How Non-Uniform Stiffness Affects the Propulsion Performance of a Biomimetic Robotic Fish
Abstract
1. Introduction
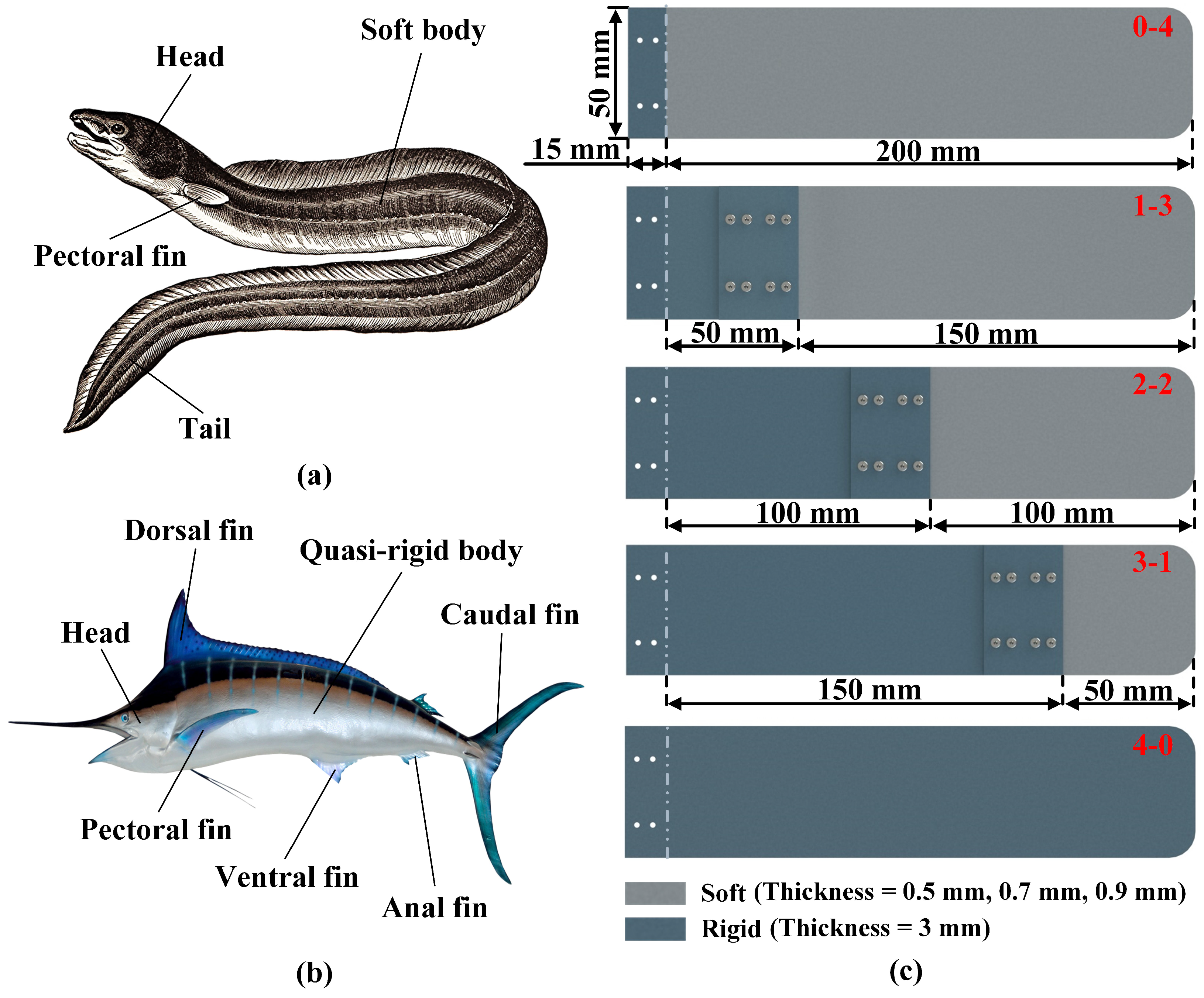
2. Materials and Methods
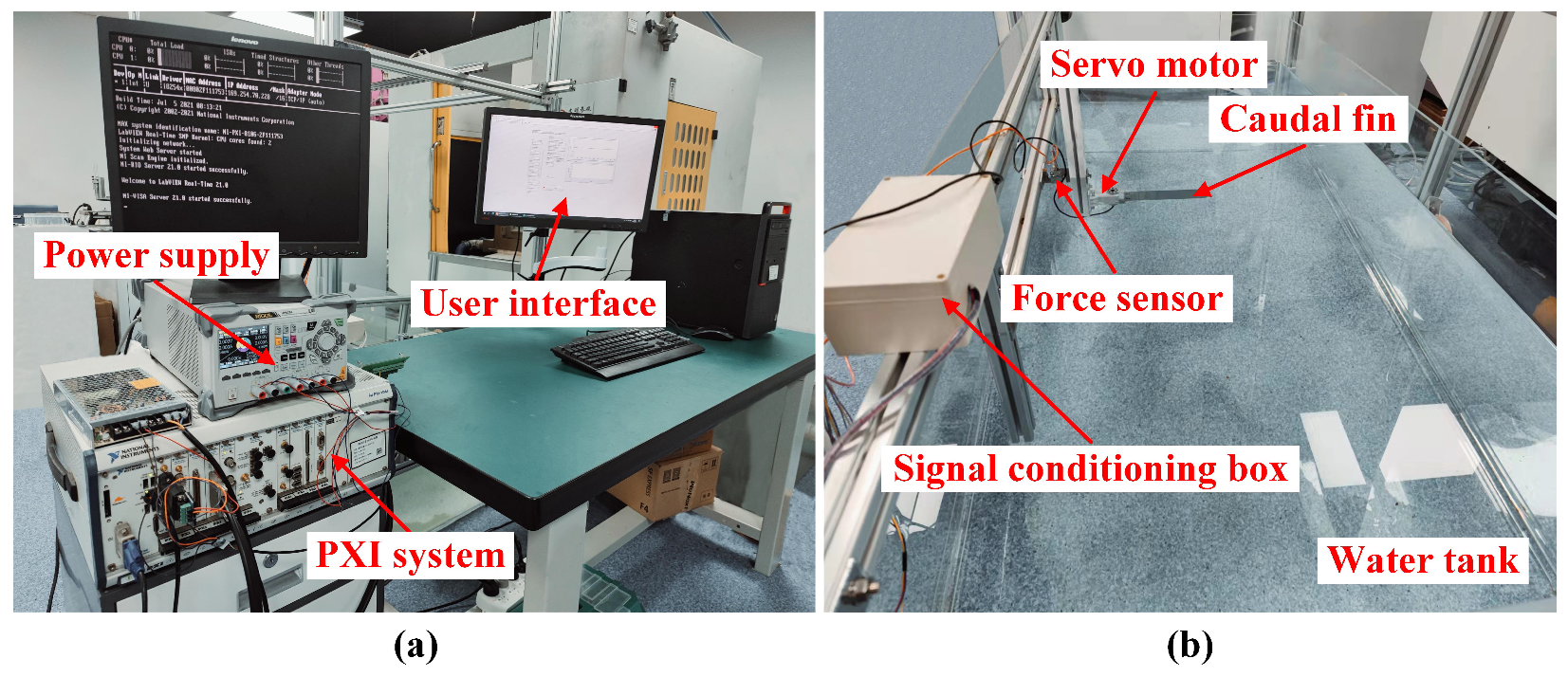
3. Experiments
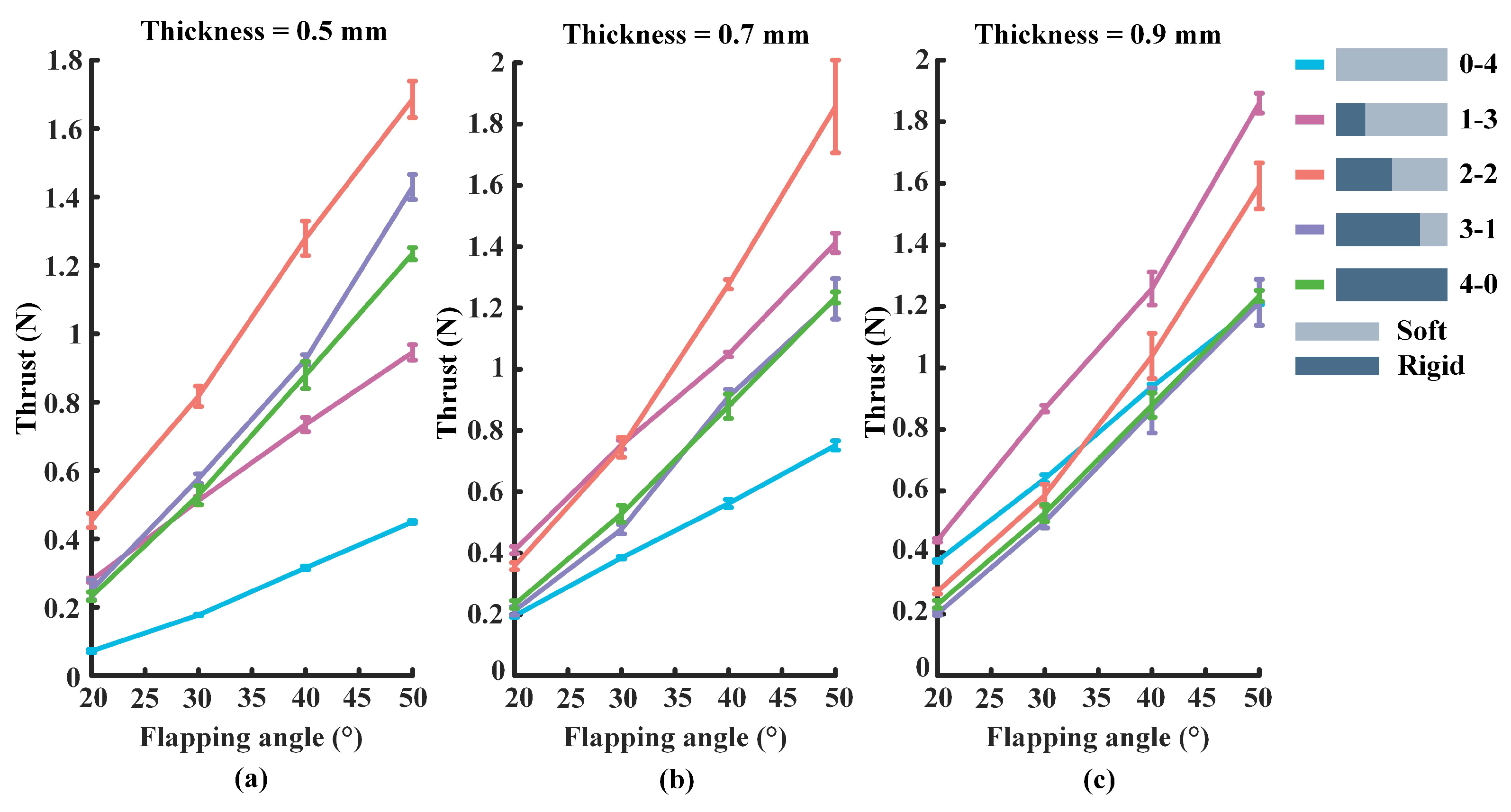
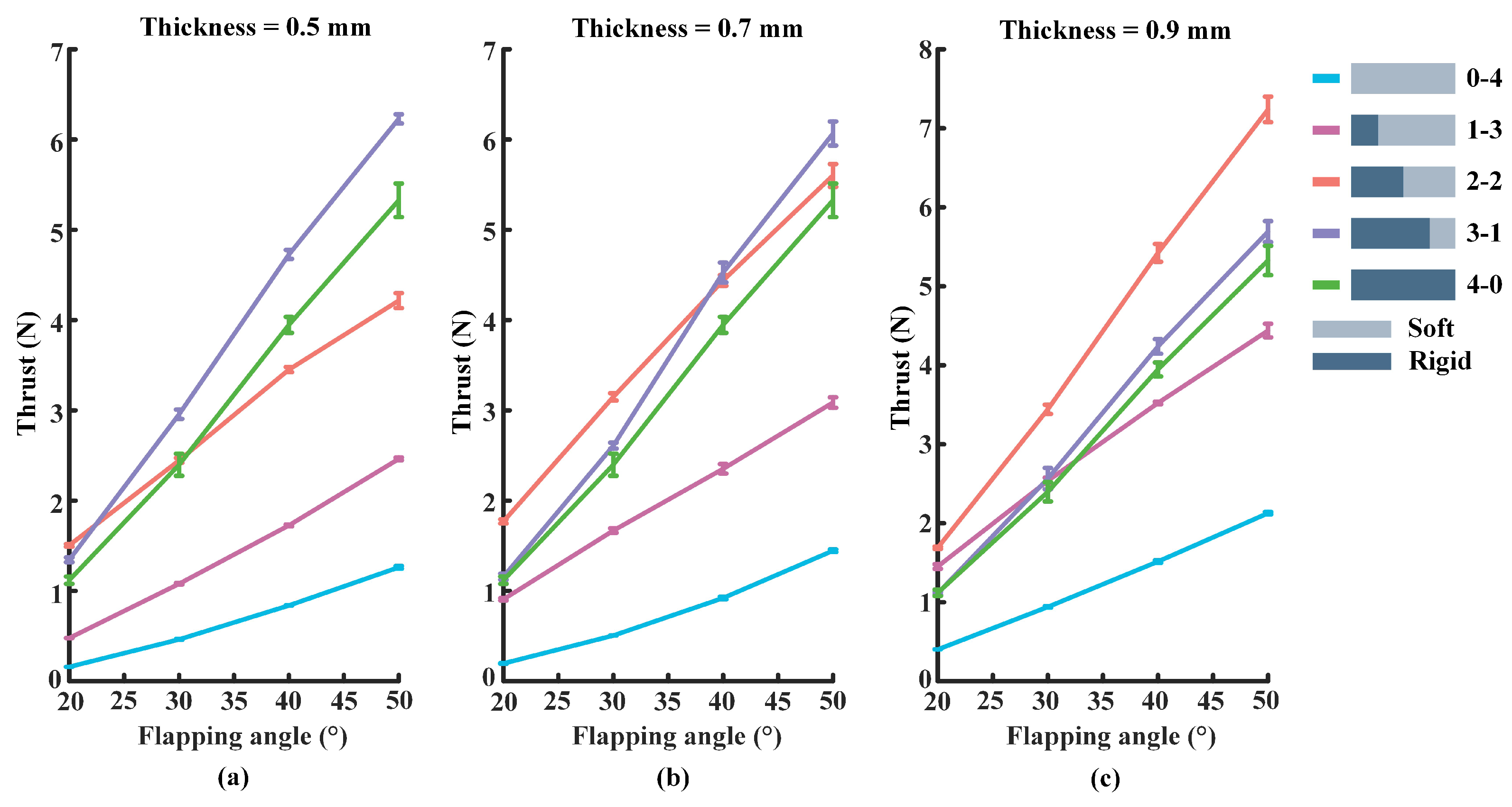
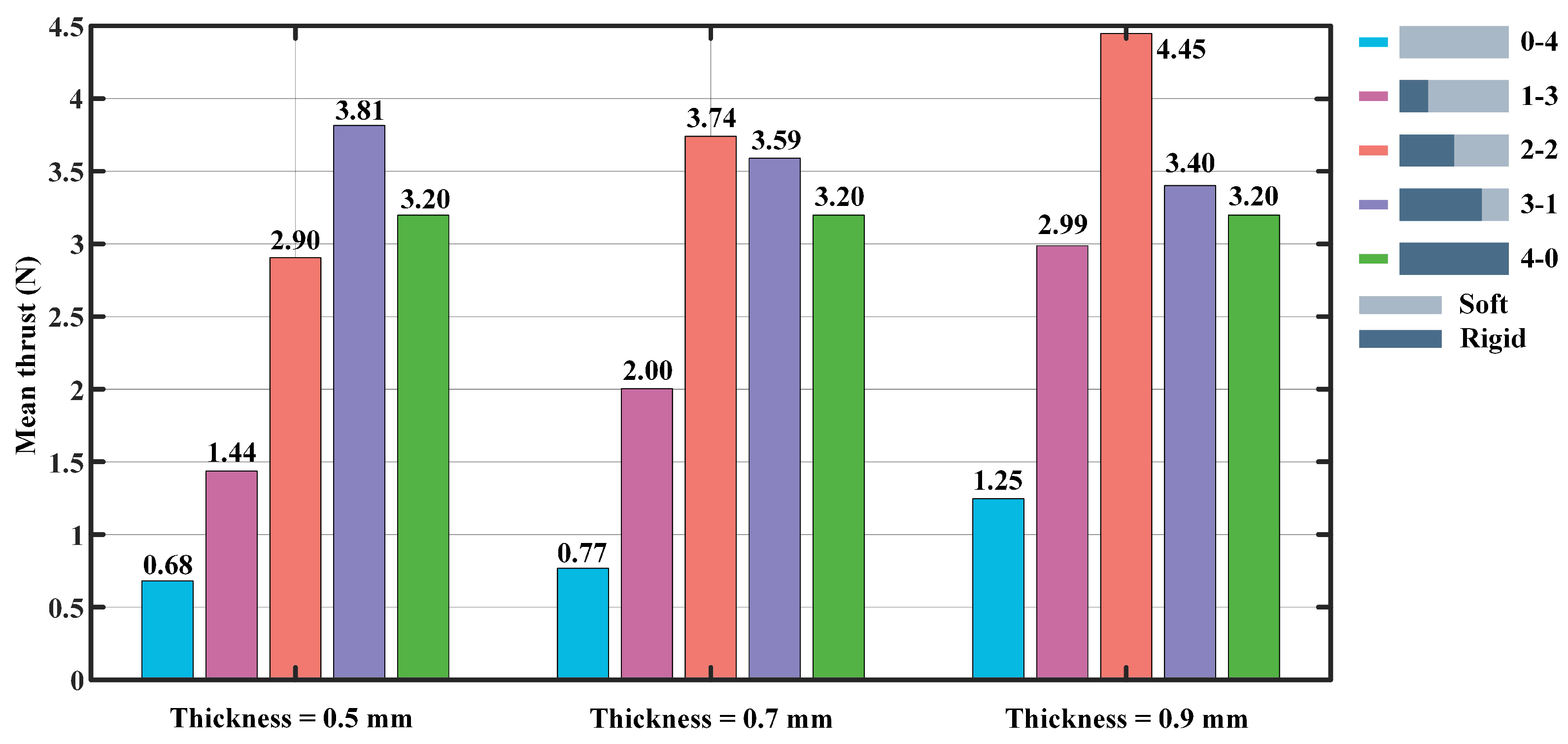
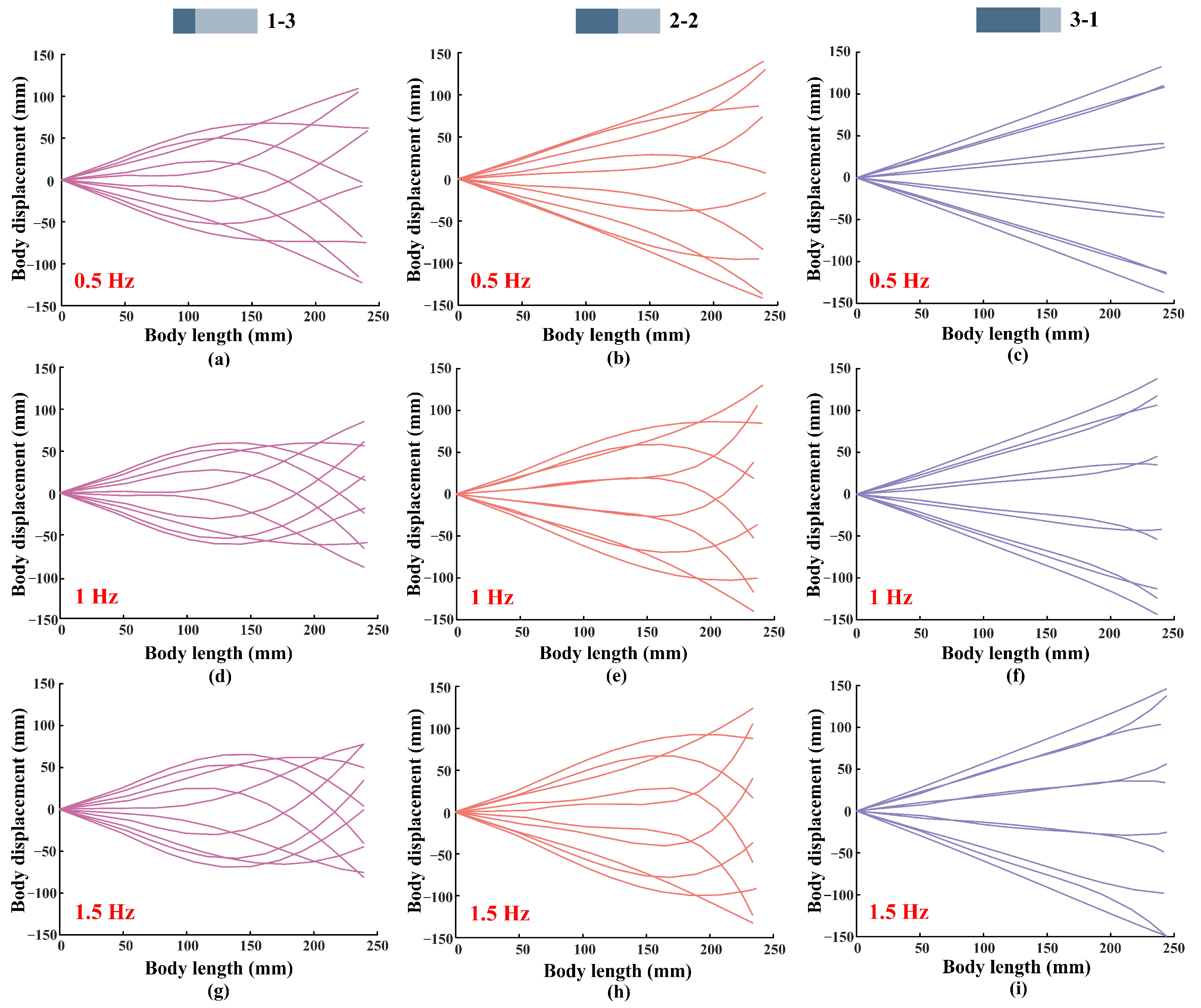
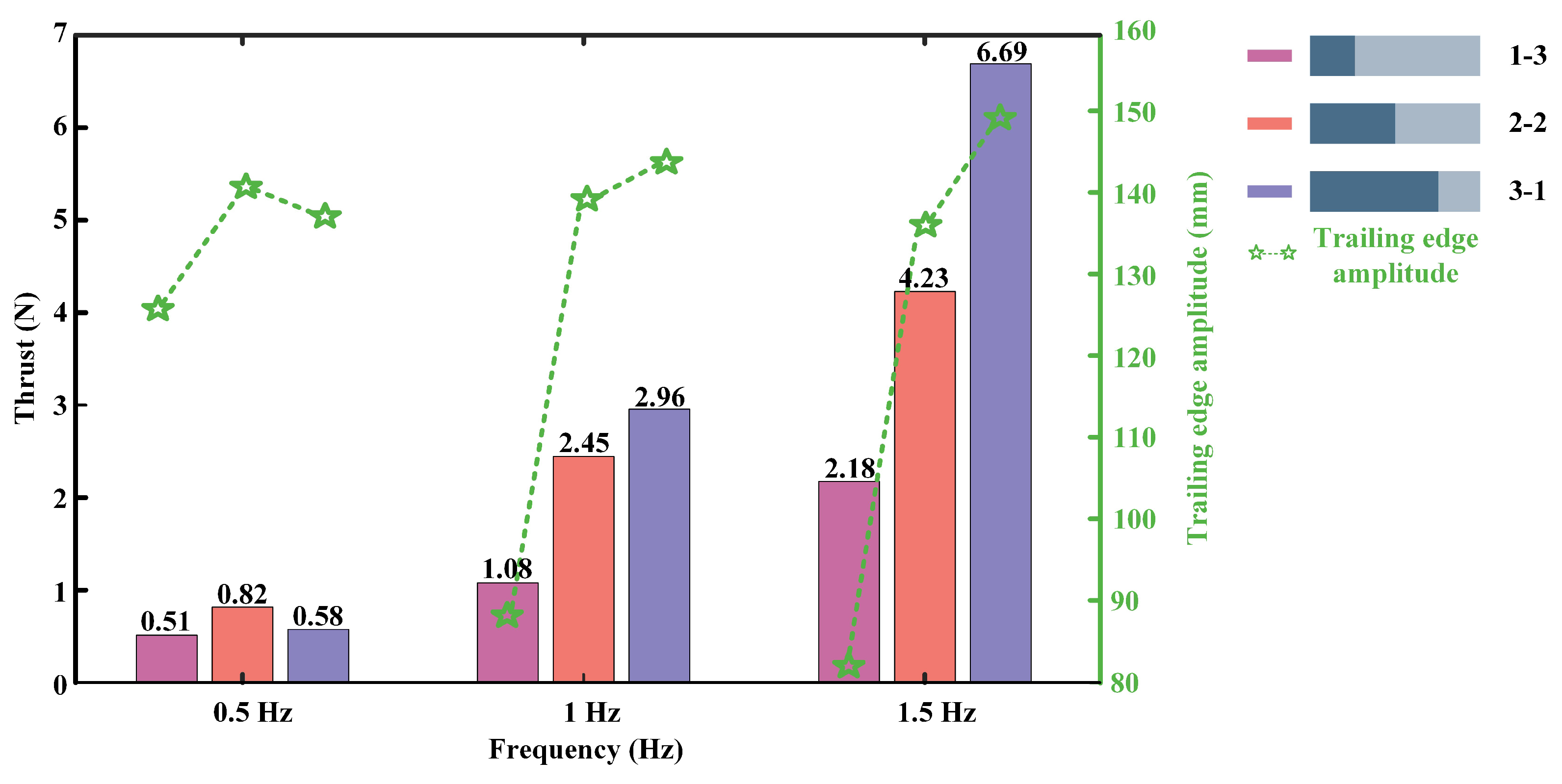
3.1. Experiment I (Frequency = 0.5 Hz)
3.2. Experiment II (Frequency = 1.0 Hz)
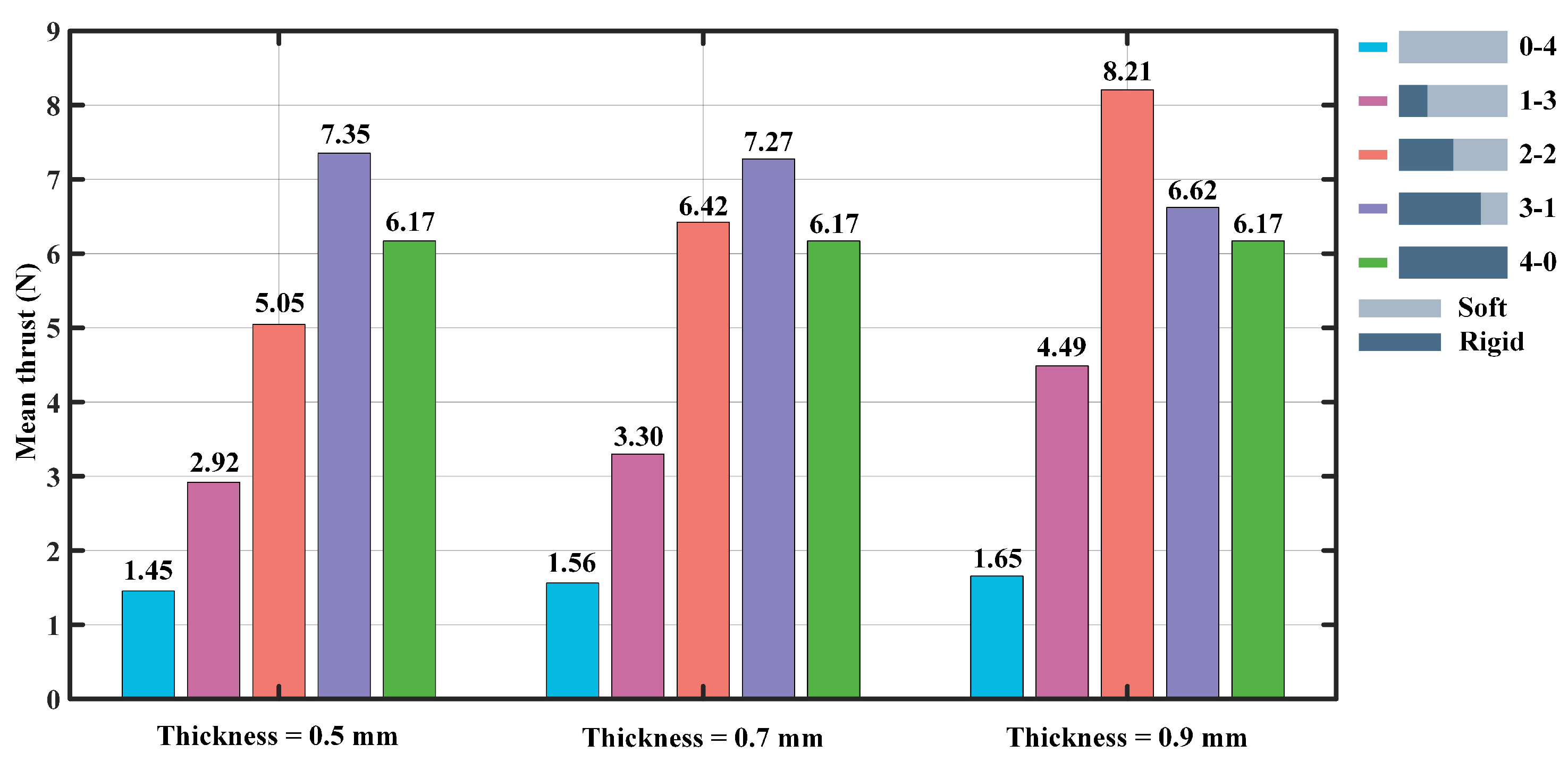
3.3. Experiment III (Frequency = 1.5 Hz)
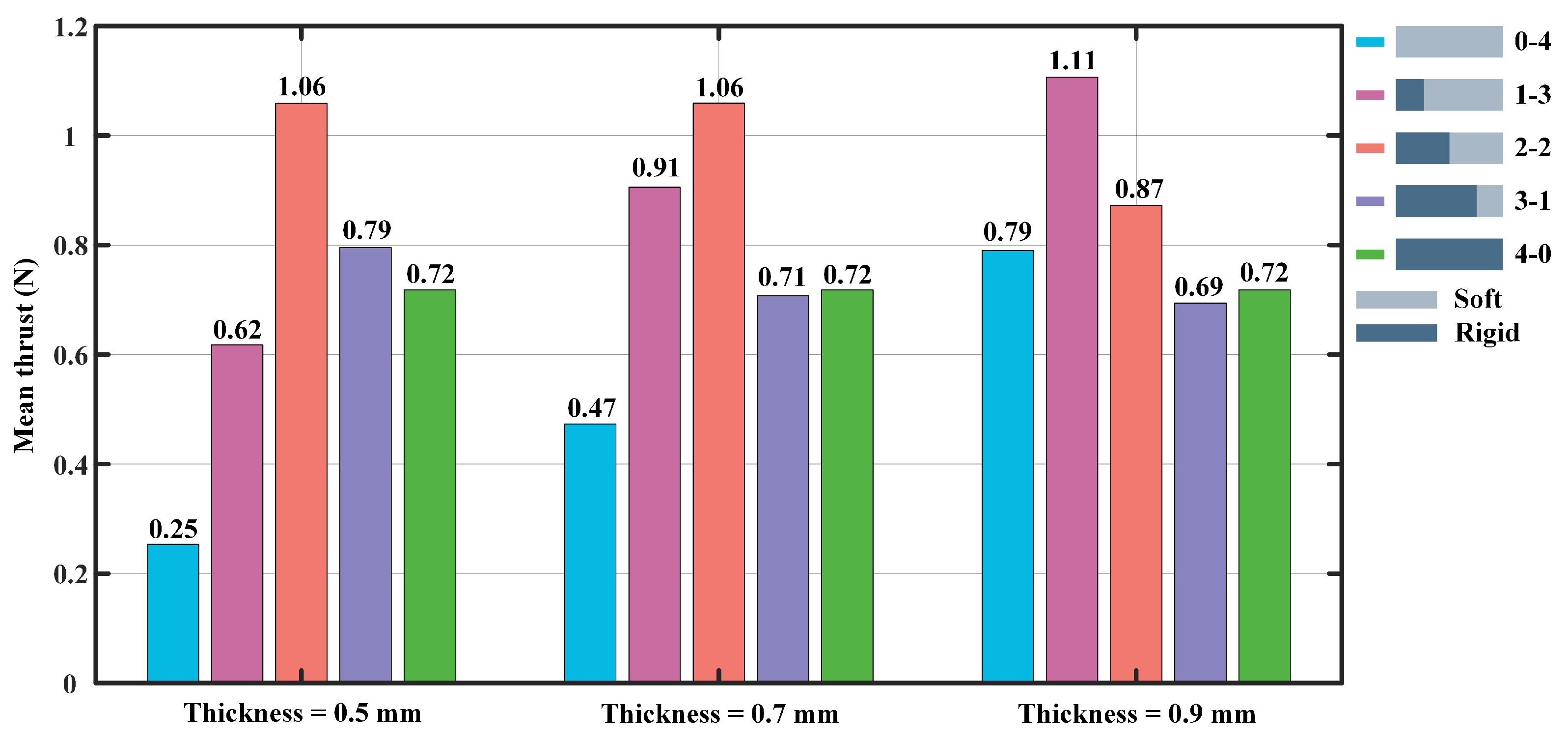
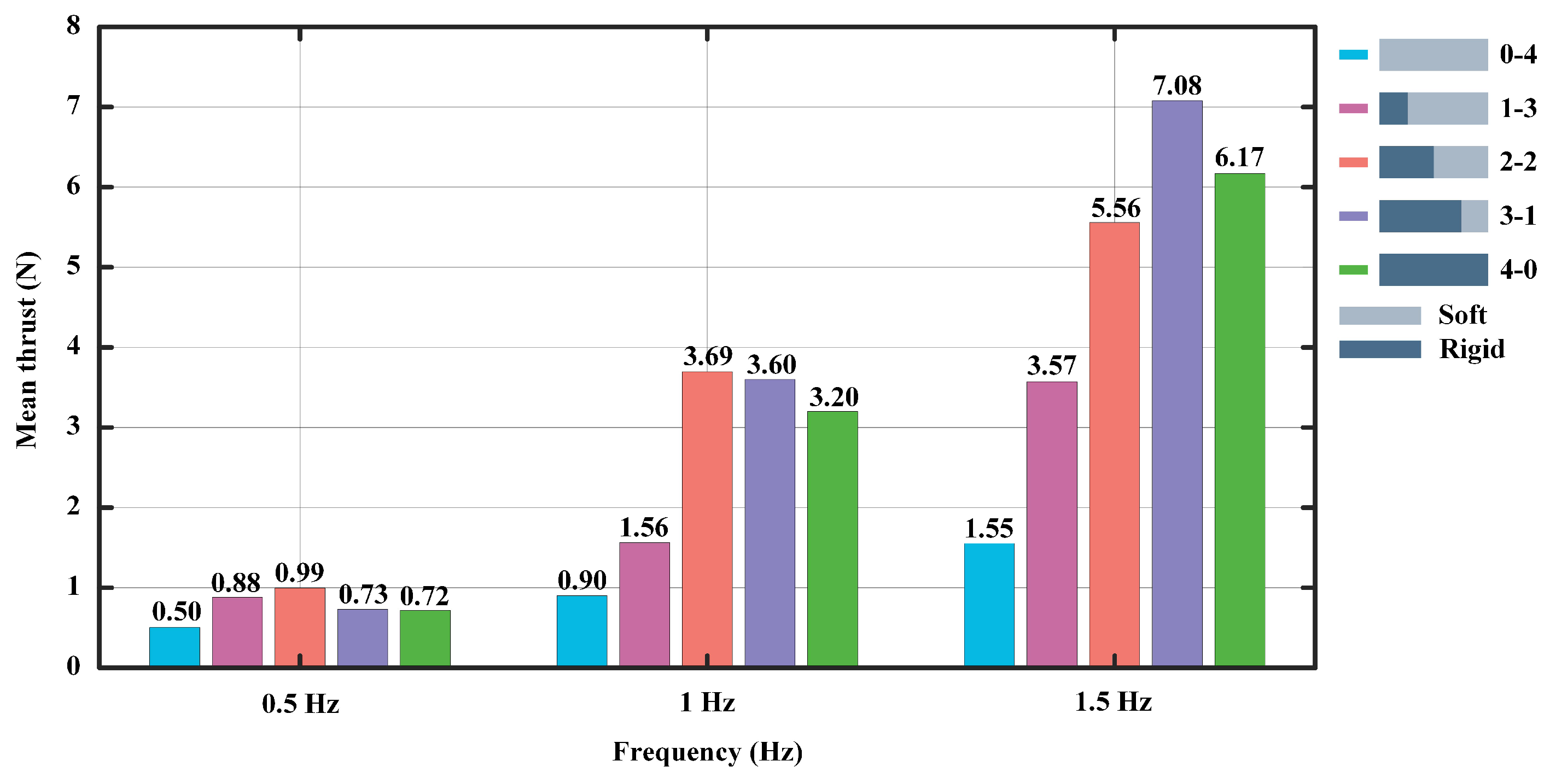
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, J.H., Jr. Muscles, elastic energy, and the dynamics of body stiffness in swimming eels. Am. Zool. 1998, 38, 771–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.H., Jr.; Nipper, K.S. The importance of body stiffness in undulatory propulsion. Am. Zool. 1996, 36, 678–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, F.E.; Lauder, G.V. Control surfaces of aquatic vertebrates: Active and passive design and function. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 351–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauder, G.V.; Madden, P.G.A.; Tangorra, J.L.; Anderson, E.; Baker, T.V. Bioinspiration from fish for smart material design and function. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 094014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, R.M.; Thornycroft, P.J.M.; Lauder, G.V. Undulatory locomotion of flexible foils as biomimetic models for understanding fish propulsion. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilich, K.L.; Lauder, G.V. Passive mechanical models of fish foils: Effects of shape and stiffness on self-propulsion. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N.J. Torsional spring is the optimal flexibility arrangement for thrust production of a flapping wing. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 091701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.D.; Li, Y.; Alexeev, A. Efficient swimming using flexible fins with tapered thickness. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2017, 2, 102101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Bi, X. Effects of stiffness distribution and spanwise deformation on the dynamics of a ray-supported caudal fin. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 026011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.N.; Thornycrof, P.J.M.; Gemmell, B.J.; Colin, S.P.; Costello, J.H.; Lauder, G.V. Effects of non-uniform stiffness on the swimming performance of a passively-flexing, fish-like foil model. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 056019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Sen, S.; Har, C. Effect of flexural stiffness distribution of a fin on propulsion performance. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 129, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floryan, D.; Clarence, W.R. Distributed flexibility in inertial swimmers. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 888, A24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Huang, H.B.; Lu, X.Y. Optimal chordwise stiffness distribution for self-propelled heaving flexible plates. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 111905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Zhu, J.; Fish, F.E.; Kerr, S.J.; Downs, A.M.; Bart-Smith, H.; Quinn, D.B. Tunable stiffness enables fast and efficient swimming in fish-like robots. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabe4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Dabiri, J.O. An overview of a Lagrangian method for analysis of animal wake dynamics. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Dabiri, J.O.; Madden, P.G.; Lauder, G.V. Non-invasive measurement of instantaneous forces during aquatic locomotion: A case study of the bluegill sunfish pectoral fin. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X. Fluid-structure interaction of bio-inspired flexible slender structures: A review of selected topics. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2022, 17, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, M.; Mivehchi, A.; Moored, K. High-efficiency can be achieved for non-uniformly flexible pitching hydrofoils via tailored collective interactions. Fluids 2021, 6, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Diana, R.; Vacher, J.; Raspa, V.; Thiria, B. On the fluid dynamical effects of synchronization in side-by-side swimmers. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ren, F.; Tang, H. Enhancing propulsion performance of a flexible heaving foil through dynamically adjusting its flexibility. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2019, 14, 064002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Xiao, Q.; Zhu, Q. Effects of time-varying flexibility on the propulsion performance of a flapping foil. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 121904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Lu, X.Y. Interplay of chordwise stiffness and shape on performance of self-propelled flexible flapping plate. Phys. Fluids. 2021, 33, 091904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; He, G.; Zhang, X. Self-propelled swimming of a flexible plunging foil near a solid wall. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2016, 11, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.G.; Kim, B.; Sung, H.J. Hydrodynamics of a self-propelled flexible fin near the ground. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 051902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; He, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Intermittent locomotion of a fish-like swimmer driven by passive elastic mechanism. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2018, 13, 056011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Huang, H.; Lu, X.Y. Hydrodynamic benefits of intermittent locomotion of a self-propelled flapping plate. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 053106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Sung, H.J. Intermittent locomotion of a self-propelled plate. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 111902. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; He, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Stable formations of self-propelled fish-like swimmers induced by hydrodynamic interactions. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jong, Y.J.; Chang, L.M.; Wu, W.L. Propulsion strategy analysis of high-speed swordfish. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 2009, 52, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakiotakis, M.; Lane, D.M.; Davies, J.B.C. Review of fish swimming modes for aquatic locomotion. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1999, 24, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.H., Jr.; Shepherd, W.; Root, R.G. Manueuverability and reversible propulsion: How eel-like fish swim forward and backward using travelling body waves. In Proceedings of the Special Session on Bio-Engineering Research Related to Autonomous Underwater Vehicles, 10th International Symposium Unmanned Untethered Submersible Technology, Durham, NH, USA, 5–11 September 1997; pp. 118–134. [Google Scholar]
- Aleyev, Y.G. The propulsive action of the body. In Nekton. The Hague: Junk; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 102–147. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, K.N.; Johnson, N.; Beaulieu, W.T.; Cathcart, E.; Tirrell, G.; Colin, S.P.; Gemmell, B.J.; Dabiri, J.O.; Costello, J.H. Bending rules for animal propulsion. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, C.; Ding, J.; Dong, B.; Lian, G.; He, K.; Xie, F. How Non-Uniform Stiffness Affects the Propulsion Performance of a Biomimetic Robotic Fish. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040187
Zheng C, Ding J, Dong B, Lian G, He K, Xie F. How Non-Uniform Stiffness Affects the Propulsion Performance of a Biomimetic Robotic Fish. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(4):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040187
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Changzhen, Jiang Ding, Bingbing Dong, Guoyun Lian, Kai He, and Fengran Xie. 2022. "How Non-Uniform Stiffness Affects the Propulsion Performance of a Biomimetic Robotic Fish" Biomimetics 7, no. 4: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040187
APA StyleZheng, C., Ding, J., Dong, B., Lian, G., He, K., & Xie, F. (2022). How Non-Uniform Stiffness Affects the Propulsion Performance of a Biomimetic Robotic Fish. Biomimetics, 7(4), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040187




