Self-Supervised Voice Denoising Network for Multi-Scenario Human–Robot Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose training the denoising model with synthetic data, using data scaling to enhance robustness in model application.
- We present a self-supervised method using a convolutional network to denoise both magnitude and phase components in the frequency domain.
- We demonstrate proof-of-concept of the proposed approach in both simulation and hardware. For the benefit of the community, we will open-source part of the scaled dataset at https://tinyurl.com/2ybfz3jt (accessed on 25 August 2025).
2. Related Work
3. Preliminaries
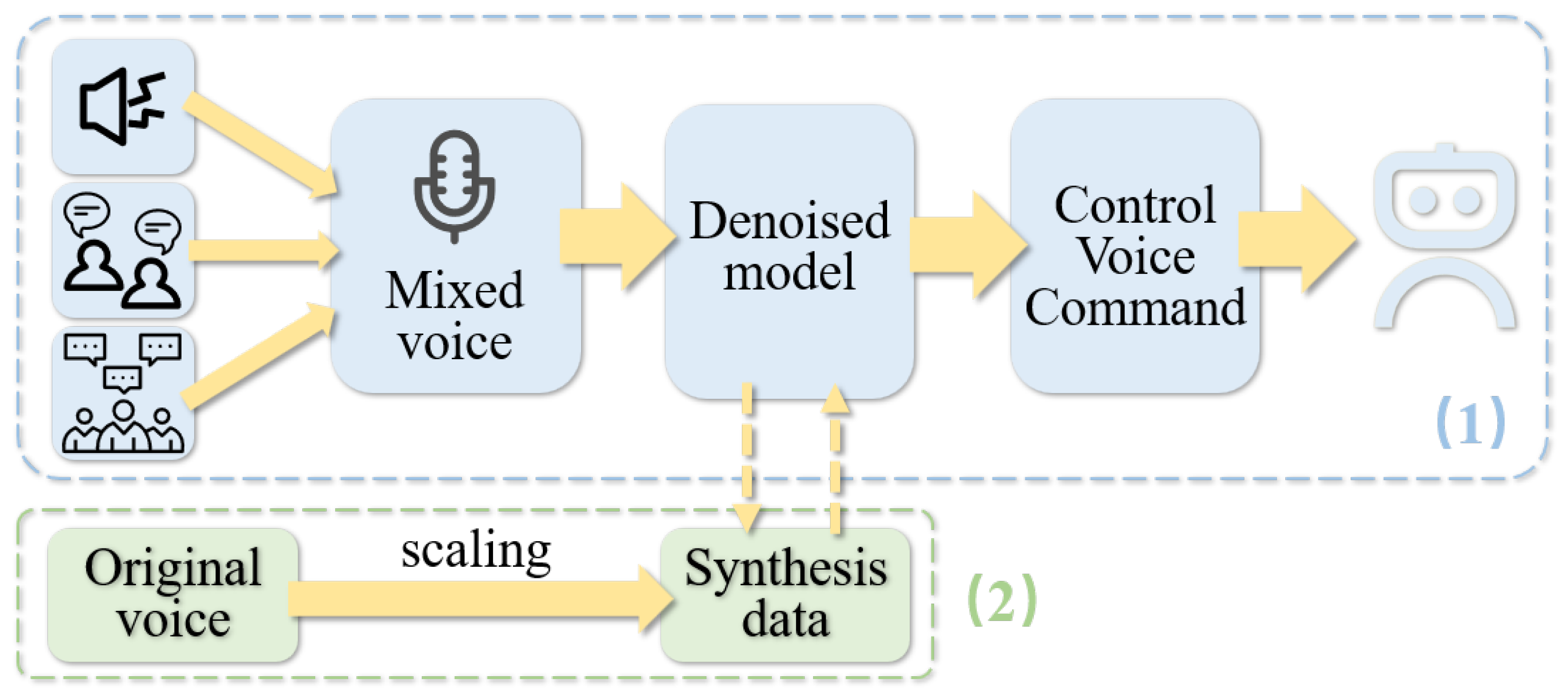
3.1. Human–Robot Voice Interaction System
3.2. Self-Supervised Denoising Strategy Foundation
4. Methodology
4.1. Voice Dataset Synthesis
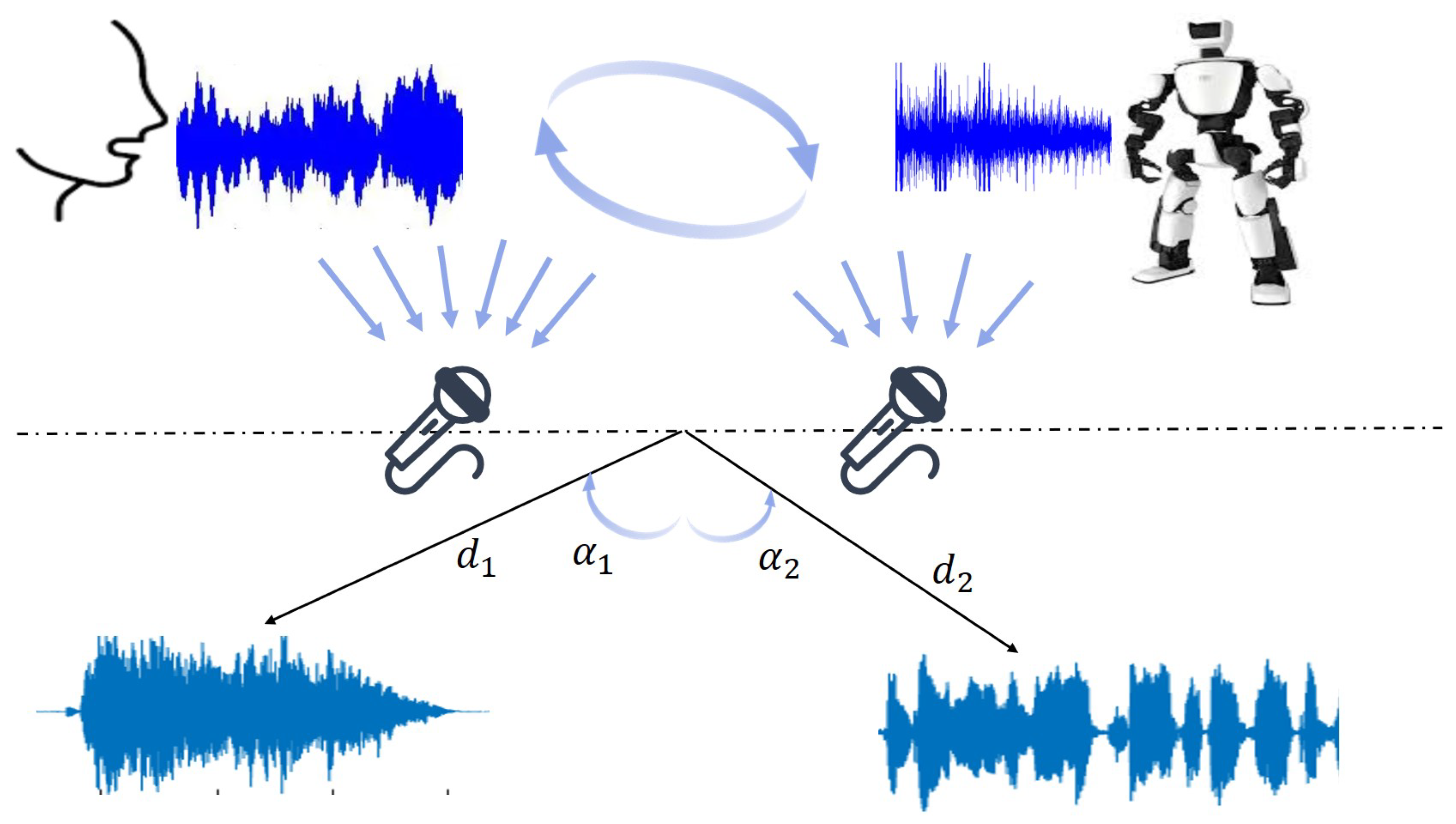
- Multi-scenario dataset: To synthesize audio in a realistic voice dataset across various environments, we employ PyDub (https://pydub.com/, (accessed on 25 August 2025)) to overlap diverse UrbanSound8K (US8K) [39] noise onto clean audio signals from the Voice Bank dataset [40], which includes 28 speakers for training and 2 for testing. The complete noisy speech sample is generated by truncating or repeating the noise to cover the entire voice segment.
- Multi-speaker dataset: Using the same methodology as for generating the multi-scenario dataset, we combine the TIMIT dataset [41], which contains recordings of 630 speaker utterances, with the Voice Bank dataset [40] to generate an audio dataset of overlapping speaker voices. However, direct training on multi-speaker audio fails to achieve effective noise reduction performance. Hence, we employ Kullback–Leibler Divergence [42] to post-process the synthesized audio, thereby generating training data that can be effectively utilized in real-world HRI scenarios (more details in Appendix C).
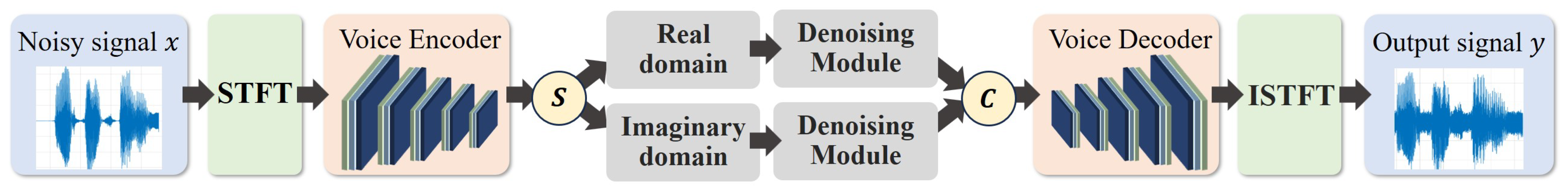
4.2. Model Encoding and Decoding Stages
4.3. Self-Supervised Denoising Strategy
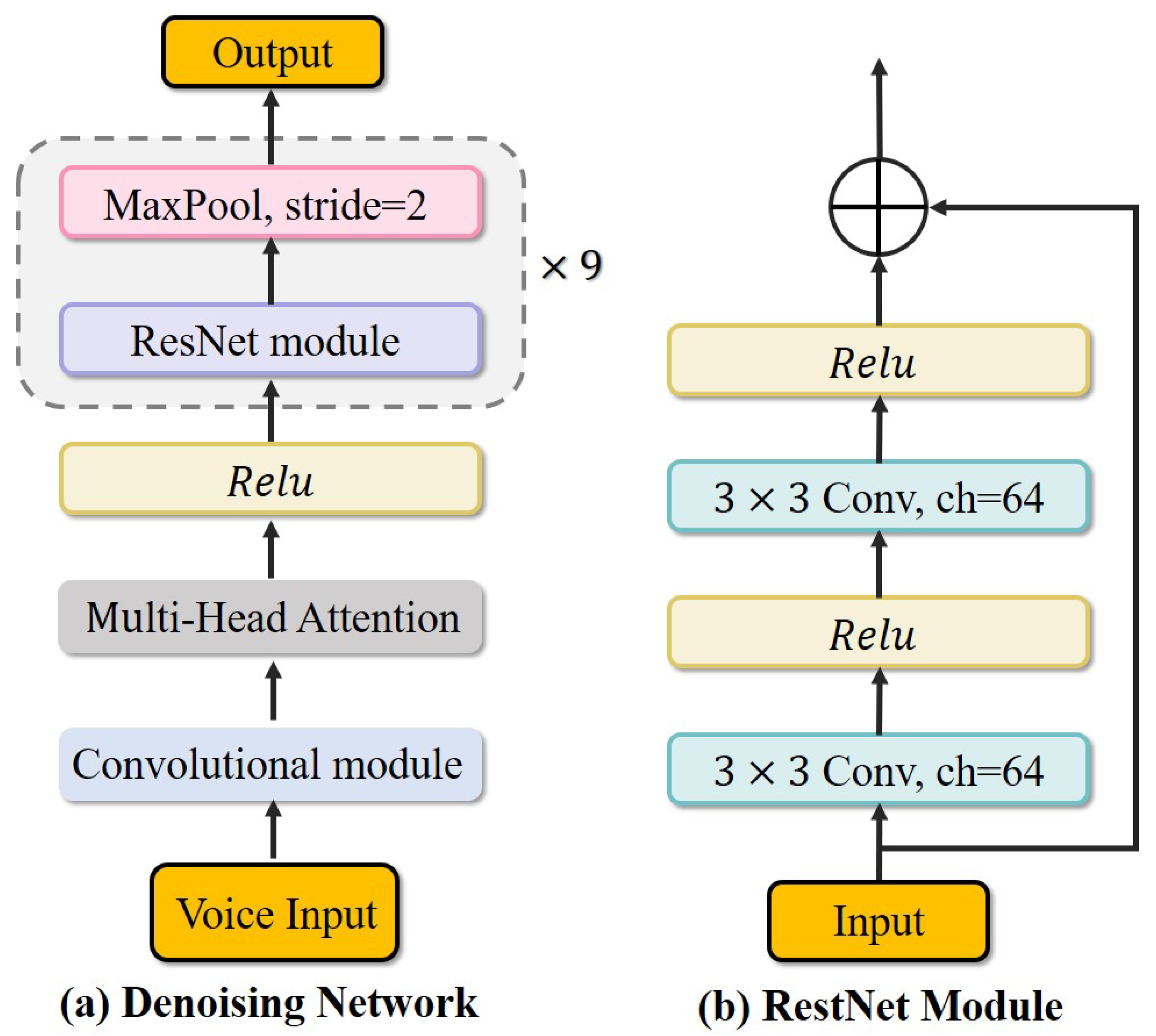
4.4. Denoising Network
4.5. Training Loss
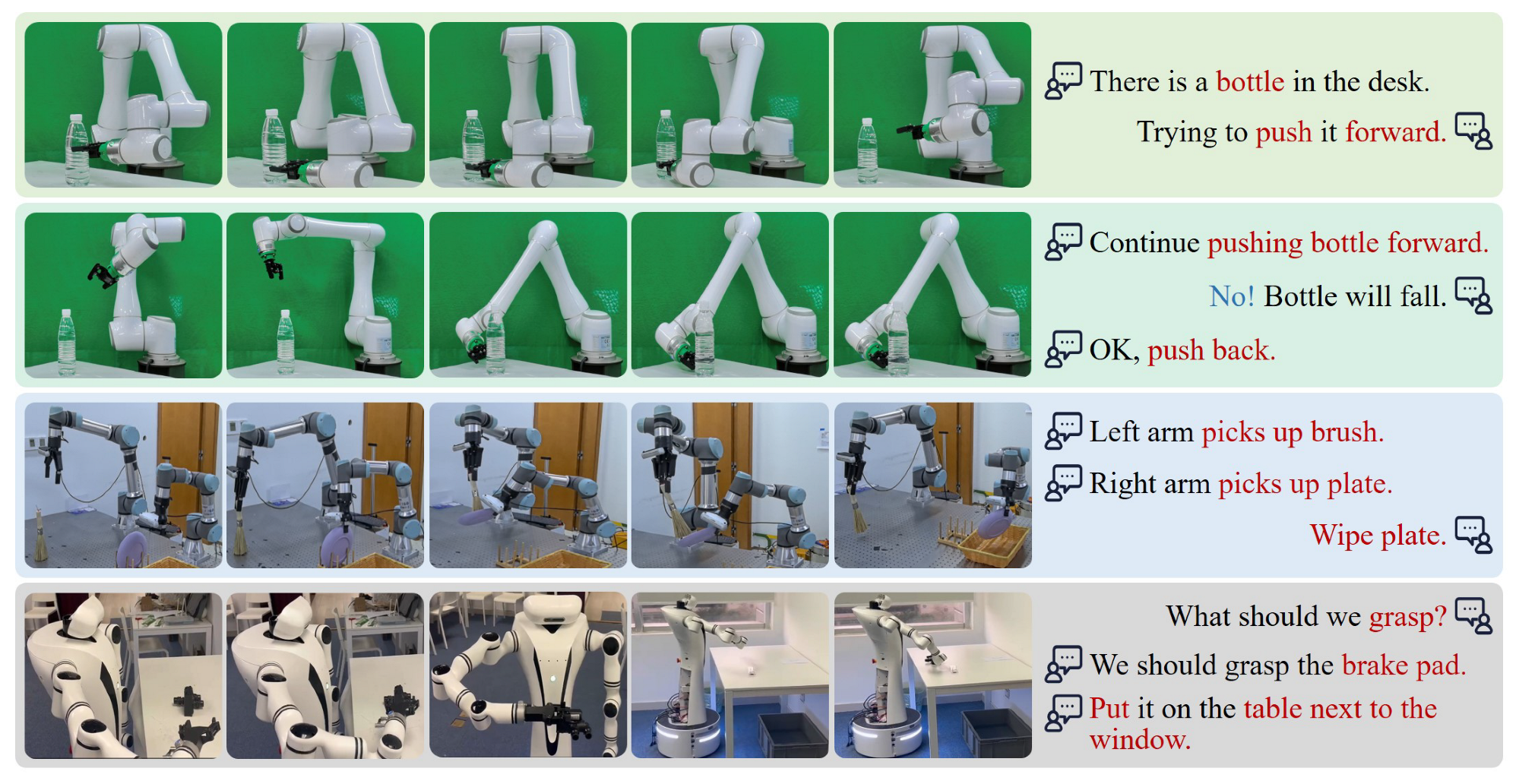
4.6. Human–Robot Voice Interaction System
- Grasp: target task action;
- Steel Pipe: target object;
- Table Behind: placing position.
| Algorithm 1 Human–robot voice interaction |
| Input: noisy voice Output: robot action RobotTask(noisy_voice) interaction_audio ← Denoise(noisy_voice) instruction ← RecognizeVoice(interaction_audio) action ← VLAModel(instruction) return RobotExecute(action) |
5. Experiment
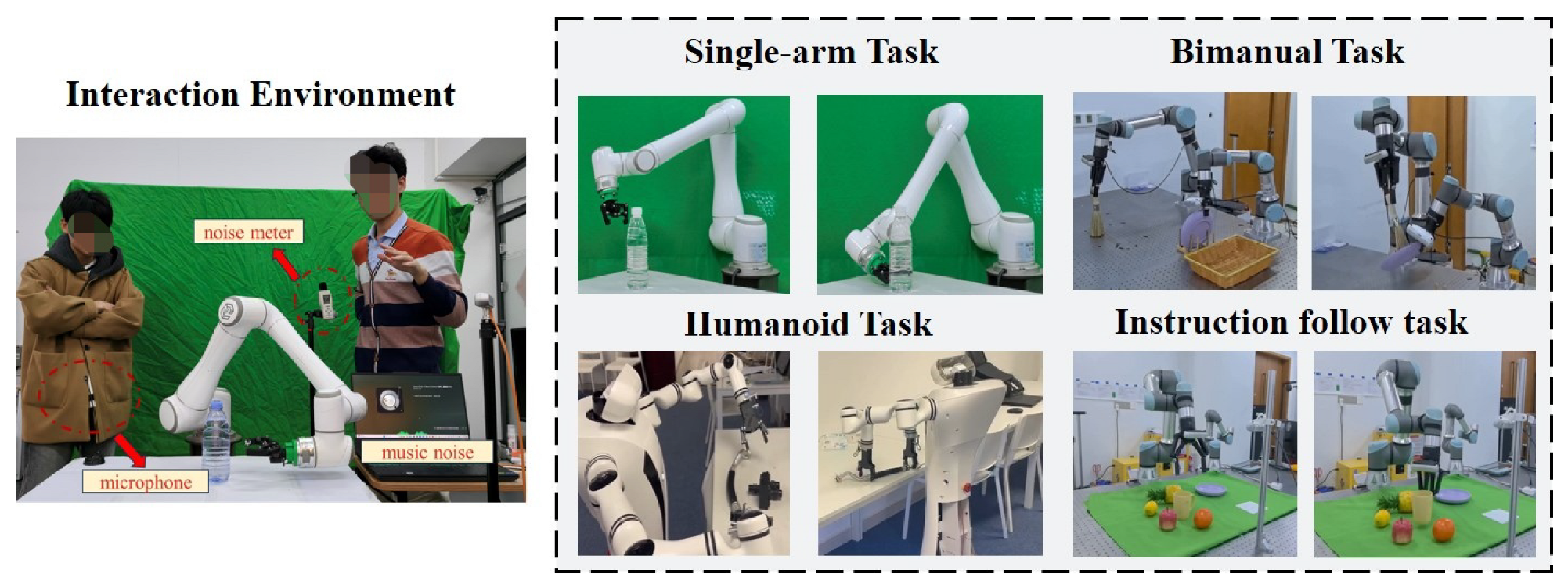
5.1. Experiment Setup
5.2. Evaluation in Simulation
5.3. Ablation Study
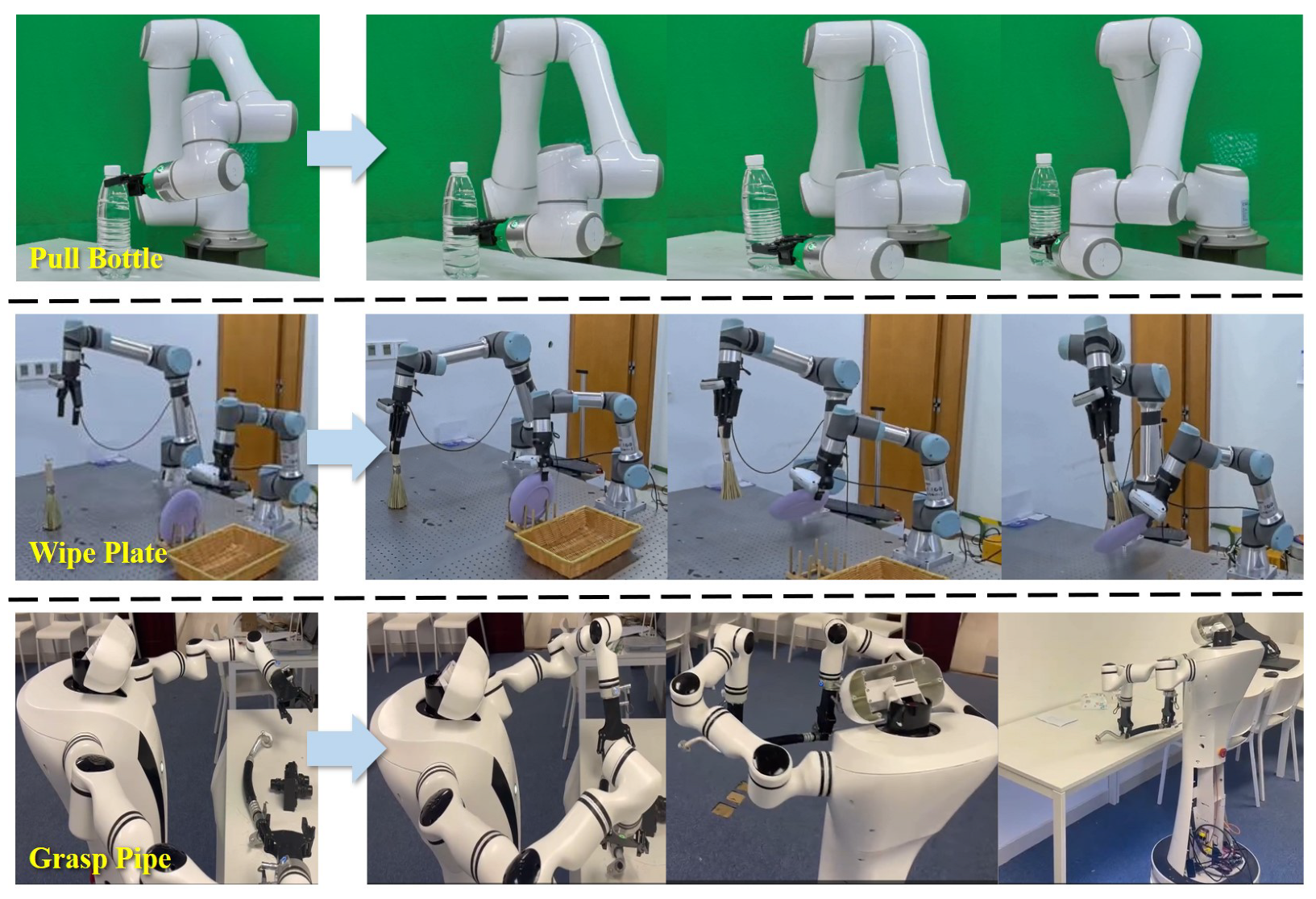
5.4. Evaluation in Real World
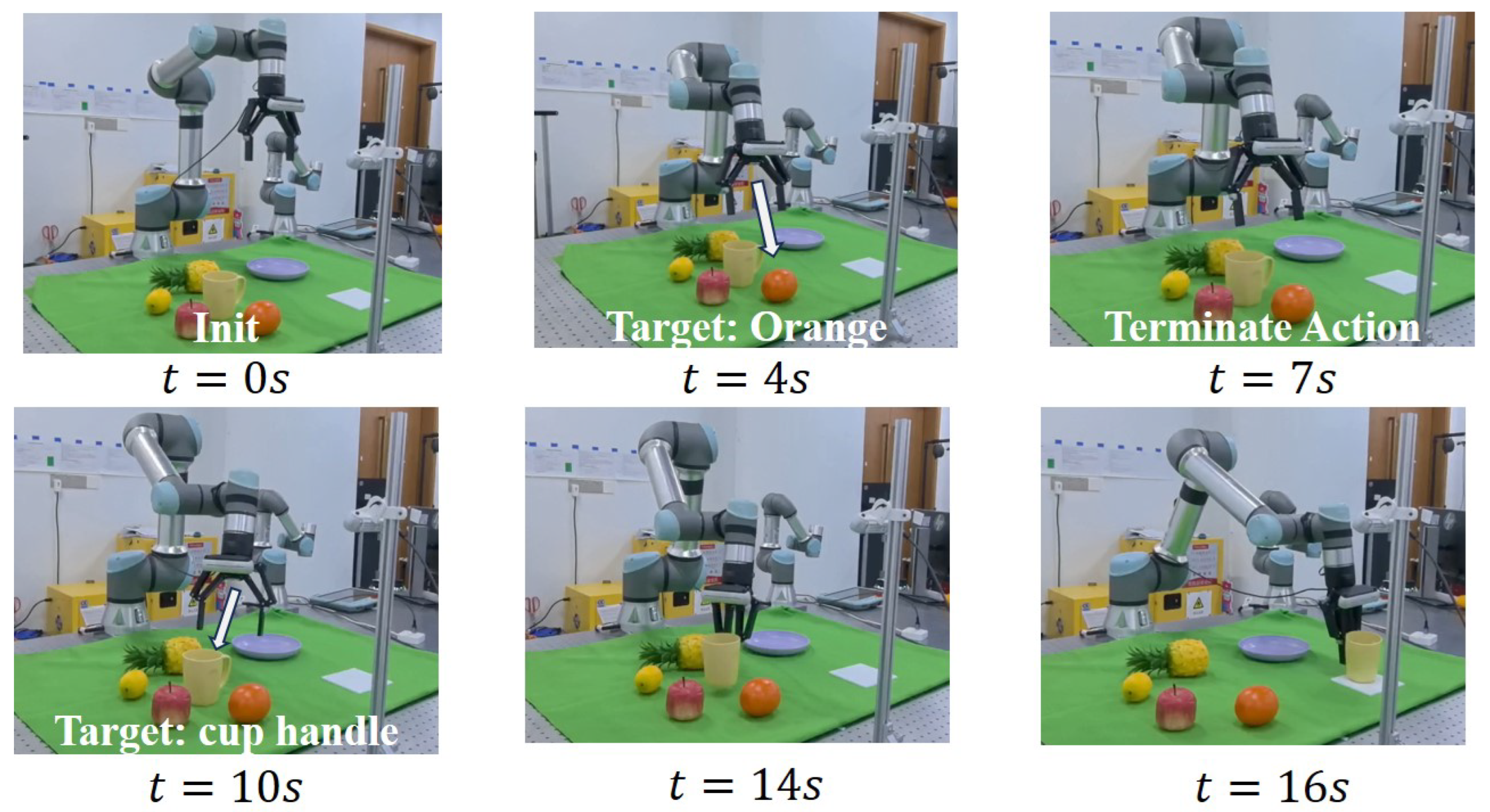
5.5. Terminate Action Test
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Appendix A. Method Overview
Appendix B. Implementation Details of Audio Synthesis
Appendix C. Implementation Details of Multi-Speaker Dataset Generation
Appendix D. Implementation Details of the Training Strategy for the Methods
| Methods | w/o Clean Voice | with Audio Separation | with CAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT | × | × | × |
| NNT | ✓ | × | × |
| NerNT | ✓ | × | × |
| ONT | ✓ | ✓ | × |
| Ours | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Appendix E. Real-World Deployment Details
References
- Chi, C.; Xu, Z.; Feng, S.; Cousineau, E.; Du, Y.; Burchfiel, B.; Tedrake, R.; Song, S. Diffusion policy: Visuomotor policy learning via action diffusion. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2023, 42, 02783649241273668. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Pertsch, K.; Karamcheti, S.; Xiao, T.; Balakrishna, A.; Nair, S.; Rafailov, R.; Foster, E.; Lam, G.; Sanketi, P.; et al. Openvla: An open-source vision-language-action model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.09246. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Li, B.; Tan, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, K.; Su, H.; Zhu, J. Rdt-1b: A diffusion foundation model for bimanual manipulation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.07864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intelligence, P.; Black, K.; Brown, N.; Darpinian, J.; Dhabalia, K.; Driess, D.; Esmail, A.; Equi, M.; Finn, C.; Fusai, N.; et al. π0. 5: A vision-language-action model with open-world generalization. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Jauhri, A.; Pandey, A.; Kadian, A.; Al-Dahle, A.; Letman, A.; Mathur, A.; Schelten, A.; Yang, A.; Fan, A.; et al. The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.21783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, F.; Busso, C. End-to-end audiovisual speech recognition system with multitask learning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devis, N.; Demerlé, N.; Nabi, S.; Genova, D.; Esling, P. Continuous descriptor-based control for deep audio synthesis. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, H.; Hao, J. Funnel Deep Complex U-Net for Phase-Aware Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Brno, Czech Republic, 30 August–3 September 2021; pp. 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura, T.; Koizumi, Y.; Yatabe, K.; Miyazaki, R. Noisy-target training: A training strategy for DNN-based speech enhancement without clean speech. In Proceedings of the 2021 29th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Dublin, Ireland, 23–27 August 2021; pp. 436–440. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, M.M.; Tambwekar, A.; Manohara, K.; Natarajan, S. Speech denoising without clean training data: A noise2noise approach. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.03838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, G.; Li, L.; Senhadji, L.; Shu, H. Self-supervised speech denoising using only noisy audio signals. Speech Commun. 2023, 149, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hindriks, K.; Kunneman, F. Single-Channel Robot Ego-Speech Filtering during Human-Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Symposium on Technological Advances in Human-Robot Interaction, Boulder, CO, USA, 9–10 March 2024; pp. 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Wu, R.; Ishiwaka, Y.; Vondrick, C.; Zheng, C. Listening to sounds of silence for speech denoising. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 9633–9648. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.; Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y. LLaMA-Omni: Seamless Speech Interaction with Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.06666. [Google Scholar]
- Ghose, S.; Prevost, J.J. Autofoley: Artificial synthesis of synchronized sound tracks for silent videos with deep learning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 1895–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Hu, Y.; Sheng, P.; Wen, C.; You, J.; Gao, Y. Data scaling laws in imitation learning for robotic manipulation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.18647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Xie, Q.; Yao, J.; Xie, L.; Su, D. Unisyn: An end-to-end unified model for text-to-speech and singing voice synthesis. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 13025–13033. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.W. Dddm-vc: Decoupled denoising diffusion models with disentangled representation and prior mixup for verified robust voice conversion. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 17862–17870. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Glas, D.F.; Kanda, T.; Ishiguro, H. Data-driven HRI: Learning social behaviors by example from human–human interaction. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 988–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, D. Divide and conquer: A deep CASA approach to talker-independent monaural speaker separation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 2092–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baby, D.; Verhulst, S. Sergan: Speech enhancement using relativistic generative adversarial networks with gradient penalty. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rouard, S.; Massa, F.; Défossez, A. Hybrid Transformers for Music Source Separation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 23), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.W.; Yu, C.; Hsieh, T.A.; Plantinga, P.; Ravanelli, M.; Lu, X.; Tsao, Y. Metricgan+: An improved version of metricgan for speech enhancement. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.03538. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Wu, Y.C.; Tobing, P.L.; Huang, W.C.; Toda, T. Direct noisy speech modeling for noisy-to-noisy voice conversion. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 6787–6791. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlenbusch, M.; Rollwage, C.; Doclo, S. Multi-microphone noise data augmentation for DNN-based own voice reconstruction for hearables in noisy environments. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 416–420. [Google Scholar]
- Zinchenko, K.; Wu, C.Y.; Song, K.T. A study on speech recognition control for a surgical robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 13, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Yuan, S.; Nassar, Y.; Fan, M.; Gopal, A.; Yorita, A.; Kubota, N.; Rätsch, M. Natural multimodal fusion-based human–robot interaction: Application with voice and deictic posture via large language model. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; An, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Gu, C.; Li, X.; Guo, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; et al. Hybridvla: Collaborative diffusion and autoregression in a unified vision-language-action model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.10631. [Google Scholar]
- Brohan, A.; Brown, N.; Carbajal, J.; Chebotar, Y.; Dabis, J.; Finn, C.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Hausman, K.; Herzog, A.; Hsu, J.; et al. Rt-1: Robotics transformer for real-world control at scale. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.06817. [Google Scholar]
- Brohan, A.; Brown, N.; Carbajal, J.; Chebotar, Y.; Chen, X.; Choromanski, K.; Ding, T.; Driess, D.; Dubey, A.; Finn, C.; et al. Rt-2: Vision-language-action models transfer web knowledge to robotic control. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.15818. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo-Badiola, S.; Canal, G.; Rizzo, C.; Aleny, G. Plancollabnl: Leveraging large language models for adaptive plan generation in human-robot collaboration. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 17344–17350. [Google Scholar]
- Zitkovich, B.; Yu, T.; Xu, S.; Xu, P.; Xiao, T.; Xia, F.; Wu, J.; Wohlhart, P.; Welker, S.; Wahid, S.; et al. Rt-2: Vision-language-action models transfer web knowledge to robotic control. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2165–2183. [Google Scholar]
- Nvidia, J.B.; Castaneda, F.; Cherniadev, N.; Da, X.; Ding, R.; Fan, L.; Fang, Y.; Fox, D.; Hu, F.; Huang, S.; et al. Gr00t n1: An open foundation model for generalist humanoid robots. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14734. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtinen, J.; Munkberg, J.; Hasselgren, J.; Laine, S.; Karras, T.; Aittala, M.; Aila, T. Noise2Noise: Learning image restoration without clean data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.04189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.; Zheng, H.; Quan, Y.; Ji, H. Recorrupted-to-recorrupted: Unsupervised deep learning for image denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2043–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Lu, H.; Liu, J. Neighbor2neighbor: Self-supervised denoising from single noisy images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14781–14790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Complex spectral mapping with attention based convolution recurrent neural network for speech enhancement. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.05267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, J.; Jacoby, C.; Bello, J.P. A dataset and taxonomy for urban sound research. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 1041–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Veaux, C.; Yamagishi, J.; King, S. The voice bank corpus: Design, collection and data analysis of a large regional accent speech database. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference Oriental COCOSDA Held Jointly with 2013 Conference on Asian Spoken Language Research and Evaluation (O-COCOSDA/CASLRE), Gurgaon, India, 25–27 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Garofolo, J.S.; Lamel, L.F.; Fisher, W.M.; Pallett, D.S.; Dahlgren, N.L.; Zue, V.; Fiscus, J.G. TIMIT Acoustic-Phonetic Continuous Speech Corpus; National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1993; Available online: https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC93s1 (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Golokolenko, O.; Schuller, G. A fast stereo audio source separation for moving sources. In Proceedings of the 2019 53rd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2019; pp. 1931–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Bartle, R.G. The Elements of Integration and Lebesgue Measure; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Wang, D. Complex spectral mapping with a convolutional recurrent network for monaural speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 6865–6869. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Wang, D. Densely connected neural network with dilated convolutions for real-time speech enhancement in the time domain. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6629–6633. [Google Scholar]
- Rix, A.W.; Beerends, J.G.; Hollier, M.P.; Hekstra, A.P. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)—A new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (Cat. No. 01CH37221), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001; pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Loizou, P.C. Evaluation of objective quality measures for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2007, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Strake, M.; Fingscheidt, T. Deep noise suppression maximizing non-differentiable PESQ mediated by a non-intrusive PESQNet. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2022, 30, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valin, J.M. A hybrid DSP/deep learning approach to real-time full-band speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29–31 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Schroter, H.; Escalante-B, A.N.; Rosenkranz, T.; Maier, A. DeepFilterNet: A low complexity speech enhancement framework for full-band audio based on deep filtering. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 7407–7411. [Google Scholar]



| Dataset | Network | SNR | SSNR | PESQ-NB | PESQ-WB | STOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Env1 | NCT | |||||
| NNT | ||||||
| NerNT | − | − | − | − | − | |
| ONT | ||||||
| ONT + rTSTM | ||||||
| ONT + cTSTM | ||||||
| Ours | ||||||
| Env2 | NCT | |||||
| NNT | ||||||
| NerNT | ||||||
| ONT | ||||||
| ONT + rTSTM | ||||||
| ONT + cTSTM | ||||||
| Ours | ||||||
| Env3 | NCT | |||||
| NNT | ||||||
| NerNT | ||||||
| ONT | ||||||
| ONT + rTSTM | ||||||
| ONT + cTSTM | ||||||
| Ours |
| Training | Testing | Network | SNR | PESQ-NB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factory | Street | NCT | ||
| NNT | ||||
| NerNT | ||||
| ONT | ||||
| ONT + rTSTM | ||||
| ONT + cTSTM | ||||
| Ours |
| Network | k = 0 | k = 1 | k = 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT | |||
| NNT | |||
| NerNT | |||
| ONT | |||
| ONT + rTSTM | |||
| ONT + cTSTM | |||
| Ours |
| Noise | δ = 0 | δ = 1 | δ = 2 | δ = 4 | δ = 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Env1 | 2.832 | 2.961 | 2.879 | 2.793 | 2.524 |
| Env2 | 2.783 | 2.818 | 2.837 | 2.774 | 2.328 |
| Env3 | 2.673 | 2.727 | 2.711 | 2.668 | 2.192 |
| Dataset | Network | SNR | SSNR | PESQ-NB | PESQ-WB | STOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Env1 | Net-1 | 16.831 | 3.996 | 2.655 | 1.728 | 0.598 |
| Net-2 | 18.274 | 7.811 | 2.864 | 1.921 | 0.816 | |
| Net-3 | 17.348 | 5.921 | 2.715 | 1.814 | 0.726 | |
| Ours | 18.671 | 9.268 | 2.96 | 2.166 | 0.864 |
| Method | Urban Music (dB) | Multi-Speaker (dB) | Avg Time (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50–70 | 70–80 | 50–70 | 70–80 | ||
| RRnoise | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 4.2 |
| DeepFilterNet | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.72 | 1.9 |
| ONT | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.79 | 3.1 |
| Llama-Omni | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 3.7 |
| Ours | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Xu, W.; Zeng, C.; Wang, N. Self-Supervised Voice Denoising Network for Multi-Scenario Human–Robot Interaction. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090603
Li M, Xu W, Zeng C, Wang N. Self-Supervised Voice Denoising Network for Multi-Scenario Human–Robot Interaction. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(9):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090603
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mu, Wenjin Xu, Chao Zeng, and Ning Wang. 2025. "Self-Supervised Voice Denoising Network for Multi-Scenario Human–Robot Interaction" Biomimetics 10, no. 9: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090603
APA StyleLi, M., Xu, W., Zeng, C., & Wang, N. (2025). Self-Supervised Voice Denoising Network for Multi-Scenario Human–Robot Interaction. Biomimetics, 10(9), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10090603







