Measuring Power of Earth Disturbances Using Radio Wave Phase Imager
Abstract
:1. Introduction—Earth’s Ionosphere Response to Waves
Response of the Ionospheric System to Man-Made Disturbances
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SDR Experimental Method
2.1.1. Transmitter and Dataset Collection
2.1.2. Receivers and Transmitter Distances
2.1.3. LWA-1 and LWA-SV Experimental Approach
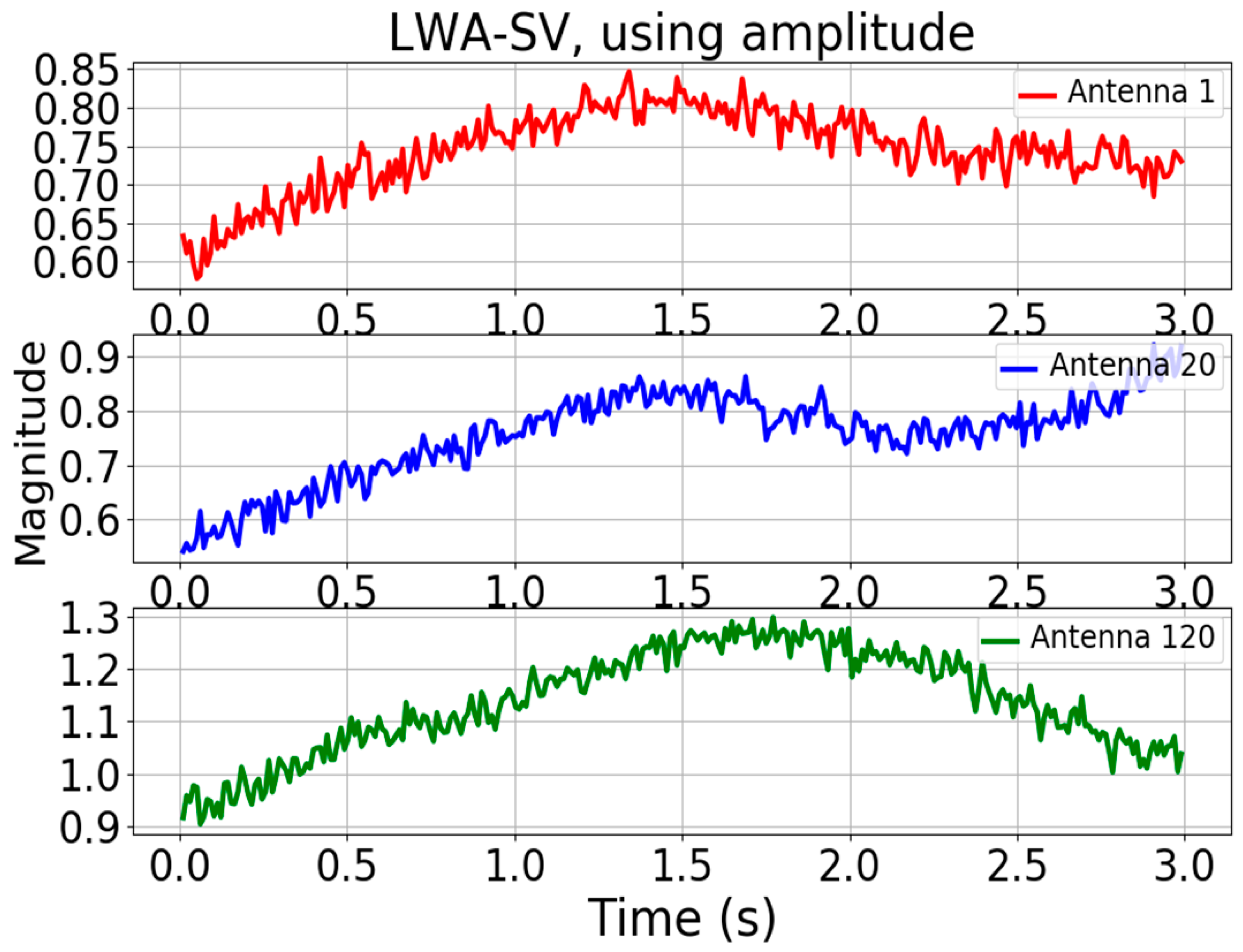
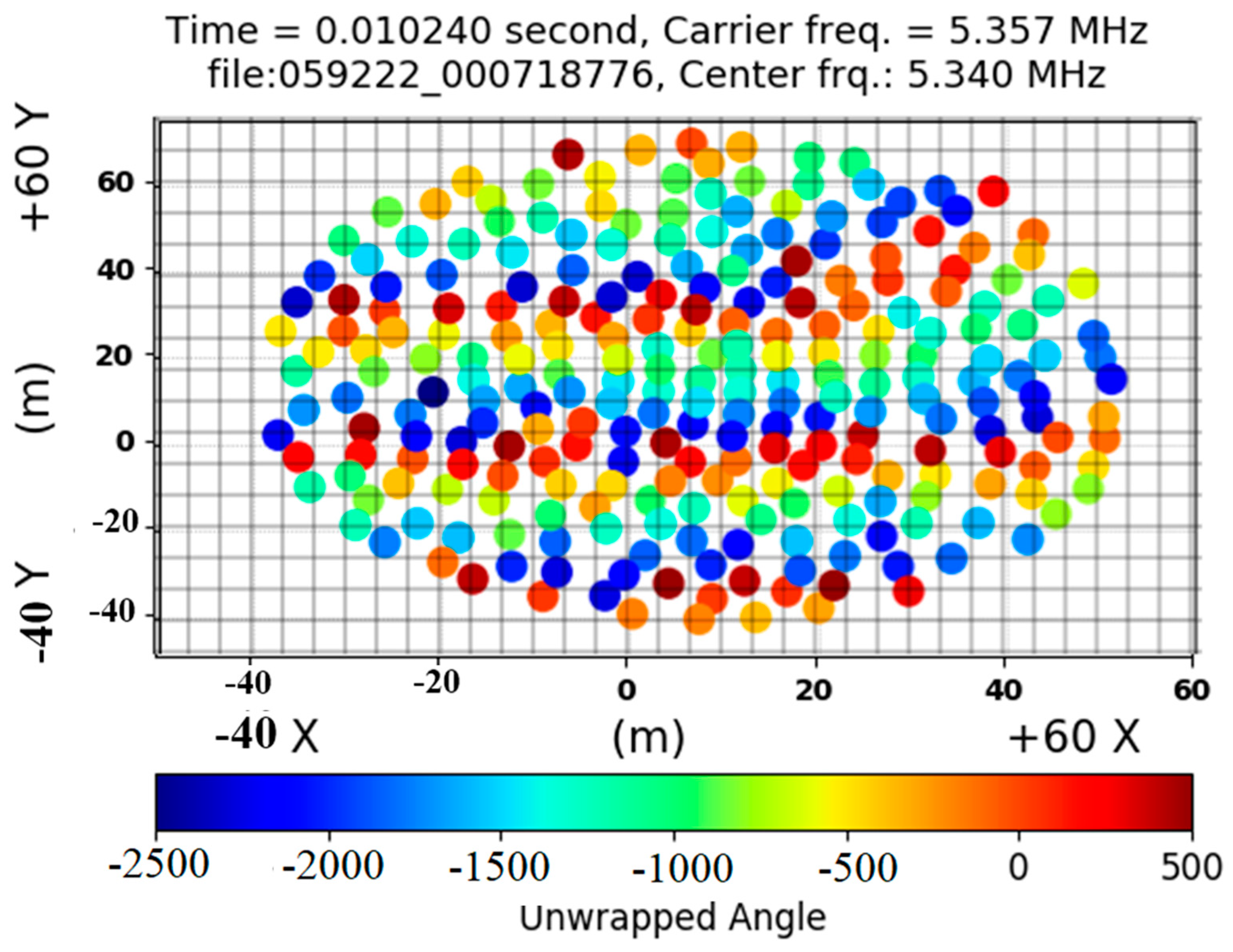
2.1.4. Amplitude and Phase Images from the Antenna Array Receiver
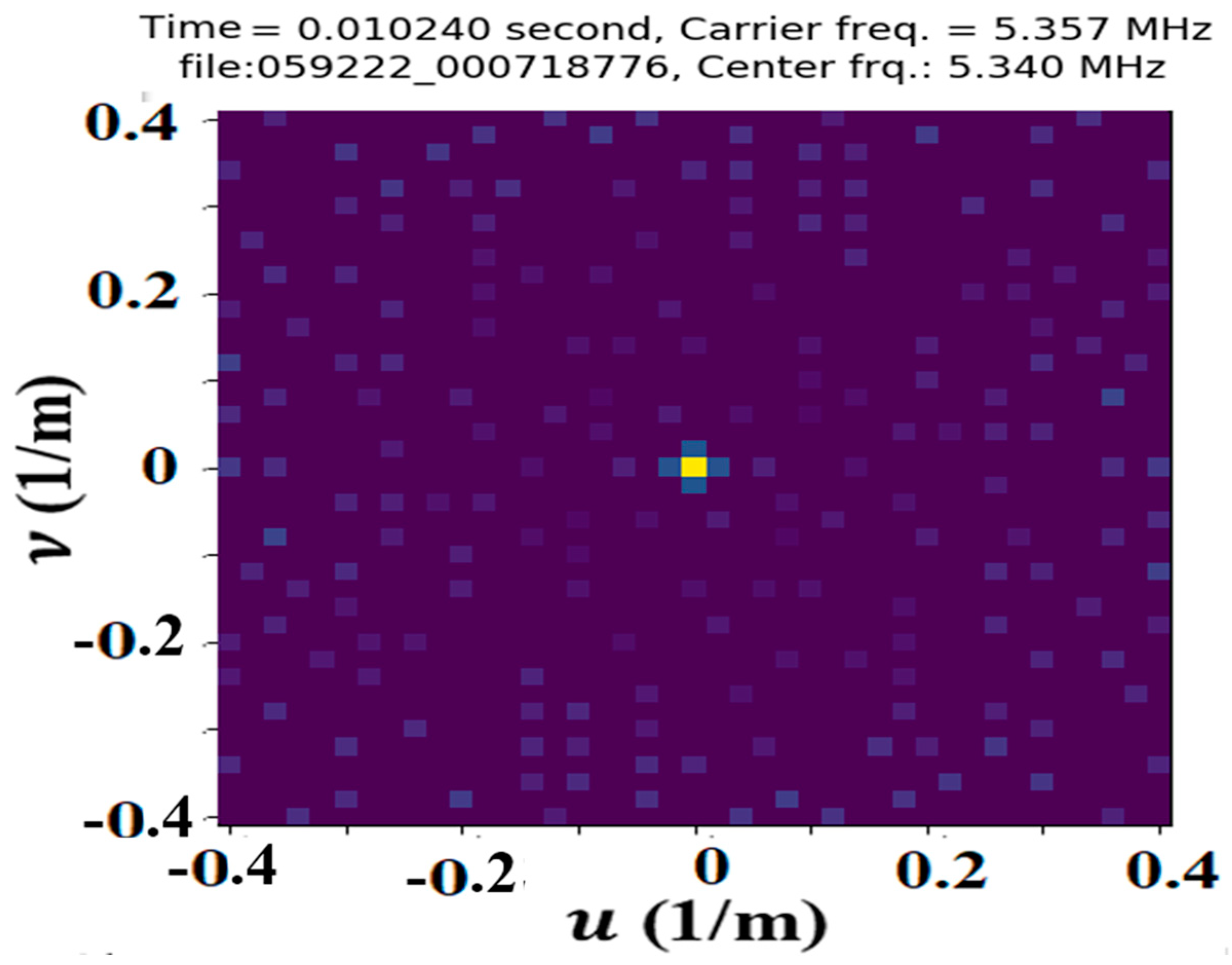
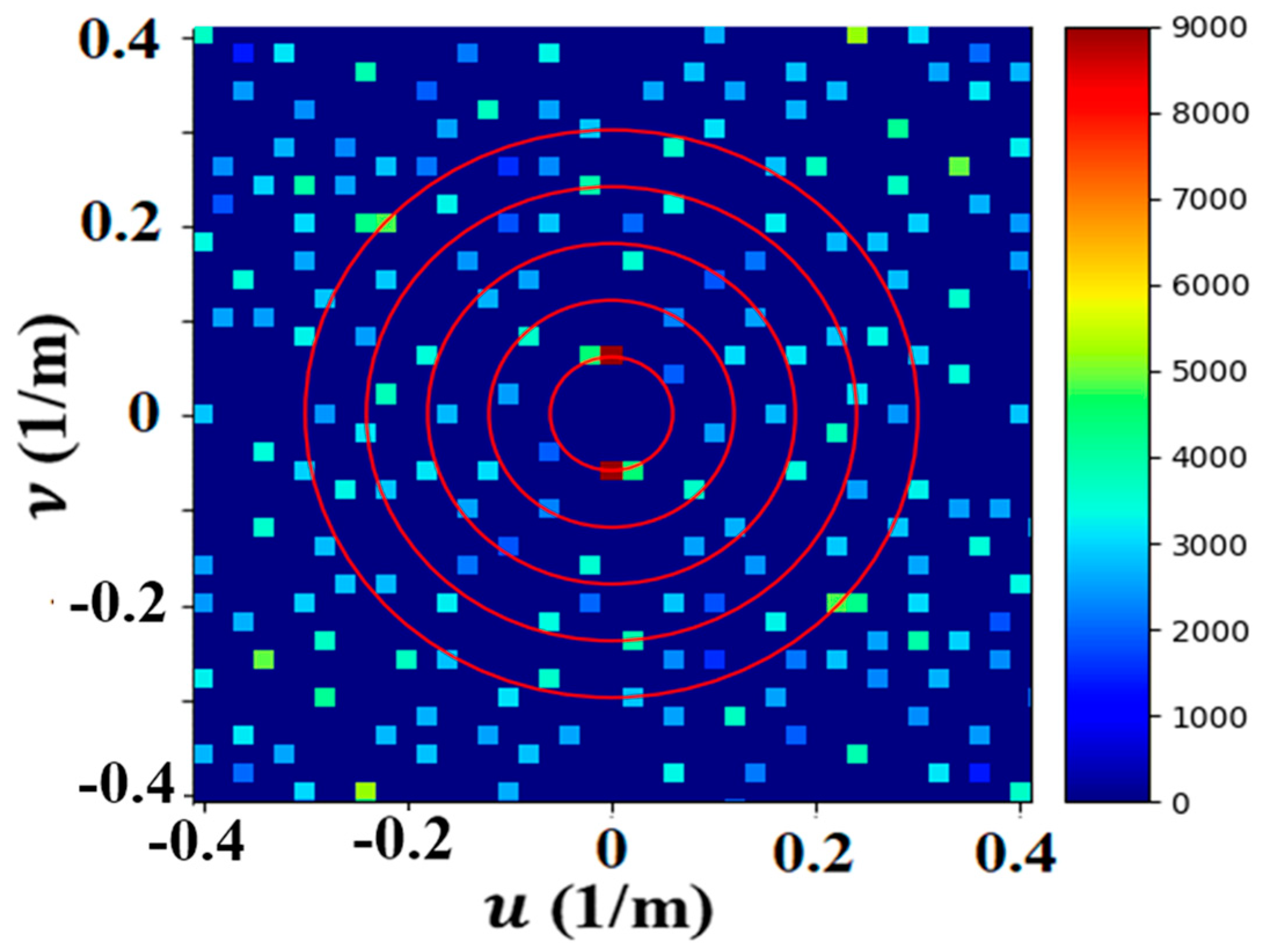
2.2. Spatial Phase Image
3. Results
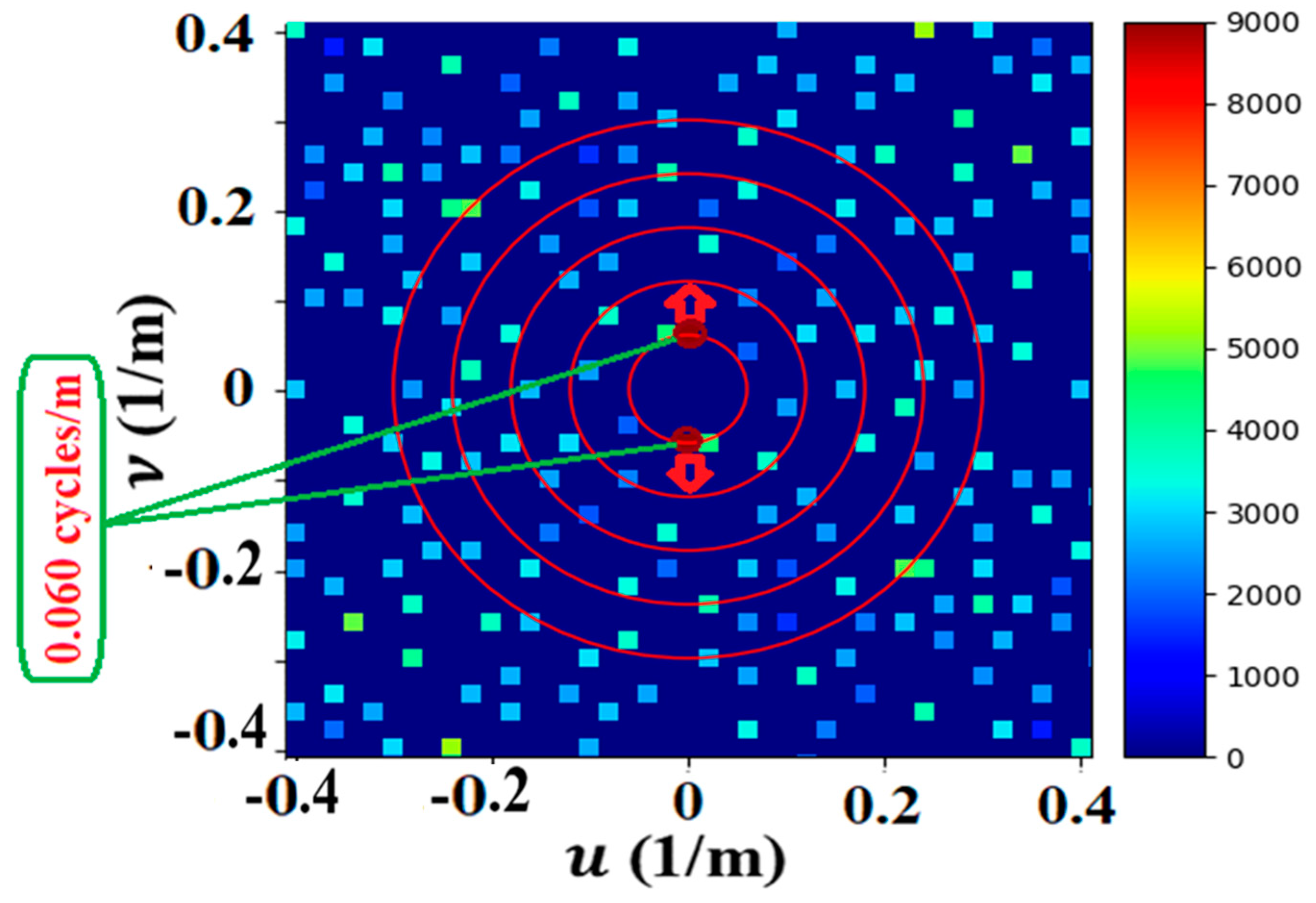
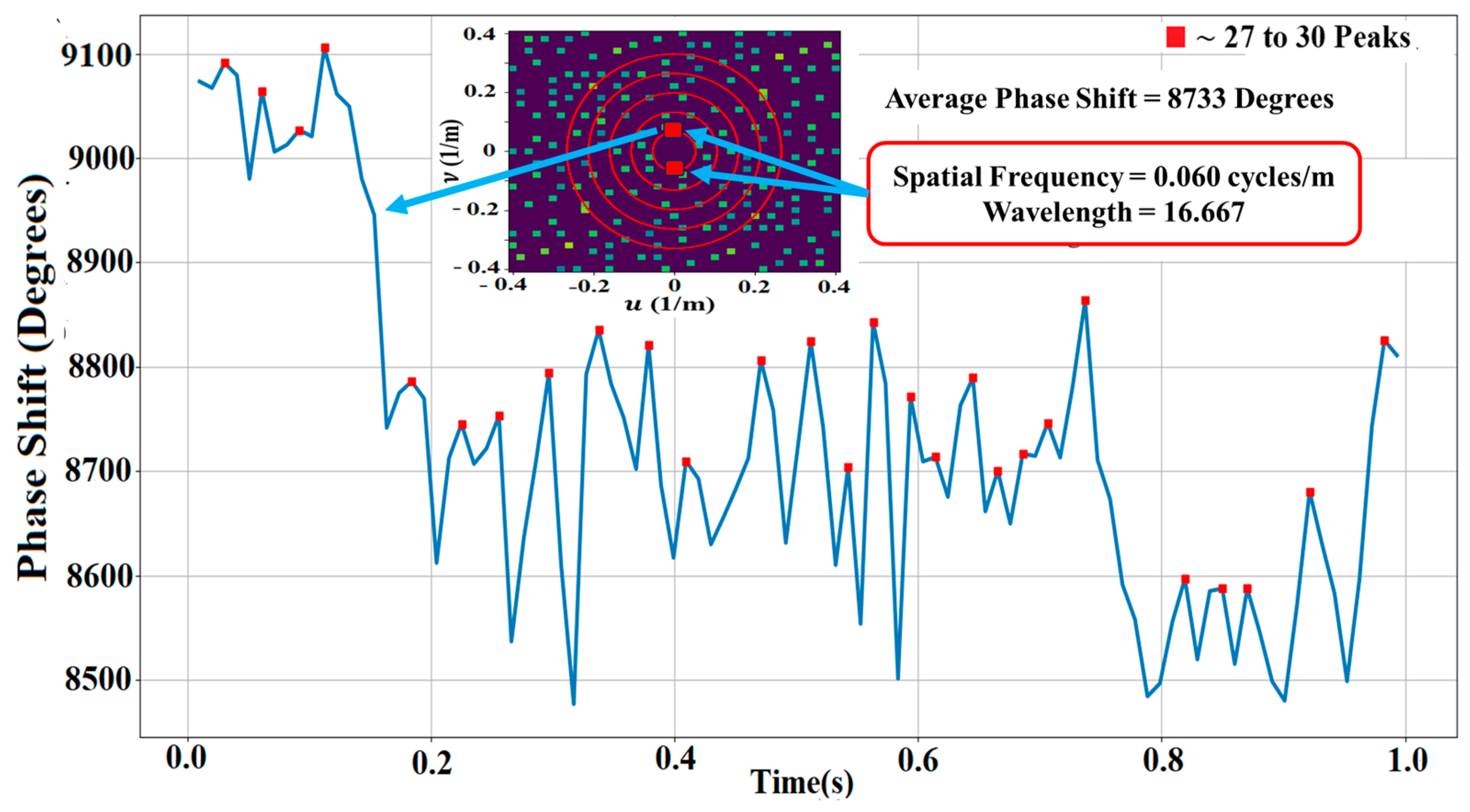
3.1. Analysis of LWA-SV and LWA-1 and Spatial Frequency Results
3.1.1. Model to Determine Wave Power
Analysis of LWA-SV Spatial Frequency Results
Local Power Generating Stations and Places of Measurements
4. Discussion of LWA-1 and LWA-2 Spatial Imaging Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ionospheric Detection of Natural Hazards—Astafyeva—2019—Reviews of Geophysics—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://agupubs-onlinelibrary-wiley-com.ezproxy.library.uvic.ca/doi/full/10.1029/2019RG000668 (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- Fedorov, E.N.; Mazur, N.G.; Pilipenko, V.A. Electromagnetic Response of the Mid-Latitude Ionosphere to Power Transmission Lines. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, Q.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Z. Geomagnetic Conjugate Observations of Ionospheric Disturbances in Response to a North Korean Underground Nuclear Explosion on 3 September 2017. Ann. Geophys. 2019, 37, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishbeth, H. F-Region Links with the Lower Atmosphere? J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G. Doppler Radar Studies of the Antarctic Ionosphere. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, G.; McCrea, I.W. A Synoptic Study of TIDs Observed in the United Kingdom during the First WAGS Campaign, October 10–18, 1985. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G.; Rodrigues, F.S. Characteristics of Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances Observed by the TIDDBIT Sounder. Radio Sci. 2012, 47, RS0L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G.; Jones, T.B.; Dudeney, J.R. Comparison of Short Period TID Morphologies in Antarctica during Geomagnetically Quiet and Active Intervals. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1987, 49, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldock, J.A.; Jones, T.B. Source Regions of Medium Scale Travelling Ionospheric Disturbances Observed at Mid-Latitudes. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1987, 49, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, H.-F.; Chen, C.-H.; Kamogawa, M. Ionospheric Disturbances Triggered by the 11 March 2011 M 9.0 Tohoku Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A06319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, T.; Saito, A.; Otsuka, Y.; Nishioka, M.; Maruyama, T.; Kato, H.; Nagatsuma, T.; Murata, K.T. Ionospheric Disturbances Detected by GPS Total Electron Content Observation after the 2011 off the Pacific Coast of Tohoku Earthquake. Earth Planets Space 2011, 63, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, M.; Tsugawa, T.; Kubota, M.; Ishii, M. Concentric Waves and Short-Period Oscillations Observed in the Ionosphere after the 2013 Moore EF5 Tornado. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5581–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G.; Azeem, I. Chapter 23—Extreme Ionospheric Storms and Their Effects on GPS Systems. In Extreme Events in Geospace; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 555–586. ISBN 978-0-12-812700-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hunsucker, R.D.; Hargreaves, J.K. Radio Techniques for Probing the Ionosphere. In The High-Latitude Ionosphere and Its Effects on Radio Propagation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 181–226. ISBN 978-0-521-33083-1. [Google Scholar]
- Selman, S. Traveling Ionospheric Disturbance (Tids) Characteristics Estimation from Gps-TEC over Ethiopian Longitudinal Sector. M.Sc Thesis, Bahir Dar University, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 9 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, X.; Mannucci, A.J.; Lindqwister, U.J.; Ho, C.M. Monitoring of Global Ionospheric Irregularities Using the Worldwide GPS Network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2283–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Prol, F.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Tadeu de Assis Honorato Muella, M.; De Oliveira Camargo, P. Tomographic Imaging of Ionospheric Plasma Bubbles Based on GNSS and Radio Occultation Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, R.; Tanyer, S.G.; Harrison, S.; Driessen, P.; Herring, R. Monitoring Earth Using SDR Earth Imager. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2022, 235, 105907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G.; Azeem, I.; Reynolds, A.; Duly, T.M.; McBride, P.; Winkler, C.; Hunton, D. Analysis of Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances (TIDs) in GPS TEC Launched by the 2011 Tohoku Earthquake. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsucker, R.D.; Hargreaves, J.K. Basic Principles of the Ionosphere. In The High-Latitude Ionosphere and Its Effects on Radio Propagation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 1–60. ISBN 978-0-521-33083-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hines, C.O. INTERNAL ATMOSPHERIC GRAVITY WAVES AT IONOSPHERIC HEIGHTS. Can. J. Phys. 1960, 38, 1441–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.C.; Liu, C.H. Acoustic-Gravity Waves in the Upper Atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1974, 12, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.H. Global Propagation of Atmospheric Gravity Waves: A Review. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1975, 37, 1011–1030, IN9, 1031–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tsai, H.-F.; Chang, L.C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-H. Ionospheric F 2 Region Perturbed by the 25 April 2015 Nepal Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 5778–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G.; Aplin, K.L.; Rycroft, M.J. Atmospheric Electricity Coupling between Earthquake Regions and the Ionosphere. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2010, 72, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, Q. Influences of Radiation from Terrestrial Power Sources on the Ionosphere above China Based on Satellite Observation. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 153, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Hayakawa, M.; Molchanov, O.A. Theoretical Analysis on the Penetration of Power Line Harmonic Radiation into the Ionosphere. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 5-1–5-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullough, K.; Tatnall, A.R.L.; Denby, M. Man-Made e.l.f./v.I.f. Emissions and the Radiation Belts. Nature 1976, 260, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, O.; Parrot, M. PLHR Emissions Observed on Satellites. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1995, 57, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guo, Q.; Yan, X.; Zhang, C. Theoretical Analysis on Affecting Factors of Power Line Harmonic Radiation. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2019, 47, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, R.; Tanyer, S.G.; Harrison, S.; Junor, W.; Driessen, P.; Herring, R. Locating Earth Disturbances Using the SDR Earth Imager. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volland, H. (Ed.) Handbook of Atmospheric Electrodynamics, Volume I; CRC Press: Bosa Roca, FL, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-203-71950-3. [Google Scholar]
- Parrot, M.; Zaslavski, Y. Physical Mechanisms of Man-Made Influences on the Magnetosphere. Surv. Geophys. 1996, 17, 67–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, R.A.; Katsufrakis, J.P.; Bell, T.F.; Raghuram, R. VLF Line Radiation in the Earth’s Magnetosphere and Its Association with Power System Radiation. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 4249–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.P.; Yearby, K. Magnetospheric VLF Line Radiation Observed at Halley, Antarctica. Planet. Space Sci. 1981, 29, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luette, J.P.; Park, C.G.; Helliwell, R.A. Longitudinal Variations of Very-Low-Frequency Chorus Activity in the Magnetosphere: Evidence of Excitation by Electrical Power Transmission Lines. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1977, 4, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G.; Miller, T.R. Sunday Decreases in Magnetospheric VLF Wave Activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1979, 84, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothkaehl, H.; Izohkina, N.; Prutensky, N.; Pulinets, S.; Parrot, M.; Lizunov, G.; Blecki, J.; Stanislawska, I. Ionospheric Disturbances Generated by Different Natural Processes and by Human Activity in Earth Plasma Environment. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 47, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malins, J.B.; Obenberger, K.S.; Taylor, G.B.; Dowell, J. Three-Dimensional Mapping of Lightning-Produced Ionospheric Reflections. Radio Sci. 2019, 54, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.S.; Obenberger, K.S.; Dowell, J.; Taylor, G.B. Detection of a Low-Frequency Cosmic Radio Transient Using Two LWA Stations. Astrophys. J. 2019, 874, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowell, J.; Wood, D.; Stovall, K.; Ray, P.S.; Clarke, T.; Taylor, G. The Long Wavelength Array Software Library. J. Astron. Instrum. 2012, 1, 1250006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chum, J.; Liu, J.-Y.; Laštovička, J.; Fišer, J.; Mošna, Z.; Baše, J.; Sun, Y.-Y. Ionospheric Signatures of the April 25, 2015 Nepal Earthquake and the Relative Role of Compression and Advection for Doppler Sounding of Infrasound in the Ionosphere. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
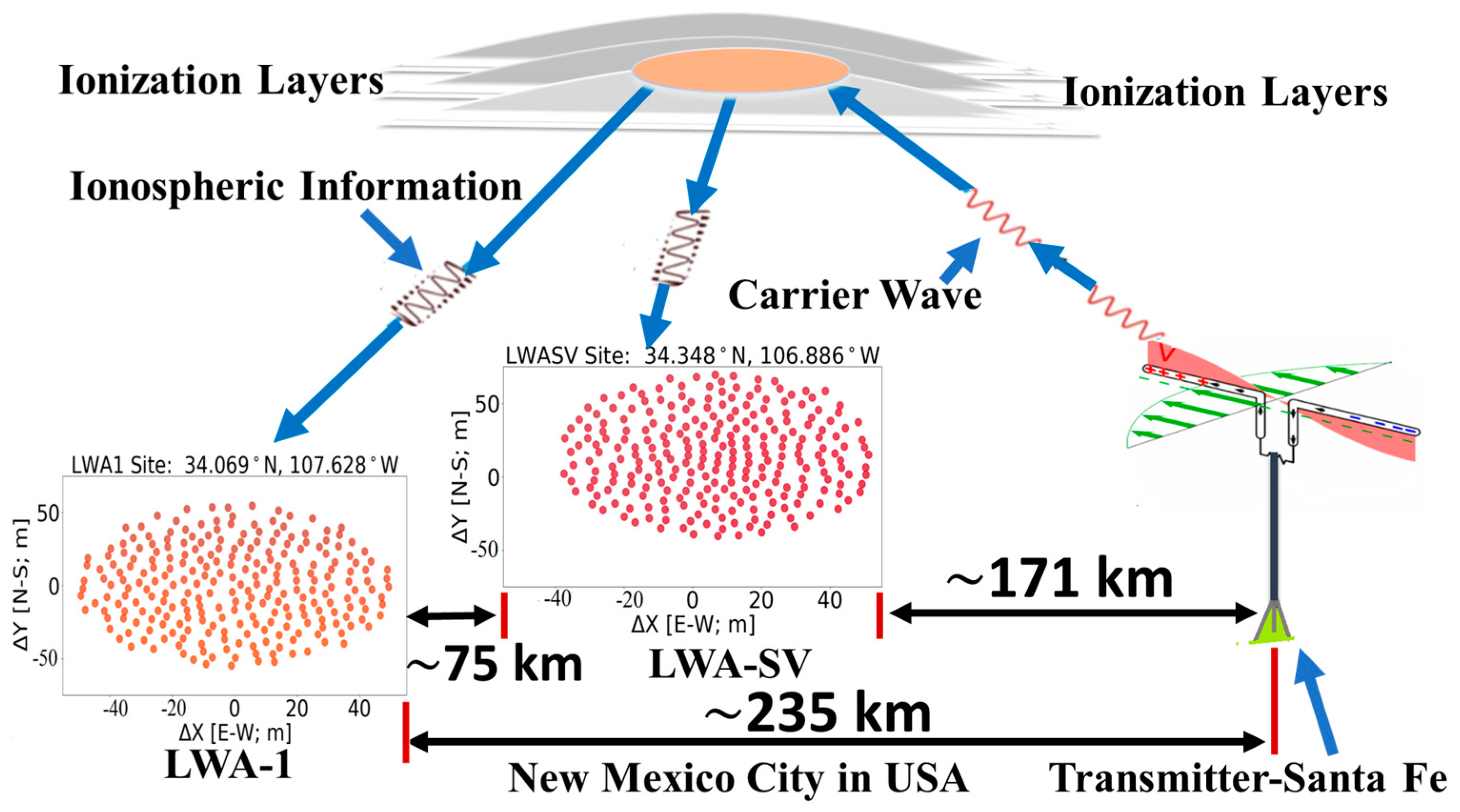


| Santa Fe Transmitter (35.71144° N, 106.0084° W) | |
| Date and Time | UT 8 January 2021, 20:29:30 |
| Transmitted Frequency | 5.3570 MHz |
| Mode -Send | CW Tone (Continuous Wave) |
| Receiver LWA-SV (34.348° N, 106.886° W) | |
| Center Frequency | 5.33999 MHz |
| Polarization | Zero |
| Date and Time of First Frame | 8 January 2021, 20:29:20 |
| Sample Rate | 100,000 Hz |
| Recorded Time | 1765.895 s |
| Receiver LWA-1 (34.069° N, 107.628° W) | |
| Center Frequency | 5.33999 MHz |
| Polarization | Zero |
| Date and Time of First Frame | 8 January 2021, 18:00:00 |
| Sample Rate: | 100,000 Hz |
| Recorded Time | 1731.281 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharif, R.N.K.; Herring, R.A. Measuring Power of Earth Disturbances Using Radio Wave Phase Imager. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100228
Sharif RNK, Herring RA. Measuring Power of Earth Disturbances Using Radio Wave Phase Imager. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(10):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100228
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharif, Radwan N. K., and Rodney A. Herring. 2023. "Measuring Power of Earth Disturbances Using Radio Wave Phase Imager" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 10: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100228
APA StyleSharif, R. N. K., & Herring, R. A. (2023). Measuring Power of Earth Disturbances Using Radio Wave Phase Imager. Journal of Imaging, 9(10), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100228





