Dynamic Motion-Based Optimization of Support and Transmission Mechanisms for Legged Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of the Mechanical Mechanism
2.1. Design Goals
- Reduce the torque and speed requirements of the joints.
- High-stiffness leg mechanism.
- Low-inertia leg mechanism.
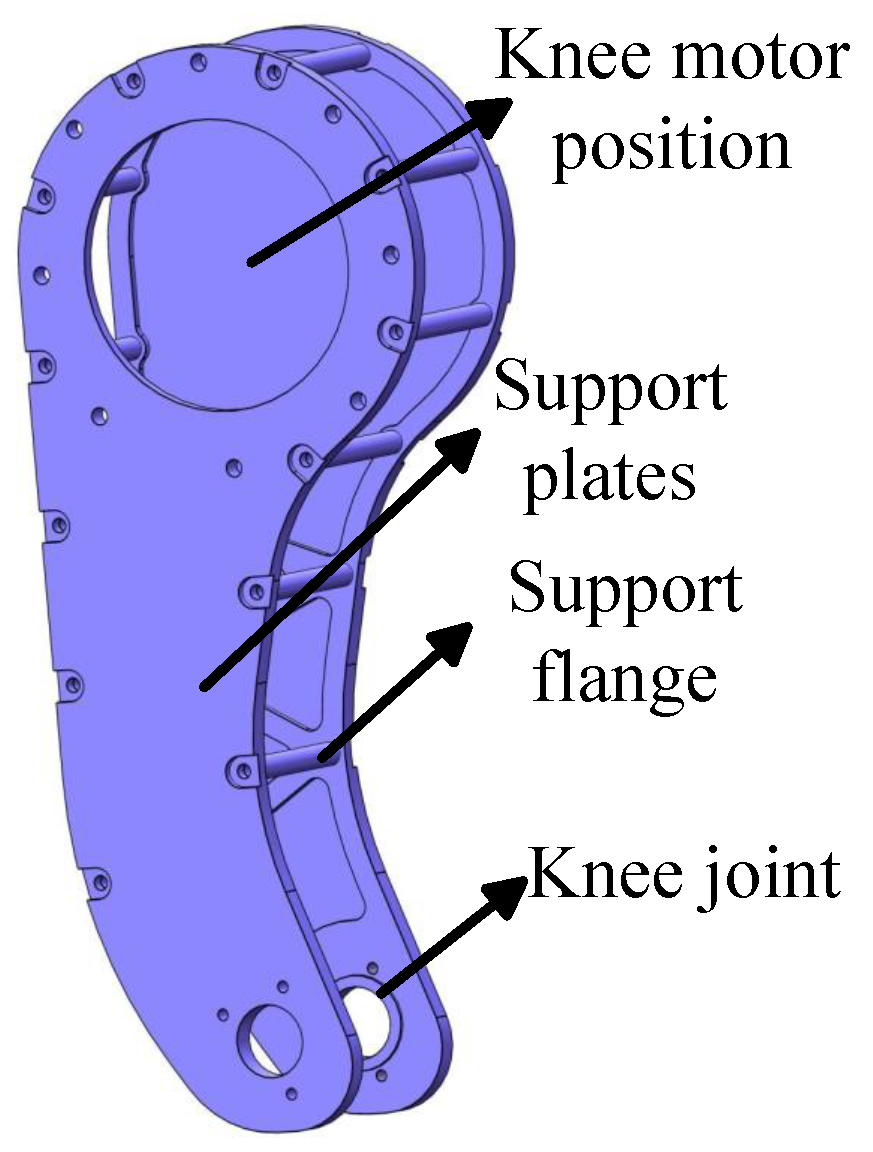
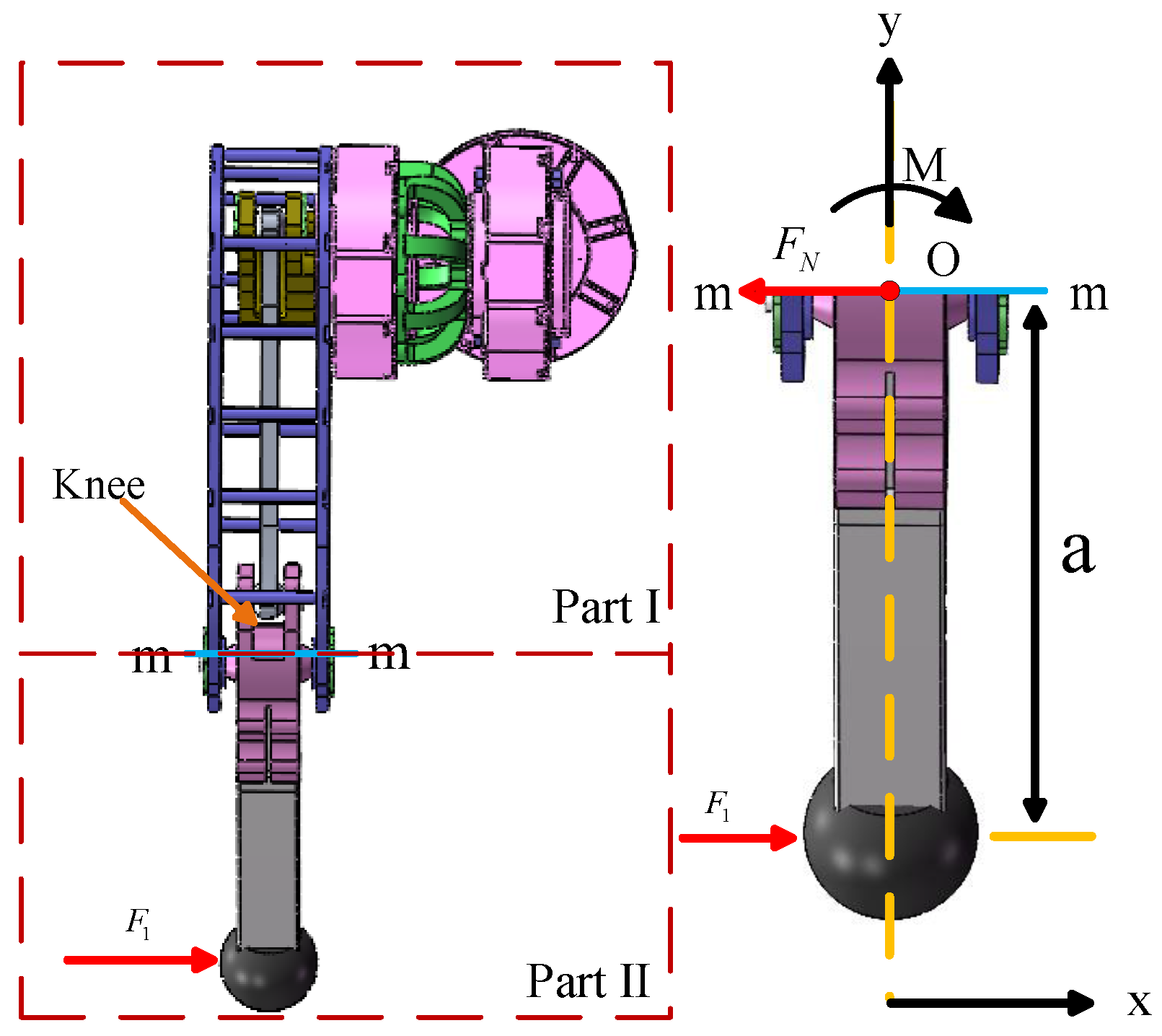
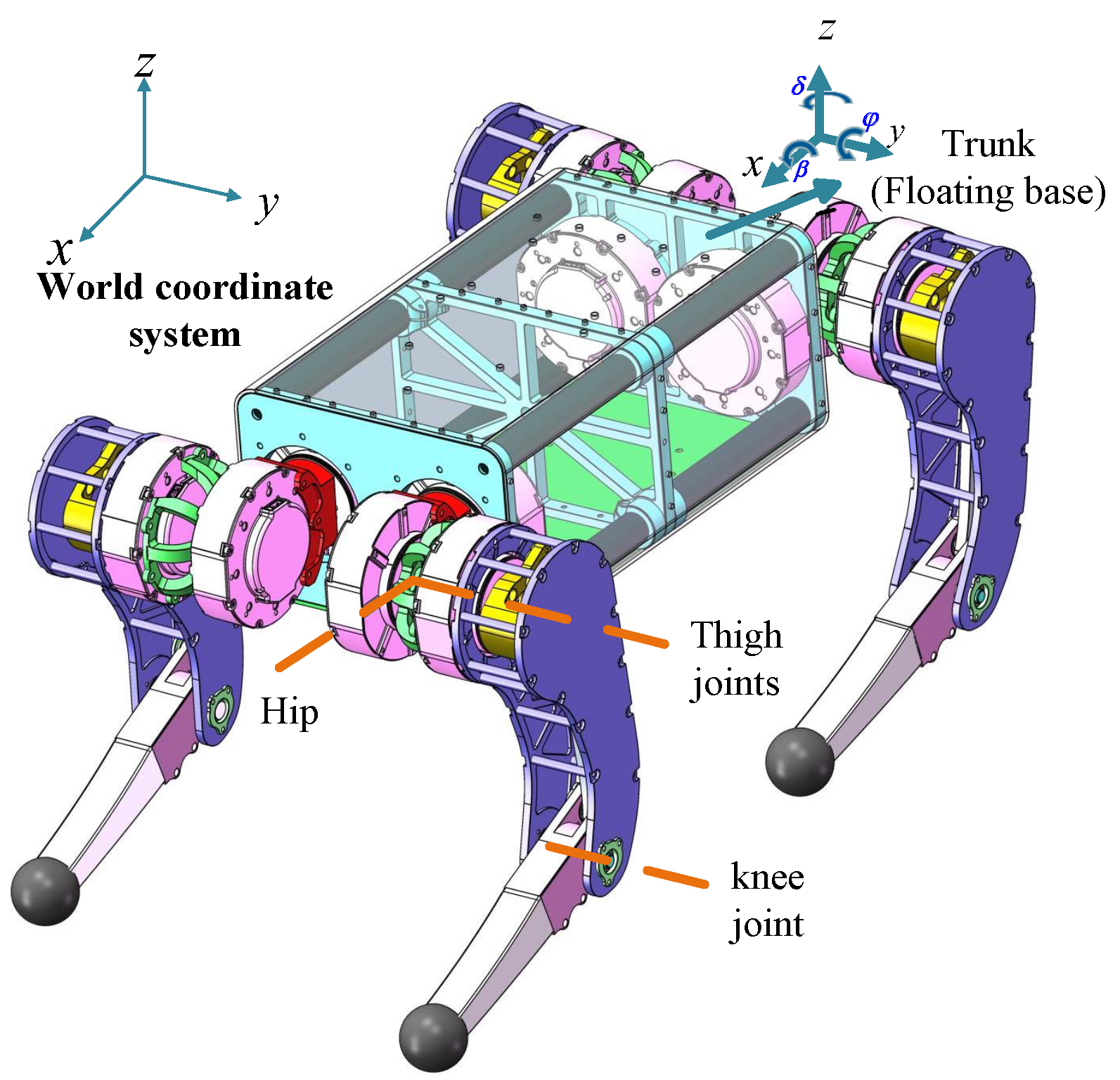
2.2. Design of the Support Mechanism
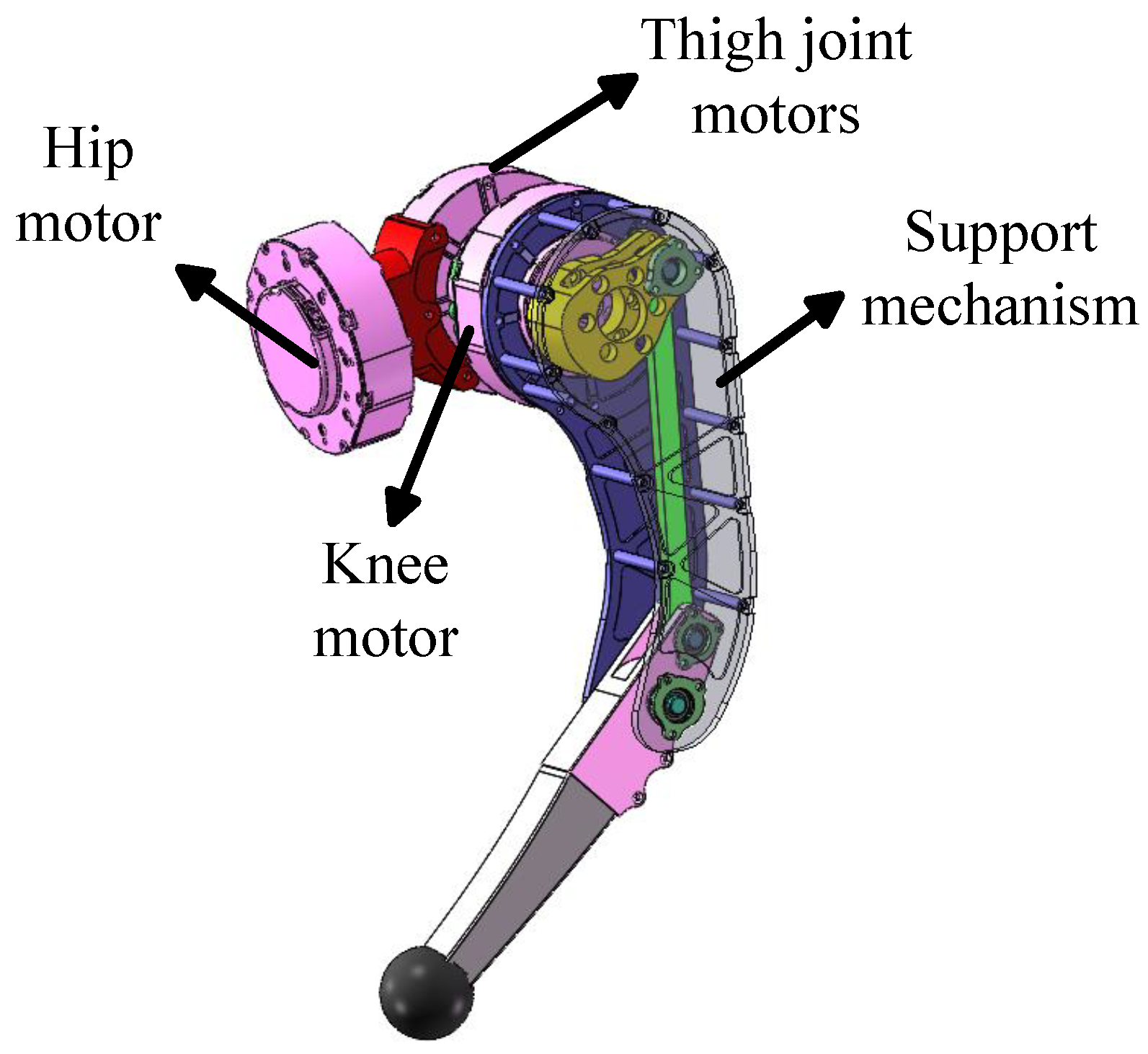
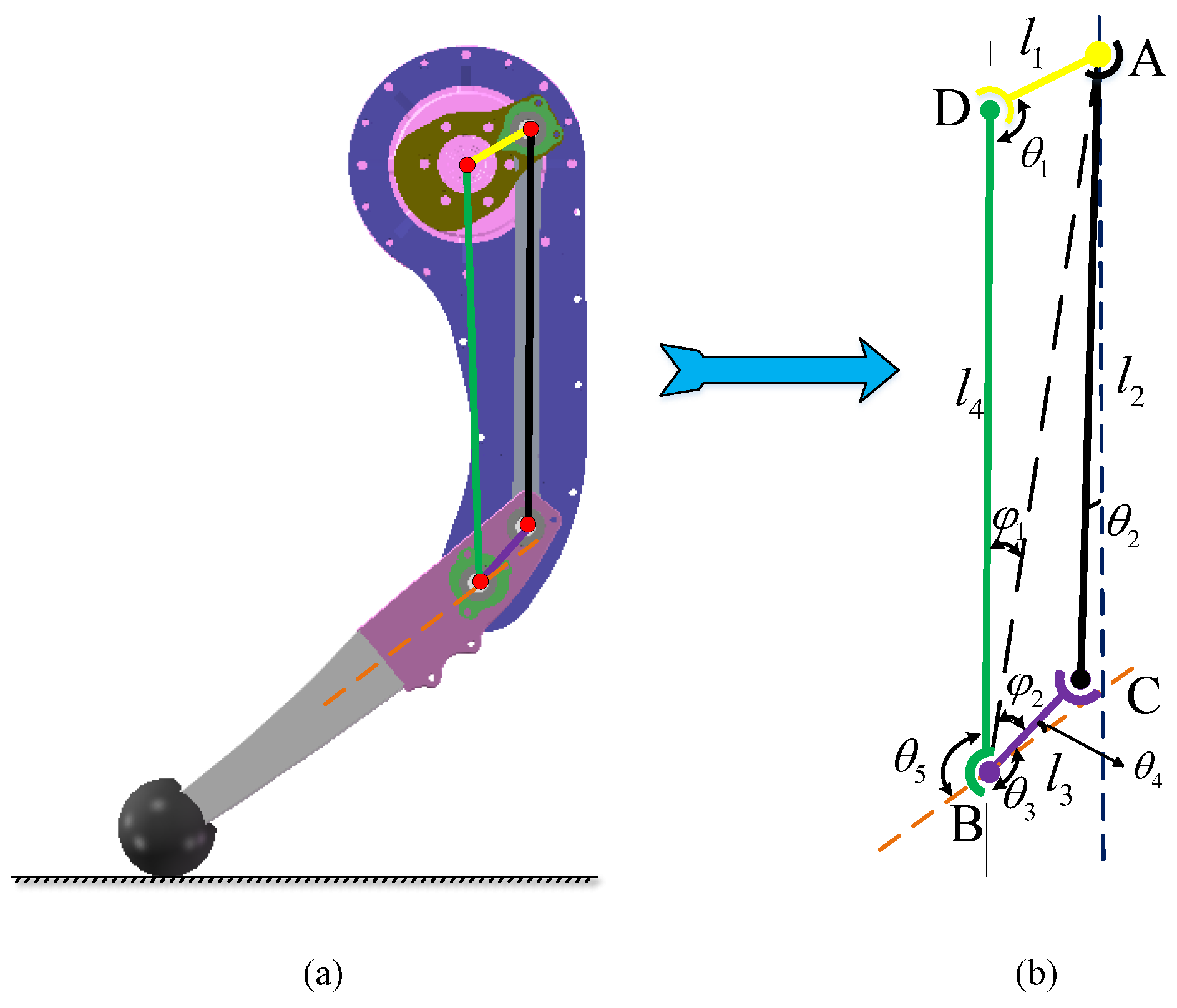
2.3. Leg Transmission Mechanism Design
2.4. Four-Link Kinematics
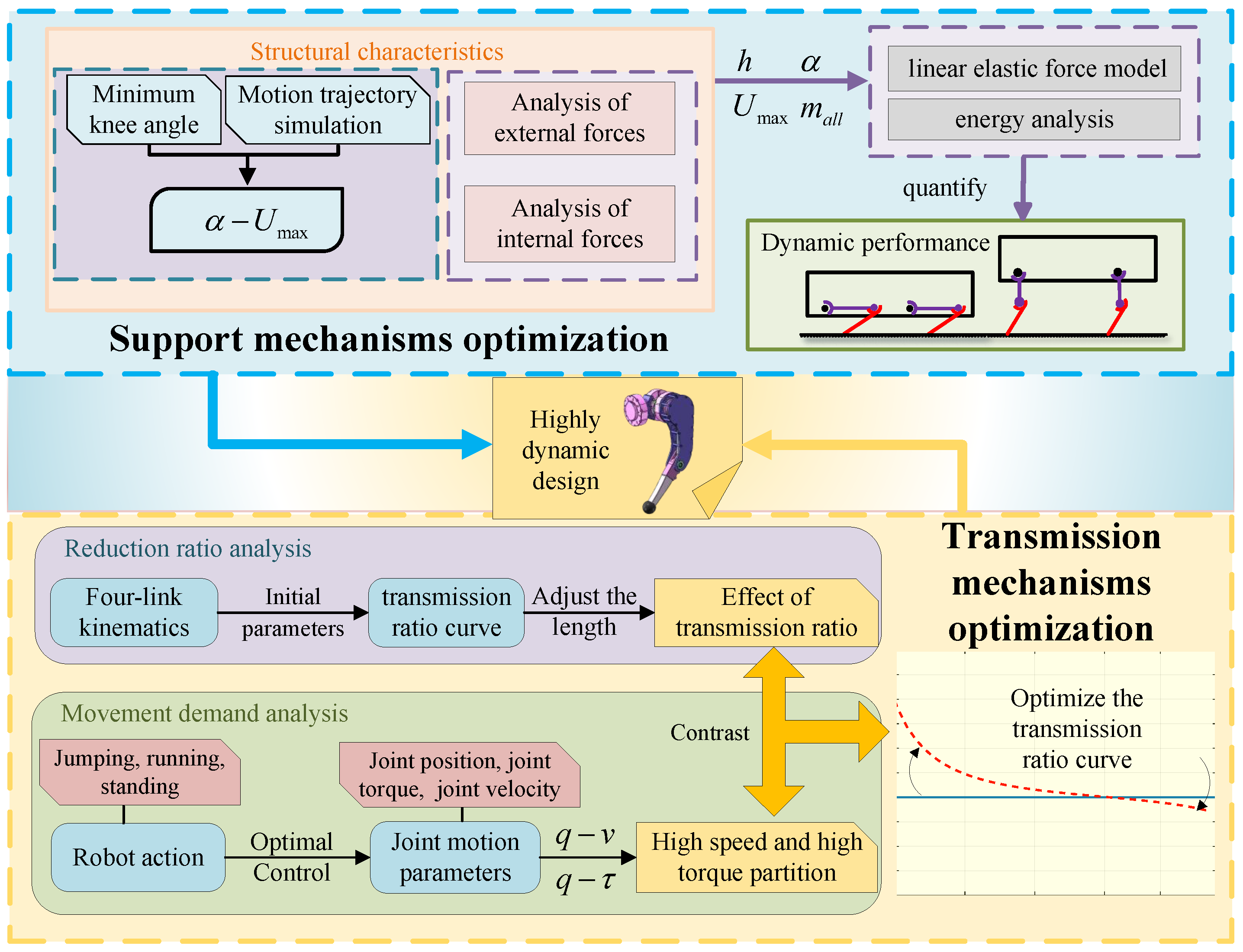
3. Support Mechanisms Optimization
3.1. Force Analysis of the Leg
3.2. Mechanical Performance Analysis of the Support Mechanism
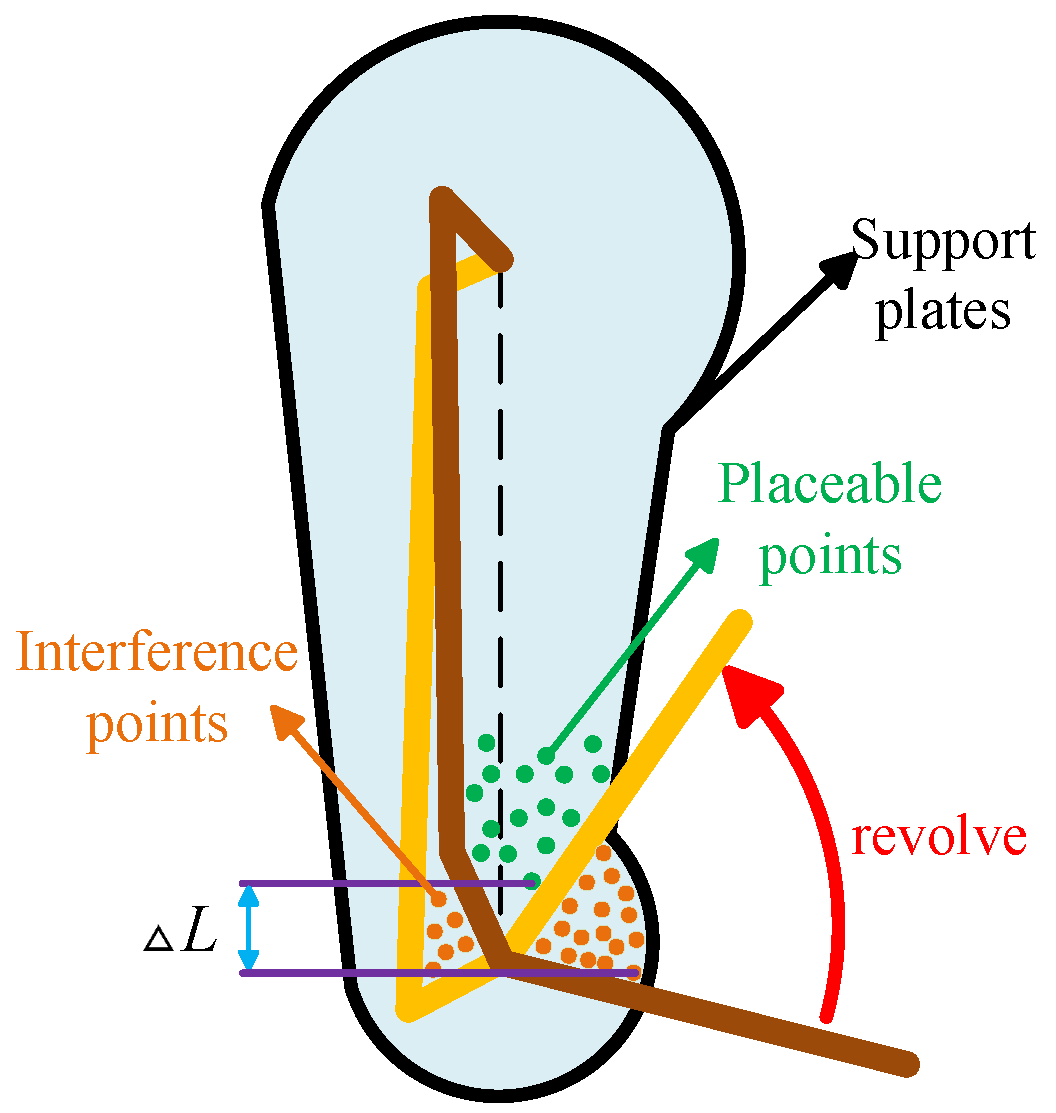
3.3. Analysis of Structure Characteristics and Motion Capabilities
4. Optimization of the Four-Bar Linkage Mechanism
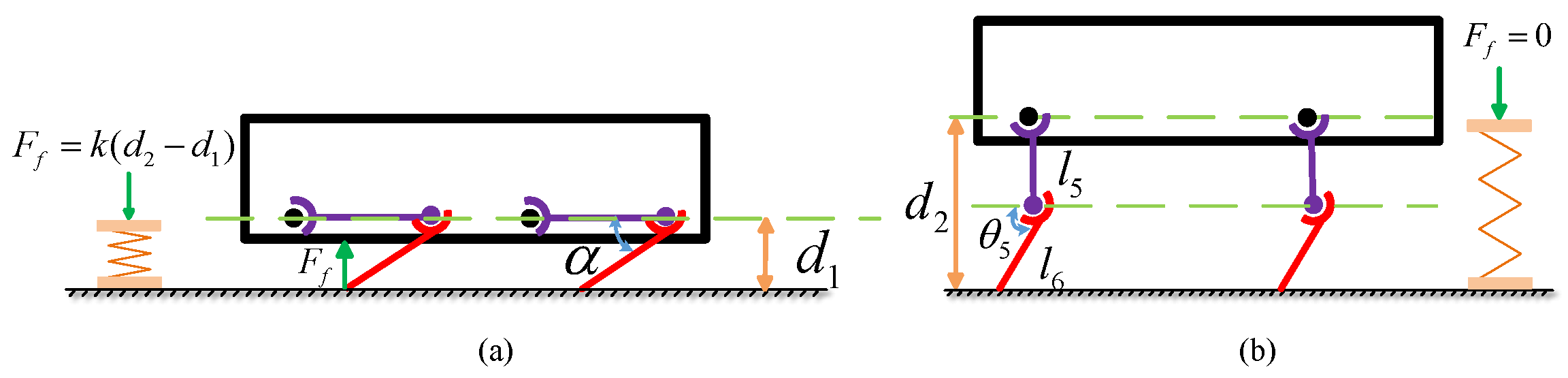
4.1. Variable Transmission Ratio
4.2. Generation of Motion Trajectories
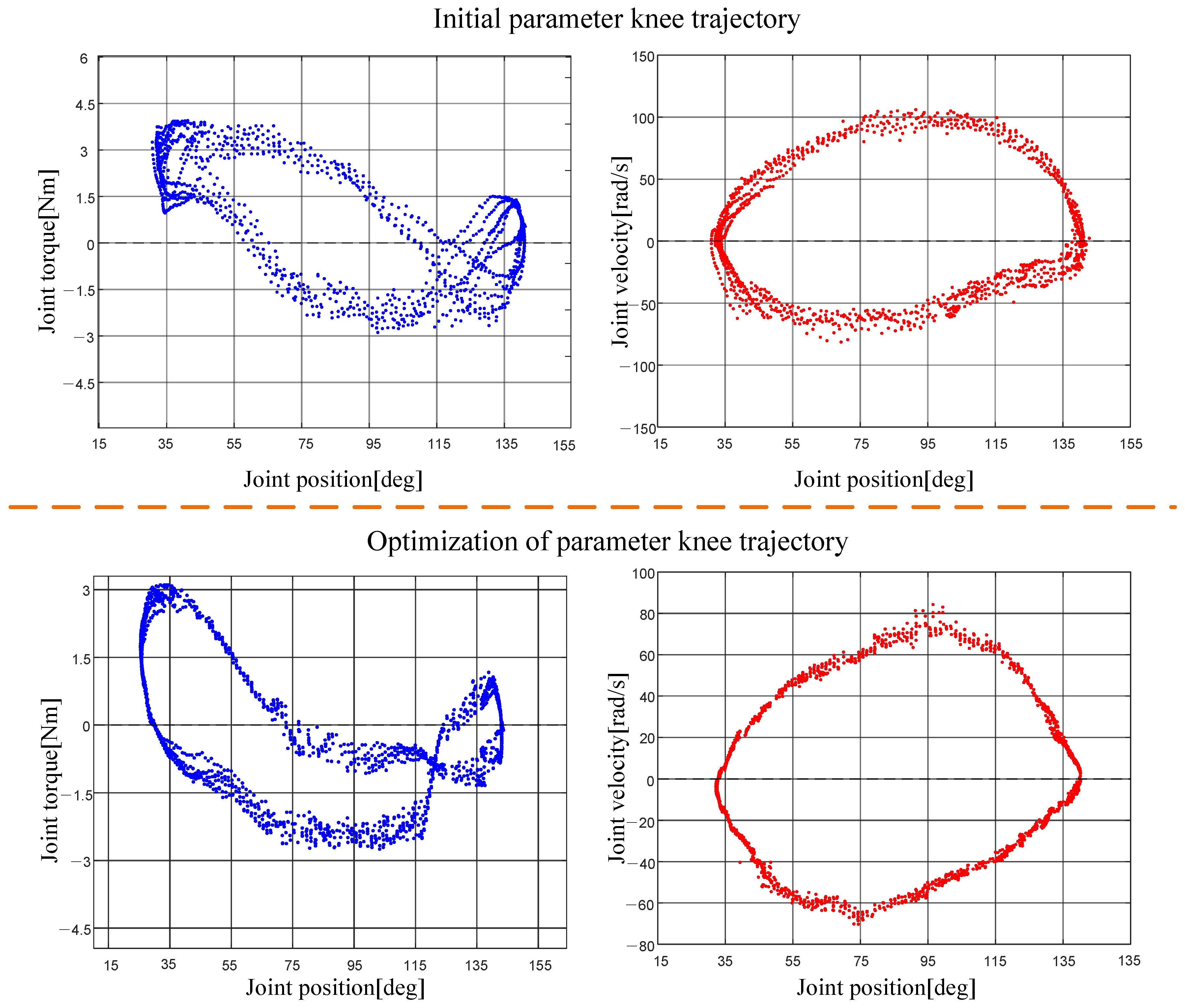
5. Experimental Validation
5.1. Support Mechanism Verification
5.1.1. Support Mechanism Simulation
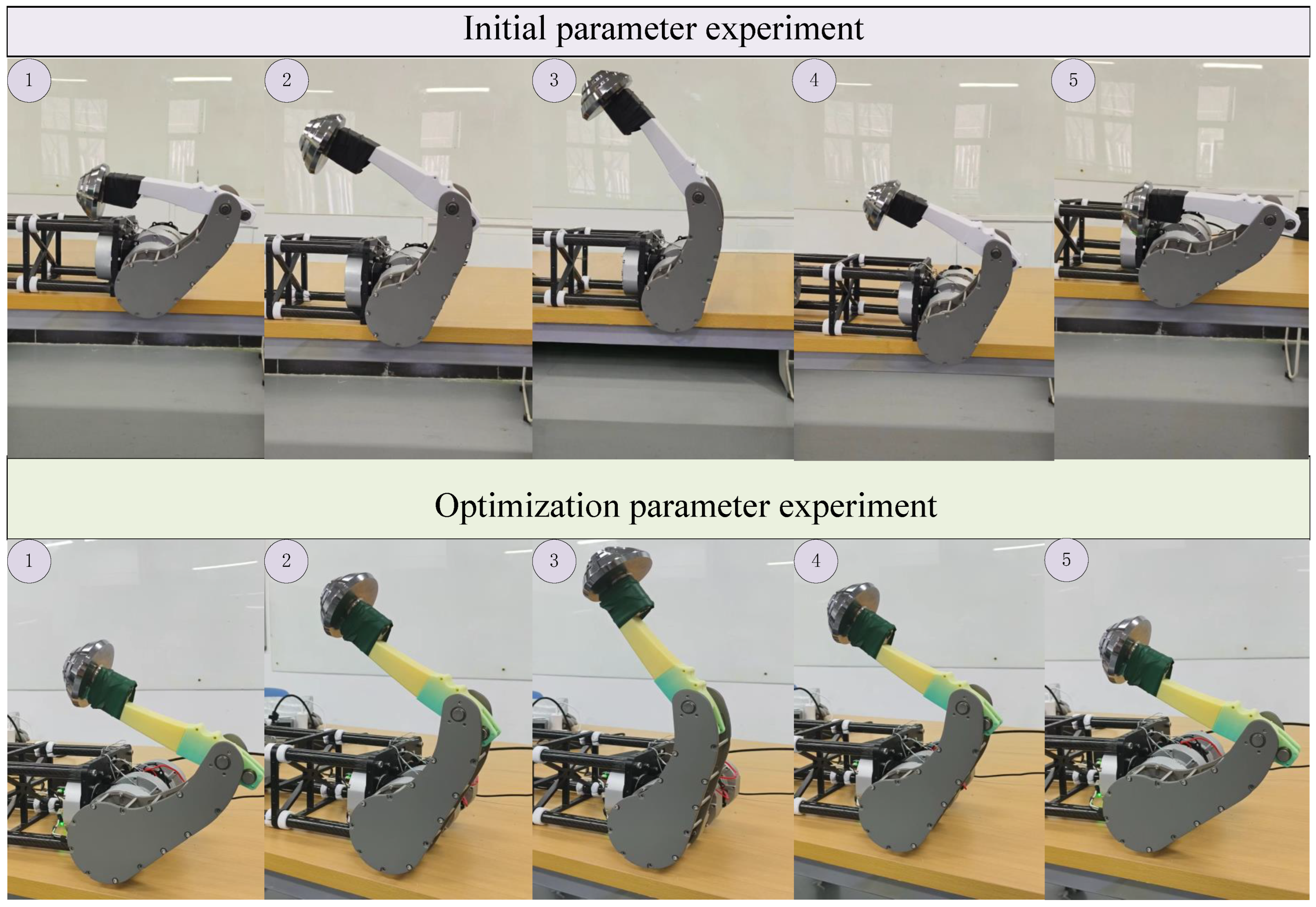
5.1.2. Comparison Experiment
5.2. Transmission Mechanism Experimental Validation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miura, K.; Yoshida, E.; Kobayashi, Y.; Endo, Y.; Kanehioro, F.; Homma, K.; Kajitani, I.; Matsumoto, Y.; Tanaka, T. Humanoid robot as an evaluator of assistive devices. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Abi-Farraj, F.; Henze, B.; Ott, C.; Giordano, P.R.; Roa, M.A. Torque-based balancing for a humanoid robot performing high-force interaction tasks. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englsberger, J.; Ott, C.; Albu-Schäffer, A. Three-dimensional bipedal walking control based on divergent component of motion. Ieee Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Cao, X.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Ceccarelli, M. Progress and development trend of space intelligent robot technology. Space Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 9832053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, N.G.; Caldwell, D.G.; Negrello, F.; Choi, W.; Baccelliere, L.; Loc, V.G.; Noorden, J.; Muratore, L.; Margan, A.; Cardellino, A.; et al. Walk-man: A high-performance humanoid platform for realistic environments. J. Field Robot. 2017, 34, 1225–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, T.; Lohmeier, S.; Ulbrich, H. Humanoid robot lola: Design and walking control. J. Physiol.-Paris 2009, 103, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboutet, Q.; Roux, J.; Janot, A.; Guadarrama-Olvera, J.R.; Cheng, G. Inertial parameter identification in robotics: A survey. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.; Lin, A.; Zhao, X.; Kuang, S. A topology optimization method of robot lightweight design based on the finite element model of assembly and its applications. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103, 0036850420936482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, B.; Zhang, P. Lightweight design optimization for legs of bipedal humanoid robot. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Santacruz, J.; Torres-Figueroa, J.; Portillo-Velez, R.D.J. Design of a human-like biped locomotion system based on a novel mechatronic methodology. Concurr. Eng. 2019, 27, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Kim, S. On extracting design principles from biology: II. Case study—The effect of knee direction on bipedal robot running efficiency. Bioinspiration Biomimetics 2015, 10, 016011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zong, C.; Pancheri, F.; Chen, T.; Lueth, T.C. Design of topology optimized compliant legs for bio-inspired quadruped robots. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthanarayanan, A.; Azadi, M.; Kim, S. Towards a bio-inspired leg design for high-speed running. Bioinspiration Biomimetics 2012, 7, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.H. Mechanical design of the humanoid robot platform, HUBO. Adv. Robot. 2007, 21, 1305–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urata, J.; Nakanishi, Y.; Okada, K.; Inaba, M. Design of high torque and high speed leg module for high power humanoid. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 4497–4502. [Google Scholar]
- Ficht, G.; Behnke, S. Bipedal humanoid hardware design: A technology review. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2021, 2, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuge, A.J.; Herron, C.W.; Beiter, B.C.; Kalita, B.; Leonessa, A. Design, development, and analysis of the lower body of next-generation 3D-printed humanoid research platform: PANDORA. Robotica 2023, 41, 2177–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reher, J.; Ma, W.L.; Ames, A.D. Dynamic walking with compliance on a cassie bipedal robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 18th European Control Conference (ECC), Naples, Italy, 25–28 June 2019; pp. 2589–2595. [Google Scholar]
- Negrello, F.; Garabini, M.; Catalano, M.G.; Kryczka, P.; Choi, W.; Caldwell, D.G.; Bicchi, A.; Tsagarakis, N.G. Walk-man humanoid lower body design optimization for enhanced physical performance. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 1817–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, W.; Ming, A. Explosive electric actuator and control for legged robots. Engineering 2022, 12, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Liu, H.; Meng, F.; Huang, Q. Swift Running Robot Leg: Mechanism Design and Motion-Guided Optimization. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2023, 29, 1702–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, M.; Kolvenbach, H.; Dubois, F.; Lau, H.F.; Hutter, M. Vitruvio: An open-source leg design optimization toolbox for walking robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6318–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, P.; Mohanty, P.K. Development of quadruped walking robots: A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 2017–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenstein, F. An analytical approach to the design of four-link mechanisms. Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1954, 76, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, P.S.; Fatemi, A. Connecting rod optimization for weight and cost reduction. Sae Trans. 2005, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Brandt, R.D. An optimal control approach to robust control of robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1998, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar]






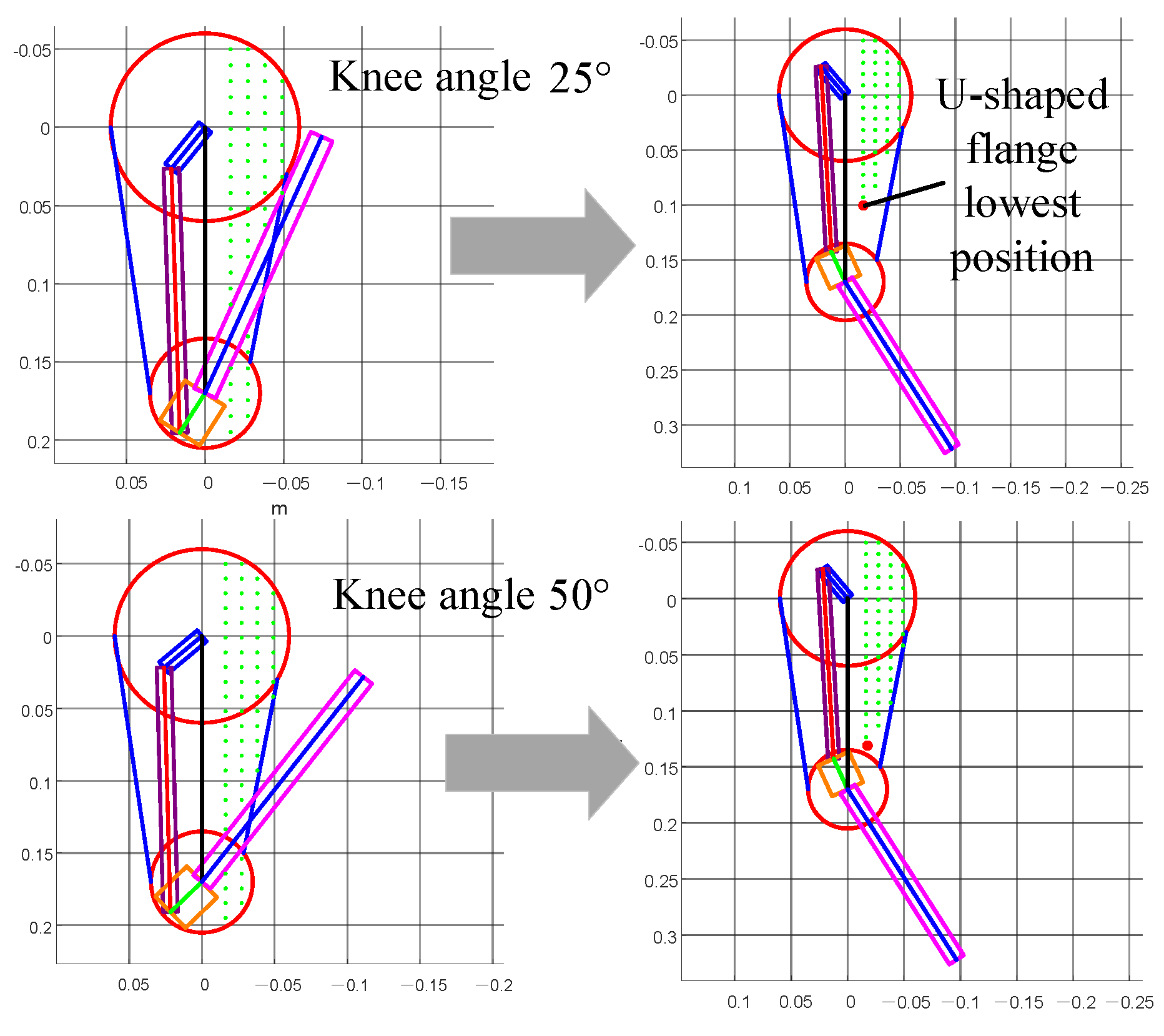
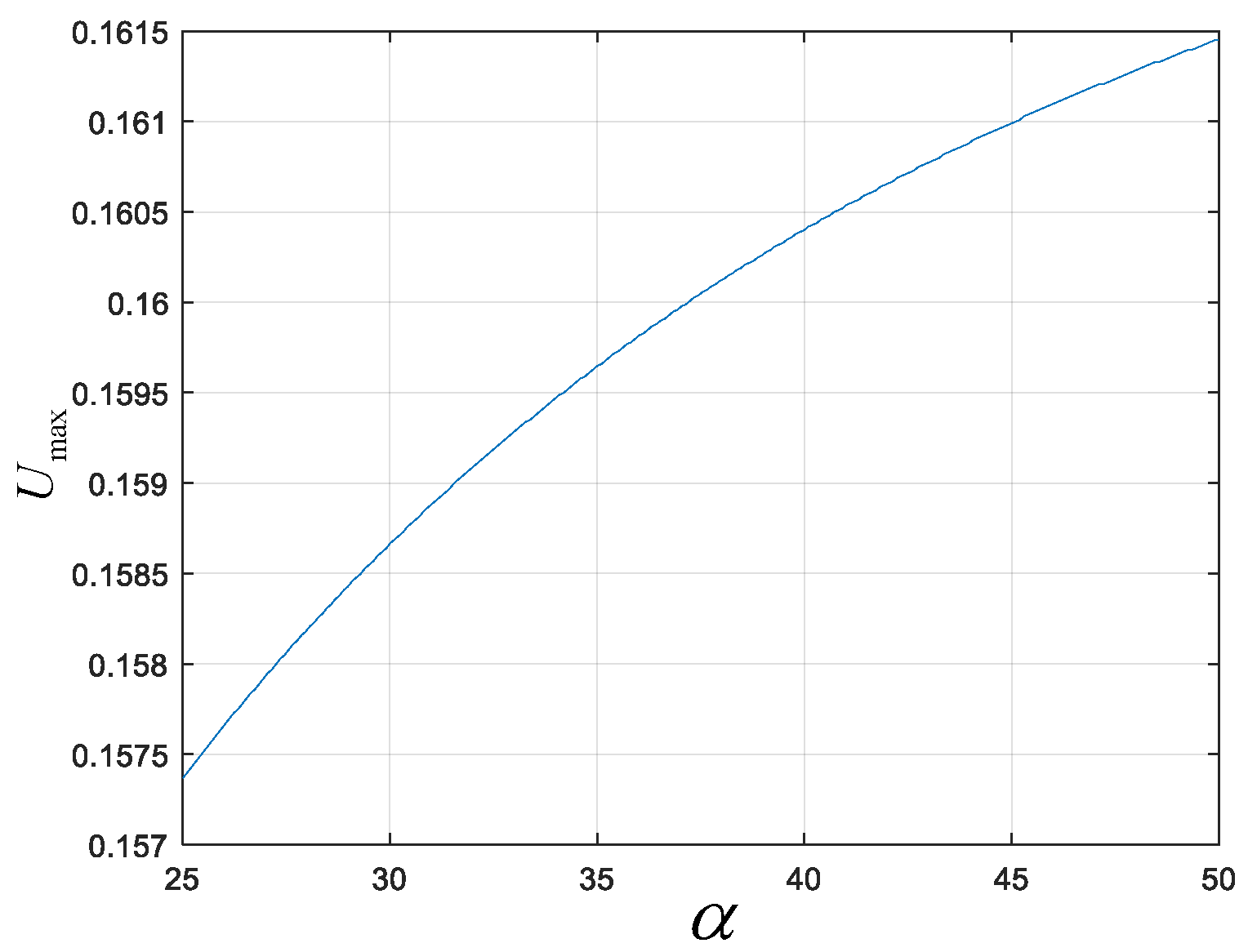

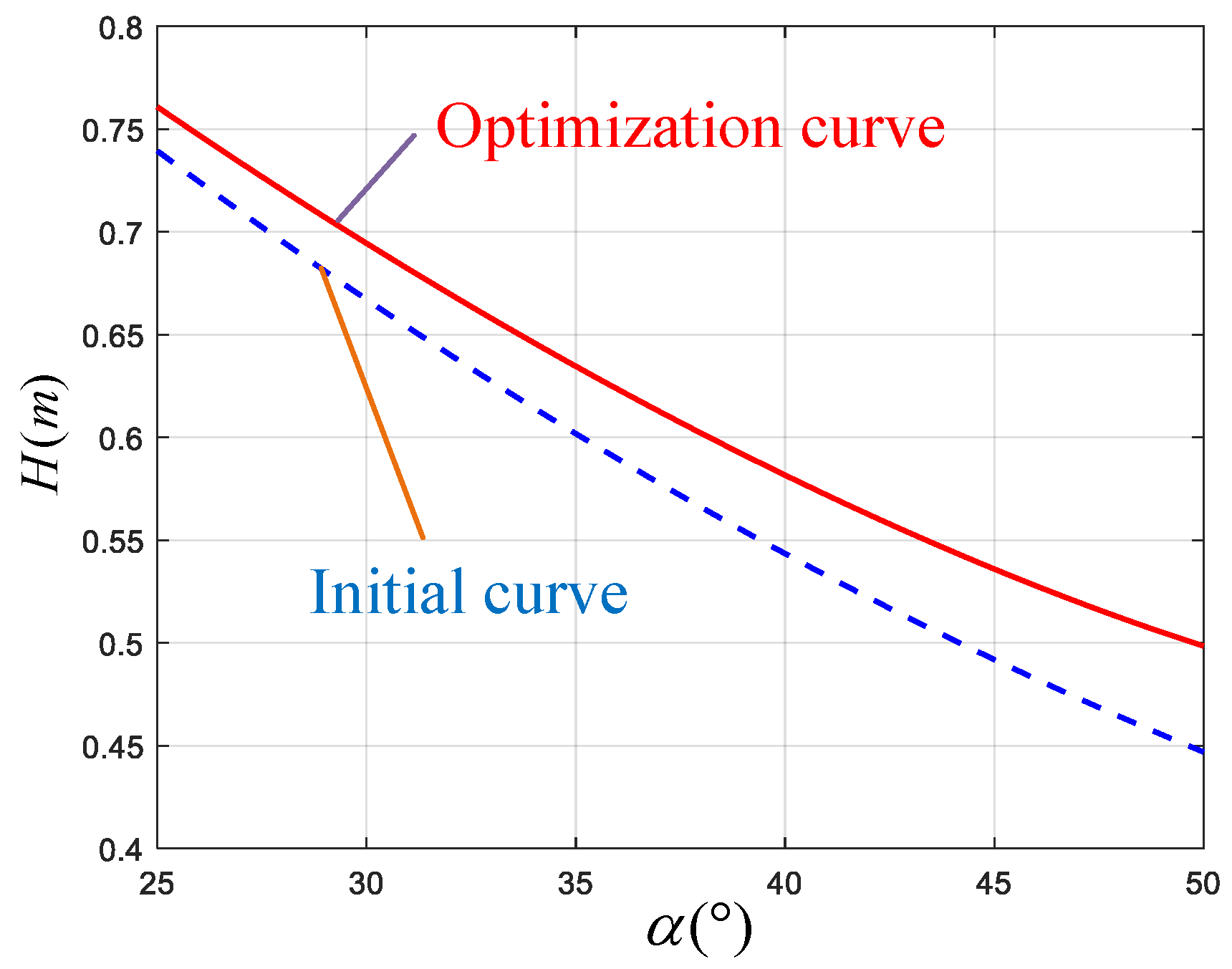
| Parameter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 150 | 0.01 | 55.2 | 75 |
| H | /m | h/m | / | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 25 | 0.1574 | 0.0055 | 0.22 |
| H | /m | h/m | / | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.59 | 30 | 0.1586 | 0.005 | 0.02 |
| Parameter | Before Optimization | After Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| (m) | 0.03 (m) | 0.029 (m) |
| (m) | 0.17 (m) | 0.179 (m) |
| (m) | 0.03 (m) | 0.03 (m) |
| (m) | 0.17 (m) | 0.17 (m) |
| 0 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Motion-Based Optimization of Support and Transmission Mechanisms for Legged Robots. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030173
Zhang K, Cai Z, Zhang L. Dynamic Motion-Based Optimization of Support and Transmission Mechanisms for Legged Robots. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(3):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030173
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kun, Zhaoyang Cai, and Lei Zhang. 2025. "Dynamic Motion-Based Optimization of Support and Transmission Mechanisms for Legged Robots" Biomimetics 10, no. 3: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030173
APA StyleZhang, K., Cai, Z., & Zhang, L. (2025). Dynamic Motion-Based Optimization of Support and Transmission Mechanisms for Legged Robots. Biomimetics, 10(3), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10030173






