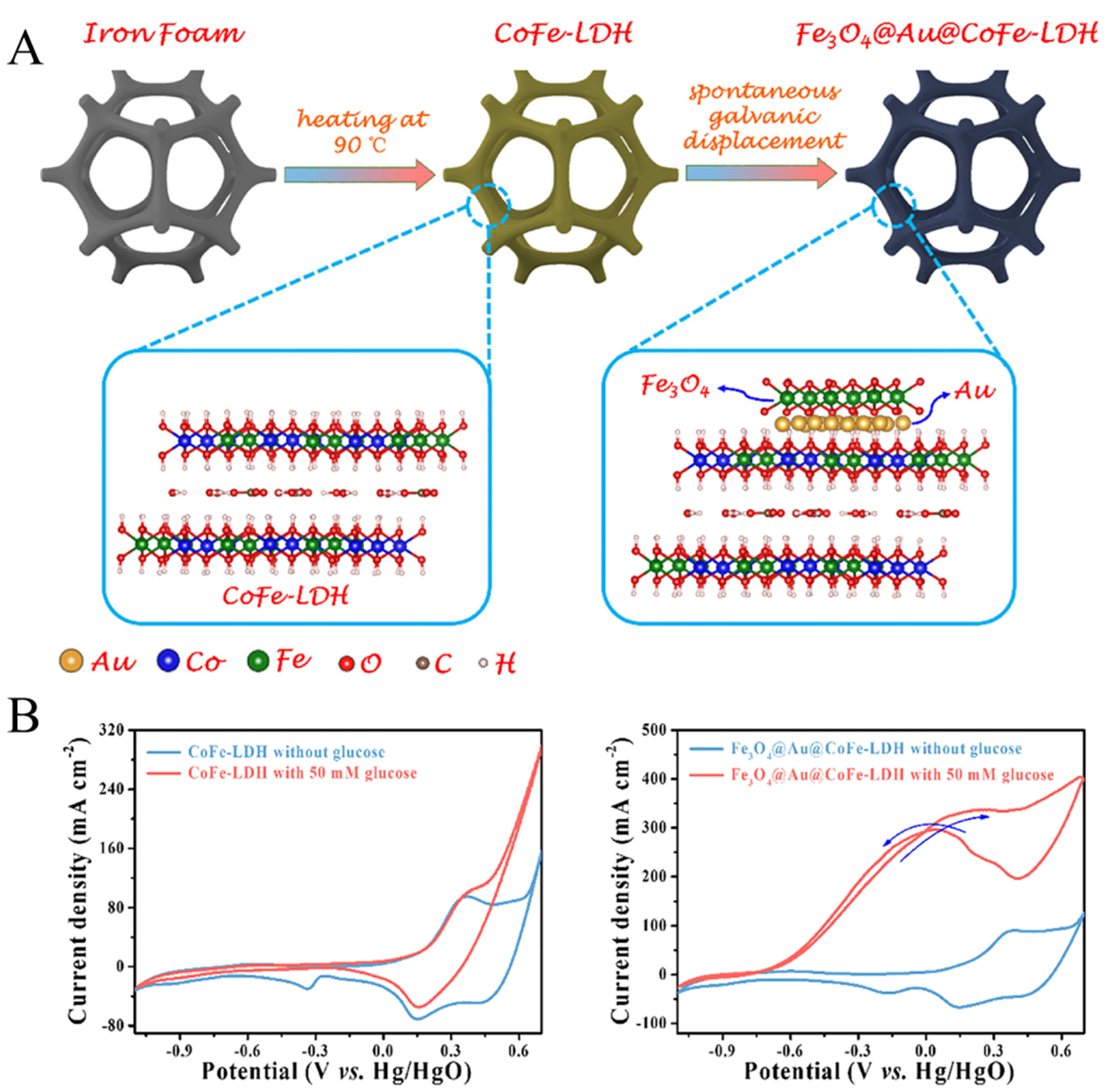
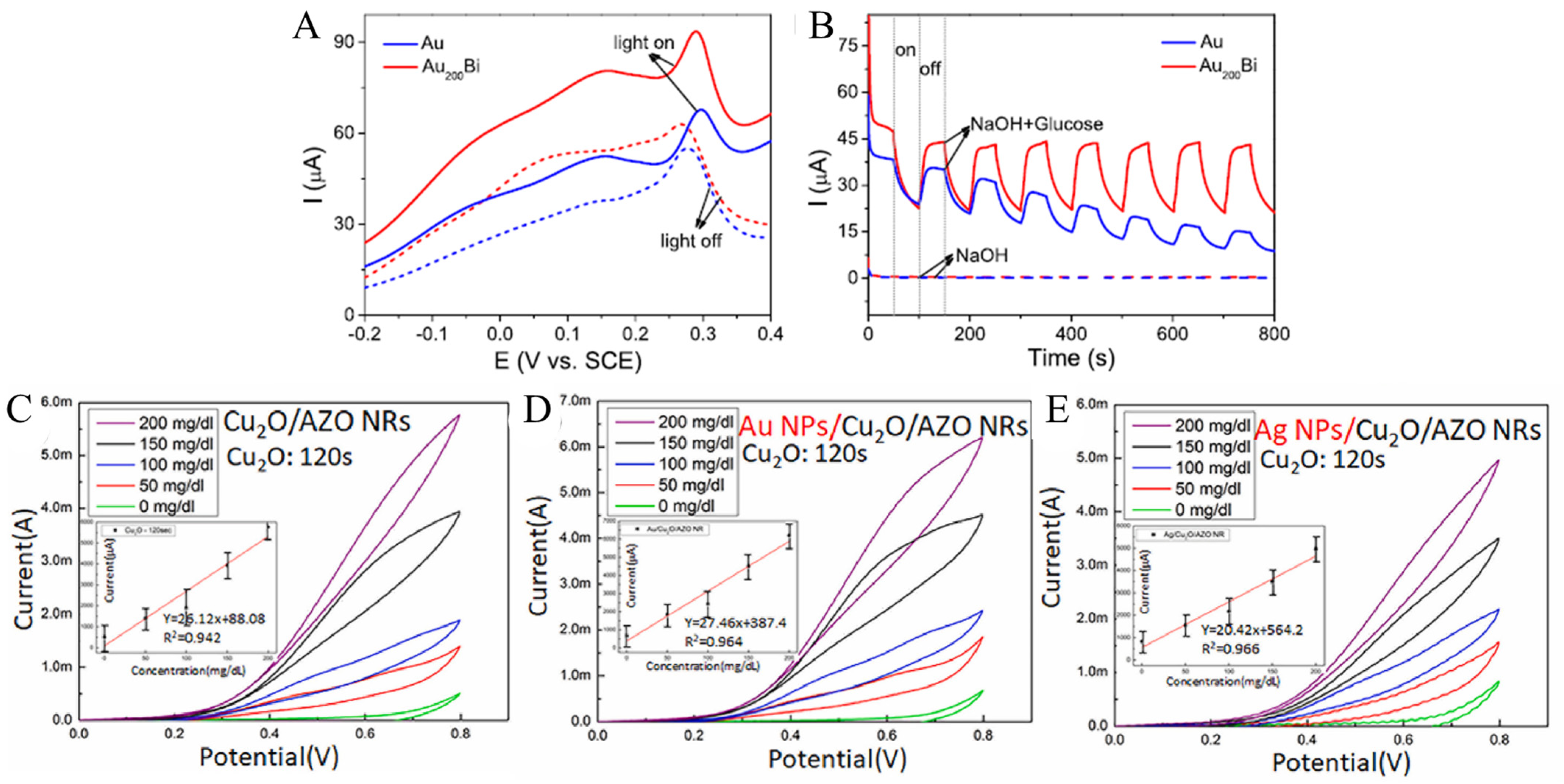
2.1. Noble-Metal-Based Biomimetic Nanomaterials
2.2. Transition-Metal-Based Biomimetic Nanomaterials
2.3. Carbon-Based Biomimetic Nanomaterials
3. Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Noninvasive Electrochemical Glucose Sensors
3.1. Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Sweat Glucose Sensors
3.2. Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Tear Glucose Sensors
3.3. Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Urine Glucose Sensors
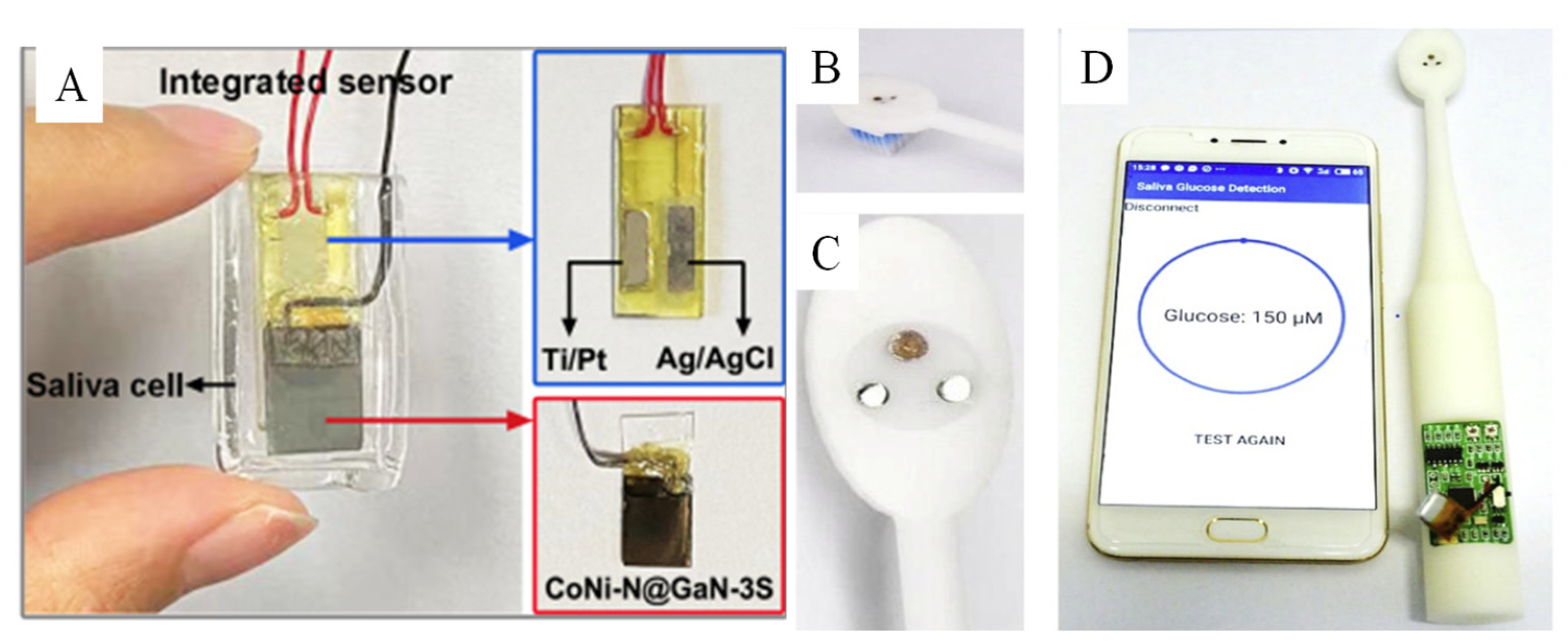
3.4. Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Saliva Glucose Sensors
4. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malena, L.; Fiser, O.; Stauffer, P.R.; Drizdal, T.; Vrba, J.; Vrba, D. Feasibility evaluation of metamaterial microwave sensors for non-invasive blood glucose monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilnezhad, J.; Firoozbakhtian, A.; Hosseini, M.; Adel, S.; Xu, G.; Ganjali, M.R. An enzyme-free Ti3C2/Ni/Sm-LDH-based screen-printed-electrode for real-time sweat detection of glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1250, 340981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/2022-reports/ (accessed on 16 April 2023).
- Wilkinson, E. World health assembly ratifies first global diabetes targets. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, L.; Shahrokhian, S.; Amini, M.K.; Hafezi Kahnamouei, M. Comparison of electrocatalytic performance of CuCo2O4 nanorods and nanospheres decorated with Co3S4 nanosheets for electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose in human serum. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 2755–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, Q.; Dong, D.; An, T.; Gong, S.; Shi, Q.; Cheng, W. Highly stretchable and strain-insensitive fiber-based wearable electrochemical biosensor to monitor glucose in the sweat. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6569–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
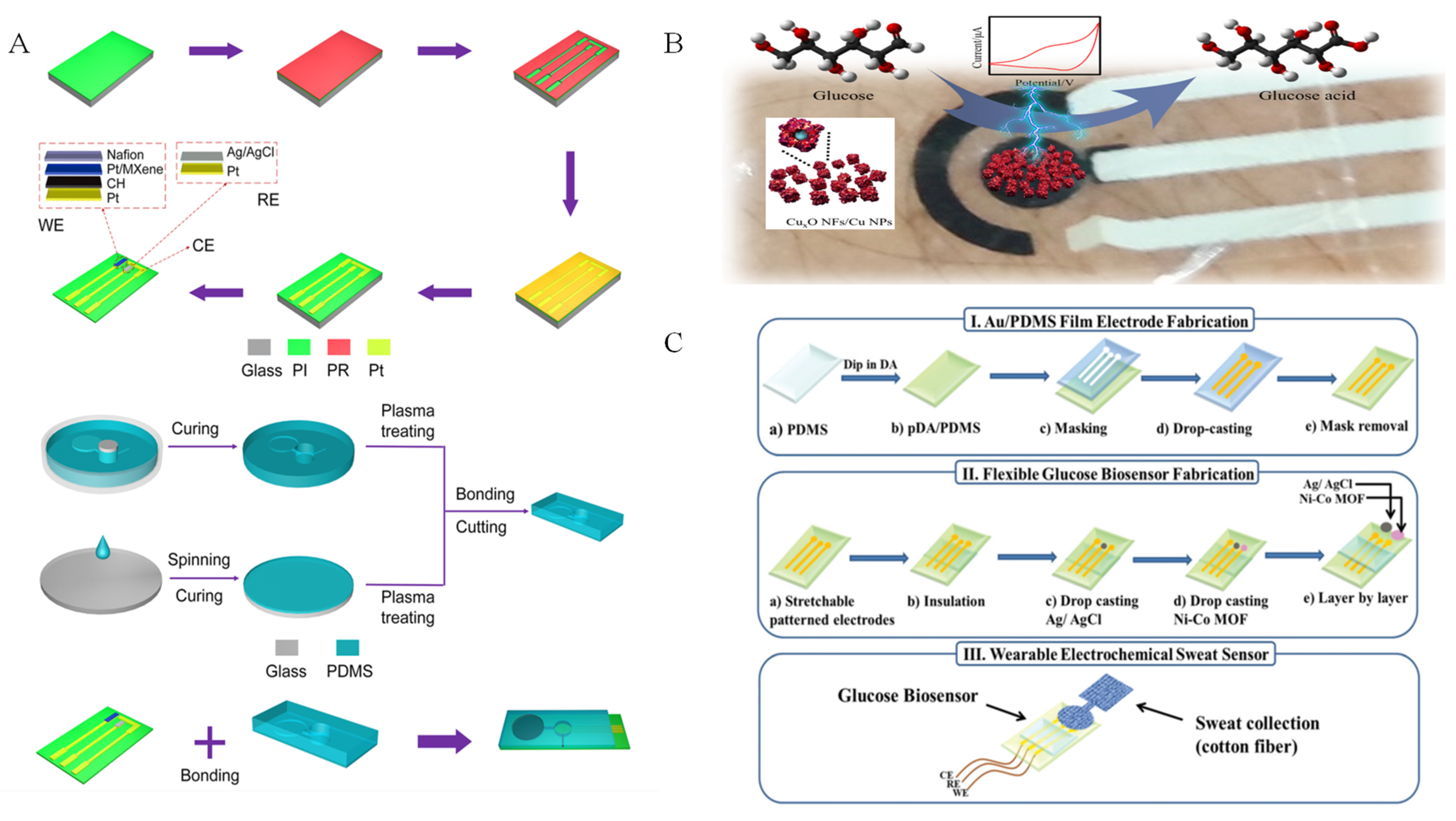
- Shu, Y.; Shang, Z.; Su, T.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X. A highly flexible Ni-Co MOF nanosheet coated Au/PDMS film based wearable electrochemical sensor for continuous human sweat glucose monitoring. Analyst 2022, 147, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xu, M.; Luo, J. Flexible biosensor based on signal amplification of gold nanoparticles-composite flower clusters for glucose detection in sweat. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 661, 130908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yao, H.; Zhao, G.; Ameer, G.A.; Sun, W.; Yang, J.; Mi, S. Flexible, wearable microfluidic contact lens with capillary networks for tear diagnostics. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 9551–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, O.; Nwahara, N.; Mwanza, D.; Nyokong, T.; Mashazi, P. Nanohybrid electrocatalyst based on cobalt phthalocyanine-carbon nanotube-reduced graphene oxide for ultrasensitive detection of glucose in human saliva. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
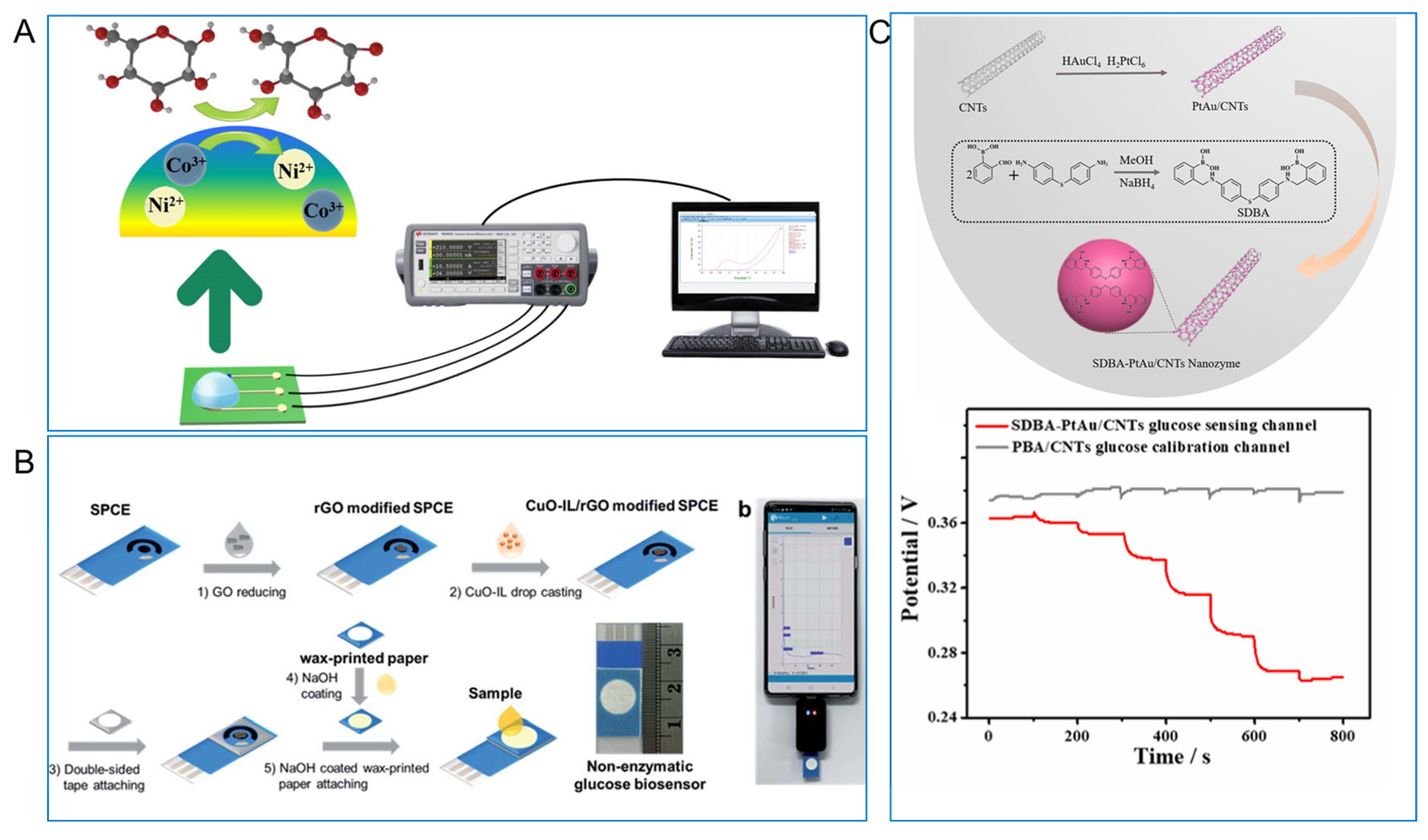
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; He, X.; He, P. A multi-calibration potentiometric sensing array based on diboronic acid-PtAu/CNTs nanozyme for home monitoring of urine glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1237, 340598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive microgel-based surface plasmon resonance transducer for glucose detection using a competitive assay with concanavalin a. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Qin, L.; Zeng, G.; Xu, P.; Li, B.; Yi, H.; Zhang, M. Peroxidase-like activity of smart nanomaterials and their advanced application in colorimetric glucose biosensors. Small 2019, 15, e1900133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.Y.; Ding, X.L.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Bi, J.S.; Song, Y.W.; Yang, P.; Ma, Y.; Tang, B. Novel enzyme-functionalized covalent organic frameworks for the colorimetric sensing of glucose in body fluids and drinks. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 3859–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Wu, L.; Zai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, E.; Gu, N. Paper-based colorimetric glucose sensor using prussian blue nanoparticles as mimic peroxidase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 219, 114787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen Prasad, S.; Anderson, S.R.; Joglekar, M.V.; Hardikar, A.A.; Bansal, V.; Ramanathan, R. Bimetallic nanozyme mediated urine glucose monitoring through discriminant analysis of colorimetric signal. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 212, 114386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawin, K.; Frank John, R.; Sameer, S. Nanomaterials integrated with microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for enzyme-free glucose quantification. Talanta 2023, 124538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Lee, W.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Han, J.; Im, C.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Lee, J.; Yin, Z.; Kim, Y.S. Self-powered illuminating glucose sensor. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.; Hu, Y.; Blyth, J.; Jiang, N.; Yetisen, A.K. Reusable dual-photopolymerized holographic glucose sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2023, 2214197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhao, S.; Qu, Q.; Yang, L. Nano-channel confined biomimetic nanozyme/bioenzyme cascade reaction for long-lasting and intensive chemiluminescence. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 202, 114020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shan, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Sun, E.; Tian, L. Synergistic enhancement effects of cobalt oxide doped silver oxide and porphyrin zinc on an electrochemiluminescence sensor for detection of glucose. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Zhang, W.H.; Tong, Z.R.; Liu, J.W. Fiber optic sensor modified by graphene oxide–glucose oxidase for glucose detection. Opt. Commun. 2021, 492, 126983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundaram Jeevarathinam, A.; Saleem, W.; Martin, N.; Hu, C.; McShane, M.J. NIR luminescent oxygen-sensing nanoparticles for continuous glucose and lactate monitoring. Biosensors 2023, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahsepar, M.; Foroughi, F.; Kim, H. A new enzyme-free biosensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene with high sensing performance for electrochemical detection of glucose at biological pH value. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hong, Y.J.; Baik, S.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.H. Enzyme-based glucose sensor: From invasive to wearable device. Adv. Health Mater. 2018, 7, e1701150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updike, S.J.; Hicks, G.P. The enzyme electrode. Nature 1967, 214, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.F.; Yang, Y.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Lou, S.L. Effects of electric potential treatment of a chromium hexacyanoferrate modified biosensor based on PQQ-dependent glucose dehydrogenase. Sensors 2010, 10, 6347–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Urbiola, I.R.; Reséndiz-Jaramillo, A.Y.; Willars-Rodriguez, F.J.; Martinez-Saucedo, G.; Arriaga, L.G.; Jesús, A.-P.; Ricardo, A.E.V.; Ledesma-García, J. Glucose biosensor based on a flexible Au/ZnO film to enhance the glucose oxidase catalytic response. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 926, 116941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalauskiene, L.; Popov, A.; Kausaite-Minkstimiene, A.; Ramanavicius, A.; Ramanaviciene, A. The impact of glucose oxidase immobilization on dendritic gold nanostructures on the performance of glucose biosensors. Biosensors 2022, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aida, A.; Morteza, H.; Ehsan, S.; Mohammad Reza, G. Peroxidase effect of Ce2(WO4)3 nanoparticles to detection of glucose as a colorimetric sensor. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202104389. [Google Scholar]
- Stasyuk, N.; Smutok, O.; Demkiv, O.; Prokopiv, T.; Gayda, G.; Nisnevitch, M.; Gonchar, M. Synthesis, catalytic properties and application in biosensorics of nanozymes and electronanocatalysts: A review. Sensors 2020, 20, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, Z.Z.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.B.; Chen, A.Z. Supercritical fluid-assisted fabrication of C-doped Co3O4 nanoparticles based on polymer-coated metal salt nanoreactors for efficient enzyme-mimicking and glucose sensor properties. Nano Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Asif, M.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, F.; Liu, H.; Xia, B.Y. Noble metal construction for electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose detection. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 8, 2200272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Ren, S.; Han, D. NiCo-LDH nanoflake arrays-supported au nanoparticles on copper foam as a highly sensitive electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1177, 338787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.V.; Nguyen, N.D.; Tran, C.T.Q.; Tran, L.T.; Le, T.D.; Tran, H.T.T.; Piro, B.; Huynh, C.D.; Nguyen, T.N.; Nguyen, N.T.T.; et al. Silver nanoparticles-decorated reduced graphene oxide: A novel peroxidase-like activity nanomaterial for development of a colorimetric glucose biosensor. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6084–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, G.; Du, Y.; Chen, S.; Fu, Y.; Xu, F.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, W.; Ji, Q. Sensitive colorimetric glucose sensor by iron-based nanozymes with controllable Fe valence. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4726–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Su, B. An overview of wearable and implantable electrochemical glucose sensors. Electroanalysis 2021, 34, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Xie, X.; Tan, Q.; Kang, H.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Feng, G. Blood glucose sensors and recent advances: A review. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2022, 15, 2230003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, W. Graphene-based electrochemical glucose sensors: Fabrication and sensing properties. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2504–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, J.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Shi, X.; Lu, W.; Sun, X. Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: Recent progress and perspectives. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 14553–14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, R.; Saha, P.; Shah, S.S.; Shaikh, M.N.; Aziz, M.A.; Ahammad, A.J.S. Nanostructured nickel-based non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Lakshmy, S.; Santhosh, S.; Kalarikkal, N.; Chakraborty, B.; Rout, C.S. Recent developments and future perspective on electrochemical glucose sensors based on 2D materials. Biosensors 2022, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Nor, N.; Ridhuan, N.S.; Abdul Razak, K. Progress of enzymatic and non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose biosensor based on nanomaterial-modified electrode. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Zhu, J.; Weng, G.J.; Li, J.J.; Zhao, J.W. Multiplex sensing based on plasmonic optics of noble metallic nanostructures. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima, T.; Fujishiro, Y.; Irie, H. Noble metal modification of CdS-covered CuInS2 electrodes for improved photoelectrochemical activity and stability. Catalysts 2020, 10, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, G.; Feng, W.; Wang, P.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q. Detection of glucose based on noble metal nanozymes: Mechanism, activity regulation, and enantioselective recognition. Small 2023, 19, 2205924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Shuaishuai, Z.; Fei, G.; Jianhan, L.; Juewen, L.; Jinkai, Z. DNA-mediated growth of noble metal nanomaterials for biosensing applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 148, 116533. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.H.; Ahn, J.; Shi, S.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.; Qin, D. Noble-metal nanoframes and their catalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 796–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azharuddin, M.; Zhu, G.H.; Das, D.; Ozgur, E.; Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P.F.; Patra, H.K. A repertoire of biomedical applications of noble metal nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6964–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumey, C. The man who understood the Feynman machine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, B.C.; Tu, L.N.Q.; Thanh, L.D.; Van Dung, N.; An, N.T.; Long, N.Q. Combined adsorption and catalytic oxidation for low-temperature toluene removal using nano-sized noble metal supported on ceria-granular carbon. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, X.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fan, F.; Qing, B.; Zhu, C.; Fan, J.; Shi, Y. The H2 sensing properties of facets-dependent Pd nanoparticles-supported ZnO nanorods. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 15331–15337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longato, A.; Vanzan, M.; Colusso, E.; Corni, S.; Martucci, A. Enhancing tungsten oxide gasochromism with noble metal nanoparticles: The importance of the interface. Small 2023, 19, 2205522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Xue, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Shi, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Interfacial coupling between noble metal nanoparticles and metal–organic frameworks for enhanced catalytic activity. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 16425–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Song, S.X.; Li, H.S.; Peng, H.L.; Li, Q.F. Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on porous foam Au/Mxene nanocomposites. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 35, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y. Reusable electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on Au-inlaid nanocages. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6490–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X.; Cheng, C.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Small naked Pt nanoparticles confined in mesoporous shell of hollow carbon spheres for high-performance nonenzymatic sensing of H2O2 and glucose. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, X.; You, Z.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Jia, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. Sandwich structure confined gold as highly sensitive and stable electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor with low oxidation potential. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 123, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.L.; Zhuang, J.; Yang, D.P.; Tang, D. Eggshell membrane-templated synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous Au networks for electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Fang, Y.J.; Hsueh, T.J.; Wang, S.H.; Chang, S.J. Nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on Au/ZnO core–shell nanostructures decorated with au nanoparticles and enhanced with blue and green light. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 2931–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Qin, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Yan, H.; Jiao, L.; Wei, X.; Li, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, M.; et al. Ultra-low content bismuth-anchored gold aerogels with plasmon property for enhanced nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensing. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 11030–11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Yen, M.H. Synthesis of Au or Ag/Cu2O/aluminum doped zinc oxide nanorods hybrid electrode for high sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor: Mechanism investigation of formation and surface plasmon resonance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 282, 125924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiran, Z.; Yong, L.; Lawrence Yoon Suk, L. Bismuth and metal-doped bismuth nanoparticles produced by laser ablation for electrochemical glucose sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 357, 131334. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.; Li, X.; Pan, J.; He, Y.; Qiu, F.; Yan, Y. Recent advances in non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on non-precious transition metal materials: Opportunities and challenges. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 84893–84905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Ling, T.; Ma, T.Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, J.; Du, X.W.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.Z. Atomically and electronically coupled Pt and CoO hybrid nanocatalysts for enhanced electrocatalytic performance. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Li, X.; Monny, S.A.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen peroxide production based on transition-metal-oxide semiconductors. Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobaldi, D.M.; Espro, C.; Leonardi, S.G.; Lajaunie, L.; Seabra, M.P.; Calvino, J.J.; Marini, S.; Labrincha, J.A.; Neri, G. Photo-electrochemical properties of CuO–TiO2 heterojunctions for glucose sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 9529–9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z. Fe doping induced formation of crystalline/amorphous NiCo2O4 core/shell heterostructure for highly sensitive nonenzymatic detection of glucose. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 907, 164503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Han, N.; Zhang, L.; Yi, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, D.; Gao, Y. Cu3Pt/Cu2O nanorod array prepared by a facile method for glucose detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 534, 147596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
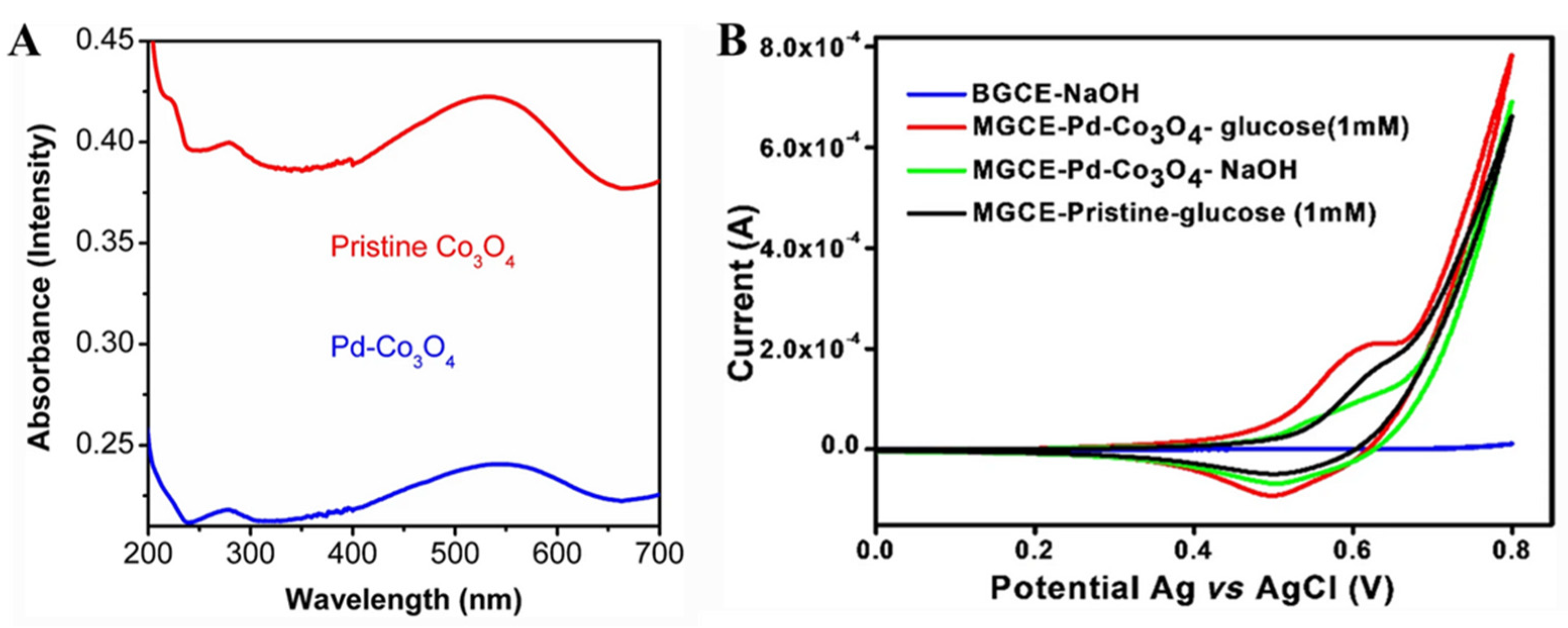
- Chang, A.S.; Tahira, A.; Solangi, Z.A.; Solangi, A.G.; Ibupoto, M.H.; Chang, F.; Medany, S.S.; Nafady, A.; Kasry, A.; Willander, M.; et al. Pd-Co3O4-based nanostructures for the development of enzyme-free glucose sensor. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2022, 45, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.K.; Gangan, A.; Chakraborty, B.; Nayak, S.K.; Rout, C.S. Enhanced nonenzymatic glucose-sensing properties of electrodeposited NiCo2O4-Pd nanosheets: Experimental and DFT investigations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23894–23903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Lu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Photoinduced phase-transition on CuO electrospun nanofibers over the TiO2 photosensitizer for enhancing non-enzymatic glucose-sensing performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 900, 163409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.; Patil, A.M.; Roy, S.B.; Lee, J.; Jun, S.C. N-doped oxygen vacancy-rich NiCo2O4 nanoarrays for supercapacitor and non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 24501–24515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y. Facile synthesis of CuCo2O4@NiCo2O4 hybrid nanowire arrays on carbon cloth for a multicomponent non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 495708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, M.; Vivekanandan, A.K.; Panomsuwan, G.; Veeramani, V.; Chen, S.H.; Jiang, Z.; Maiyalagan, T. Flower-like NiCo2O4 nanoflake surface covered on carbon nanolayer for high-performance electro-oxidation of non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zeng, W.; Liu, S.; Li, Y. In situ formation of Co3O4 hollow nanocubes on carbon cloth-supported NiCo2O4 nanowires and their enhanced performance in non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 265501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Xiang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhu, L. MOF-derived spinel NiCo2O4 hollow nanocages for the construction of non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Electroanalysis 2019, 32, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Prakash, P.; Jeyaprabha, B.; Abraham, R.; Mathew, R.M.; Zacharia, E.S.; Thomas, V.; Thomas, J. Principle, design, strategies, and future perspectives of heavy metal ion detection using carbon nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors: A review. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2023, 20, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanvand, Z.; Jalali, F.; Nazari, M.; Parnianchi, F.; Santoro, C. Carbon nanodots in electrochemical sensors and biosensors: A review. ChemElectroChem 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour-Haratbar, A.; Mohammadpour-Haratbar, S.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.J. A review on non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensors of glucose using carbon nanofiber nanocomposites. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, L.M.; Oliveira, H.A.; Xing, Y.; Passos, F.B. Cobalt supported on carbon nanotubes for methane chemical vapor deposition for the production of new carbon nanotubes. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 14218–14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lu, F.; Tu, Y.; Ren, Z. Glucose biosensors based on carbon nanotube nanoelectrode ensembles. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheza, M.; Mohsin, J.; Sohail, N.; Muhammad Adeel, A.; Ali, H.; Muhammad, A.; Ahmad Raza, A.; Arif, N.; Munawar, I.; Norah, A.; et al. Carbon nanotube fiber-based flexible microelectrode for electrochemical glucose sensors. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 2272–2280. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoth, V.; Subramaniyam, G.; Anandan, S.; Valdés, H.; Manidurai, P. Non-enzymatic glucose sensor and photocurrent performance of zinc oxide quantum dots supported multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 265, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liang, G.; Qiu, F.; Ye, Z.; Liu, D. A simple, cost-effective and selective analysis of glucose via electrochemical impedance sensing based on copper and nitrogen co-doped carbon quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 12723–12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaoui, H.; Teodoresu, F.; Wang, Q.; Pan, G.H.; Addad, A.; Chtourou, R.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Non-enzymatic glucose sensing using carbon quantum dots decorated with copper oxide nanoparticles. Sensors 2016, 16, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipnusu, W.K.; Doñate-Buendía, C.; Fernández-Alonso, M.; Lancis, J.; Mínguez-Vega, G. Nonlinear optics to glucose sensing: Multifunctional nitrogen and boron doped carbon dots with solid-state fluorescence in nanoporous silica films. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37, 2000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhu, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, N.; Hong, Y.; Wang, W.; Huang, W.; Si, W.; Dong, X. NH2-GQDS-doped nickel-cobalt oxide deposited on carbon cloth for nonenzymatic detection of glucose. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 7, 1901578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, L.F.; de Freitas, A.D.; Ferreira, A.L.; Maciel, C.C.; Ferreira, M.; de Araujo, W.R. Enzymeless glucose sensor based on disposable ecoflex®/graphite thermoplastic composite substrate modified with Au@GQDS. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asen, P.; Esfandiar, A.; Kazemi, M. Nonenzymatic sweat-based glucose sensing by flower-like Au nanostructures/graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 13361–13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Deng, X.; Xia, L. Non-enzymatic sensor for determination of glucose based on PtNi nanoparticles decorated graphene. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Li, T.; Wang, Z. Ni/NiO multivalent system encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene realizing efficient activation for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 22869–22880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, R.; Turek, E.; Zawisza, B.; Malicka, E.; Jan, T. Adsorption of divalent metal ions from aqueous solutions using graphene oxide. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 5682–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, S.; Li, M.; Bao, Y.; Chu, L.; Leng, K.; Lu, H. A non-dispersion strategy for large-scale production of ultra-high concentration graphene slurries in water. Nat. Commun. 2020, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, S. A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetsang, S.; Kidkhunthod, P.; Chanlek, N.; Jakmunee, J.; Mungkornasawakul, P.; Ounnunkad, K. Copper/reduced graphene oxide film modified electrode for non-enzymatic glucose sensing application. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, K.L.; Ho, M.Y.; Lee, X.Y.; Yee, M.S.L. A review on the development of non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on graphene-based nanocomposites. Nano 2020, 15, 2030004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.M.V.; Rajendran, V.; Mishra, R.K.; Jayaraman, M. Recent advances and perspectives in sweat based wearable electrochemical sensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, M.; Kubota, N.; Kadowaki, T. Study of the correlation between tear glucose concentrations and blood glucose concentrations. Diabetes 2018, 67, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, M.; Alam, F.; Salih, A.E.; AlQattan, B.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Wearable Bifocal Contact Lens for Continual Glucose Monitoring Integrated with Smartphone Readers. Small 2021, 17, 2102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayushman, R.; Anupma, M.; Surinder, S. Design of a triple-layered plasmonic biosensor for glucose monitoring from urine sample for diabetes prevention. MAPAN 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Yu, J. Electrochemical sensor made with 3D micro-/mesoporous structures of CoNi-N/GaN for noninvasive detection of glucose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 49035–49046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Peng, H.L. Pt/MXene-based flexible wearable non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor for continuous glucose detection in sweat. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13290–13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
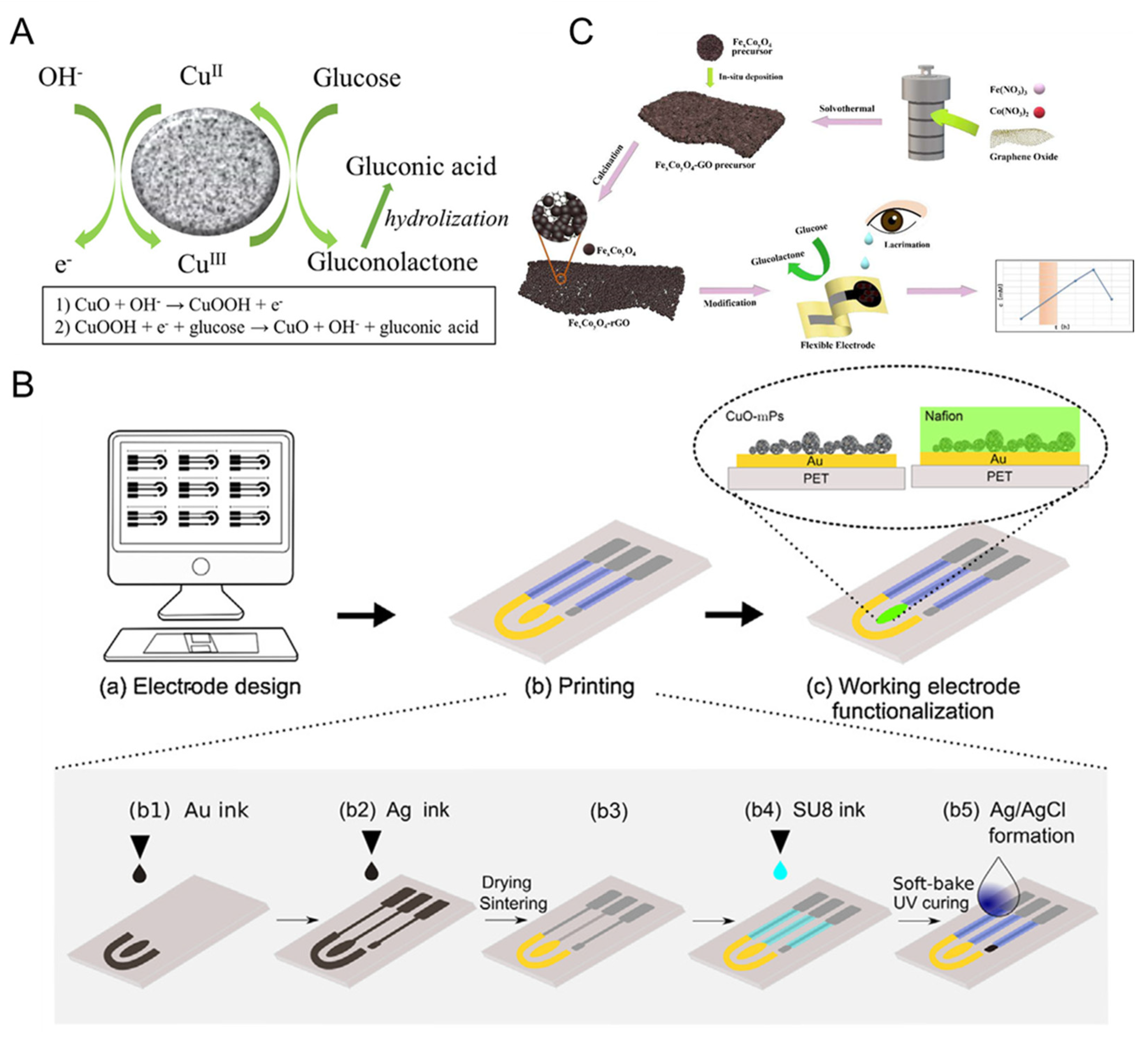
- Yu, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Lv, J.; Kong, C. Wearable noninvasive glucose sensor based on CuxO NFs/Cu NPs nanocomposites. Sensors 2023, 23, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Su, T.; Lu, Q.; Shang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X. Highly stretchable wearable electrochemical sensor based on Ni-Co MOF nanosheet-decorated Ag/rGO/PU fiber for continuous sweat glucose detection. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16222–16230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, A.; Moya, A.; Leung, T.S.; Gabriel, G.; Villa, R.; Sánchez, S. Inkjet printed flexible non-enzymatic glucose sensor for tear fluid analysis. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari Kheirabadi, Z.; Rabbani, M. Samiei Foroushani, M. Green fabrication of nonenzymatic glucose sensor using multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with copper (ii) oxide nanoparticles for tear fluid analysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 3689–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhao, H.; Chen, K.; Cao, S.; Shi, Z.; Lan, M. Flexible electrochemical sensor with Fe/Co bimetallic oxides for sensitive analysis of glucose in human tears. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1243, 340781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Song, X. An electrochemical nonenzymatic microsensor modified by nickel cobaltate nanospheres for glucose sensing in urine. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13074–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmee, N.; Preechakasedkit, P.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O.; Potiyaraj, P.; Ruecha, N. A non-enzymatic disposable electrochemical sensor based on surface-modified screen-printed electrode cuo-il/rgo nanocomposite for a single-step determination of glucose in human urine and electrolyte drinks. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2796–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, E.; Gong, F.; Li, F. Co3O4 nanoparticles as a noninvasive electrochemical sensor for glucose detection in saliva. Nano 2020, 16, 2150009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, V.E.; Kandjani, A.E.; Field, M.R.; Hartley, P.; Chen, M.; Sabri, Y.M.; Bhargava, S.K. Co3O4 needles on Au honeycomb as a non-invasive electrochemical biosensor for glucose in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Xue, Q.; Jiao, C.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, H.; Yang, Q. A non-enzymatic nanoceria electrode for non-invasive glucose monitoring. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Dhar, S.; Debnath, K.; Majumder, T.; Mondal, S.P. Non-enzymatic and non-invasive glucose detection using au nanoparticle decorated CuO nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Dhar, S.; Deka, N.; Debnath, K.; Mondal, S.P. Non-enzymatic salivary glucose detection using porous CuO nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 302, 127134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Z.; Ou, R.; Gao, S.; Yang, Z. A miniature CuO nanoarray sensor for noninvasive detection of trace salivary glucose. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 656, 114857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Deka, N.; Patra, D.C.; Debnath, K.; Mondal, S.P. Salivary glucose sensing using highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic porous NiO nanostructured electrodes. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Sheng, K.; Liu, W.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Song, H. Engineered IrO2@NiO core-shell nanowires for sensitive non-enzymatic detection of trace glucose in saliva. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12346–12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Ju, Y.; Ma, B.; Zhao, C.; Liu, H. Electrocatalytic oxidation of glucose on bronze for monitoring of saliva glucose using a smart toothbrush. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.; Kim, J.; Kurniawan, J.F.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Moreto, J.R.; Tang, G.; Campbell, A.S.; Shin, A.; Lee, M.Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Epidermal microfluidic electrochemical detection system: Enhanced sweat sampling and metabolite detection. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.C.; Park, B.S.; Ha, T.J. Highly sensitive wearable glucose sensor systems based on functionalized single-wall carbon nanotubes with glucose oxidase-nafion composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, F.; Zanfrognini, B.; Favaretto, L.; Quintano, V.; Sun, J.; Treossi, E.; Melucci, M.; Palermo, V.; Zanardi, C. Continuous capillary-flow sensing of glucose and lactate in sweat with an electrochemical sensor based on functionalized graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Bariya, M.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Kivimäki, L.; Uusitalo, S.; Jansson, E.; Ji, W.; Yuan, Z.; Happonen, T.; Liedert, C.; et al. Porous enzymatic membrane for nanotextured glucose sweat sensors with high stability toward reliable noninvasive health monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Wearable biosensor for sensitive detection of uric acid in artificial sweat enabled by a fiber structured sensing interface. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Khorshed, A.A.; Ahmed, A.; De Loyola e Silva, A.N.; Barfidokht, A.; Yin, L.; Goud, K.Y.; Mohamed, M.A.; Bailey, E.; May, J.; et al. Epidermal enzymatic biosensors for sweat vitamin C: Toward personalized nutrition. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1804–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimegala, P.; Mary, X.A.; Biji, N.; Shiny, V.S. Dehydration measurement using sweat sensor patch and pulse sensor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1937, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.H.; Sheu, S.C.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, S.C.; Li, B.R. Wearable hydrogel patch with noninvasive, electrochemical glucose sensor for natural sweat detection. Talanta 2022, 241, 123187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, P.; Rahman, M.I.; Perumal, A.; Nallaiyan, R.; Basha, S.H.; Dakshanamoorthy, A. Non-invasive, non-enzymatic, biodegradable and flexible sweat glucose sensor and its electrochemical studies. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 11305–11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gu, K.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Silk-based electrochemical sensor for the detection of glucose in sweat. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 3928–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C. A sample-to-answer, wearable cloth-based electrochemical sensor (WCECS) for point-of-care detection of glucose in sweat. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 343, 130131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, W.; Jin, Y.; Wo, F.; Xi, F.; Wu, J. Ratiometric fluorescent nanohybrid for noninvasive and visual monitoring of sweat glucose. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Asif, M.; Ashraf, G.; Iftikhar, T.; Hussain, W.; Wang, S. Environmental significance of wearable sensors based on MXene and graphene. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 36, e00180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cui, H.; Gong, W.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y. Highly sensitive nonenzymetic glucose sensing based on multicomponent hierarchical NiCo-LDH/CCCH/CuF nanostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. A novel nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor modified with Ni/Al layered double hydroxide. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshghi, A.; Kheirmand, M. Graphene/Ni–Fe layered double hydroxide nano composites as advanced electrode materials for glucose electro oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 15064–15072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.M.; Muench, F.; Kunz, U.; Ensinger, W. 3D NiCo-layered double hydroxide@Ni nanotube networks as integrated free-standing electrodes for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 591, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Dong, Q.; Tang, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, K.; Zou, Z.; Jiang, X.; Xiong, X. 3D CoxP@NiCo-LDH heteronanosheet array: As a high sensitivity sensor for glucose. Microchem. J. 2022, 172, 106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Miao, X.; Qu, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, B.; Yu, Q.; Gao, J.; Song, D.; Li, Y.; Yin, Z. Rattle-type Au@NiCo LDH hollow core-shell nanostructures for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 858, 113810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Mei, H.; Xie, Y.; Long, D.; Zhu, F.; Gong, W. Nonenzymetic glucose sensitive device based on morchella shaped nickel-copper layered double hydroxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 597, 153658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; He, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, K.; Jiang, S.; Duan, G.; Zhang, K. Nanocellulose and its derived composite electrodes toward supercapacitors: Fabrication, properties, and challenges. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, J. Advances and challenges of cellulose functional materials in sensors. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2023, 8, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeon, H.J.; Park, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Chung, E. Tear glucose measurement by reflectance spectrum of a nanoparticle embedded contact lens. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baca, J.T.; Finegold, D.N.; Asher, S.A. Tear glucose analysis for the noninvasive detection and monitoring of diabetes mellitus. Ocul. Surf. 2007, 5, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Koh, E.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.G.; Jung, H.S. Plasmonic contact lens materials for glucose sensing in human tears. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioli, J.M.; Kuwana, T. Electrochemical characterization of carbohydrate oxidation at copper electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 1992, 37, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Q.; Huber, C.O. Electrocatalysis and amperometric detection using an electrode made of copper oxide and carbon paste. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, J.; Emran, M.Y.; Kotb, A.; Bo, X.; Zhou, M. Universal Fully Integrated Wearable Sensor Arrays for the Multiple Electrolyte and Metabolite Monitoring in Raw Sweat, Saliva, or Urine. Anal. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Highly sensitive on-site detection of glucose in human urine with naked eye based on enzymatic-like reaction mediated etching of gold nanorods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitanda, I.; Fujimura, Y.; Takarada, T.; Suzuki, R.; Aikawa, T.; Itagaki, M.; Tsujimura, S. Self-powered diaper sensor with wireless transmitter powered by paper-based biofuel cell with urine glucose as fuel. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3409–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elakkiya, R.; Maduraiveeran, G. A three-dimensional nickel–cobalt oxide nanomaterial as an enzyme-mimetic electrocatalyst for the glucose and lactic acid oxidation reaction. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 14756–14762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, J.; Wilson, D.; Finkelshtein, I.; Wong, B.; Potts, R. Correlation between sweat glucose and blood glucose in subjects with diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi; Shashikanth, M.C.; Shambulingappa, P. Comparison of serum glucose and salivary glucose in diabetic patients. J. Indian Acad. Oral Med. Radiol. 2008, 20, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elraheem, S.E.; El Saeed, A.M.; Mansour, H.H. Salivary changes in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2017, 11, S637–S641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchbhai, A.S. Correlation of salivary glucose level with blood glucose level in diabetes mellitus. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2012, 3, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Biomimetic Nanomaterials | LOD (μM) | Sensitivity (μA mM−1 cm−2) | Linear Range (mM) | Electrolyte | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-doped Co3O4 | 3.86 | / | 0.1–0.6 | / | [32] |
| Au/MXene | 200 | 22.45 | 1–12 | 0.1 M NaOH | [55] |
| Au@Ni-Fe PBA | 4.686 | 8.037 | 0.010–16 | 0.1 M NaOH | [56] |
| Pt/HCS | 100 | / | 0.3–10 10–50 | 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4) | [57] |
| Fe3O4@Au@CoFe-LDH | 12.7 | 6342 | 0.0375–15.64 | 1.0 M KOH | [58] |
| Au200Bi | 8.7 | 664 | 0.013–3.3 | 0.1 M NaOH | [61] |
| Au/Cu2O/AZO NRs Ag/Cu2O/AZO NRs | / | 186.3 221.6 | 2.22–11.11 3.33–11.11 | 0.1 M NaOH | [62] |
| CuO-TiO2 | 0.6 | 244.2 | / | 0.1 M KOH | [67] |
| Fe-doped NiCo2O4 | 0.19 | 3055.7 | 0.0002–3.1 | 0.1 M NaOH | [68] |
| Cu3Pt/Cu2O | / | 5082 3331 118 | 0.005–0.1 0.1–1.5 1.5–10 | 0.5 M NaOH | [69] |
| Pd-Co3O4 | 10 | / | 1–6.0 | 0.1 M NaOH | [70] |
| Pd-doped NiCo2O4 | 0.28 | 40.03 | 0.005–0.09 | 0.1 M NaOH | [71] |
| 5%TiO2/Cu2O/CuO/ITO | 0.25 | 2074.7 1099.1 | 0–2 2–5 | 0.1 M NaOH | [72] |
| N-Ov/NiCo2O4-350 | 0.02 | 29,811.53 | 0–555 | 1.0 M KOH | [73] |
| CuCo2O4@NiCo2O4 | 0.35 | 11.12 | 0.001–1.158 | 0.1 M NaOH | [74] |
| NiCo2O4 | 86 | 779.35 | 0.0001–15.28 | 0.5 M NaOH | [75] |
| Co3O4/NiCo2O4/CC | 0.64 | 12.835 | 0.001–1.127 | 0.1 M NaOH | [76] |
| NiCo2O4 HNCs | 0.027 | 1306 | 0.000180–5.1 | 0.1 M NaOH | [77] |
| CuO@CNTFs | 1.4 | 3000 | 0–13 | 0.1 M KOH | [83] |
| MWCNT/ZnO QDs | 0.208 | / | 0.0001–0.002.5 | 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.0) | [84] |
| Cu, N-CQDs | 1.22 | / | 5–700 | 0.1 M NaOH | [85] |
| CQDs/Cu2O | 6 | 2900 ± 200 | 0.0013–6 | 0.1 M NaOH | [86] |
| NH2-GQDs/NiCo2O4 | 0.27 | 1185.58 2521.33 | 0.001–0.159 0.159–0.949 | 0.1 M NaOH | [88] |
| Au@GQDs | 9.12 | / | / | 0.1 M NaOH | [89] |
| PtNi | 16 | 24.03 | 0.5–15 | 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4) | [91] |
| Ni/NiO | 0.032 | 3251.8 | 0.001–3.568 | 0.1 M NaOH | [92] |
| Cu(II)/rGO | 65 | 172 | 0.10–12.5 | 0.1 M NaOH | [96] |
| Biomimetic Nanomaterials | Electrolyte | Potential (V) | LOD (μM) | Linear Range (μM) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-Co MOF/Au/PDMS | Human sweat | 0.55 | / | 20–790 | [7] |
| SWCNT/rGO/CoPc | NaOH (adding saliva) | 0.55 | 0.12 | 0.3–500 500–5000 | [10] |
| PtAu/CNT | M PBS (pH 6.1) | / | / | 900–40,000 | [11] |
| Pt/MXene | PBS (pH 7.4) (adding sweat) | 0.1 | / | 0–8000 | [103] |
| CuxO NFs | Human sweat | 0.55 | 0.0791 | >2500 | [104] |
| Ni-Co MOF/Ag/rGO/PU | Human sweat | 0.5 | / | 10–660 | [105] |
| MWCNT/CuO | NaOH (adding tears) | 0.4 | 1.7 | 5–620 | [106] |
| CuO-µPs | NaOH (adding tears) | 0.4 | 2.99 | 3–700 | [107] |
| FexCoyO4-rGO | Human tears | 0.55 | 0.07 | 0.1–906.4 906.4–1906.4 | [108] |
| NiCo2O4 | Human urine | 1.16 | 0.376 | 1–100,000 | [109] |
| CuO-IL/rGO | PBS(adding urine) | 0.4 | 190 | 30–7000 | [110] |
| Co3O4 | NaOH (adding saliva) | 0.535 | 0.0093 | 0–3000 | [111] |
| Au/Co3O4 | Synthetic saliva | 0.1 | 20 | 20–1000 | [112] |
| AuNP/Chitosan/CeO2 | NaOH (adding saliva) | 0.2 | 2.86 | 20–600 | [113] |
| Au/CuO | NaOH (adding saliva) | 0.55 | 0.17 | 5–1325 | [114] |
| porous CuO | NaOH (adding saliva) | 0.6 | 0.41 | 5–225 | [115] |
| CuO nanoarray | NaOH (adding saliva) | 0.55 | 0.1 | 1–6000 | [116] |
| NiO | NaOH (adding saliva) | / | 0.084 | 5–825 | [117] |
| IrO2@NiO | NaOH (adding saliva) | 0.35 | 5 | 0–180 | [118] |
| CoNi-N@GaN-3S | Human saliva | 0.55 | 5 | 5–1000 | [102] |
| Bronze | Human saliva | 0.65 | 4.7 | 20–320 | [119] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, X.; Sun, H.; He, M.; Guo, C. Research Progress on Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020167
Chi L, Zhang C, Wu X, Qian X, Sun H, He M, Guo C. Research Progress on Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(2):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020167
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Lili, Chunmei Zhang, Xuanyu Wu, Xianghao Qian, Hao Sun, Mengru He, and Chunxian Guo. 2023. "Research Progress on Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Glucose Sensors" Biomimetics 8, no. 2: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020167
APA StyleChi, L., Zhang, C., Wu, X., Qian, X., Sun, H., He, M., & Guo, C. (2023). Research Progress on Biomimetic Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. Biomimetics, 8(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020167







