Abstract
Hearing loss is one of the more common occupation health hazards across the globe yet is preventable. Extensive research has been done across a number of industries measuring the magnitude and frequency of hearing impairment. This study uses the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data to analyze hearing impairment in the United States. Regression and structural equation models were developed utilizing this publicly available data. A statistically significant correlation exists between general hearing condition and ethnicity, χ2 (30, N = 8897) = 264.817, p < 0.001. A statistically significant correlation exists in this database between general hearing condition and gender, χ2 (6, N = 8897) = 40.729, p < 0.001. An ordinal logistic regression was significant between the general health and ethnicity, χ2 (30, N = 5968) = 212.123, p < 0.001. A structural equation model presents the first of its type for this area of research. Focusing on addressing diversity issues may be the foundation for hearing health improvement. Tools such as smartphone apps may be useful for tracking hearing loss within the workforce.
1. Introduction
There is a lack of awareness regarding hearing loss, the impacts it poses, and its management among policymakers and the public [1,2]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), “approximately 50% of hearing loss could be prevented and most of the remainder could be treated effectively” [2]. “Healthy People 2020 has identified several goals to address the rising burden of hearing loss” [3]. This program, now rebranded as “Healthy People 2030” for the new decade, has the national goals of health promotion and disease prevention. According to Goman, Reed, and Lin, “by providing baseline measures, ambitious yet achievable targets, and tools and guidance to reach population health goals, the Healthy People initiative serves as a roadmap for the nation’s health. Healthy People is a federally led, stakeholder-driven initiative housed in U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (ODPHP)” [4].
As the average life expectancy in the United States continues to rise, along with an increasing age of retirement, the number of persons with hearing loss will grow [5]. “The risk of hearing loss due to occupational exposure is substantial” and the ‘implementation of hearing conservation programs in occupational settings will decrease this risk” [6,7]. A reduction in noise levels, improved regulations, and the use of protective equipment are effective strategies to lessen the incidence of occupational hearing loss [8].
Noise mitigations are needed to prevent citizens from being exposed to a level of noise that will lead to negative health effects such as sleep disorders with awakenings [9], learning impairment [10], impaired work performance [11,12], and hypertension [13,14]; other factors include intensity variation over time, the impulsivity of events, the frequency distribution, and psychoacoustics parameters [15].
2. Background
2.1. Violation History
Between 1972 and 2019, 119,305 violations were recorded involving four noise standards: “29 CFR 1910.95, occupational noise exposure in general industry; 1926.52, occupational noise exposure in construction; 1926.101, hearing protection in construction, and 1904.10, recording criteria for cases involving occupational hearing loss” [16]. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (“OSHA”) has set occupational hearing loss recordable criteria using a standard threshold shift (“STS”), a “change from an ear’s audiometric baseline of 10 dB averaged over 2 kHz, 3 kHz, and 4 kHz [17].”
The most commonly violated noise standard was 1910.95, Occupational Noise Control, in manufacturing [16]. Park states that the four most frequently cited noise standards were a lack of feasible administrative or engineering controls (1910.95 [b] and 1926.52 [d]) and an inadequate hearing conservation program (1910.95 [c] and 1926.52 [b]). These violations were more highly penalized (μ = $1036.50) than other subparagraph violations (μ = $915.80).
2.2. Hearing as a Public Health Issue
Compared with other health conditions that are common in the United States, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, relatively little is known about the public health burden associated with hearing loss, and the condition tends to go untreated and underreported [18]. Workers with hearing loss earned an average of $35,000, compared with $47,000 for those with typical hearing [19]. Lost productivity was estimated at $1.8 billion to $194 billion annually in the United States [20]. Diminished quality of life (DQL) is another factor in hearing impairment, quantifying the likelihood of biological consequences of an exposure incident [21].
Hearing impairment does not exclude any industry. Dental professionals, particularly dental assistants and technicians, have a risk of hearing impairment three to twenty times higher than other occupations and can be directly attributable to noise generated by faulty or worn dental equipment [22]. Workers exposed to organic solvents have been shown to be at increased risk of high-frequency hearing loss [23]. Associations between hearing loss and benzene [OR 1.50; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.15–1.94], ethylbenzene (OR 1.31; 95% CI 1.04–1.67), and toluene (OR 1.29; 95% CI 1.04–1.60) were statistically significant as reported by Staudt and others.
Epidemiological evidence demonstrates that farm youth are at disproportionate risk for negative health effects of noise exposure, with risk factors including frequent exposure to high farm noise, including firearms and all-terrain vehicles, from an early age [24,25,26]. These farm youth have lower hearing ability than their urban peers [26,27]. Logistic regression analyses have shown that “occupational noise exposure partially accounted for higher levels of hearing difficulties in the agricultural industry compared with finance, and occupational noise exposure, older age, low socioeconomic status, and non-white ethnic background partially accounted for higher levels of hearing difficulties in the construction industry” [28].
Differences in demographic, health, and lifestyle factors could also contribute to high levels of hearing difficulties and tinnitus in some industries [28]. The levels of tinnitus were greatest for music and construction industries compared with finance, and these differences were accounted for by occupational and music noise exposure, as well as older age [29,30]. Blue collar compared with white collar workers were significantly more likely to have hearing loss (p < 0.05) [31].
3. Methodology
All analyses were conducted with Stata/MP 16.1 for Mac (64-bit Intel) by StataCorp (www.stata.com, accessed 10 April 2023). Stata’s Survey Data Analysis feature was utilized to adjust for sample weighting. Data were provided by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (“NHANES”) [32]. Four databases were used: Audiometry (“AUQ_J”), Demographics (“DEMO_J”), Current Health Status (“HSQ_J”), and Occupation (“OCQ_J”). Records between the four databases were matched by the respondent sequence number. Terminology, including genders and ethnicities, were taken directly from the NHANES survey (https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm accessed on 5 March 2023). Significance levels were set to 0.01, with confidence intervals at 99 percent for all tests.
3.1. Variables
A total of 88 variables across the sample population (N = 9254) were analyzed. Interaction variables were created to evaluate the effects of an additional variable on another exploratory variable to a response.
3.2. Statistical Analyses
Several bivariate analyses were conducted to examine the relationships between some of the other variables collected in this study. They consist mostly of Pearson’s chi-square in order to reveal any significant association between two variables. The χ2 test of independence can be used with data in which each subject is measured by two categorical variables. The test assumes a χ2 distribution. The statistical procedure follows the same type of process, as does the χ2 test of independence, in which the observed frequency of cases in each cell is compared to an expected number. The observed frequencies in each cell are then compared to the frequencies that were expected for significance [33].
In the case where we have multiple independent samples, and where we would ordinarily perform a between-subjects ANOVA, the Kruskal–Wallis test is the designated nonparametric alternative test [34].
Sometimes, treating the outcome variable as a quantitative, interval-level measure is problematic. Many surveys have response options, such as agree, do not know, and disagree. In such cases, we can score these so that 1 is agree, 2 is do not know, and 3 is disagree, and then we can do an ANOVA. However, some researchers might say that the score was only an ordinal-level measure, so we should not use ANOVA. The Kruskal–Wallis rank test lets us compare the median score across the groups [35].
Logistic regressions incorporated a number of predictor variables on the outcome of hearing damage (0 = no hearing damage, 1 = at least some hearing damage occurred). Where outcomes were discrete rather than continuous (i.e., ordinal responses), an ordinal logistic regression was conducted. These ordinal regressions were used where responses to survey data provided an outcome variable whose value existed on an arbitrary and ordered scale [36,37].
3.3. Structural Equation Modeling (“SEM”)
Regression models test hypotheses about relationships between predictor and outcome variables. Unlike standard regression models, SEM accommodates regression relationships between several latent variables and between observed and latent variables [38].
SEM presents models as a path diagram as in Figure 1.
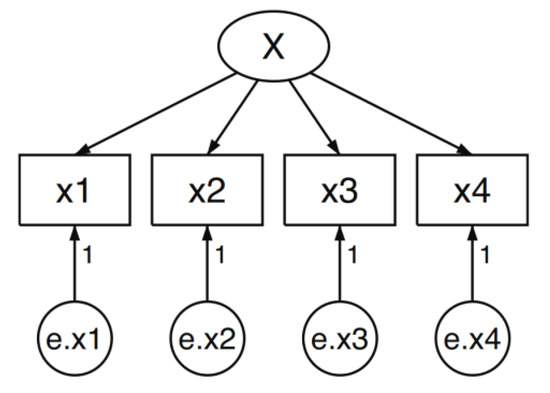
Figure 1.
Structural equation model.
Boxes contain variables that are observed in the data. Circles contain variables that are unobserved, or latent variables. Arrows, called paths, connect the boxes and circles.
4. Results
4.1. Analysis by Ethnicity
Self-reported hearing conditions were scored in the survey as 1 = “Excellent”, 2 = “Good”, 3 = “A little trouble hearing,” 4 = “Moderate trouble hearing”, 5 = “A lot of trouble hearing”, and 6 = “Deaf”. A statistically significant correlation exists in this database between the general hearing condition and ethnicity, χ2 (30, N = 8897) = 264.817, p < 0.001. Table 1 presents the data analysis.

Table 1.
Means of self-reported hearing condition by ethnicity.
A Kruskal–Wallis H-test was conducted to determine if hearing conditions differed by ethnicity: “Mexican American” (N = 1294), “Other Hispanic” (N = 782), “Non-Hispanic White” (N = 3006), “Non-Hispanic Black” (N = 2050), “Non-Hispanic Asian” (N = 1163), and “Other Race” (N = 602). This H-test showed that there was a statistically significant difference in self-reported hearing condition, χ2 (5) = 204.553, p < 0.001.
4.2. Analysis by Gender
Self-reported hearing conditions were scored in the survey as 1 = “Excellent”, 2 = “Good”, 3 = “A little trouble hearing”, 4 = “Moderate trouble hearing”, 5 = “A lot of trouble hearing”, and 6 = “Deaf”. A statistically significant correlation exists in this database between general hearing condition and gender, χ2 (6, N = 8897) = 40.729, p < 0.001. Females (µ = 1.791, 99% CI [1.735, 1.847]) reported a generally better hearing health than males (µ = 1.887, 99% CI [1.823, 1.951]).
4.3. Analysis by Preexisting Conditions
Self-reported general health was scored in the survey as 1 = “Excellent,” 2 = “Very good,” 3 = “Good,” 4 = “Fair,” and 5 = “Poor.” A statistically significant correlation exists in this database between general health and hearing conditions, χ2 (36, N = 5968) = 401.477, p < 0.001). Table 2 presents the data analysis results.

Table 2.
Respondent health and hearing condition.
4.4. Logistic Regression
Ordinal variables are typically coded as consecutive integers from “1” to the number of categories. Analyzing ordinal outcomes with a linear regression model is appealing yet incorrect as they violate the assumptions of linear regression models [39].
The literature review did not reveal any previous studies that used ordinal logistic regression to analyze reported hearing conditions, particularly using demographics as the predictors. Gender (binary), age (interval), and general health (ordinal) showed statistical significance with a relatively low effect. The results are presented in Table 3. The model developed is statistically significant (p < 0.001) when weighted for population size (N = 13,887,180).

Table 3.
NHANES factors and their impact on general hearing.
The six cut points above (“/cut”) are for the levels of the latent response variable not accounted for within the database. Figure 2 and Equation (1) below represent the observed general hearing variable mapped to a latent continuous hearing variable and its solved equations [39]. Those who receive a latent score less than 2.567 are classified as having “Excellent” hearing; those who receive a latent score between 3.823 and 4.527 are classified as having “Good” hearing, and so on.
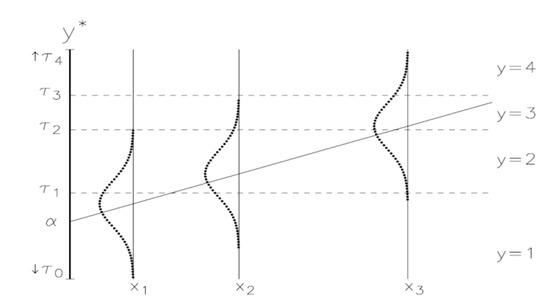
Figure 2.
Model of latent variable cutoffs from ordered logistic regression.
A system of equations for this ordinal logistic regression can be represented as:
The general hearing condition was recoded into a binary variable where “Excellent” and “Good” were coded as a “1” and the remaining options were coded as a “0.” A multiple logistic regression was applied with this new dependent variable and the NHANES factors from the ordinal logistic regression, but no significance was revealed.
General health was further investigated after its significance was revealed during the ordinal logistic regression. Table 4 presents the data analysis for general health scores by ethnicity, where the scale ranged from 1 (“Excellent”) to 5 (“Poor”). There is statistical significance between the two variables, χ2 (30, N = 5968) = 212.123, p < 0.001. A Kruskall–Wallis rank test shows a statistically significant difference for those who identified as “Other Hispanic” and “Other Race,” χ2 (5) = 163.089, p < 0.001.

Table 4.
Mean general health scores by ethnicity.
4.5. Structural Equation Modeling
Demographics (“DEM”) was created as a latent variable—one not directly observed—and was analyzed through the Structural Equation Modeling feature in Stata 16. Five variables taken from NHANES were used to build DEM: “riagendr” (gender), “ridageyr” (age), “ridreth3” (ethnicity), “dmdeduc2” (education), and “indhhin2” (income). Techniques used for these types of variables followed standard reported SEM modeling guidelines [40]. Table 5 and Figure 3 present the Stata output for the model as well as the path diagram created by it. It is crucial to clarify that the SEM built and analyzed a latent variable and not the typical dependent variable used earlier—hearing condition.

Table 5.
Socioeconomics as a latent variable on general hearing.
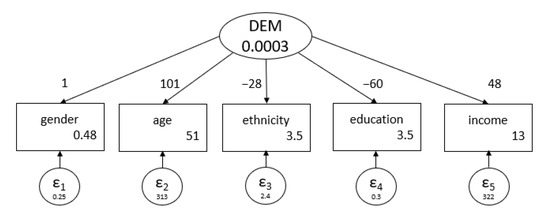
Figure 3.
Path diagram of DEM as a latent variable.
The path diagram displays the coefficients of association between the latent variable and the observed variables on the arrows [38,40,41]. The 95% confidence intervals span a wide range under statistically significant outcomes. This is likely due to the mixture of the different types of observed variables, including dichotomous, ordinal, and interval. The errors, reported as “e.variable_name”, had a narrow 95% confidence interval. A goodness of fit for the model indicated that the observed variables predicted 80.76% of the variance (R2 = 0.8076, p < 0.01).
5. Discussion
An analysis of the self-reported data indicates correlations between certain demographics and general hearing health. Non-Hispanic White respondents recorded a significantly better hearing condition than other ethnicities. This is consistent with reported disparities associated in hearing health care in the United States [42]. Preexisting conditions and gender are strongly correlated with hearing health are magnified by demographic variables.
Hearing loss has an impact on work ability, communication, the understanding of instructions, and the awareness of hazards in the immediate vicinity.
This was the first ordinal logistic regression conducted on this set of NHANES data, and we correlated the associations between hearing condition and age, general health, and gender. The unobserved latent variables associated with general hearing conditions were measured, and the accompanying expressions were developed.
A latent variable was created based on demographic data to develop a path model between the observed and unobserved variables.
As smartphones continue to evolve into personal health monitoring devices, hearing conservation apps are becoming commonplace on the Google Play Store (Android devices) and the Apple App Store (iOS devices). One study used a repeated measures (RM) analysis of variance (ANOVA), testing for significance between noise signal sources for different phone models and sound levels [43]. McLennon [43] reports a significant between-phone effect in the RM-ANOVA completed for each phone type based on operating system: F(1,4)iOS = 10.4, p = 0.03, F(1,4) Android = 8.4, p = 0.04). Android apps were found to underreport sound levels at the 90 dBA sound level. iOS apps presented a smaller error ranges than their Android versions. A strong positive correlation between hearing assessment apps and standard procedures (i.e., otoscopy and tympanometry) has been measured (r = 0.79) [44]. Smartphone-based solutions may prove to be useful in resource-limited settings [45], and any necessary calibration, as well as frequency checks, should be followed.
6. Conclusions
Safety managers and employers in general can be the driving force in meeting and exceeding the Healthy People Objective of hearing conservation. Focusing in on addressing diversity issues may be the foundation for hearing health improvement. A foundation can be built by promoting diversity in the safety workforce, which may foster innovative ideas, viewpoints, and tactics, ultimately bringing in measurable change [46,47].
Smartphone apps show promise as a tool for capturing hearing loss progression. Apps using a pure tone threshold have shown high sensitivity and specificity in hearing loss detection [48]. Employers using apps need to ensure that background noises are kept to a minimum when using tone thresholds as they can interfere with the subjects [49].
Noise-induced hearing loss attributed to a workplace condition may result in an employee’s eligibility for compensation [50], so safety managers and human resource professionals need to address this occupational health issue with a toolset as diverse as their workforce.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available through NHANES https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm accessed on 5 March 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mackenzie, I.; Smith, A. Deafness—The neglected and hidden disability. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2009, 103, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.S.; Tucci, D.L.; Merson, M.H.; O’Donoghue, G.M. Global hearing health care: New findings and perspectives. Lancet 2017, 390, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reavis, K.M.; Tremblay, K.L.; Saunders, G. How Can Public Health Approaches and Perspectives Advance Hearing Health Care? Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, A.K.; Kramer, K.T.; Teitelbaum, J.B. Healthy People: The Role of Law and Policy in the Nation’s Public Health Agenda. J. Law Med. Ethics 2019, 47, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goman, A.M.; Reed, N.S.; Lin, F.R. Addressing Estimated Hearing Loss in Adults in 2060. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lie, A.; Skogstad, M.; Johannessen, H.A.; Tynes, T.; Mehlum, I.S.; Nordby, K.-C.; Engdahl, B.; Tambs, K. Occupational noise exposure and hearing: A systematic review. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2016, 89, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Addressing the Rising Prevalence of Hearing Loss; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.R. Hearing Loss Prevalence in the United States. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzet, A. Environmental noise, sleep and health. Sleep Med. Rev. 2007, 11, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minichilli, F.; Gorini, F.; Ascari, E.; Bianchi, F.; Coi, A.; Fredianelli, L.; Licitra, G.; Manzoli, F.; Mezzasalma, L.; Cori, L. Annoyance Judgment and Measurements of Environmental Noise: A Focus on Italian Secondary Schools. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukić, L.; Mihanović, V.; Fredianelli, L.; Plazibat, V. Seafarers’ Perception and Attitudes towards Noise Emission on Board Ships. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Prato, A.; Lesina, L.; Schiavi, A. Effects of low-frequency noise on human cognitive performances in laboratory. Build. Acoust. 2018, 25, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dratva, J.; Phuleria, H.C.; Foraster, M.; Gaspoz, J.-M.; Keidel, D.; Künzli, N.; Liu, L.-J.S.; Pons, M.; Zemp, E.; Gerbase, M.W.; et al. Transportation Noise and Blood Pressure in a Population-Based Sample of Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, D.; Licitra, G.; Vigotti, M.A.; Fredianelli, L. Effects of Exposure to Road, Railway, Airport and Recreational Noise on Blood Pressure and Hypertension. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredianelli, L.; Lercher, P.; Licitra, G. New Indicators for the Assessment and Prevention of Noise Nuisance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Johnson, M.D.; Hong, O. Analysis of Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) noise standard violations over 50 years: 1972 to 2019. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2020, 63, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royster, J.D. Preventing Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. N. C. Med. J. 2017, 78, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sataloff, R.T. Hearing Loss: Economic Impact. Ear Nose Throat J. 2012, 91, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitzel, R.L.; Swinburn, T.K.; Hammer, M.S.; Eisenberg, D. Economic Impact of Hearing Loss and Reduction of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in the United States. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddle, M.G.; Goman, A.M.; Kernizan, F.C.; Foley, D.M.; Price, C.; Frick, K.D.; Lin, F.R. The Economic Impact of Adult Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Pons, D.; Pearse, J. Measuring Industrial Health Using a Diminished Quality of Life Instrument. Safety 2018, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omoush, S.A.; Abdul-Baqi, K.J.; Zuriekat, M.; Alsoleihat, F.; Elmanaseer, W.R.; Jamani, K.D. Assessment of occupational noise-related hearing impairment among dental health personnel. J. Occup. Health 2020, 62, e12093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudt, A.M.; Whitworth, K.W.; Chien, L.-C.; Whitehead, L.W.; Gimeno Ruiz de Porras, D. Association of organic solvents and occupational noise on hearing loss and tinnitus among adults in the U.S., 1999–2004. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2019, 92, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humann, M.; Sanderson, W.; Flamme, G.; Kelly, K.M.; Moore, G.; Stromquist, A.; Merchant, J.A. Noise Exposures of Rural Adolescents: Noise Exposures of Rural Adolescents. J. Rural Health 2011, 27, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlenga, B.; Berg, R.L.; Linneman, J.G.; Wood, D.J.; Kirkhorn, S.R.; Pickett, W. Determinants of early-stage hearing loss among a cohort of young workers with 16-year follow-up. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 69, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullagh, M.C.; Yang, J.J.; Cohen, M.A. Community-based program to increase use of hearing conservation practices among farm and rural youth: A cluster randomized trial of effectiveness. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.J.; Arcury, T.A. Occupational Injury and Illness in Farmworkers in the Eastern United States. In Latinx Farmworkers in the Eastern United States; Arcury, T.A., Quandt, S.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 41–81. ISBN 978-3-030-36642-1. [Google Scholar]
- Couth, S.; Mazlan, N.; Moore, D.R.; Munro, K.J.; Dawes, P. Hearing Difficulties and Tinnitus in Construction, Agricultural, Music, and Finance Industries: Contributions of Demographic, Health, and Lifestyle Factors. Trends Hear. 2019, 23, 233121651988557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.I.; Nelson, R.Y.; Concha-Barrientos, M.; Fingerhut, M. The global burden of occupational noise-induced hearing loss. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2005, 48, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwinska-Kowalska, M.; Davis, A. Noise-induced hearing loss. Noise Health 2012, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, K.; Michaud, D.; McNamee, J.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Davies, H.; Leroux, T. Prevalence of Hazardous Occupational Noise Exposure, Hearing Loss, and Hearing Protection Usage Among a Representative Sample of Working Canadians. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 59, 92–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC); National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2017.
- Janicak, C.A. Applied Statistics in Occupational Safety and Health, 3rd ed.; Bernan Press: Lanham, MD, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-59888-889-8. [Google Scholar]
- Denis, D.J. Univariate, Bivariate, and Multivariate Statistics Using R: Quantitative Tools for Data Analysis and Data Science, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-119-54993-2. [Google Scholar]
- Acock, A.C. A Gentle Introduction to Stata, 6th ed.; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-59718-269-0. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Applied Ordinal Logistic Regression Using Stata: From Single-Level to Multilevel Modeling; Sage: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4833-1975-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-470-58247-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, N.K.; Guo, S. Structural Equation Modeling; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-536762-1. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.S.; Freese, J. Regression Models for Categorical Dependent Variables Using Stata; Stata Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-1-881228-62-2. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, J.B.; Nora, A.; Stage, F.K.; Barlow, E.A.; King, J. Reporting Structural Equation Modeling and Confirmatory Factor Analysis Results: A Review. J. Educ. Res. 2006, 99, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, D.W. A structural equation model of New York restaurant grades over a 2-year period. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2016, 19, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Accessible and Affordable Hearing Health Care for Adults; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Health and Medicine Division; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Hearing Health Care for Adults: Priorities for Improving Access and Affordability; Blazer, D.G., Domnitz, S., Liverman, C.T., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; p. 23446. ISBN 978-0-309-43926-8. [Google Scholar]
- McLennon, T.; Patel, S.; Behar, A.; Abdoli-Eramaki, M. Evaluation of smartphone sound level meter applications as a reliable tool for noise monitoring. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2019, 16, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, J.C.; Adibi, S.; Wickramasinghe, N.; Nguyen, L.; Angelova, M.; Islam, S.M.S. Smartphone as a Disease Screening Tool: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdi, M.; Riha, C.; Neff, P.; Dode, A.; Pryss, R.; Schlee, W.; Reichert, M.; Hauck, F.J. Smartphone Apps in the Context of Tinnitus: Systematic Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balanay, J.A.G.; Richards, S.L. Insights into Diversity in the Environmental Health Science Workforce. Environ. Health Insights 2022, 16, 117863022210775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S. The importance of diversity, equity, and inclusion in our profession. J. Environ. Health 2021, 83, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, I.M.M.; Silva, A.R.X.; Camargo, R.; Cavalcanti, H.G.; Ferrari, D.V.; Taveira, K.V.M.; Balen, S.A. Accuracy of smartphone-based hearing screening tests: A systematic review. CoDAS 2022, 34, e20200380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufarrij, I.; Dillon, H.; Dawes, P.; Moore, D.R.; Yeung, W.; Charalambous, A.-P.; Thodi, C.; Munro, K.J. Web- and app-based tools for remote hearing assessment: A scoping review. Int. J. Audiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.C.J.; Lowe, D.A.; Cox, G. Guidelines for Diagnosing and Quantifying Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Trends Hear. 2022, 26, 233121652210931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).