Abstract
Municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash (MSWI-FA) was used synergistically with volcanic ash (VA) to synthesize Geopolymer cement. The effects of the incorporation of 0%, 30%, and 50% of VA and the alkalinity of activating solution on the structure and properties were studied by using the X-ray diffractometer (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), and mechanical testing. The encapsulation efficiency of the cements was carried out by using a toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP). The geopolymerization of MSWI-FA promoted the formation of new minerals such as Thernadite (Na2SO4), Hydrocalumite (Ca4Al2O6(CO3)0.67(SO3)0.33), C-S-H, and Faujasite-Na(Na2Ca)0.075(Al0.3Si0.7)O2(H2O)0.22. The Geopolymer cement synthesized with the addition of 50% of VA at 6M NaOH concentration, which exhibited the most compact microstructure. This was the highest strength with the best encapsulation ability. The microstructure analysis of the MSWI-FA-VA system revealed the coexistence of C-S-H and N-A-S-H phases as the main cementitious binders. The TCLP results of cement vis a vis raw MSWI-FA showed the leaching of metals reduced to a great extent. This was much lower than the permissible limit fixed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) for the toxicity characteristic. Furthermore, an attempt was made to correlate the microstructure with mechanical properties.
1. Introduction
The rapid growth of urbanization has resulted in the generation of huge amounts of municipal solid waste (MSW) in Cameroon. The amount of MSW generated by each habitant in urban cities of Cameroon is estimated at about 0.79 kg per day and with an estimated 2.62 million tons per year [1]. Currently, MSW is disposed as landfills and it poses serious environmental problems. One of the upcoming trends to treat MSW is incineration, which significantly reduces the mass and volume of waste. Furthermore, incineration is accompanied with the benefit of thermal energy production, which can be harnessed for electricity generation [2]. At the same time, incineration generates larger quantities of fly ash and bottom ash, which are waste materials.
The disposal of Municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash (MSWI-FA) presents another unresolved environmental concern. It is potentially harmful to the environment due to its high concentration of heavy metals content. Therefore, MSWI-FA is classified as a hazardous waste [3,4]. Owing to its chemistry, fine particle size, and pozzolanic behavior, MSWI-FA has the potential to be used as a mineral additive in cement. However, its high chlorine content restricts its application in construction material. Although the cement paste is not much affected by chloride except for increased solubilization of cement solids, chlorine is detrimental to the passivation of embedded steel [5]. To avoid this problem, some pre-treatment methods such as water washing and thermal treatment have been proposed [3,6,7]. These pre-treatments certainly eliminate the chlorides and inorganic salts in MSWI-FA but generate other wastes and increase the quantity of energy required for the synthesis and the total cost of the product. The efficient way to valorize MSWI-FA in construction is its use in the process, which displays limited signs of heavy metals leaching and the formation of the corrosion product in the presence of chlorine such as geopolymerization [8,9,10].
Geopolymer cement are considered eco-friendly binder materials and potential alternative to Portland cement (OPC) in specific applications since they produce around 80% less CO2 than Portland cement [11]. It has the potential to use alumina-silicate materials either from natural occurring waste, synthetic waste, or from industrial waste. Thus, varieties of alumina-silicate and industrial waste used for Geopolymer cement synthesis involve volcanic ash, glass powder, fly ash, slags, and red mud [12,13,14]. Recently, the use of the MSWI-FA along with coal fly ash, metakaolin, kaolin, and blast furnace slag for Geopolymer cement synthesis has been reported [3,15,16,17]. Using these combinations, various products such as geobrick, hearth (the floor of a fireplace), patios (the paved outdoor area adjoining a house), pavement, etc. have been developed. The monolithic products also presented good immobilization efficiency for heavy metals. The main objective of these previously mentioned works was to improve the Si/Al and Ca/Al ratios in the MSWI-FA in order to promote the coexistence of C-(A)-S-H and (N,C)-A-S-H phases. Yip et al. (2005) [18] reported that such a system exhibits superior physical and mechanical properties than a system with only one of these phases.
One of the natural sources of alumina-silicates that abounds in large quantities in Cameroon is volcanic ash (VA) [19]. Researchers have reported that Cameroon’s volcanic ashes has a chemical characteristic that allow it to be used as a staple in the Geopolymer field [20,21,22]. The Geopolymer cement developed by using these volcanic ashes have relatively good mechanical properties and durability. However, there have been limited literacy on the use of MSWI-FA (a calcium alumina-silicates based material) for the production of Geopolymer cement. Thus, the present study aims to synthesize Geopolymer cement from MSWI-FA by compensating the deficiency of alumina and silica through the addition of 0%, 30%, and 50% by weight of volcanic ash (VA).
2. Materials and Analytical Methods
2.1. Materials
MSWI-FA collected from the City of Douala-Cameroon was used as the main precursor in this study. Volcanic ash used as a mineral additive originated from the volcanic deposit of Loum located N 04430210500 and altitude 482 meters (Littoral Region of Cameroon). This volcanic ash was previously used by Djobo et al. as a precursor for the development of Geopolymer cement [19,21]. The VA was oven dried and pulverized in a ball mill in order to have particles less than 200 µm. The MSWI-FA was only oven dried for 24 h at 105 °C. The bulk oxide composition of both ashes was determined by x-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF). The content of heavy metals in MSWI-FA and VA was carried out through an inductive coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) (Vista MPX, Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA) after acid digestion treatment. Particle size distribution (PSD) analysis of MSWI-FA and VA were carried out by using a laser particle size analyzer (Mastersizer 2000, Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Malvern, UK).
Analytical grade sodium hydroxide in flake form (98% purity, make: Emplura Chemical, Mumbai, India) was used to prepare alkaline solutions. Sodium hydroxide was dissolved in distilled water in order to have a desired concentration. The sodium silicate solution used in the experiments was supplied by SDFCL-India (With 28.7 wt% SiO2, 8.9 wt% Na2O and 62.4 wt% H2O, density 1.37 g/mL). Distilled water was used throughout the experiments.
2.2. Preparation of Geopolymer Samples
Sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate solutions were used for the preparation of the alkaline solution. Analytical grade sodium hydroxide in flake form (98% purity) was used to prepare 6, 8, and 10 M NaOH solution. After 24 h, the NaOH solution was combined with commercial sodium silicate with the sodium silicate/sodium hydroxide ratio of 1. Three SiO2/Na2O molar ratio (Ms = 0.66, 0.56, and 0.36 for 6, 8, and 10 M, respectively) were prepared. The solution was prepared at least 24 h before use. The hot liquid was sealed to avoid carbonation and left overnight to cool to an ambient temperature to allow complete de-polymerization of sodium silicate. During the handling test, the pastes obtained with a silicate/sodium hydroxide ratio greater than 1 hardened in less than 5 min. This justifies the choice of the previously mentioned ratio. The specimens for the compressive strength test were prepared by mixing MSWI-FA-VA powder with the alkaline activator solution in the liquid/MSWI-FA-VA ratio varying from 0.45 to 0.75 depending on the fluidity of paste. The matrix was mixed for 5 min. The fresh paste was cast in 25 mm cubic molds, which was followed by vibration for 2 min to remove entrapped air bubbles during pouring. After casting, the samples were cured at room temperature (18 ± 2 °C), then demolded after 24 h, and stored in sealed plastic bags awaiting further tests. Table 1 represents the composition and batch mixing of Geopolymer cement.

Table 1.
Bulk composition and batch mixing of Geopolymer cement.
2.3. Analytical Methods
Mineralogical phases of both ashes (fly and volcanic) and Geopolymer products were identified through XRD analysis obtained by a Bruker X-ray diffractometer (D8 Discovery, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) using CuKα radiation (step increment was 0.02). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (Nicolet 5700 FTIR, Thermo Electron Co., Waltham, MA, USA) in a reflectance mode was used to record the absorption spectra of the bonds in the range of 400 to 4000 cm−1. The KBr pellet method was used to prepare the samples. The micrometer scale study of Geopolymer samples was carried out by using a Field emission gun scanning electron microscope (FEG-SEM) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) operating at 15.0 kV (Nova NanoSEM, FEI 430, FEI Co., Hillsboro, OR, USA). Compressive strength analyses was carried out based on Indian Standards (IS 4031) using an Automatic Compression Testing Machine (AIMIL COMPTEST 2000, New Delhi, India). The rate of loading was 0.5 mm/min.
For FTIR, XRD, and FEG-SEM analysis, the samples cured in a sealed bottle at 18 ± 5 °C were used. The samples were taken out and immersed in acetone for 24 h in order to stop the reaction. The samples were then dried at 60 °C in an electric oven. Dry samples were crushed and powdered to 100 µm for FTIR and XRD and the broken, small pieces were used for FEG-SEM.
The USEPA 1311 standard was used for the Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Protocol (TCLP). The cube samples were dried at 105 °C, crushed, and then sieved at 10 mm aperture size. The samples (10 g) were then extracted with an amount of TCLP extraction fluid (nitric acid, pH = 3.2 ± 2) equal to 20 times the weight of the solid phase for 18 h on the Millipore Rotary Agitator (Y132 ORA HW-India) at an agitation speed of 30 ± 2 r·min−1. The TCLP extract was separated from the solid phase by filtering through a 0.6 micron filter via Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA). The TCLP extract was combined with any liquid from the initial separation and the sample was analyzed using ICP-OES.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Raw Materials
Table 2 shows the result of XRF analysis and physical properties of MSWI-FA and VA. The main constituents of MSWI-FA are CaO followed by SiO2, Cl, and SO3. It also contained considerable amount of alkalis such as Na2O, K2O, and MgO. The high content of CaO and chlorine are the result of calcic adsorbent during the incineration process in order to control and neutralize the acidic gases such as sulphides and chlorides [23,24]. SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3 are the main oxide in VA. These oxides are suitable ingredients for geopolymerization. CaO provides extra nucleation sites for gelation and, thus, yields good hardening of a Geopolymer in a shorter curing time [18]. The MSWI-FA exhibited high loss on ignition (28%), associated with the decomposition of the carbonates and other inorganic salts [25].

Table 2.
Chemical composition of MSWI-FA and VA.
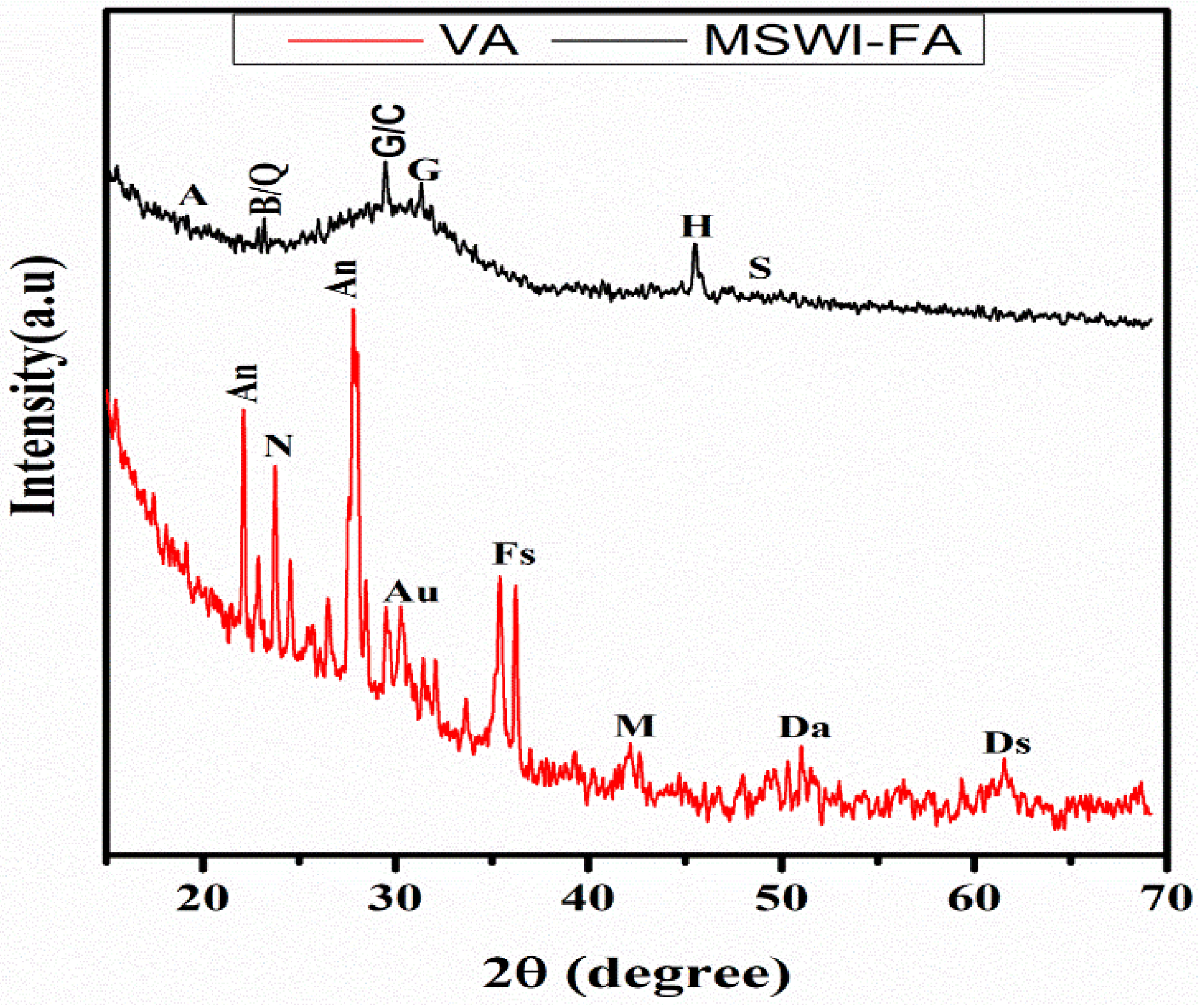
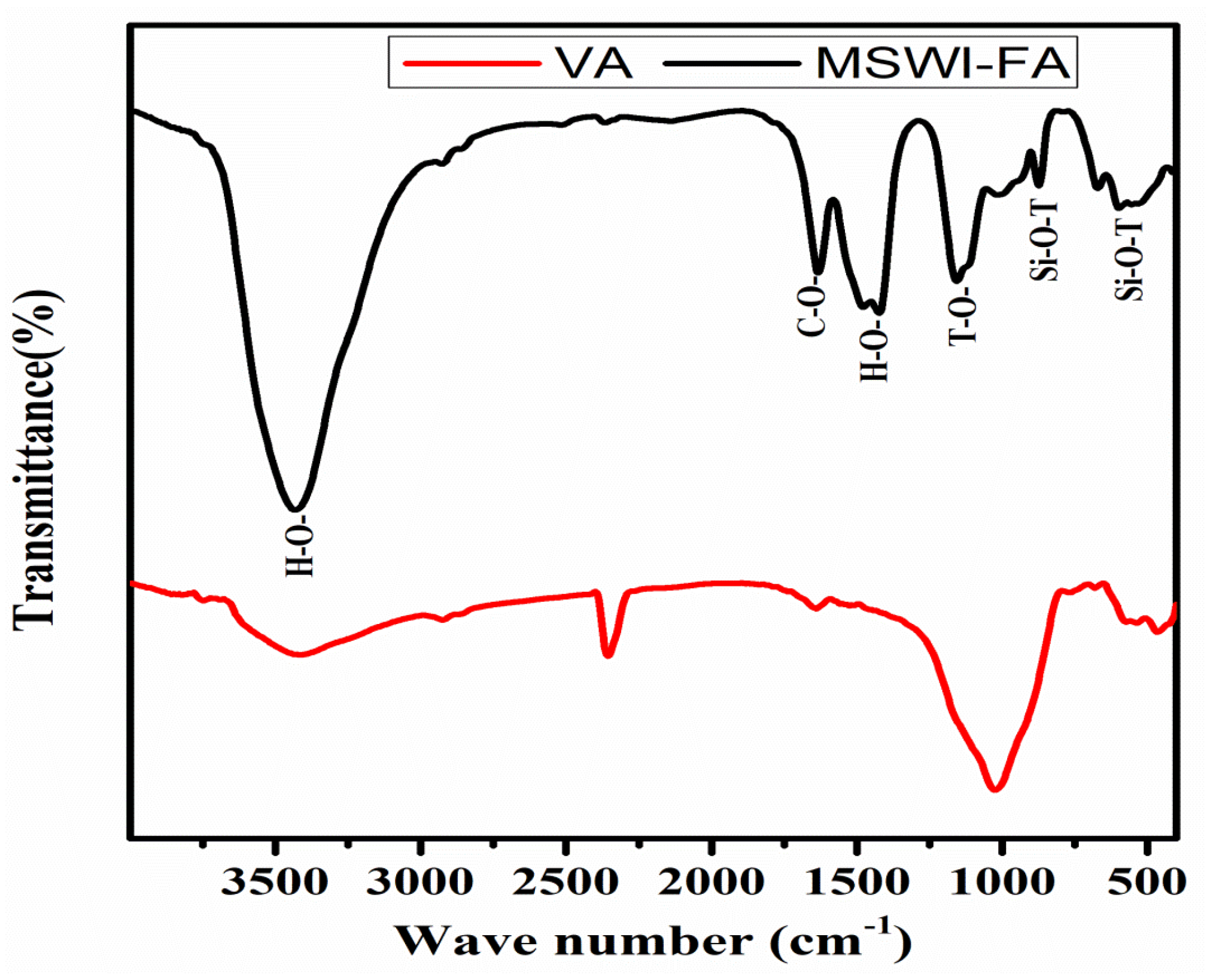
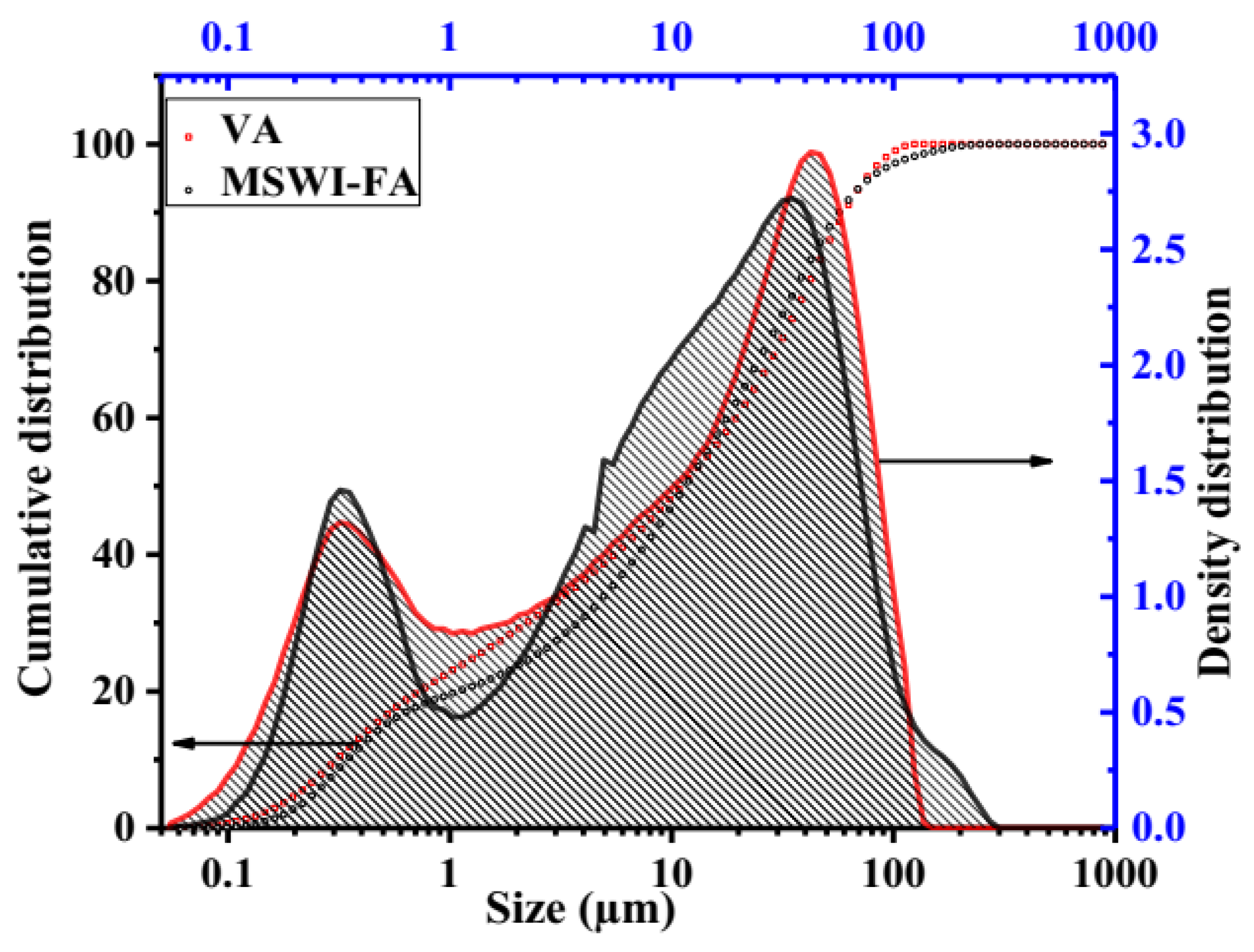
Figure 1 shows the X-ray patterns of MSWI-FA and VA. The phase identification was carried out by comparing with the JCPDF files of expected phases. The broad hump centered at 2ϴ = 34° and 2ϴ = 28° in MSWI-FA and VA, respectively, which shows that these raw materials contain a glassy phase but of a different nature appearing at different 2ϴ. The crystalline phases identified in MSWI-FA includes: Anhydrite (A), CaSO4, PDF#03-0163, Basanite (B), CaSO4·0.5 H2O, PDF#33-0310, Gypsum (G), CaSO4∙2H2O, PDF#03-0053, Sylvite (S), K0.6Na0.4Cl3.0160, PDF#26-0920, Calcite (C), CaCO3 3.02, PDF#72-1650 and Quartz (SiO2, PDF#89-3433), Halite (NaCl, PDF#75-0306). The mineralogical composition of VA includes Anorthite (An), Na(AlSi3O8), PDF#89-8575, Feldspar-Na (F), PDF#89-8575, Nepheline (N), K0.48Na3.48(Al0.99Si0.01O4)4, PDF#84-0686, Maghemite (M), Fe2O3, PDF#15-0615, Forsteritesyn (Fs), Mg2SiO4, PDF#85-1462, Augite(Au(Ca0.61Na0.25Fe0.07Mg)Mg0.65FeO0.10FeO0.03Al0.22)(Si2O6), PDF#801864, Diopside alumina (Da), Ca(Mg, Fe, Al)(Si, Al)2O6, PDF#38-0466, Diopsidesodian (Ds), Ca(Mg, Fe, Al)(Si, Al)2O6, PDF#38-466. Figure 2 illustrates the FTIR spectrum ofMWSI-FA and VA. Both spectra exhibited the bond characteristic of the asymmetric stretching vibrations of Si-O-T (T = Si or Al) with peaks at around 1030 and 1161 cm−1 for VA and MSWI-FA, respectively [26,27]. The peaks center at 579 (VA) and 675 cm−1 (MSWI-FA) and correspond to Si-O bending vibration of quartz [28] and the peak at 472 cm−1 for VA represents the vibration of Si-O-Fe bond [29]. The characteristic bonds of silanol group and water molecules are situated at 3421 and 1643 cm−1 for VA and at 3436 cm−1 and 1621 cm−1 for MSWI-FA, respectively. The calcite identified in X-ray patterns of MSWI-FA explain the presence of peak characteristic of vibration of the carbonate group appearing at 1427 and 1481 cm−1. The particles size distributions of MSWI-FA and VA are represented in Figure 3. The density of particle distribution curves shows that both powders have a bimodal distribution due to their heterogeneous composition. The first mode varies from 0.05 to 1.03 µm (MSWI-FA) and 0.05 to 0.85 µm (VA) while the second one varies from 1.03 to 299.8 µm (MSWI-FA) and 1.03 to 137.2 µm (VA). The mean diameters of particles are 22.57 and 21.85 µm for the MSWI-FA and VA, respectively.
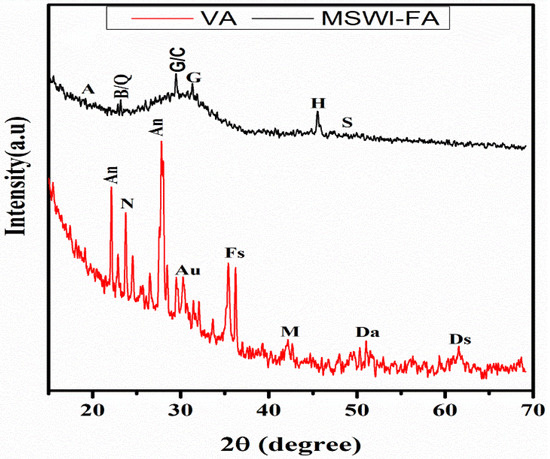
Figure 1.
X-ray diffractogram of MSWI-FA and VA (A = Anhydrite, B = Bassanite, G = Gypsium, S = Sylvite, C = Calcite, Q = Quartz, H = Halite, An = Anorthite, F = Feldspar-Na, N = Nepheline, M = Maghemite, F = Forsterite, A = Augite, Ds = Diopside Sodian, Da = Diopside Alumina).
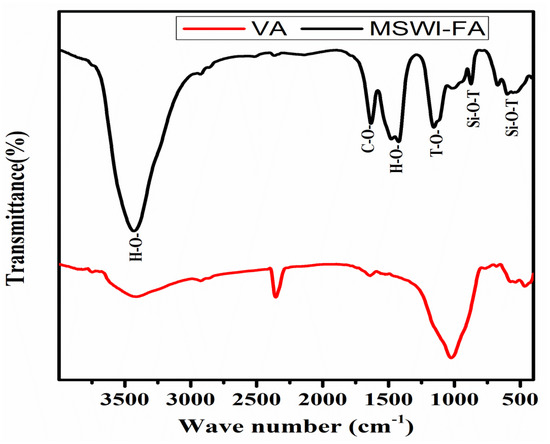
Figure 2.
FTIR spectrum of MSWI-FA and VA.
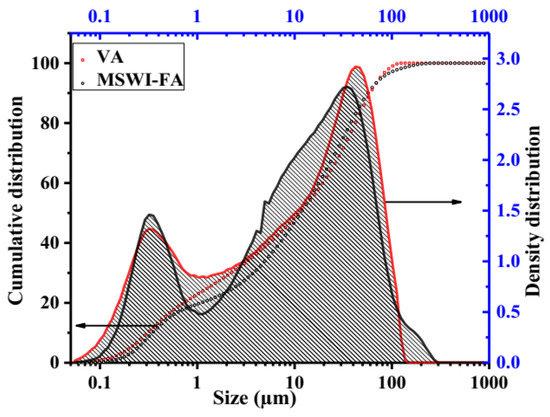
Figure 3.
Particle size and density distribution of MSWI-FA and VA.
3.2. The Effect of Adding VA in Workability and Consistency of the Paste
The paste prepared from unamended MSWI-FA required a high amount of alkaline solution (ratio liquid/solid = 0.75) to have good workability. However, when 50% volcanic ash was incorporated in the MSWI-FA, good workability at the ratio 0.5 was achieved. This is traceable to the difference in bulk density (0.71 g/cm3 and 1.51 g/cm3 for MSWI-FA and VA, respectively) and specific surface area (7.5 m2/g and 3.6 m2/g for MSWI-FA and VA, respectively) of these materials.
3.3. Characterization of Geopolymer Samples
3.3.1. XRD Analysis
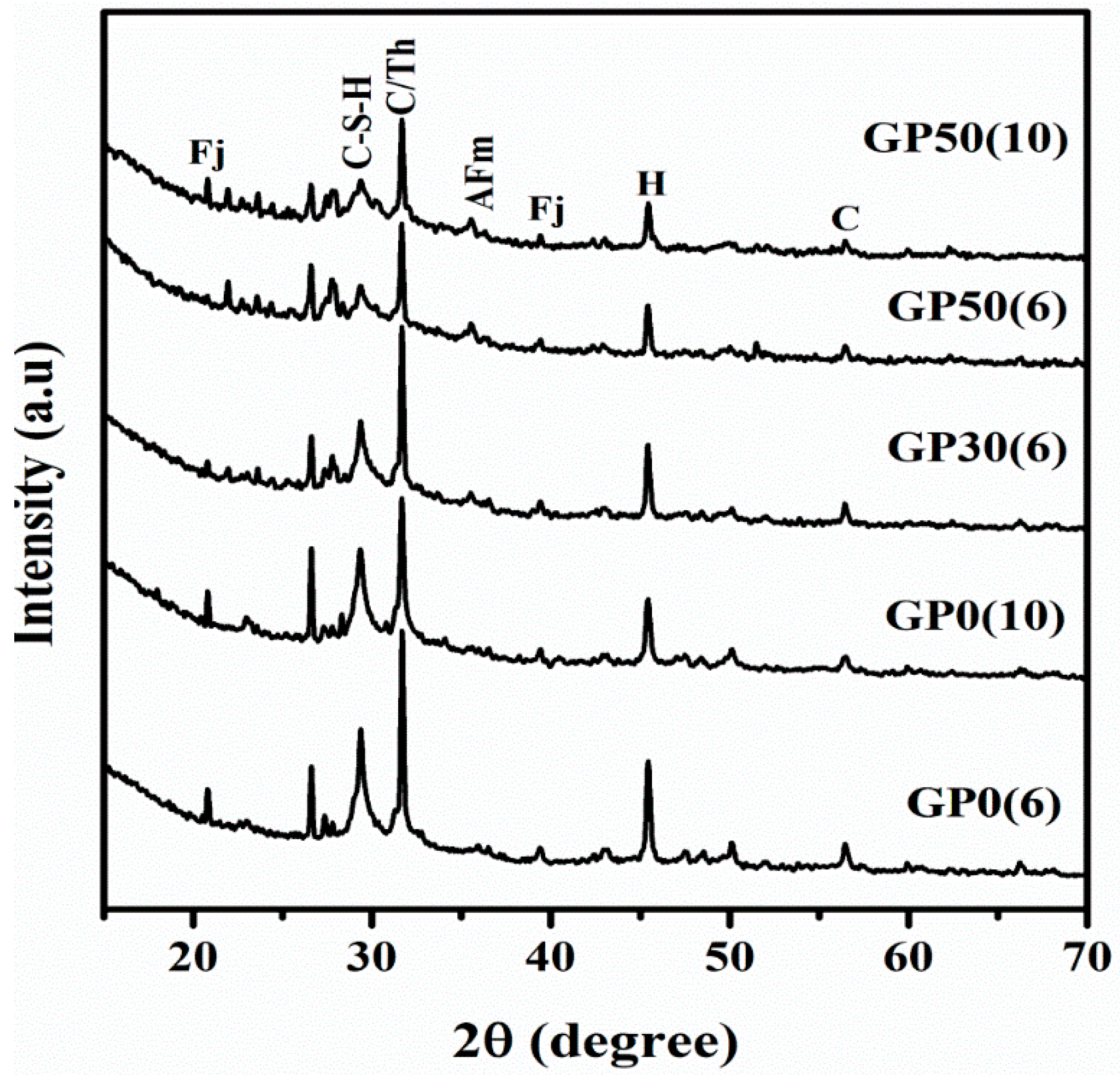
Figure 4 represents the XRD patterns of synthesized Geopolymer cements. Relative to the X-ray patterns of the raw MSWI-FA (Figure 1), prominent differences are evident. The glassy hump centered at around 2ϴ = 34° in MSWI-FA shifted to around 2ϴ = 29°, denoting structural changes that occurred during the reaction with concomitant formation of new crystalline phases [30]. The shift in amorphous hump was also reported by Kumar et al. (2017) [31] while studying the geopolymerisation of fly ash. The observed shift is associated with a change in the Si/Al and Na/Al ratio. It is noteworthy that after the reaction, the peaks (2ϴ = 31.3°, 22.8°, 29.5°) corresponding to calcium sulphate phases such as gypsum, Anhydrite and Basanite, previously present in MSWI-FA were significantly diminished. The reaction of calcium sulphate phases in the alkaline medium promoted the formation of the crystalline phase namely Thernadite (Th) (Na2SO4, PDF#02-0805) as shown in Equation (1).
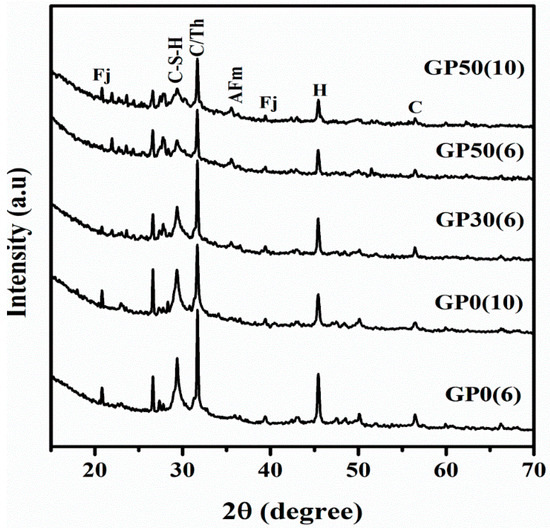
Figure 4.
X-ray diffractogram of Geopolymer cement without and with VA (C-S-H = Calcium silicate hydrate, C = Calcite, Th = Thernadite, Fj = Faujasite-Na, AFm = Hydrocalcumite and H= Halite).
There are also the formations of new minerals such as Hydrocalumite (AFm) (PDF#31-0245 Ca4Al2O6(CO3)0.67(SO3)0.33), Calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) (PDF#31-0301), and Faujasite-Na (Fj)(Na2Ca)0.075(Al0.3Si0.7)O2(H2O)0.22, (PDF#76-0843). The last mineral belongs to the zeolite type and was also observed earlier during alkali activation of volcanic ash with a calcium source by hydrothermal treatment (60 °C and 80 °C) [32]. In this study, zeolitic phases were obtained at room temperature due to the rapid dissolution of glassy MSWI-FA which promoted the formation of crystalline and amorphous alumina-silicates phase [33]. The peak intensity and width of Calcium silicate hydrate and Thernadite at 2ϴ = 30° varied inversely and directly with an increase in alkalinity, respectively. This is due to the fact that low alkalinity promote the C-S-H phase [34] and the high alkalinity promotes the poorly crystalline C-(A)-S-H phase owing to the prominence of substitution of Si in the C-S-H phase by Al and N-A-S-H phases [35]. The decreased intensity of this peak with the increase in VA content is attributed to the co-existence of C-S-H and N-A-S-H phases resulting from an increased Si/Al ratio. The emergence of the aforementioned crystalline phases could also be justified by the change of the degree of crystallinity after geopolymerization as shown in Table 3. The peak intensity of s calcite increased with a growing alkali concentration. Obviously, the presence of high amount of OH− promoted the formation of calcium hydroxide which undergoes the carbonation reaction as depicted by Equation (2) [36]. Moreover, due to the high content in Na+ ion, formation of sodium carbonate is generally expected and observed in cement and Geopolymers [34]. However, the peaks of sodium carbonate are of very low intensities, attributed to precautions taken to limit the carbonation of sodium after hardening.

Table 3.
IR Characteristic bands of Geopolymer MSWI-FA and MSWI-FA-VA.
3.3.2. FTIR Analysis
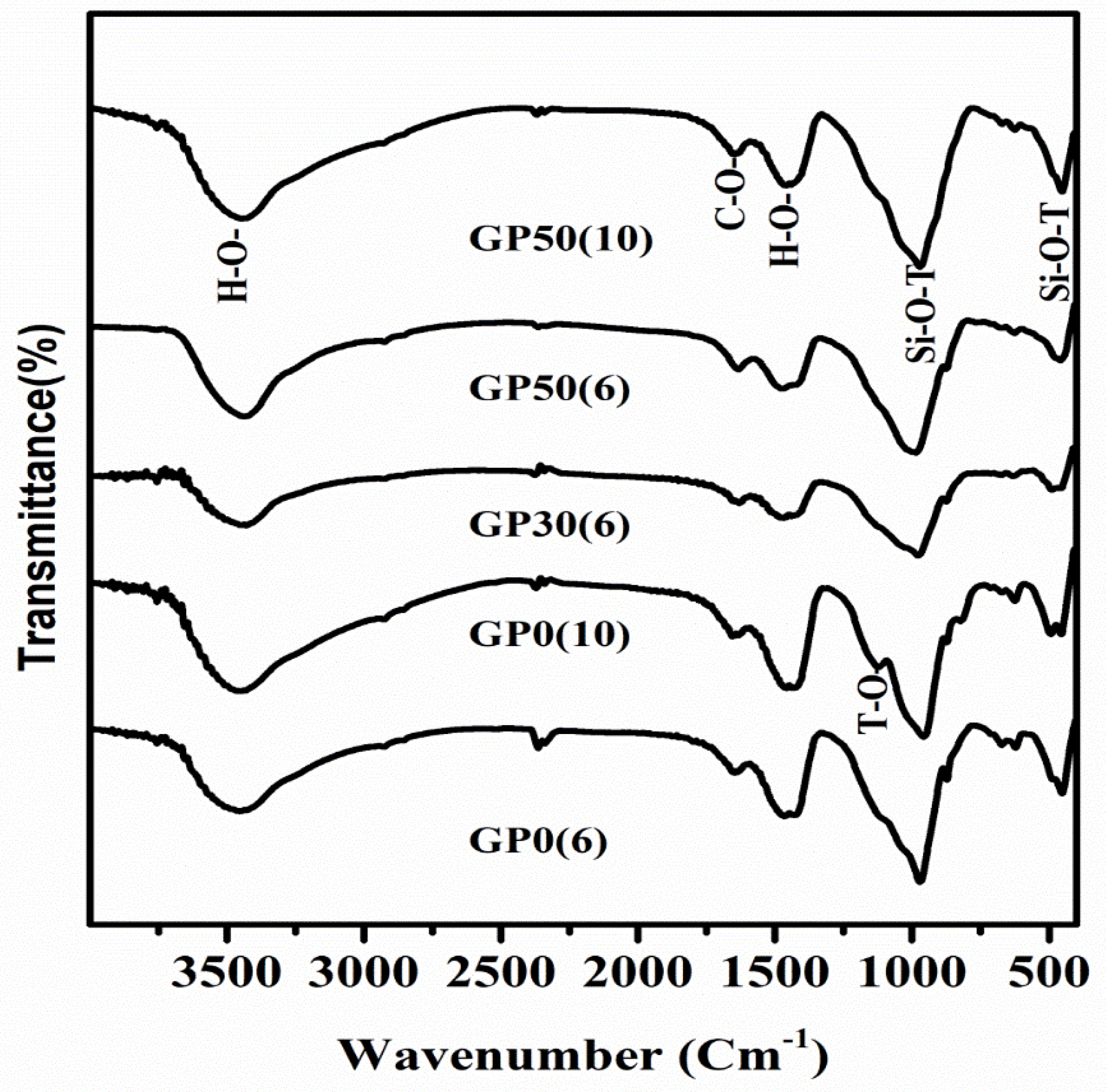
Figure 5 depicts the FTIR spectra for the Geopolymer samples after 28 days of curing at room temperature and at different concentration of alkalis in the range of 4000 to 400 cm−1. The bands at 951–968 cm−1 are assigned to the Si-O-T (T = Al, Si) asymmetric stretching vibrations characteristic of aluminosilicates and calcium silicate hydrate phases [18,37]. The left shoulder of this band is attributed to asymmetric stretching of T–O bonds originating from individual tetrahedral [38], suggesting the presence of the zeolite phase [39]. The presence of the zeolitic phase is hitherto confirmed by the XRD analysis. The series of bands in the 450–650 cm−1 range is assigned to Si-O-T deformation vibrations [40,41]. The peaks at around 1420 cm−1 and the one at 872 cm−1 were attributed to the carbonate bond from calcite or Na2CO3 [40]. The bands at the 3477–3466 cm−1 range and 1645–1648 cm−1 range are attributed to the stretching vibration and deformation of O-H bonds and H-O-H, respectively. The wavenumber of these characteristics bands are shown in Table 3. Comparing these values to the same characteristic bands of MSWI-FA several changes are observed. A shift of Si-O-T vibrational and deformation bands to high and low values, respectively is noticeable. This is due to a change in the microstructure during the alkaline activation reaction [42]. The vibrational wave numbers not only increase after alkaline activation of MSWI-FA but also are observed to decrease with a rise in alkalinity. As seen in the present work, this phenomenon has been previously reported during alkaline activation of calcium-silica rich systems [43,44,45]. Precisely, the low concentration of alkali and the high content of the reactive calcium favor the formation of the C-S-H phase. On the contrary, high alkali concentration is detrimental to C-S-H formation due to the precipitation of Ca(OH)2. The shift of Si-O-T bands is more pronounced in the Geopolymer MSWI-FA-VA system than in those without VA, implying the extent of the reaction is higher in the former than in the later. The incorporation of VA promotes the substitution of silicate in this gel by Al to form the C-S(A)-H gel and growth of aluminosilicate phases via dissolution of VA’s glassy phase. GP50(6) posted the highest shifting of the wave number possibly due to the coexistence of C-S-H gel and Geopolymer in this system after equilibration of the alkalization and geopolymerization reactions. This is consistent with the results by Yip et al. [18], which demonstrated that the coexistence of these two gels occurs only in a system which contain sufficient amount of calcium source (20 wt%) at low alkalinity (NaOH ˂ 7.5 M). The wave number of band C-O also increases in the Geopolymer cement relative to MWSI-FA consistent with the formation of calcite in a high alkalinity medium. Higher wavenumbers denote higher force constant which means greater bond strength in the VA-impregnated Geopolymer.
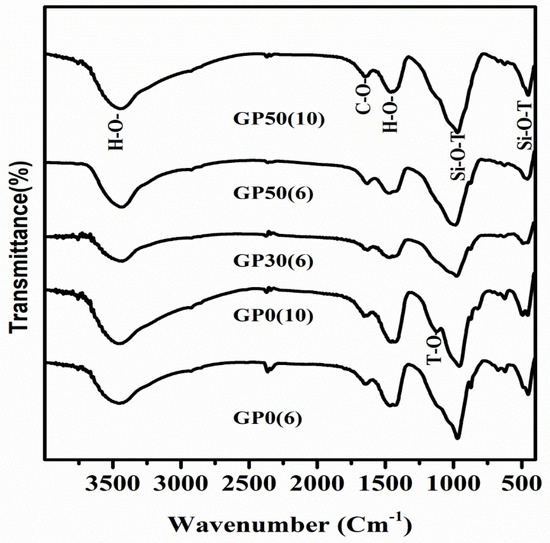
Figure 5.
FTIR spectra for the Geopolymer cement without VA and Geopolymer cement based MSWI-FA-VA system.
3.3.3. FEG-SEM/EDS Analysis
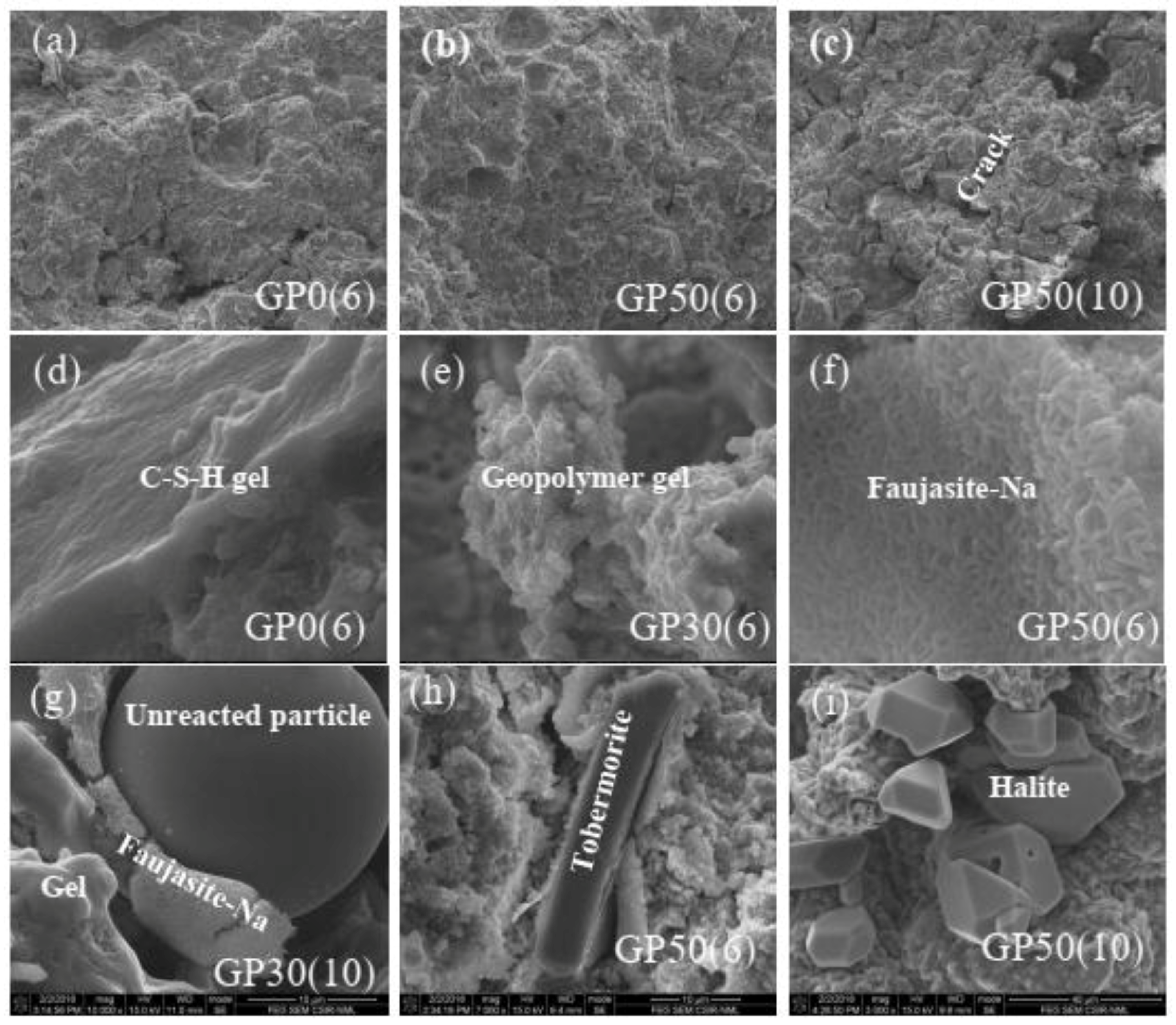
Figure 6 shows the selected micrographs taken during FEG-SEM/EDX analysis. The spots are classified in three groups. The first group (micrographs a, b, and c) shows the bulk feature of Geopolymer samples at the same magnification. The densification of the microstructure increases with the incorporation of VA (spots (a) and (b)) while the increase of concentration increases the cracks [27]. From micrographs (c), the cracks are prominent in GP(10). This fact is due to the migration of free Na+ and K+ ions outside the Geopolymer and could also be attributed to the negative effect of some crystalline phases. The second group (micrographs d and e) exhibits the different gels formed during the reaction. These features were found in all the samples used for microstructural analyses. The micrograph (d) represents the C-S-H gel. The addition of VA and the change of concentration of alkali medium lead to the modification of this gel. The ratio of (Ca+Mg)/Si, (Na+K)/Si and Si/Al calculated for all the samples via the EDS result range from 0.47–6.09, 0.644–1.16 and 8.26–3, respectively. The morphology feature of micrographs (f) depicted the N-A-S-H gel, which is more dense in Geopolymer cement with a high amount of VA and a high concentration of the alkali solution (GP50(10)). The ratio of (Ca+Mg)/Si, (Na+K)/Si and Si/Al ranges to 0.33–1.14, 0.64–3.15, and 2.34–2.61 respectively. The last group represents the crystalline phases and the unreacted particles. From these spots, the crystalline phases and unreacted particles are embedded in different gels. The microstructure and EDS analysis (micrographs) suggested the presence of C-S-H, halite, and Faujasite-Na corroborating the XRD results. C-S-H results from the precipitation of Ca2+ and silicate ions. The EDS result shows that the Ca/Si ratio of C-S-H is 0.65. This value is slightly lower than that of natural C-S-H (0.67–1.5) [18] possibly due to the substitution of some Si by Al to form Al-C-S-H. This imbues the material with a better heavy metal encapsulation capacity. Halite was prominent in the Geopolymer synthesized with 10 M as shown in the micrograph (i), due to the increase in free sodium ions. This leads to precipitation with chorine ions available in the system. Micrograph (e) shows the characteristics of the zeolite. Based on the Si/Al molar ratio of zeolite in the different Geopolymer samples (Si/Al = 5), this feature can be classified/graded as “intermediate zeolite silica” and according to this classification, the mineral name and their framework codes is Na-Y faujasite which correlate with the XRD and FTIR results [46]. The EDS analysis of the different phases formed after reaction highlight that their respective compositions are constantly modified according to the composition and the alkaline medium of the synthesis. In the present study, the (M(II),M(I))-(A)-S-H, and (M(I),M(II))-A-S-H formed resulted from the C-S-H and N-A-S-H, respectively; where M(II) = Ca, Mg and (M(I) = Na, K. The heterogeneity of the gel is due to the high reactivity of its ingredients gel [32].
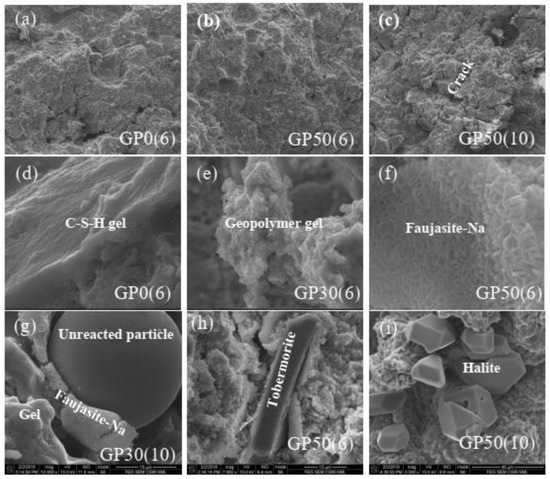
Figure 6.
FEG-SEM/EDS analysis of GPX(6) and GPX(10). (a,d) micrographs of GP0(6); (b,f,h) micrographs of GP50(6); (c,i) micrographs of GP50(10); (e) micrograph of GP30(6) and (g) micrograph of GP50(10).
3.3.4. Leaching Result
To study the encapsulation efficiency of these cements, toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) was carried out by following the USEPA method 1311 and the results are shown in Table 4. The leached metals from the Geopolymer samples were far much lower than the maximum concentration of each contaminant stipulated by USEPA for toxicity characteristics. This confirms the efficiency of the developed Geopolymer to stabilize heavy metals. The concentration of Cd released was less than the instrumental detection limit for all Geopolymer samples. This depicts high stabilization of Cd after geopolymerization due to the very low solubility of Cd(OH)2 and is in agreement with previous reports [3,15,47]. Noteworthy, the encapsulation phenomenon was most prominent in the Geopolymer synthesize at 6 M medium. It is conceivable that the reduced leachability in Geopolymer samples prepared in 6 M media was due to the emergence of in situ absorbents such as zeolite, Al-C-S-H, AFm, the C-S-H gel, and the Geopolymer gel.

Table 4.
Leaching concentration (mg·L−1) of MSWI-FA, VA, MSWI-VA based Geopolymer, landfill limit, and percentage of leach metal.
3.3.5. Compressive Strength
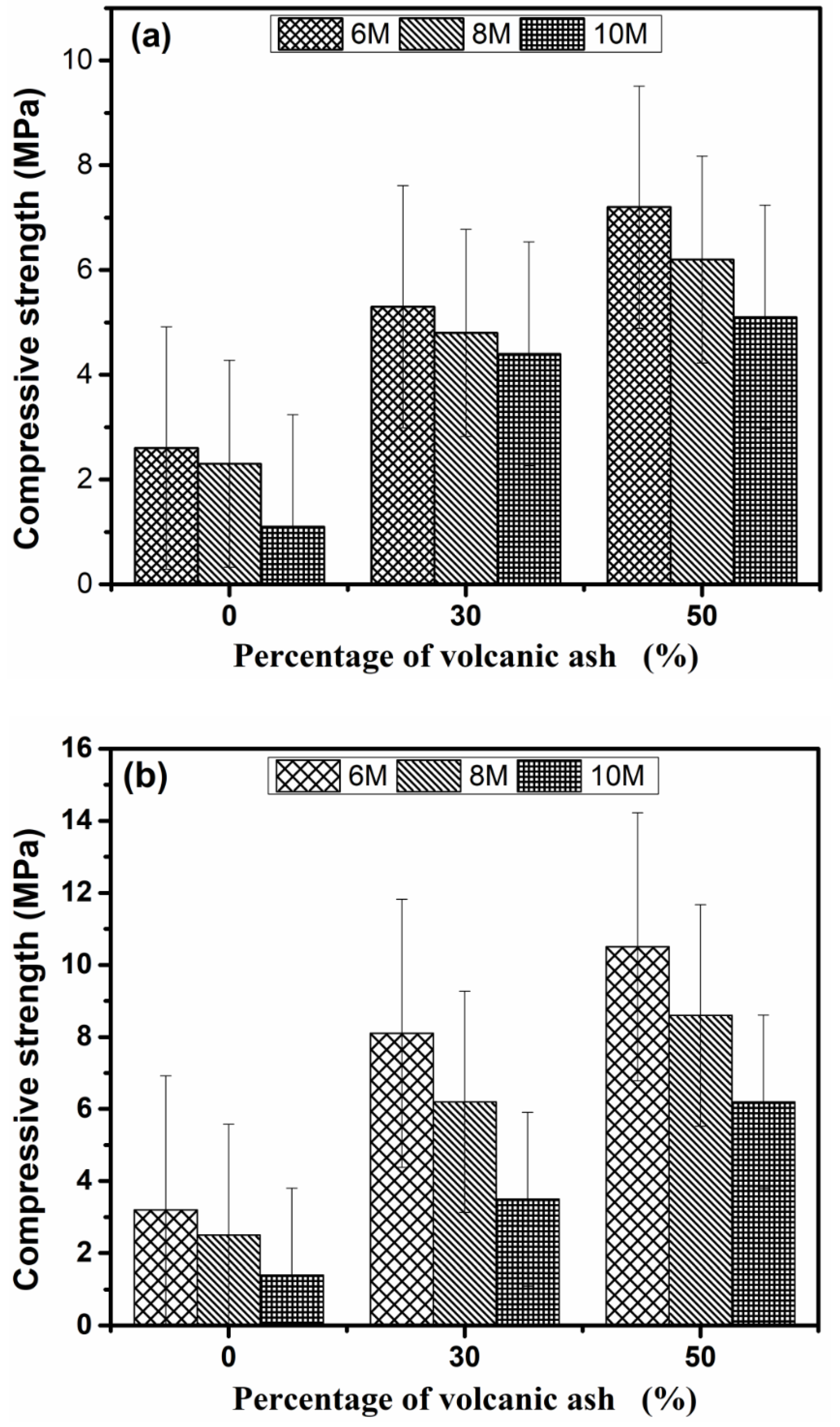
Figure 7a,b display the compressive strength of Geopolymer samples after 14 and 28 days respectively. In general, the compressive strength was lower than the many reported values because of (a) 25 mm size samples were used for testing and (b) the test was conducted on hardened paste samples. Notably, the compressive strength decreased with the increase in alkali and was directly proportional to the VA content. The percentages of strength gained for Geopolymers synthesized at 6 M from 14 days to 28 days are 13.04%, 52.83%, and 45.83% for GP0(6), GP30(6), and GP50(6), respectively. These percentages decrease with the rise in the alkali of the concentration. Considering the VA content, the concentration of the alkaline solution, and 28 days of compressive strength, the optimal addition dosage of MSWI-FA is 50 wt% at 6 M (10.5 MPa). This behavior is due to the fact that the high alkalinity (10 M) not only promotes the dissolution of glassy phases in the precursor, but also inhibits the precipitation reaction which is responsible for the formation of different gels responsible for the material’s strength [48]. The high alkalinity also results in excess alkali ions. The excess of alkali causes the diffusion of the alkali ions out of the matrix, which increases the formation of cracks throughout the structure [49] with concomitant precipitation of halite which has low mechanic properties. At 6M concentration, the quantity of OH− is sufficient to simultaneously generate the precipitation of the C-S-H and geopolymerization gels without remarkable free alkali. The coexistence of these two phases is beneficial for the material strength. The substitution of MSWI-FA by VA densifies the structure, brings supplementary Si4+, Al3+ ions thus leads to the formation of the aluminosilicates phases, and enhances the modification of C-S-H, which increases the strength [50].
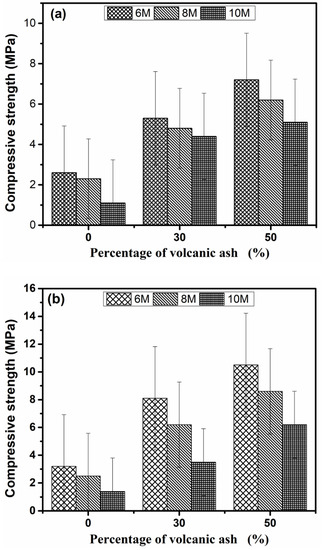
Figure 7.
Compressive strength of Geopolymer samples cured at 14 days (a) and 28 days (b).
4. Conclusions
This study, for the first time, reported the addition of VA to compensate the low alumina and silica content in MSWI-FA in order to synthesize eco-friendly cement (Geopolymer), thus contributing to the recycling via stabilization/solidification of this toxic waste. Studies on the effect of the VA dose incorporated and alkalinity of the activating solution were evaluated. Following conclusions can be drawn from the study:
- The incorporation of VA reduces the Liquid/Solid (L/S) ratio required to obtain a good workability of cement paste from 0.75 for MSWI-FA system to 0.5 for the MSWI-FA-50%VA system. It also enhances the coexistence of the Geopolymer gel and the C-S-H gel in the matrix, thus improving the mechanical properties and encapsulation efficiency of the heavy metals present in MSWI-FA.
- A high alkalinity of the activating solution (10 M, Ms = 0.36) reduces the mechanical properties of the cement obtained and the low alkalinity (6 M, Ms = 0.66) led to the best mechanical property (10.5 MPa for the 50% MSWI-FA-50%VA system).
- Due to the moderated mechanical properties of the products obtained, this Geopolymer cement based on the MSWI-FA-VA system can be used in the manufacturing of non-structural materials such as bricks and paving stones, which are subject to further tests such as the durability of cement.
- This work, thus, shows the possibility of using VA as an adjuvant to MSWI-FA based Geopolymer cement in the same way as calcined clays, fly ash, slag, red mud etc.
Author Contributions
Methodology, T.S. and S.K.; Supervision, E.J.; Writing—original draft, T.S.; Writing—review & editing, E.M.-A. and S.K.
Funding
The work presented in the paper has been carried out under CSIR-TWAS Sandwich Postgraduate Fellowship Award FR No 3240293597 awarded to the first author and is greatly acknowledged.
Acknowledgments
The authors are also grateful to Director, CSIR-National Metallurgical Laboratory, Jamshedpur, India for extending the facility to carry out this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Innocent, N.M.; Dieudonné, B.; Jose, S.N. Modeling the Temporal Variations of Municipal Solid Waste Generation for Future Projection in the Douala Municipality, Cameroon. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2016, 3, 5288–5295. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, C.H.K.; Ip, A.W.M.; Barford, J.P.; McKay, G. Use of incineration MSW ash: A review. Sustainability. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1943–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferone, C.; Colangelo, F.; Messina, F.; Santoro, L.; Cioffi, R. Recycling of pre-washed municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash in the manufacturing of low temperature setting geopolymer materials. Materials 2013, 6, 3420–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbas, T.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Astrup, T.; Hjelmar, O.; Mostbauer, P.; Cappai, G.; Magel, G.; Salhofer, S.; Speiser, C.; et al. Management of municipal solid waste incineration residues. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, I.; Glasser, F.P. Chloride in cement. Adv. Cem. Res. 2014, 27, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Gao, X. Immobilization of MSWI fly ash through geopolymerization: Effects of water-wash. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash via co-sintering with waste-derived vitrified amorphous slag. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekara, C.; Bhuiyan, S.; Law, D.; Setunge, S.; Ward, L. Corrosion Resistance in Different Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Concretes. In Proceedings of the 11th High Performance Concrete (HPC) and the 2nd Concrete Innovation Conference (CIC), Tromsø, Norway, 6–8 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kupwade-Patil, K.; Allouche, E.N. Examination of Chloride-Induced Corrosion in Reinforced Geopolymer Concretes. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennakoon, C.; Shayan, A.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Xu, A. Chloride ingress and steel corrosion in geopolymer concrete based on long term tests. Mater. Des. 2017, 116, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, P.J. Heavy metals waste encapsulation. In Environmentally Driven Geopolymer Cement Applications. Proceedings of the Geopolymer 2002 Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 28–29 October 2002; Geopolymer Institute: Saint-Quentin, France; pp. 1–9.
- Djobo, J.N.Y.; Tchadjié, L.N.; Tchakoute, H.K.; Kenne, B.B.D.; Elimbi, A.; Njopwouo, D. Synthesis of geopolymer composites from a mixture of volcanic scoria and metakaolin. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 2, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas, F.; Torres-Carrasco, M. Use of glass waste as an activator in the preparation of alkali-activated slag. Mechanical strength and paste characterisation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 57, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Development of paving blocks from synergistic use of red mud and fly ash using geopolymerization. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, I.; Kamseu, E.; Michelazzi, M.; Barbieri, L.; Corradi, A.; Leonelli, C. Chemical stability of geopolymers containing municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Reid, A.; Provis, J.L.; Bullen, F. Using fly ash to partially substitute metakaolin in geopolymer synthesis. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 88–89, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, S.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, B.; Huang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Hu, J.; Wu, X. Co-disposal of MSWI fly ash and Bayer red mud using an one-part geopolymeric system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, C.K.; Lukey, G.C.; van Deventer, J.S.J. The coexistence of geopolymeric gel and calcium silicate hydrate at the early stage of alkaline activation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, J.; Djobo, Y.; Elimbi, A.; Tchakouté, H.K. Volcanic ash-based geopolymer cements/concretes: The current state of the art and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4433–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakoute Kouamo, H.; Elimbi, A.; Mbey, J.A.; Ngally Sabouang, C.J.; Njopwouo, D. The effect of adding alumina-oxide to metakaolin and volcanic ash on geopolymer products: A comparative study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankwa Djobo, J.N.; Elimbi, A.; Tchakouté, H.K.; Kumar, S. Mechanical activation of volcanic ash for geopolymer synthesis: Effect on reaction kinetics, gel characteristics, physical and mechanical properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39106–39117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamseu, E.; Leonelli, C.; Perera, D.S.; Melo, U.C.; Lemougna, P.N. Investigation of volcanic ash based geopolymers as potential building materials. InterCeram Int. Ceram. Rev. 2009, 58, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, L.; Jin, Z. Resistance of metakaolin-MSWI fly ash based geopolymer to acid and alkaline environments. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2016, 450, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.R. Metals Emissions Control Technologies for Waste Incineration. Davy Environ. 1991, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar]
- Vanesa, G.; Taboada, C.; Ferna, A. Recycling Industrial By-Products in Hybrid Cements: Mechanical and Microstructure Characterization. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, M.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A.; Sobrados, I.; Sanz, J. Effect of the SiO2/Na2O ratio on the alkali activation of fly ash. Part II:29Si MAS-NMR Survey. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 109, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriskova, L.; Machiels, L.; Pontikes, Y. Inorganic Polymers from a Plasma Convertor Slag: Effect of Activating Solution on Microstructure and Properties. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, B.J.; Parthasarathy, G.; Sarmah, N.C. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic estimation of crystallinity in sio2 based rocks. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2008, 31, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Kong, S.; Djobo, J.N.Y.; Tchadjié, L.N.; Njopwouo, D. A comparative study of two methods to produce geopolymer composites from volcanic scoria and the role of structural water contained in the volcanic scoria on its reactivity. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 12568–12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, Z.; Abdullah, M.; Hussin, K.; Ismail, K.; Razak, R.; Sandu, A. Effect of Solids-To-Liquids, Na2SiO3-To-NaOH and Curing Temperature on the Palm Oil Boiler Ash (Si + Ca) Geopolymerisation System. Materials 2015, 8, 2227–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mucsi, G.; Kristály, F.; Pekker, P. Mechanical activation of fly ash and its influence on micro and nano-structural behaviour of resulting geopolymers. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djobo, J.N.Y.; Tchakouté, H.K.; Ranjbar, N.; Elimbi, A.; Tchadjié, L.N.; Njopwouo, D. Gel composition and strength properties of alkali-activated oyster shell-volcanic ash: Effect of synthesis conditions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, C.A. Mechanisms and Kinetics of Gel Formation in Geopolymers. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC, Australia.
- Yip, C.K.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Microanalysis of calcium silicate hydrate gel formed within a geopolymeric binder. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 3851–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, B.; Nicolas, R.S.; Sani, M.A.; Rees, G.J.; John, V.; van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L. Phase evolution of C-(N)-A-S-H/N-A-S-H gel blends investigated via alkali-activation of synthetic calcium aluminosilicate precursors. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Application of Ca-based geopolymer with blast furnace slag, a review. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Slag Valorisation Symposium, Leuven, Belgium, 18–20 April 2011; pp. 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Puligilla, S.; Mondal, P. Co-existence of aluminosilicate and calcium silicate gel characterized through selective dissolution and FTIR spectral subtraction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 70, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortego, J.D.; Barroeta, Y.; Cartledge, F.K.; Akhter, H. Leaching Effects on Silicate Polymerization–an Ftir and Si-29 Nmr-Study of Lead and Zinc in Portland-Cement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W.; Król, M.; Barczyk, K. FT-IR studies of zeolites from different structural groups. Chemik 2011, 65, 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Povnnennykh, A.S. The use of infrared spectra for the determination of minerals. Am. Mineral. 1978, 63, 956–959. [Google Scholar]
- Rosas-Casarez, C.A.; Arredondo-Rea, S.P.; Gómez-Soberón, J.M.; Alamaral-Sánchez, J.L.; Corral-Higuera, R.; Chinchillas-Chinchillas, M.J.; Acuña-Agüero, O.H. Experimental study of XRD, FTIR and TGA techniques in geopolymeric materials. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2014, 4, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, C.A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Van Deventer, J.S.J. In situ ATR-FTIR study of the early stages of fly ash geopolymer gel formation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9076–9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Lodeiro, I.; Macphee, D.E.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. Effect of alkalis on fresh C-S-H gels. FTIR analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, A.; Boonserm, K.; Waisurasingha, C.; Sata, V.; Chindaprasirt, P. Use of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) bottom ash in high calcium fly ash geopolymer matrix. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yuan, B.; Yu, Q.L.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Characterization and application of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) bottom ash and waste granite powder in alkali activated slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, B.; Singh, D.N. A Review on Synthesis, Characterization and Industrial Applications of Flyash Zeolites. J. Mater. Educ. 2011, 33, 65–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna Galiano, Y.; Fernández Pereira, C.; Vale, J. Stabilization/solidification of a municipal solid waste incineration residue using fly ash-based geopolymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Rose, V.; Mejía De Gutierrez, R. Evolution of binder structure in sodium silicate-activated slag-metakaolin blends. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonelli, C.; Kamseu, E.; Lancellotti, I.; Barbieri, L. Geopolymerization as Cold-Consolidation Techniques for Hazardous and Non-Hazardous Wastes. Key Eng. Mater. 2017, 751, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Lodeiro, I.; Fernández-Jimenez, A.; Palomo, A.; Macphee, D.E. Effect on fresh C-S-H gels of the simultaneous addition of alkali and aluminium. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).