Quantitative Evaluation of Low-Dose CT Image Quality Using Deep Learning Reconstruction: A Comparative Study of Philips Precise Image and GE TrueFidelity
Abstract
1. Introduction
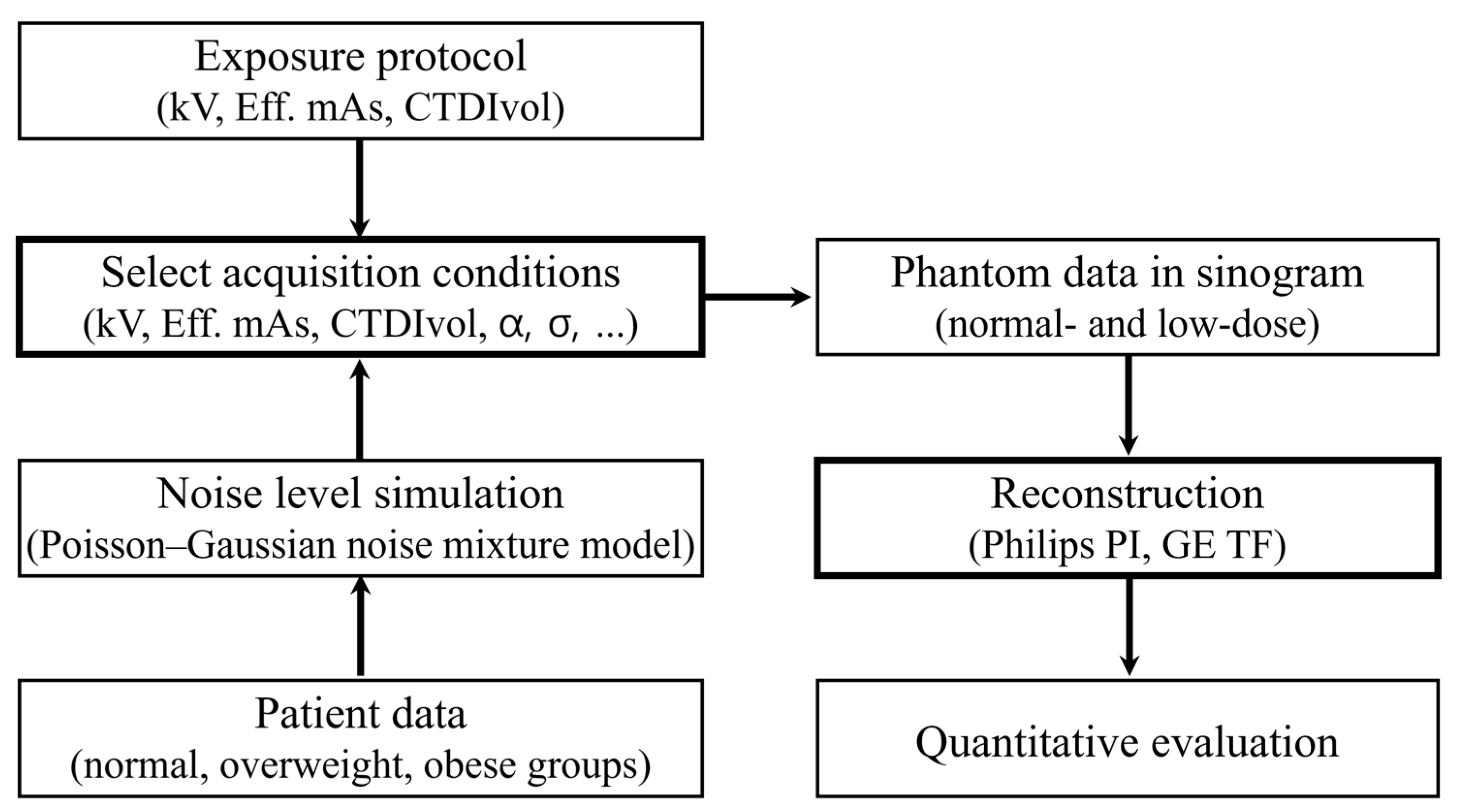
2. Materials and Methods
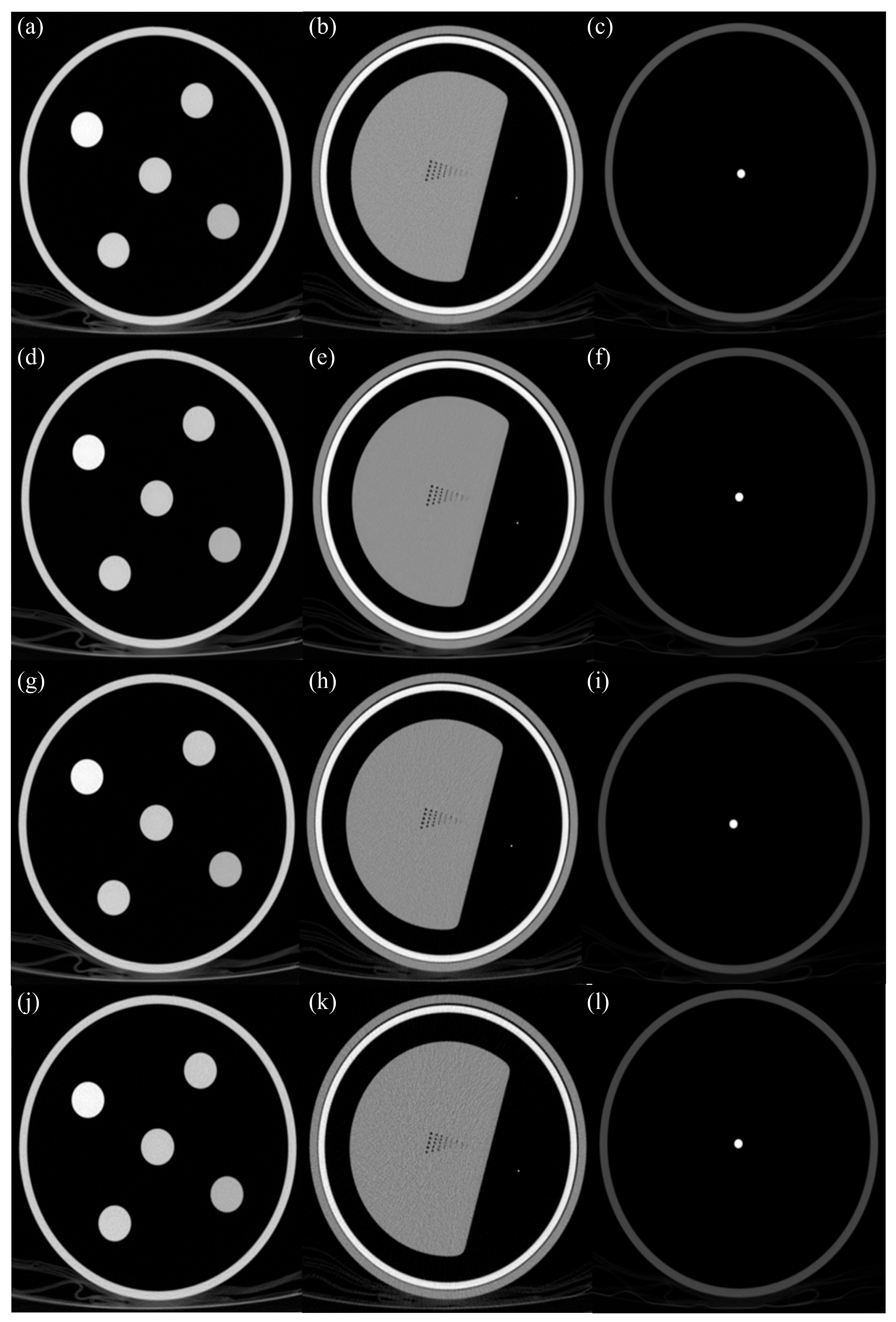
2.1. Quantitative Physical Phantom
2.2. CT Equipment and Scanning Parameters
2.3. Image Reconstruction
2.4. Quantitative Image Quality Assessment
3. Results
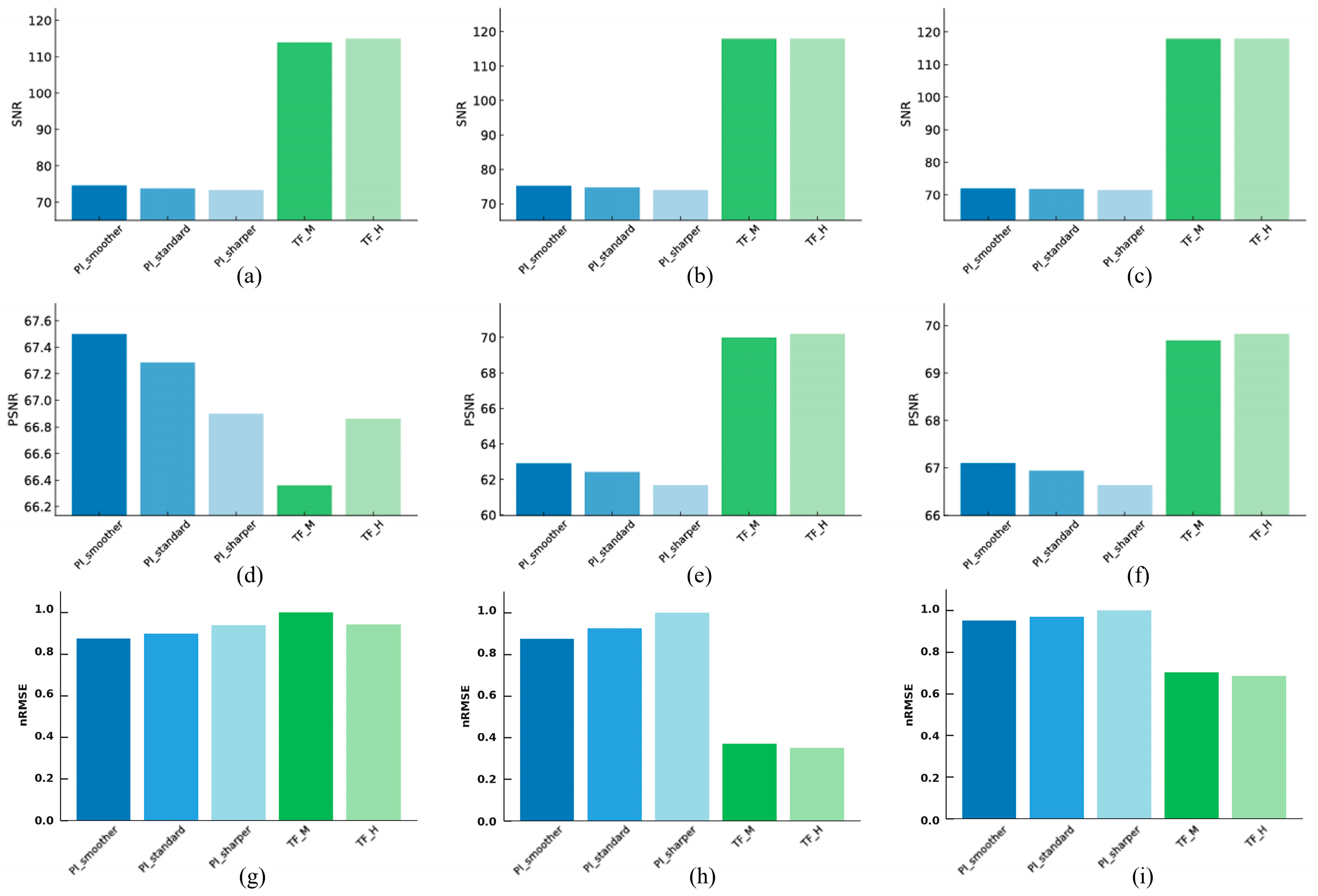
3.1. Noise and Signa
3.1.1. Linearity
3.1.2. High-Resolution
3.1.3. Artifact
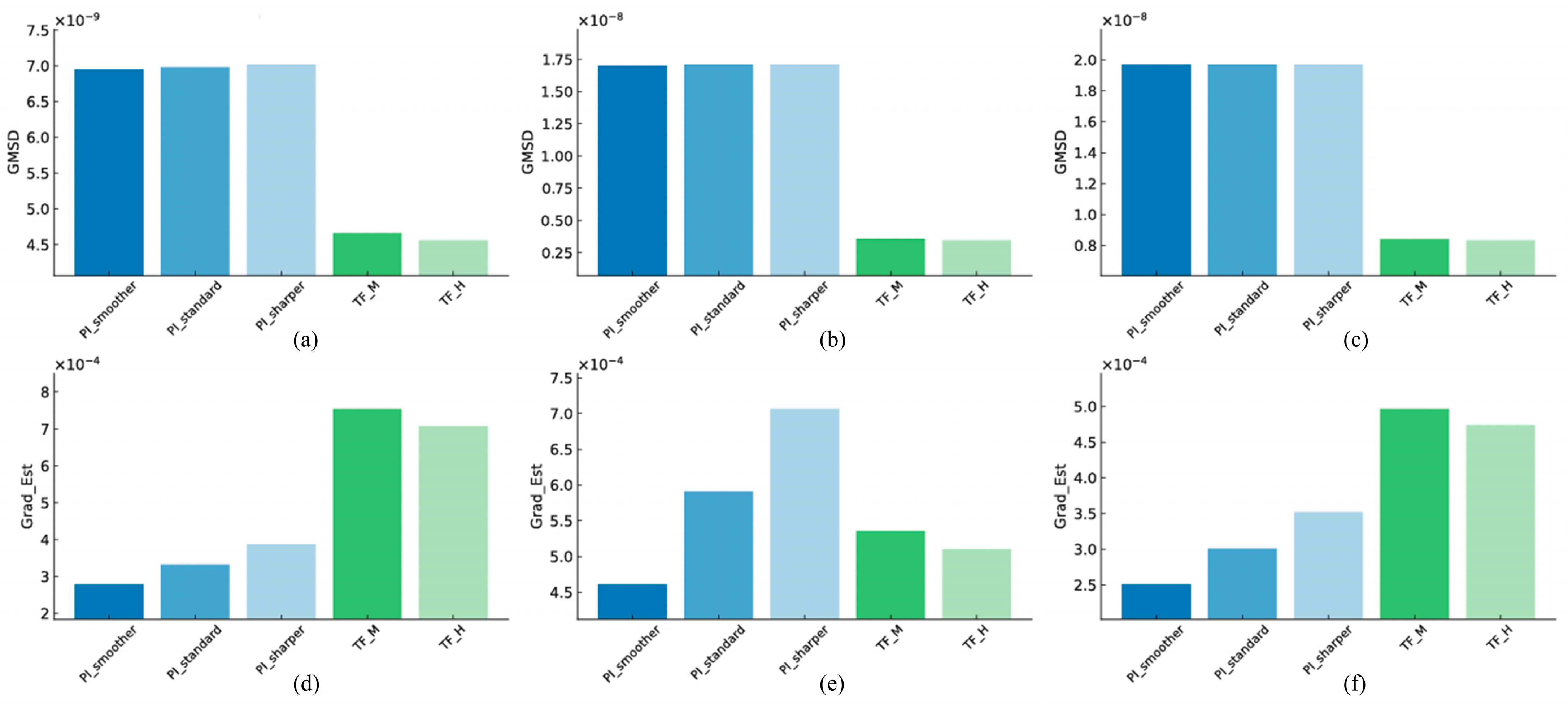
3.2. Structural Similarity
3.2.1. Linearity
3.2.2. High-Resolution
3.2.3. Artifact
3.3. Edge Sharpness and Fine Structure Preservation
3.3.1. Linearity
3.3.2. High-Resolution
3.3.3. Artifact
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith-Bindman, R.; Chu, P.W.; Azman Firdaus, H.; Stewart, C.; Malekhedayat, M.; Alber, S.; Bolch, W.E.; Mahendra, M.; Berrington de González, A.; Miglioretti, D.L. Projected lifetime cancer risks from current computed tomography imaging. JAMA Intern. Med. 2025, 185, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch de Basea, M.; Thierry-Chef, I.; Harbron, R.; Hauptmann, M.; Byrnes, G.; Bernier, M.-O.; Le Cornet, L.; Dabin, J.; Ferro, G.; Istad, T.S.; et al. Risk of hematological malignancies from CT radiation exposure in children, adolescents and young adults. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 3111–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, D.; Guberina, N.; Zensen, S.; Opitz, M.; Forsting, M.; Wetter, A. Radiation exposure in computed tomography. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 2023, 120, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, I.S.; Mohd Yusof, M.I.M. Techniques and strategies to minimize radiation exposure in pediatric computed tomography (CT) abdominal examinations: A review. Cureus 2024, 16, e67494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, R.S.; Dinakaran, P.M. Radiation safety concerns and diagnostic reference levels for computed tomography scanners in Tamil Nadu. J. Med. Phys. 2011, 36, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Xu, L.; Wan, J. Effectiveness of AI for enhancing computed tomography image quality and radiation protection in radiology: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e66622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, M.O.; Pendem, S.; Priya, P.S.; Chacko, C.; Priyanka; Kadavigere, R. Influence of deep learning image reconstruction algorithm for reducing radiation dose and image noise compared to iterative reconstruction and filtered back projection for head and chest computed tomography examinations: A systematic review. F1000Res 2024, 15, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, Y.; Goto, M.; Sakabe, D.; Emoto, T.; Shigematsu, S.; Taguchi, N.; Maruyama, N.; Takada, S.; Uchimura, R.; Hayashi, H.; et al. Radiation dose optimization potential of deep learning-based reconstruction for multiphase hepatic CT: A clinical and phantom study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 151, 110280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, L.-L.; Shang, J.; Song, J.; Liu, B. Application of deep learning image reconstruction in low-dose chest CT scan. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamabuchi, N.; Ohno, Y.; Kimata, H.; Ito, Y.; Fujii, K.; Akino, N.; Takenaka, D.; Yoshikawa, T.; Oshima, Y.; Matsuyama, T.; et al. Effectiveness of deep learning reconstruction on standard to ultra-low-dose high-definition chest CT images. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2023, 41, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mileto, A.; Yu, L.; Revels, J.W.; Kamel, S.; Shehata, M.A.; Ibarra-Rovira, J.J.; Wong, V.K.; Roman-Colon, A.M.; Lee, J.M.; Elsayes, K.M.; et al. State-of-the-art deep learning CT reconstruction algorithms in abdominal imaging. RadioGraphics 2024, 44, e240095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetzier, L.R.; Mastrodicasa, D.; Szczykutowicz, T.P.; van der Werf, N.R.; Wang, A.S.; Sandfort, V.; van der Molen, A.J.; Fleischmann, D.; Willemink, M.J. Deep learning image reconstruction for CT: Technical principles and clinical prospects. Radiology 2023, 306, e221257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertl, M.; Hahne, F.-G.; Gräger, S.; Heinrich, A. Impact of deep learning-based image reconstruction on tumor visibility and diagnostic confidence in computed tomography. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delabie, A.; Bouzerar, R.; Pichois, R.; Desdoit, X.; Vial, J.; Renard, C. Diagnostic performance and image quality of deep learning image reconstruction (DLIR) on unenhanced low-dose abdominal CT for urolithiasis. Acta Radiol. 2022, 63, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, A.; Yasaka, K.; Inui, S.; Okimoto, N.; Abe, O. Comparison of deep-learning image reconstruction with hybrid iterative reconstruction for evaluating lung nodules with high-resolution computed tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2023, 47, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.G.; Ahn, C.; Choi, H.; Hong, W.; Park, J.; Kim, J.H.; Goo, J.M. Image quality of ultralow-dose chest CT using deep learning techniques: Potential superiority of vendor-agnostic post-processing over vendor-specific techniques. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5139–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaura, T.; Awai, K.; Oda, S.; Funama, Y.; Harada, K.; Uemura, S.; Yamashita, Y. Low-kilovoltage, high-tube-current MDCT of liver in thin adults: Pilot study evaluating radiation dose, image quality, and display settings. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, F.; Nyman, U.; Siemund, R.; Geijer, M.; Söderberg, M. Impact of iterative reconstructions on image noise and low-contrast object detection in low kVp simulated abdominal CT: A phantom study. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.R.; Nersissian, D.Y.; Umisedo, N.K.; Gonzales, A.H.L.; Fernández-Varea, J.M. A comprehensive Monte Carlo study of CT dose metrics proposed by the AAPM Reports 111 and 200. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, M.S.; Kang, M.G. Poisson-Gaussian noise analysis and estimation for low-dose x-ray images in the NSCT domain. Sensors 2018, 18, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White Paper—AI for significantly lower dose and improved image quality—Precise Image. PHILIPS-Comput. Tomogr. 2021. Available online: https://www.philips.com/c-dam/b2bhc/master/resource-catalog/landing/precise-suite/incisive_precise_image.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Hsieh, J.; Liu, E.; Nett, B.; Tang, J.; Thibault, J.-B.; Sahney, S. A New Era of Image Reconstruction: TrueFidelity™: Technical White Paper on Deep Learning Image Reconstruction. 2019. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d0f8/e1e8868e9f8ed22ad5972420139551552e91.pdf?_ga=2.233526110.1531411842.15947093202066918258.1594709320 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Jiang, B.; Li, N.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; de Bock, G.H.; Vliegenthart, R.; Xie, X. Deep learning reconstruction shows better lung nodule detection for ultra-low-dose chest CT. Radiology 2022, 303, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Shoemaker, A.C.; Tsui, K.L.; León, R.V.; Parr, W.C.; Nair, V.N.; Pregibon, D.; Carroll, R.; Ruppert, D.; Gunter, B.; et al. Signal-to-noise ratios, performance criteria, and transformations. Technometrics 1988, 30, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horé, A.; Ziou, D. Is there a relationship between peak-signal-to-noise ratio and structural similarity index measure? IET Image Process 2013, 7, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, T.O. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): When to use them or not. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. FSIM: A feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2011, 20, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Hao, M.; Zhang, J.; Hu, B.; Lu, Q. A universal hypercomplex color image quality index. In Proceedings of the IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Technology Conference, Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A.C. Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2014, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffier, J.; Hamard, A.; Pereira, F.; Barrau, C.; Pasquier, H.; Beregi, J.P.; Frandon, J. Image quality and dose reduction opportunity of deep learning image reconstruction algorithm for CT: A phantom study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3951–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.-A.; Kim, K.-U.; Hwang, M.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, K.-I.; Song, Y.-S.; Lee, I.-S.; Jeong, Y.-J. Emphysema quantification using ultra-low-dose chest CT: Efficacy of deep learning-based image reconstruction. Medicina 2022, 58, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ai, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, M.; Han, Q.; Ma, K.; Xiang, Z. Clinical value of deep learning image reconstruction on the diagnosis of pulmonary nodule for ultra-low-dose chest CT imaging. Clin. Radiol. 2024, 78, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompe, E.; Strand, M.; van Rikxoort, E.M.; Hoffman, E.A.; Barr, R.G.; Charbonnier, J.P.; Humphries, S.; Han, M.K.; Hokanson, J.E.; Make, B.J.; et al. Five-year Progression of Emphysema and Air Trapping at CT in Smokers with and Those without Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Results from the COPDGene Study. Radiology 2020, 295, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mets, O.M.; Buckens, C.F.M.; Zanen, P.; Isgum, I.; van Ginneken, B.; Prokop, M.; Gietema, H.A.; Lammers, J.-W.J.; Vliegenthart, R.; Oudkerk, M.; et al. Identification of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in lung cancer screening computed tomographic scans. JAMA 2022, 306, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppot, R.N. Technical challenges of imaging & image-guided interventions in obese patients. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Phantom Study | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Philips CT 5300 | GE Revolution | |||
| FBP | Lowdose | FBP | Lowdose | |
| kVp | 120 | 80, 100, 120 | 120 | 80 |
| Eff. mAs | 33 | 19, 11, 6 | 80 | 45 |
| Pitch | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.992:1 | 0.992:1 |
| Scan time | 7.8 s | 7.8 s | 3.23 s | 3.23 s |
| Rotation time | 0.5 s | 0.5 s | 0.5 s | 0.5 s |
| Slice thickness | 1 mm | 1 mm | 1 mm | 1 mm |
| Increment | 1 mm | 1 mm | 1 mm | 1 mm |
| Scan mode | Helical | Helical | Helical | Helical |
| Direction | Craniocaudal | Craniocaudal | Craniocaudal | Craniocaudal |
| Image reconstruction | - | Smoother, Standard, Sharper | - | Middle, High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shim, J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, K. Quantitative Evaluation of Low-Dose CT Image Quality Using Deep Learning Reconstruction: A Comparative Study of Philips Precise Image and GE TrueFidelity. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11090317
Shim J, Lee Y, Kim K. Quantitative Evaluation of Low-Dose CT Image Quality Using Deep Learning Reconstruction: A Comparative Study of Philips Precise Image and GE TrueFidelity. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(9):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11090317
Chicago/Turabian StyleShim, Jina, Youngjin Lee, and Kyuseok Kim. 2025. "Quantitative Evaluation of Low-Dose CT Image Quality Using Deep Learning Reconstruction: A Comparative Study of Philips Precise Image and GE TrueFidelity" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 9: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11090317
APA StyleShim, J., Lee, Y., & Kim, K. (2025). Quantitative Evaluation of Low-Dose CT Image Quality Using Deep Learning Reconstruction: A Comparative Study of Philips Precise Image and GE TrueFidelity. Journal of Imaging, 11(9), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11090317






