Development and Validation of Four Different Methods to Improve MRI-CEST Tumor pH Mapping in Presence of Fat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
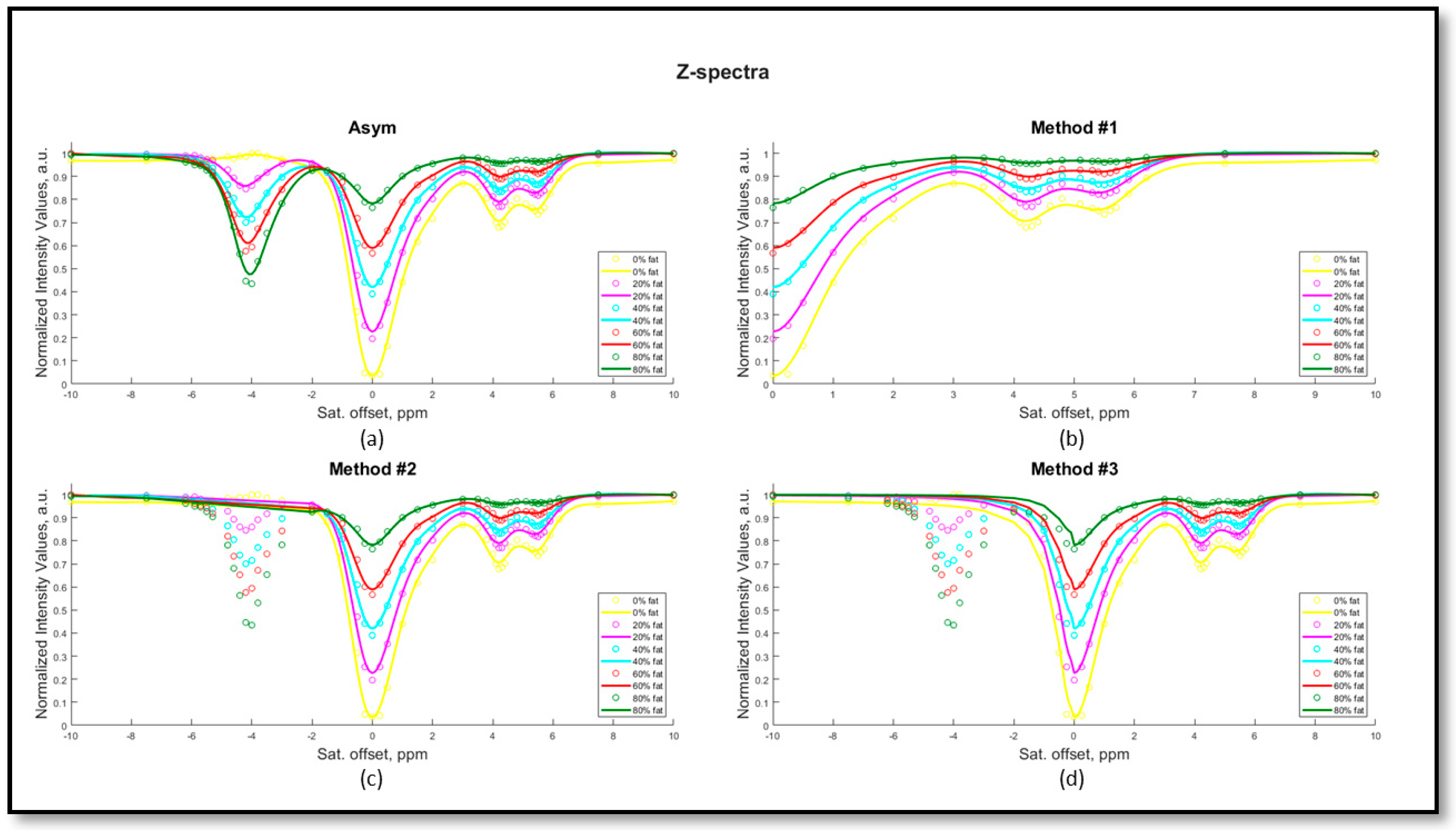
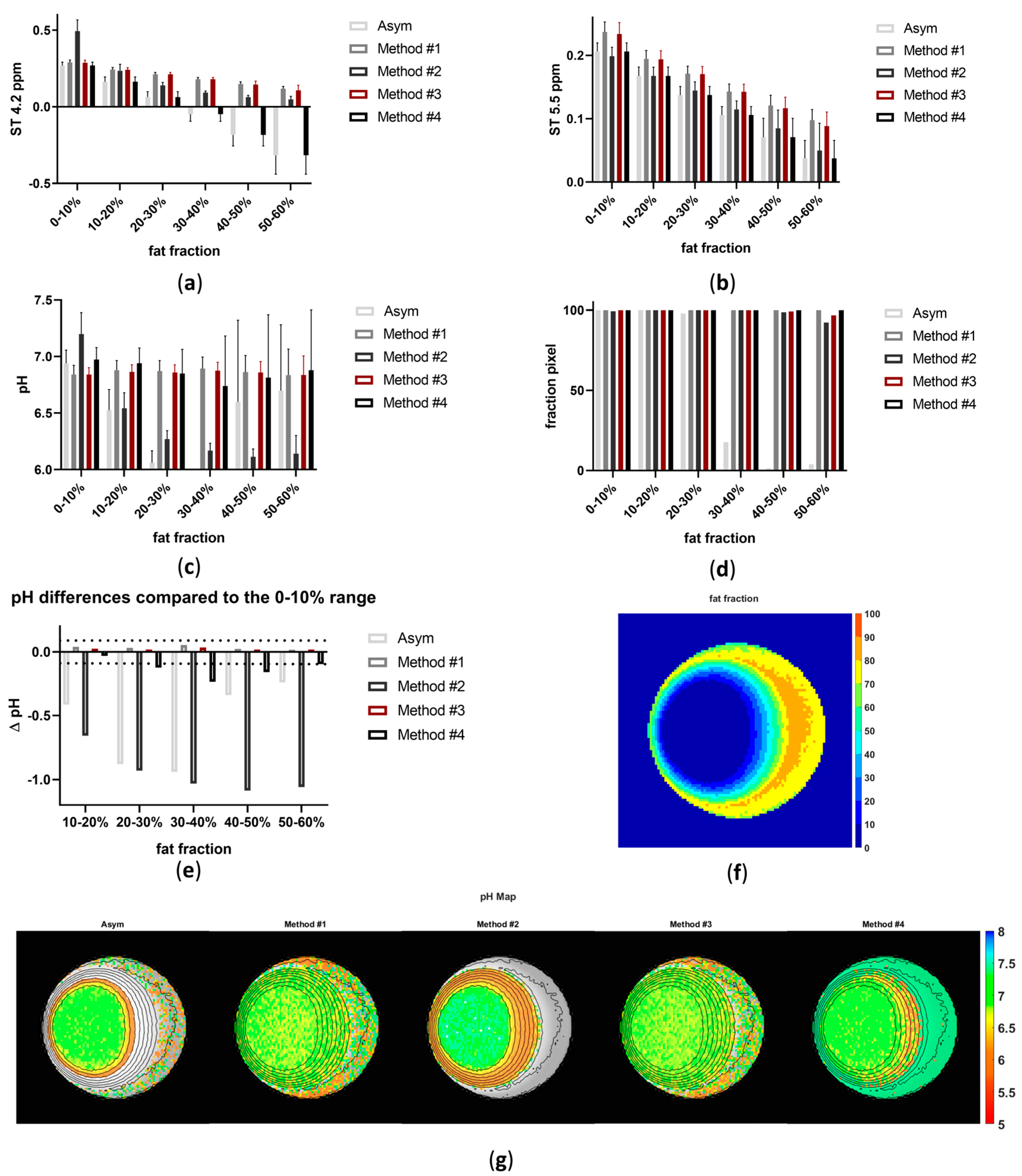
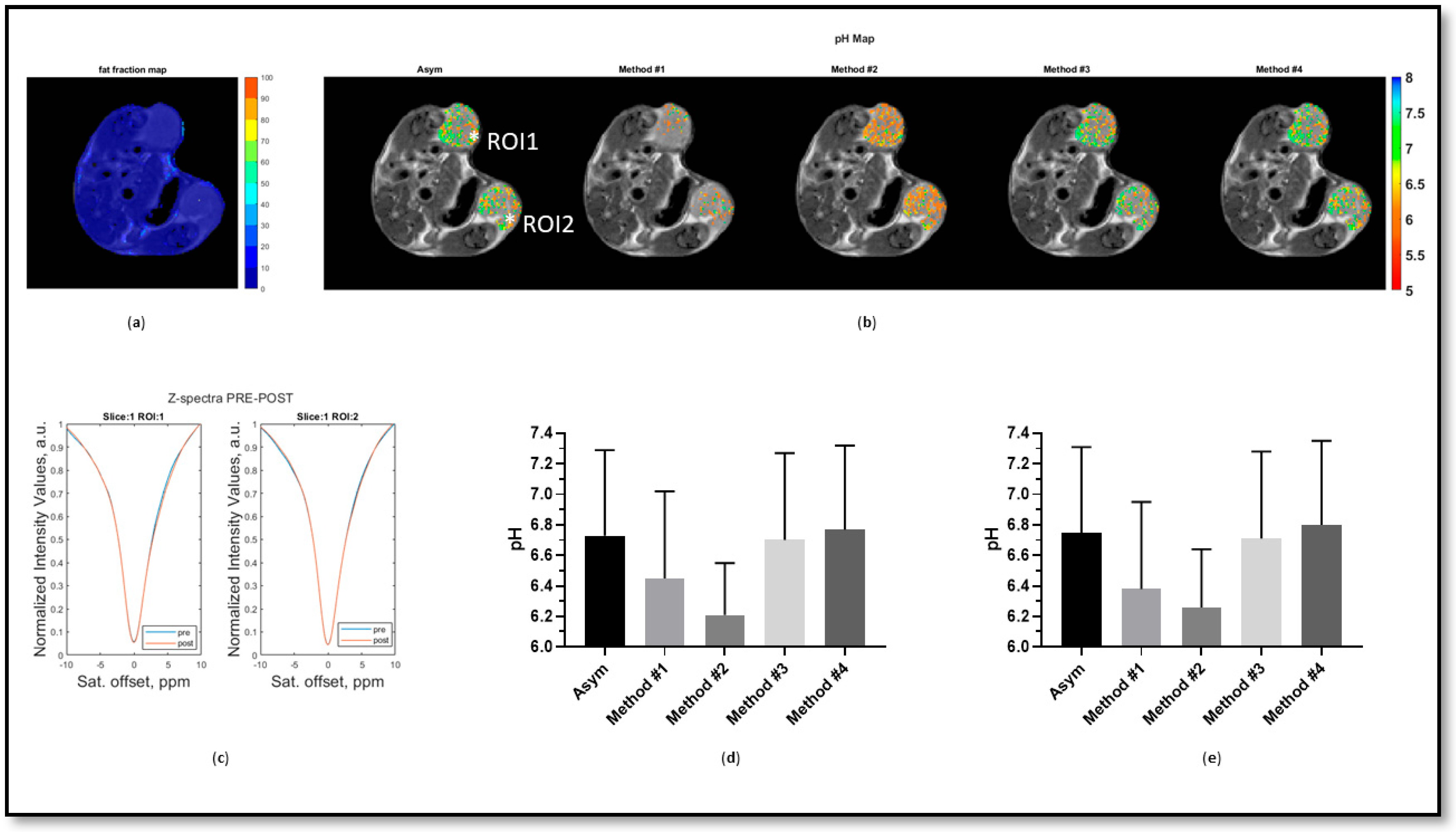
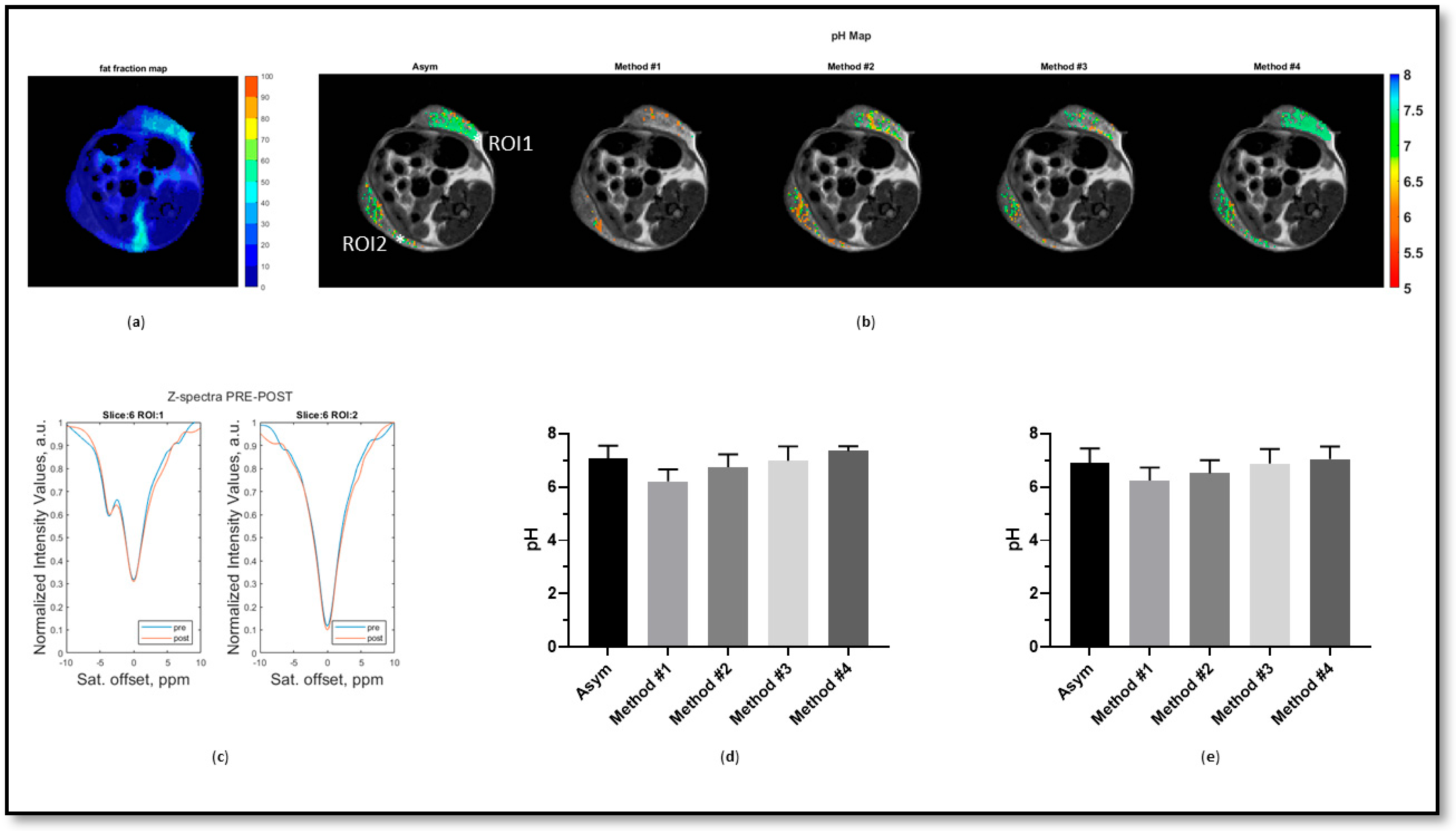
2.1. Theory
- Method #1 calculates the contrast considering only the positive part of the Z-spectrum using the following equation:where is the water signal intensity in the presence of a saturation pulse at an offset ∆ω, and is the water signal intensity without any saturation.
- Method #2 consists of removing the fat frequencies (in the range of −2 to −5.9 ppm) and replacing the missing range with a linear interpolation. The CEST contrast is then calculated by asymmetry analysis using equation #1.
- Method #3 consists of replacing the negative part of the Z-spectrum with the water pool contribution upon Lorentzian fitting of the spectrum, and the contrast is then calculated by asymmetry analysis using the same equation #1.
- Method #4 corrects the calculated ratiometric values according to the measured fat fraction levels by interpolating the ratiometric values with cubic splines to correct for the proper pH values in the absence of fat (more details in the Supplementary Materials).
2.2. In Vitro MRI Studies
2.3. In Vivo MRI Studies
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Song, X.; Chan, K.W.; McMahon, M.T. Nuts and bolts of chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 810–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zijl, P.C.; Yadav, N.N. Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST): What is in a name and what isn’t? Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, E.; Sherry, A.D.; Lenkinski, R.E. CEST: From basic principles to applications, challenges and opportunities. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 229, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consolino, L.; Anemone, A.; Capozza, M.; Carella, A.; Irrera, P.; Corrado, A.; Dhakan, C.; Bracesco, M.; Longo, D.L. Non-invasive Investigation of Tumor Metabolism and Acidosis by MRI-CEST Imaging. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anemone, A.; Consolino, L.; Arena, F.; Capozza, M.; Longo, D.L. Imaging tumor acidosis: A survey of the available techniques for mapping in vivo tumor pH. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, D.L.; Carella, A.; Corrado, A.; Pirotta, E.; Mohanta, Z.; Singh, A.; Stabinska, J.; Liu, G.; McMahon, M.T. A snapshot of the vast array of diamagnetic CEST MRI contrast agents. NMR Biomed. 2022, 36, e4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High, R.A.; Randtke, E.A.; Jones, K.M.; Lindeman, L.R.; Ma, J.C.; Zhang, S.; LeRoux, L.G.; Pagel, M.D. Extracellular acidosis differentiates pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in mouse models using acidoCEST MRI. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, L.R.; Randtke, E.A.; High, R.A.; Jones, K.M.; Howison, C.M.; Pagel, M.D. A comparison of exogenous and endogenous CEST MRI methods for evaluating in vivo pH. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 2766–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavuluri, K.; McMahon, M.T. pH Imaging Using Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST) MRI. ISR. J. Chem. 2017, 57, 862–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albatany, M.; Meakin, S.; Bartha, R. Brain pH Measurement Using AACID CEST MRI Incorporating the 2 ppm Amine Resonance. Tomography 2022, 8, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, I.Y.; Lu, D.; Manderville, E.; Lo, E.H.; Zheng, H.; Sun, P.Z. pH-sensitive amide proton transfer effect dominates the magnetization transfer asymmetry contrast during acute ischemia-quantification of multipool contribution to in vivo CEST MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.Z.; Cheung, J.S.; Wang, E.; Lo, E.H. Association between pH-weighted endogenous amide proton chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI and tissue lactic acidosis during acute ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delli Castelli, D.; Ferrauto, G.; Cutrin, J.C.; Terreno, E.; Aime, S. In vivo maps of extracellular pH in murine melanoma by CEST-MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Sun, D.; Hitchens, T.K.; Modo, M.; Bandos, A.; Mettenburg, J.; Wang, P.; Jin, T. Dual contrast CEST MRI for pH-weighted imaging in stroke. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.S.; Yao, J.; Cho, N.S.; Sanvito, F.; Tessema, K.; Alvarado, A.; Dudley, L.; Rodriguez, F.; Everson, R.; Cloughesy, T.F.; et al. pH-Weighted Amine Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Echo Planar Imaging (CEST-EPI) Visualizes Infiltrating Glioblastoma Cells. Neuro Oncol. 2023, 26, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.Z. Numerical simulation-based assessment of pH-sensitive chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI quantification accuracy across field strengths. NMR Biomed. 2023, 36, e5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Lu, D.; Sun, P.Z.; Zhou, I.Y. In vivo pH mapping with omega plot-based quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anemone, A.; Consolino, L.; Conti, L.; Irrera, P.; Hsu, M.Y.; Villano, D.; Dastru, W.; Porporato, P.E.; Cavallo, F.; Longo, D.L. Tumour acidosis evaluated in vivo by MRI-CEST pH imaging reveals breast cancer metastatic potential. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, D.L.; Bartoli, A.; Consolino, L.; Bardini, P.; Arena, F.; Schwaiger, M.; Aime, S. In Vivo Imaging of Tumor Metabolism and Acidosis by Combining PET and MRI-CEST pH Imaging. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6463–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrera, P.; Roberto, M.; Consolino, L.; Anemone, A.; Villano, D.; Navarro-Tableros, V.; Carella, A.; Dastru, W.; Aime, S.; Longo, D.L. Effect of Esomeprazole Treatment on Extracellular Tumor pH in a Preclinical Model of Prostate Cancer by MRI-CEST Tumor pH Imaging. Metabolites 2022, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irrera, P.; Consolino, L.; Roberto, M.; Capozza, M.; Dhakan, C.; Carella, A.; Corrado, A.; Villano, D.; Anemone, A.; Navarro-Tableros, V.; et al. In Vivo MRI-CEST Tumor pH Imaging Detects Resistance to Proton Pump Inhibitors in Human Prostate Cancer Murine Models. Cancers 2022, 14, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozza, M.; Anemone, A.; Dhakan, C.; Della Peruta, M.; Bracesco, M.; Zullino, S.; Villano, D.; Terreno, E.; Longo, D.L.; Aime, S. GlucoCEST MRI for the Evaluation Response to Chemotherapeutic and Metabolic Treatments in a Murine Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Comparison with [(18)F]F-FDG-PET. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anemone, A.; Consolino, L.; Conti, L.; Reineri, F.; Cavallo, F.; Aime, S.; Longo, D.L. In vivo evaluation of tumour acidosis for assessing the early metabolic response and onset of resistance to dichloroacetate by using magnetic resonance pH imaging. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, J.M.; Cardenas-Rodriguez, J.; Pagel, M.D. Preliminary Results that Assess Metformin Treatment in a Preclinical Model of Pancreatic Cancer Using Simultaneous [(18)F]FDG PET and acidoCEST MRI. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Q.; Howison, C.M.; Spier, C.; Stopeck, A.T.; Malm, S.W.; Pagel, M.D.; Baker, A.F. Assessment of carbonic anhydrase IX expression and extracellular pH in B-cell lymphoma cell line models. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 56, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyse, C.; Joudiou, N.; Warscotte, A.; Richiardone, E.; Mignion, L.; Corbet, C.; Gallez, B. Evaluation of Syrosingopine, an MCT Inhibitor, as Potential Modulator of Tumor Metabolism and Extracellular Acidification. Metabolites 2022, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyse, C.; Joudiou, N.; Corbet, C.; Feron, O.; Mignion, L.; Flament, J.; Gallez, B. Impact of Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier on the Tumor Extracellular pH as Measured by CEST-MRI. Cancers 2021, 13, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrucco, D.; Cutrin, J.C.; Longo, D.L.; Botto, E.; Cong, L.; Aime, S.; Delli Castelli, D. In Situ Insonation of Alkaline Buffer Containing Liposomes Leads to a Net Improvement of the Therapeutic Outcome in a Triple Negative Breast Cancer Murine Model. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2301480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakan, C.; Anemone, A.; Ventura, V.; Carella, A.; Corrado, A.; Pirotta, E.; Villano, D.; Romdhane, F.; Gammaraccio, F.; Aime, S.; et al. Assessing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Proton Transport Inhibitors in a Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Murine Model with Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Tumor pH Imaging. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Irrera, P.; Oluwatola, O.E.; Abrahams, D.; Estrella, V.C.; Ordway, B.; Byrne, S.R.; Ojeda, A.A.; Whelan, C.J.; Kim, J.; et al. L-DOS47 Elevates Pancreatic Cancer Tumor pH and Enhances Response to Immunotherapy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopf, P.; Stowbur, D.; Hoffmann, S.H.L.; Hermann, N.; Maurer, A.; Bucher, V.; Poxleitner, M.; Tako, B.; Sonanini, D.; Krishnamachary, B.; et al. Acidosis-mediated increase in IFN-gamma-induced PD-L1 expression on cancer cells as an immune escape mechanism in solid tumors. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.M.; Pollard, A.C.; Pagel, M.D. Clinical applications of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Lutz, A.; Khalil, N.; Schmitt, B.; Jellus, V.; Pentang, G.; Oeltzschner, G.; Antoch, G.; Lanzman, R.S.; Wittsack, H.J. Pilot study of Iopamidol-based quantitative pH imaging on a clinical 3T MR scanner. MAGMA 2014, 27, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, A.F.; Ma, Y.; Jang, H.; Jerban, S.; Tang, Q.; Searleman, A.C.; Meyer, R.S.; Du, J.; Chang, E.Y. AcidoCEST-UTE MRI Reveals an Acidic Microenvironment in Knee Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High, R.A.; Ji, Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Tang, Q.; Murphy, M.E.; Du, J.; Chang, E.Y. In vivo assessment of extracellular pH of joint tissues using acidoCEST-UTE MRI. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.J.; High, R.A.; Tang, Q.; Wan, L.; Jerban, S.; Du, J.; Chang, E.Y. AcidoCEST-UTE MRI for the Assessment of Extracellular pH of Joint Tissues at 3 T. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Sedaghat, F.; Pavuluri, K.; Rowe, S.P.; Cohen, A.; Kates, M.; McMahon, M.T. Dynamic Contrast Enhanced-MR CEST Urography: An Emerging Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction. Tomography 2021, 7, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Shen, Z.; Zhuang, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Guan, J.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Noninvasive Detection of Extracellular pH in Human Benign and Malignant Liver Tumors Using CEST MRI. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 578985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.A. CEST MRI pH Mapping of Tumor Acidity as a Predictor of Breast Cancer Metastatic Potential. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e219003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, W.; Lin, C.E.; Ding, H.; Shen, Y.; Dou, C.; Qian, L.; Wen, B.; Wu, B. Chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging and its main and potential applications in pre-clinical and clinical studies. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1747–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, D.L.; Dastru, W.; Digilio, G.; Keupp, J.; Langereis, S.; Lanzardo, S.; Prestigio, S.; Steinbach, O.; Terreno, E.; Uggeri, F.; et al. Iopamidol as a responsive MRI-chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agent for pH mapping of kidneys: In vivo studies in mice at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, H.; Bornert, P. Chemical shift encoding-based water-fat separation methods. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, F.; Korzowski, A.; Breitling, J.; Meissner, J.E.; Schuenke, P.; Loi, L.; Zaiss, M.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Schott, S.; Schlemmer, H.P.; et al. A novel normalization for amide proton transfer CEST MRI to correct for fat signal-induced artifacts: Application to human breast cancer imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, E.; Keupp, J.; Dimitrov, I.E.; Seiler, S.; Pedrosa, I. CEST-MRI for body oncologic imaging: Are we there yet? NMR Biomed. 2023, 36, e4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, M.; Anaby, D.; Nissan, N.; Zaiss, M.; Deshmane, A.; Navon, G.; Sklair-Levy, M. Breast cancer imaging with glucosamine CEST (chemical exchange saturation transfer) MRI: First human experience. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 7365–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, L.; Goerke, S.; Zimmermann, F.; Korzowski, A.; Meissner, J.E.; Breitling, J.; Schott, S.; Bachert, P.; Ladd, M.E.; Schlemmer, H.P.; et al. Assessing the influence of the menstrual cycle on APT CEST-MRI in the human breast. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 91, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Rauch, G.M.; Adrada, B.E.; Boge, M.; Mohamed, R.M.M.; Abdelhafez, A.H.; Son, J.B.; Sun, J.; Elshafeey, N.A.; White, J.B.; et al. Assessment of Early Response to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Using Amide Proton Transfer-weighted Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer MRI: A Pilot Study. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e200155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Song, X.; Liu, G.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Yadav, N.N. Deep learning-based classification of preclinical breast cancer tumor models using chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging. NMR Biomed. 2022, 35, e4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescenzi, R.; Donahue, P.M.C.; Mahany, H.; Lants, S.K.; Donahue, M.J. CEST MRI quantification procedures for breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema therapy evaluation. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 1760–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krikken, E.; Khlebnikov, V.; Zaiss, M.; Jibodh, R.A.; van Diest, P.J.; Luijten, P.R.; Klomp, D.W.J.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Wijnen, J.P. Amide chemical exchange saturation transfer at 7 T: A possible biomarker for detecting early response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, M.J.; Donahue, P.C.; Rane, S.; Thompson, C.R.; Strother, M.K.; Scott, A.O.; Smith, S.A. Assessment of lymphatic impairment and interstitial protein accumulation in patients with breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema using CEST MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dula, A.N.; Dewey, B.E.; Arlinghaus, L.R.; Williams, J.M.; Klomp, D.; Yankeelov, T.E.; Smith, S. Optimization of 7-T chemical exchange saturation transfer parameters for validation of glycosaminoglycan and amide proton transfer of fibroglandular breast tissue. Radiology 2015, 275, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klomp, D.W.; Dula, A.N.; Arlinghaus, L.R.; Italiaander, M.; Dortch, R.D.; Zu, Z.; Williams, J.M.; Gochberg, D.F.; Luijten, P.R.; Gore, J.C.; et al. Amide proton transfer imaging of the human breast at 7T: Development and reproducibility. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, B.; Zamecnik, P.; Zaiss, M.; Rerich, E.; Schuster, L.; Bachert, P.; Schlemmer, H.P. A new contrast in MR mammography by means of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging at 3 Tesla: Preliminary results. RoFo 2011, 183, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, M.J.; Donahue, P.M.C.; Jones, R.S.; Garza, M.; Lee, C.; Patel, N.J.; Cooper, A.; De Vis, J.B.; Meszoely, I.; Crescenzi, R. In Vivo lymph node CEST-Dixon MRI in breast cancer patients with metastatic lymph node involvement. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaric, O.; Farr, A.; Poblador Rodriguez, E.; Mlynarik, V.; Bogner, W.; Gruber, S.; Asseryanis, E.; Singer, C.F.; Trattnig, S. 7T CEST MRI: A potential imaging tool for the assessment of tumor grade and cell proliferation in breast cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 59, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlGhuraibawi, W.; Stromp, T.; Holtkamp, R.; Lam, B.; Rehwald, W.; Leung, S.W.; Vandsburger, M. CEST MRI reveals a correlation between visceral fat mass and reduced myocardial creatine in obese individuals despite preserved ventricular structure and function. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabinska, J.; Muller-Lutz, A.; Wittsack, H.J.; Tell, C.; Rump, L.C.; Ertas, N.; Antoch, G.; Ljimani, A. Two point Dixon-based chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI in renal transplant patients on 3 T. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 90, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivlin, M.; Navon, G. CEST MRI of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose on different breast cancer models. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, E.; Schache, D.; Holtke, C.; Soltwisch, J.; Niland, S.; Krahling, T.; Bergander, K.; Grewer, M.; Geyer, C.; Groeneweg, L.; et al. Multiparametric chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI detects metabolic changes in breast cancer following immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Lam, W.W.; Czarnota, G.J.; Stanisz, G.J. Chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI to assess cell death in breast cancer xenografts at 7T. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31490–31501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.J.; Larkin, J.R.; Tee, Y.K.; Khrapitchev, A.A.; Karunanithy, G.; Barber, M.; Baldwin, A.J.; Chappell, M.A.; Sibson, N.R. Determination of an optimally sensitive and specific chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI quantification metric in relevant biological phantoms. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 1624–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, Y.; Iima, M.; Imai, H.; Yoshizawa, A.; Kataoka, M.; Isoda, H.; Le Bihan, D.; Nakamoto, Y. Investigation of breast cancer microstructure and microvasculature from time-dependent DWI and CEST in correlation with histological biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, B.; Trattnig, S.; Schlemmer, H.P. CEST-imaging: A new contrast in MR-mammography by means of chemical exchange saturation transfer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81 (Suppl. S1), S144–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krikken, E.; van der Kemp, W.J.M.; Khlebnikov, V.; van Dalen, T.; Los, M.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Luijten, P.R.; van den Bosch, M.; Klomp, D.W.J.; Wijnen, J.P. Contradiction between amide-CEST signal and pH in breast cancer explained with metabolic MRI. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, K.L.; Kamp, B.; Adriaenssens, V.; Stabinska, J.; Gallinnis, P.; Wittsack, H.J.; Antoch, G.; Muller-Lutz, A. Deep Learning-Based Denoising of CEST MR Data: A Feasibility Study on Applying Synthetic Phantoms in Medical Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, L.; Wei, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L. Boosting quantification accuracy of chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI with a spatial-spectral redundancy-based denoising method. NMR Biomed. 2023, 37, e5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Bie, C.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Song, X. Hierarchical K-means clustering method for accelerated Lorentzian estimation (KALE) in chemical exchange saturation transfer-magnetic resonance imaging quantification. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 4350–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Lin, L.; Cai, S.; Cai, C.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, L. Learned spatiotemporal correlation priors for CEST image denoising using incorporated global-spectral convolution neural network. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 90, 2071–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, L.; Rajput, J.R.; Klein, K.; Mennecke, A.; Fabian, M.S.; Schmidt, M.; Glang, F.; Herz, K.; Liebig, P.; Nagel, A.M.; et al. DeepCEST 7 T: Fast and homogeneous mapping of 7 T CEST MRI parameters and their uncertainty quantification. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, F.; Villano, D.; Irrera, P.; Consolino, L.; Longo, D.L. Evaluation of a similarity anisotropic diffusion denoising approach for improving in vivo CEST-MRI tumor pH imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 3479–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Cao, S.; Koehler, R.C.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Xu, J. High-sensitivity CEST mapping using a spatiotemporal correlation-enhanced method. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 3342–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitling, J.; Deshmane, A.; Goerke, S.; Korzowski, A.; Herz, K.; Ladd, M.E.; Scheffler, K.; Bachert, P.; Zaiss, M. Adaptive denoising for chemical exchange saturation transfer MR imaging. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Cardenas-Rodriguez, J.; Trakru, P.N.; Pagel, M.D. A machine learning approach that measures pH using acidoCEST MRI of iopamidol. NMR Biomed. 2023, 36, e4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittsack, H.J.; Radke, K.L.; Stabinska, J.; Ljimani, A.; Muller-Lutz, A. calf—Software for CEST Analysis with Lorentzian Fitting. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bie, C.; Liang, Y.; He, X.; Song, X. Voxel-wise Optimization of Pseudo Voigt Profile (VOPVP) for Z-spectra fitting in chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1714–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, I.Y.; Wang, E.; Cheung, J.S.; Zhang, X.; Fulci, G.; Sun, P.Z. Quantitative chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI of glioma using Image Downsampling Expedited Adaptive Least-squares (IDEAL) fitting. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, A.; Frahm, J.; Hanicke, W.; Matthaei, D. 1H NMR chemical shift selective (CHESS) imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 1985, 30, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schick, F. Simultaneous highly selective MR water and fat imaging using a simple new type of spectral-spatial excitation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1998, 40, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.H.; Pauly, J.M.; Macovski, A.; Nishimura, D.G. Simultaneous spatial and spectral selective excitation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1990, 15, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bydder, G.M.; Young, I.R. MR imaging: Clinical use of the inversion recovery sequence. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1985, 9, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinsky, G.; Rofsky, N.M.; Weinreb, J.C. Nonspecificity of short inversion time inversion recovery (STIR) as a technique of fat suppression: Pitfalls in image interpretation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 166, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepponen, R.E.; Sipponen, J.T.; Tanttu, J.I. A method for chemical shift imaging: Demonstration of bone marrow involvement with proton chemical shift imaging. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1984, 8, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.T. Simple proton spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 1984, 153, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Kurita, Y.; Arimoto, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Sato, T.; Imajo, K.; Hosono, K.; Kobayashi, N.; et al. Three-dimensional analysis of pancreatic fat by fat-water magnetic resonance imaging provides detailed characterization of pancreatic steatosis with improved reproducibility. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkert, T.; Block, K.T.; Heller, S.; Moccaldi, M.; Sodickson, D.K.; Kim, S.G.; Moy, L. Comprehensive Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced 3D Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Breast With Fat/Water Separation and High Spatiotemporal Resolution Using Radial Sampling, Compressed Sensing, and Parallel Imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasu, M.; Kaichi, Y.; Tani, C.; Date, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; Sakai, A.; Awai, K. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL) magnetic resonance imaging as a biomarker for symptomatic multiple myeloma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bley, T.A.; Wieben, O.; Francois, C.J.; Brittain, J.H.; Reeder, S.B. Fat and water magnetic resonance imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Jones, C.K.; van Zijl, P.C.; Barker, P.B.; Zhou, J. Fast 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging of the human brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Guo, B.; Yan, X.; Gochberg, D.F.; Li, J. Effectiveness of fat suppression using a water-selective binomial-pulse excitation in chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020, 33, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkotz, K.; Liebert, A.; Gast, L.V.; Zeiger, P.; Uder, M.; Zaiss, M.; Nagel, A.M. Multi-echo-based fat artifact correction for CEST MRI at 7 T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2024, 91, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, S.; Herrler, J.; Liebert, A.; Tkotz, K.; Fabian, M.S.; Eisen, C.; Grodzki, D.; Uder, M.; Dorfler, A.; Zaiss, M.; et al. Clinically compatible subject-specific dynamic parallel transmit pulse design for homogeneous fat saturation and water-excitation at 7T: Proof-of-concept for CEST MRI of the brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, W.; Huang, J.; van Zijl, P.C. Suppression of lipid artifacts in amide proton transfer imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Cai, C.; Cai, S.; Chen, Z. Observation of true and pseudo NOE signals using CEST-MRI and CEST-MRS sequences with and without lipid suppression. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Keupp, J.; Wang, X.; Dimitrov, I.; Madhuranthakam, A.J.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Vinogradov, E. Z-spectrum appearance and interpretation in the presence of fat: Influence of acquisition parameters. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 2731–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Seiler, S.; Wang, X.; Madhuranthakam, A.J.; Keupp, J.; Knippa, E.E.; Lenkinski, R.E.; Vinogradov, E. CEST-Dixon for human breast lesion characterization at 3 T: A preliminary study. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Self-adapting multi-peak water-fat reconstruction for the removal of lipid artifacts in chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, L.; Zimmermann, F.; Goerke, S.; Korzowski, A.; Meissner, J.E.; Deike-Hofmann, K.; Stieber, A.; Bachert, P.; Ladd, M.E.; Schlemmer, H.P.; et al. Relaxation-compensated CEST (chemical exchange saturation transfer) imaging in breast cancer diagnostics at 7T. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 129, 109068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotti, A.; Tain, R.W.; Li, W.; Gil, V.; Liew, C.W.; Cai, K. Mapping brown adipose tissue based on fat water fraction provided by Z-spectral imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, D.; Romdhane, F.; Irrera, P.; Consolino, L.; Anemone, A.; Zaiss, M.; Dastru, W.; Longo, D.L. A fast multislice sequence for 3D MRI-CEST pH imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, D.L.; Pirotta, E.; Gambino, R.; Romdhane, F.; Carella, A.; Corrado, A. Tumor pH Imaging Using Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST)-MRI. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2614, 287–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaiss, M.; Schmitt, B.; Bachert, P. Quantitative separation of CEST effect from magnetization transfer and spillover effects by Lorentzian-line-fit analysis of z-spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 211, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Gochberg, D.F.; Gore, J.C.; Zu, Z. Accuracy in the quantification of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) and relayed nuclear Overhauser enhancement (rNOE) saturation transfer effects. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glang, F.; Fabian, M.S.; German, A.; Khakzar, K.M.; Mennecke, A.; Liebert, A.; Herz, K.; Liebig, P.; Kasper, B.S.; Schmidt, M.; et al. Linear projection-based chemical exchange saturation transfer parameter estimation. NMR Biomed. 2023, 36, e4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Lu, D.; Sun, P.Z. Comparison of model-free Lorentzian and spinlock model-based fittings in quantitative CEST imaging of acute stroke. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 90, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terreno, E.; Stancanello, J.; Longo, D.; Castelli, D.D.; Milone, L.; Sanders, H.M.H.F.; Kok, M.B.; Uggeri, F.; Aime, S. Methods for an improved detection of the MRI-CEST effect. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2009, 4, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, H.; Sun, P.Z. A review of optimization and quantification techniques for chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI toward sensitive in vivo imaging. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2015, 10, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gammaraccio, F.; Villano, D.; Irrera, P.; Anemone, A.A.; Carella, A.; Corrado, A.; Longo, D.L. Development and Validation of Four Different Methods to Improve MRI-CEST Tumor pH Mapping in Presence of Fat. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070166
Gammaraccio F, Villano D, Irrera P, Anemone AA, Carella A, Corrado A, Longo DL. Development and Validation of Four Different Methods to Improve MRI-CEST Tumor pH Mapping in Presence of Fat. Journal of Imaging. 2024; 10(7):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070166
Chicago/Turabian StyleGammaraccio, Francesco, Daisy Villano, Pietro Irrera, Annasofia A. Anemone, Antonella Carella, Alessia Corrado, and Dario Livio Longo. 2024. "Development and Validation of Four Different Methods to Improve MRI-CEST Tumor pH Mapping in Presence of Fat" Journal of Imaging 10, no. 7: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070166
APA StyleGammaraccio, F., Villano, D., Irrera, P., Anemone, A. A., Carella, A., Corrado, A., & Longo, D. L. (2024). Development and Validation of Four Different Methods to Improve MRI-CEST Tumor pH Mapping in Presence of Fat. Journal of Imaging, 10(7), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10070166






