Biased Deep Learning Methods in Detection of COVID-19 Using CT Images: A Challenge Mounted by Subject-Wise-Split ISFCT Dataset
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
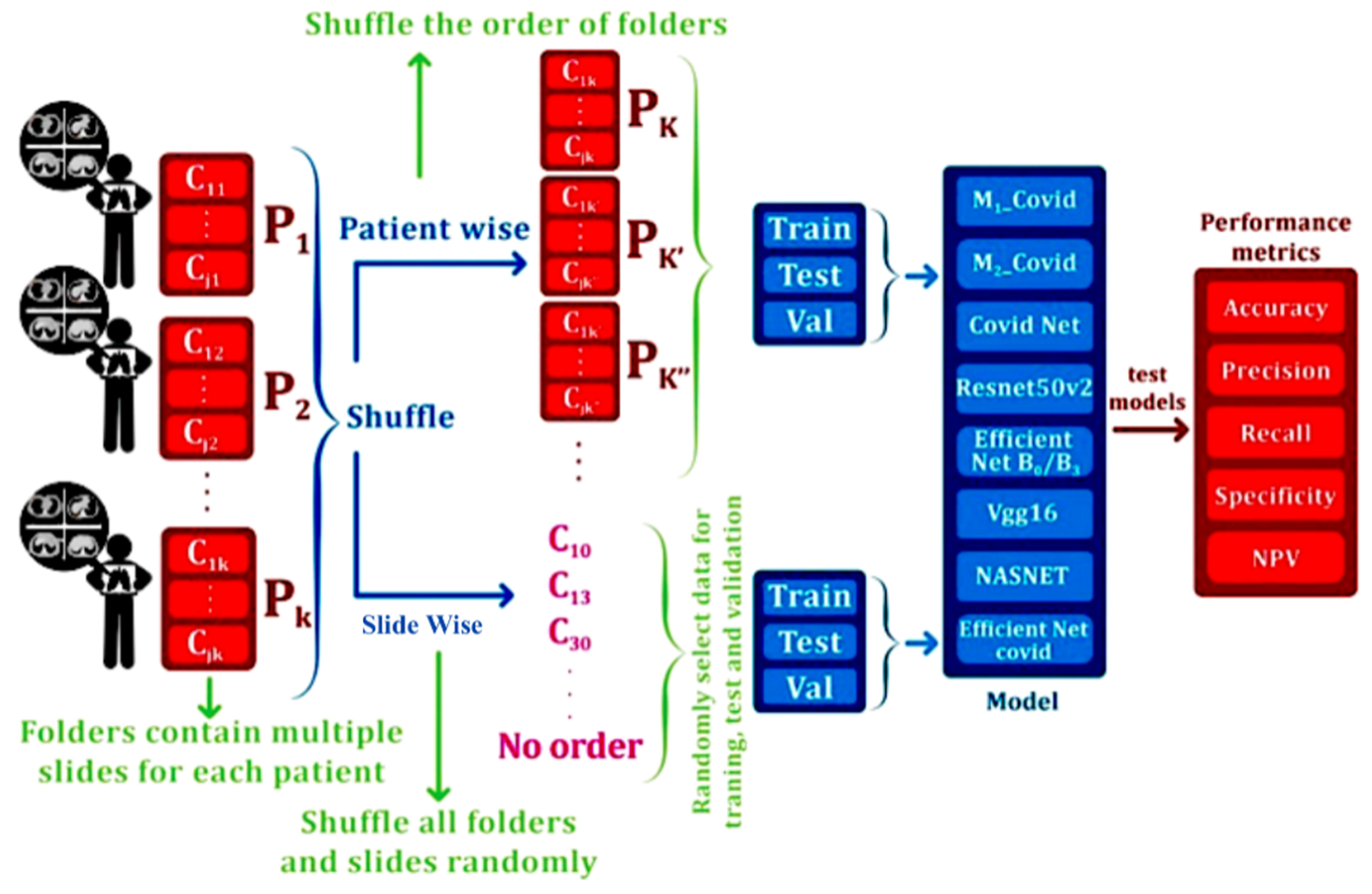
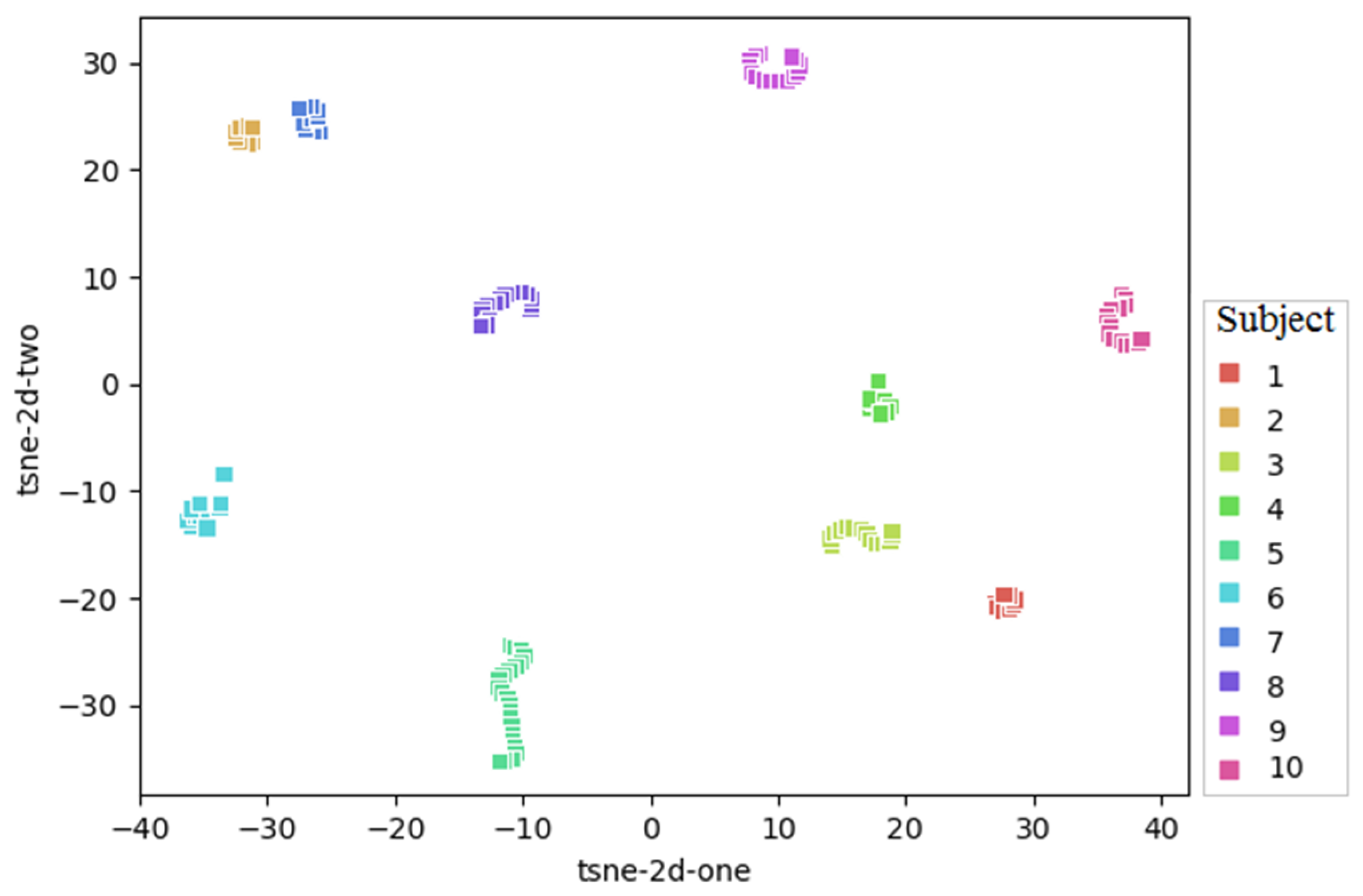
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Algorithms Based on Transfer Learning
2.4. Shallow Algorithms
2.5. Implementation Details
- For evaluating the performance of these models on our new dataset, the model was trained from scratch;
- For transfer learning, fully connected layers were substituted and retrained.
2.6. Performance Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
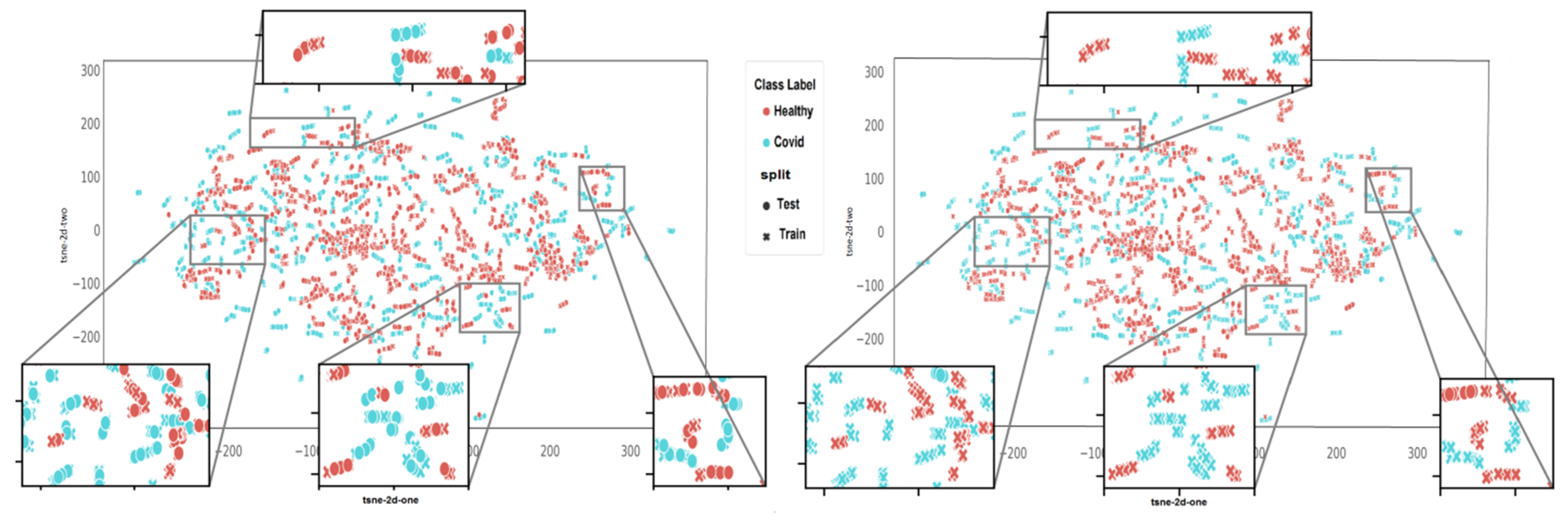
3.1. Comparison of Algorithms in Slice-Wise and Subject-Wise Splits
- In slice-wise setting, the data are randomly divided, and CT slices from the same subject maybe present in both the training and test data;
- In subject-wise setting, the data are split such that the training and test splits contain slides from different subjects.
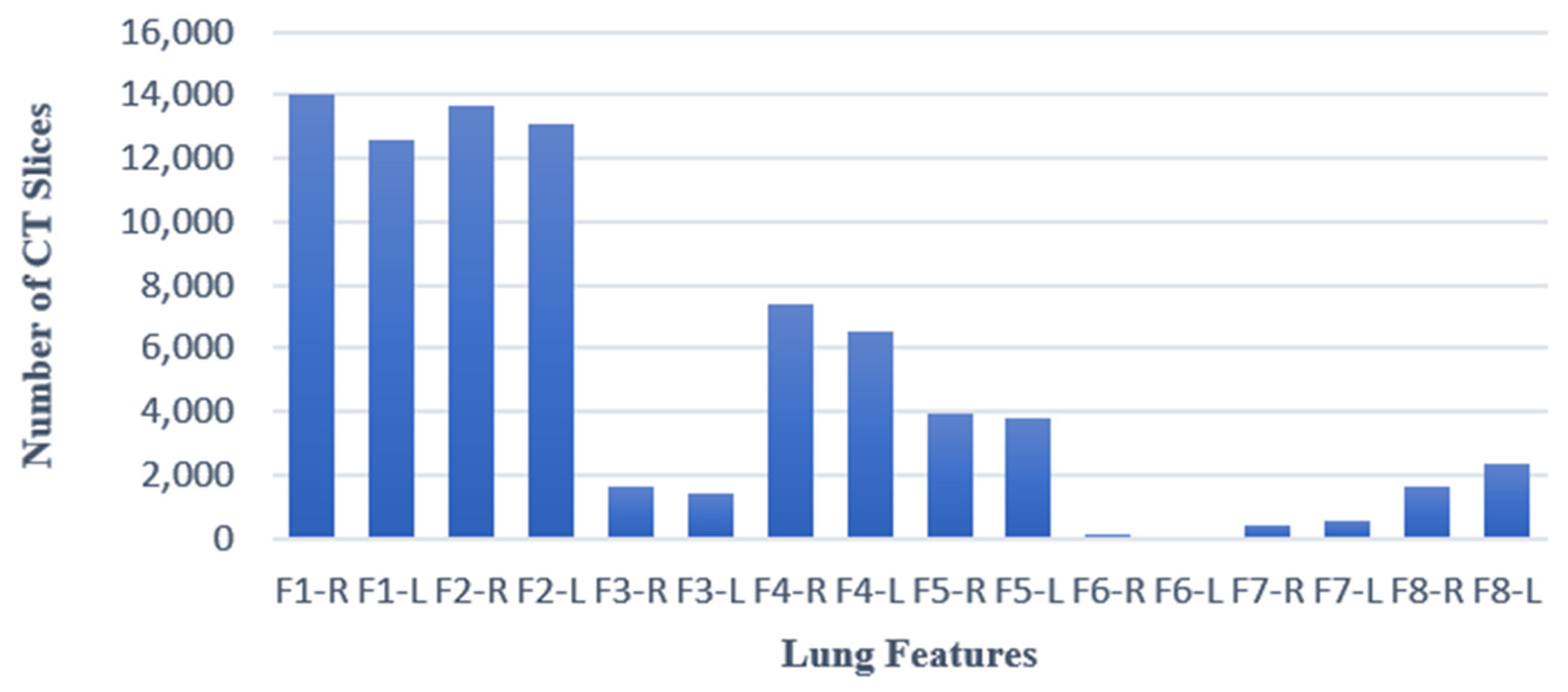
3.2. Average Accuracy of DL Models in Classification of Sub-Class Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, F.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; He, K.; Shi, Y.; Shen, D. Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation, and diagnosis for COVID-19. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ye, T.; Sun, P.; Gui, S.; Liang, B.; Li, L.; Zheng, D.; Wang, J.; Hesketh, R.L.; Yang, L. Time course of lung changes at chest CT during recovery from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Radiology 2020, 295, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loey, M.; Manogaran, G.; Khalifa, N.E.M. A deep transfer learning model with classical data augmentation and CGAN to detect COVID-19 from chest CT radiography digital images. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devnath, L.; Luo, S.; Summons, P.; Wang, D. Performance comparison of deep learning models for black lung detection on chest X-ray radiographs. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Software Engineering and Information Management, Sydney, Australia, 12–15 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaraman, S.; Siegelman, J.; Alderson, P.O.; Folio, L.S.; Folio, L.R.; Antani, S.K. Iteratively pruned deep learning ensembles for COVID-19 detection in chest X-rays. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115041–115050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, S.; Lonini, L.; Jayaraman, A.; Mohr, D.C.; Kording, K.P. The need to approximate the use-case in clinical machine learning. Gigascience 2017, 6, gix019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaibub Neto, E.; Pratap, A.; Perumal, T.M.; Tummalacherla, M.; Snyder, P.; Bot, B.M.; Trister, A.D.; Friend, S.H.; Mangravite, L.; Omberg, L. Detecting the impact of subject characteristics on machine learning-based diagnostic applications. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, P. COVID-CT-dataset: A CT scan dataset about COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaderzadeh, M.; Asadi, F.; Jafari, R.; Bashash, D.; Abolghasemi, H.; Aria, M. Deep convolutional neural network–based computer-aided detection system for COVID-19 using multiple lung scans: Design and implementation study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Jiang, W.; Qiu, X. Deep learning for COVID-19 detection based on CT images. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbalenya, A.; Baker, S.; Baric, R.; De Groot, R.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.; Haagmans, B.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.; Neuman, B. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikov, A.; Beyer, L.; Zhai, X.; Puigcerver, J.; Yung, J.; Gelly, S.; Houlsby, N. Big Transfer (BiT): General Visual Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Li, Z.; Sang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zha, Y.; Liang, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, K. Clinically applicable AI system for accurate diagnosis, quantitative measurements, and prognosis of COVID-19 pneumonia using computed tomography. Cell 2020, 181, 1423–1433.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassania, S.H.; Kassanib, P.H.; Wesolowskic, M.J.; Schneidera, K.A.; Detersa, R. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in X-ray and CT images: A machine learning based approach. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L.; Roth, K.; Duong, T.Q.; Ghassemi, M. COVID-19 image data collection: Prospective predictions are the future. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaggle, R. Pneumonia Detection Challenge. 2020. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna-pneumonia-detection-challenge (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Tiwari, P.; Rathi, V.K.; Qian, J.; Pandey, H.M.; Albuquerque, V.H.C. Covidpen: A novel COVID-19 detection model using chest x-rays and ct scans. Medrxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogilavani, S.; Prabhu, J.; Sandhiya, R.; Kumar, M.S.; Subramaniam, U.; Karthick, A.; Muhibbullah, M.; Imam, S.B.S. COVID-19 detection based on lung ct scan using deep learning techniques. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 7672196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouat, I.; Echtioui, A.; Khemakhem, R.; Zouch, W.; Ghorbel, M.; Hamida, A.B. COVID-19 detection in CT and CXR images using deep learning models. Biogerontology 2022, 23, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.E.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Al Emadi, N. Can AI help in screening viral and COVID-19 pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Qiblawey, Y.; Tahir, A.; Kiranyaz, S.; Kashem, S.B.A.; Islam, M.T.; Al Maadeed, S.; Zughaier, S.M.; Khan, M.S. Exploring the effect of image enhancement techniques on COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouch, W.; Sagga, D.; Echtioui, A.; Khemakhem, R.; Ghorbel, M.; Mhiri, C.; Hamida, A.B. Detection of COVID-19 from CT and Chest X-ray Images Using Deep Learning Models. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 50, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://github.com/UCSD-AI4H/COVID-CT/tree/master/Images-processed (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Ortiz, A.; Trivedi, A.; Desbiens, J.; Blazes, M.; Robinson, C.; Gupta, S.; Dodhia, R.; Bhatraju, P.K.; Liles, W.C.; Lee, A. Effective deep learning approaches for predicting COVID-19 outcomes from chest computed tomography volumes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misztal, K.; Pocha, A.; Durak-Kozica, M.; Wątor, M.; Kubica-Misztal, A.; Hartel, M. The importance of standardisation–COVID-19 CT & Radiograph Image Data Stock for deep learning purpose. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 127, 104092. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pijls, B.G.; Jolani, S.; Atherley, A.; Derckx, R.T.; Dijkstra, J.I.; Franssen, G.H.; Hendriks, S.; Richters, A.; Venemans-Jellema, A.; Zalpuri, S. Demographic risk factors for COVID-19 infection, severity, ICU admission and death: A meta-analysis of 59 studies. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-M.; Bai, P.; He, W.; Wu, F.; Liu, X.-F.; Han, D.-M.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.-K. Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: Focus on severity and mortality. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunderman, R.B. Essential Radiology: Clinical Presentation, Pathophysiology, Imaging, 2nd ed.; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, H.J.; Lim, S.; Choe, J.; Choi, S.-H.; Sung, H.; Do, K.-H. Radiographic and CT features of viral pneumonia. Radiographics 2018, 38, 719–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacking, C.; Weerakkody, Y.; Bell, D. Left lower lobe consolidation. Radiopedia 2021, 66157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.E.; Erasmus, J.J.; Volpacchio, M.; Franquet, T.; Castiglioni, T.; McAdams, H.P. “Crazy-paving” pattern at thin-section CT of the lungs: Radiologic-pathologic overview. Radiographics 2003, 23, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarenza, A.; Ultimo, L.E.; Falsaperla, D.; Travali, M.; Foti, P.V.; Torrisi, S.E.; Schisano, M.; Mauro, L.A.; Sambataro, G.; Basile, A. Chest imaging using signs, symbols, and naturalistic images: A practical guide for radiologists and non-radiologists. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Luz, E.; Silva, G.; Moreira, G.; Silva, R.; Lucio, D.; Menotti, D. COVID-19 detection in CT images with deep learning: A voting-based scheme and cross-datasets analysis. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 20, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu Lin, Z.; Javad Shafiee, M.; Bochkarev, S.; St Jules, M.; Wang, X.Y.; Wong, A. Do Explanations Reflect Decisions? A Machine-centric Strategy to Quantify the Performance of Explainability Algorithms. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.07387. [Google Scholar]
- Cheplygina, V. Cats or CAT scans: Transfer learning from natural or medical image source data sets? Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 9, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Published DL Work | Dataset | Slice-Wise or Subject-Wise | Number of CT Slices | Number of Subjects | DL Models | Reported Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yang et al. [8] | COVID-CT dataset [8] | IW | C: 349 NC: 463 | C: 216 NC: VD | Transfer-Learning: DenseNet-169, ResNet-50, and contrastive self-supervised transfer learning | F1-Score = 0.90 AUC = 0.98 Accuracy = 0.89 |
| Ghaderzadeh et al. [9] | Ghaderzadeh et al. [9] | IW | C: 7644 NC: 2509 | C: 190 NC: 59 | Transfer-Learning: NASNet | Sensitivity = 0.999 Specificity = 0.986 Accuracy = 0.996 |
| Zhao et. al [10] | COVIDx CT 2A [11] | IW | C, SARS-CoV-2 and CP: 194,922 N: ND | C, SARS-CoV-2, and CP: 3475 N: ND | BigTransfer (BIT) [12] | Accuracy = 0.992 Sensitivity = 0.987 Specificity = 0.995 NPV= 0.996 PPV=0.985 |
| Zhang et al. [13] | CC-CCll; Zhang et al. [13] | IW | C: 156,070 viral pneumonia: 159,700 N: 95,459 | C: 839 viral pneumonia: 874 N: 758 | A 3D classification networks | Accuracy = 0.924 Sensitivity = 0.943 Specificity = 0.911 |
| Kassania et al. [14] | Cohen et al. [15], and KaggleRSNAPneumonia Detection dataset [16] | IW | C: 20 N: 20 | C: ND N: ND | Examination of transfer learning with a range of methods, including: DenseNet121, Xception, InceptionV3, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, NASNETLarge, NASNetMobile, ResNet50v2, ResNet101V2, and ResNet152V2 | Accuracy = 0.99 Precision = 0.99 Recall = 0.99 F1-Score= 0.99 |
| Jaiswal et al. [17] | COVID CT slices [8] | IW | C: 746 N: ND | C: ND Normal: ND | COVIDPEN: Pruned EfficientNet-B0 | Accuracy = 0.85 AUC = 0.84 F1-Score = 0.86 |
| Kogilavani et al. [18] | Kaggle | IW | C: 1958 N: 1915 | C: ND N: ND | VGG16, DenseNet, MobileNet, Xception, EfficientNet, and NASNet | Accuracy = 0.97 F1-Score = 0.98 Precision = 0.99 Recall = 1 |
| Chouat et al. [19] | GitHub repository [8], and Kaggle [20,21] | IW | C: 408 N: 325 | C: ND N: ND | VGGNet-19, ResNet50, Xception, and InceptionV3 | Accuracy = 0.905 F1-Score = 0.905 Precision = 0.915 Recall= 0.903 |
| Zouch et al. [22] | Database of CT slices provided in GitHub [23] | IW | C: 349 NC: 408 | C: ND NC: ND | VGG19 and ResNet50 | Accuracy = 0.98 F1-Score = 100 Precision = 0.993 Recall = 100 |
| Ortiz et al. [24] | CC-CCll; Zhang et al. [13] | SW | C: 156,070 viral pneumonia: 159,700 N: 95,459 | C: 839 viral pneumonia: 874 N: 758 | Inception ResNetV2 | Accuracy = 0.95 AUC = 0.96 Sensitivity = 0.94 |
| Wang et al. [2] | COVIDx [2] | SW | C: 358 CXR N: not determined | C: 266 NC: 5538 no pneumonia: 8066 | COVID-Net | Accuracy = 0.933 Sensitivity = 0.91 PPV = 0.989 |
| Feature | Explanation | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
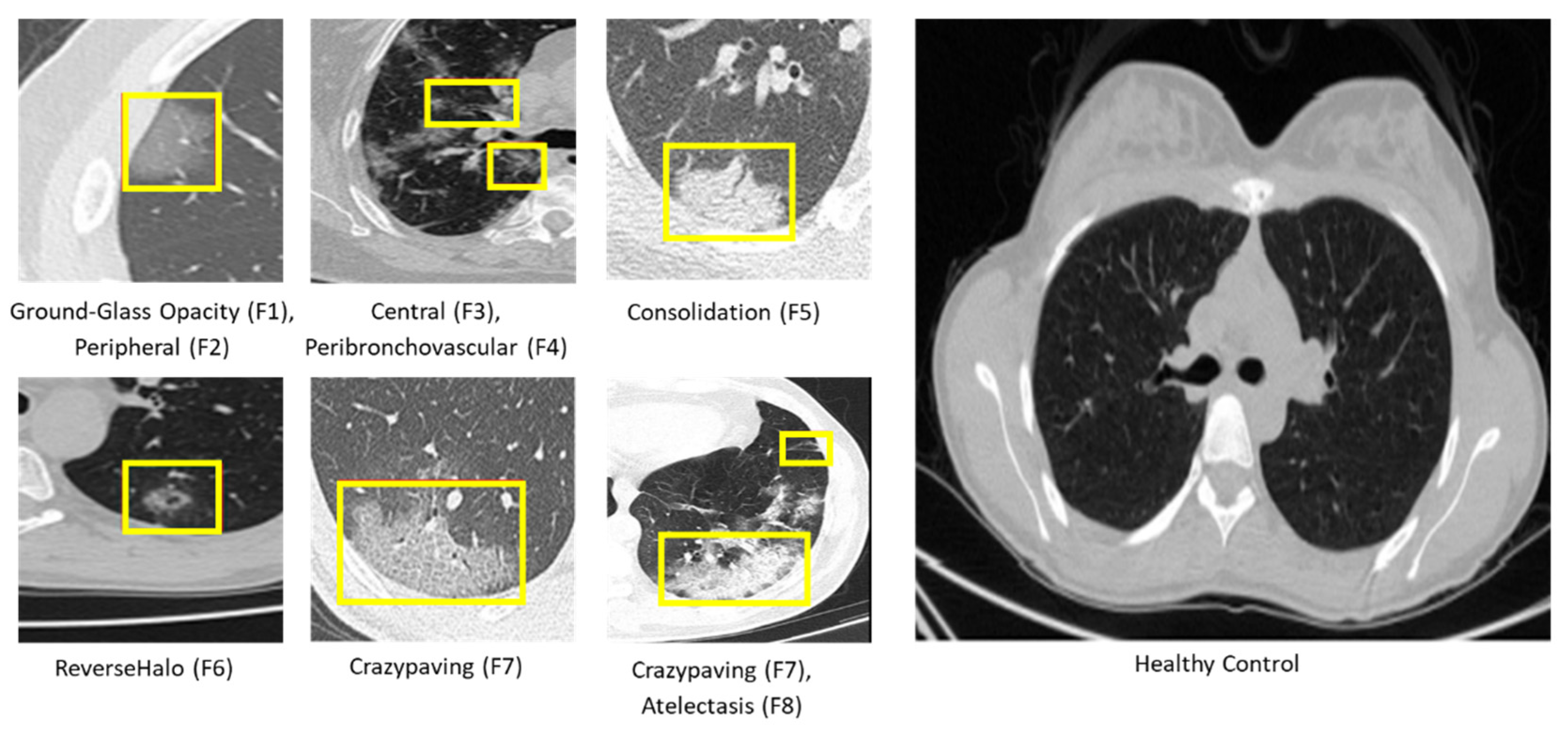
| Ground-Glass Opacity | The hazy gray indicates increased density inside the lungs [25]. | F1 |
| Peripheral | The feature is situated on the edge or periphery of the lung. | F2 |
| Central | The feature is located in the middle of the lung. | F3 |
| Peribronchovascular | Thickening of the interstitial or bronchial wall [28]. | F4 |
| Consolidation | The alveolar air spaces are filled with fluid, cells, tissue, or other material [29]. | F5 |
| Reverse Halo | Central ground-glass opacity surrounded by denser consolidation of a crescent shape or a complete ring of at least 2 mm in thickness [30]. | F6 |
| Crazy Paving | Scattered diffuse ground-glass attenuation with superimposed interlobular septal thickening and intralobular lines [31]. | F7 |
| Atelectasis | Complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area(lobe) of the lung [32]. | F8 |
| Classification Models | Input Slice Size | FC | Initial Weights |
|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50v2 | (224 × 24 × 3) | AveragePooling2D Flatten layer Dense 256 Drop out 0.5 Dense 2 | ImageNet |
| VGG16 | (224 × 224 × 3) | MaxPooling2D Flatten Dense256 Dense 2 | ImageNet |
| EfficientNetB0 | (224 × 224 × 3) | MaxPooling2D Flatten Dense256 Dense 2 | ImageNet |
| EfficientNetB3 | (300 × 300 × 3) | MaxPooling2D Flatten Dense256 Dense 2 | ImageNet |
| MobileNet | (224 × 224 × 3) | AveragePooling2D Flatten layer Dense 256 Dropout 0.5 Dense 2 | ImageNet |
| COVIDnetwork based on NASNET | (224 × 224 × 3) | No change | ImageNet and Ghaderzadeh et al. [9] COVID-19 dataset |
| COVID-Net | (224 × 224 × 3) | Dense 2 | COVIDx [2] |
| Models | Slice-Wise | Subject-Wise | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | Precision | Recall | Specificity | NPV | ACC | Precision | Recall | Specificity | NPV | ||
| Transfer Learning Models | ResNet50V2 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.46 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.59 | 0.35 | 0.11 | 0.84 | 0.55 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 0.52 | 0.50 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.44 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.56 | |
| EfficientNetB3 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0 | |
| VGG16 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 0.38 | 0.87 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.69 | 0.37 | 0.79 | 0.55 | |
| COVID network based on NASNET | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.66 | |
| MobileNet | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.57 | 0.50 | |
| COVID-NET | 0.99 | 1 | 0.99 | 1 | 0.99 | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.54 | 0.7 | 0.50 | |
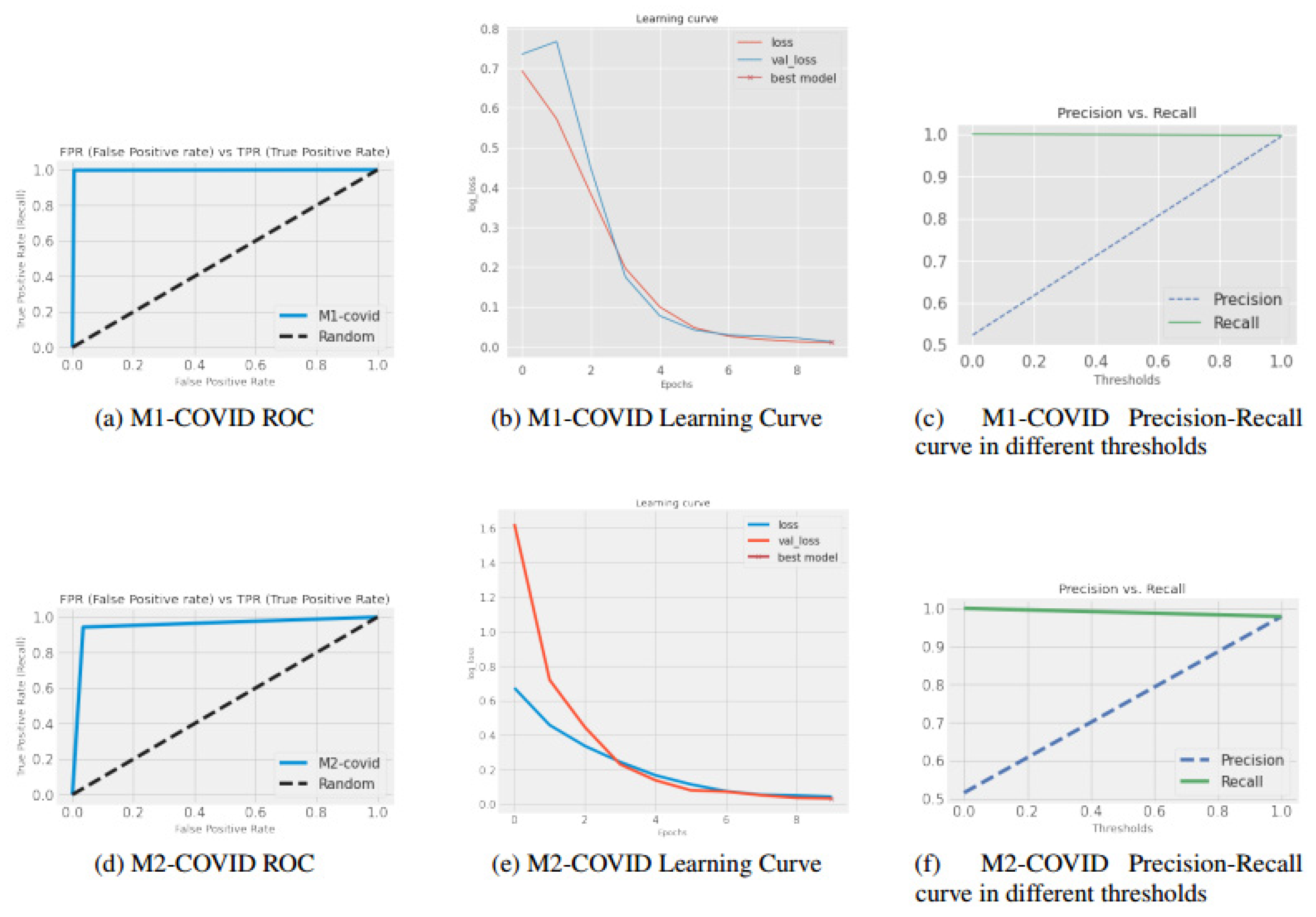
| Shallow Models | M1-COVID | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.58 |
| M2-COVID | 0.99 | 1 | 0.98 | 1 | 0.98 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.40 | 0.78 | 0.53 | |
| Models | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer Learning Models | ResNet50v2 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.57 | 0.51 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.37 | |
| EfficientNetB3 | 0.74 | 0.40 | 0.69 | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.40 | |
| VGG16 | 0.74 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.46 | 0.64 | 0.64 | |
| COVID network based on NASNET | 0.80 | 0.53 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 0.66 | |
| MobileNet | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.68 | |
| COVIDNET | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.60 | |
| Shallow Models | M1-COVID | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.40 |
| M2-COVID | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.59 | 0.52 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parsarad, S.; Saeedizadeh, N.; Soufi, G.J.; Shafieyoon, S.; Hekmatnia, F.; Zarei, A.P.; Soleimany, S.; Yousefi, A.; Nazari, H.; Torabi, P.; et al. Biased Deep Learning Methods in Detection of COVID-19 Using CT Images: A Challenge Mounted by Subject-Wise-Split ISFCT Dataset. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080159
Parsarad S, Saeedizadeh N, Soufi GJ, Shafieyoon S, Hekmatnia F, Zarei AP, Soleimany S, Yousefi A, Nazari H, Torabi P, et al. Biased Deep Learning Methods in Detection of COVID-19 Using CT Images: A Challenge Mounted by Subject-Wise-Split ISFCT Dataset. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(8):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080159
Chicago/Turabian StyleParsarad, Shiva, Narges Saeedizadeh, Ghazaleh Jamalipour Soufi, Shamim Shafieyoon, Farzaneh Hekmatnia, Andrew Parviz Zarei, Samira Soleimany, Amir Yousefi, Hengameh Nazari, Pegah Torabi, and et al. 2023. "Biased Deep Learning Methods in Detection of COVID-19 Using CT Images: A Challenge Mounted by Subject-Wise-Split ISFCT Dataset" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 8: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080159
APA StyleParsarad, S., Saeedizadeh, N., Soufi, G. J., Shafieyoon, S., Hekmatnia, F., Zarei, A. P., Soleimany, S., Yousefi, A., Nazari, H., Torabi, P., S. Milani, A., Madani Tonekaboni, S. A., Rabbani, H., Hekmatnia, A., & Kafieh, R. (2023). Biased Deep Learning Methods in Detection of COVID-19 Using CT Images: A Challenge Mounted by Subject-Wise-Split ISFCT Dataset. Journal of Imaging, 9(8), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9080159








