Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Histopathological Gastric Biopsies Using Deep Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
Related Work
2. Materials and Methods
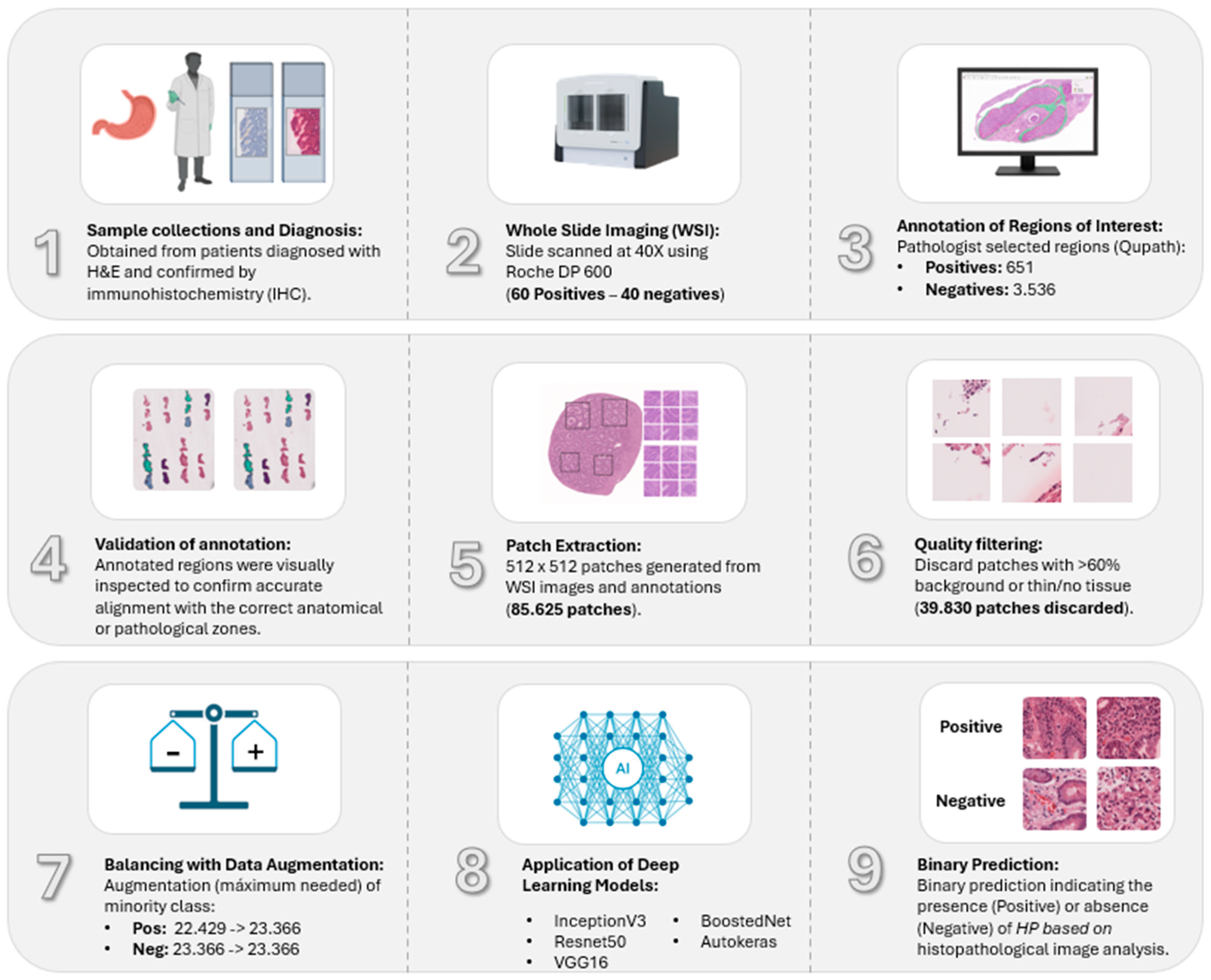
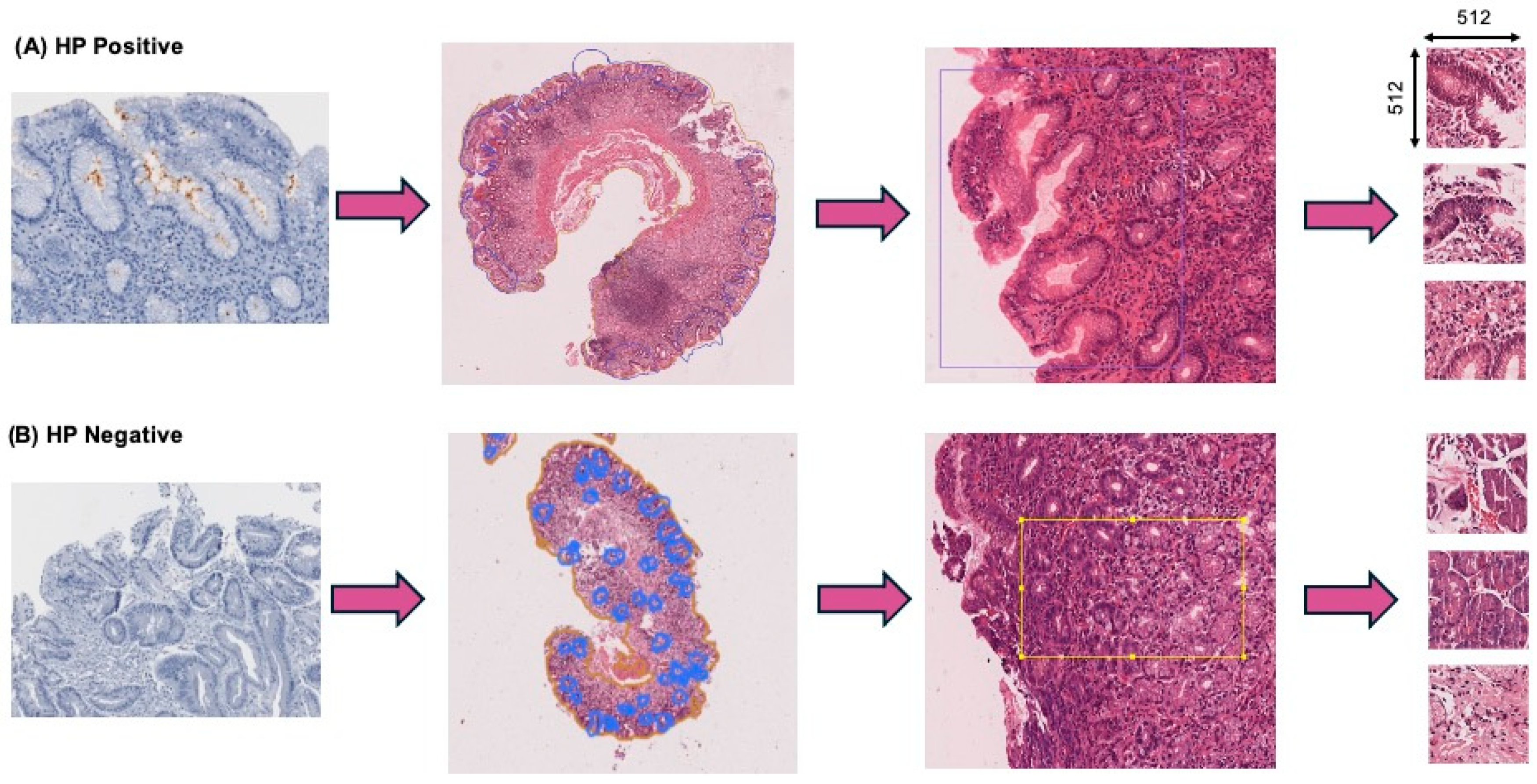
2.1. Dataset and Annotations
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.3. Image Pre-Processing
2.4. Dataset Filtering and Quality Assurance
2.5. Data Augmentation and Class Balancing
2.6. Deep Convolutional Neural Network Models
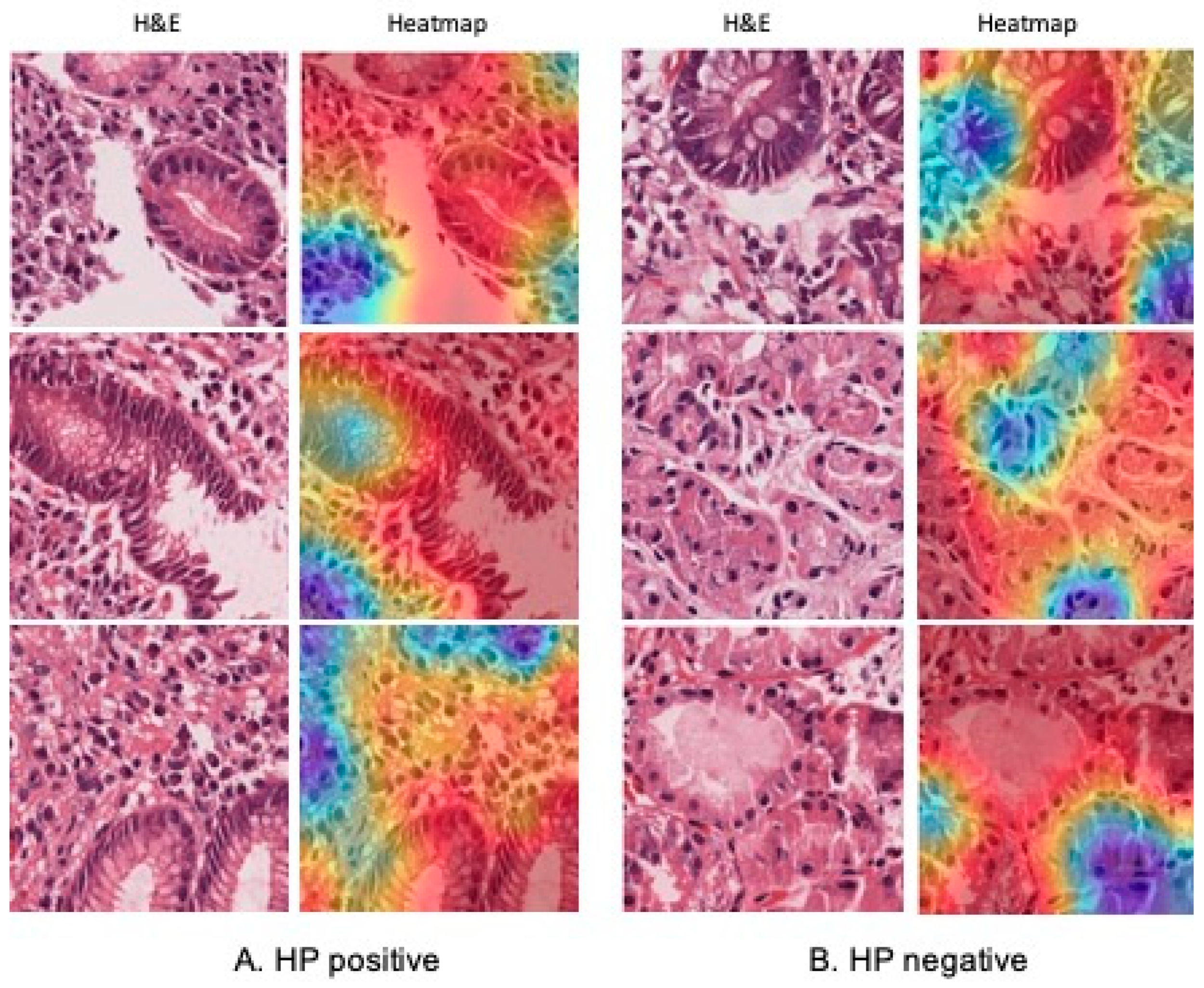
2.7. Validation and Interpretability with GradCAM
2.8. Experimental Design
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dataset Curation and Augmentation Strategy
3.2. Model Performance
3.3. External Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Connor, A.; O’Morain, C.A.; Ford, A.C. Population Screening and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, J.; Cao, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Cao, X.; Positive, H. Pylori Status Predicts Better Prognosis of Non-Cardiac Gastric Cancer Patients: Results from Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.M.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testerman, T.L.; Morris, J. Beyond the Stomach: An Updated View of Helicobacter pylori Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12781–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batts, K.P.; Ketover, S.; Kakar, S.; Krasinskas, A.M.; Mitchell, K.A.; Wilcox, R.; Westerhoff, M.; Rank, J.; Gibson, J.; Mattia, A.R.; et al. Appropriate Use of Special Stains for Identifying Helicobacter pylori: Recommendations from the Rodger C. Haggitt Gastrointestinal Pathology Society. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, e12–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebkhan, Y.; Mohammadi, M.; Rakhshani, N.; Abdirad, A.; Fayaz Moughadam, K.; Fereidooni, F. Interobserver Variations in Histopathological Assessment of Gastric Pathology. Pathology 2009, 41, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, S.; Parwani, A.V. Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostic Pathology. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Fenyö, D. Deep Learning and Its Applications in Computational Pathology. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, W.G.E.; Santos, M.H.P.D.; Brito, L.M.; Palheta, H.G.A.; Lobato, F.M.F.; Demachki, S.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â.; Araújo, G.S.D. DeepHP: A New Gastric Mucosa Histopathology Dataset for Helicobacter pylori Infection Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gildenblat, J.; Ihle, M.A.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Noh, K.W.; Peifer, M.; Quaas, A.; Büttner, R. Deep Learning for Sensitive Detection of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Biopsies. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscia, D.S.; D’Andrea, M.; Biletta, E.; Bellis, D.; Demo, K.; Ferrero, F.; Petti, A.; Butinar, R.; D’Andrea, E.; Davini, G. Use of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence for the Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Biopsies. Pathologica 2022, 114, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.R.; Hanson, J.A.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Schultz, F.A.; Sethi, A.; Clark, D.P. A Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network Can Recognize Common Patterns of Injury in Gastric Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.U.; Dirilenoğlu, F.; Hacisalihoğlu, U.P.; Ilhan, A.; Mirzaei, O. Classification of H. Pylori Infection from Histopathological Images Using Deep Learning. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 37, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Marklund, H.; Blaha, O.; Desai, M.; Martin, B.; Bingham, D.; Berry, G.J.; Gomulia, E.; Ng, A.Y.; Shen, J. Deep Learning Assistance for the Histopathologic Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori. Intell. Based Med. 2020, 1–2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Anu, K.V.; Paulose, R. BoostedNet: A Decision Support Model for the Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori from Gastric Histopathology Images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 96, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Chen, C.C.; Lee, C.H.; Yeh, C.Y.; Jeng, Y.M. Two-Tiered Deep-Learning-Based Model for Histologic Diagnosis of Helicobacter Gastritis. Histopathology 2023, 83, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, P.; Musulen, E.; Gil, D. Diagnosing Helicobacter pylori Using Autoencoders and Limited Annotations through Anomalous Staining Patterns in IHC Whole Slide Images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2025, 20, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Urresta, Á.; Yépez, Y.; Calvache, D.; Cifuentes, Y.; Lucero, N.; González, P.; Bedoya G, Á.; Manosalva, E.; Martínez, T.; Peñalosa, A.; et al. Proyecto Urkunina 5000-Investigación de La Prevalencia de Lesiones Precursoras y Del Efecto de La Erradicación de Helicobacter pylori Como Prevención Primaria Del Cáncer Gástrico En El Departamento de Nariño. Rev. Colomb. Cirugía 2018, 33, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open Source Software for Digital Pathology Image Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, A.; Gilbert, B.; Harkes, J.; Jukic, D.; Satyanarayanan, M. OpenSlide: A Vendor-Neutral Software Foundation for Digital Pathology. J. Pathol. Inform. 2013, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, S. Shapely: Manipulation and Analysis of Geometric Objects. Available online: https://Github.Com/Shapely/Shapely (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onakpojeruo, E.P.; Mustapha, M.T.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Ozsahin, I. Enhanced MRI-based brain tumour classification with a novel Pix2pix generative adversarial network augmentation framework. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onakpojeruo, E.P.; Mustapha, M.T.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Ozsahin, I. A Comparative Analysis of the Novel Conditional Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model, Using Conditional Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network-Generated Synthetic and Augmented Brain Tumor Datasets for Image Classification. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi-Aghbolaghi, M.; Darbandsari, A.; Zhang, A.; Contreras-Sanz, A.; Boschman, J.; Ahmadvand, P.; Köbel, M.; Farnell, D.; Huntsman, D.G.; Churg, A.; et al. Learning generalizable AI models for multi-center histopathology image classification. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Alzubaidi, M.; Al-Thelaya, K.; Cal, C.; Boughorbel, S.; Schneider, J.; Agus, M. Advancing open-source visual analytics in digital pathology: A systematic review of tools, trends, and clinical applications. J. Pathol. Inform. 2025, 18, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.M.; Schultz, F.A.; Tafoya, M.A.; Kerwin, A.A.; Broehm, C.J.; Fischer, E.G.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Clark, D.P.; Hanson, J.A.; Martin, D.R. A Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network Can Differentiate Between Helicobacter pylori Gastritis and Autoimmune Gastritis With Results Comparable to Gastrointestinal Pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2022, 146, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, N. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori by Invasive Test: Histology. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, A.T.; Boechat, A.C. How Automated Machine Learning Can Improve Business. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elangovan, K.; Lim, G.; Ting, D. A Comparative Study of an on Premise AutoML Solution for Medical Image Classification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ziebell, J.; Arole, V.; Parkinson, B.; Yu, L.; Dai, H.; Frankel, W.L.; Yearsley, M.; Esnakula, A.; Sun, S.; et al. Comparing Accuracy of Helicobacter pylori Identification Using Traditional Hematoxylin and Eosin–Stained Glass Slides With Digital Whole Slide Imaging. Lab. Investig. 2024, 104, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phase | Patients | Biopsies | Patches Included | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 16 (10 HP+/6HP−) | 80 (48 HP+/32HP−) | Yes | Used for model fitting and augmentation |
| Test | 4 (2 HP+/2HP−) | 20 (12 HP+/8HP−) | Yes | Held-out internal test set |
| DL Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Specificity | F1 Score | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| InceptionV3 | 98% | 97% | 100% | 97% | 98% | 97% |
| VGG16 | 98% | 97% | 100% | 97% | 98% | 96% |
| ResNet50 | 97% | 97% | 99% | 96% | 98% | 95% |
| BoostedNet | 85% | 87% | 84% | 87% | 86% | 82% |
| AutoKeras | 89% | 92% | 85% | 93% | 88% | 78% |
| DL Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Specificity | F1 Score | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| InceptionV3 | 97% | 94% | 100% | 94% | 97% | 93% |
| VGG16 | 96% | 94% | 98% | 94% | 96% | 92% |
| ResNet50 | 96% | 94% | 97% | 94% | 96% | 91% |
| BoostedNet | 83% | 84% | 83% | 84% | 84% | 68% |
| AutoKeras | 82% | 85% | 80% | 84% | 82% | 64% |
| Authors and Year (Ref) | Databases | Validation Stain | AUC (IC 95%) | DL Architecture | Additional Pre-Processing | xAI | Metadata | Total Number of WSIs | Patch Size (Pixel) | Training Set (WSIs) | Validation Set (WSIs) | Test Set (WSIs) | External Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present article | Institutional | H&E | 1.0 (N/A) | InceptionV3 | Quality filtering: patches containing more than 60% background or minimal/no visible tissue were discarded. Data augmentation (rotation, horizontal flip, zoom, and width and height shift) | No | Yes | 100 | 512 × 512 | 80 | N/A | 20 | Yes |
| 1.0 (N/A) | VGG16 | ||||||||||||
| 1.0 (N/A) | ResNet50 | ||||||||||||
| 0.92 (N/A) | BoostedNet | ||||||||||||
| 0.92 (N/A) | AutoKeras | ||||||||||||
| Cano, et al., 2025 [17] | Institutional | IHC | 0.961 (N/A) | Autoencoder | Morphological operations, conversion to HSV and pixel filtering, sliding windows on the edges | No | No | 245 | 256 × 256 | 123 | N/A | 122 | No |
| 0.77 (N/A) | ResNet18 | ||||||||||||
| 0.92 (N/A) | ResTreshold | ||||||||||||
| 0.88 (N/A) | UNI Vit | ||||||||||||
| Krishna, et al., 2024 [15] | Public dataset | H&E, Giemsa | 0.990 (N/A) | BoostedNet: CNN + XGBoost | Resize to 256 × 256, Gaussian filter, data augmentation (rotation, zoom, shear, flip) | Yes | No | 19 | 256 × 256 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Yes |
| Ibrahim, et al., 2024 [13] | Institutional | H&E | 0.941 (N/A) | ResNet-101 | N/A | No | No | 204 | 960 × 1280 | CV | CV | CV | No |
| 0.930 (N/A) | DenseNet-201 | ||||||||||||
| 0.903 (N/A) | MobileNet-v2 | ||||||||||||
| 0.917 (N/A) | InceptionV3 | ||||||||||||
| 0.907 (N/A) | Xception | ||||||||||||
| Lin, et al., 2023 [16] | Institutional | H&E | 0.973 (0.954–0.993) | ESCNN + Logistic Regression | N/A | Yes | No | 1075 | N/A | 885 | N/A | 190 | Yes |
| Franklin, et al., 2022 [27] | Institutional | H&E | N/A | HALO-AI software (fully convolutional VGG network) | Data augmentation: rotations variations in hue, saturation, contrast, and brightness | No | Yes | 187 | 400 × 400 | 112 | N/A | 75 | No |
| Liscia, et al., 2022 [11] | Institutional | W-S | 0.938 (N/A) | CNN-based model via Microsoft Custom Vision (VGG-based model) | NDPI to TIFF conversion | No | Yes | 185 | 2000 × 2000 | N/A | N/A | N/A | No |
| Gonçalves, et al., 2022 [9] | Institutional | H&E | 0.998 | VGG16 | Noise correction, grayscale, binarization, augmentation (rotation, flip, zoom) | No | No | 19 | 256 × 256 | N/A | N/A | N/A | No |
| 0.994 | InceptionV3 | ||||||||||||
| 0.994 | ResNet50 | ||||||||||||
| Martin, et al., 2020 [12] | Institutional | H&E | 1.00 (N/A) | HALO-AI software (fully convolutional VGG network) | Data augmentation with random rotations and random changes in hue, saturation, contrast, and brightness | No | Si | 300 | 400 × 400 | 210 | 90 | N/A | Yes |
| Klein, et al., 2020 [10] | Institutional | Giemsa | 0.950 (N/A) | Compact VGG-style deep neural network | Data augmentation, Rgb to Hsv conversion, Otsu’s thresholding, morphological operations, contour detection | Yes | Yes | 627 | 224 × 224 | 477 | 150 | N/A | Yes |
| 0.902 (N/A) | |||||||||||||
| 0.810 (N/A) | |||||||||||||
| Zhou, et al., 2020 [14] | Institutional | H&E | 0.965 (0.934–0.987) | MobileNet-V2 | Laplacian filtering, data augmentation through horizontal inversion | Yes | Yes | 108 | 299 × 299 | 77 | 31 | N/A | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parra-Medina, R.; Zambrano-Betancourt, C.; Peña-Rojas, S.; Quintero-Ortiz, L.; Caro, M.V.; Romero, I.; Gil-Gómez, J.H.; Sprockel, J.J.; Cancino, S.; Mosquera-Zamudio, A. Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Histopathological Gastric Biopsies Using Deep Learning Models. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070226
Parra-Medina R, Zambrano-Betancourt C, Peña-Rojas S, Quintero-Ortiz L, Caro MV, Romero I, Gil-Gómez JH, Sprockel JJ, Cancino S, Mosquera-Zamudio A. Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Histopathological Gastric Biopsies Using Deep Learning Models. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(7):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070226
Chicago/Turabian StyleParra-Medina, Rafael, Carlos Zambrano-Betancourt, Sergio Peña-Rojas, Lina Quintero-Ortiz, Maria Victoria Caro, Ivan Romero, Javier Hernan Gil-Gómez, John Jaime Sprockel, Sandra Cancino, and Andres Mosquera-Zamudio. 2025. "Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Histopathological Gastric Biopsies Using Deep Learning Models" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 7: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070226
APA StyleParra-Medina, R., Zambrano-Betancourt, C., Peña-Rojas, S., Quintero-Ortiz, L., Caro, M. V., Romero, I., Gil-Gómez, J. H., Sprockel, J. J., Cancino, S., & Mosquera-Zamudio, A. (2025). Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Histopathological Gastric Biopsies Using Deep Learning Models. Journal of Imaging, 11(7), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070226






