Interpretability of Deep High-Frequency Residuals: A Case Study on SAR Splicing Localization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We show that DHFRs extracted from spliced amplitude SAR images present different appearance depending on the nature of the editing operation executed on them;
- We link this phenomenon to the ability of DHFR to capture high-frequency-related traces, in particular, the energy content of the image in the high-frequency range.
2. Background
2.1. Multimedia Forensics and High-Pass Frequency Residuals
2.2. SAR Imagery and Forensics
3. Amplitude SAR Imagery Splicing Localization
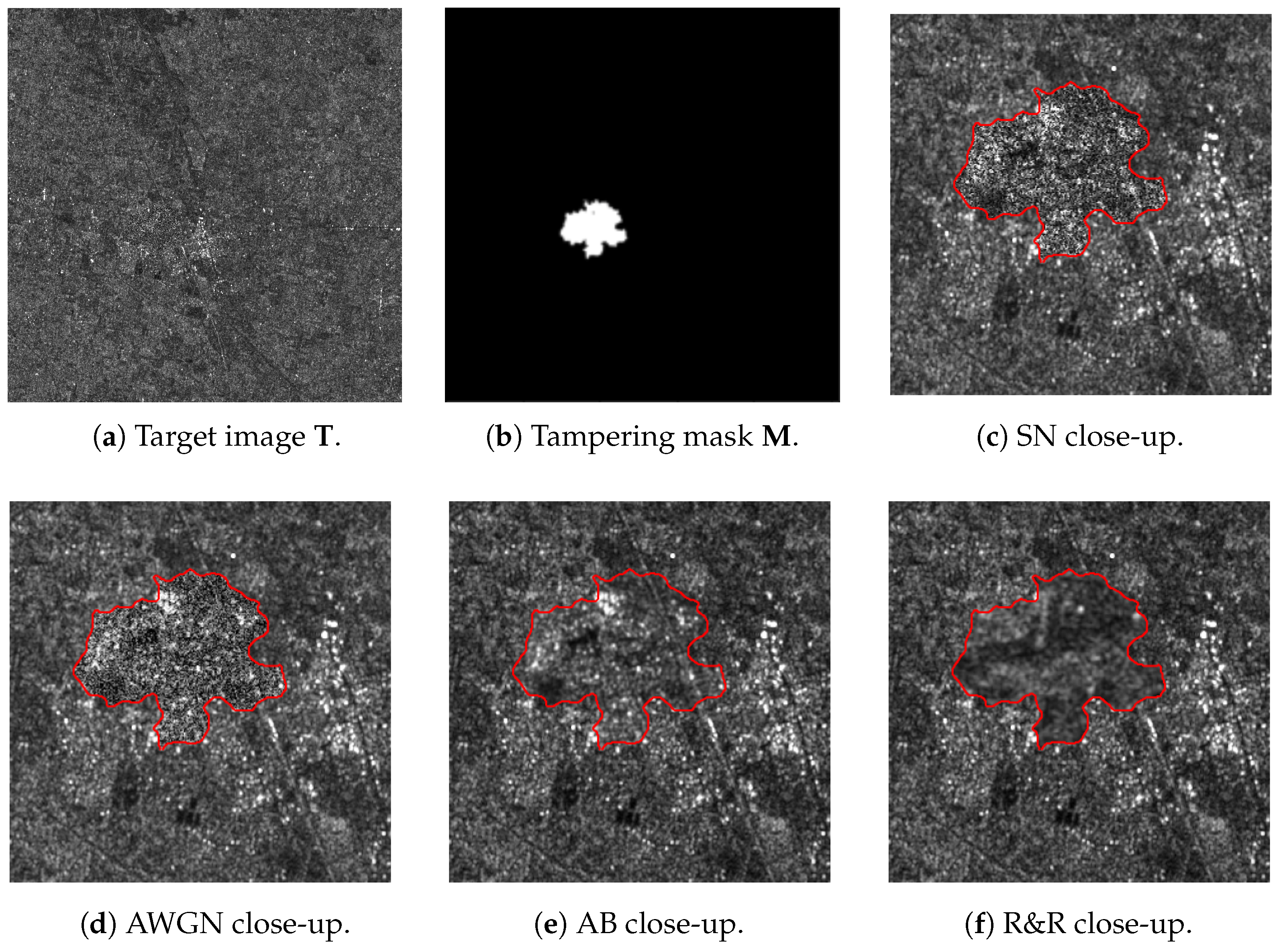
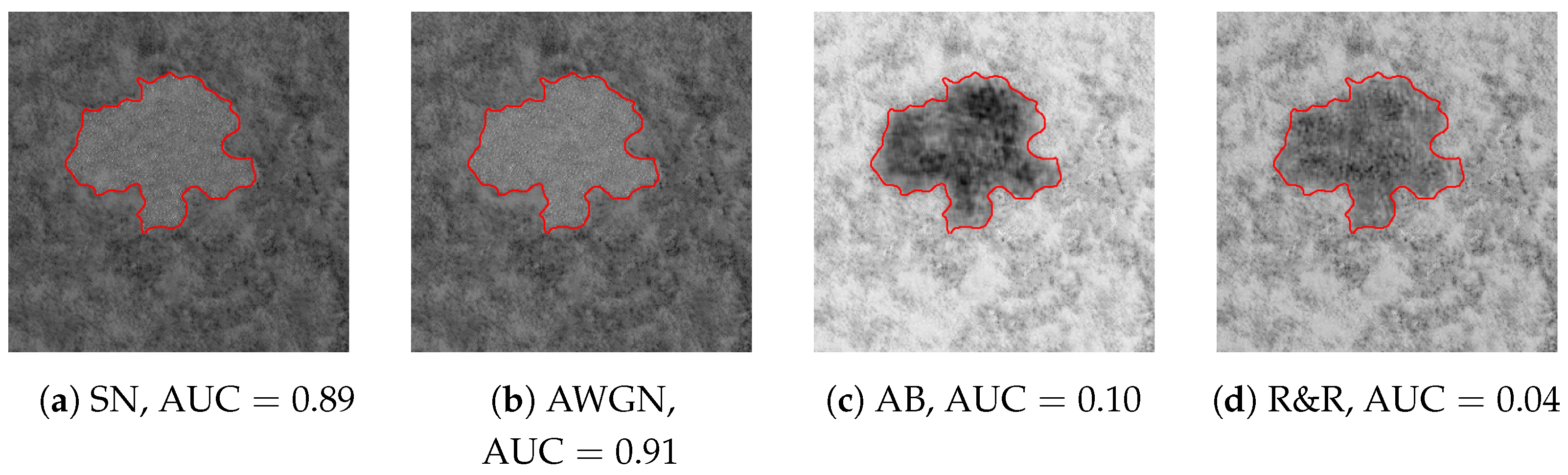
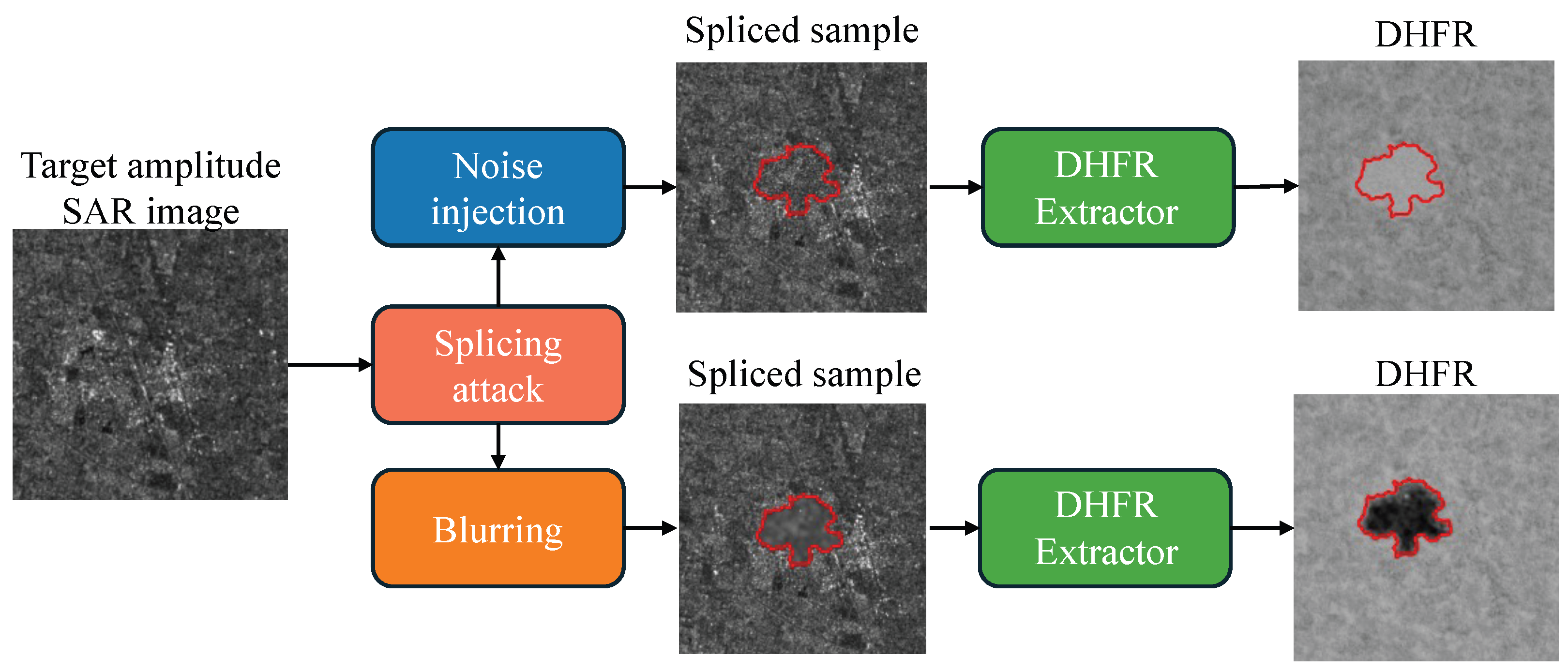
4. SAR DHFR Interpretability Analysis
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. DHFR Visual Inspection
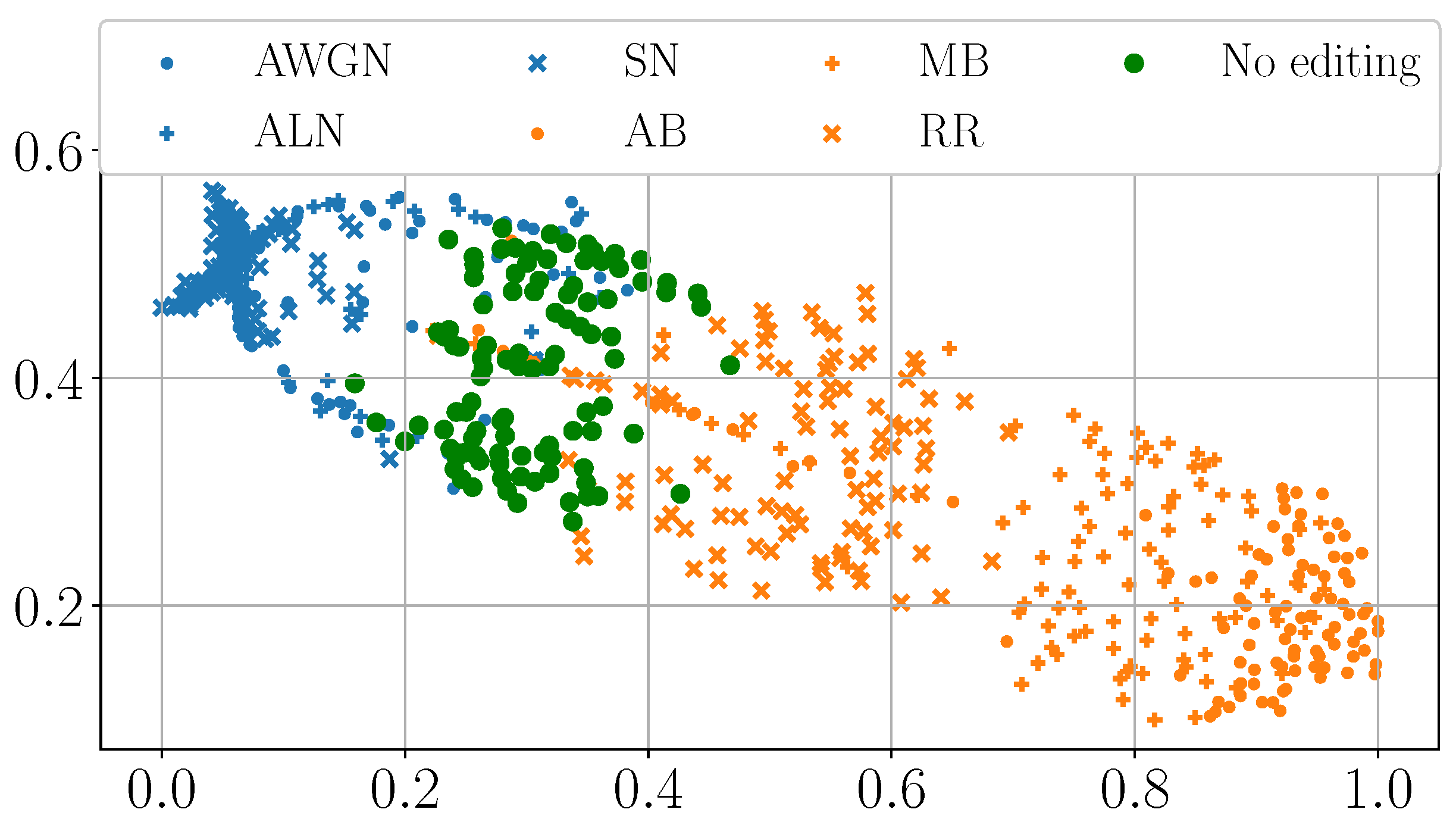
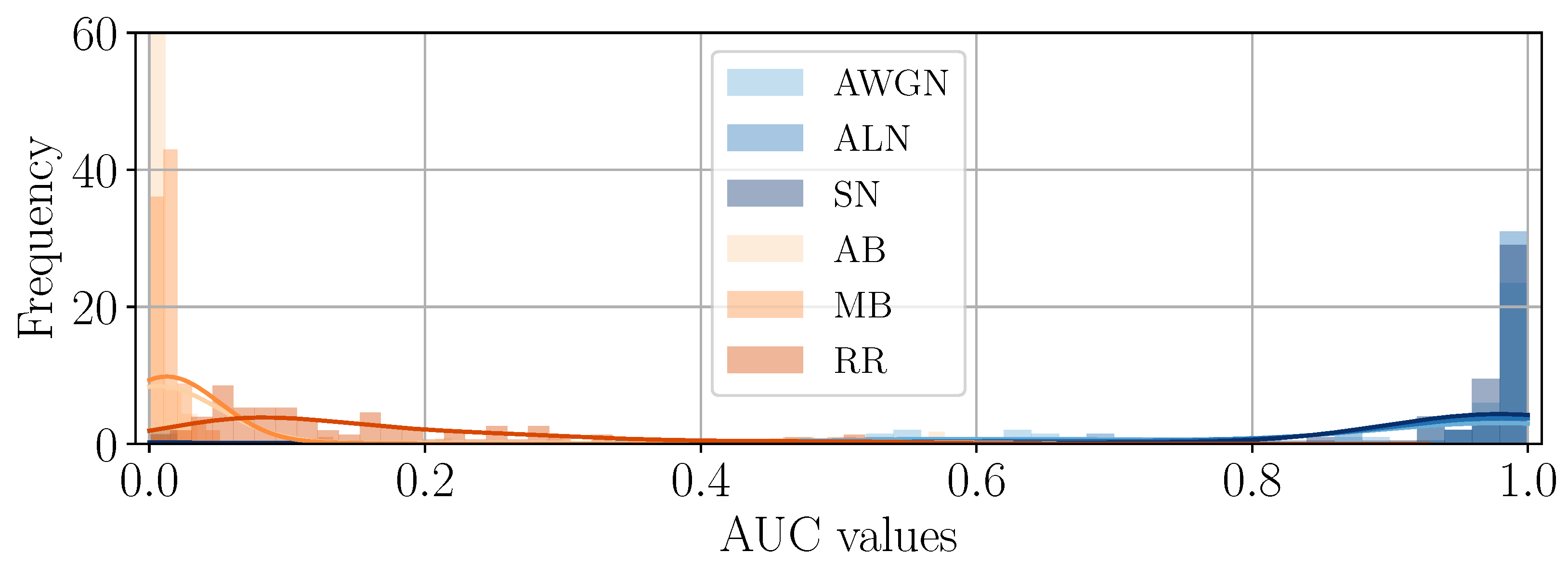
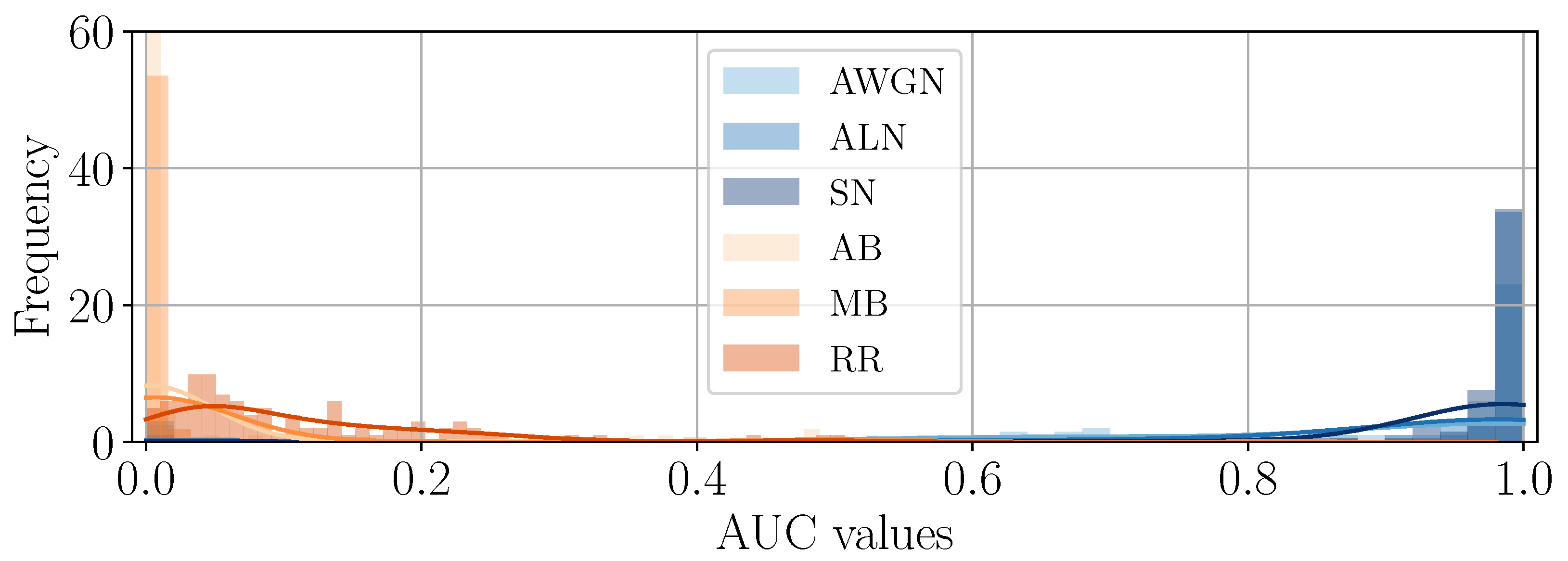
4.3. Consistency Across the Dataset
4.4. Interpretation of DHFR Appearance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abady, L.; Cannas, E.D.; Bestagini, P.; Tondi, B.; Tubaro, S.; Barni, M. An Overview on the Generation and Detection of Synthetic and Manipulated Satellite Images. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2022, 11, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, A. An Overview on Image Forensics. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 496701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoliva, L. Media Forensics and DeepFakes: An Overview. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2020, 14, 910–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4765–4774. [Google Scholar]
- Rudin, C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraetzer, C.; Hildebrandt, M. Explainability and interpretability for media forensic methods: Illustrated on the example of the steganalysis tool stegdetect. In Proceedings of the 19th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, Rome, Italy, 27–29 February 2024; SCITEPRESS—Science and Technology Publications: Setúbal, Portugal, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.W.; Sakzad, A.; Choo, K.K.R. Explainable artificial intelligence for digital forensics. WIREs Forensic Sci. 2022, 4, e1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannas, E.D.; Bonettini, N.; Mandelli, S.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S. Amplitude SAR Imagery Splicing Localization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 33882–33899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L. Noiseprint: A CNN-Based Camera Model Fingerprint. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaro, F.; Cozzolino, D.; Sud, A.; Dufour, N.; Verdoliva, L. Trufor: Leveraging all-round clues for trustworthy image forgery detection and localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 20606–20615. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiyasu, K. Tutorial review of synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) with applications to imaging of the ocean surface. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, C.; Quegan, S. Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images; SciTech Publishing: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, F.; Yu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, Y. Object detection capability evaluation for SAR image. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.L.; Anagaw, A.; Chang, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Lee, W.H. Ship Detection Based on YOLOv2 for SAR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, R. Model-based ATR using synthetic aperture radar. In Proceedings of the Record of the IEEE 2000 International Radar Conference [Cat. No. 00CH37037], Alexandria, VA, USA, 12 May 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency, E.S. Product Slicing. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/technical-guides/sentinel-1-sar/products-algorithms/product-slice-handling (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Program, C. Sentinel-1 Mission User Guide. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-1-sar (accessed on 2 January 2022).
- Stamm, M.C.; Wu, M.; Liu, K.J.R. Information Forensics: An Overview of the First Decade. IEEE Access 2013, 1, 167–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.; Farid, H. Exposing digital forgeries in color filter array interpolated images. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 3948–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, M. Fast and reliable resampling detection by spectral analysis of fixed linear predictor residue. In Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Multimedia and Security (MM&Sec), Oxford, UK, 22–23 September 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Padín, D.; Pérez-González, F. Prefilter design for forensic resampling estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Iguacu Falls, Brazil, 29 November–2 December 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, R.; Yu, L.; Tian, H. Forensic detection of median filtering in digital images. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Singapore, 19–23 July 2010; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner, M.; Fridrich, J. On detection of median filtering in digital images. In Proceedings of the Media Forensics and Security II. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–21 January 2010; Volume 7541, p. 754110. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, T.; Piva, A. Detection of nonaligned double JPEG compression based on integer periodicity maps. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2011, 7, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, T.H.; Cogranne, R.; Retraint, F.; Doan, T.N.C. JPEG quantization step estimation and its applications to digital image forensics. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 12, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelli, S.; Bonettini, N.; Bestagini, P.; Lipari, V.; Tubaro, S. Multiple JPEG compression detection through task-driven non-negative matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 2106–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, S.; Pan, X.; Zhang, X. Exposing region splicing forgeries with blind local noise estimation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2014, 110, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. Splicebuster: A new blind image splicing detector. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Rome, Italy, 16–19 November 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L. Single-image splicing localization through autoencoder-based anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 4–7 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Ni, J. A deep learning approach to detection of splicing and copy-move forgeries in images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 4–7 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, Q.; Zhao, X.; Cao, Y. Image Forgery Localization Based on Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, Innsbruck, Austria, 20–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, B.; Stamm, M.C. A Deep Learning Approach to Universal Image Manipulation Detection Using a New Convolutional Layer. In Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, Vigo, Spain, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bayar, B.; Stamm, M.C. Design Principles of Convolutional Neural Networks for Multimedia Forensics. In Proceedings of the IS&T International Symposium on Electronic Imaging: Media Watermarking, Security, and Forensics, Burlingame, CA, USA, 29 January–2 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonettini, N.; Bondi, L.; Güera, D.; Mandelli, S.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S.; Delp, E.J. Fooling PRNU-Based Detectors Through Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannas, E.D.; Baireddy, S.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S.; Delp, E.J. Enhancement Strategies For Copy-Paste Generation & Localization in RGB Satellite Imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Nürnberg, Germany, 4–7 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mashable. Satellite Images Show Clearly That Russia Faked Its MH17 Report. Available online: http://mashable.com/2015/05/31/russia-fake-mh17-report (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- BBC. Conspiracy Files: Who Shot Down MH17? April 2016. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-35706048 (accessed on 11 August 2023).
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, F.M.; Lewis, A.J. Principles and Applications of Imaging Radar. Manual of Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Wiley Publisher: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Tan, S.; Pan, Z.; Xing, J.; Yuan, Z.; Xing, X.; Zhang, P. A New Framework for Automatic Airports Extraction from SAR Images Using Multi-Level Dual Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannas, E.D.; Mandelli, S.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S.; Delp, E.J. Deep Image Prior Amplitude SAR Image Anonymization. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, I.; Groenen, P. Modern Multidimensional Scaling: Theory and Applications; Springer Series in Statistics: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cannas, E.D.; Beaus, P.; Bestagini, P.; Marques, F.; Tubaro, S. A One-Class Approach to Detect Super-Resolution Satellite Imagery with Spectral Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP 2024, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Durall, R.; Keuper, M.; Keuper, J. Watch your Up-Convolution: CNN Based Generative Deep Neural Networks are Failing to Reproduce Spectral Distributions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Corvi, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Poggi, G.; Nagano, K.; Verdoliva, L. Intriguing Properties of Synthetic Images: From Generative Adversarial Networks to Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 973–982. [Google Scholar]
- Mandelli, S.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S. When synthetic traces hide real content: Analysis of stable diffusion image laundering. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Rome, Italy, 2–5 December 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]






| Detector | Task | Modality |
|---|---|---|
| Bonettini [36] | PRNU anonymization | Natural images |
| Noiseprint [10] | Image splicing localization | Natural images |
| Noiseprint++ [11] | Image splicing localization and detection | Natural images |
| ASAE [9] | Image splicing localization | SAR |
| SatNoiseprint [37] | Image splicing localization | Satellite RGB |
| Operation | Low Frequencies | Medium Frequencies | High Frequencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| No editing | 3731 | 3888 | 2132 |
| AB | 1725 | 346 | 247 |
| MB | 2708 | 956 | 732 |
| RR | 3828 | 2527 | 971 |
| AWGN | 4014 | 4741 | 4449 |
| ALN | 4147 | 5273 | 5778 |
| SN | 3980 | 5555 | 6817 |
| Operation | Low Frequencies | Medium Frequencies | High Frequencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| No editing | 7400 | 7755 | 4166 |
| AB | 3016 | 560 | 394 |
| MB | 5137 | 1774 | 1334 |
| RR | 7518 | 5070 | 1782 |
| AWGN | 7353 | 9093 | 8559 |
| ALN | 7797 | 10,411 | 11,694 |
| SN | 7596 | 11,391 | 14,687 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cannas, E.D.; Mandelli, S.; Bestagini, P.; Tubaro, S. Interpretability of Deep High-Frequency Residuals: A Case Study on SAR Splicing Localization. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100338
Cannas ED, Mandelli S, Bestagini P, Tubaro S. Interpretability of Deep High-Frequency Residuals: A Case Study on SAR Splicing Localization. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(10):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100338
Chicago/Turabian StyleCannas, Edoardo Daniele, Sara Mandelli, Paolo Bestagini, and Stefano Tubaro. 2025. "Interpretability of Deep High-Frequency Residuals: A Case Study on SAR Splicing Localization" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 10: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100338
APA StyleCannas, E. D., Mandelli, S., Bestagini, P., & Tubaro, S. (2025). Interpretability of Deep High-Frequency Residuals: A Case Study on SAR Splicing Localization. Journal of Imaging, 11(10), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11100338






