Spectro-Image Analysis with Vision Graph Neural Networks and Contrastive Learning for Parkinson’s Disease Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets and Data Availability
2.1.1. Dataset Characteristics
2.1.2. Individual Dataset Descriptions
2.1.3. Multi-Institutional Dataset Integration and Validation
2.2. Data Preprocessing and Feature Engineering
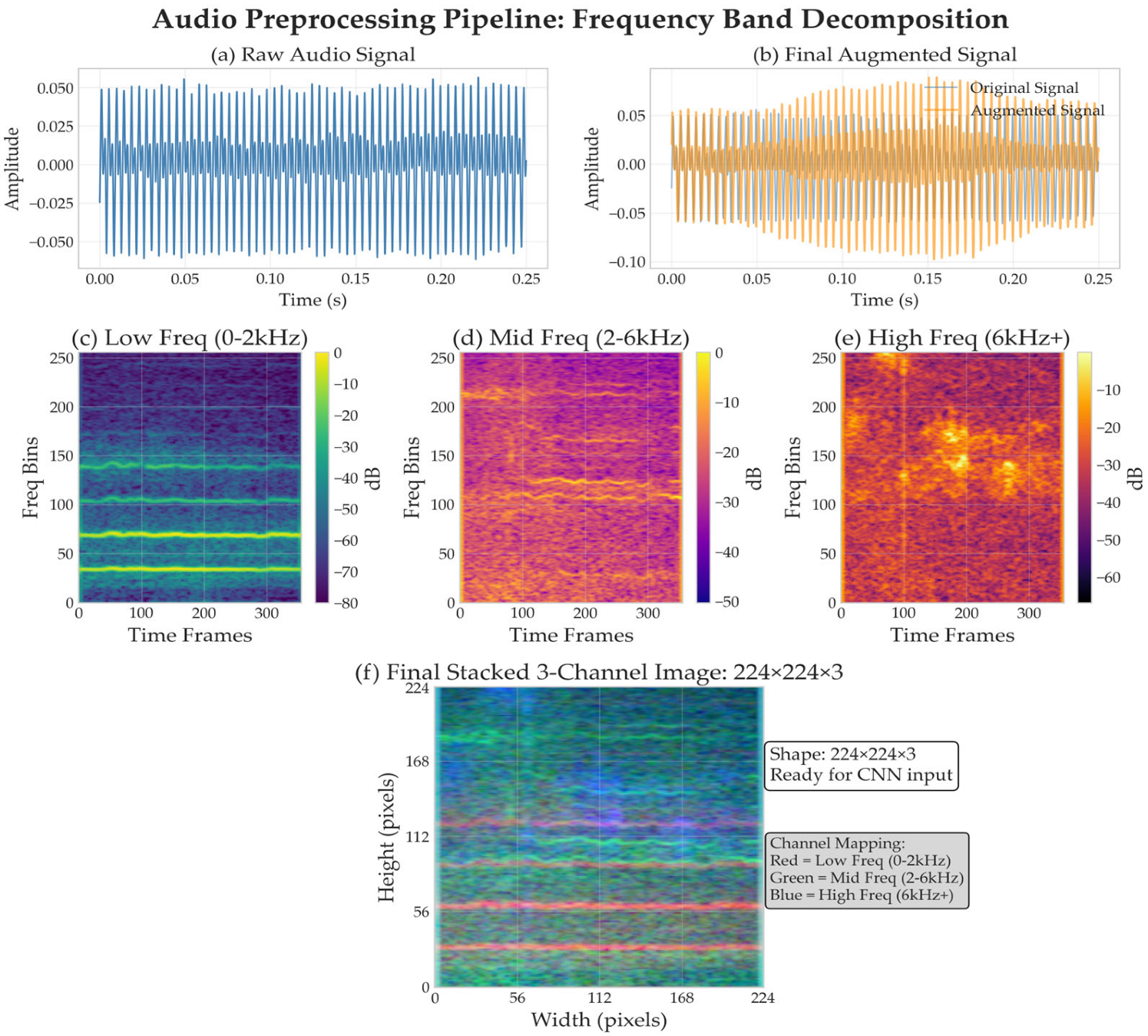
2.2.1. Audio Preprocessing Pipeline
2.2.2. Multi-Scale Data Augmentation Framework
2.3. Proposed Architecture
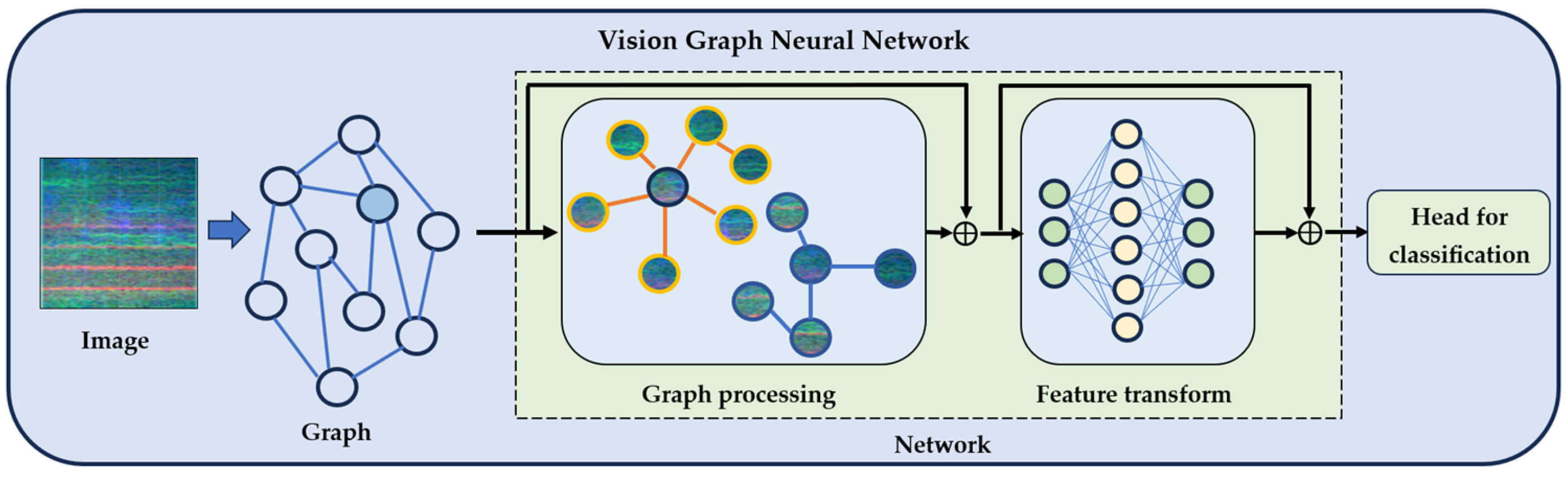
2.3.1. Vision Graph Neural Network Architecture
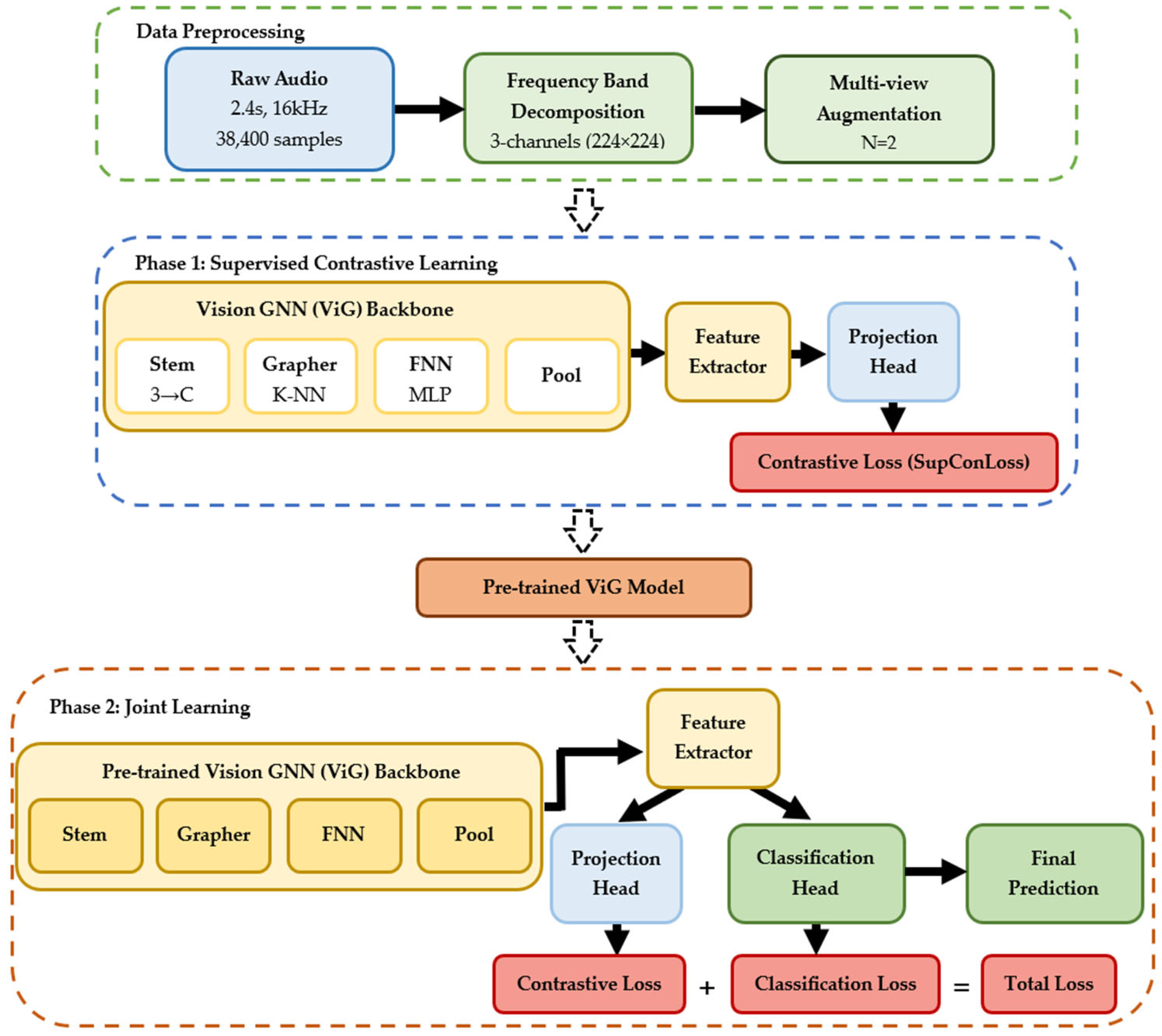
2.3.2. System Overview and Design Principles
2.4. Training Methodology
2.4.1. Supervised Contrastive Learning Framework
2.4.2. Supervised Contrastive Loss Formulation
- represents all anchor indices.
- defines positive samples sharing the same label.
- includes all samples except the anchor.
- is the temperature parameter controlling distribution concentration.
2.4.3. Two-Phase Training Protocol
3. Experimental Setup and Implementation
3.1. Dataset Preparation and Augmentation
3.2. Hyperparameter Optimization
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Architecture Performance Comparison
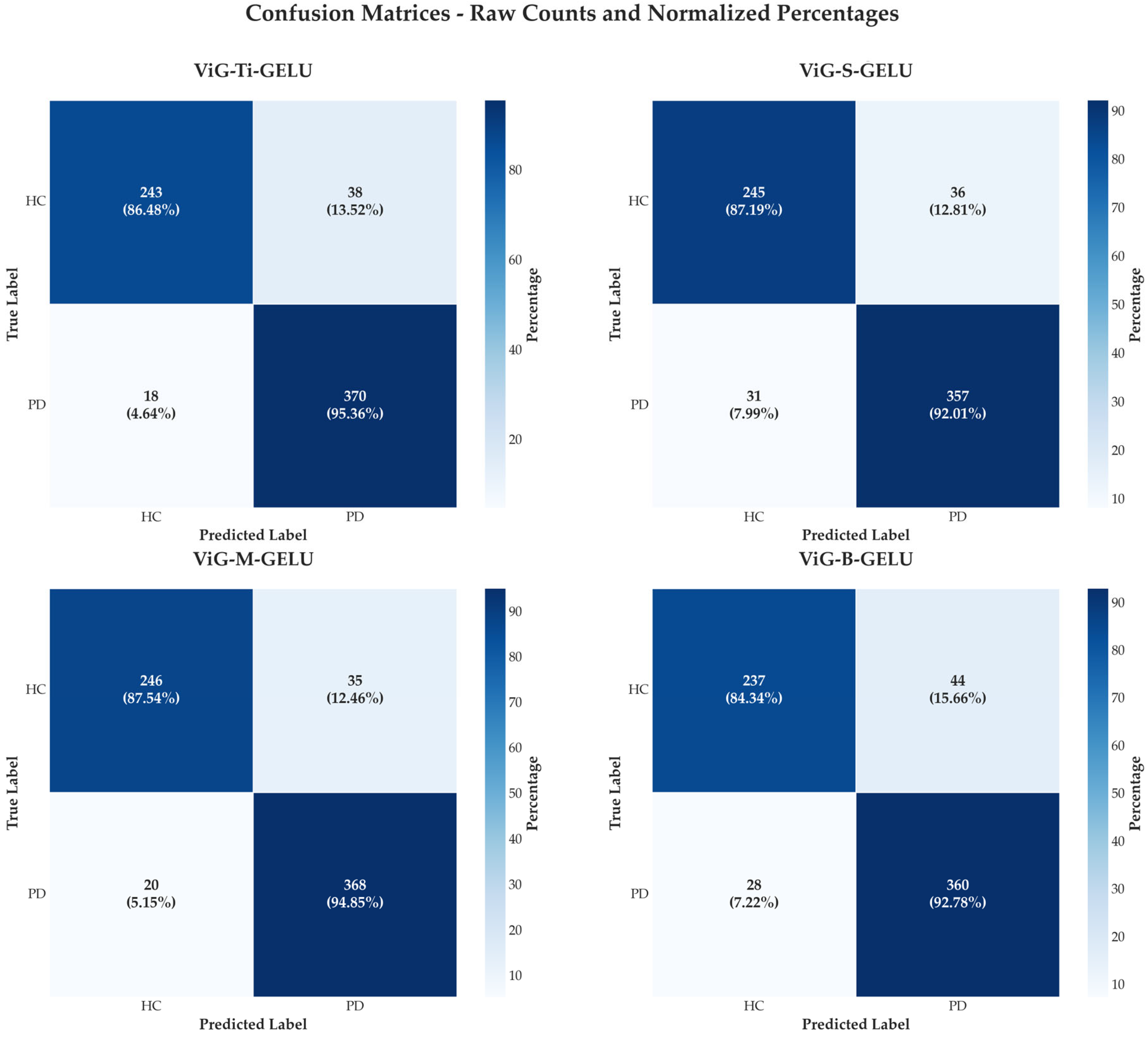
4.2. Confusion Matrix Analysis
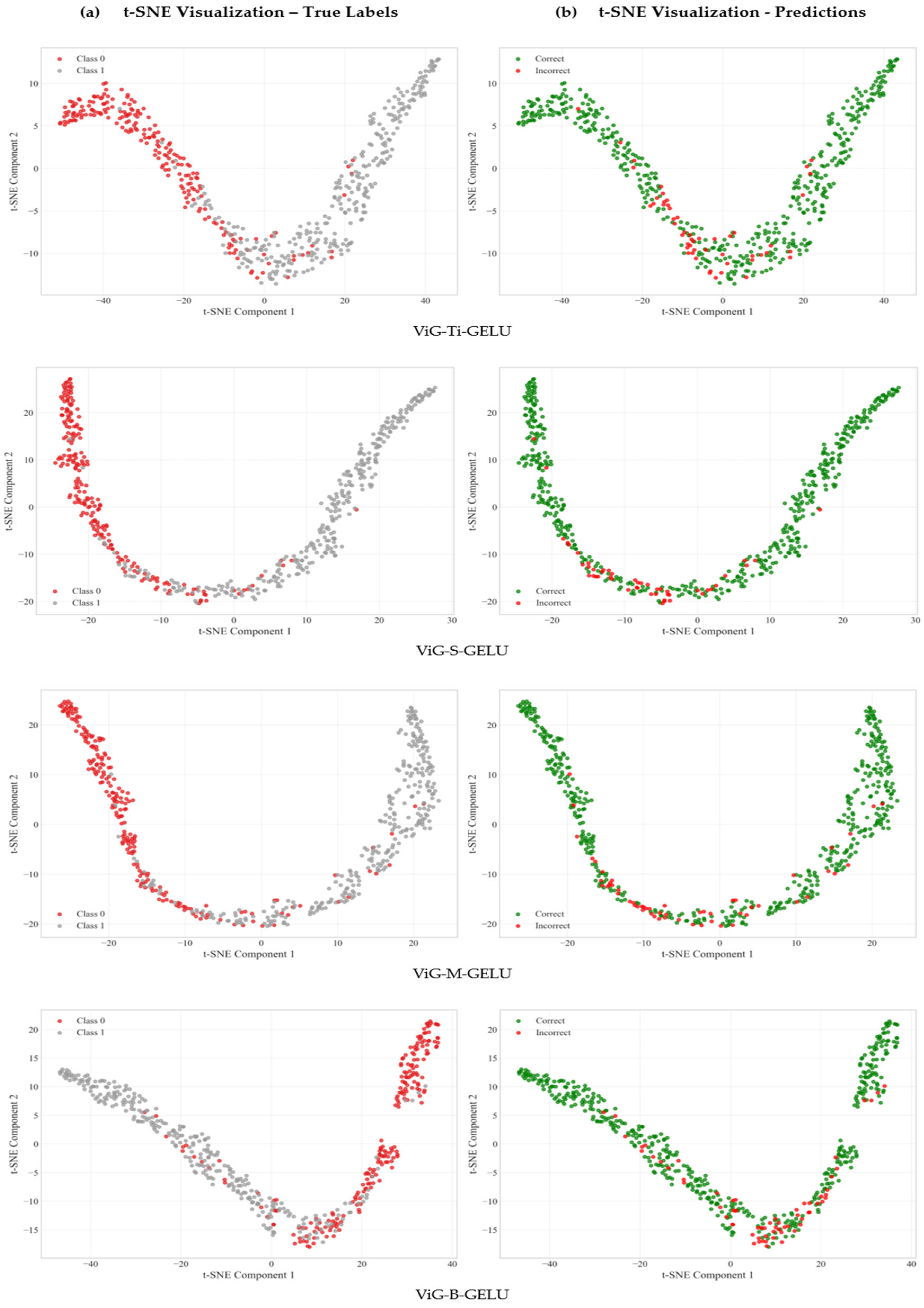
4.3. Feature Representation Quality Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC-ROC | Area Under the Curve-Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| dB | Decibels |
| GELU | Gaussian Error Linear Unit |
| GNN | Graph Neural Networks |
| HC | Healthy Controls |
| kHz | Kilohertz |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MFCC | Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients |
| PC-GITA | Parkinson’s Disease-Group of Intelligent Technologies for Assessment |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| STFT | Short-Time Fourier Transform |
| t-SNE | t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding |
| ViGs | Vision Graph Neural Networks |
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Projected Number of People with Parkinson Disease in the Most Populous Nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 2007, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.I.; Jansen Steur, E.N.H.; Braak, E. Staging of Brain Pathology Related to Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J. Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Hunter, E.J.; Spielman, J.; Ramig, L.O. Suitability of Dysphonia Measurements for Telemonitoring of Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanas, A.; Little, M.A.; McSharry, P.E.; Ramig, L.O. Accurate Telemonitoring of Parkinson’s Disease Progression by Noninvasive Speech Tests. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusz, J.; Cmejla, R.; Ruzickova, H.; Ruzicka, E. Quantitative Acoustic Measurements for Characterization of Speech and Voice Disorders in Early Untreated Parkinson’s Disease. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 350–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapir, S.; Spielman, J.L.; Ramig, L.O.; Story, B.H.; Fox, C. Effects of Intensive Voice Treatment (the Lee Silverman Voice Treatment [LSVT]) on Vowel Articulation in Dysarthric Individuals with Idiopathic Parkinson Disease: Acoustic and Perceptual Findings. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Kemp, A.; Rahmatallah, Y.; Pillai, L.; Glover, A.; Prior, F.; Larson-Prior, L.; Virmani, T. A Machine Learning Method to Process Voice Samples for Identification of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatallah, Y.; Kemp, A.S.; Iyer, A.; Pillai, L.; Larson-Prior, L.J.; Virmani, T.; Prior, F. Pre-Trained Convolutional Neural Networks Identify Parkinson’s Disease from Spectrogram Images of Voice Samples. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, O.P. Harnessing Voice Analysis and Machine Learning for Early Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease: A Comparative Study Across Three Datasets. J. Voice 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran Reddy, M.; Alku, P. Automatic Detection of Parkinsonian Speech Using Wavelet Scattering Features. JASA Express Lett. 2025, 5, 055202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare, M.G.; Perpetuini, D.; Cardone, D.; Merla, A. Machine Learning-Assisted Speech Analysis for Early Detection of Parkinson’s Disease: A Study on Speaker Diarization and Classification Techniques. Sensors 2024, 24, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.H.; Ogudo, K.A. Ensemble Machine Learning Approach for Parkinson’s Disease Detection Using Speech Signals. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, I.; Ditta, A.; Mazhar, T.; Anwar, M.; Saeed, M.M.; Hamam, H. Voice Biomarkers as Prognostic Indicators for Parkinson’s Disease Using Machine Learning Techniques. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashum, T.; Snyder, R.C.; O’Brien, M.K.; Albert, M. V Machine Learning Models for Parkinson Disease: Systematic Review. JMIR Med. Inf. 2024, 12, e50117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Vergara, T.; Klumpp, P.; Vasquez-Correa, J.C.; Nöth, E.; Orozco-Arroyave, J.R.; Schuster, M. Multi-Channel Spectrograms for Speech Processing Applications Using Deep Learning Methods. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Hasan, M.; Sarkar, A.K.; Khan, F. Classification of Parkinson’s Disease Using Speech Signal with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches. Eur. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2023, 7, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, K.P.; Samal, S.R.; Ravi, V.; Nayak, S.R.; Alahmadi, T.J.; Singh, P.; Diwakar, M. Towards Early Intervention: Detecting Parkinson’s Disease through Voice Analysis with Machine Learning. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2024, 18, e18741207294056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Quatra, M.; Turco, M.F.; Svendsen, T.; Salvi, G.; Orozco-Arroyave, J.R.; Siniscalchi, S.M. Exploiting Foundation Models and Speech Enhancement for Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Speech in Real-World Operative Conditions. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2024, Kos, Greece, 1–5 September 2024; ISCA: Singapore, 2024; pp. 1405–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Graph Neural Networks: A Review of Methods and Applications. AI Open 2020, 1, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph Attention Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, Y.; Wu, E. Vision GNN: An Image Is Worth Graph of Nodes. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 8291–8303. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Che, T.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Graph Neural Networks for Image-guided Disease Diagnosis: A Review. iRADIOLOGY 2023, 1, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedt-Aristizabal, D.; Armin, M.A.; Denman, S.; Fookes, C.; Petersson, L. Graph-Based Deep Learning for Medical Diagnosis and Analysis: Past, Present and Future. Sensors 2021, 21, 4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised Contrastive Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 18661–18673. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.; Kim, J.-W.; Cho, W.-Y.; Baek, H.; Son, S.; Lee, B.; Ha, C.; Tae, K.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.-Y. Patch-Mix Contrastive Learning with Audio Spectrogram Transformer on Respiratory Sound Classification. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Alavi, A.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Self-Supervised Contrastive Learning for Medical Time Series: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Grangier, D.; Zeghidour, N. Contrastive Learning of General-Purpose Audio Representations. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3875–3879. [Google Scholar]
- Moummad, I.; Farrugia, N. Pretraining Respiratory Sound Representations Using Metadata and Contrastive Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), New Paltz, NY, USA, 22–25 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dimauro, G.; Caivano, D.; Bevilacqua, V.; Girardi, F.; Napoletano, V. VoxTester, Software for Digital Evaluation of Speech Changes in Parkinson Disease. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Benevento, Italy, 15–18 May 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dimauro, G.; Di Nicola, V.; Bevilacqua, V.; Caivano, D.; Girardi, F. Assessment of Speech Intelligibility in Parkinson’s Disease Using a Speech-To-Text System. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 22199–22208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Arroyave, J.R.; Arias-Londoño, J.D.; Vargas-Bonilla, J.F.; González-Rátiva, M.C.; Nöth, E. New Spanish Speech Corpus Database for the Analysis of People Suffering from Parkinson’s Disease. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’14), Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; Calzolari, N., Choukri, K., Declerck, T., Loftsson, H., Maegaard, B., Mariani, J., Moreno, A., Odijk, J., Piperidis, S., Eds.; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Reykjavik, Iceland, 2014; pp. 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Moro-Velazquez, L.; Gomez-Garcia, J.A.; Godino-Llorente, J.I.; Grandas-Perez, F.; Shattuck-Hufnagel, S.; Yagüe-Jimenez, V.; Dehak, N. Phonetic Relevance and Phonemic Grouping of Speech in the Automatic Detection of Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Laureano, J.; Gómez-García, J.A.; Guerrero-López, A.; Luque-Buzo, E.; Arias-Londoño, J.D.; Grandas-Pérez, F.J.; Godino-Llorente, J.I. NeuroVoz: A Castillian Spanish Corpus of Parkinsonian Speech. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFee, B.; Raffel, C.; Liang, D.; Ellis, D.; McVicar, M.; Battenberg, E.; Nieto, O. Librosa: Audio and Music Signal Analysis in Python. In Proceedings of the SciPy, Austin, TX, USA, 6–12 July 2015; pp. 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A Survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.; Chan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, C.-C.; Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V. SpecAugment: A Simple Data Augmentation Method for Automatic Speech Recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Chen, Q.; You, X. MelTrans: Mel-Spectrogram Relationship-Learning for Speech Emotion Recognition via Transformers. Sensors 2024, 24, 5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, F.; Serra, A.; Lamberti, F.; Morra, L. Data Augmentation for Medical Imaging: A Systematic Literature Review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, C.; Strik, H. Two-Stage Data Augmentation for Improved ASR Performance for Dysarthric Speech. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 189, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusz, J.; Hlavnička, J.; Čmejla, R.; Růžička, E. Automatic Evaluation of Speech Rhythm Instability and Acceleration in Dysarthrias Associated with Basal Ganglia Dysfunction. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavnička, J.; Čmejla, R.; Tykalová, T.; Šonka, K.; Růžička, E.; Rusz, J. Automated Analysis of Connected Speech Reveals Early Biomarkers of Parkinson’s Disease in Patients with Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behaviour Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skodda, S.; Grönheit, W.; Schlegel, U. Impairment of Vowel Articulation as a Possible Marker of Disease Progression in Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, P.; Kundu, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. Vision HGNN: An Image Is More than a Graph of Nodes. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 19821–19831. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Liu, Y. ViG-UNet: Vision Graph Neural Networks for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 20th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Cartagena, Colombia, 18–21 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
| Dataset | Participants | Demographics (Age) | Country/ Institution | Complete Speech Tasks Available | Audio Specs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Italian PVS | 50 (28 PD, 22 HC) | 67.1 ± 5.2 (HC), 67.2 ± 4.8 (PD) | Italy/University of Bari | Sustained vowels (/a/, /e/, /i/, /o/, /u/), phonemically balanced text reading, syllable repetitions (/pa/, /ta/), phonemically balanced words | 16 kHz (harmonized) |
| PC-GITA | 100 (50 PD, 50 HC) | 31–86 years, gender-matched | Colombia/ Clínica Noel, Medellín | Sustained vowels (/a/, /e/, /i/, /o/, /u/), diadochokinetic evaluation, 45 isolated words, 10 sentences, reading text, monologues | 44.1 kHz, 16-bit |
| Neurovoz | 108 (53 PD, 55 HC) | Age-matched adults | Spain/UPM and Hospital Gregorio Marañón | Sustained vowels (/a/, /e/, /i/, /o/, /u/) in triplicate, diadochokinetic tests (/pa-ta-ka/), 16 listen-and-repeat utterances, spontaneous monologues | 16 kHz |
| Combined (This Study) | 258 (131 PD, 127 HC) | Multi-demographic | Multi institutional | Sustained vowels (/a/, /e/, /i/, /o/, /u/) only | 16 kHz (harmonized) |
| Split | Total Segments | Healthy Control | PD | Class Balance Ratio (HC: PD) | Augmentation Applied |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 6027 | 2616 (43.35%) | 3411 (56.65%) | 1:1.30 | Multi-view + Augment |
| Validation | 660 | 324 (49.10%) | 336 (50.90%) | 1:1.04 | No |
| Test | 669 | 321 (48.00%) | 348 (52.00%) | 1:1.08 | No |
| Total | 7356 | 3261 (43.88%) | 2103 (56.12%) | 1:1.26 | - |
| Rank | Val Accuracy | Val Loss | Temperature | Projection Dimensions | Contrastive Weight | Classification Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91.82% | 1.247 | 0.05 | 128 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 90.60% | 1.428 | 0.05 | 128 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| 3 | 90.15% | 1.568 | 0.05 | 256 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 89.54% | 1.259 | 0.05 | 256 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 5 | 89.39% | 1.921 | 0.10 | 128 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 6 | 88.93% | 2.560 | 0.10 | 256 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| 7 | 88.18% | 2.177 | 0.10 | 256 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| 8 | 87.72% | 1.933 | 0.10 | 64 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Architecture | Training Acc | Validation Acc | Test Acc | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | AUC-ROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ViG-Ti-GELU + Contrastive Learning | 98.46% | 89.85% | 91.63% | 90.69% | 95.36% | 92.96% | 0.965 |
| ViG-Ti-GELU | 79.38% | 79.94% | 78.68% | 79.25% | 78.68% | 79.25% | 0.851 |
| ViG-S-GELU + Contrastive Learning | 99.24% | 89.24% | 89.99% | 90.84% | 92.01% | 91.42% | 0.961 |
| ViG-S-GELU | 83.16% | 81.83% | 82.64% | 83.13% | 82.16% | 82.62% | 0.886 |
| ViG-M-GELU + Contrastive Learning | 99.26% | 90.52% | 91.78% | 91.32% | 94.85% | 93.05% | 0.966 |
| ViG-M-GELU | 85.28% | 84.77% | 85.22% | 85.64% | 84.82% | 85.26% | 0.911 |
| ViG-B-GELU + Contrastive Learning | 99.86% | 88.67% | 89.24% | 89.11% | 92.78% | 90.91% | 0.950 |
| ViG-B-GELU | 84.82% | 84.26% | 84.81% | 85.28% | 84.46% | 84.83% | 0.907 |
| Architecture | Silhouette Score | Calinski–Harabasz Index | Davies-Bouldin Index | Intra-Class Distance | Inter-Class Distance | Separation Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ViG-Ti-GELU | 0.4788 | 938.92 | 0.6712 | 22.21 | 46.83 | 2.11 |
| ViG-S-GELU | 0.4840 | 914.15 | 0.6384 | 38.78 | 81.02 | 2.09 |
| ViG-M-GELU | 0.5505 | 1217.87 | 0.5845 | 30.13 | 76.29 | 2.53 |
| ViG-B-GELU | 0.4227 | 739.03 | 0.7829 | 37.48 | 70.64 | 1.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madusanka, N.; Malekroodi, H.S.; Herath, H.M.K.K.M.B.; Hewage, C.; Yi, M.; Lee, B.-I. Spectro-Image Analysis with Vision Graph Neural Networks and Contrastive Learning for Parkinson’s Disease Detection. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070220
Madusanka N, Malekroodi HS, Herath HMKKMB, Hewage C, Yi M, Lee B-I. Spectro-Image Analysis with Vision Graph Neural Networks and Contrastive Learning for Parkinson’s Disease Detection. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(7):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070220
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadusanka, Nuwan, Hadi Sedigh Malekroodi, H. M. K. K. M. B. Herath, Chaminda Hewage, Myunggi Yi, and Byeong-Il Lee. 2025. "Spectro-Image Analysis with Vision Graph Neural Networks and Contrastive Learning for Parkinson’s Disease Detection" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 7: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070220
APA StyleMadusanka, N., Malekroodi, H. S., Herath, H. M. K. K. M. B., Hewage, C., Yi, M., & Lee, B.-I. (2025). Spectro-Image Analysis with Vision Graph Neural Networks and Contrastive Learning for Parkinson’s Disease Detection. Journal of Imaging, 11(7), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070220








