Abstract
Wood ash has been widely used as an additive for excreta from dry compost toilets to sanitize it for reuse. However, there is dearth of quantitative information about its efficiency in sanitizing partially digested sludge from wet onsite sanitation systems. This paper presents findings of a series of two experimental studies to assess optimum wood ash dosages required to raise the pH of partially digested fecal sludge to sanitizing levels (pH > 11) in a tropical climate. The study monitored the variation of pH of the sludge containing between 0 (control) and 180 g of ash per litre of sludge. Average initial pH and total solids of the sludge were 7.79 and 72 g/L respectively. Generally, the magnitude and rapidity of pH spike was correlated with the ash dosage (r = 0.988) and was statistically significant (p = 0.0015; Fcrit = 2.3157) among all dosages. Drastic increase in pH (from 7.81 to 11.60 ± 0.07) was recorded in the first 24 h for ash dosages between 140 g/L and 180 g/L, whereas dosages below 140 g/L had pH values less than 10. The difference in variation of pH between the first 24 h and the successive 24 h was statistically significant (P(T ≤ t)two-tail = 0.00; tcrit = 2.09). On the average, 97% of the overall pH increment within a 48-h monitoring period occurred in the first 24 h for the 140–180 g/L ash dosages. The optimum ash dosages are 7–15 times higher than reported lime dosages but ash provides a cheaper alternative than lime for recycling plant nutrients. Further studies on pathogen inactivation efficiency are ongoing.
1. Introduction
The use of human excreta to support plant growth has been a long tradition in many parts of the world in a bid to close the nutrient loop [1,2,3]. Interest in this practice is growing all over the world and fecal sludge treatment technologies which produce reusable compost material from human excreta are therefore being promoted following the principles of environmental sustainability [4,5,6]. These technologies are among others, expected to remove completely or reduce to the barest minimum the wide range and numerous microbial pathogens present in human excreta to pre-empt the potential health and environmental effects [7]. The World Health Organization recommends a pathogen reduction of 8–9 log units in excreta before being used as a soil conditioner for agricultural purposes [8]. Available literature [9,10,11,12] indicate that pathogen destruction in human excreta can be achieved by a host of technologies including ammonia treatment, irradiation, dewatering, mesophilic or thermophilic anaerobic digestion, membrane filtration and a combination of these methods. The efficiency of pathogen removal for these technologies has been well documented [12,13,14,15,16,17].
Another sanitization method; alkaline treatment, which involves the addition of an alkaline material such as lime or ash has been demonstrated in several empirical studies to be effective in inactivation of pathogens in human excreta. The alkaline material increases the pH to sanitizing levels (generally above 11) where pathogens are destroyed [11]. Likewise, temperature, moisture content and UV light have also been linked to pathogen reduction in excreta [8,18]. In an experimental study to determine the effectiveness of lime on fecal sludge pH variation, it was shown that, the addition of 4% and 6%–10% of quicklime (CaO) to fecal sludge can maintain the pH of the resulting mixture above 12 for 20–60 days and three months, respectively [19]. Apart from increasing the pH to sanitizing levels, the addition of quicklime increases the temperature to 70 °C which causes pathogen destruction [19]. Similar findings are also reported by Kazama and Otaki [20] who demonstrated that, using CaO as an additive can increase pH to levels lethal to bacteria and viruses. Another related study in Iran, which assessed the microbial quality of sewage sludge with varying amounts of lime, also revealed that the addition of 12.3 g of lime to 1 L of sludge with an initial pH of 6.6 increased the pH to 12.5 and maintained it for five days [21]. Conversely, a 9.8 g/L dosage raised the pH of the sludge to 11.4 within 2 h but reduced to 9.3 after five days. Boost and Poon [22] also investigated the combined effect of pulverized fuel ash (PFA) and CaO on faecal sludge. They demonstrated that a mixture of 60% sludge (600 g/kg): 40% CaO/PFA (44.44 g/kg/355.56 g/kg) can maintain the pH of sludge above 11 for at least 7 days and limit bacterial growth as well.
Wood ash has also been reported in research studies in China, Vietnam, South Africa, El Savador, Guatemala, and other countries to be effective in raising the pH of feces to sanitizing levels resulting in the inactivation of pathogens [8,23,24]. All these studies were however limited to raw excreta from dry onsite sanitation systems (Urine Diverting Dry Toilet) and failed to investigate the rate of pH change with time upon addition of varying quantities of wood ash. Information on the optimum quantity of ash required to increase the pH of fecal sludge from wet onsite sanitation systems to sanitizing levels therefore remains unknown although that of lime has been severally reported in literature. In most urban communities in Ghana where wet sanitation systems are common, as in other Sub-Saharan countries, the fecal sludge from these systems is mainly disposed of untreated into nearby storm drains or water courses raising public health concerns [25,26,27]. Only few treatment systems exist countrywide and are mainly detention ponds, which discharge their effluents into adjoining waterbodies although the sludge can be sanitized and reused for agricultural purposes [28].
We report findings of an experimental study in which fecal sludge from a wet onsite sanitation system in an urban community in Ghana was dosed with varying amounts of wood ash (a waste material requiring disposal) to determine the optimum dosage required to increase the pH to sanitizing levels reported in literature (pH > 11). The rate of change of pH with time was also monitored to determine the rapidity with which the sanitizing level can be reached. This study is intended to contribute to efforts aimed at developing simple technologies or retrofitting existing ones to generate reusable compost from the huge tons of fecal sludge produced daily in urban communities in Ghana. The process is being investigated further to determine die-off rate of pathogens in fecal sludge upon addition of varying quantities of wood ash.
2. Experimental Section
A sample of raw fecal sludge from a septic tank was taken from the Dompoase Landfill and Wastewater Treatment Site in the Kumasi Metropolis and transferred to the Environmental Quality Engineering Laboratory, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana. The average pH and total solids of the sludge were determined at the laboratory. pH was determined using a pH meter by inserting its probe into the mixture and recording the final stable pH value whilst total solids was measured according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, Section 2540 B [29].
Five out of 6 plastic containers each containing 3 L of the fecal sludge samples were dosed with varying amounts of wood ash and mixed thoroughly. One of the plastic containers was used as a control, and therefore no ash was added to it. All the containers were left under a shed without covering them since covering with a lid could cause accumulation of heat, which will affect pH. The quantity of ash added to the five plastic containers represented 1%, 5%, 10% and 15% and 20% of the total solids volume respectively. The pH of these samples were recorded daily for 16 days, after stirring them thoroughly each time. This was done to ensure uniform dispersion of ash in the fecal sludge. Single factor ANOVA was conducted to determine the statistical significance of the association between pH of fecal sludge and the dosage of wood ash in the fecal sludge. This initial study was conducted in the month of April where average daily temperatures are known to be between a minimum of 22.3 °C and a maximum of 32.5 °C.
The results of the initial set-up informed the design of a second phase of the study in which the wood ash proportions were increased. This was conducted in the month of May which has average daily temperatures of 22.7 °C and 31.9 °C. This time, the dosage was dependent on the volume of sludge sample used instead of the total solids. Therefore, 20 out of 21 plastic containers, containing 1 L of fecal sludge each was dosed with relatively higher quantities of wood ash than before (ranging between 1 g/L to 180 g/L) in a bid to determine the optimum dosage that would contribute to the most rapid pH increase to 11 or above. The remaining plastic container with 1 L of fecal sludge served as the control and therefore no ash was added. Again, all the containers were left under a shed without covering them. The pH of the sludge in all the containers were measured following thorough stirring in 24 h intervals to determine the rate of change of pH with time in each of the containers. Monitoring of pH was conducted on a 24-h basis for two consecutive times to determine the rate of change of pH with time based on the varying quantities of wood ash. T-test was conducted at 5% significance level to determine the statistical significance of the pH change with time for fecal sludge with dosages between 140 and 180 g/L.
3. Results and Discussion
The faecal sludge used in this study had an initial pH of 7.79 and total solids of 72 g/L. Upon addition of varying amounts of ash, the pH increased sharply within the first 24 h. The pattern of pH variation was similar to the control which had no ash added to the fecal sludge although it had the least increments in pH and the highest reduction in pH (Figure 1a). The increase in pH in the first 24 h was generally higher for those with higher ash dosages, particularly for the 20% Ash/TS dosage. However, this subsequently reduced after 24 h but the reduction was also lower for the sample with the highest ash dosage. This pattern is in line with other similar studies where a drastic increase in pH was recorded in the first few hours but was followed by a reduction in pH [20]. The alkaline nature of ash (pH: 9–13.5) [30,31,32,33] caused the increase in pH within the first 24 h. However, this pH is not sufficient to kill off the pathogens present. Respiration of the microorganisms present in the sludge, according to Warts [34], produces carbon dioxide, which eventually increases carbonic acid concentration thereby causing the pH to plummet. Moreover, the reduction in pH can be attributed to ammonia volitalization because the containers were kept opened. Per available studies [35,36], desorption of ammonia from wastewater occurs at high pH when the wastewater comes into contact with large amounts of air and eventually results in a decrease in pH.
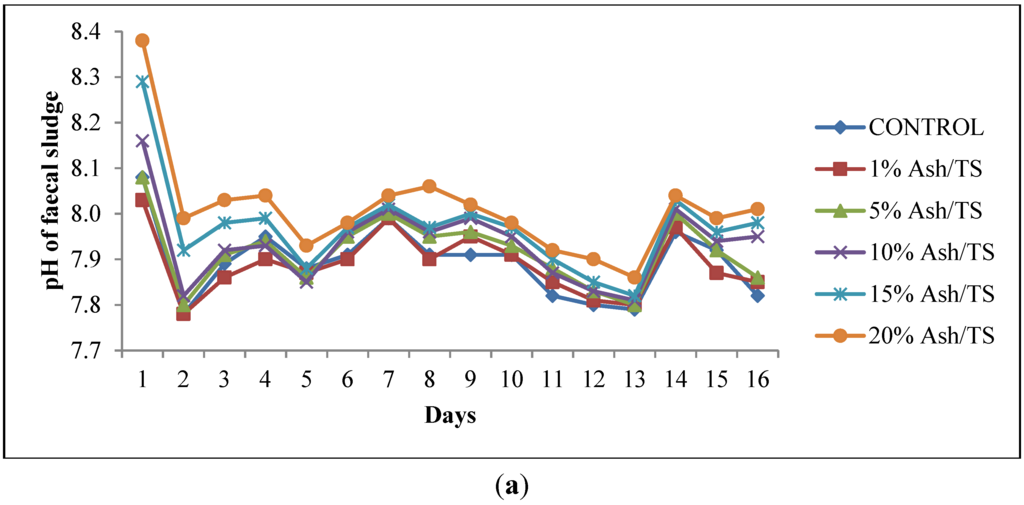
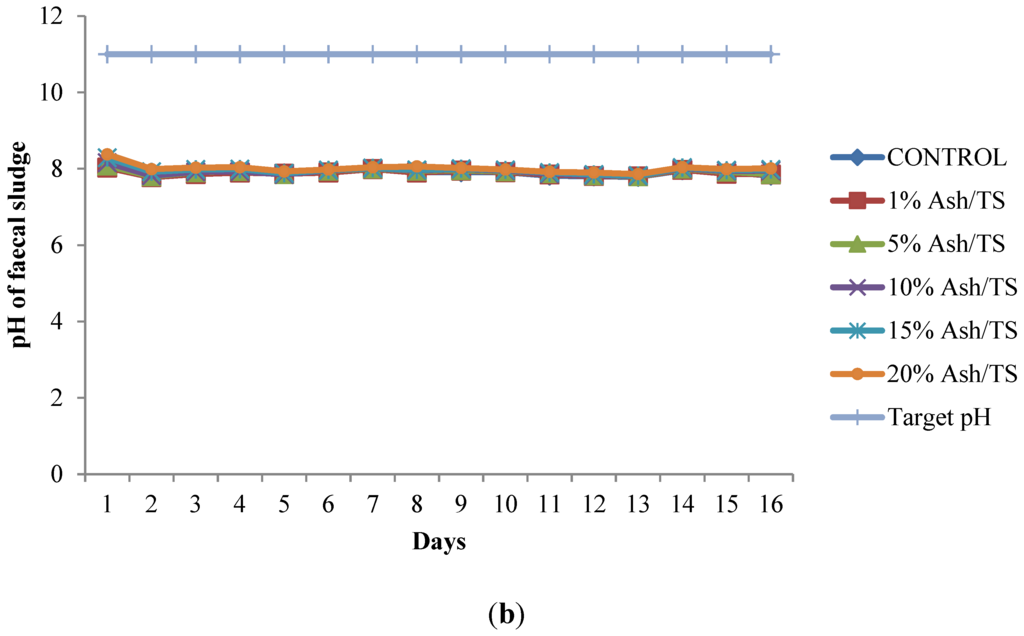
Figure 1.
(a) Behavior of pH of fecal sludge with different wood ash quantities; (b) Comparison of pH variation of fecal sludge with target pH.
Figure 1.
(a) Behavior of pH of fecal sludge with different wood ash quantities; (b) Comparison of pH variation of fecal sludge with target pH.
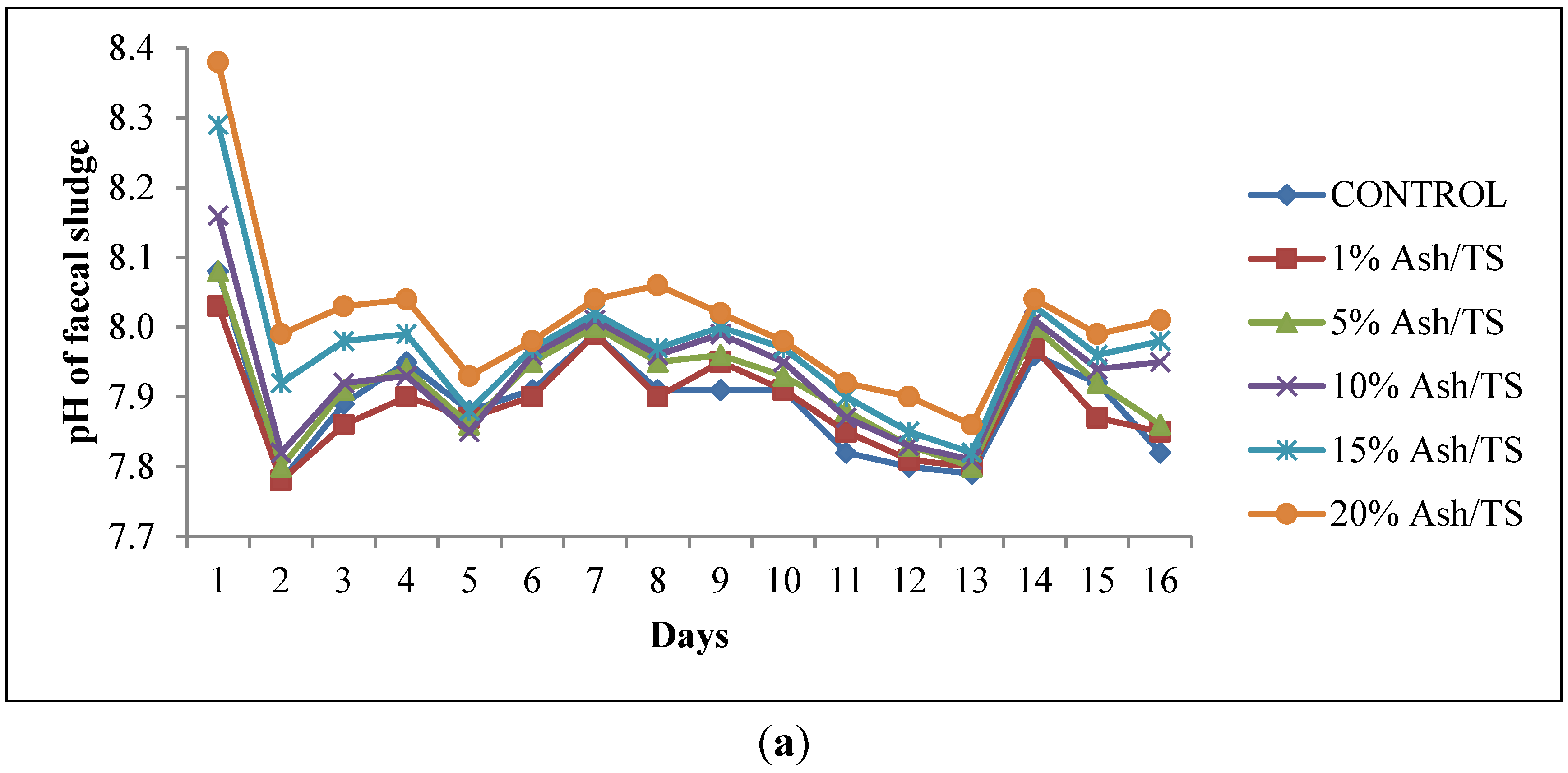
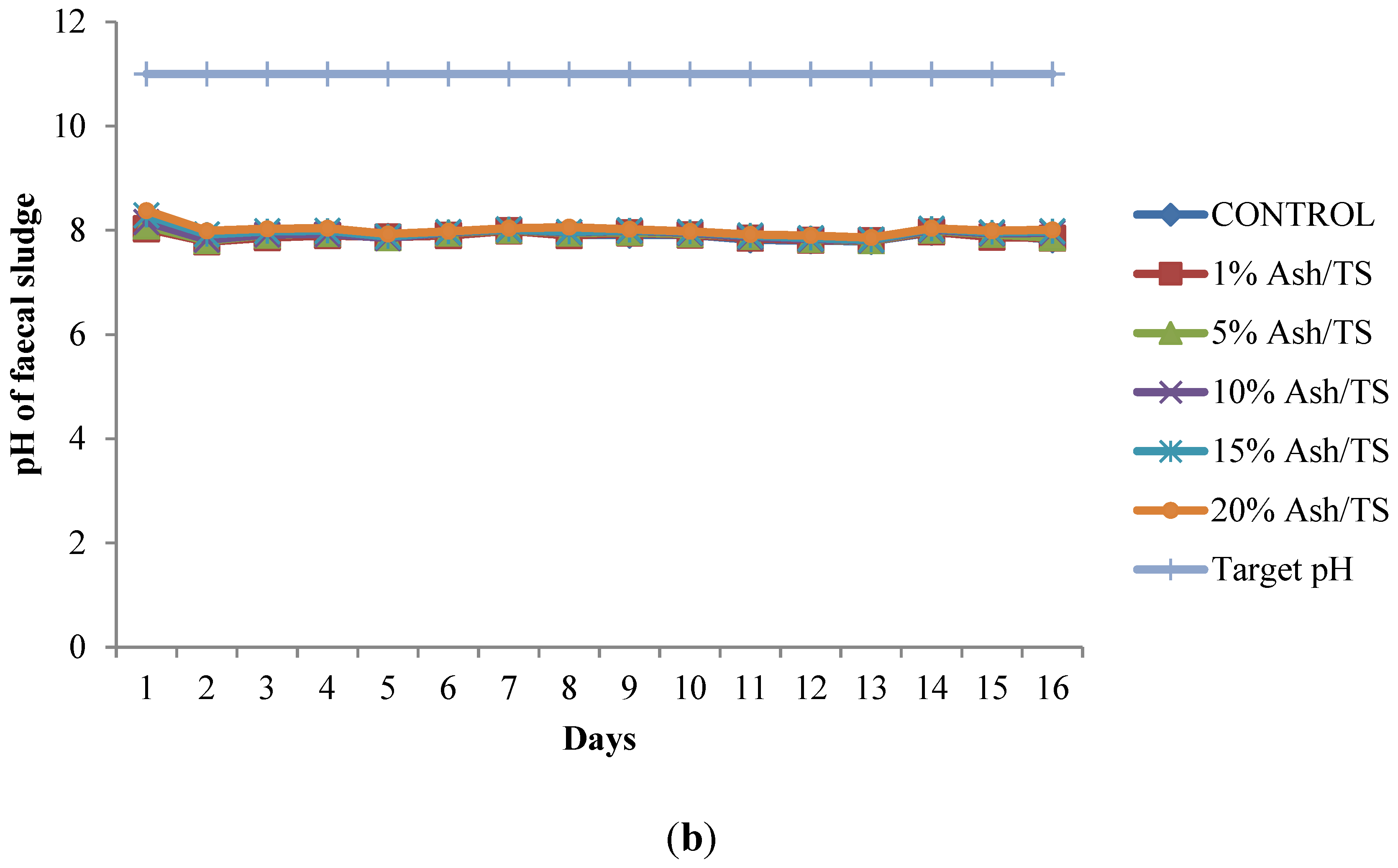
The pH of all the mixtures for the 16-day monitoring period ranged between a minimum of 7.8 and a maximum of 8.38 (Figure 1a). None of the mixtures reached the target pH of 11 or above, even after 16 days (Figure 1b). Raising the pH of fecal sludge above 11 is very crucial since at that level, pathogen survival rate, microbial reactions and time for inactivation of pathogens are significantly reduced [22,37,38]. Although the target pH was not reached, it can be observed from the pattern of variation that the mixture with the highest proportion of ash in the sludge consistently recorded the highest pH (Figure 1a).
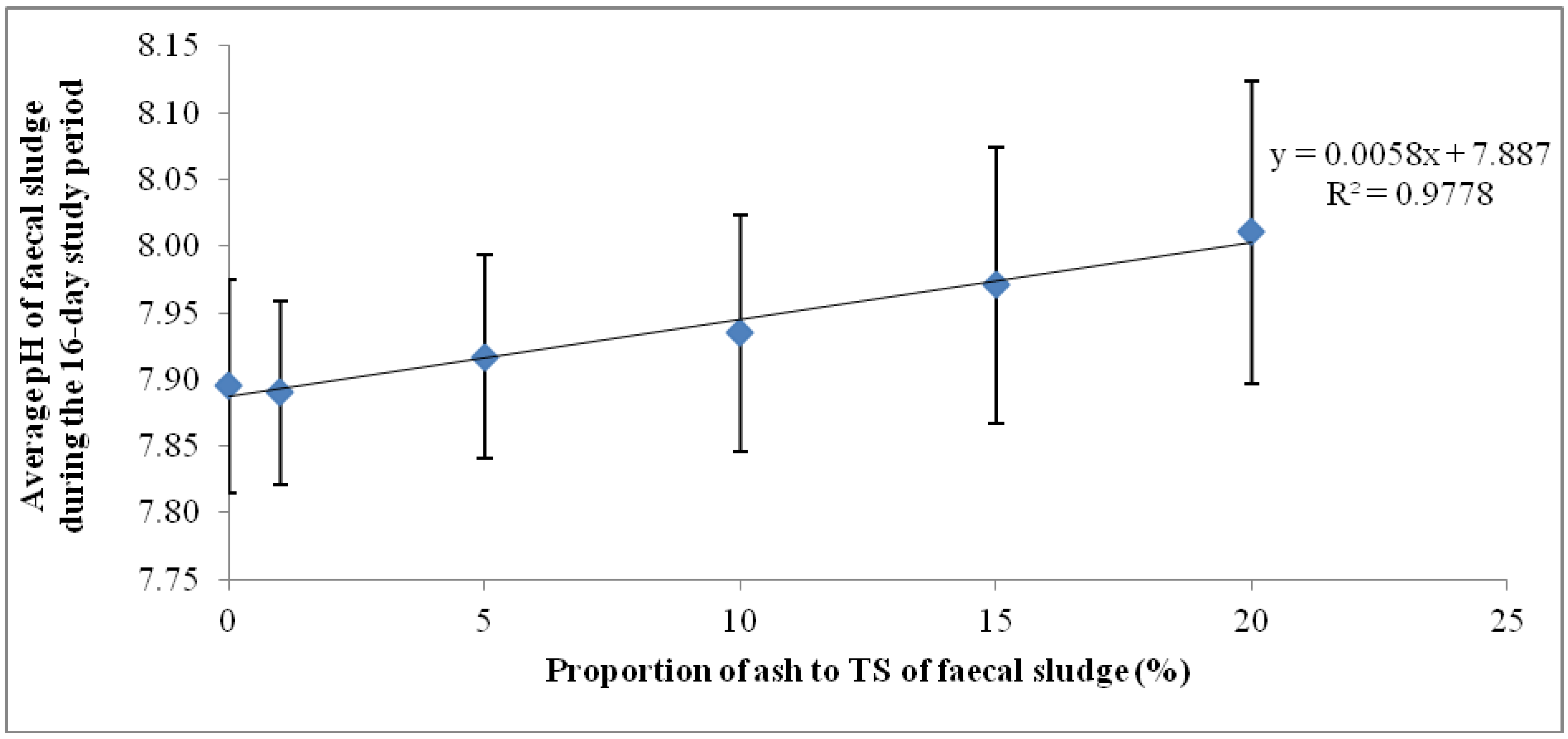
The mean pH values shown in Figure 2 represent the average pH of each of the ash/fecal sludge mixtures over the 16-day study period (n = 16): 0%, 1%, 5%, 10% and 15% and 20% ash/ TS of fecal sludge. The error bars also represent the standard deviation of the pH values over the study period. Regarding overall variation for the 16-day monitoring period, the results show that the highest dosage of ash (20% ash/TS) had the highest average pH and the highest standard deviation (8.01 ± 0.11). Conversely, the least variation in pH about the mean was recorded in sludge samples with lower concentrations of ash (1% ash/TS and 5% ash/TS) and in the control. A higher standard deviation indicates a wider variation from the mean value while a smaller standard deviation shows a smaller variation from the mean. This shows that a higher ash dosage causes a higher variation in pH from the mean pH value. Generally, the variation of pH in all the mixtures over the 16-day observation period was statistically significant (p = 0.0015; Fcrit = 2.3157). The quantity of ash added, therefore, has a very strong positive correlation (r = 0.988) with the resulting pH in the mixture (Figure 2). A higher wood ash dosage resulted in a higher pH and corroborates findings by Pescon et al. [37]. This outcome informed the development of a follow-up experimental set up where the ash proportions were increased whilst the volume of sludge was reduced.
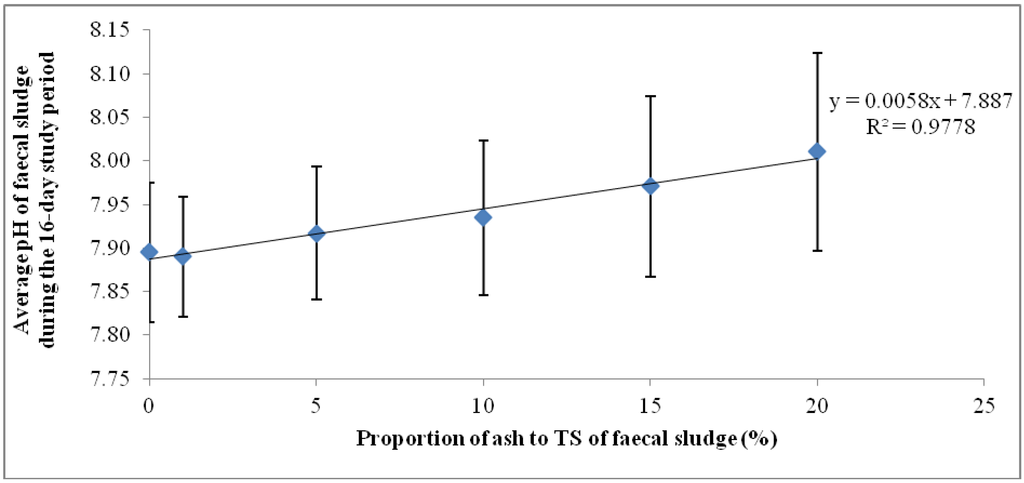
Figure 2.
Mean pHs and standard deviations of ash/fecal sludge mixtures for the 16-day trial.
Figure 2.
Mean pHs and standard deviations of ash/fecal sludge mixtures for the 16-day trial.
Results of the second phase experiment confirmed those of the first phase: the quantities of ash added to the fecal sludge were shown to have a significant influence on the rapidity and magnitude of increase in pH. Whilst ash dosages between 1 g/L and 130 g/L caused marginal incremental change in pH after 48 h, dosages of 140 g/L and above were associated with significant changes in pH, particularly in the first 24 h (Figure 3). Meanwhile, in the control experiment, the changes in pH during the monitoring period were insignificant and rather reduced after the first 24 h. The target pH of 11 was exceeded within 24 h in mixtures containing between 140 g/L and 180g/L (Figure 3).
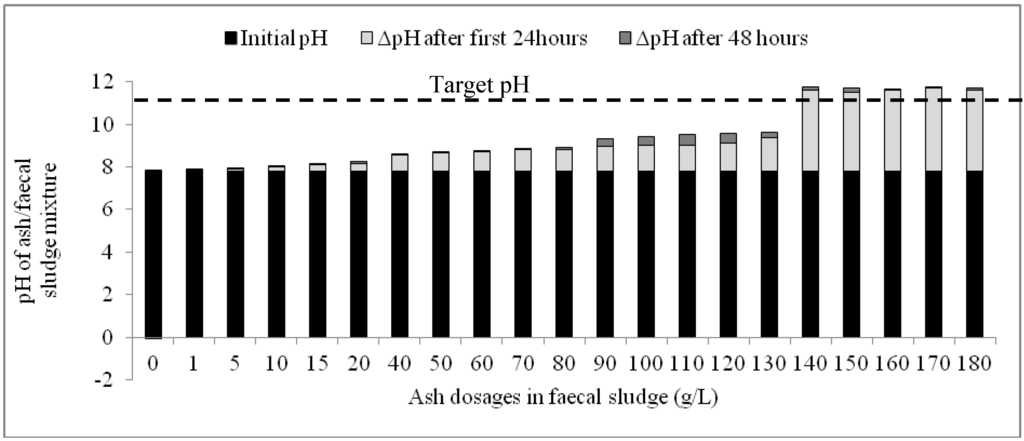
Figure 3.
Variation of pH with time based on different ash dosages in faecal sludge.
Figure 3.
Variation of pH with time based on different ash dosages in faecal sludge.
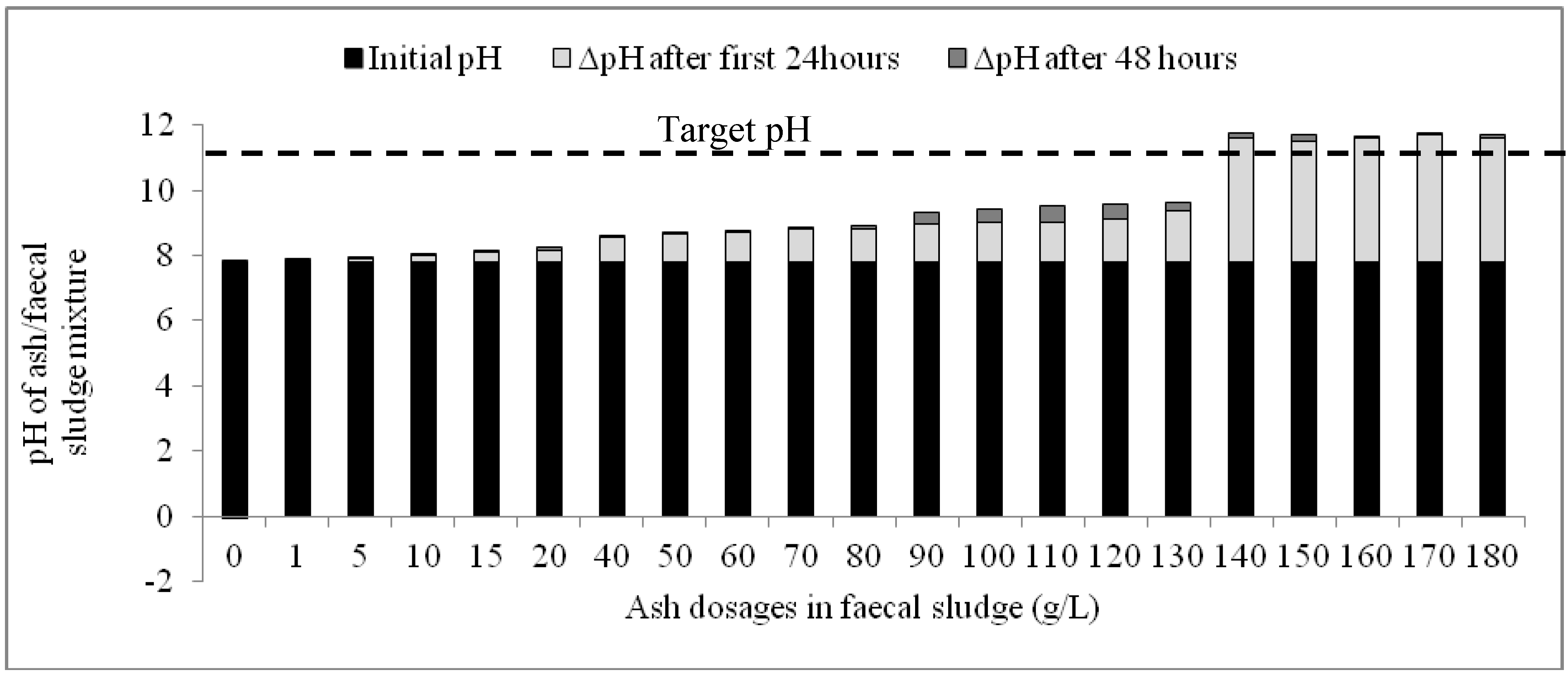
The change in pH (ΔpH) was drastic in the first 24 h in all the mixtures but decreased in the subsequent 24 h. When the overall pH increase within the 48-h period is disaggregated for each mixture of ash and fecal sludge, it is observed that the variation of pH for the first 24 h and the successive 24 h was statistically significant (P(T ≤ t)two tail = 0.00; tcrit = 2.09). Additionally, although ash dosages between 140 g/L and 180 g/L all caused the highest ΔpH within the 48-h period, the increments caused by these dosages during the first 24 h were higher than the subsequent 24 h. Average ΔpH during the first 24 h was 3.79 ± 0.07 while the average ΔpH in the subsequent 24 h was 0.19 ± 0.06. This indicates a consistent pH variation pattern in the first 24 h for these dosages and could indicate that any dosage within 140–180 g/L would cause a similar increase in pH particularly in the first 24 h.
A significant proportion of the overall ΔpH occurs in the first 24 h upon addition of ash to the faecal sludge. In general, an average of 85% of the overall ΔpH occurs within this time period for all the mixtures except the control. Particularly for ash dosages between 140 g/L and 180 g/L, an average of 97% of the overall ΔpH occurred in the first 24 h.
The findings of this study are comparable with that of Bina et al. [21], as shown in Table 1 and suggest that, compared to lime, relatively higher quantity of ash is required to raise the pH of fecal sludge to sanitizing levels within the first 24 h. Ash dosages required to raise the pH to 11 and above are about 7 to 15 times higher than lime dosages reported by Bina et al. [21]. Inactivation of pathogens at pH levels above 11 has been shown to be more significant during the first 24 h as per the findings of Bina et al. [21]. Specifically, for helminth eggs, the minimum exposure times reportedly range between 2 h and more than 180 days in order to achieve more than 90% inactivation of the helminth eggs [35]. This is however dependent on the type of alkaline agent, dosage and temperature.

Table 1.
Comparison of study results with other related studies.
| Additive | Dosage (g/L) | pH of Faecal Sludge | pH of Mixture after 24 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lime [21] | 9.8 | 6.6 | 10.7 * |
| 21.3 | 6.6 | 12.5 | |
| Ash (This study) | 140 | 7.81 | 11.59 |
| 180 | 7.81 | 11.60 |
* Reduced from 12.5 after the first 2 h.
The study findings underscores the potential of ash as an alternative additive for increasing pH of fecal sludge to sanitizing levels although further studies are required to accentuate the pathogen reduction efficiency. Given that ash from burning of wood products generates another waste, which requires disposal, utilizing ash as an additive for sanitizing fecal sludge can provide a cheaper alternative than lime and concurrently provide a means of disposal for wood ash. In Ghana, lime is sold in 25 kg bags for approximately GH¢39 (US$10) but wood ash is free and requires only collection. Large quantities of ash can be collected for free from bakeries, restaurants and public eating places where wood is used as fuel.
4. Conclusions
It is concluded that application of wood ash to fecal sludge can, similar to lime, increase pH to sanitizing levels. This however requires that optimum amounts be added to ensure that there can be sufficient increase in pH. A very strong positive correlation (r = 0.988) between ash dosage and increases in pH was observed and this association was statistically significant (p = 0.0015; Fcrit = 2.3157). For ash/fecal sludge mixtures between 1 and 180 g/L, a larger proportion (85%) of the overall pH increment occurs in the first 24 h. The difference in variation of pH between the first 24 h and the successive 24 h was statistically significant (P(T ≤ t)two tail = 0.00; tcrit = 2.09). Overall, the most promising dosage range was 140–180 g of ash per litre of fecal sludge. This dosage range causes a significant and consistent increase in pH from an almost neutral pH of 7.81 to an average of 11.60 ± 0.07 in just 24 h. Additionally, within this dosage range, an average of 97% of the overall increase in pH occurs in the first 24 h. Compared to lime, the study points out that, relatively higher quantities of ash dosage (about 7 to 15 times higher dosage) is required to raise the pH of fecal sludge to sanitizing levels within the first 24 h. The study findings indicate that wood ash can also be efficient for increasing fecal sludge pH to sanitizing levels although further studies on the pathogen reduction efficiency are needed. Utilizing wood ash for such a purpose instead of direct disposal into landfills would help in the production of a usable soil conditioner to support agricultural purposes. Further studies are underway to assess the pathogen inactivation efficiency considering other inactivation factors, such as desiccation and temperature.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the effort of staff of the Environmental Quality Engineering Laboratory of the Civil Engineering Laboratory, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana.
Author Contributions
Esi Awuah had the original idea for the study, Isaac Monney (corresponding author) carried out the study and drafted the manuscript. Both authors conducted the data analyses. Drafted manuscript was revised and approved by both authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schönning, C.; Stenström, T.A. Guidelines on the Safe Use of Urine and Faeces in Ecological Sanitation Systems; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dreschel, P.; Cofie, O.; Danso, G. Closing the Rural-Urban Food and Nutrient Loops in West Africa: A Reality Check. Urban Agric. Mag. 2010, 23, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Beal, C.; Gardner, T.; Ahmed, W.; Walton, C.; Hamlyn-Harris, D. Closing the nutrient loop: a urine-separation and reuse trial in the Currumbin ecovillage, QLD. In Innovation and Technology for On-site Systems: Proceedings of On-site 2007 Conference; University of New England: Armidale, Australia, 2007; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mosiej, J.; Karczmarczyk, A. Closing the nutrient loop between urban and rural area—Wastewater and sludge utilization in Ner River Valley. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. Ecohydrol. Implement. Eur. Water Framew. Dir. 2006, 6, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.K.; Phuc, P.D.; Dalsgaard, A.; Konradsen, F. Successful sanitation promotion must recognize the use of latrine wastes in agriculture—The example of Vietnam. WHO Bull. 2005, 83, 273–274. [Google Scholar]
- Phuc, P.D.; Konradsen, F.; Phuong, P.T.; Cam, P.D.; Dalsgaard, A. Use of human excreta as fertilizer in agriculture in Nghe An province, Viet Nam. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2006, 37, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater: Wastewater Use in Agriculture, 2; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater: Excreta and Greywater Use in Agriculture, 4; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chaggu, E.J. Sustainable Environmental Protection Using Modified Pit-Latrines. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Niwagaba, B.C. Treatment Technologies for Human Faeces and Urine. Ph.D. Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Laboy-Nieves, E.N.; Schaffner, F.C.; Abdelhadi, A.H.; Goosen, M.F.A. Environmental Management, Sustainable Development and Human Health; Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Strande, L.; Ronteltap, M.; Brdjanovic, D. Faecal Sludge Management: Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 45–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cofie, O.; Agbottah, S.; Strauss, M.; Esseku, H.; Montangero, A.; Awuah, E.; Kone, D. Solid–liquid separation of faecal sludge using drying beds in Ghana: Implications for nutrient recycling in urban agriculture. Water Res. 2006, 40, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koné, D.; Gallizzi, K.; Drescher, S.; Cofie, O.; Zurbrugg, C.; Forster, D.; Montangero, A.; Awuah, E.; Strauss, M. Efficiency of Helminth eggs removal in dewatered faecal sludge by co-composting. In Proceedings of the 30th WEDC International Conference on People-Centered Approaches to Water and Environmental Sanitation, Vientiane, Laos, 25–28 October 2004.
- Mensah, P.Y.; Kuffour, R.A.; Baidoo, P.K.; Awuah, E. The effect of different percentages of bulking agent (sawdust) on microbial quality of faecal sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1728–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mara, D. Domestic Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries; Earthscan: London, UK, 2004; pp. 85–182. [Google Scholar]
- Cabirol, N.; Oropeza, M.R.; Noyola, A. Removal of helminth eggs and faecal coliforms by anaerobic thermophilic sludge digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koné, D.; Cofie, O.; Zurbrugg, C.; Gallizzia, K.; Mosera, D.; Dreschera, S.; Strauss, M. Helminth eggs inactivation efficiency by faecal sludge dewatering and co-composting in tropical climates. Water Res. 2007, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, P. Chemical Stabilization Sludge into Biosolids: Processing, Disposal, Utilization; Spinosa, L., Vesilind, P.A., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kazama, S.; Otaki, M. Mechanism for Inactivation of Bacteria and Viruses in Sawdust Used in Composting Toilet. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2011, 9, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bina, B.; Movahedian, H.; Kord, I. The Effect of Lime Stabilization on the Microbiological Quality of Sewage Sludge. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2004, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Boost, M.V.; Poon, C.S. The effect of a modified method of lime-stabilisation sewage treatment on enteric pathogens. Environ. Int. 1998, 24, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater and Excreta in Agriculture and Aquaculture: Measures for Public Health Protection. WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/41681 (11 September 2015).
- Magri, M.E.; Philippi, L.S.; Vinneras, B. Inactivation of Pathogens in Feces by Desiccation and Urea Treatment for Application in Urine-Diverting Dry Toilets. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taweesan, A.; Koottatep, T.; Polprasert, C. Effective faecal sludge management measures for on-site sanitation systems. J. Water Sanit. Hyg. Dev. 2015, 5, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodounhessi, A.; von Münch, E. Financial Challenges to Making Faecal Sludge Management an Integrated Part of the Ecosan Approach: Case Study of Kumasi, Ghana. Water Pract. Technol. 2006, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingallinella, A.M.; Sanguinetti, G.; Koottatep, T.; Montangero, A.; Strauss, M. The challenge of faecal sludge management in urban areas—Strategies, regulations and treatment options. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huibers, F.P.; Seghezzo, L.; Mels, A. Wastewater and Irrigated Agriculture Lessons Learned and Possible Applications in Africa. Afr. Technol. Policy Stud. Netw. Spec. Paper Ser. No. 23 2006, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, A.G. Recycling and Disposing of Wood Ash. Tappi J. 1990, 9, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Adekayode, F.O.; Olojugba, M.R. The utilization of wood ash as manure to reduce the use of mineral fertilizer for improved performance of maize (Zea mays L.) as measured in the chlorophyll content and grain yield. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2012, 1, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, C.; Watmough, S.A. Evaluating the effects of liming and wood-ash treatment on forest ecosystems meta-analysis. Can. J. For. Res. 2014, 44, 867–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, R.M. Wood ash use in forestry—A review of the environmental impacts. Forestry 2006, 79, 563–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurts, W.A. Daily pH Cycle and Ammonia Toxicity. World Aquac. 2003, 34, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Patoczka, J.; Wilson, D.J. Kinetics of the desorption of ammonia from water by diffused aeration. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1984, 19, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyas, H.; Zhang, S.; Otterpohl, R. Pretreating stored human urine for solar evaporation by low-technology ammonia stripping. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 5, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescon, B.M.; Barrios, J.A.; Jimenez, B.E.; Nelson, K.L. The effects of temperature, pH, and ammonia concentration on the inactivation of Ascaris eggs in sewage sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzadkia, M.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Loveimi, A. Optimization of bacteriological quality of biosolids by lime addition. Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng. 2009, 6, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
