On the Fluid Dynamical Effects of Synchronization in Side-by-Side Swimmers
Abstract
1. Introduction
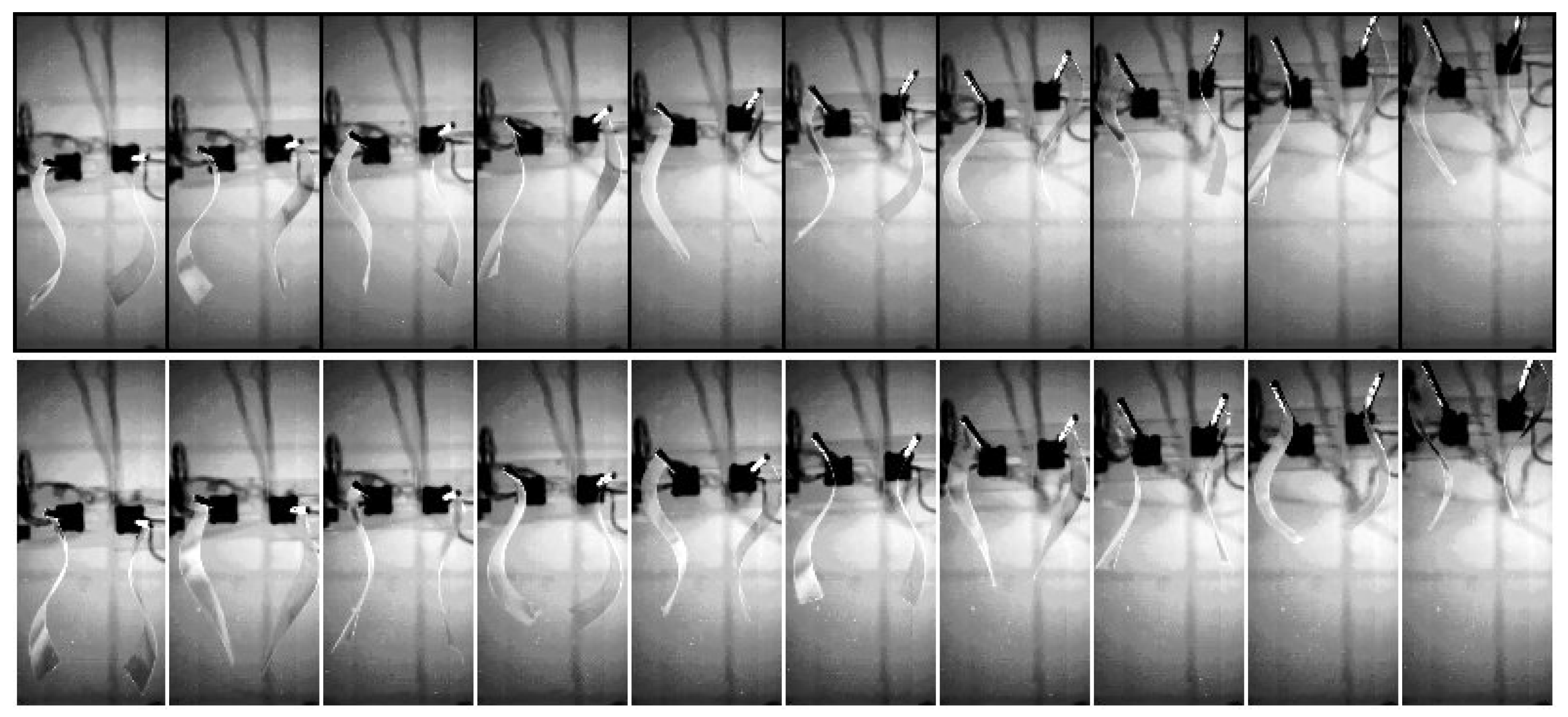
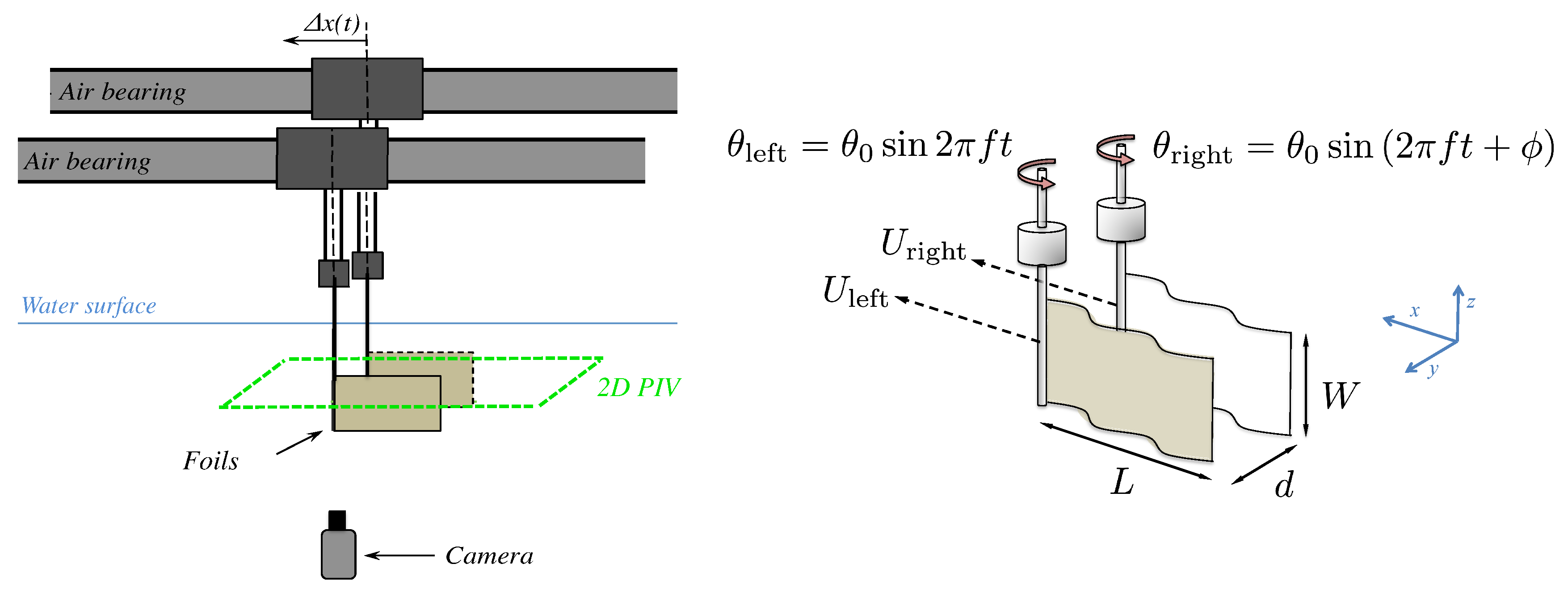
2. Experimental Setup
Particle Image Velocimetry
3. Results
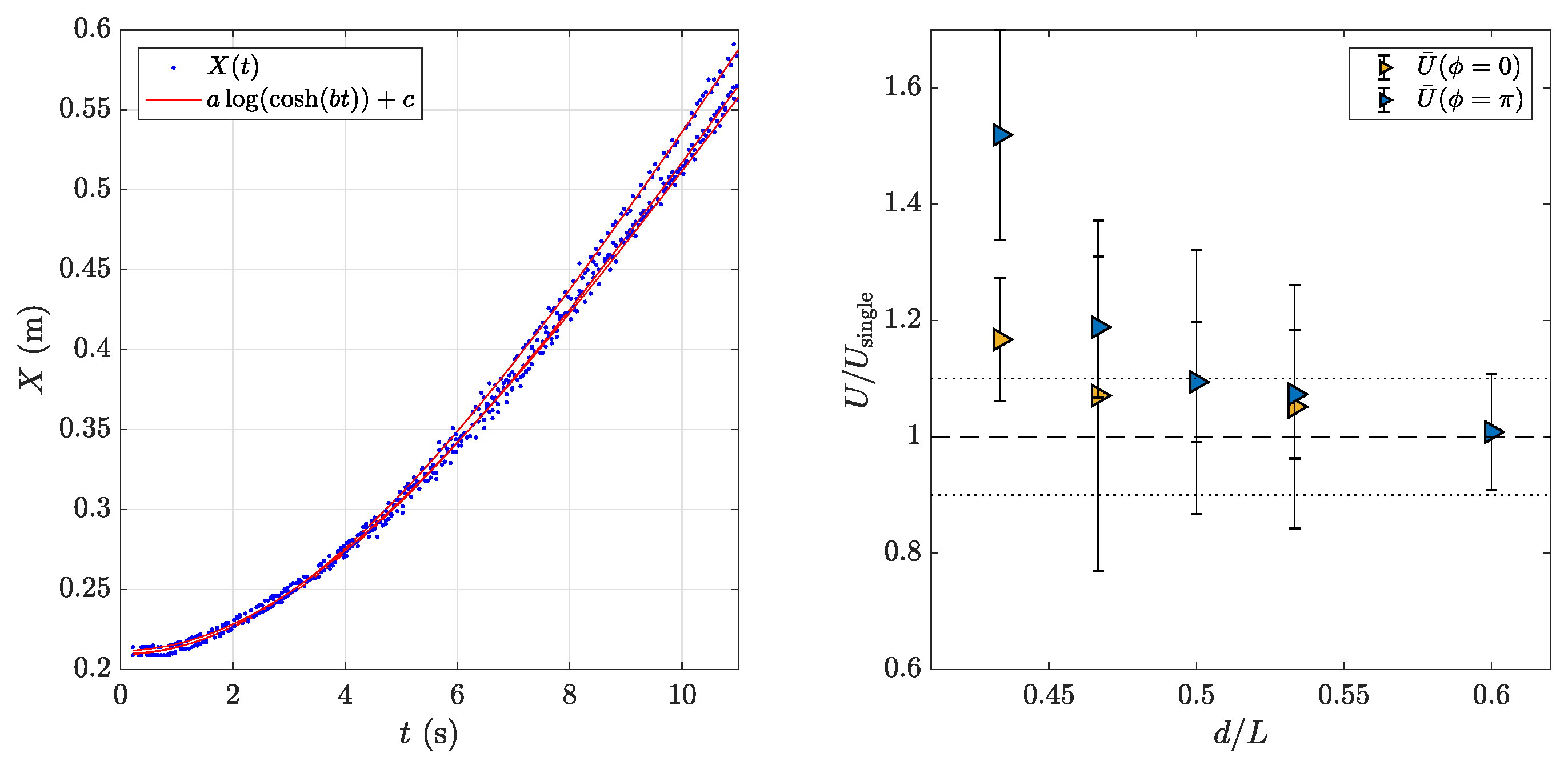
3.1. Cruising Speed
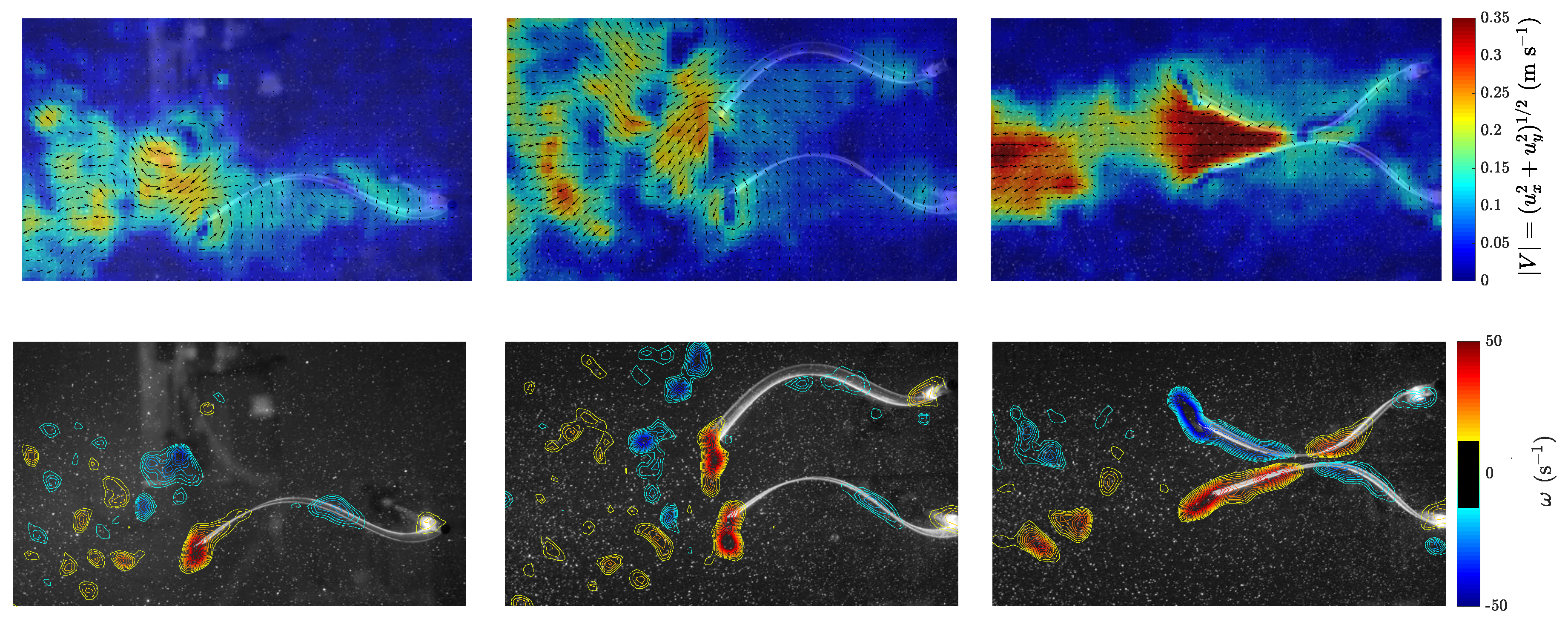
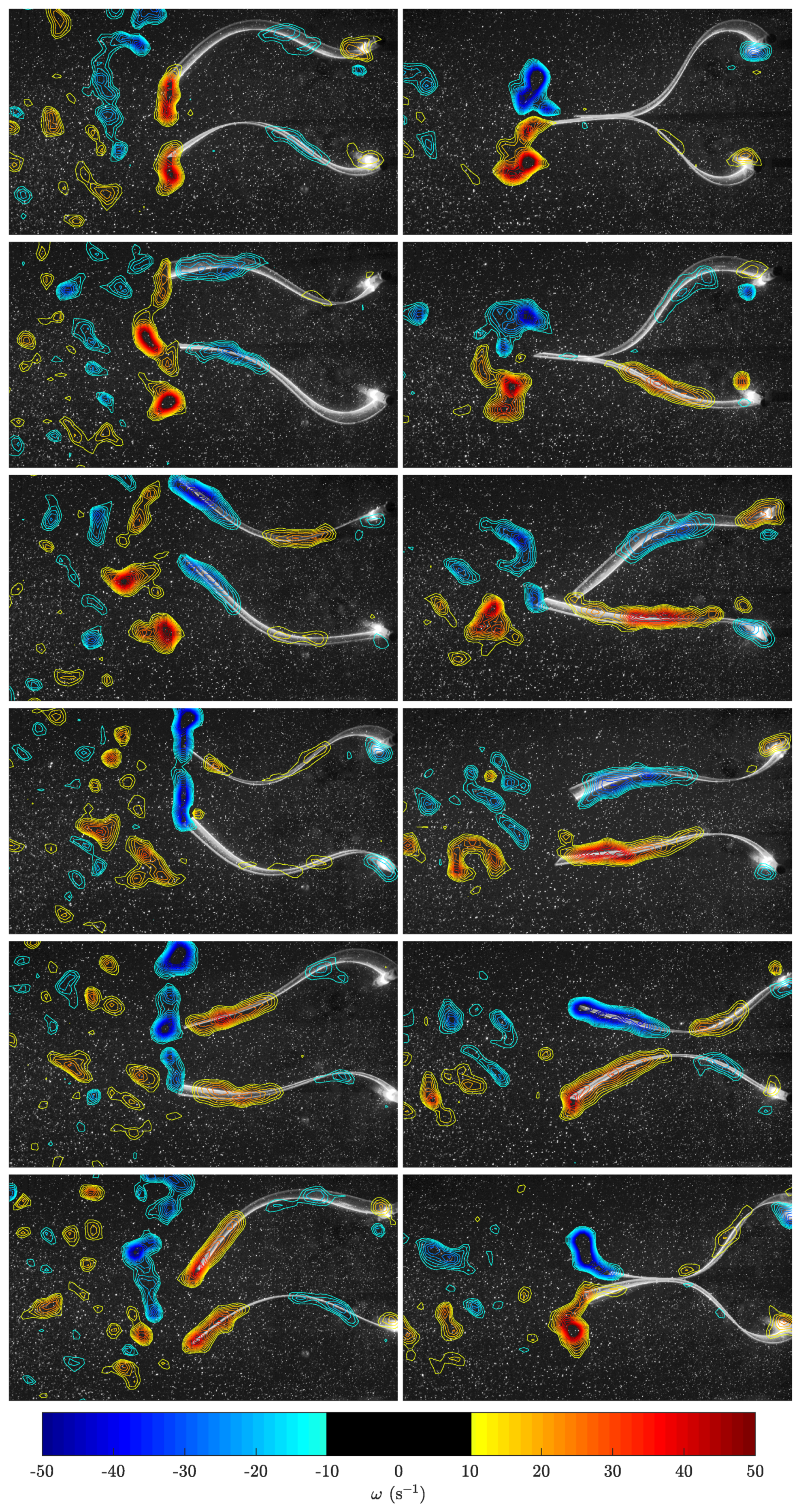
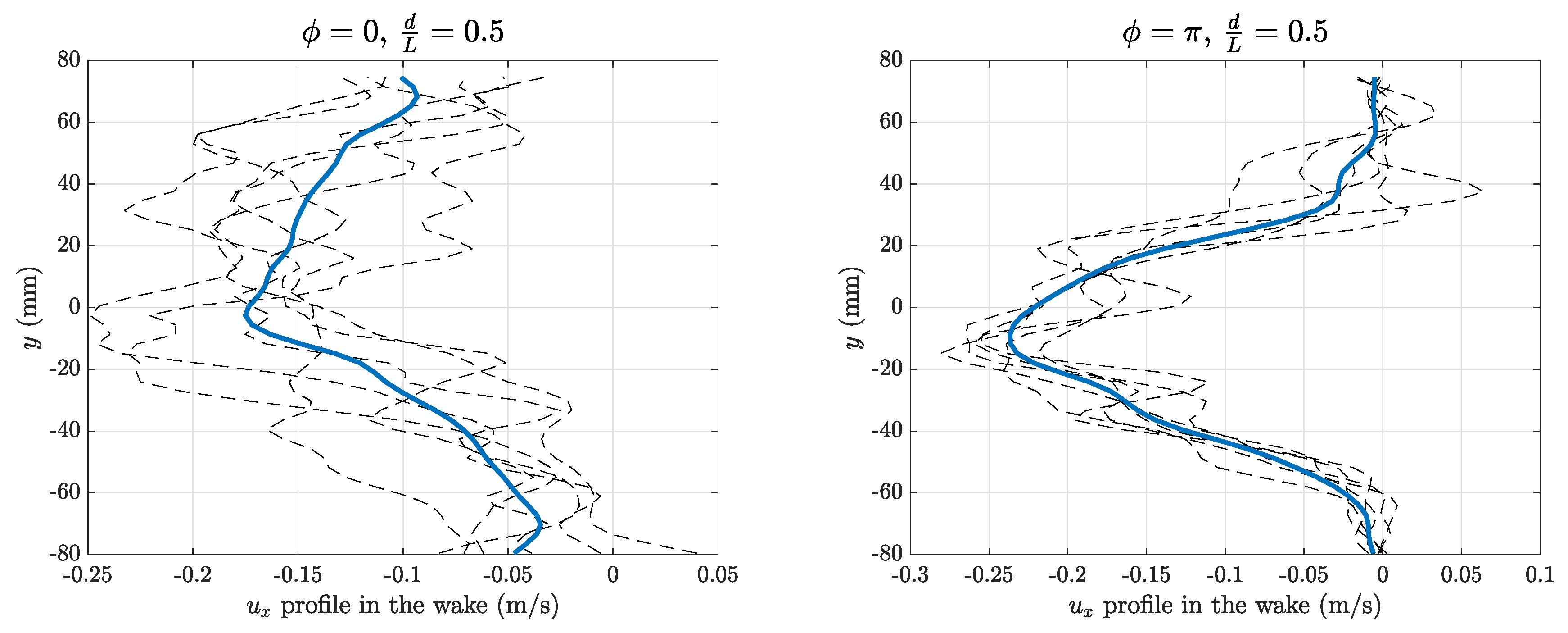
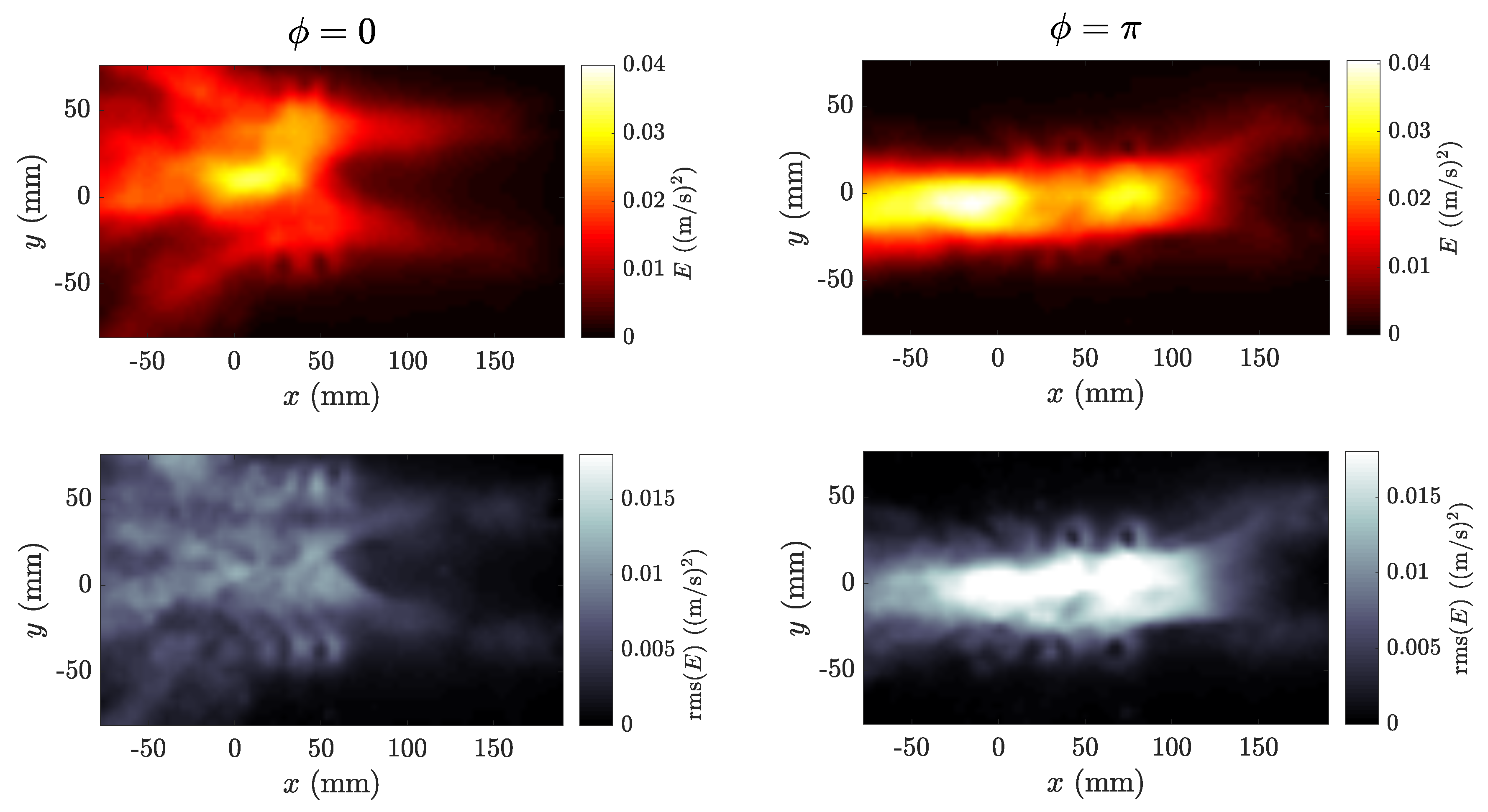
3.2. Flow Field Measurements
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PIV | particle image velocimetry |
| NND | nearest-neighbor distance |
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
References
- Vicsek, T.; Zafeiris, A. Collective motion. Phys. Rep. 2012, 517, 71–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kube, C.R.; Zhang, H. Collective robotics: From social insects to robots. Adapt. Behav. 1993, 2, 189–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, R.; Cornforth, D.M.; McNally, L.; Brown, S.P. Collective sensing and collective responses in quorum-sensing bacteria. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20140882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdya, P.; Lichocki, P.; Cruchet, S.; Frisch, L.; Tse, W.; Floreano, D.; Benton, R. Mechanosensory interactions drive collective behavior in Drosophila. Nature 2015, 519, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halloy, J.; Sempo, G.; Caprari, G.; Rivault, C.; Asadpour, M.; Tâche, F.; Saïd, I.; Durier, V.; Canonge, S.; Amé, J.M.; et al. Social integration of robots into groups of cockroaches to control self-organized choices. Science 2007, 318, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.; Thakur, A. Fish-inspired robots: Design, sensing, actuation, and autonomy—A review of research. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2016, 11, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, U.; Gautrais, J.; Couzin, I.D.; Theraulaz, G. From behavioral analyses to models of collective motion in fish schools. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, A.; Nadal, F.; Sire, C.; Kanso, E.; Eloy, C. Model of collective fish behavior with hydrodynamic interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 198101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighthill, M.J. Note on the swimming of slender fish. J. Fluid Mech. 1960, 9, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, E.; Lauder, G.V. Swimming near the substrate: A simple robotic model of stingray locomotion. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, D.B.; Moored, K.W.; Dewey, P.A.; Smits, A.J. Unsteady propulsion near a solid boundary. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 742, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Prats, R.; Raspa, V.; Thiria, B.; Huera-Huarte, F.; Godoy-Diana, R. Large-amplitude undulatory swimming near a wall. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, M.; Cochran-Carney, J.; Zhong, Q.; Mivehchi, A.; Quinn, D.B.; Moored, K.W. Swimming freely near the ground leads to flow-mediated equilibrium altitudes. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 875, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihs, D. Hydromechanics of fish schooling. Nature 1973, 241, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemelrijk, C.K.; Reid, D.; Hildenbrandt, H.; Padding, J.T. The increased efficiency of fish swimming in a school. Fish Fish. 2015, 16, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghooghi, M.; Borazjani, I. The hydrodynamic advantages of synchronized swimming in a rectangular pattern. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 056018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Godoy-Diana, R.; Halloy, J.; Collignon, B.; Thiria, B. Synchronization and collective swimming patterns in fish (Hemigrammus bleheri). J. R. Soc. Interface 2016, 13, 20160734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Bradshaw, H.; Ha, T.T.; Halloy, J.; Godoy-Diana, R.; Thiria, B. Simple phalanx pattern leads to energy saving in cohesive fish schooling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9599–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collignon, B.; Séguret, A.; Chemtob, Y.; Cazenille, L.; Halloy, J. Collective departures and leadership in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alben, S.; Witt, C.; Baker, T.; Anderson, E.; Lauder, G. Dynamics of freely swimming flexible foils. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 051901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, P.A.; Boschitsch, B.M.; Moored, K.W.; Stone, H.A.; Smits, A.J. Scaling laws for the thrust production of flexible pitching panels. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 732, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeirua, M.; Thiria, B.; Godoy-Diana, R. Modelling of an actuated elastic swimmer. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 829, 731–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspa, V.; Ramananarivo, S.; Thiria, B.; Godoy-Diana, R. Vortex-induced drag and the role of aspect ratio in undulatory swimmers. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 041701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kolomenskiy, D.; Liu, H.; Thiria, B.; Godoy-Diana, R. On the energetics and stability of a minimal fish school. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kolomenskiy, D.; Liu, H.; Thiria, B.; Godoy-Diana, R. On the interference of vorticity and pressure fields of a minimal fish school. J. Aero Aqua-Bio-Mech. 2019, 8, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspa, V.; Godoy-Diana, R.; Thiria, B. Topology-induced effect in biomimetic propulsive wakes. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 729, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihs, D. Some hydrodynamical aspects of fish schooling. In Swimming and Flying in Nature; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1975; pp. 703–718. [Google Scholar]
- Kanso, E.; Newton, P.K. Locomotory Advantages to Flapping Out of Phase. Exp. Mech. 2009, 50, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huera-Huarte, F.J. Propulsive performance of a pair of pitching foils in staggered configurations. J. Fluids Struct. 2018, 81, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramananarivo, S.; Fang, F.; Oza, A.; Zhang, J.; Ristroph, L. Flow interactions lead to orderly formations of flapping wings in forward flight. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2016, 1, 071201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godoy-Diana, R.; Vacher, J.; Raspa, V.; Thiria, B. On the Fluid Dynamical Effects of Synchronization in Side-by-Side Swimmers. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040077
Godoy-Diana R, Vacher J, Raspa V, Thiria B. On the Fluid Dynamical Effects of Synchronization in Side-by-Side Swimmers. Biomimetics. 2019; 4(4):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040077
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodoy-Diana, Ramiro, Jérôme Vacher, Veronica Raspa, and Benjamin Thiria. 2019. "On the Fluid Dynamical Effects of Synchronization in Side-by-Side Swimmers" Biomimetics 4, no. 4: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040077
APA StyleGodoy-Diana, R., Vacher, J., Raspa, V., & Thiria, B. (2019). On the Fluid Dynamical Effects of Synchronization in Side-by-Side Swimmers. Biomimetics, 4(4), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics4040077




