Temporal-Spatial Redundancy Reduction in Video Sequences: A Motion-Based Entropy-Driven Attention Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Video Understanding
2.2. Frame Sampling
2.3. Attention Mechanism
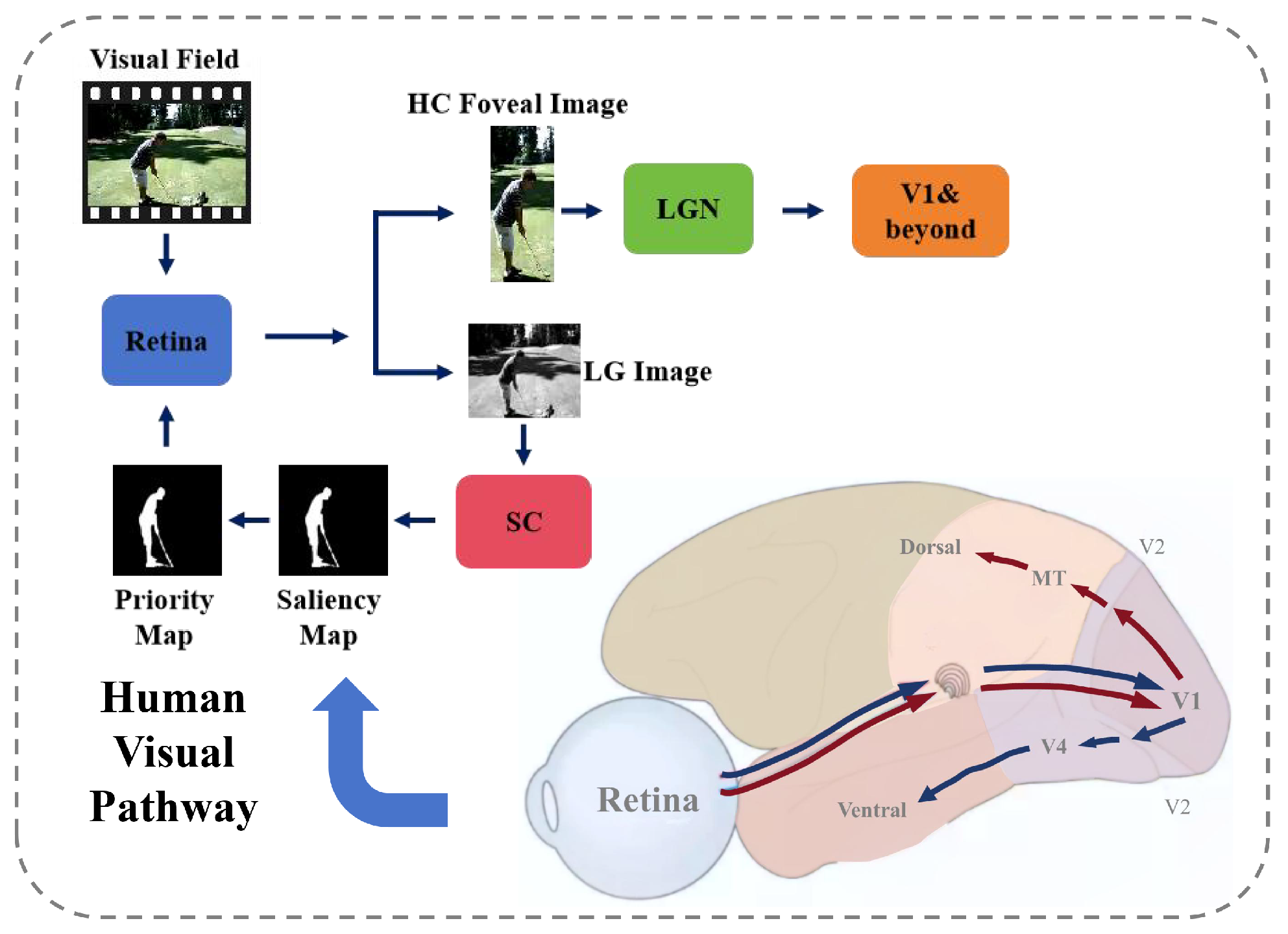
3. Methods
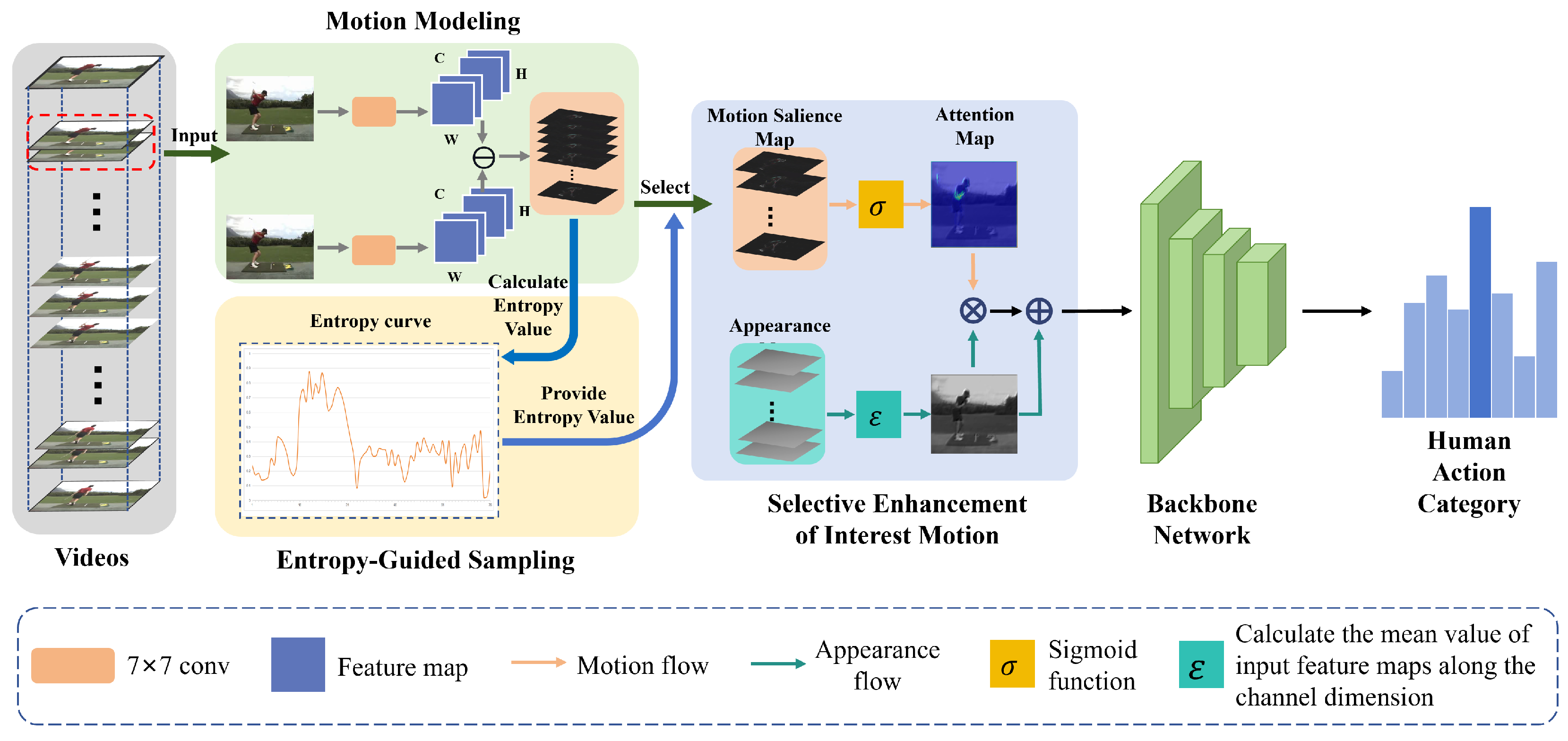
3.1. Overview
3.2. Overall Architecture
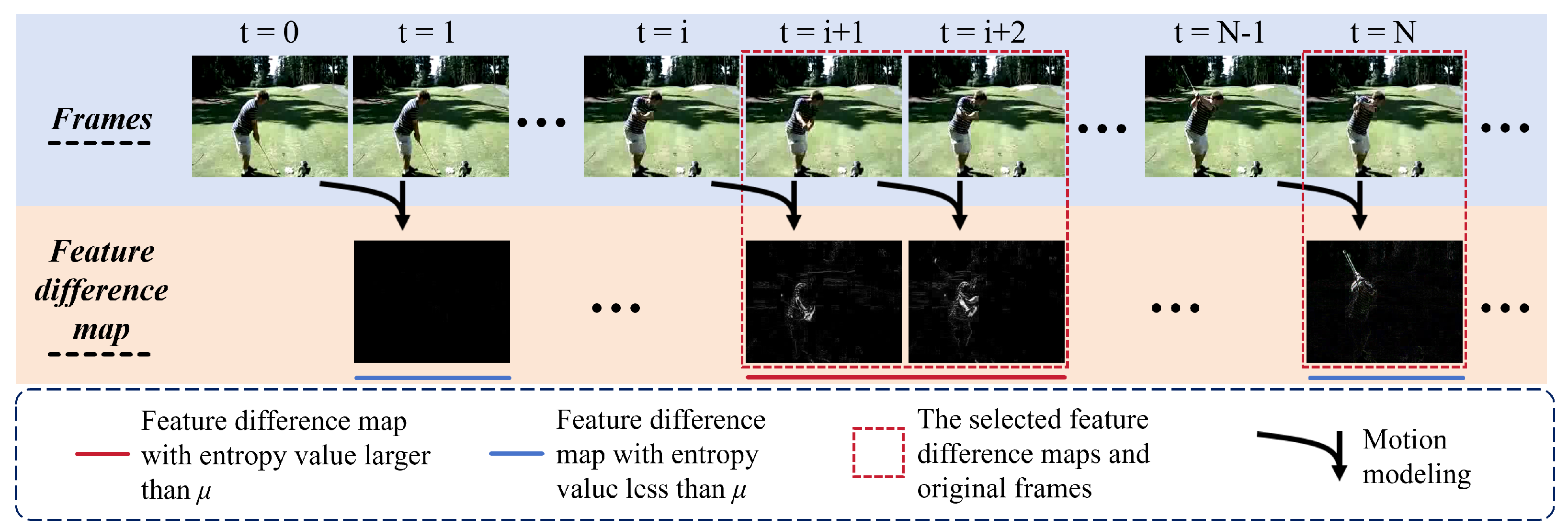
3.3. Motion Modeling
3.4. Entropy-Guided Sampling
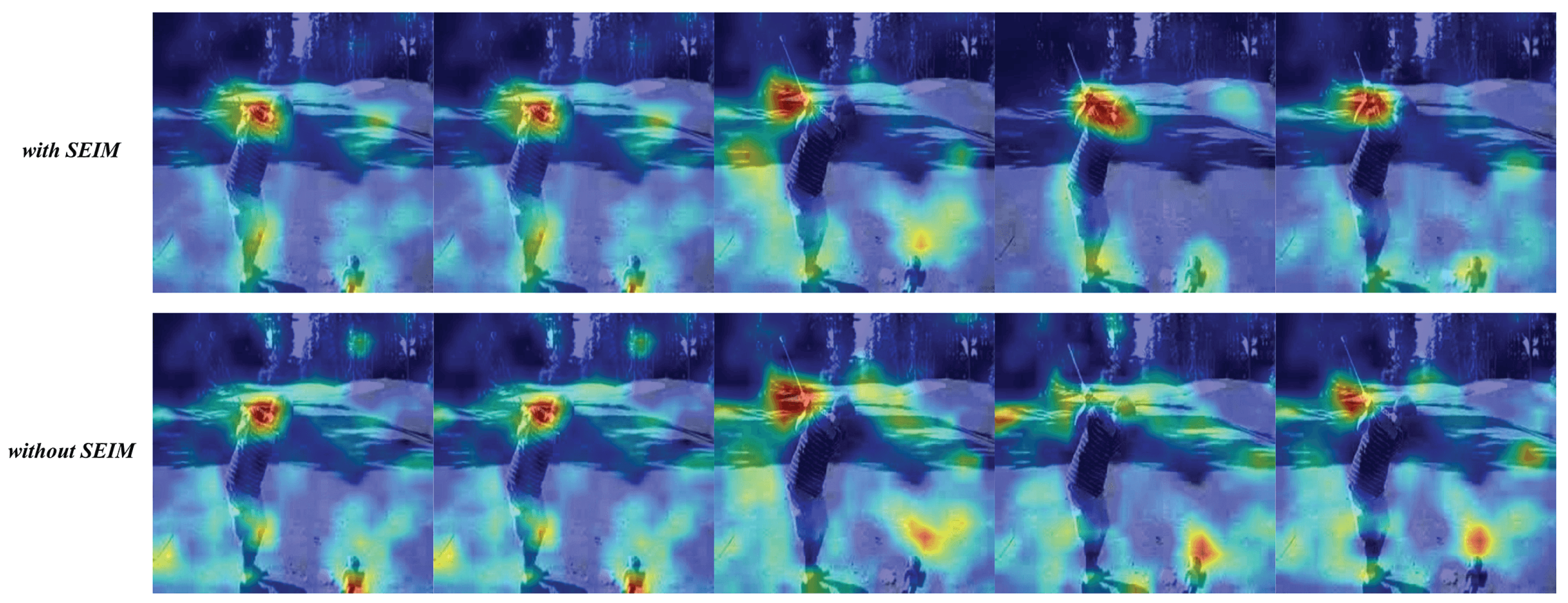
3.5. Selective Enhancement of Interest Motion (SEIM)
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Implementations
4.2. Experiment Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borji, A.; Sihite, D.N.; Itti, L. Quantitative analysis of human-model agreement in visual saliency modeling: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 22, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tseng, P.H.; Cameron, I.G.; Pari, G.; Reynolds, J.N.; Munoz, D.P.; Itti, L. High-throughput classification of clinical populations from natural viewing eye movements. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Ng, T.Y.; Liu, Y. Perception-oriented video saliency detection via spatio-temporal attention analysis. Neurocomputing 2016, 207, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, G. Mgsampler: An explainable sampling strategy for video action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1513–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fan, H.; Zhuo, T.; Lim, J.H.; Kankanhalli, M. Entropy guided attention network for weakly-supervised action localization. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 129, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, H.; Hu, H. Appearance and motion enhancement for video-based person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11394–11401. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, K.; Zamir, A.R.; Shah, M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.0402. [Google Scholar]
- Kuehne, H.; Jhuang, H.; Garrote, E.; Poggio, T.; Serre, T. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2556–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Materzynska, J.; Berger, G.; Bax, I.; Memisevic, R. The jester dataset: A large-scale video dataset of human gestures. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.Y.; Ho, C.H.; Vasconcelos, N. ProTeCt: Prompt Tuning for Taxonomic Open Set Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, R.; Ebrahimi Kahou, S.; Michalski, V.; Materzynska, J.; Westphal, S.; Kim, H.; Haenel, V.; Fruend, I.; Yianilos, P.; Mueller-Freitag, M.; et al. The ”something something” video database for learning and evaluating visual common sense. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5842–5850. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Wei, N.; Sheng, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.J. TS-CNN: Text steganalysis from semantic space based on convolutional neural network. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.08136. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6299–6308. [Google Scholar]
- Arandjelovic, R.; Gronat, P.; Torii, A.; Pajdla, T.; Sivic, J. NetVLAD: CNN architecture for weakly supervised place recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5297–5307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cai, W.; Cai, D.; Cai, Z.; Zhong, H.; Li, M. End-to-end language identification using NetFV and NetVLAD. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), Taipei City, Taiwan, 26–29 November 2018; pp. 319–323. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Yao, T.; Mei, T. Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3d residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5533–5541. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; LeCun, Y.; Paluri, M. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6450–6459. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Sun, C.; Huang, J.; Tu, Z.; Murphy, K. Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning: Speed-accuracy trade-offs in video classification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 305–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Fan, H.; Malik, J.; He, K. Slowfast networks for video recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6202–6211. [Google Scholar]
- Korbar, B.; Tran, D.; Torresani, L. Scsampler: Sampling salient clips from video for efficient action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6232–6242. [Google Scholar]
- Schiappa, M.C.; Rawat, Y.S.; Shah, M. Self-supervised learning for videos: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elharrouss, O.; Akbari, Y.; Almadeed, N.; Al-Maadeed, S. Backbones-review: Feature extractor networks for deep learning and deep reinforcement learning approaches in computer vision. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2024, 53, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D.; Tang, X.; Van Gool, L. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; He, D.; Tan, X.; Chen, S.; Wen, S. Multi-agent reinforcement learning based frame sampling for effective untrimmed video recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6222–6231. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Shi, P.; He, H.; He, H.; Zhao, B. Senet: Spatial information enhancement for semantic segmentation neural networks. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 3427–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Huang, T.; Xu, J.; Min, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z. RCNU-Net: Reparameterized convolutional network with convolutional block attention module for improved polyp image segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 93, 106138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Si, P.; Xia, C. Fast tracking via spatio-temporal context learning based on multi-color attributes and pca. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), Macau, China, 18–20 July 2017; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Ji, L.; Chen, S.; Duan, W. Spatial–temporal-channel collaborative feature learning with transformers for infrared small target detection. Image Vis. Comput. 2025, 154, 105435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ji, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Kang, B.; Wang, L. Tea: Temporal excitation and aggregation for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 909–918. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Tang, M.; Yang, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhao, M. Spatio-temporal adaptive convolution and bidirectional motion difference fusion for video action recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124917. [Google Scholar]
- Contributors, M. OpenMMLab’s Next Generation Video Understanding Toolbox and Benchmark. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmaction2 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Lin, J.; Gan, C.; Han, S. Tsm: Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7083–7093. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Bors, A.G. BQN: Busy-Quiet Net Enabled by Motion Band-Pass Module for Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 4966–4979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Tu, Z. Motion-driven visual tempo learning for video-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 4104–4116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Yuille, A.L. Grouped spatial-temporal aggregation for efficient action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5512–5521. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, J.; Luo, D.; Wang, Y.; Tai, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Huang, F.; Jiang, X.; Yuan, J. Temporal distinct representation learning for action recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; He, D.; Lin, T.; Li, F.; Gan, C.; Ding, E. Mvfnet: Multi-view fusion network for efficient video recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 2943–2951. [Google Scholar]
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top-1 | 56.1 | 57.2 | 58.6 | 59.7 | 59.2 | 59.4 | 58.4 |
| Method | Top-1 |
|---|---|
| Fixed stride sampling | 54.7 |
| TSN | 58.4 |
| MGSampler | 60.1 |
| EGMESampler (ours) | 59.7 |
| Method | UCF101 | HMDB51 |
|---|---|---|
| TSN (each video) | 6.5 ms | 4.7 ms |
| MGSampler (each videos) | 6.9 ms | 5.0 ms |
| Ours (each video) | 4.8 ms | 4.6 ms |
| Dataset | EGMSampler (With SEIM) | EGMSampler (Without SEIM) |
|---|---|---|
| UCF-101 | 95.1 | 94.7 |
| HMDB-51 | 73.7 | 72.8 |
| Jester | 97.2 | 96.7 |
| Diving-48 | 39.4 | 36.1 |
| Method | UCF-101 | Diving-48 |
|---|---|---|
| Feature difference with SEIM | 95.1 | 39.4 |
| Feature difference without SEIM | 94.7 | 36.1 |
| Image difference with SEIM | 94.3 | 36.6 |
| Image difference without SEIM | 93.4 | 34.9 |
| Model | Backbone | Frames | Sth-V1 (Top-1) | Sth-V2 (Top-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I3D [14] | 3D ResNet50 | 32 × 3 × 2 | 41.6 | - |
| NL I3D [37] | 3D ResNet50 | 32 × 3 × 2 | 44.4 | - |
| TSN [25] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 19.7 | 27.8 |
| TSM [36] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 20.9 | 28.1 |
| BQN [38] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 51.7 | - |
| TCM [39] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 48.2 | 50.8 |
| GST [40] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 45.8 | 49.2 |
| TIDRL [41] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 49.7 | 48.8 |
| MVNet [42] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 50.1 | 50.2 |
| TEA [33] | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 48.9 | 60.9 |
| Ours (TSM) | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 58.8 | 59.7 |
| Ours (TEA) | ResNet50 | 8 × 1 × 1 | 55.7 | 63.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Wu, B.; Mo, Z.; Liu, W.; Hong, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, N. Temporal-Spatial Redundancy Reduction in Video Sequences: A Motion-Based Entropy-Driven Attention Approach. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040192
Yuan Y, Wu B, Mo Z, Liu W, Hong J, Li Z, Liu J, Liu N. Temporal-Spatial Redundancy Reduction in Video Sequences: A Motion-Based Entropy-Driven Attention Approach. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(4):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040192
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Ye, Baolei Wu, Zifan Mo, Weiye Liu, Ji Hong, Zongdao Li, Jian Liu, and Na Liu. 2025. "Temporal-Spatial Redundancy Reduction in Video Sequences: A Motion-Based Entropy-Driven Attention Approach" Biomimetics 10, no. 4: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040192
APA StyleYuan, Y., Wu, B., Mo, Z., Liu, W., Hong, J., Li, Z., Liu, J., & Liu, N. (2025). Temporal-Spatial Redundancy Reduction in Video Sequences: A Motion-Based Entropy-Driven Attention Approach. Biomimetics, 10(4), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040192







