Investigation of Bioinspired Nacreous Structure on Strength and Toughness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. XFEM and Models
2.1. XFEM
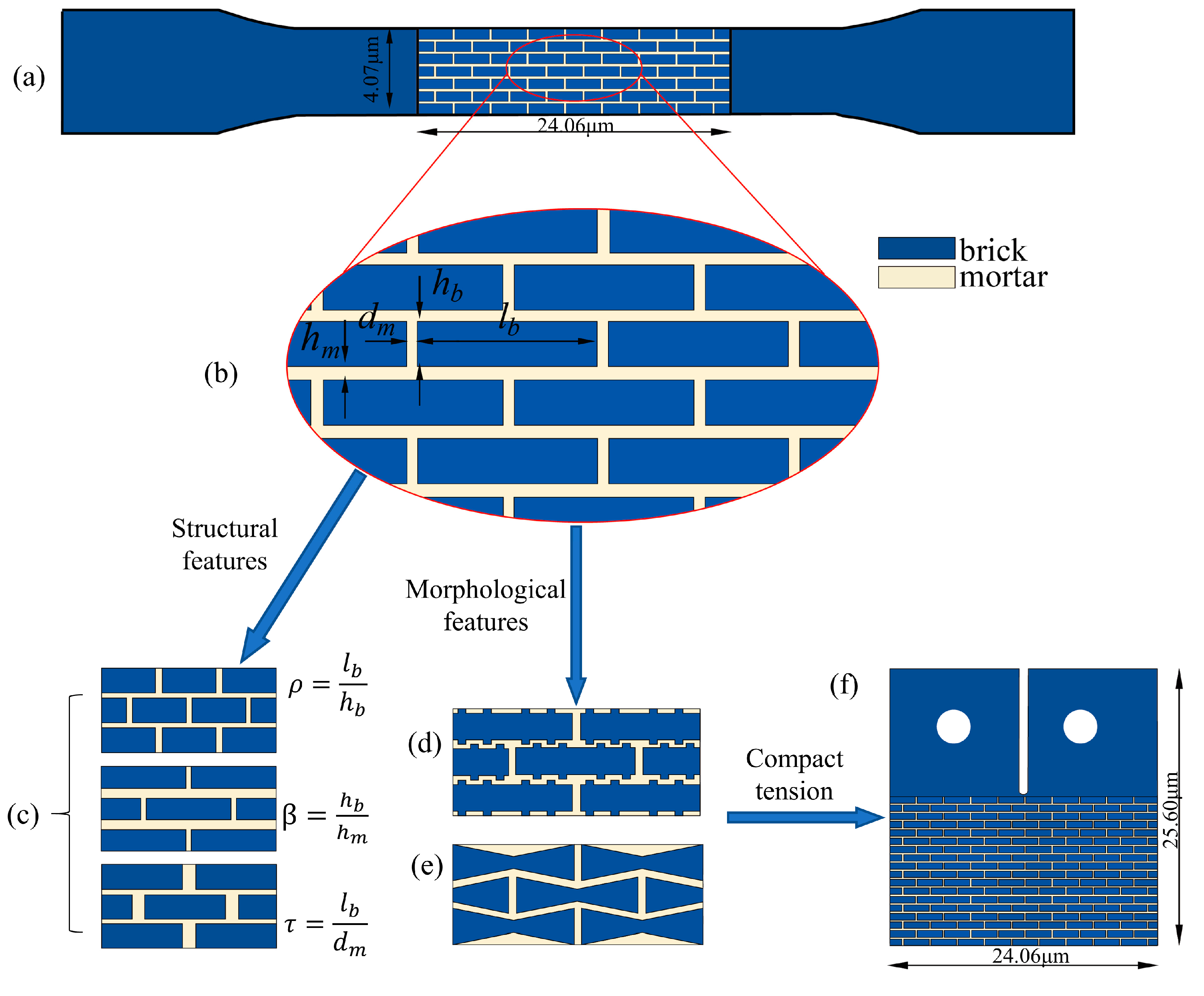
2.2. Materials and Models
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Model Validation
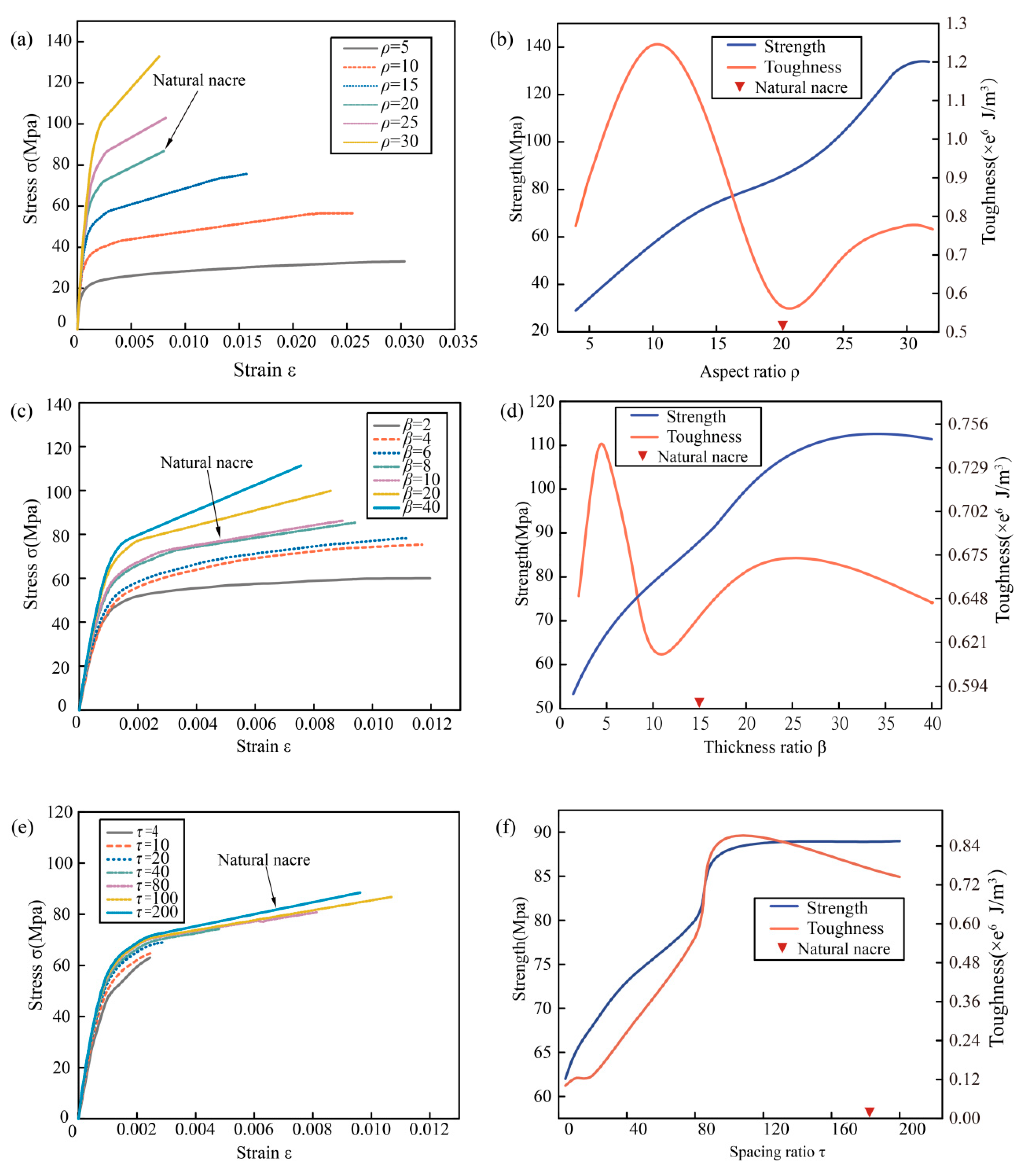
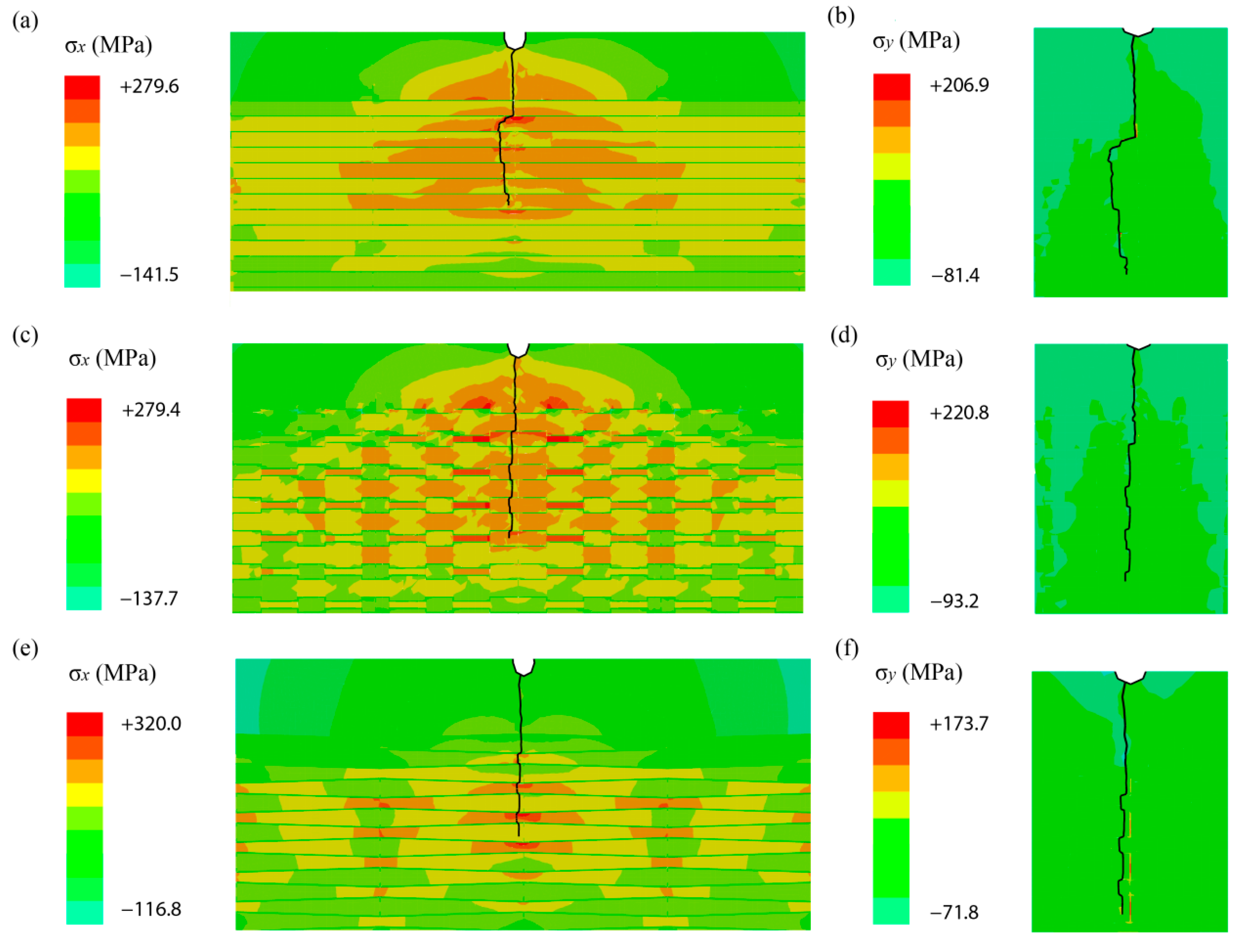
3.2. Structural Effect on Strength and Toughness
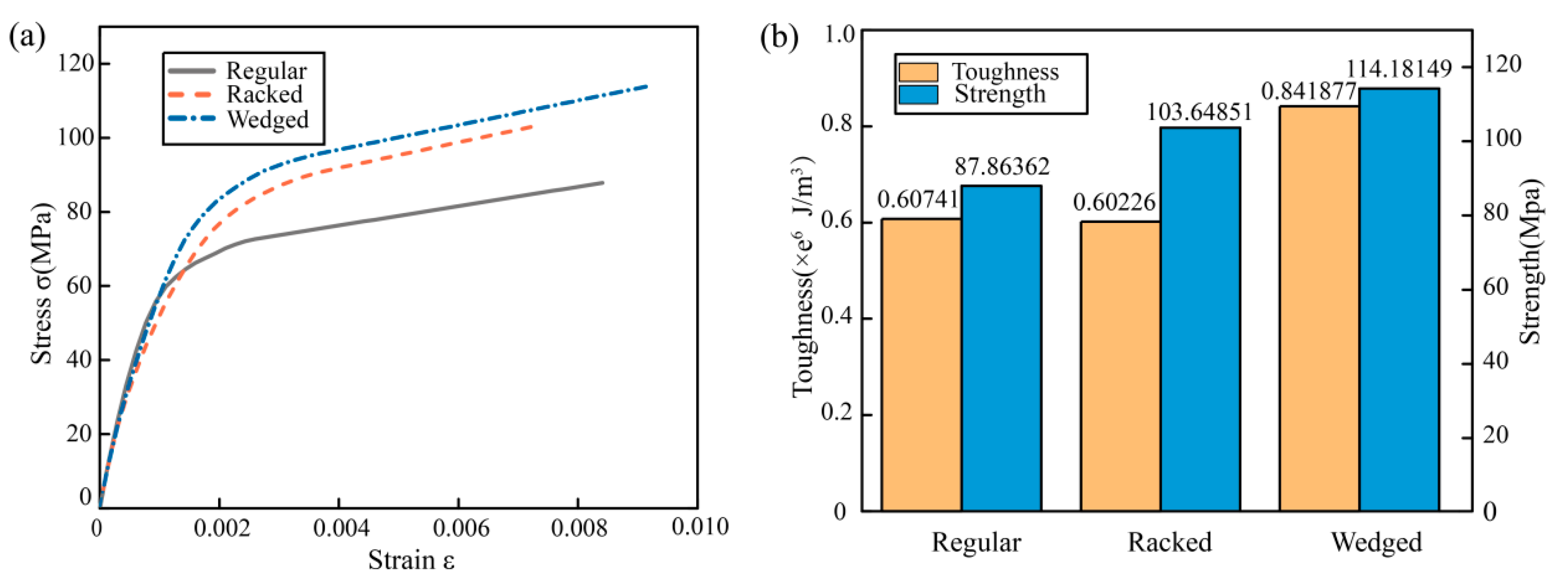
3.3. Morphology Effect on Strength and Toughness
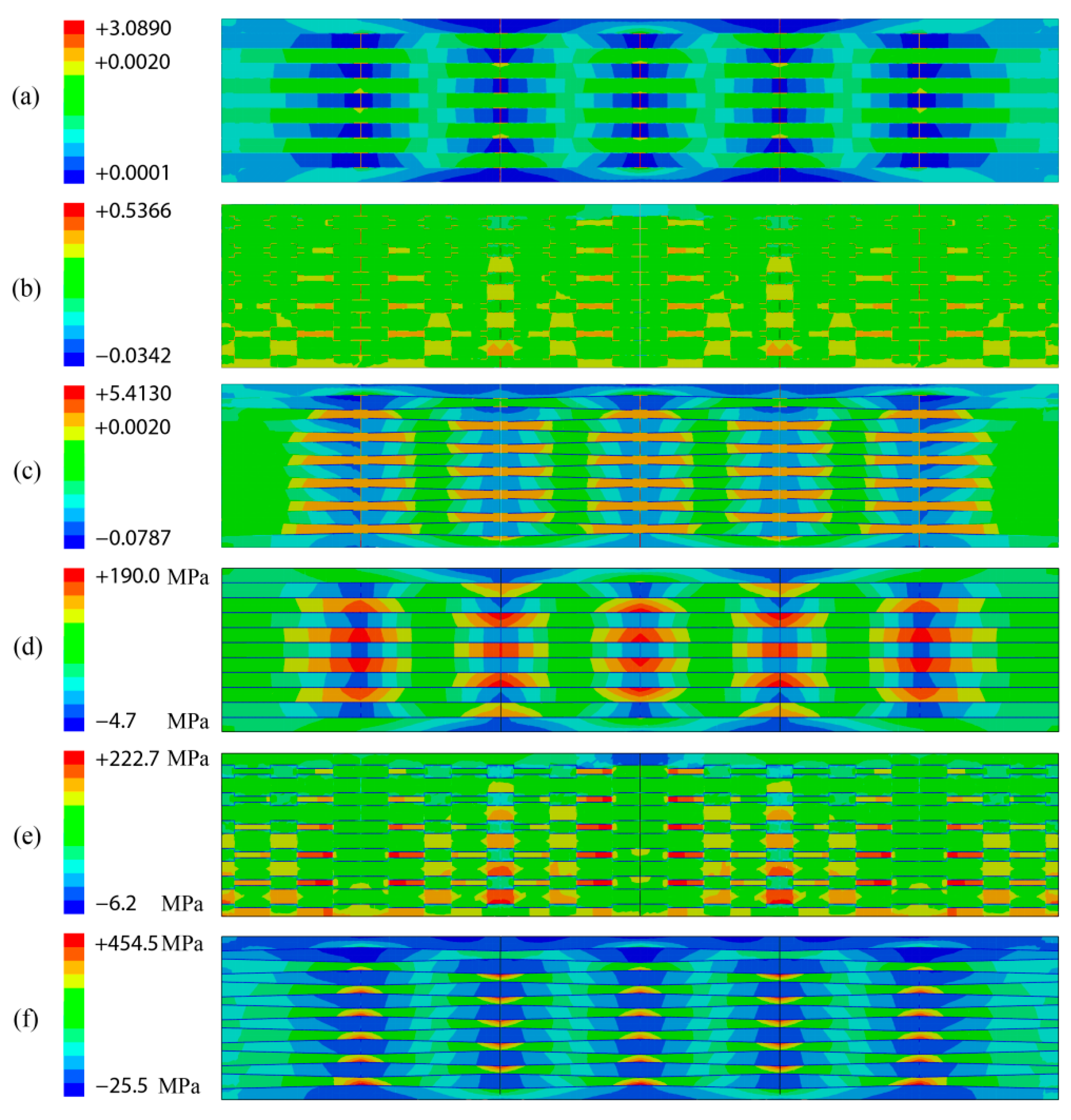
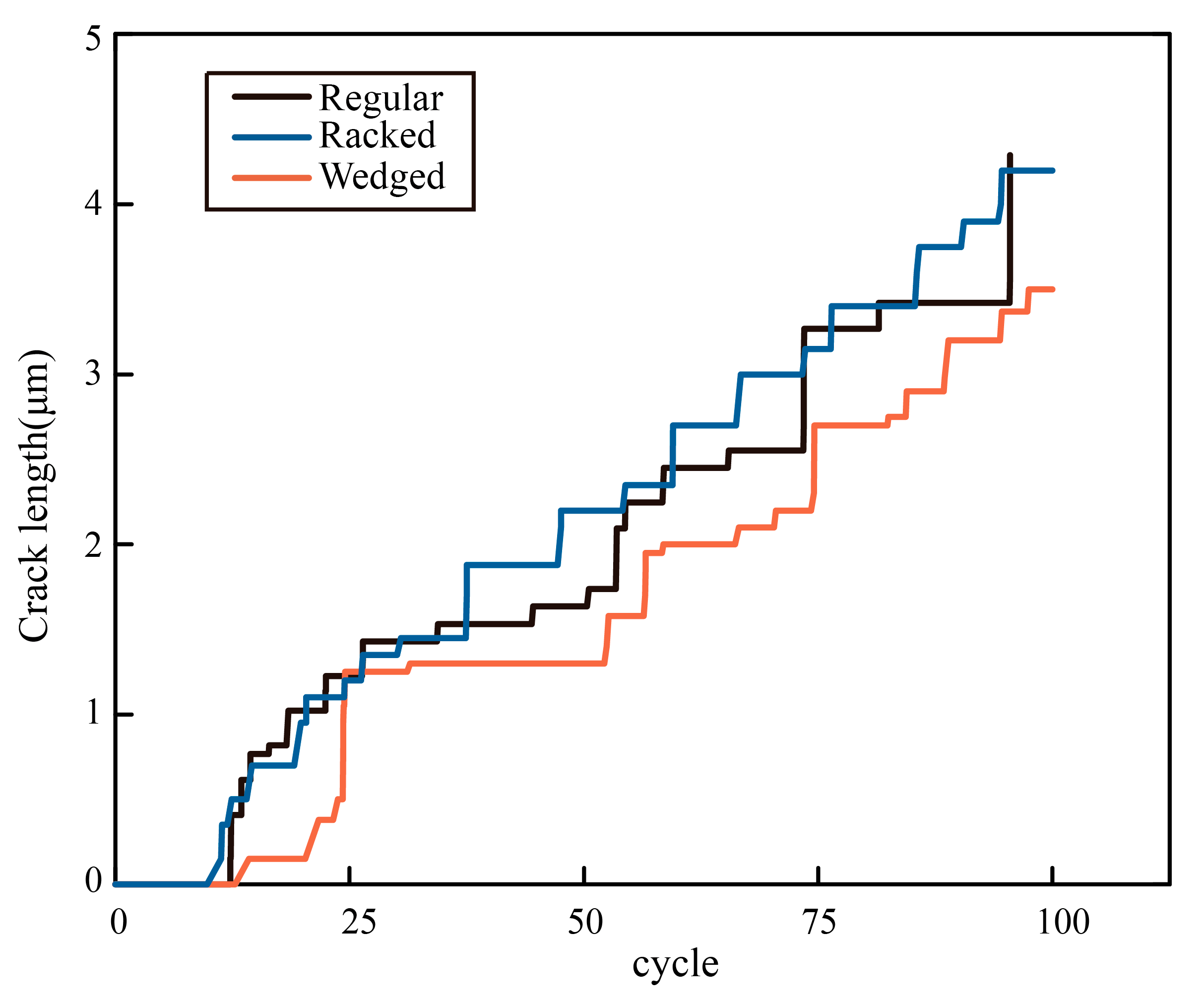
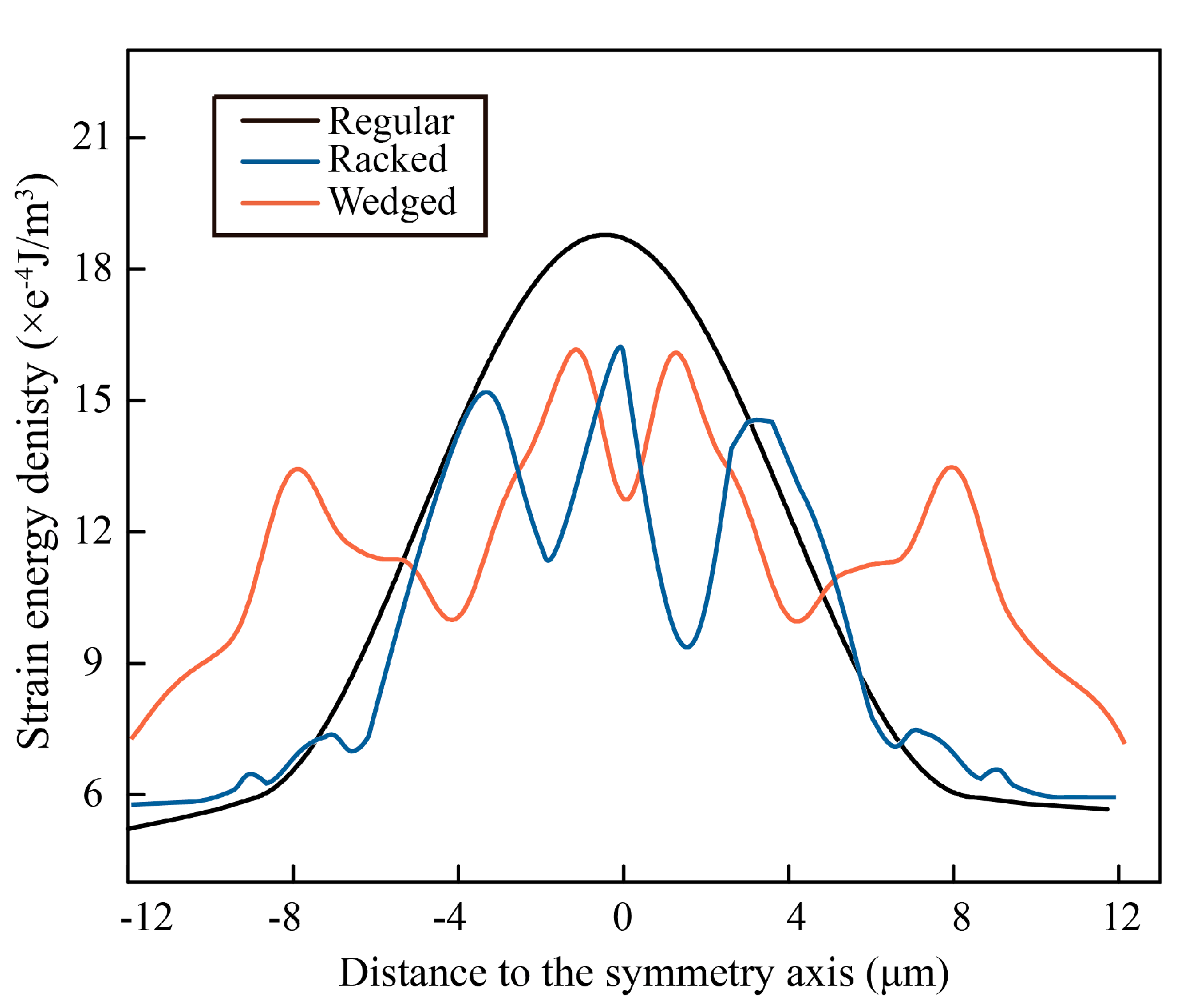
3.4. Morphology Effect on Crack Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, Z.; Wang, L. 3D Printing of Biomimetic Composites with Improved Fracture Toughness. Acta Mater. 2019, 173, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naleway, S.E.; Porter, M.M.; McKittrick, J.; Meyers, M.A. Structural Design Elements in Biological Materials: Application to Bioinspiration. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5455–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegst, U.G.K.; Bai, H.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Bioinspired Structural Materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelat, F.; Espinosa, H.D. An Experimental Investigation of Deformation and Fracture of Nacre—Mother of Pearl. Exp. Mech. 2007, 47, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Suo, Z.; Evans, A.G.; Yao, N.; Aksay, I.A. Deformation Mechanisms in Nacre. J. Mater. Res. 2001, 16, 2485–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Katti, K.; Katti, D. Photoacoustic FTIR Spectroscopic Study of Undisturbed Nacre from Red Abalone. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2006, 64, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-A.; Le, H.; Huang, Y. Rapid Assembly Processes of Ordered Inorganic/Organic Nanocomposites. In Biomimetics Learning from Nature; Mukherjee, A., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2010; pp. 217–240. [Google Scholar]
- Currey, J.D. Mechanical Properties of Mother of Pearl in Tension. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1977, 196, 443–463. [Google Scholar]
- Barthelat, F.; Dastjerdi, A.K.; Rabiei, R. An Improved Failure Criterion for Biological and Engineered Staggered Composites. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelat, F.; Li, C.-M.; Comi, C.; Espinosa, H.D. Mechanical Properties of Nacre Constituents and Their Impact on Mechanical Performance. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 21, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.Y.-M.; Chen, P.-Y.; Meyers, M.A. The Growth of Nacre in the Abalone Shell. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.I.; Meza Martinez, P.E.; Meyers, M.A. Organic Interlamellar Layers, Mesolayers and Mineral Nanobridges: Contribution to Strength in Abalone (Haliotis rufescence) Nacre. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelat, F.; Tang, H.; Zavattieri, P.; Li, C.; Espinosa, H. On the Mechanics of Mother-of-Pearl: A Key Feature in the Material Hierarchical Structure. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2007, 55, 306–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, S.; Arnoldi, M.; Khoshnavaz, S.; Treccani, L.; Kuntz, M.; Mann, K.; Grathwohl, G.; Fritz, M. The Nacre Protein Perlucin Nucleates Growth of Calcium Carbonate Crystals. J. Microsc. 2003, 212, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.L.; Cui, F.Z.; Pu, G.; Wang, R.Z.; Li, H.D. Crystal Orientation, Toughening Mechanisms and a Mimic of Nacre. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2000, 11, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Bai, Y. Nanostructure of Nacre and Its Mechanical Effects. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2002, 3, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Gao, H. Mechanical Properties of Nanostructure of Biological Materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2004, 52, 1963–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Song, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yu, S.-H.; He, L. Optimization Design of Strong and Tough Nacreous Nanocomposites through Tuning Characteristic Lengths. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2015, 81, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Yu, Z.; Wei, X. Size Effects in Layered Composites—Defect Tolerance and Strength Optimization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 165, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, T.-P.; Belytschko, T. The Extended/Generalized Finite Element Method: An Overview of the Method and Its Applications: The GEFM/XFEM: An Overview of the Method. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 2010, 84, 253–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belytschko, T.; Black, T. Elastic Crack Growth in Finite Elements with Minimal Remeshing. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 1999, 45, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mose, N.; Dolbow, J.; Belytschko, T. A Finite Element Method for Crack Growth without Remeshing. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 1999, 46, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, Y.; Hamouine, A. A Survey of the Extended Finite Element. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Sukumar, N.; Prévost, J.-H. Modeling Quasi-Static Crack Growth with the Extended Finite Element Method Part II: Numerical Applications. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 7539–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenk, J.M.; Babuška, I. The Partition of Unity Finite Element Method: Basic Theory and Applications. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1996, 139, 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camanho, P.P. Mixed-Mode Decohesion Finite Elements for the Simulation of Delamination in Composite Materials. NASA 2002, TM-2002–211737, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.V.; Ghazlan, A.; Ngo, T.; Nguyen, T. Performance of a Bio-Mimetic 3D Printed Conch-like Structure under Quasi-Static Loading. Compos. Struct. 2020, 246, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.P.; Vincent, J.F.V.; Turner, R.M. The Mechanical Design of Nacre. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1988, 234, 415–440. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, M.A.; McKittrick, J.; Chen, P.-Y. Structural Biological Materials: Critical Mechanics-Materials Connections. Science 2013, 339, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bhushan, B. Hierarchical Structure and Mechanical Properties of Nacre: A Review. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphin, Y.; Luquet, G.; Salome, M.; Bellot-Gurlet, L.; Cuif, J.P. Structure and Composition of Unio Pictorum Shell: Arguments for the Diversity of the Nacroprismatic Arrangement in Molluscs: Structure and Composition of Unio Pictorum Shell. J. Microsc. 2018, 270, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelat, F.; Zhu, D. A Novel Biomimetic Material Duplicating the Structure and Mechanics of Natural Nacre. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 26, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Z. Effect of Interlocking Structure on Mechanical Properties of Bio-Inspired Nacreous Composites. Compos. Struct. 2019, 226, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, B.; Niu, S.; Yang, J.; Shao, C.; Wang, M.; Ni, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Investigation of Bioinspired Nacreous Structure on Strength and Toughness. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030120
Tang B, Niu S, Yang J, Shao C, Wang M, Ni J, Zhang X, Yang X. Investigation of Bioinspired Nacreous Structure on Strength and Toughness. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(3):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030120
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Biao, Shichao Niu, Jiayi Yang, Chun Shao, Ming Wang, Jing Ni, Xuefeng Zhang, and Xiao Yang. 2022. "Investigation of Bioinspired Nacreous Structure on Strength and Toughness" Biomimetics 7, no. 3: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030120
APA StyleTang, B., Niu, S., Yang, J., Shao, C., Wang, M., Ni, J., Zhang, X., & Yang, X. (2022). Investigation of Bioinspired Nacreous Structure on Strength and Toughness. Biomimetics, 7(3), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7030120







