Abstract
Developing cities have historically looked to developed cities as exemplary models for waste management systems and practices without considering the consequent resource requirements or the key characteristics of the local setting. However, direct adoption of developed cities’ approaches without proper consideration of the local circumstances may lead to unsustainable future waste management in developing cities. This study evaluates waste management in London and Kuala Lumpur, representing developed and developing cities, focusing on the integration of policy changes, socio-economic background and waste data trends on a multi-decadal scale. This analysis reveals the gradual implementation of initiatives, the challenges faced and the attempted solutions that were applied differently in both cities. Conceptual models of waste management status in different scenarios for both cities were developed. These models highlight that societal behaviour shifts from minimal waste generation (wasteless) to throw-away society (wasteful) and a drive to achieve sustainable waste behaviour with integration of resource recovery and waste minimization (wasting less). A detailed understanding of the evolution of waste management systems towards fulfilling public needs alongside rapid urbanization can provide new perspectives on future waste scenarios, especially in developing cities. Ultimately, reliable and accurate data are crucial to avoid inaccuracies in planning for future waste management.
1. Introduction
Urbanization, rapid economic growth and increasing urban populations have resulted in a marked escalation in quantities of waste generated, heterogeneity and complexity [1,2]. Inadequate waste management has impacted adversely on public health [3] and has caused environmental degradation and resource depletion [4]. The challenge of designing localised waste management strategies that are economically viable, environmentally effective and socially acceptable continues to be of major concern to municipal authorities [5,6].
There are clear differences in waste management systems between developed and developing cities. For instance, waste management practices in developed cities currently focus on optimization strategies for resource conservation [7,8] whilst approaches to waste management in developing cities are often underdeveloped [9], operationally inefficient, and inadequately managed, with limited knowledge and expertise to hand [1,10]. These distinct shortcomings have led to an urgent need for developing cities to seek advice towards shaping waste management systems that are workable and acceptable in local settings.
Integrated waste management can be applied in both developed and developing cities depending on local circumstances and factors that have influenced preceding initiatives [11]. Developing cities have historically looked to developed cities as exemplary models for waste management systems and techniques. However, when trying to select a suitable, durable and sustainable approach to waste management, it is important for decision-makers to (i) understand the local scenario; (ii) evaluate the adaptability of management systems and practices from developed cities; and (iii) consider the consequent resource and logistical requirements, including human and technical resources. Previous studies have addressed the evolution of waste management systems from the viewpoints of societal background [12], policy design [13], technological development and system innovations [14] and the experiences of a single country or city [6,15,16,17,18,19]. To facilitate the improvement of future systems, there is a need to compare the evolution of waste management systems between developed and developing cities in a comprehensive manner, particularly relationships between socio-economic developments, strategy/policy changes and waste arisings.
This study reviews the history of urban waste management in developed and developing cities, focusing on the integration of policy changes, socio-economic background and waste data trends. In this context, we specifically appraise historical evidence over a 44-year period (1970–2014) for London and Kuala Lumpur, representing developed and developing cities, respectively. These cities were selected because:
- After more than 300 years of British colonial rule, there has been a strong British influence on administrative systems in Malaysia.
- Malaysia has been a member of the Commonwealth since 1957, status which has facilitated the maintenance of a British-modelled government administration.
- Development in Kuala Lumpur has followed, with a substantial time-lag, a similar trajectory to London in terms of its population and development.
Through long-term historical comparison, the development of waste management systems may be evaluated as a means to question whether developed cities can influence positively the adoption of waste management systems in developing cities. Evolution of their waste management systems is thus examined in terms of waste generation, composition, collection systems, disposal methods, recycling and the overarching waste strategies implemented. We consider how changes in societal circumstances and behaviour are associated with indicators of waste management systems over time and provide insights into how future waste management systems may evolve, especially in developing cities.
2. Materials and Methods
Whilst there are various definitions of urban waste, the simplest version makes reference to non-liquid waste materials that have been discarded or are unwanted and need to be disposed from domestic, trade, commercial, industrial, agriculture as well as public services [20,21,22].
In the UK, waste is defined in the Environmental Protection Regulations (1991) according to the European Union (EU) Directive 91/156/EEC as “any substance or object in the categories set out in Annex I which the holder discards or intends or is required to discard” [23]. Annex 1 in Directive 91/156/EEC contains a list of 16 different categories of waste, mainly used to determine whether or not a substance or object has been discarded. In Malaysia, the general terms of waste are defined in the Solid Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act (2007) as:
- (a)
- any scrap material or other unwanted surplus substance or rejected products arisings. from the application of any process;
- (b)
- any substance required to be disposed of as being broken, worn out, contaminated or otherwise spoiled; or
- (c)
- any other material that according to this Act or any other written law is required by the authority to be disposed of, but does not include scheduled wastes as prescribed under the Environmental Quality Act 1974 (Act 127), sewage as defined in the Water Services Industry Act 2006 (Act 655) or radioactive waste as defined in the Atomic Energy Licensing Act 1984 (Act 304)” [24].
In this study, three key indicators have been selected to illustrate pertinent changes and trends; population growth, economic growth and waste arisings. The study focuses on the period 1970–2014. Population growth rate is the increase in a country’s population during a period of time, and includes the number of births and deaths and the number of people migrating to and from a country [25]. Economic growth is evaluated by annual Gross Domestic Product (GDP), i.e., market value of products and services in a country. Data on population growth and GDP for both cities were mainly gathered from the World Bank’s global development indicators [26]. Table 1 shows the sources of data used in this study.

Table 1.
Sources of data used as basis for waste arisings, trends and composition changes in Malaysia and the United Kingdom from 1970 to 2014.
Standardization of the data is impractical; some required data were unavailable, some have questionable accuracy, and there have been changes in the type of waste included in or defined as solid waste over time. For instance, the definition and classification of solid waste changed over the period depending on its necessity in the local waste scenario. In order to provide better comparisons, data for waste generation used in this study were grouped into the same timeline. The number of accessible historical databases on waste management in Malaysia is limited and there is a lack of organised documentation to record such data, often resulting in outdated and possibly inaccurate databases [43].
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Historical Waste Management
Waste generation trends and composition can provide information required for future planning [44]. Historians consider that environmental knowledge and developed strategies about earlier civilisations can be gained by examining waste profiles and trends over time [16,45]. As cities became modernized, higher amounts of waste of increasingly complex composition were produced from diverse sources. As national GDP increases, per capita waste generation also increases, suggesting higher waste generation in the future [46]. Table 2 summarizes the population growth and waste arisings for London and Kuala Lumpur over 44 years. After independence in 1957, Kuala Lumpur benefited from economic prosperity that significantly improved standards of living. The expansion of the manufacturing sector stimulated Malaysia’s economic growth, but the consequences of economic activities on the environment triggered public anxiety about waste arisings and their means of disposal throughout the 1980s.

Table 2.
Population trends and waste arisings for Kuala Lumpur and London (1970s–2014). (Data sources shown in Table 1).
London was the first city to establish formal door-to-door waste collections by 1900; a similar system exists today. With more complex challenges to manage waste in London, the inherited systems have failed to meet the consequences of economic growth and population expansion [47]. The overall system evolved initially in response to the high fraction of coal ash in municipal waste that had potential market value [48]. The dust-yard operations reached their peak by the mid-19th century when coal ash prices dropped gradually and changed the waste characterization and composition [48].
3.2. Trends in Waste Generation, Population and Economic Growth
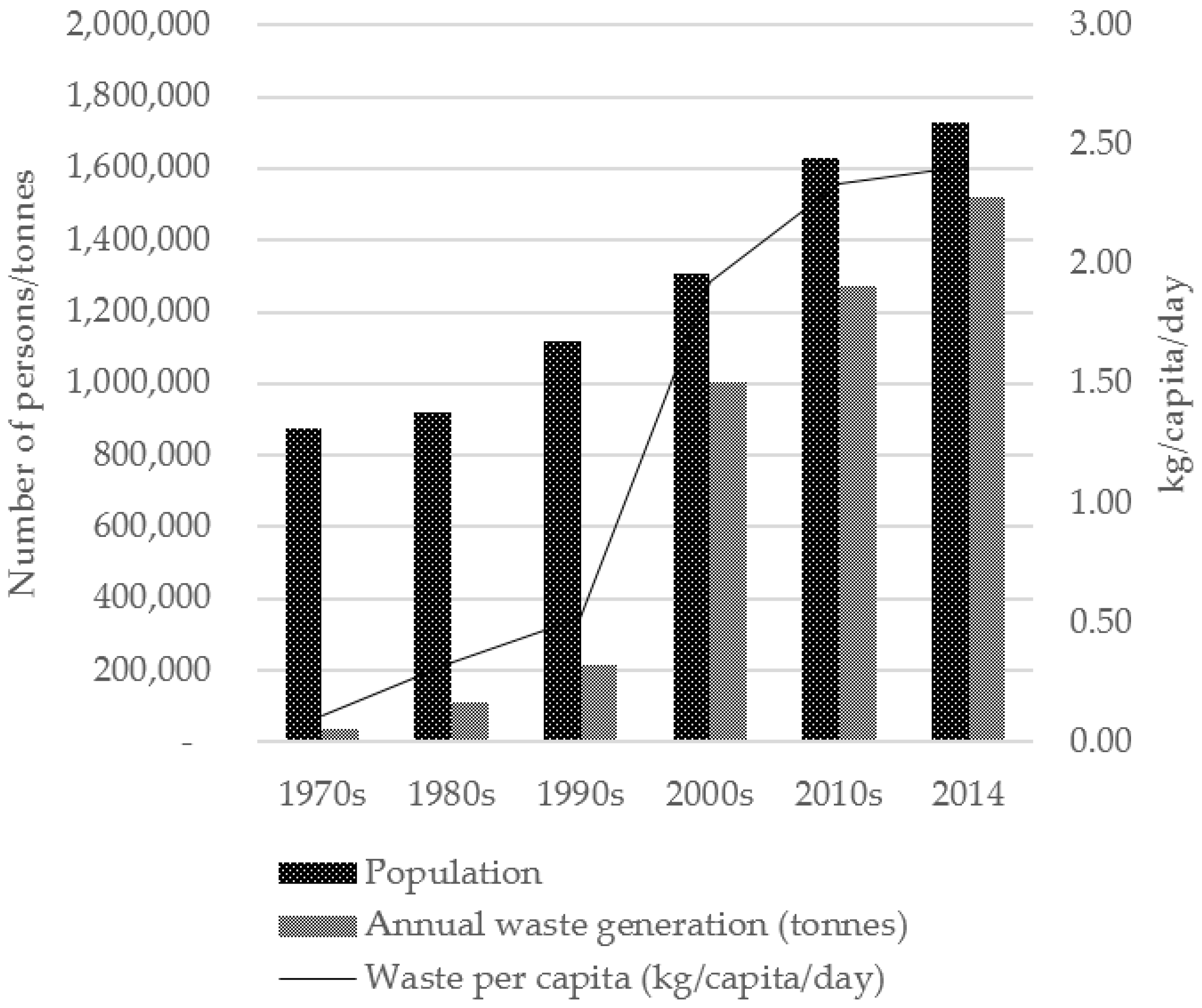
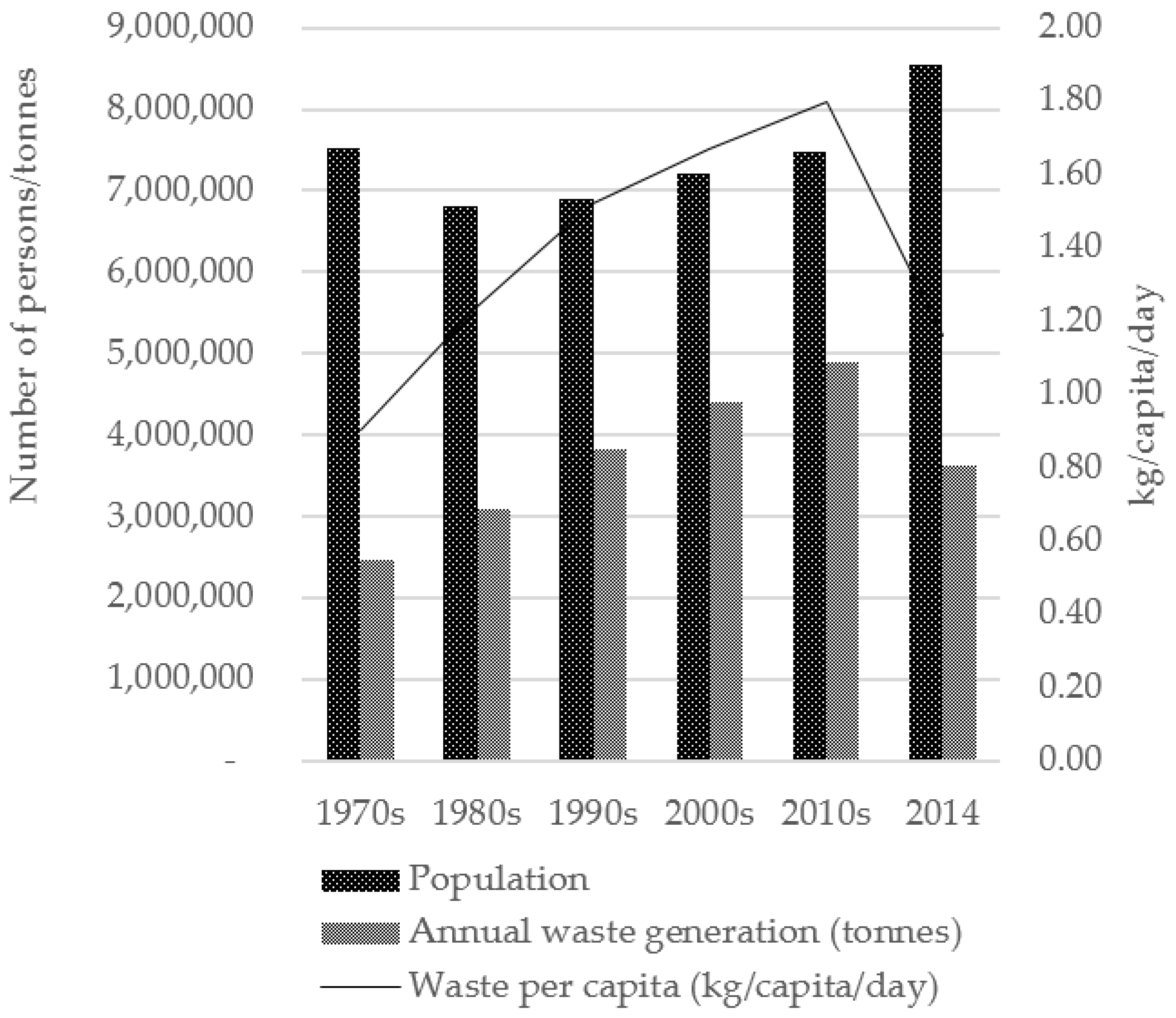
Generally, waste generation and its management have a direct association with socio-economic development and human health [12,49], degree of urbanization, standard of living, and a nation’s prosperity [50,51]. The Malaysian economy has undergone a transformation over the last four decades, driven by the increased trade, higher domestic demand and financial integration. The economic activities during the 1970s, under the New Economic Policy (NEP), led to a continued increase in waste generation through the 1980s. Hence, it is conceivable that much of the growth in waste arisings can be attributed to GDP growth and population concentration in urban areas. Kuala Lumpur’s population has doubled from 1970 to 2014. There is an indicative increase of 24% in population growth from 2000s to 2010s alongside high economic growth with a 163% increase in GDP within the same period. However, waste generation increased faster than population growth in the city, with a notable increase in the 1990s–2000s, which marked a period when extensive data collection on waste was properly recorded by the government. The increase in waste generation as recorded from the 1990s to 2000s was mainly due to the initiatives taken by the Ministry of Local Government, the authority responsible for establishing a reliable waste database at the national level; this period also saw the implementation of interim contracts for solid waste management that were initially awarded to private companies in 1998. With the implementation of the interim contract, data collection was more systematic and centralized, more accurately reflecting current waste generation, specifically for Kuala Lumpur. Under these circumstances, the earliest regulations imposed included the Street Drainage and Building Act 1974, Town and Country Planning Act 1976 and Environmental Quality Act 1974, with specific clauses on waste management within the acts [52]. Per capita waste generation in Kuala Lumpur increased from 0.11 kg in 1970 to 2.41 kg in 2014, a 20-fold increase in 44 years. The average household size in urban areas decreased over the study period with 6.1 persons in 1970 and 4.3 persons in 2010 [53]. Alongside the household size decrease, per capita waste generation tended to increase, mainly driven by household-level waste such as mail and newspapers, which are not affected by a reduction in the size of the household [54]. Organic matter contributed the highest percentage of material in household waste composition [55]. Kuala Lumpur’s population is expected to reach 4.2 million with average daily waste generation of 9207 tonnes in 2023 [27,55]. The trends of population growth and waste generation for Kuala Lumpur and London are as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.

Figure 1.
Trends in population, waste generation and per capita waste in Kuala Lumpur. (Data sources shown in Table 1).
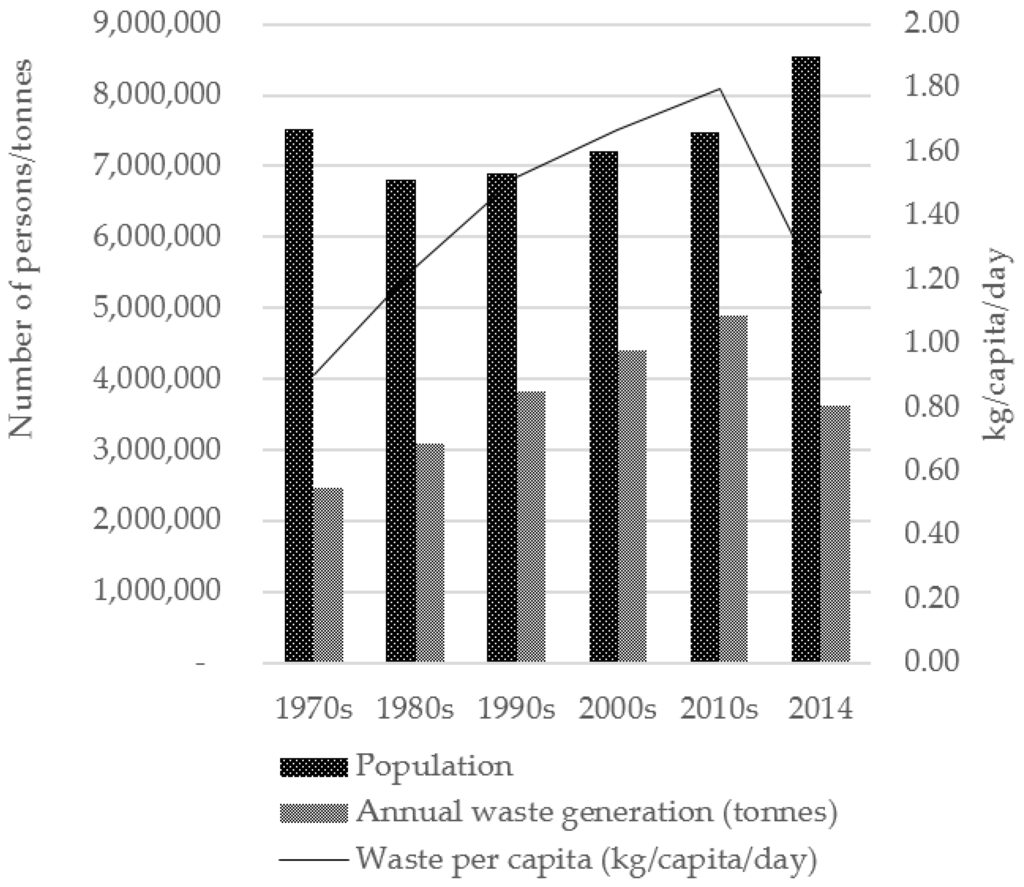
Figure 2.
Trends in population, waste generation and per capita waste in London. (Data sources shown in Table 1).
Towards the new millennium, UK waste management was mainly influenced by the EU Landfill Directive of 1999 which aimed to mitigate impacts on human health and the environment caused by landfilling of waste [34]. This resulted in a significant increase (133%) in landfill tax, from £24 per tonne in 2007 to £56 per tonne in 2011 [56]. Efforts in waste minimization and reduction are reflected in the reduction of waste generated and an increase in the recycling rate from 6% to 45% from the 1970s to 2014. Alongside the 25% reduction in waste generation from 2010 to 2014, the UK’s recycling rate increased steadily from 17.8% in the early 2000s to 44.9% in 2014. However, the reduction in waste arisings was also partially caused by the economic crisis and downturn around late 2007–2012 [57] which saw a fall in consumer spending and a decline in production of consumer goods [56]. In London, population decline was reported in the 1970s–1980s as a result of the city’s redevelopment in which housing estates were rebuilt as commercial centres, thus forcing city centre residents to move outwards [58]. London’s decline in population reversed slowly in early 2000. However, as residential numbers in outer London increased, more daily commuters travelled to the city centre for business and work. The increase in the number of daily commuters in addition to tourists has no doubt contributed to increased waste generation within central areas of the city.
3.3. Waste Collection, Treatment and Disposal Methods
Since there is no reported evidence of a formal waste management system before independence from the UK in 1957, waste disposal methods in Malaysia were probably by burning, burying or disposal into water bodies. Not until the late 1970s was collection, treatment and disposal of waste in Kuala Lumpur under the authority of the Kuala Lumpur City Hall (KLCH). Gradually, the upgrading of facilities for waste treatment and disposal in Kuala Lumpur city was completed in line with the increase in waste generation and concern for the adverse environmental impacts of poor waste management on public health [2]. With the mixture of dwelling types, waste collection was aligned to suit disposal behaviour in terms of the type of container used and the source of waste generated. Operational costs for waste management subsequently increased and became the most challenging issue for the authority. Although there were no direct payments collected from households for waste collection and disposal, the cost has been included in the local tax contribution. KLCH allocated 66% of the council tax revenue for waste management services paid to the interim contractors and for tipping fees, which was not sufficient for investment in high technology facilities. Taman Beringin Landfill, which commenced operation in 1991, was the only waste disposal site for domestic and commercial waste located within the city. Due to the quantities of waste generated as the city grew rapidly in the late 1990s, the expected lifespan of the landfill was reduced and it was closed in 2005. Taman Beringin Transfer Station was developed in 2002 as an integrated solution for waste disposal and land scarcity in Kuala Lumpur.
Incineration is the preferred disposal method for Malaysia but the high capital investment costs are not affordable for most Malaysian cities. A few small-scale incinerators were built on a trial basis, mostly adopting technology from Europe with customised design to suit local waste characteristics, especially for high moisture content waste. All reportedly failed, mainly due to flawed design or inadequate capacity that caused high operation and maintenance costs [59,60]. The government has proposed a large-scale incineration plant in Kuala Lumpur to reduce dependency on landfill, however, the plan was strongly rejected by the public in view of the potential harm to the environment and human health [59]. The government’s intention to build an incinerator arguably provides an indication of the unsuccessful implementation of previous waste minimisation and recycling efforts.
In London, early garbage removal trucks were simply open-bodied dump trucks pulled by a team of horses. They became motorized in the early part of the 20th century and the first closed-body trucks (to eliminate odours) with a dumping lever mechanism were introduced in the 1920s in Britain. Transport and collection costs are the most significant elements to be considered in the financial matters of waste management. Waste treatment facilities were first operated in London in 1874 with novel “waste destructors” in which waste was burned. Almost a hundred years later, in 1971, the London Ecopark incinerator was launched to handle more than a quarter of London’s waste while generating electricity. However, waste problems in the city continue to escalate, and new innovations initiated such as the vacuum system using underground pipes that became operational in Wembley City in December 2008. In this system, sorted recyclables and waste were automatically transported through enclosed vacuum pipes to central collection points and stored for collection [61]. The breakthrough of innovative systems may lead to improvement of conventional waste collection system towards more sustainable waste management system in megacities like London.
3.4. Waste Composition
In Kuala Lumpur, waste composition has changed little over the studied period. Like some other developing countries, organic waste is the major component (45%–60%) of the total waste generated (see Table 3). Paper, plastic, metal and glass are the common recyclables found in the waste stream. Early waste management in Malaysia generally involved dealing with relatively homogenous organic waste and major components of recyclable items [29]. The change in the composition indicates the change of lifestyle and consumer patterns during the period. The changes also were also contributed to by the enforcement of the Solid Waste Management Act (2007) whereby initiatives towards improving waste management systems and practices were implemented that reflected an increase in the recycling rate.

Table 3.
Waste composition (%) for London and Kuala Lumpur (1970–2014). (Data sources shown in Table 1).
Realizing the potential to generate energy from organic waste, the Malaysian Government introduced organic waste separation at source in 2005 with the intention to develop high technology facilities in the future, including thermal treatment and anaerobic digestion. Residents’ actions were not, however, aligned with the Government’s initiatives, as the facilities developed did not complement the awareness campaign, thus leading to a continued increase in organic matter in the waste stream. Limited knowledge of plastic recycling and a lack of suitable recycling facilities for plastics resulted in a significant increase in the non-recovered plastic fraction in the waste stream. In addition, due to its durability, cheapness and convenience, plastics are primary materials for packaging that are easily discarded after single use.
One of the local activities that contribute to the high volume of single use plastic is the presence of night markets. In Kuala Lumpur, night markets are popular due to the variety of stalls and abundance of daily essentials for sale. They consist of stalls selling a range of goods and foods that are “ready-to-eat” or prepared-on-demand food, which is to be eaten on-site, or takeaways and mainly use single-use plastics for packaging.
Coal was the main source of heat and energy in the 18th century to late 20th century in most parts of the UK. Coal ash from households formed the major portion of waste composition in London and, after collection, it was sent to the dust-yards to be reused as a soil conditioner [48]. High levels of coal burning during cold weather and coal-fired power station operations in London during the 1950s led to the Great Smog of 1952 [62]. The general trends of United Kingdom waste from the 1930s to the 1980s highlights the appearance of plastic in waste in the 1960s as well as a reduction in ash in the early 1970s as a result of a smoke control policy [63]. Materials such as plastics and paper subsequently started to dominate waste composition, mainly driven by the packaging of goods and food. Waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) appeared in the waste stream in the new millennium due to the rapid emergence of technology, its increasingly affordable price and limited lifespan, exacerbated by the short-term obsolescence of many electrical and electronic consumer goods. The United Kingdom disposed of almost 1 million tonnes of WEEE in 2003 with 70% comprising large household appliances [64]. The proportion of organic waste increased steadily from 19% in the 1960s to 32% in 2010. Biodegradable waste has been recently diverted from landfill due to concern about methane gas released to the atmosphere and its contribution to climate change. Therefore, resource recovery from the waste stream became a preferred option and there is a move towards supporting the circular economy framework in the future.
3.5. Waste Minimisation Strategy and Recycling Policies
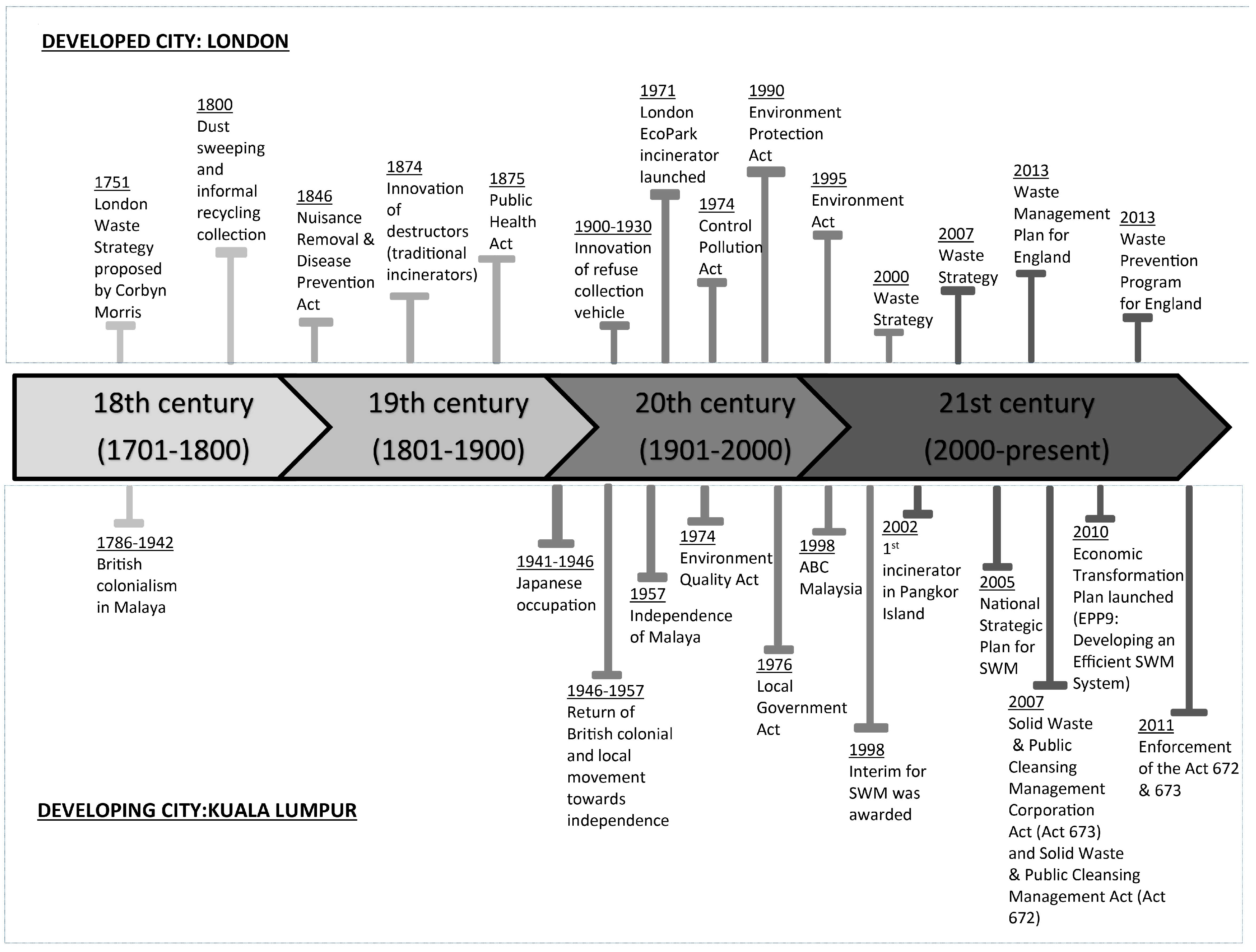
A timeline illustrating the evolution of waste management systems in both cities (Figure 3) reveals the gradual implementation of waste management initiatives, the challenges faced and the attempted solutions. This analysis in turn indicates how waste management systems have evolved towards fulfilling public needs alongside sometimes rapid economic development and population expansion. In Malaysia, waste management became a responsibility of federal authorities when the Environmental Quality Act (EQA) was formulated in 1974, which later migrated to the Local Government Act in 1976. The implementation of waste management in Kuala Lumpur was initiated with the Action Plan for Beautiful and Clean (ABC) Malaysia in 1998, which focused on recycling and strengthening local authority roles in waste management. Recycling and waste minimisation were seen as mechanisms to deal with escalating waste generation. A national recycling campaign commenced in 1993 but it failed to achieve the target recycling rate due to low participation by the public and inadequate provision of recycling facilities [27]. The National Strategic Plan for Solid Waste Management was established in 2005 with inspiration from the ABC Plan in 1998 in which the government continues to promote waste minimisation and recycling as the preferred solutions for waste management.
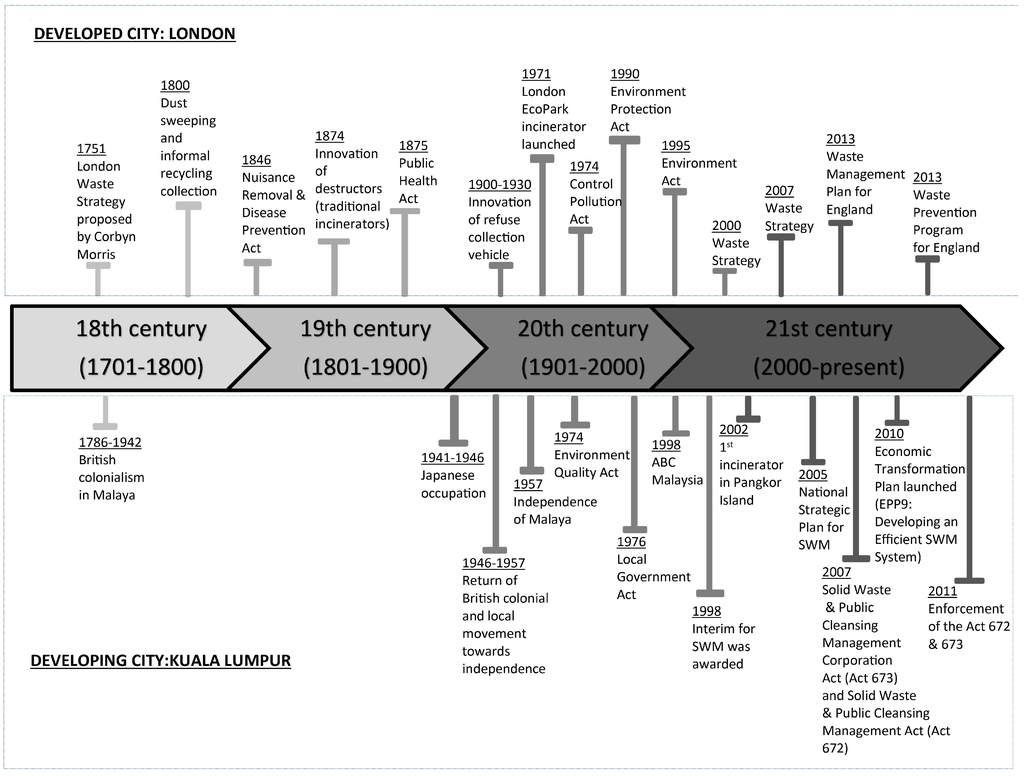
Figure 3.
The evolution of waste management policies for London and Kuala Lumpur.
More recycling facilities and centres were developed around the city that offer cash incentives in exchange for recyclables, which created a “spoon-feed” recycling habit among the public and depended on each household’s willingness to bring items to the nearest recycling centre [65]. Recycling has thus become attractive to the public for personal economic gain rather than for environmental reasons. This situation has indicated a false start to sustainable recycling practice in the city, where it is anticipated that the biggest challenge to implement separation at source is to shift from the incentive-driven recycling to voluntary practice.
In Kuala Lumpur, a significant contribution to recycling is made by the informal sector via recovery of usable materials from waste stream whilst in London, recycling systems are more uniform and administered formally by the municipalities. Informal systems—often involving scavengers or informal waste collectors—can be more efficient and dynamic in developing cities and some successful transitions from the informal to the formal sector have occurred [66]. During the 1980s and 1990s, scavengers were mainly local people from lower income levels in society and their activities focused on recovering materials from landfills. Also, municipal waste collection crews carried out collection of recyclables from households, a practice often known as “tailgate recycling” that is not allowed by law, but, sales of recyclables provide extra income to the crew [28].
Scavenging by municipal crews, however, reduced the efficiency of waste collection thus increasing the operational cost to the municipal authority. Scavenging also led to the loss of control of tracking recycling activities and data collection as the informal recycling industries grew more rapidly than expected. Consequently, although the recycling rate in Malaysia was almost certainly higher than officially reported, it is still unknown on an accurate basis.
In the 1990s, there was an ingress of foreign labour from neighbouring countries to address labour shortages in the manufacturing sector. Foreign labour then started to dominate waste collection activities, particularly via informal recycling activities. The informal recycling sector became aggressive due to poverty and a lack of regulation and a lack of guidelines for more sustainable recycling programmes. The informal recycling is generally considered to be more efficient than the formal sector due to skilful manual sorting by workers who manage to extract waste according to its value. Informal recycling businesses operate without licences and operate using unregulated work procedures with cheap labour, thus creating broad marginal profit on its activities [67].
Environmental and solid waste management (SWM) policies in Malaysia have evolved from simple informal policies to national level strategies and legislation [68]. This transition was from general waste policies in the Environmental Quality Act (1974) to the implementation of the Solid Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act (2007) in 2011 which demonstrated the government’s commitment towards achieving an effective and sustainable waste management system. Along with this transition, other strategies and plans have been implemented, some of which were influenced by other countries’ experiences, whilst others were designed in response to local scenarios. The evolution of waste management in Kuala Lumpur had improved residents’ social serenity, economic stability and environmental efficiency [69]. However, a series of failures in waste strategies occurred, mainly due to lack of awareness and participation from the public as well as the limited funds allocated for development of plans for waste management. In fact, due to political intervention and conflicts of interest between the federal and state governments in the late 2000s, the long-delayed Solid Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act was rejected by opposition states, pushing the ultimate goal towards achieving sustainable waste management even further from realisation.
The development of recycling systems in London can be seen as a long-term continuum from the early dust-yard operations until recycling operations were stimulated by EU directives towards the end of the 20th century. Consequently, the waste industry has changed from treating waste as a homogenous material for disposal to developing specialist systems for recovery of different components in the waste stream; the collection, sorting, dissembling and delivery of materials has had to be developed in such a way as to align with this change. The UK was relatively shifting its focus from waste to resource management, alongside other industrialised countries such as the United States of America, Canada, Germany, Austria and the Scandinavian countries, where average recycling rates of 30%–50% [14].
4. Discussion
4.1. Conceptual Models from Waste to Resource Management
As society has evolved and the global population has expanded, the consumption of natural resources has changed rapidly. Before the Industrial Revolution, there was a scarcity of resources and little waste was discarded without some form of recovery. The behaviour of such a society can be considered “wasteless” in that few materials were disposed and resource efficiency was high. Because populations were relatively poor, consumption was low, recovery of materials was high and little waste was produced. Zero-waste operations in the dust-yards of London in the 18th century are good examples of behaviour in a wasteless society. Along with modernization and urbanization, the lifestyle in London has become more challenging in terms of balancing economic stability with improvement to the quality of life. Strong economic stability and higher living standards have shaped society into a throw-away or “wasteful” society, wherein an abundance of resources has allowed the manufacture of easily-available and affordable products, and recovery of materials was deemed financially unattractive. Subsequently, large amounts of waste were generated that required disposal and this eventually placed significant burdens on the environment. This situation is regarded as unsustainable as the potential environmental degradation has increased as a consequence of over-consumption of natural resources and increases in waste generation. A stepwise shift up the waste hierarchy turns to recycling as the preferred option to recover secondary value from resources.
Moving towards the future, where depletion of natural resources is predicted, it is crucial to shift the present society’s waste behaviour, from being wasteful to “wasting less”. Anticipating increased future waste arisings, a society that wastes less will have access to resources from reuse/recycling/composting, though it is predicted that resource consumption will be higher due to increased demand for goods. Shifting from waste management to sustainable resource management clearly is the desired way to manage waste in the future in all countries.
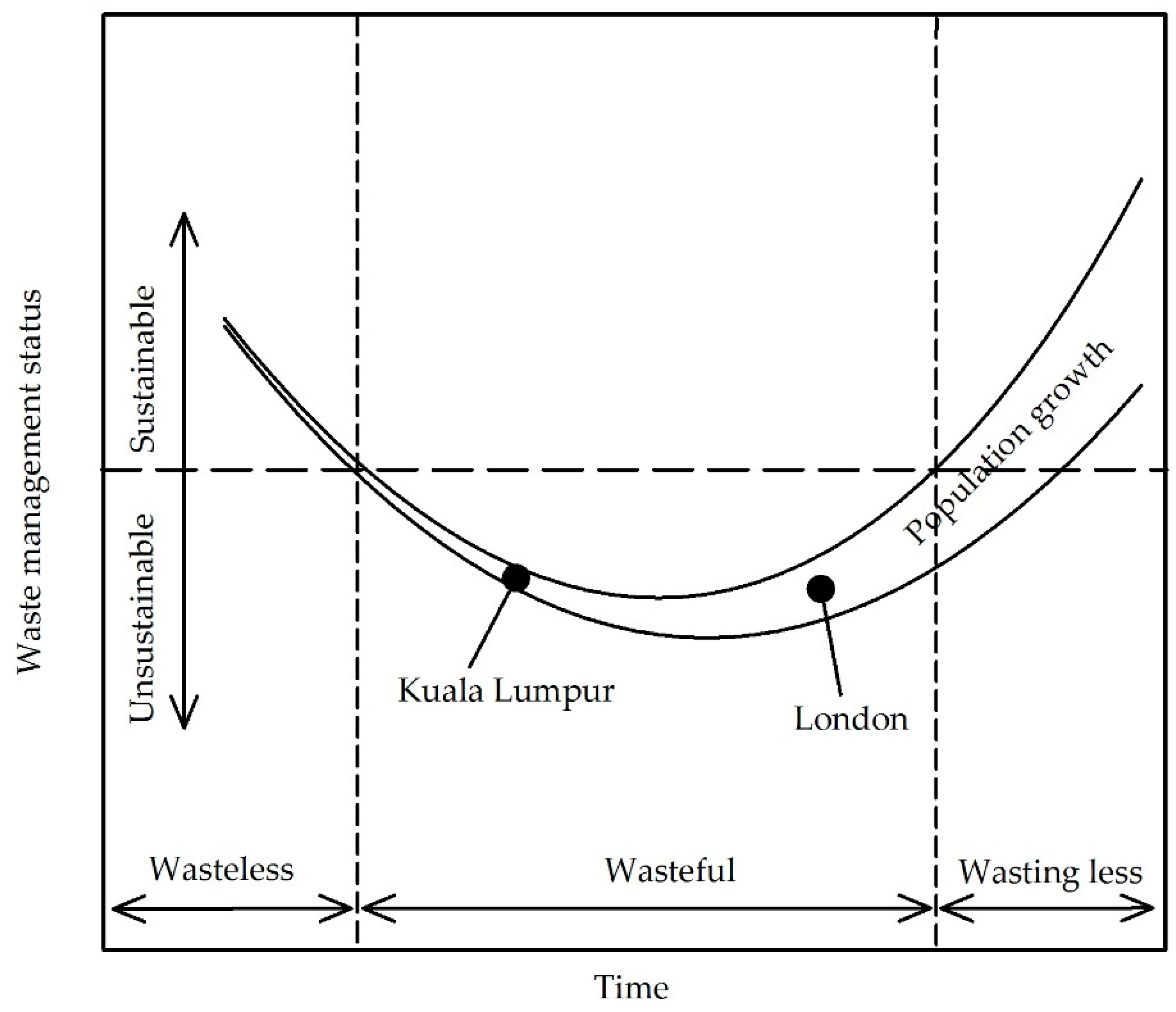
Sustainability in waste management can be defined as efficient resource consumption that reduces the amount of waste produced and contributes to sustainable economic development, environmental protection and social equity and harmony. On the basis of this study, we have created conceptual models to represent the evolution of waste management in developed and developing cities, representing by Kuala Lumpur and London (Figure 4). The lowest point of the curve in the figure indicates maximum resource utilization with low recovery rate. Upon reaching this point, at which the waste management practice is at its worst, initiatives to improve the system have to be implemented to avoid deleterious environmental consequences. London had experienced a slow societal behavioural shift and was considered to be a wasteful society for long period due to the incapability of the existing waste management system that was inherited from the earlier waste management system in the 18th century to serve the rapid population growth and massive amount of waste generated from economic activities. As the population is projected to be expanded in the future, it is crucial for London to shift the societal behaviour into wasting less to mitigating the adverse environmental impacts resulting from poor waste management systems. By comparison with London’s waste management status over time, Kuala Lumpur might maintain its waste management status if the current society’s waste behaviour continues in the future. Current societal waste behaviour in Kuala Lumpur can be considered as wasteful regardless of various initiatives for waste recovery and minimization implemented either by the government or the public. The absence of regional directives on waste management and a lack of enforcement of waste management policies are inevitably hindering progress towards achieving sustainable waste management. There is nonetheless concern about the marked increase in waste generation over the last decade in addition to the rapid increase of population in the city. We would expect London to have moved beyond being a wasteful society and to have started implementing initiatives towards becoming a society that wastes less as a result of EU Directives and national initiatives towards sustainable practice and behaviours relating to waste management. Undeniably, various factors have influenced initiatives striving for sustainable waste management systems, however, in each unique waste scenario, the interactions and strengths of the factors might be different. There is a need for further study on the interconnections of these factors in localised waste scenarios and these have to be elucidated in a local context in order to help planners design practical and workable local waste plans. Detailed analysis is recommended in terms of how local factors can contribute to accelerating the process of improving the waste management system.
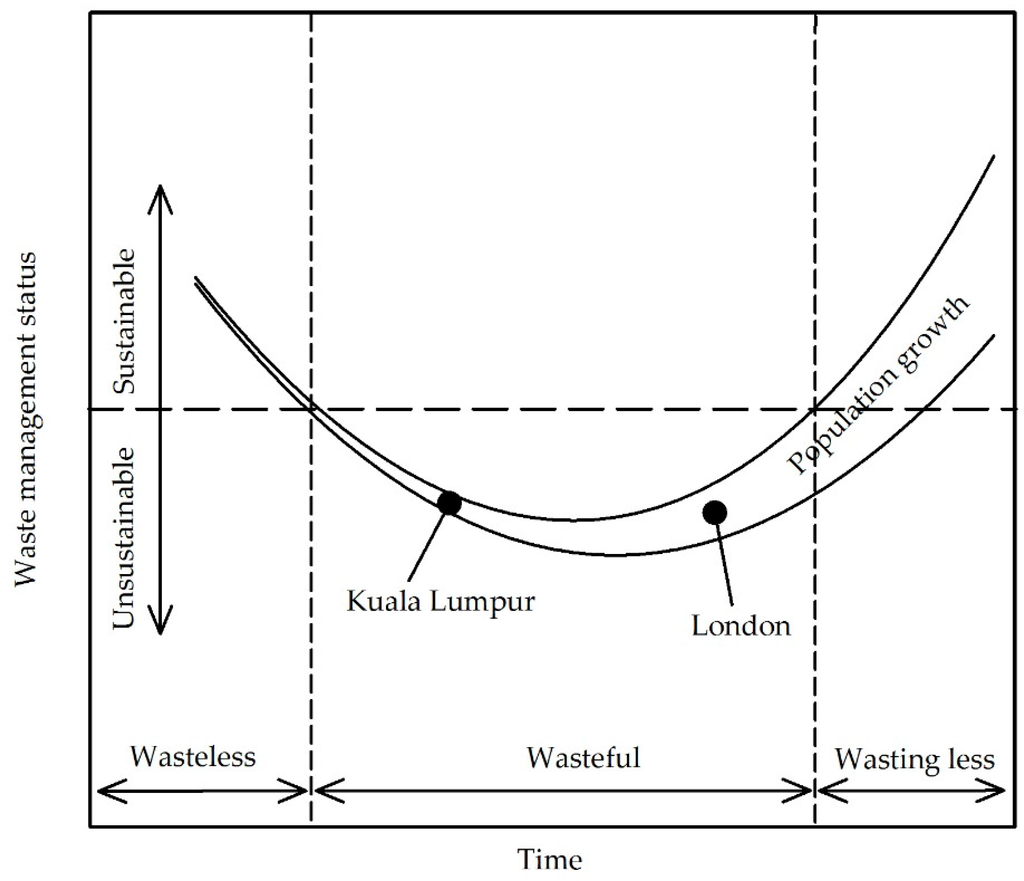
Figure 4.
A conceptual model representing the evolution of waste management in developed and developing cities. Population growth is represented by the increasing gap between the curved solid lines. The horizontal dashed line represents the threshold between sustainable and unsustainable waste management practice. Periods of waste management characterized by “wasteless”, “wasteful” and “wasting less” status are delineated by vertical dotted lines. The indicative current positions of Kuala Lumpur and London on the route from wasteless to wasting less status are shown.
4.2. Developing Cities Adopting Practices from Developed Cities
Developing cities’ waste regulations are often prototypes that emerge from past regulations for developed cities. However, such prototypes often do not necessarily work well or fit suitably with local scenarios. Prior to a decision to adopt such regulations, social, economic, environmental and local political factors need to be considered carefully. Straight adoption of technologies that work well in developed cities may not work effectively in developing cities for various reasons, including poor fit with local waste characteristics and quantities, infrastructure, collection and transport systems, temperature, climate, culture, household or business practices and the local economy. Even customisation of technologies to suit local conditions may not ensure the success of its operation. Developing cities such as Kuala Lumpur often cannot afford trials and research, in terms of finance and time, and hence adaptation of methods and systems from developed cities’ experiences and success can be seen as a “fast track” option to deal with waste generated from the city areas. As Kuala Lumpur is planning to build many incinerators as a solution for waste disposal, failures from previous small-scale incinerators across the country may shed some light on anticipated challenges in terms of operational costs, social rejection, environmental impacts and eventual likelihood of success—or failure.
4.3. Economic Influences on Waste Arisings
As economic prosperity increased, living standards in Kuala Lumpur were raised, increasing purchasing power and waste generation along. Kuala Lumpur has developed economically for the past 50 years with the amount of waste generated escalating much more rapidly than economic growth. It has been spending the majority of earmarked municipal funds on waste management and disposal and relatively little on development of facilities. Likewise, in London, when the benefits of formal and mature waste management outweigh the cost implications, the level of government spending on upgrading facilities and improving waste management system increases.
4.4. Colonial Influence
In general, there is some commonality between London and Kuala Lumpur in terms of application of laws and regulations as well as strategies and approaches to waste management. Although both cities’ waste management systems have historically been dominated by “end-of pipe” solutions (i.e., orientated around disposal), London is moving towards resource management via increased recovery and recycling. Waste management policy in London has been achieved via decades of development and transformation of factors that have influenced the kind of systems implemented today; EU directives have had a very strong recent influence in this regard. Legal, financial, operational, technical, social and, to some extent, political factors are the main determinants of successful implementation of waste strategies and systems in developed cities; these factors are less developed or more inconsistent in developing cities and hence sustainable waste management systems are still far from realisation in these locations. Although the British influence on Kuala Lumpur’s waste management system is not obvious, Kuala Lumpur has taken up experiences and practices of London’s waste management and matched them with local conditions for better implementation. In future, if Kuala Lumpur is developing towards London’s characteristics in terms of demographic patterns, London’s experiences in waste management may be able to help Kuala Lumpur’s authorities to plan for future waste management systems.
4.5. External Factors
In developing cities, local factors that support waste management systems could be identified with more detailed analysis and evaluation of how these factors interact in a local waste scenario. These are external forces that drive the city to enhance sustainable waste management initiatives to suit societal lifestyles, resource consumption and expanding economic activities. Factors such as weather and climate significantly impact waste degradation and methods of waste treatment. Without sufficient funding, it is crucial to conduct cost-benefit analyses as well as having the custom-fitted facilities to suit local conditions and needs. Waste management policies for both Kuala Lumpur and London have been integrated with other national environmental policies. However, these policies have derived from different components such as characteristics of the waste, degree of the environmental impacts, and disposal methods as well as tools for waste management activities. The enthusiasm of Kuala Lumpur’s authorities to develop waste systems into the most sophisticated and sustainable form at low financial cost has driven the authorities to study other cities’ successes and adapt them to suit local conditions.
5. Conclusions
A historical comparison and critical evaluation of trends and systems in a developing and developed city has enabled the identification of key milestones in waste management practices, policies and strategies. A developing nation should be able to observe the successes and failures of developed cities’ waste management initiatives and learn from them for its own purposes. The analysis has led to the development of conceptual models of waste management status—illustrating the possible transition of societies from “wasteless” to “wasteful” and, eventually, to “wasting less”—that may apply more broadly to cities similar to Kuala Lumpur and London. In addition, the impact of adopting practices and influences from economic, colonial and external factors have been evaluated and the dis/advantages discussed.
Future improvements may not require total system changes. In some cases, incremental enhancements of localised factors may be the most sensible mechanism to make a city’s system more effective and sustainable. However, comprehensive waste management policies with full implementation plans need to be properly formulated. These should be based on a clear understanding of local circumstances rather than by default via direct adoption from other cities’ experiences. The “big picture” for waste management needs to be addressed at national and global levels. Stakeholders need to ensure their functionality to support the system. The public is the biggest stakeholder; they need to understand the connections between their daily lifestyles, resource consumption and the quality of the environment that they live in presently and for the future. An appropriate waste management database is undeniably crucial to help planners for future projections. In developing cities where data are estimated, possible inaccuracies may lead to misinterpretation of the current scenario and could result in incorrect projections or inhibit the realisation of sustainable waste management. Careful historical analysis allied to good quality data, a detailed understanding of key technical and localised factors, and recognition of a city’s status on our conceptual model could assist the more rapid emergence of realistic, practically attainable and potentially sustainable waste management infrastructure, service provision and behaviour change systems in developed and developing countries.
Acknowledgments
This study forms a part of the first author’s PhD research, funded by the Majlis Amanah Rakyat (MARA), Malaysia.
Author Contributions
Erni M. Mukhtar has taken part in planning the study, conducting the data collection, analysing the results, and has been the principal writer of the manuscript. Ian D. Williams, Peter J. Shaw and Francis O. Ongondo have contributed to planning the study, evaluating the results and writing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Guerrero, L.A.; Maas, G.; Hogland, W. Solid waste management challenges for cities in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periathamby, A.; Hamid, F.S.; Khidzir, K. Evolution of solid waste management in Malaysia: Impacts and implications of the solid waste bill, 2007. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2009, 11, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffron, L.; Giusti, L.; Pheby, D. The human health impact of waste management practices: A review of the literature and an evaluation of the evidence. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2003, 14, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, A.D.; Griffiths, A.J.; Williams, K.P. An in-depth study of the effects of socio-economic conditions on household waste recycling practices. Waste Manag. Res. 2003, 21, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, F.; White, P.; Franke, M.; Hindle, P. Integrated Solid Waste Management: A Life Cycle Inventory, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Yabar, H. Historical evolution and development of waste management and recycling systems—Analysis of Japan’s experiences. J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2012, 2, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.C. Development drivers for waste management. Waste Manag. Res. 2007, 25, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, W.; Braungart, M.; Anastas, P.T.; Zimmerman, J.B. Applying the Principles of Green Engineering to Cradle-to-Cradle Design. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 434A–441A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badgie, D.; Abu Samah, M.A.; Abd Manaf, L.; Muda, A.B. Assessment of municipal solid waste composition in Malaysia: Management, practice, and challenges. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 539–547. [Google Scholar]
- Zurbrügg, C.; Schertenleib, R. Main Problems and Issues of Municipal Solid Waste Management in Developing Countries with Emphasis on Problems Related to Disposal by Landfill. In Third Swedish Landfill Research Symposia; Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) and Swiss Federal Institute for Environmental Science & Technology (EAWAG): Lulea, Sweden, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Asase, M.; Yanful, E.K.; Mensah, M.; Stanford, J.; Amponsah, S. Comparison of municipal solid waste management systems in Canada and Ghana: A case study of the cities of London, Ontario, and Kumasi, Ghana. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2779–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, G.E. A historical context of municipal solid waste management in the United States. Waste Manag. Res. 2004, 22, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.R.; Kopits, E.; Simpson, D. Policy monitor-the evolution of solid and hazardous waste regulation in the United States. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2008, 3, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.; Dolphin, G.; Ackerly, P. Re-Inventing Waste: Towards a London Waste Strategy; Ecologika: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Seik, F.T. Recycling of domestic waste: Early experiences in Singapore. Habitat Int. 1997, 21, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollikkathara, N.; Feng, H.; Stern, E. A purview of waste management evolution: Special emphasis on USA. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, M.; Liu, W.; Tao, X. Evolution and assessment on China’s urbanization 1960–2010: Under-urbanization or over-urbanization? Habitat Int. 2013, 38, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, L. Centenary History of Waste and Waste Managers in London and South. East. England; The Chartered Institutions of Wastes Management: Northampton, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shekdar, A.V. Sustainable solid waste management: An integrated approach for Asian countries. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongrácz, E.; Pohjola, V.J. Re-defining waste, the concept of ownership and the role of waste management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2004, 40, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, S.H. A crisis in governance: Urban solid waste management in Bangladesh. Habitat Int. 2010, 34, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan A Kadir, W.R. The Development of a Framework for Sustainable Waste Management Policy and Strategy for Malaysia. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Salford, Salford, UK, 26 September 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Environment Food and Affairs (DEFRA). Guidance on the Legal Definition of Waste and Its Application. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/69590/pb13813-waste-legal-def-guide.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2014).
- Malaysia Government. Laws of Malaysia Act. 672: Solid Waste and Public Cleansing Management Act, 2007; Percetakan Nasional Malaysia Berhad: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2007; pp. 1–3.
- The World Bank Group. Population Growth Rate. Available online: http://www.worldbank.org/depweb/english/modules/social/pgr/ (accessed on 16 June 2015).
- World Bank. World Development Indicators. Available online: http://databank.worldbank.org/data/views/reports/tableview.aspx (accessed on 24 April 2015).
- Periathamby, A. Solid Waste: Principles and Management, 1st ed.; Universiti Malaya Press: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.N.; Rahman, R.A.; Chong, T.L.; Zakaria, Z.; Awang, M. Waste recycling in Malaysia: Problems and prospects. Waste Manag. Res. 2000, 18, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periathamby, A. Municipal Solid Waste Management in Malaysia: Changes for Sustainability. In Municipal Solid Waste Management in Asia and the Pacific Islands; Indonesia Institute Technology Bandung Press: Bandung, Indonesia, 2014; pp. 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Yatim, S.R.; Arshad, M.A. Household solid waste characteristics and management in low cost apartment in Petaling Jaya, Selangor. Heal. Environ. J. 2010, 1, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, J.R. Refuse, Recycling and Recovery; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wasteonline. History of Waste and Recycling Information Sheet. Available online: http://wasteonline.brix.fatbeehive.com/resources/InformationSheets/HistoryofWaste.htm (accessed on 27 April 2015).
- OECD. OECD Environmental Performance Reviews: United Kingdom 2002; OECD Publications Service: Paris, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Timlett, R. Recycling in High and Medium Density Housing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 21 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Audit Commission. Local Authority Waste Management: Using Data from the Value for Money Profiles. Available online: http://www.audit-commission.gov.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/Waste-vfm-briefing-26-March-FINAL.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2015).
- WasteDataFlow. WasteDataFlow Waste Management. Available online: http://www.wastedataflow.org/reports/default.aspx (accessed on 10 May 2016).
- Greater London Authority. Rethinking Rubbish in London: The Mayor’s Municipal Waste Strategy in London; Greater London Authority: London, UK, 2003.
- Greater London Authority. London’s Wasted Resource. The Mayor's Municipal Waste Management Strategy; Greater London Authority: London, UK, 2011.
- Department of Environment Food and Affairs (DEFRA). Statistics on Waste Managed by Local Authorities in England in 2013–2014. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/375945/Statistics_Notice_Nov_2014_Final__3_.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2015).
- Greater London Authority. Local Authority Collected Waste Management, London. Available online: http://data.london.gov.uk/dataset/local-authority-collected-waste-management-london/resource/4d88d88c-31a7-468b-95e9-49fba78ad20e# (accessed on 10 May 2016).
- Poll, J.; Kahlon, M. Variations in the Composition of Household Collected Waste—A Report Produced for EB Nationwide (Shanks First Fund); AEA Technology and Waste Research Ltd.: Oxfordshire, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mayor of London. Emissions Performance Standard (EPS) Annual Performance Review 2013/14. Available online: https://www.london.gov.uk/what-we-do/environment/environment-publications/emissions-performance-standard-eps-annual (accessed on 11 May 2015).
- Tarmudi, Z.; Abdullah, M.L.; Tap, A.B.U.O. An overview of municipal solid wastes generation in Malaysia. J. Teknol. 2009, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigl, P.; Lebersorger, S.; Salhofer, S. Modelling municipal solid waste generation: A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hounsell, P. London’s Rubbish; Amberley Publishing: Gloucestershire, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Terazono, A.; Moriguchi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Inane, B.; Yang, J.; Siu, S.; Shekdar, A.V.; Lee, D.; Idris, A.B.; Magalang, A.A.; et al. Waste management and recycling in Asia. Int. Rev. Environ. Strateg. 2005, 5, 477–498. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, J. London Remade—Provocation #1: The Analogies from History. Available online: http://londonremade.com/londons-waste-management-system/ (accessed on 2 June 2016).
- Velis, C.A.; Wilson, D.C.; Cheeseman, C.R. 19th century london dust-yards: A case study in closed-loop resource efficiency. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melosi, M.V. Garbage in the Cities: Refuse, Reform and the Environment; University of Pittsburgh Press: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbonna, D.; Amangabara, G.; Ekere, T. Urban solid waste generation in Port Harcourt metropolis and its implications on waste management. Manag. Environ. Qual. An. Int. J. 2007, 18, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.; Babakina, O.; Pennock, A.; Shi, H.; Chi, Y.; Wang, T.; Graedel, T.E. Quantitative guidelines for urban sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauziah, S.H.; Periathamby, A. Policy and Strategies towards Sustainable Waste Management in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Solid Waste 2013—Innovation in Technology and Management, Hong Kong, China, 5–9 May 2013; pp. 63–66.
- Department of Statistics Malaysia. Population and housing census of Malaysia 2010: Preliminary Count Report. Available online: http://www.statistics.gov.my/portal/download_Population/files/BPD/Laporan_Kiraan_Permu laan2010.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2015).
- Burnley, S.J. A review of municipal solid waste composition in the United Kingdom. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, M.O.; Hassan, M.N.; Mujeebu, M.A. Development of municipal solid waste generation and recyclables components rate of Kuala Lumpur: Perspective study. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2209–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkalter, H. The Impact of the Economic Downturn on Productivity Growth. Available online: http://apse.org.uk/apse/index.cfm/members-area/briefings/2013/13-35-impact-of-economic-recession-on-waste-generationpdf/ (accessed on 5 April 2016).
- WRAP. Decoupling of Waste and Economic Indicators. Available online: http://www.wrap.org.uk/sites/files/wrap/Decoupling of Waste and Economic Indicators.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2016).
- White, J. London in the 20th Century; The Random House Group Ltd.: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jereme, I.A.; Siwar, C.; Bhuiyan, A.H. Incineration and its implications: The need for a sustainable waste management system in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 367–378. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.K.Z. Incinerator for Municipal Solid Waste in Kuala Lumpur. Available online: http://greenbluegroup.blogspot.co.uk/2012/04/incinerator-for-municipal-solid-waste.html (accessed on 18 May 2015).
- Ween, C. London, England: A Global and Sustainable Capital City. In Green Cities of Europe: Global Lesson on Green Urbanism; Beatley, T., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 181–214. [Google Scholar]
- Laskin, D. The great London smog. Weatherwise 2006, 59, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V.V. Refuse composition projections and recycling technology. Resour. Conserv. 1986, 12, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, I.; Wright, N.; Kellner, R.; Bains, N.; Geraghty, K.; Goosey, M.; Lightfoot, L. An integrated approach to electronic waste (WEEE) recycling. Circuit World 2007, 33, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, I.S.; Noor, Z.Z.; Yusuf, R.O. The profiles of household solid waste recyclers and non-recyclers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Habitat Int. 2014, 42, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, P.J.M.; Jaffe, R. Informal waste management. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2004, 6, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.C.; Velis, C.; Cheeseman, C. Role of informal sector recycling in waste management in developing countries. Habitat Int. 2006, 30, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, D.; Periathamby, A. Policy trends of strategic environmental assessment in Asia. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 41, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, M.A.; Wee, S.T. Municipal Solid Waste Management in Malaysia: An Insight towards Sustainability. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Human Habitat & Environment 2014, 31 May 2014; Volume 1957, pp. 192–206. Available online: http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2714755 (accessed on 1 July 2016).
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).