Bio-Inspired Central Pattern Generator for Adaptive Gait Generation and Stability in Humanoid Robots on Sloped Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
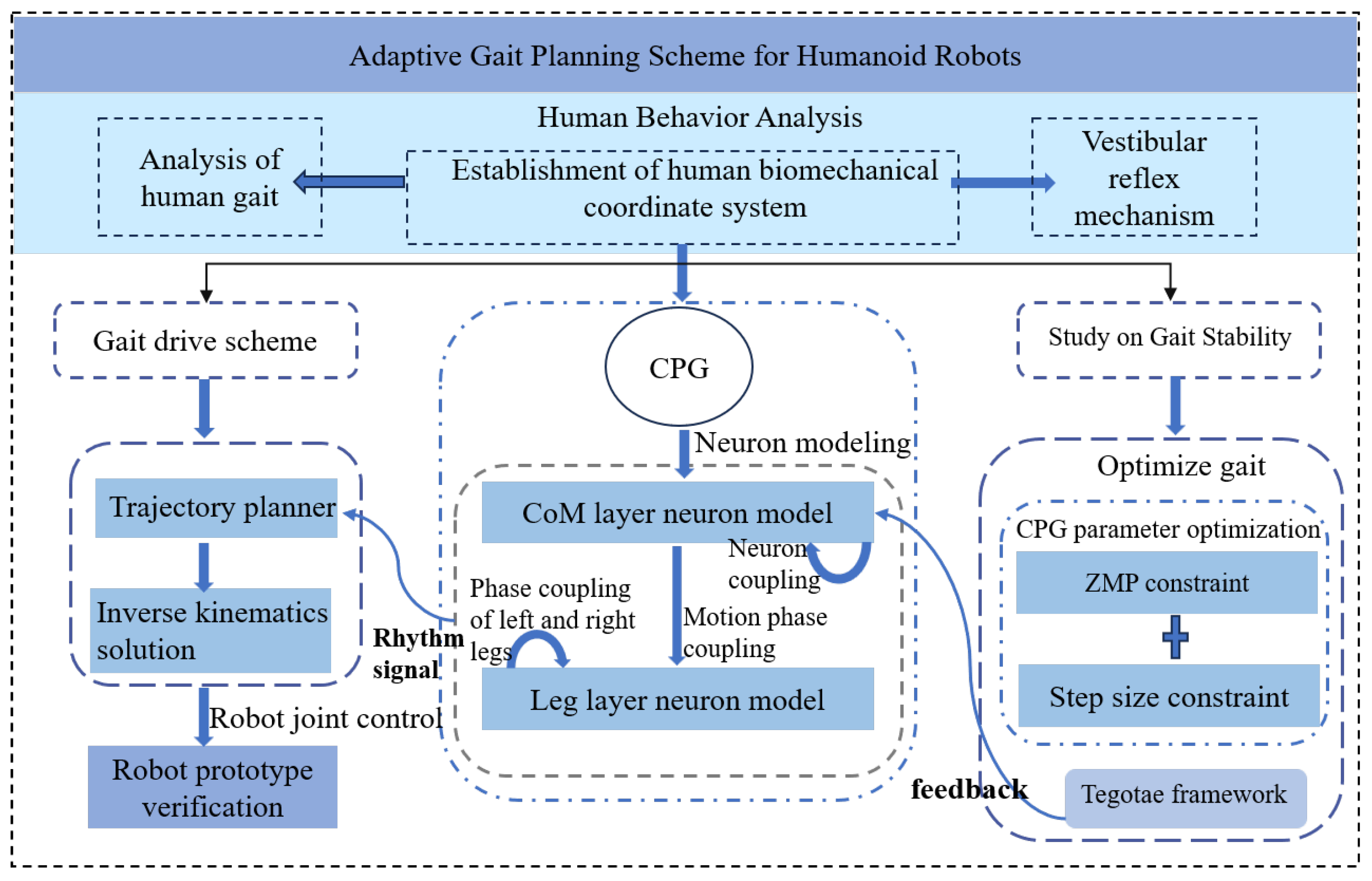
2. Motion Trajectory Generation Based on CPG
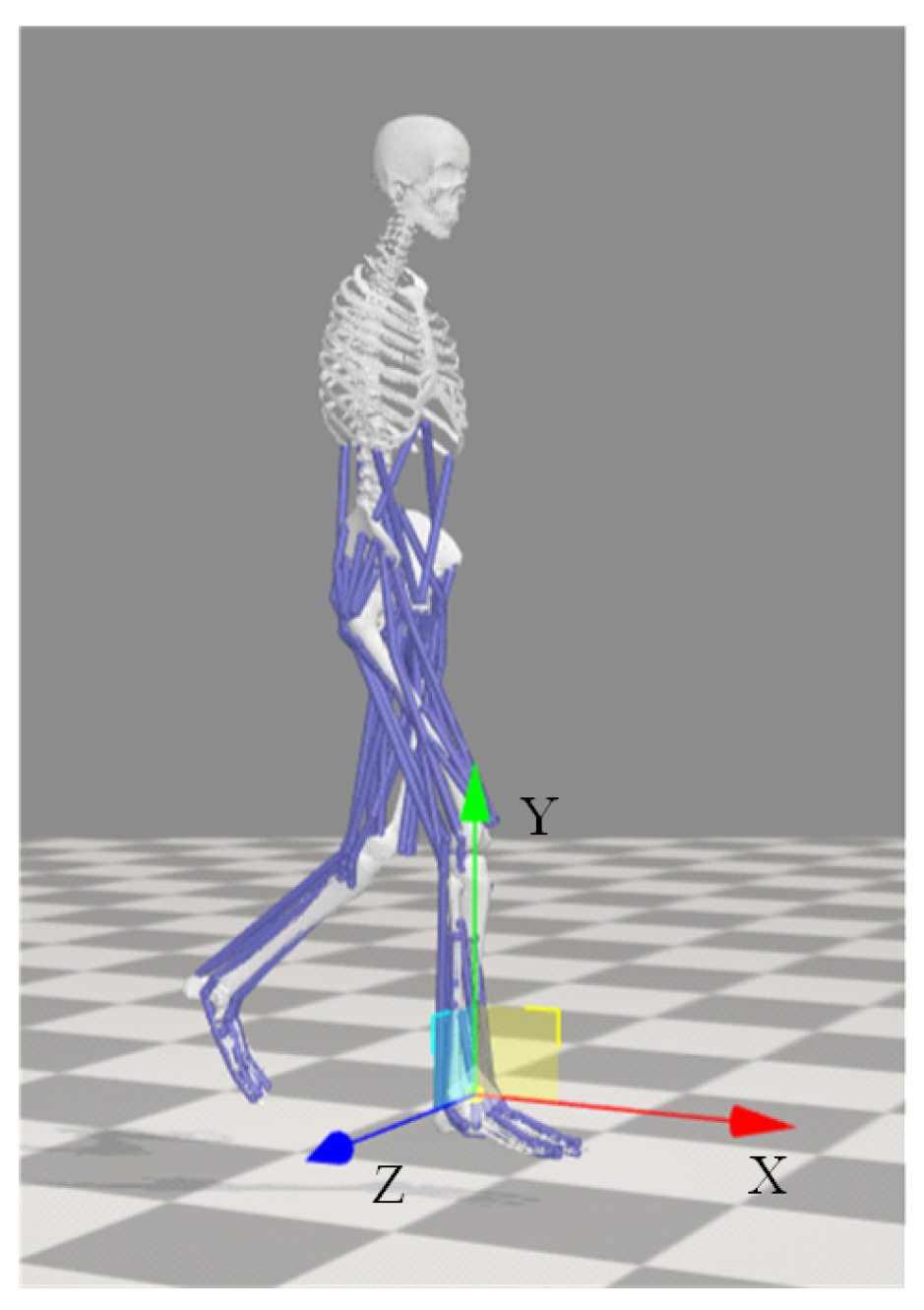
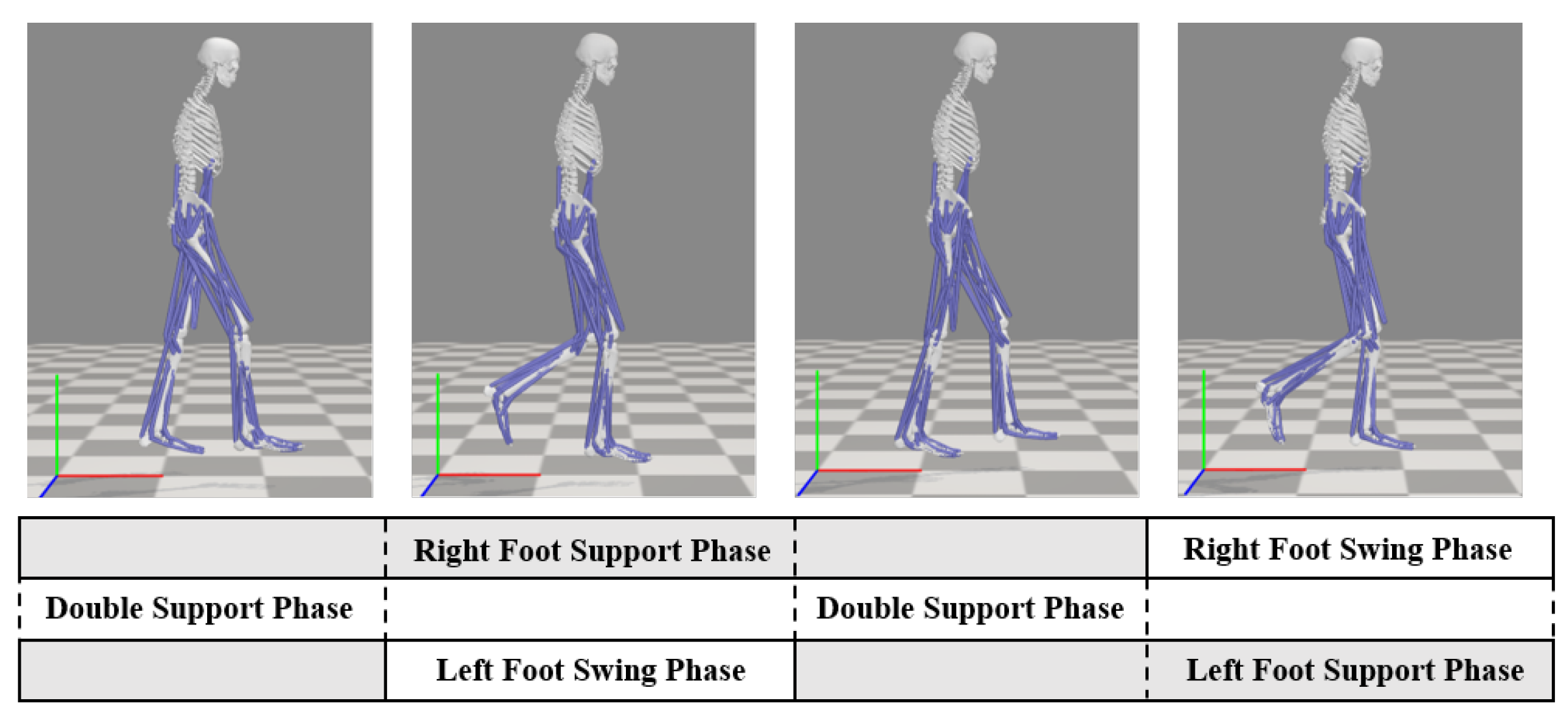
2.1. Description of Human Motion Model
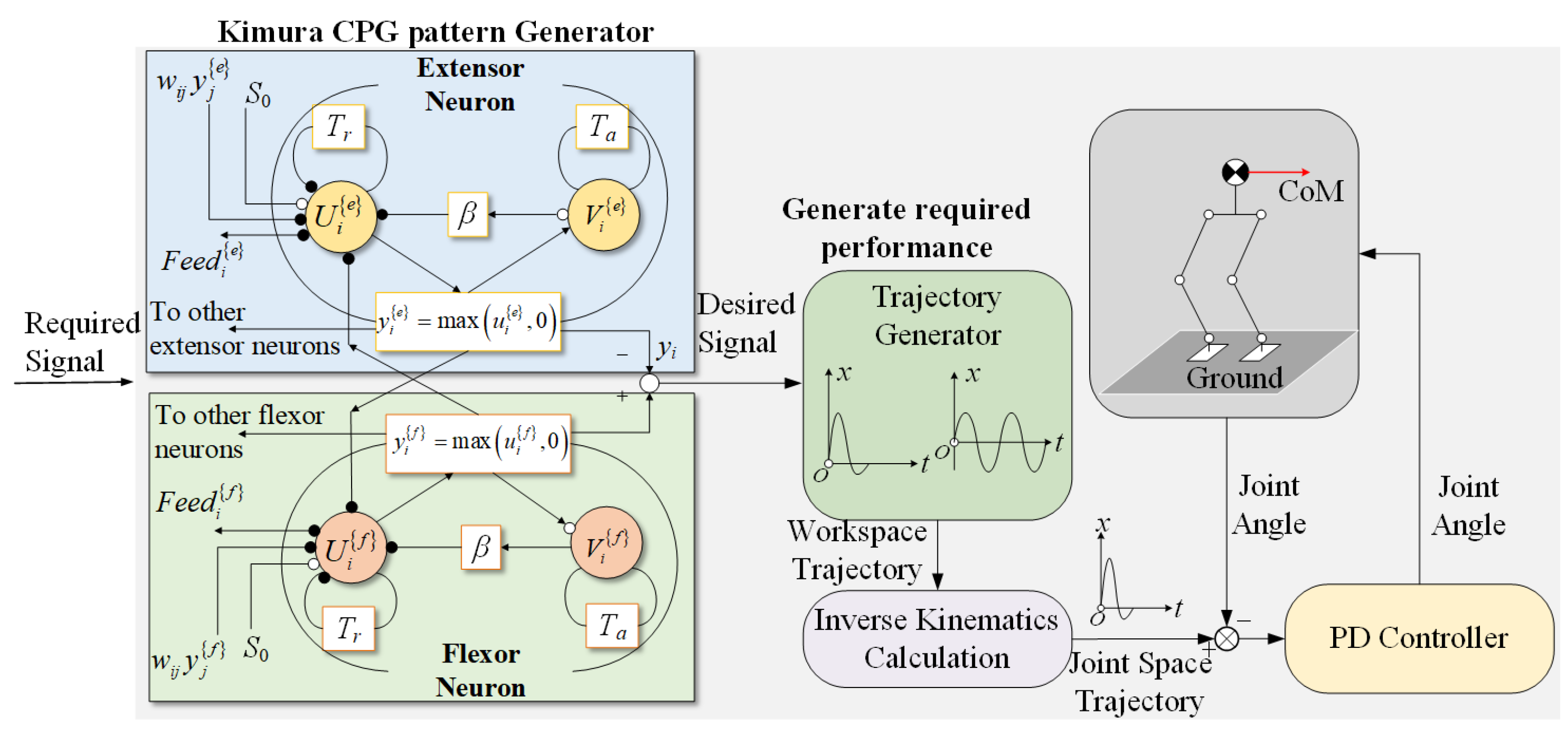
2.2. Concept and Design of the CPG Model
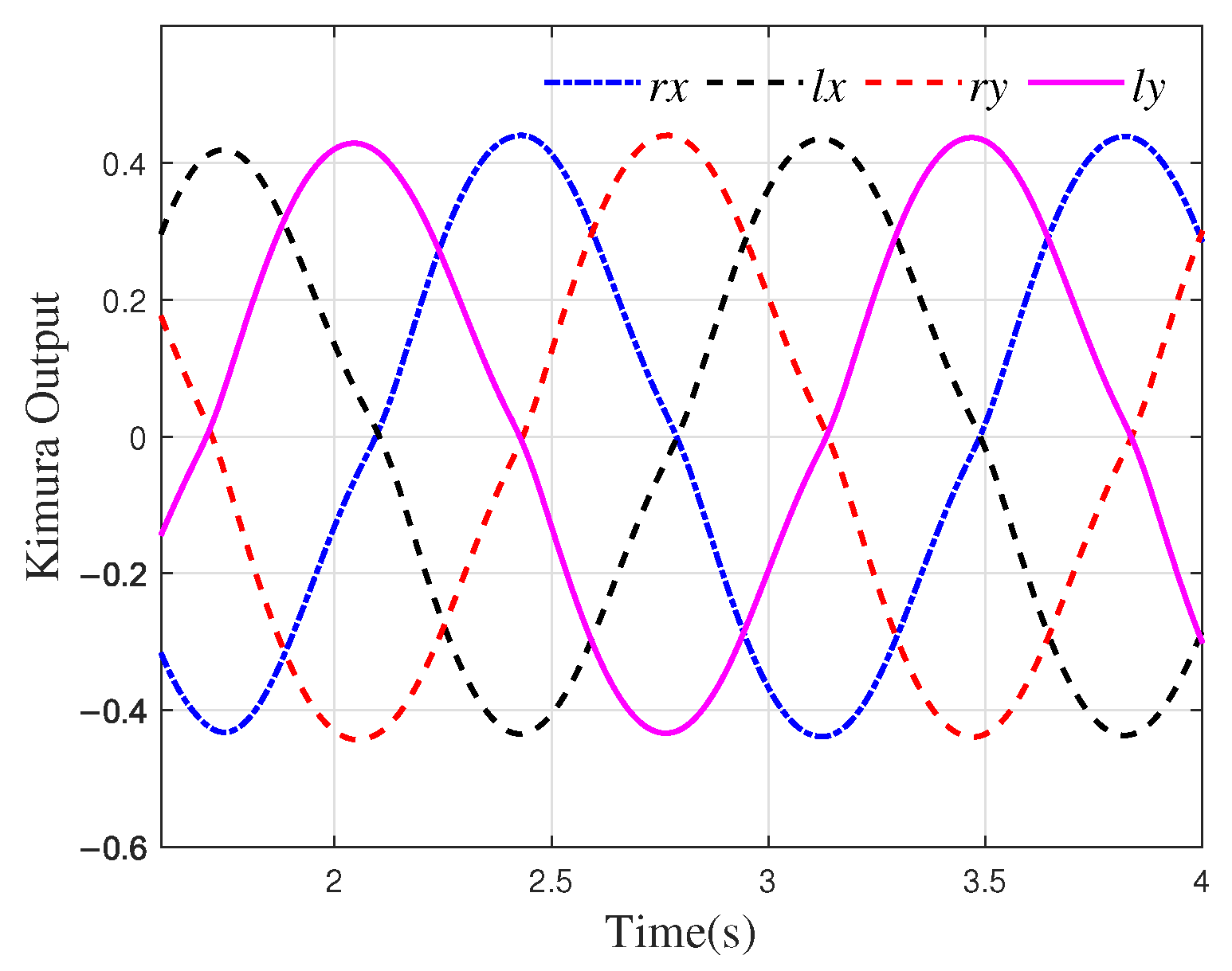
2.3. CPG-Based Trajectory Generators
3. Research on Stable Walking and Environmental Adaptability
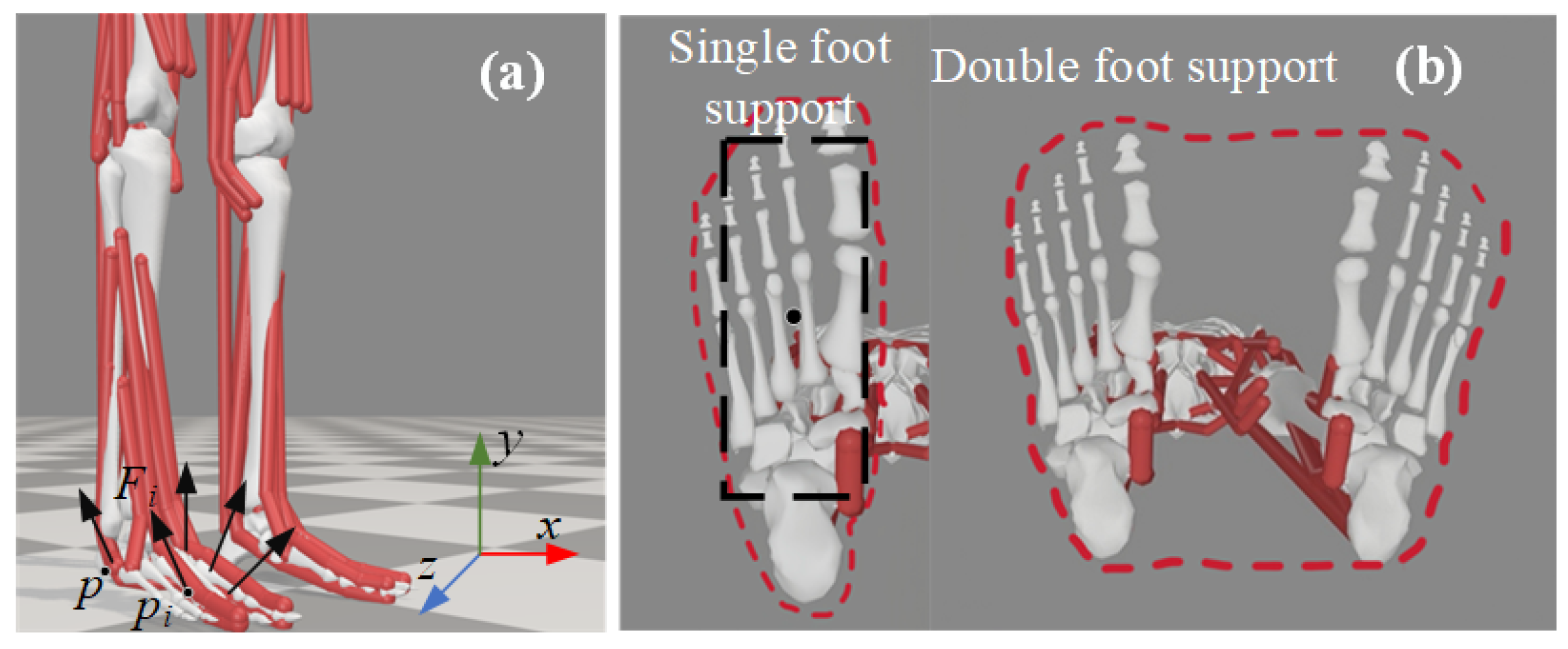
3.1. Exploring Walking Stability with ZMP Criterion
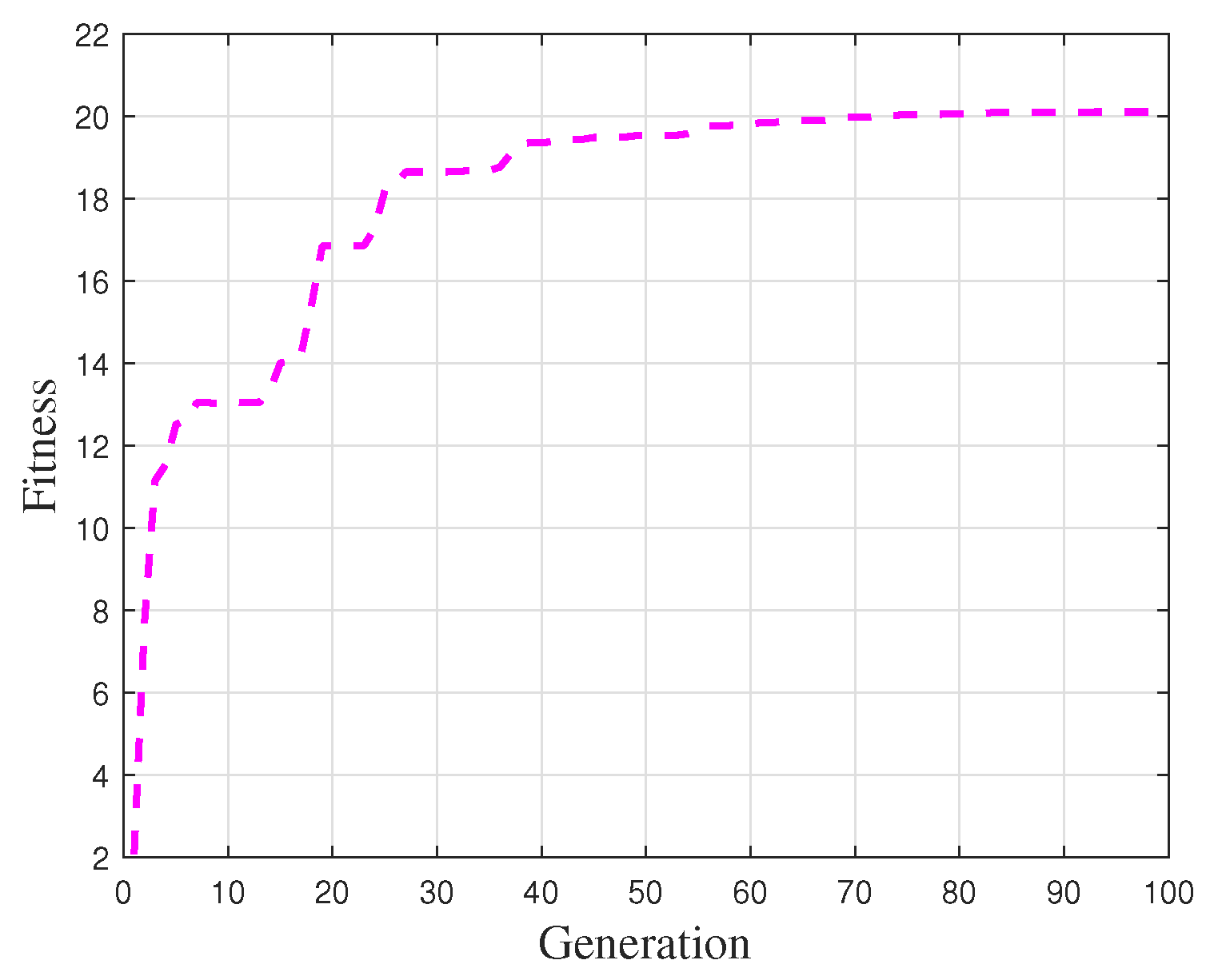
3.2. Parameter Optimization Through Genetic Algorithm Approach
3.3. Research on Vestibular Reflex in Sloping Terrain
4. Simulation and Experiment of Humanoid Robot Walking
4.1. CPG Parameter Optimization and Trajectory Generation
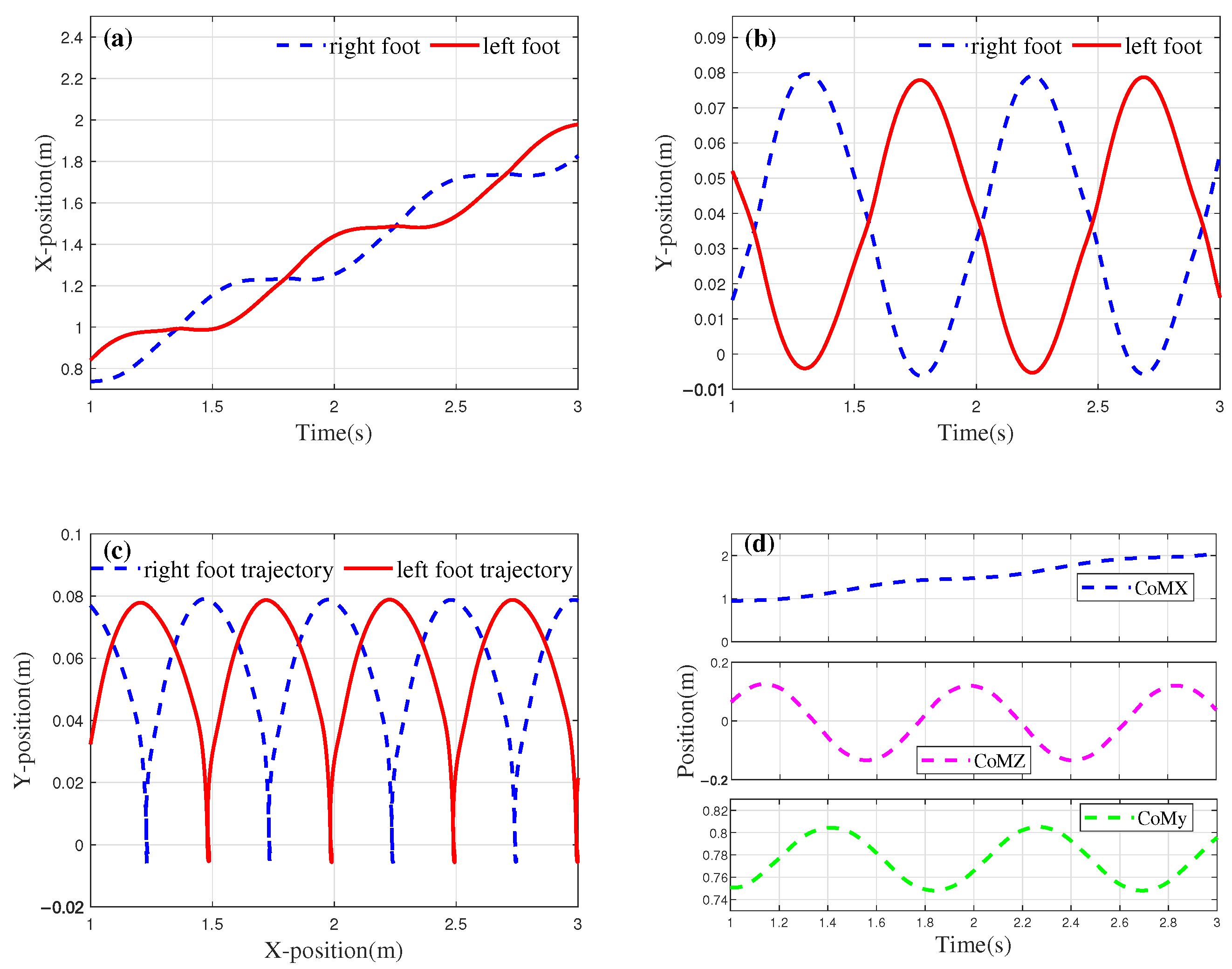
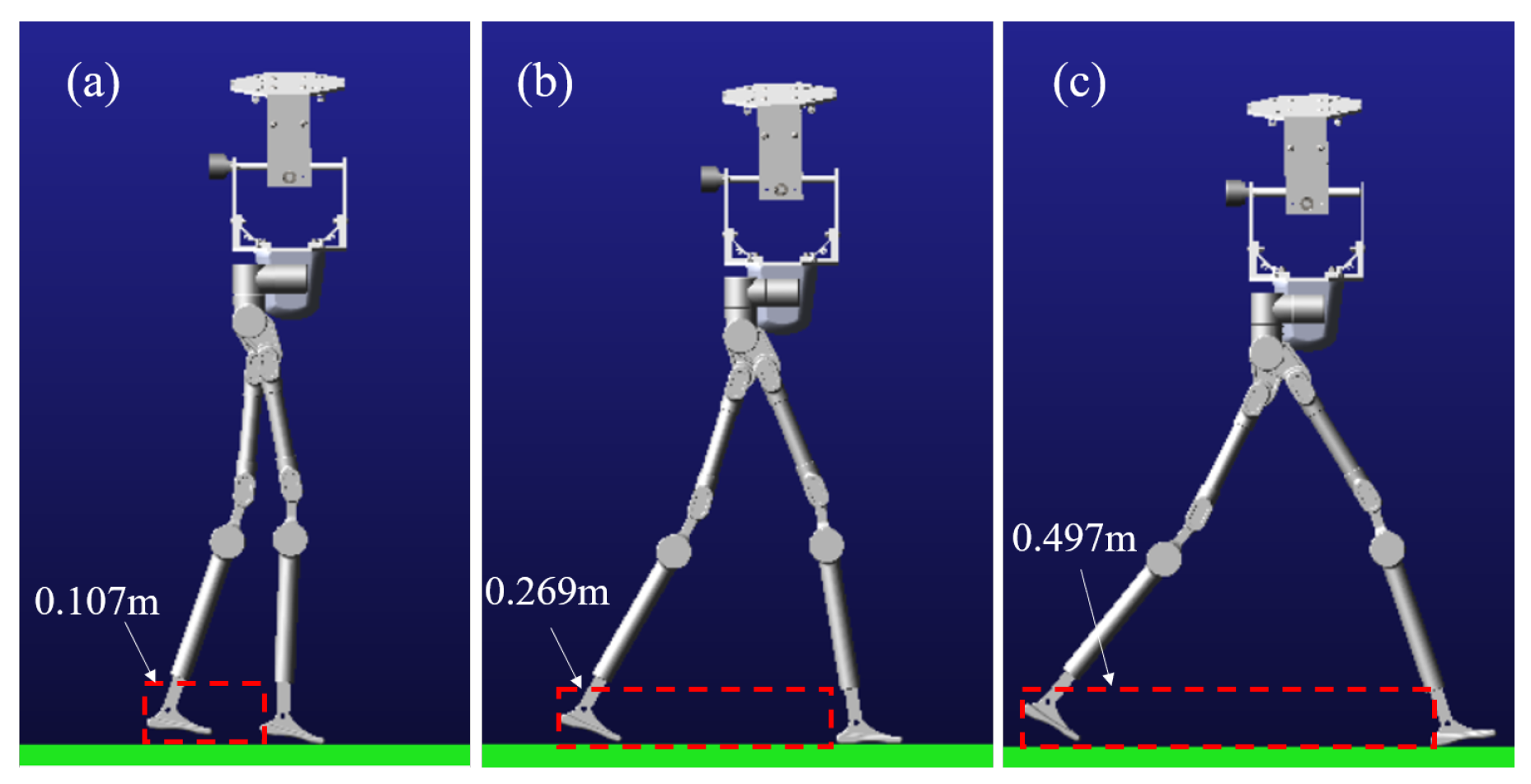
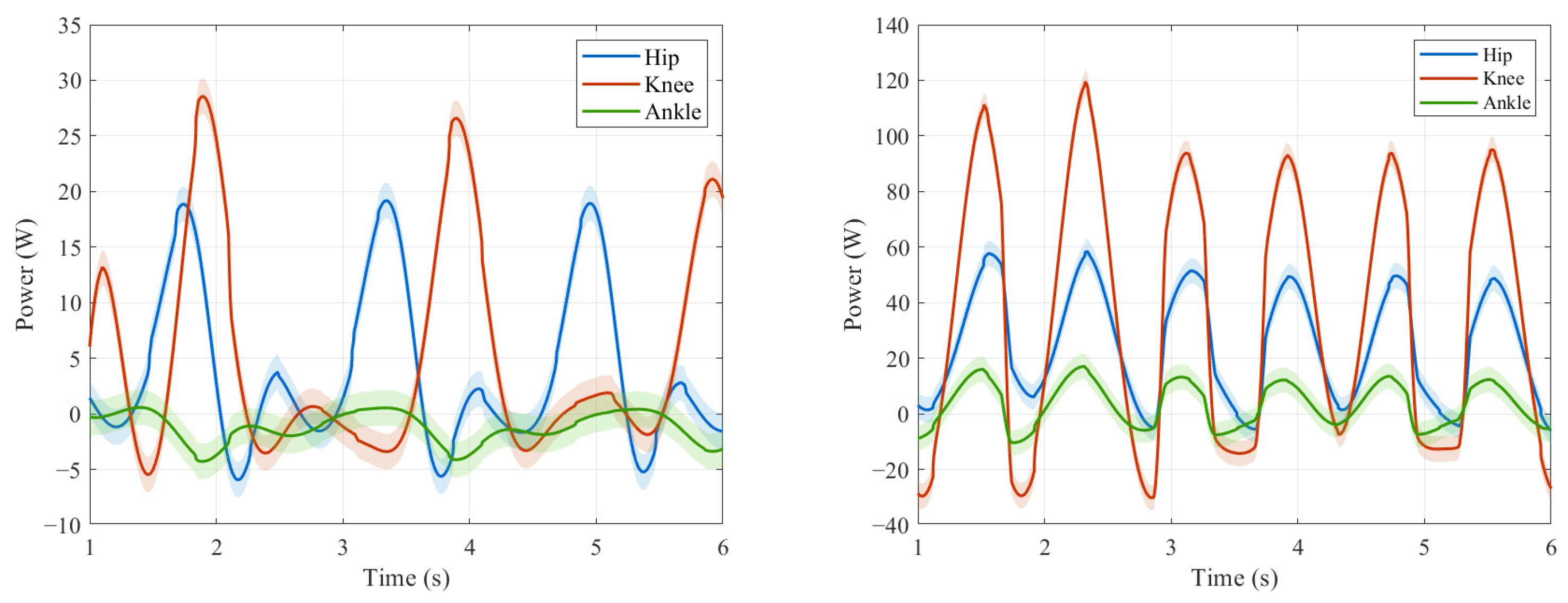
4.2. Simulation Verification of Walking on Flat Ground and Step Size Optimization
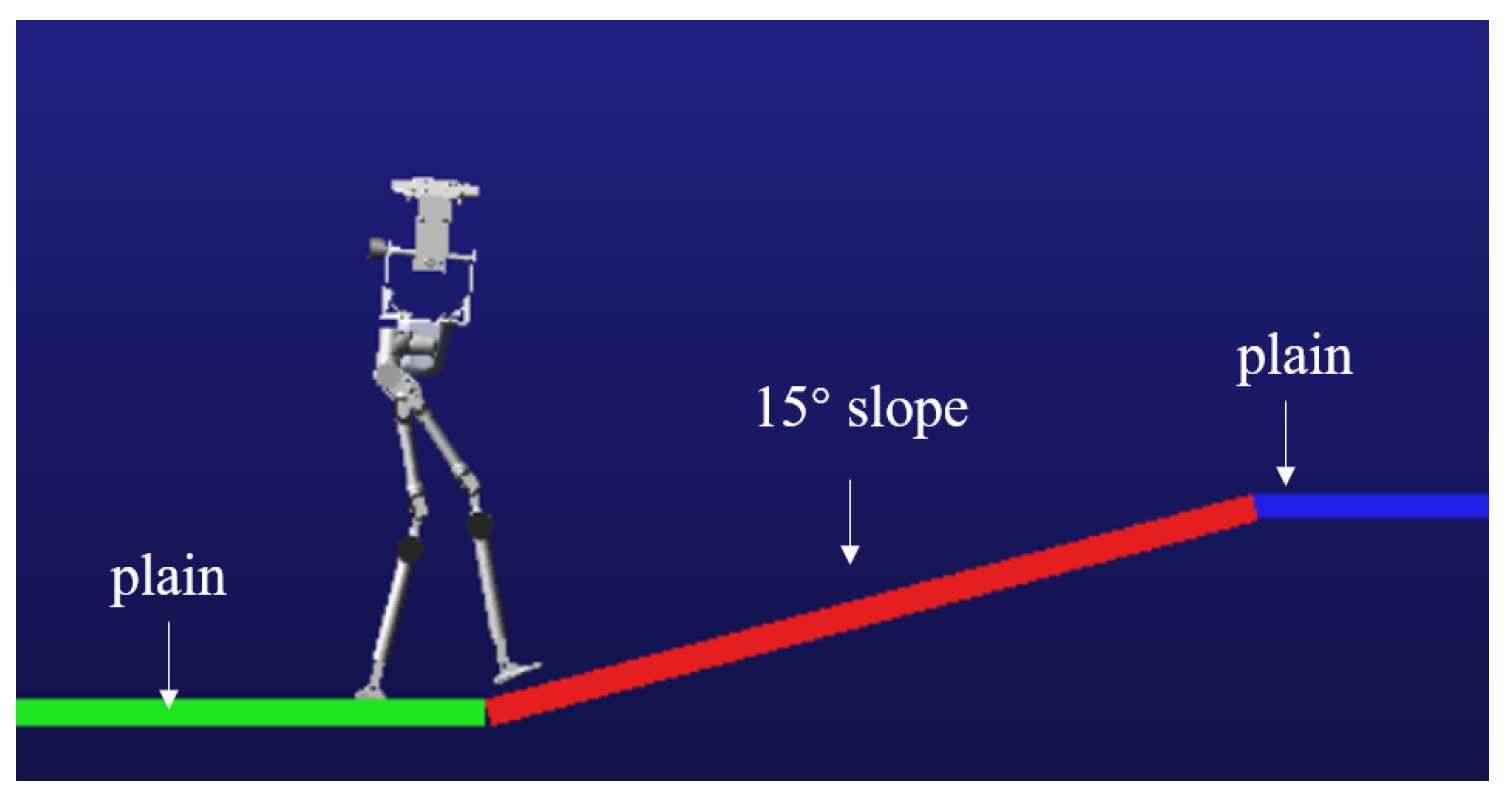
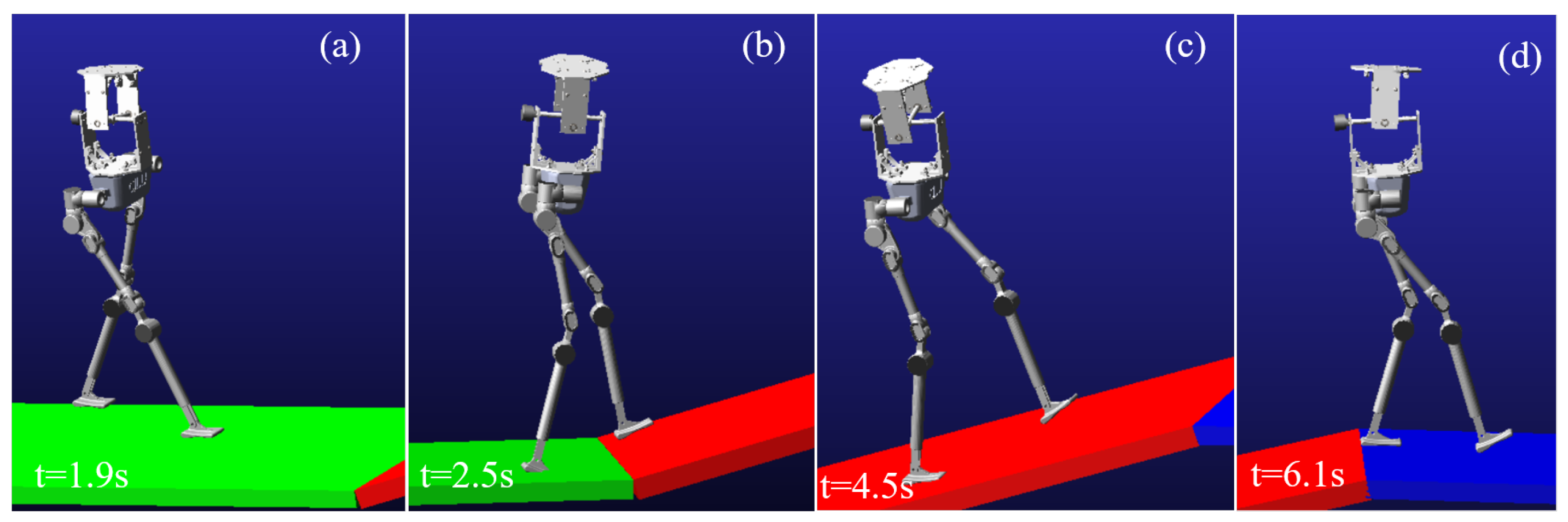
4.3. Changing Slope-Terrain Adaptive Walking
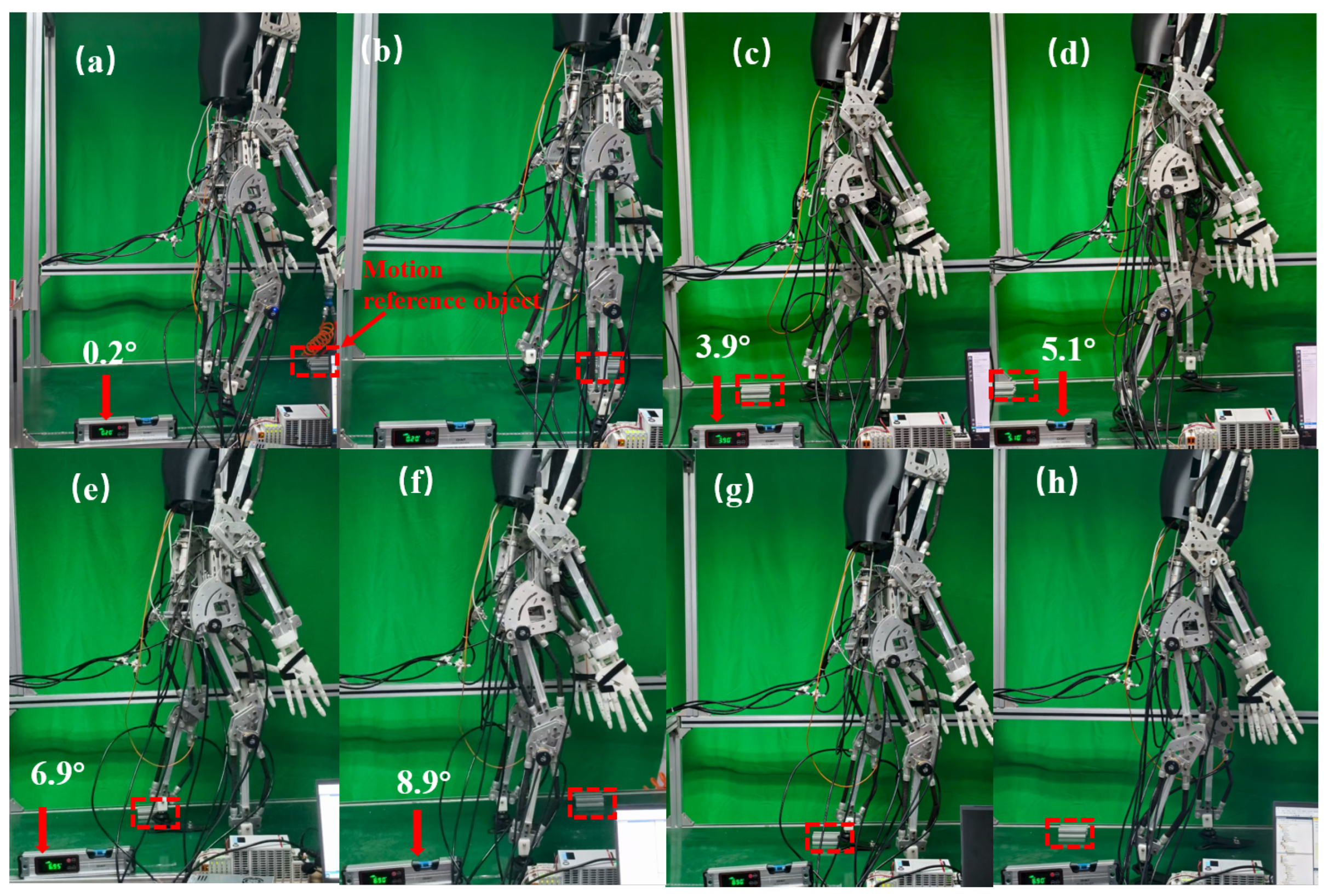
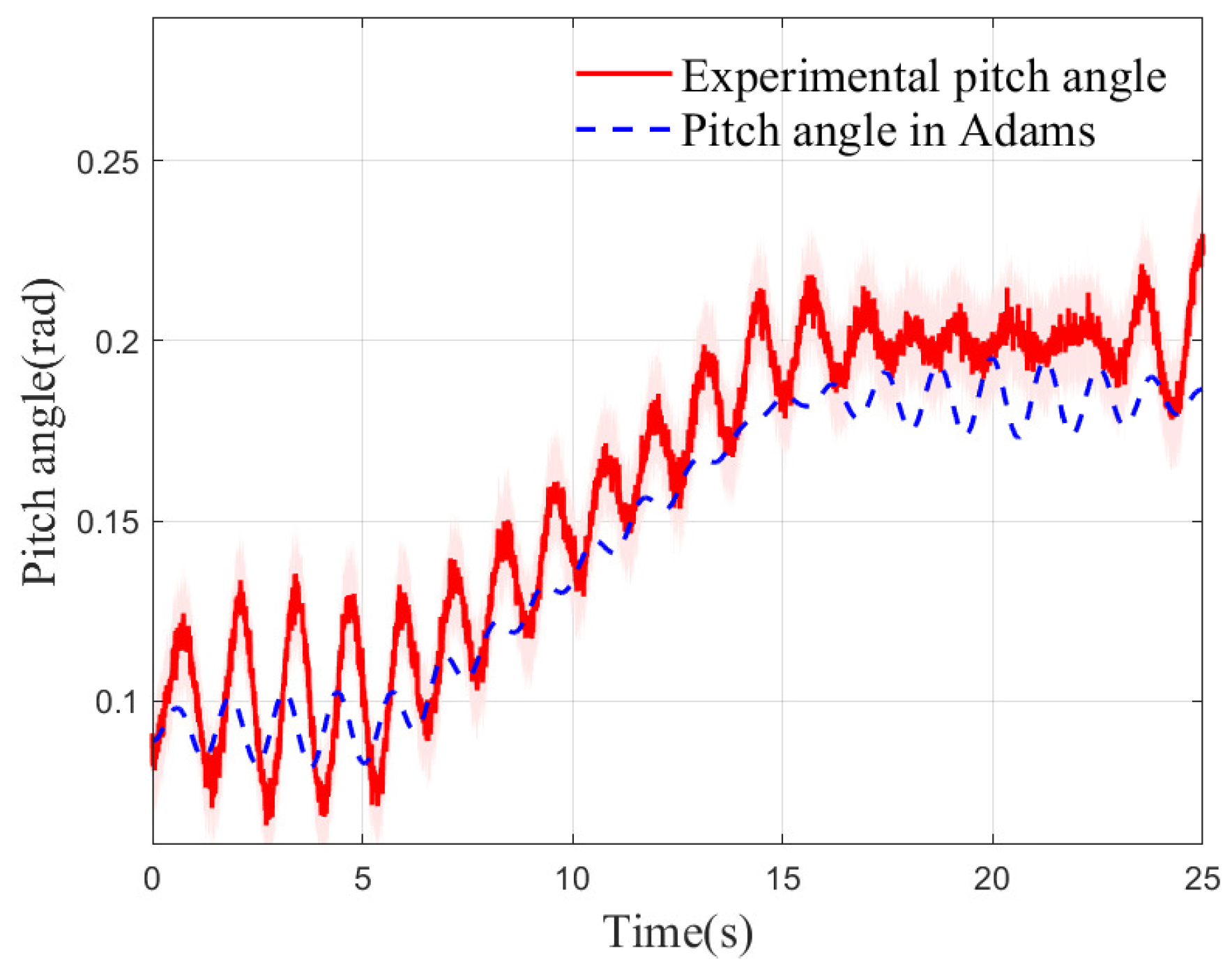
4.4. Slope Walking Experiment of Humanoid Robot
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| symbols | Physical meaning | abbreviations | Full name |
| Foot trajectory, x-component | CPG | Central Pattern Generator | |
| Foot trajectory, y-component | ISB | International Society of Biomechanics | |
| CoM trajectory, x-component | ZMP | Zero Moment Point | |
| CoM trajectory, y-component | CoM | Center of Mass | |
| CoM trajectory, z-component | GA | Genetic Algorithm | |
| Stability margin | CoT | Cost of Transport | |
| Fitness function | / | / | |
| Torso pitch angle | / | / | |
| Slope angle | / | / |
References
- Slade, P.; Atkeson, C.; Donelan, J.M.; Houdijk, H.; Ingraham, K.A.; Kim, M.; Kong, K.; Poggensee, K.L.; Riener, P.; Steinert, M.; et al. On human-in-the-loop optimization of human–robot interaction. Nature 2024, 633, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Reconfigurable exomuscle system employing parameter tuning to assist hip flexion or ankle plantarflexion. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ijspeert, A.; Hayashibe, M. Ai-cpg: Adaptive imitated central pattern generators for bipedal locomotion learned through reinforced reflex neural networks. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 5190–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Ding, H. DCM-based dynamic stable walking under terrain-induced time-varying disturbances for humanoid robots. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2025, 68, 1420301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M. Squat motion of a humanoid robot using three-particle model predictive control and whole-body control. Sensors 2025, 25, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guo, W.; He, Z.; Li, R.; Zha, F.; Sun, L. Bionic jumping of humanoid robot via online centroid trajectory optimization and high dynamic motion controller. J. Bionics Eng. 2024, 21, 2759–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Huang, S.; Ge, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, M. Balanced standing on one foot of biped robot based on three-particle model predictive control. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Qi, H.; Yi, C. Single sequential trajectory optimization with centroidal dynamics and whole-body kinematics for vertical jump of humanoid robot. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, S.I.; Wood, R.J.; Majidi, C. Untethered soft robotics. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diggelen, F.; Cambier, N.; Ferrante, E.; Eiben, A.E. A model-free method to learn multiple skills in parallel on modular robots. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijspeert, A.J.; Crespi, A.; Ryczko, D.; Cabelguen, J.M. From swimming to walking with a salamander robot driven by a spinal cord model. Science 2007, 315, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shi, Y.; Guo, Q. Gait planning and multimodal human-exoskeleton cooperative control based on central pattern generator. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 315, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Pei, Z.; Chen, J. Gait-generation strategy for lower limb exoskeleton based on central pattern generator. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 4191–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkawutvanich, C.; Manoonpong, P. Personalized symmetrical and asymmetrical gait generation of a lower limb exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 9798–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Fang, Q.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q. Central pattern generator with defined pulse signals for compliant-resistant control of biped robots. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Onal, C.D.; Fu, J. Reinforcement learning of CPG-regulated locomotion controller for a soft snake robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 3382–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namura, N.; Nakao, H. A central pattern generator network for simple control of gait transitions in hexapod robots based on phase reduction. Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 113, 10105–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, F.; Badri-Spröwitz, A. Learning plastic matching of robot dynamics in closed-loop central pattern generators. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dong, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. Control and optimization of a bionic robotic fish through a combination of CPG model and PSO. Neurocomputing 2019, 337, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, M.; Zhong, P.; Yang, S.; Liang, Z.; Song, Q. Optimization of Biped Robot Walking Based on the Improved Particle Swarm Algorithm. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2024, 6689071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tang, B.; Tang, J.; Qiao, S.; Pang, X.; Guo, L. Stable Walking of a Biped Robot Controlled by Central Pattern Generator Using Multivariate Linear Mapping. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Y. CPG-Based Hierarchical Locomotion Control for Modular Quadrupedal Robots Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7193–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Manoonpong, P. Generic Mechanism for Waveform Regulation and Synchronization of Oscillators: An Application for Robot Behavior Diversity Generation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 4495–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Kamimura, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nishii, S.; Sato, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sano, A. Bipedal Robot Running: Human-Like Actuation Timing Using Fast and Slow Adaptations. Adv. Robot. 2024, 38, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Matsumoto, O.; Kawasetsu, T.; Hosoda, K. Enhancing Postural Stability in Musculoskeletal Quadrupedal Locomotion through Tension Feedback for CPG-Based Controller. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2024, 20, 016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasandi, V.; Sadeghian, H.; Keshmiri, M.; Pucci, D. An Integrated Programmable CPG with Bounded Output. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 4658–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.H.; Hamker, F.; Nassour, J. A Humanoid Robot Learns to Recover Perturbation during Swinging Motion. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 50, 3701–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J. Gaits Generation of Quadruped Locomotion for the CPG Controller by the Delay-Coupled VDP Oscillators. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 18461–18479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owaki, D.; Goda, M.; Miyazawa, S.; Ishiguro, A. A Minimal Model Describing Hexapedal Interlimb Coordination: The Tegotae-Based Approach. Front. Neurorobot. 2017, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, B. Anti-Disturbance Control of CPG Bionic Reflection in Pneumatic Muscle Actuator. iScience 2024, 27, 108665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herneth, C.; Hayashibe, M.; Owaki, D. Learnable tegotae-based feedback in CPGs with sparse observation produces efficient and adaptive locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 1155–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Cavanagh, P.R. ISB recommendations for standardization in the reporting of kinematic data. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Goodman, E.D.; Chen, Q. Adaptive walking control of biped robots using online trajectory generation method based on neural oscillators. J. Bionics Eng. 2016, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, X.; Chen, B. Matsuoka’s CPG with desired rhythmic signals for adaptive walking of humanoid robots. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 50, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, R. A robust approach for the control of the center of mass with inverse kinetics. Comput. Graph. 1999, 20, 693–701. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, K. Computed torque control and force analysis for mechanical leg with variable rotation axis powered by servo pneumatic muscle. ISA Trans. 2023, 140, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


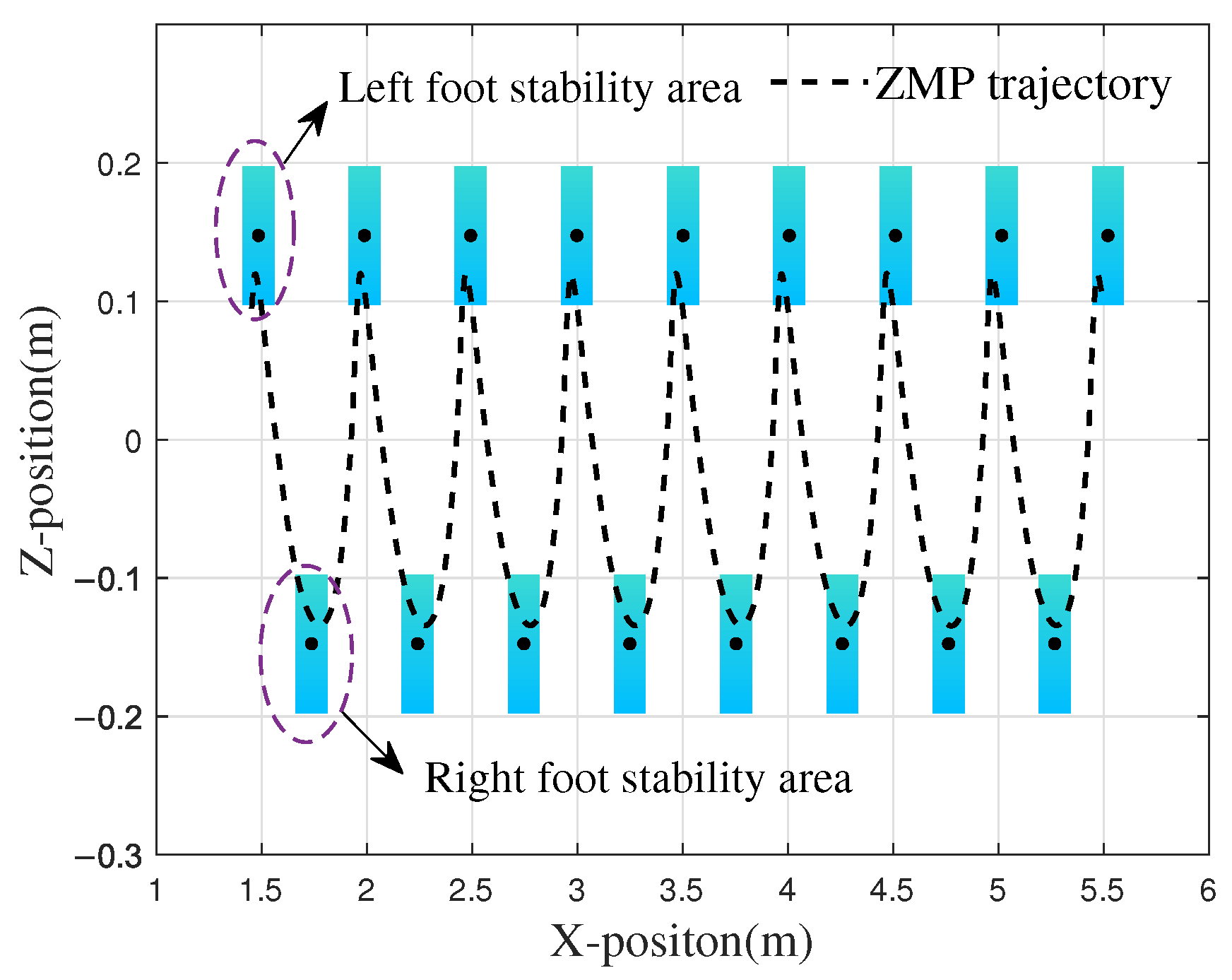
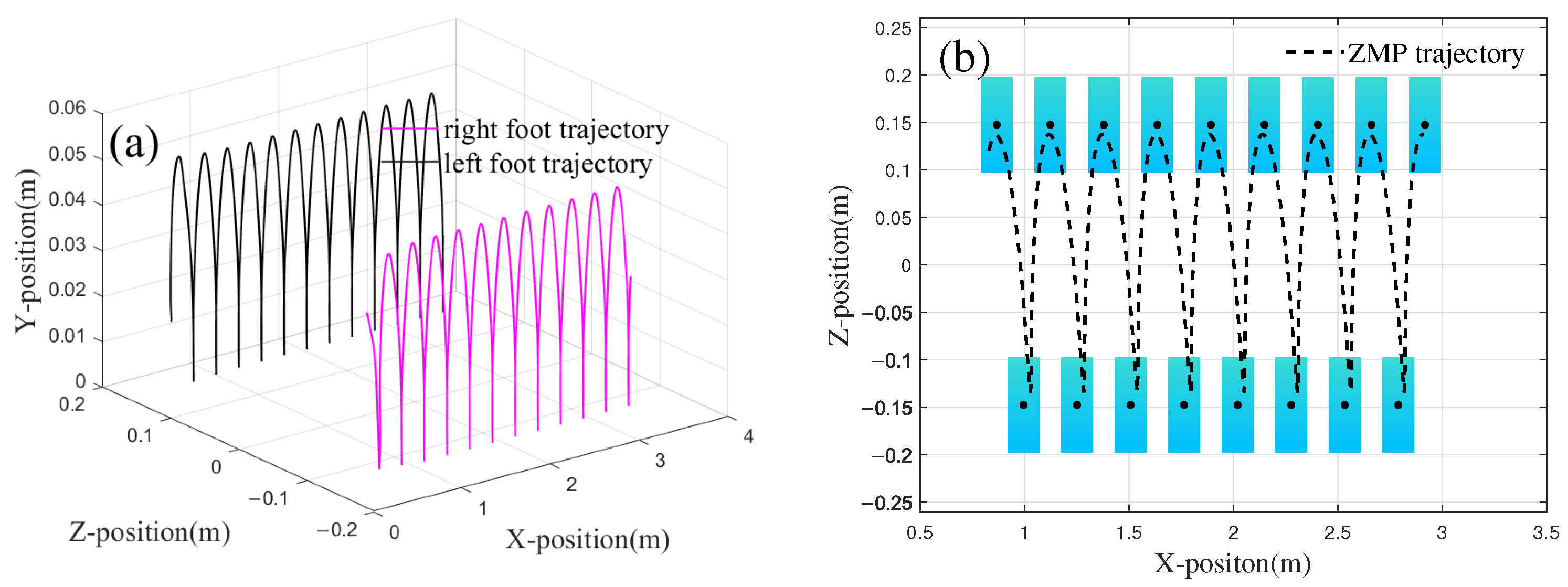
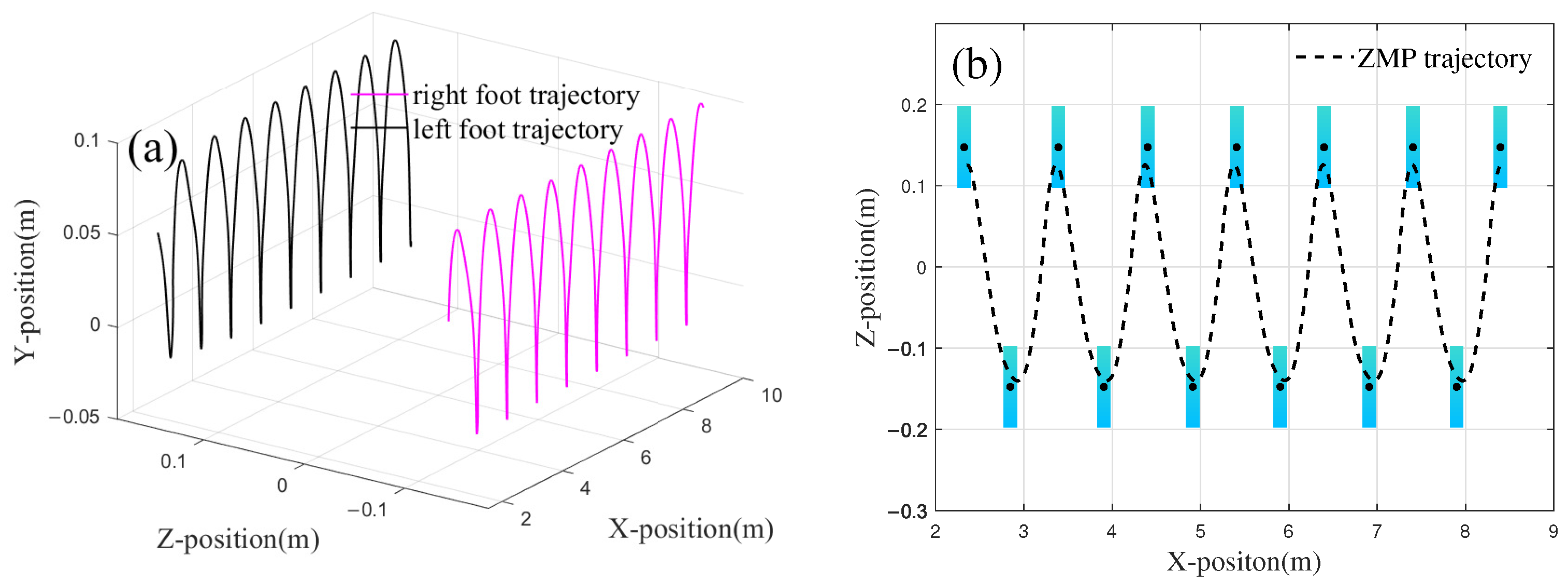
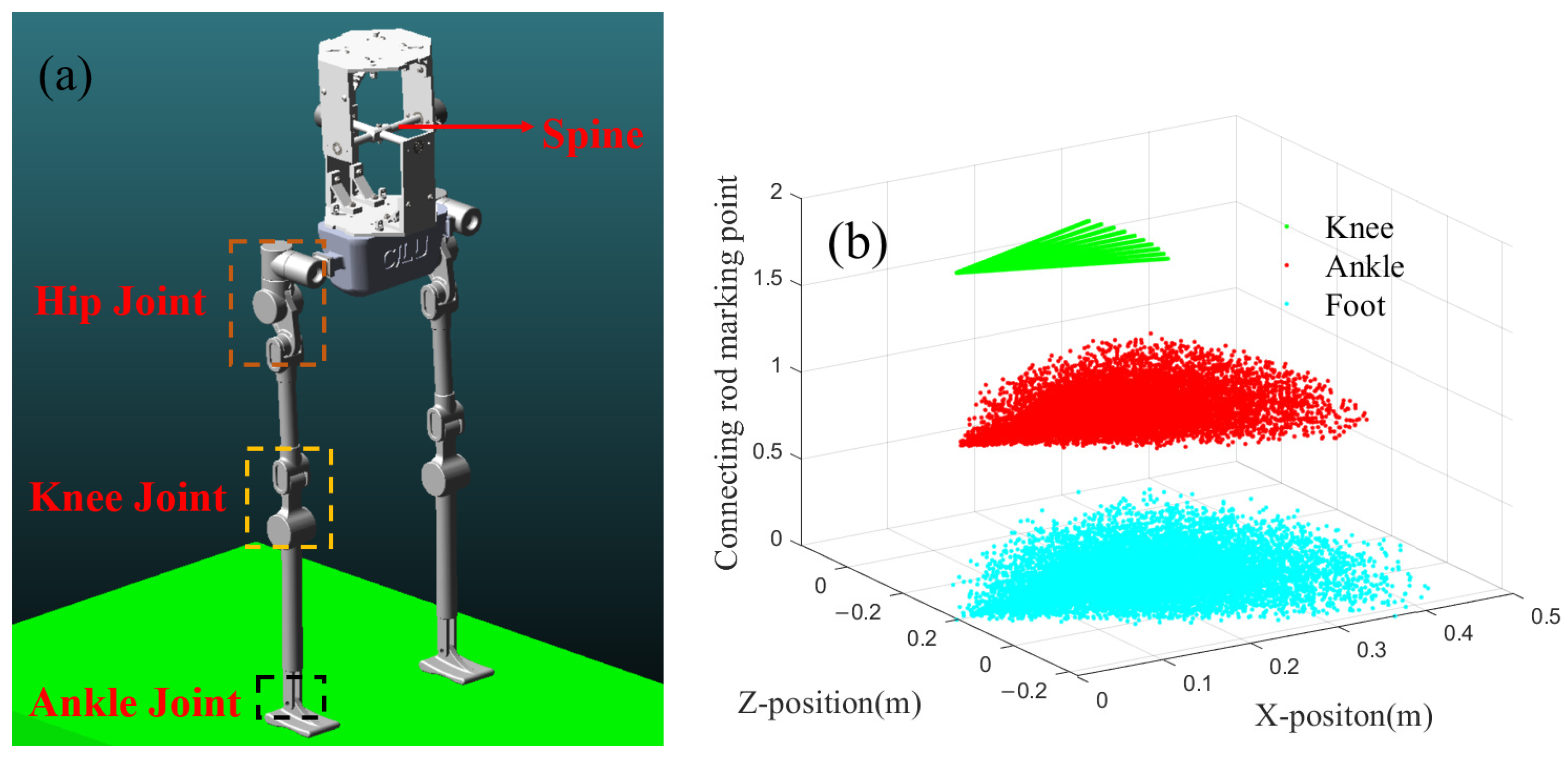
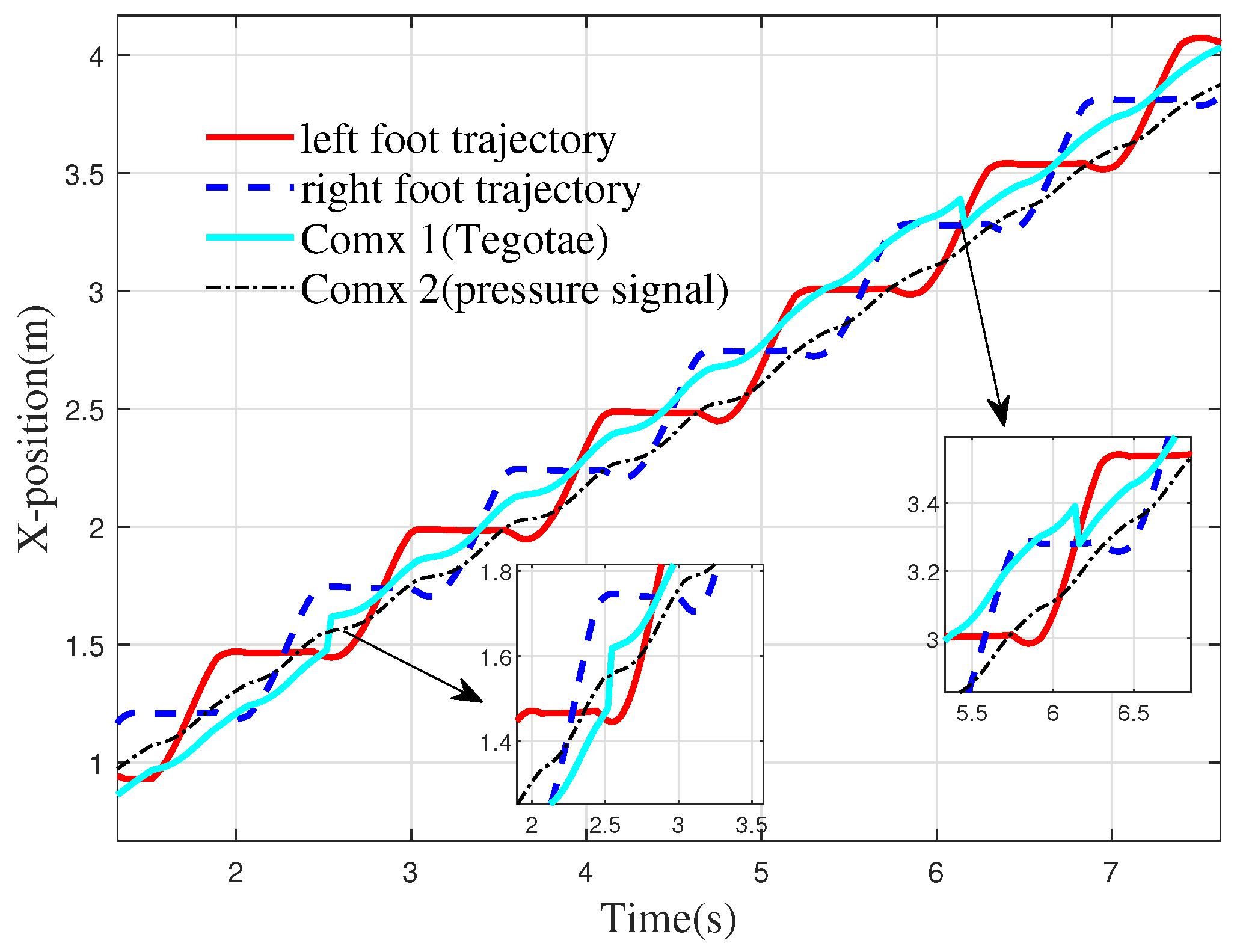
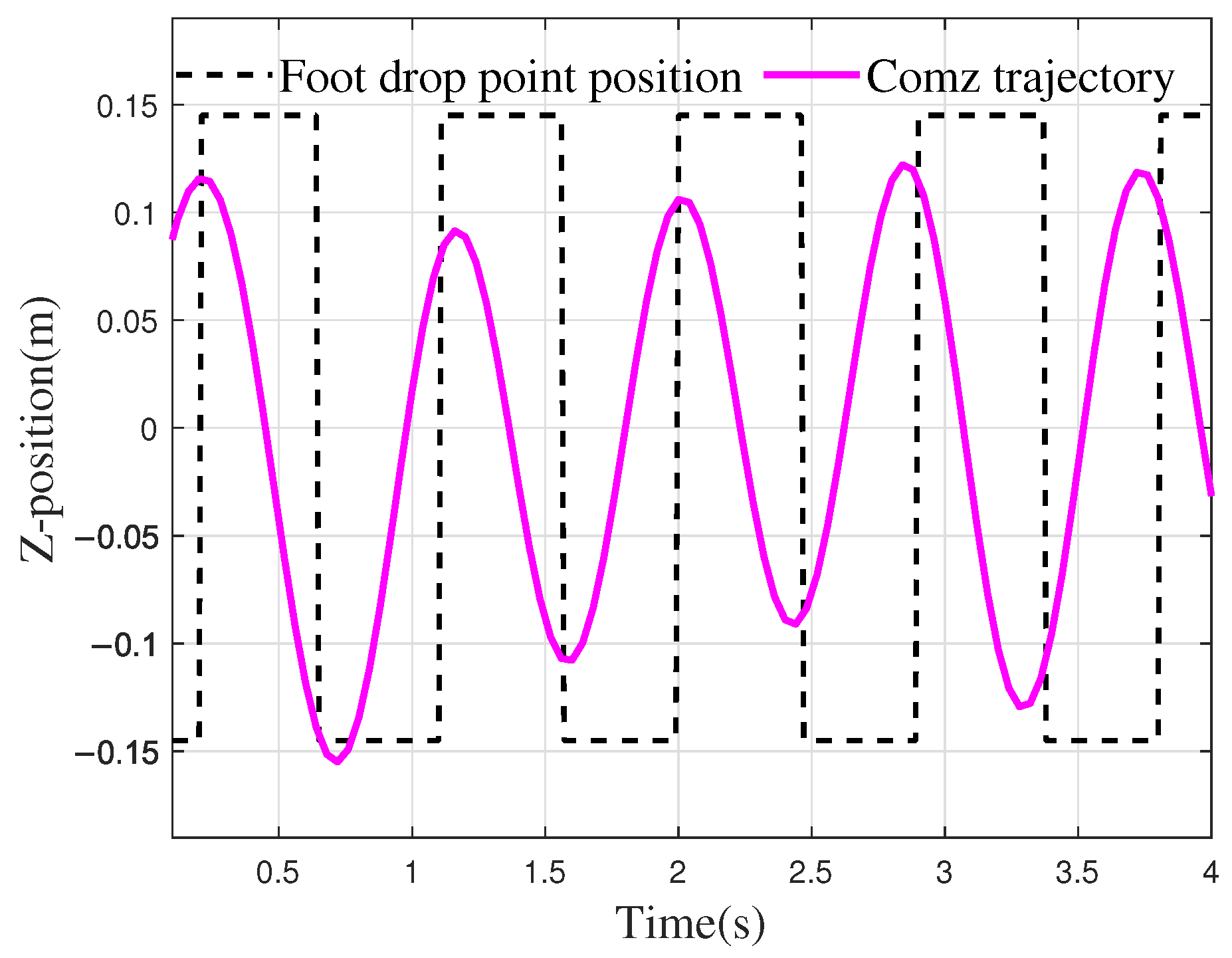
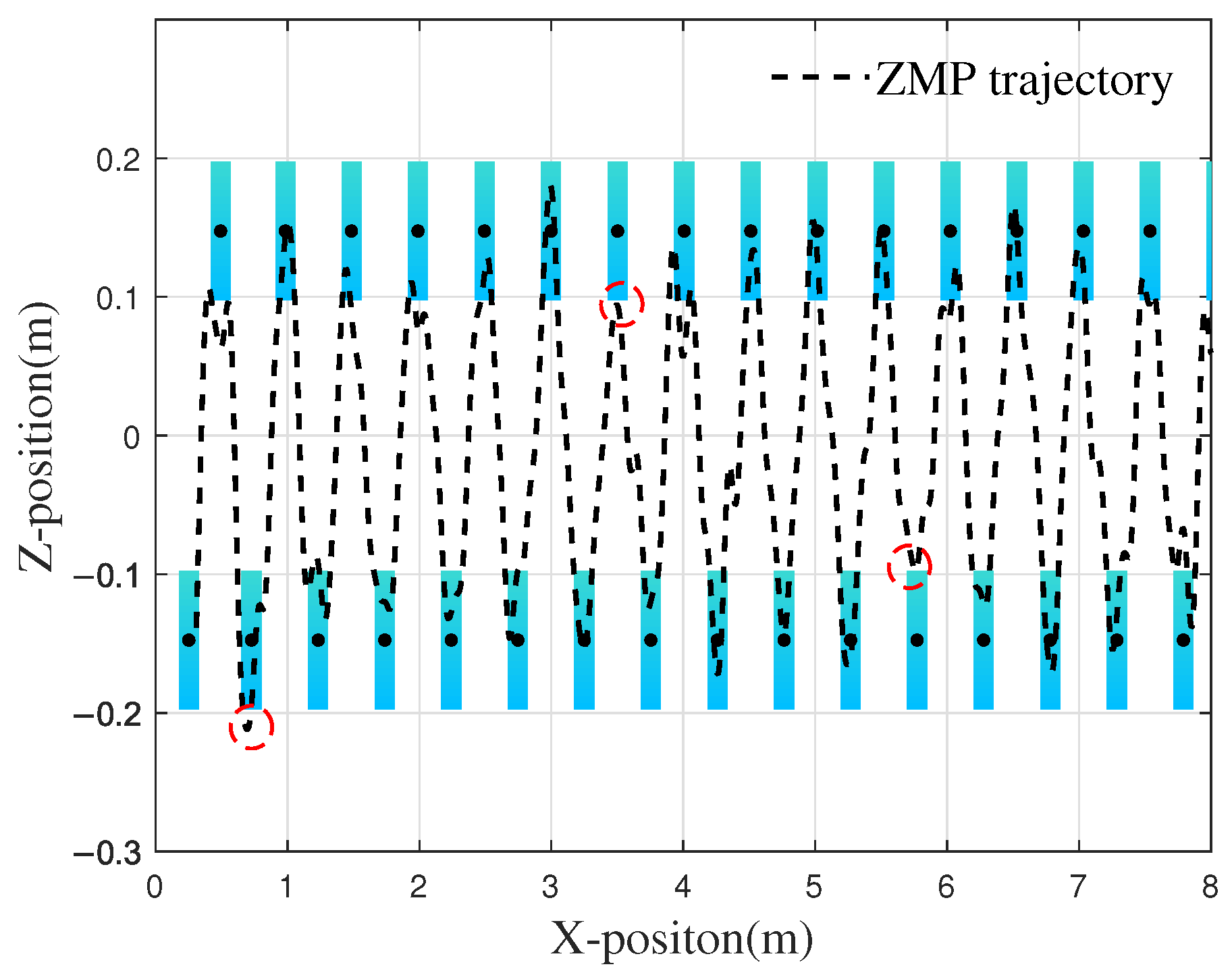
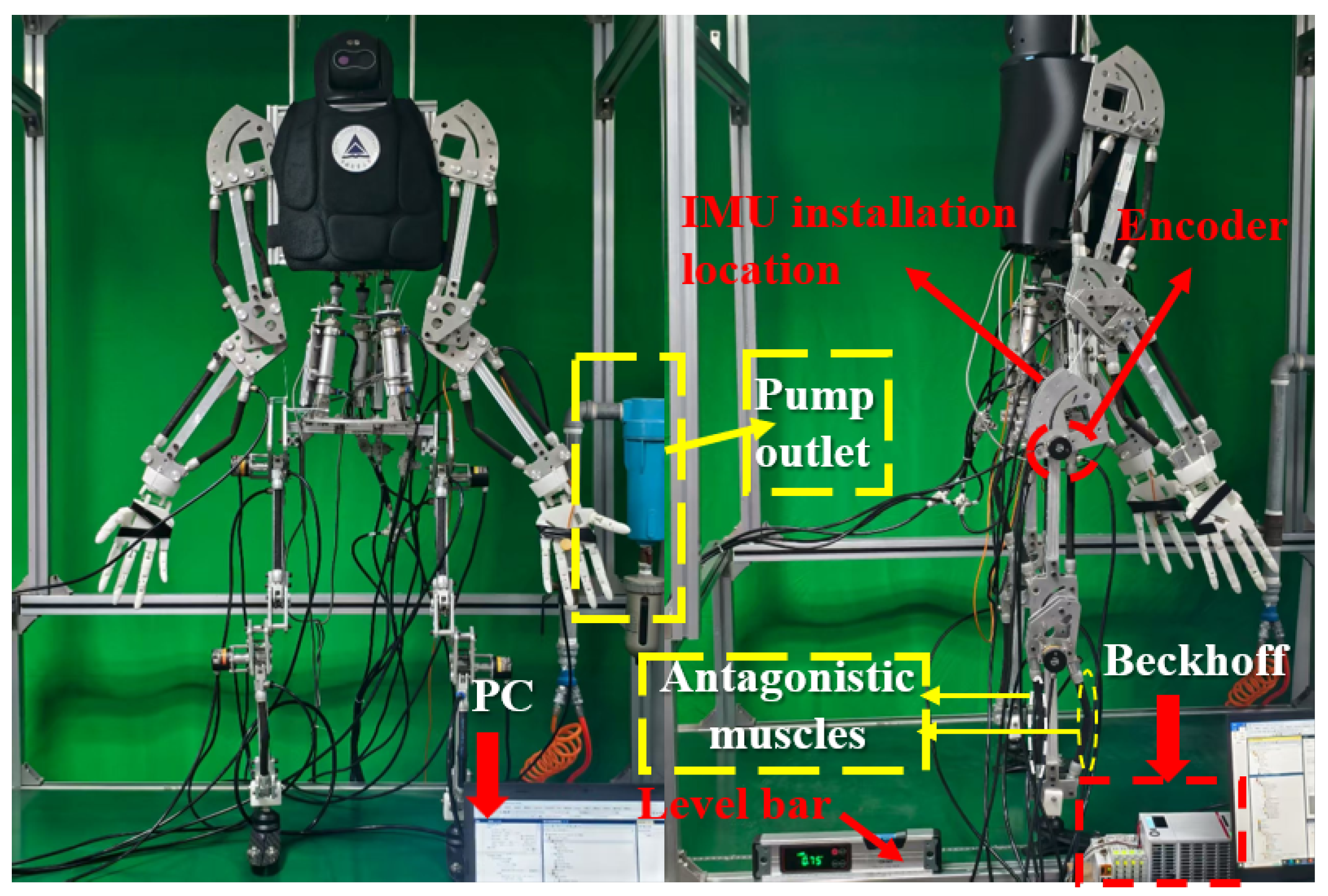
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| , | 0.123, 0.255 |
| , , a | 0.365, −3.614, −1.930 |
| , , | 0.338, 0.776, −0.0072 |
| , , , | 0.197, 0.101, 0.451, 0.586 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| , | 0.139, 0.246 |
| , , a | 0.375, −3.414, −1.790 |
| , | 0.238, 0.037 |
| , , | 0.388, 0.176, 0.555 |
| Joint | Consumption Index | Near Natural Gait | Uncoordinated Gait |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hip | Total Energy (J) | 44.9 | 247 |
| Knee | Total Energy (J) | 90.7 | 425.3 |
| Ankle | Total Energy (J) | 4.4 | 54.3 |
| Total | CoT | 1.75 | 4.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, K.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z. Bio-Inspired Central Pattern Generator for Adaptive Gait Generation and Stability in Humanoid Robots on Sloped Surfaces. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090637
Fang J, Jin Y, Wang B, Zhou K, Wang M, Liu Z. Bio-Inspired Central Pattern Generator for Adaptive Gait Generation and Stability in Humanoid Robots on Sloped Surfaces. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(9):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090637
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Junwei, Yinglian Jin, Binrui Wang, Kun Zhou, Mingrui Wang, and Ziqi Liu. 2025. "Bio-Inspired Central Pattern Generator for Adaptive Gait Generation and Stability in Humanoid Robots on Sloped Surfaces" Biomimetics 10, no. 9: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090637
APA StyleFang, J., Jin, Y., Wang, B., Zhou, K., Wang, M., & Liu, Z. (2025). Bio-Inspired Central Pattern Generator for Adaptive Gait Generation and Stability in Humanoid Robots on Sloped Surfaces. Biomimetics, 10(9), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090637








