The Electrochemical Characterization of Nanostructured Bi2Se3 Thin Films in an Aqueous Na Electrolyte
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Bi2Se3 Thin Films
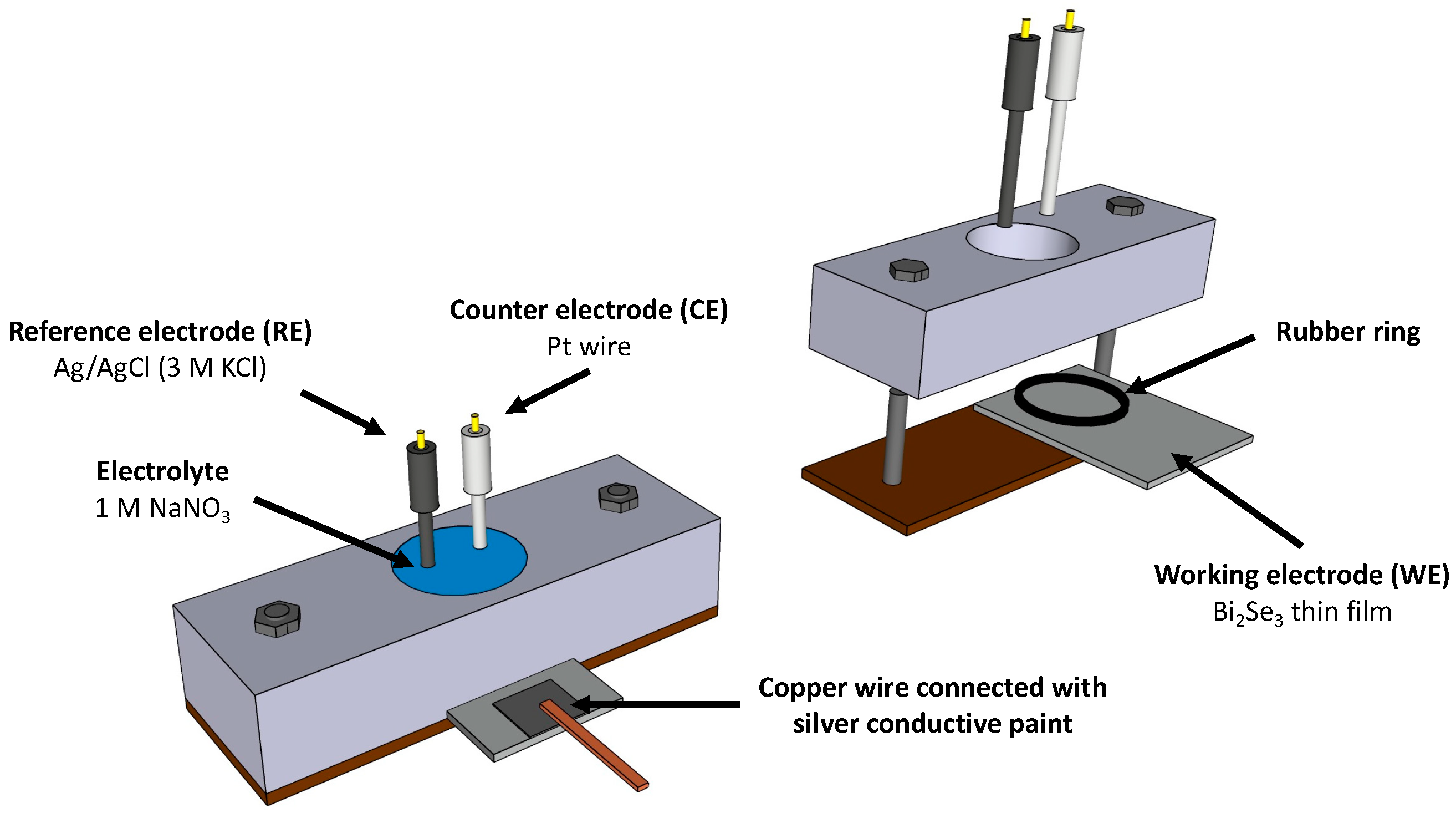
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Morphology of the Synthesized Structures
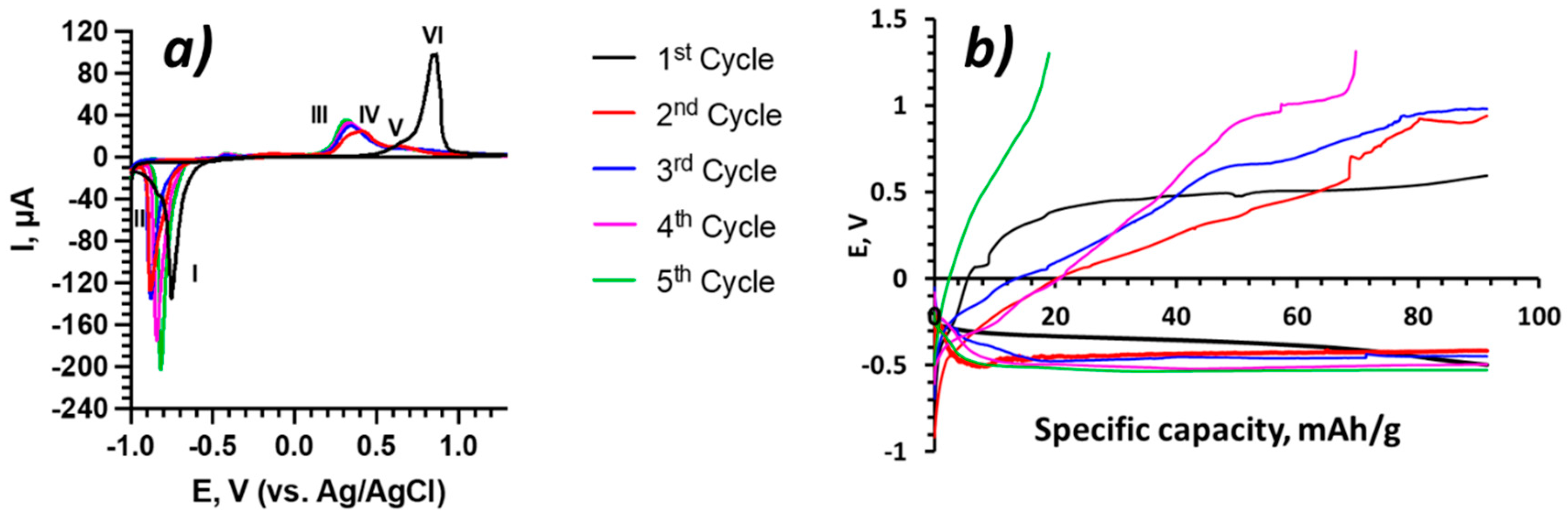
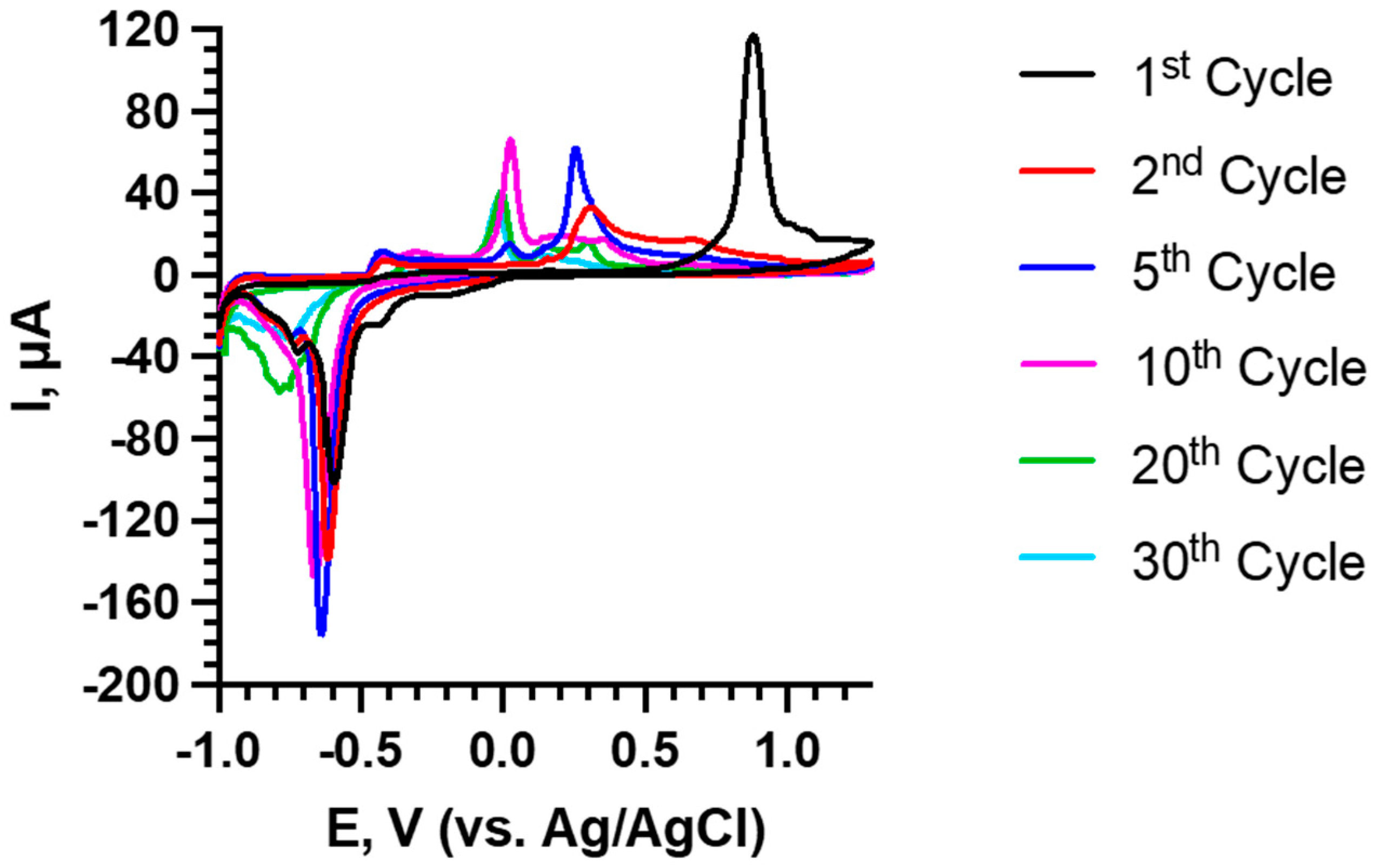
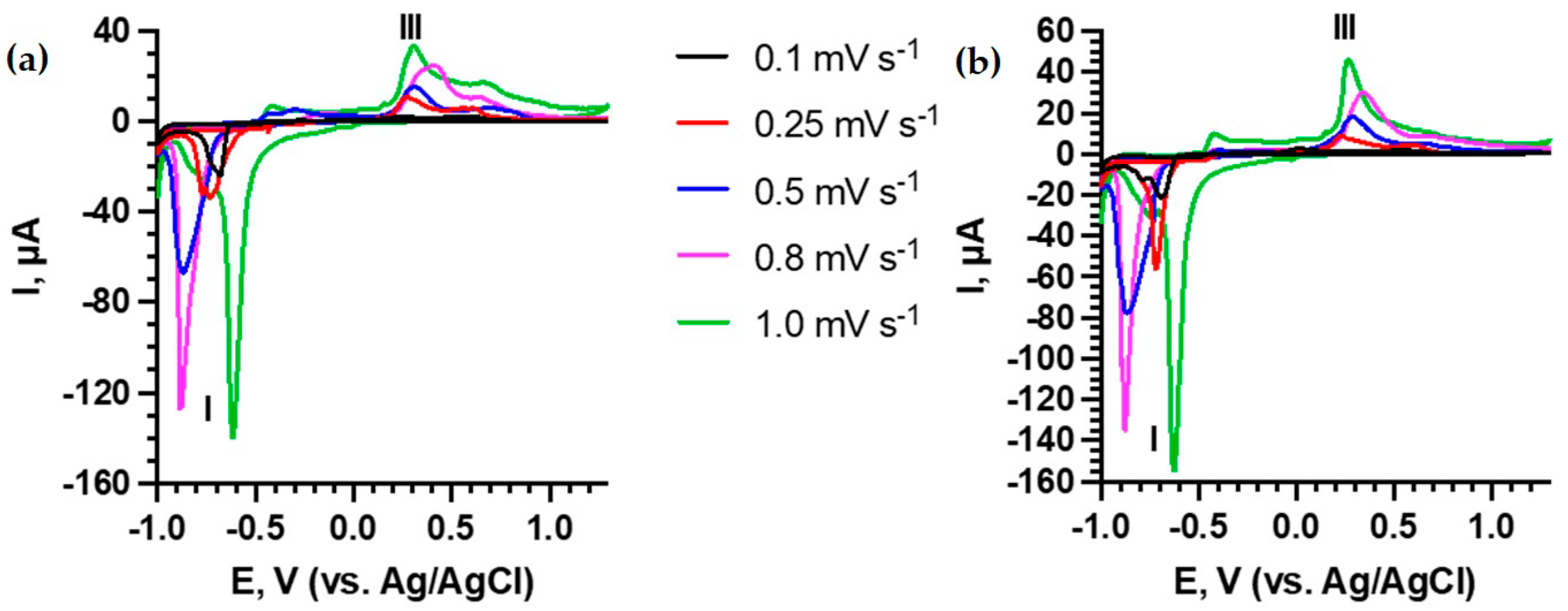
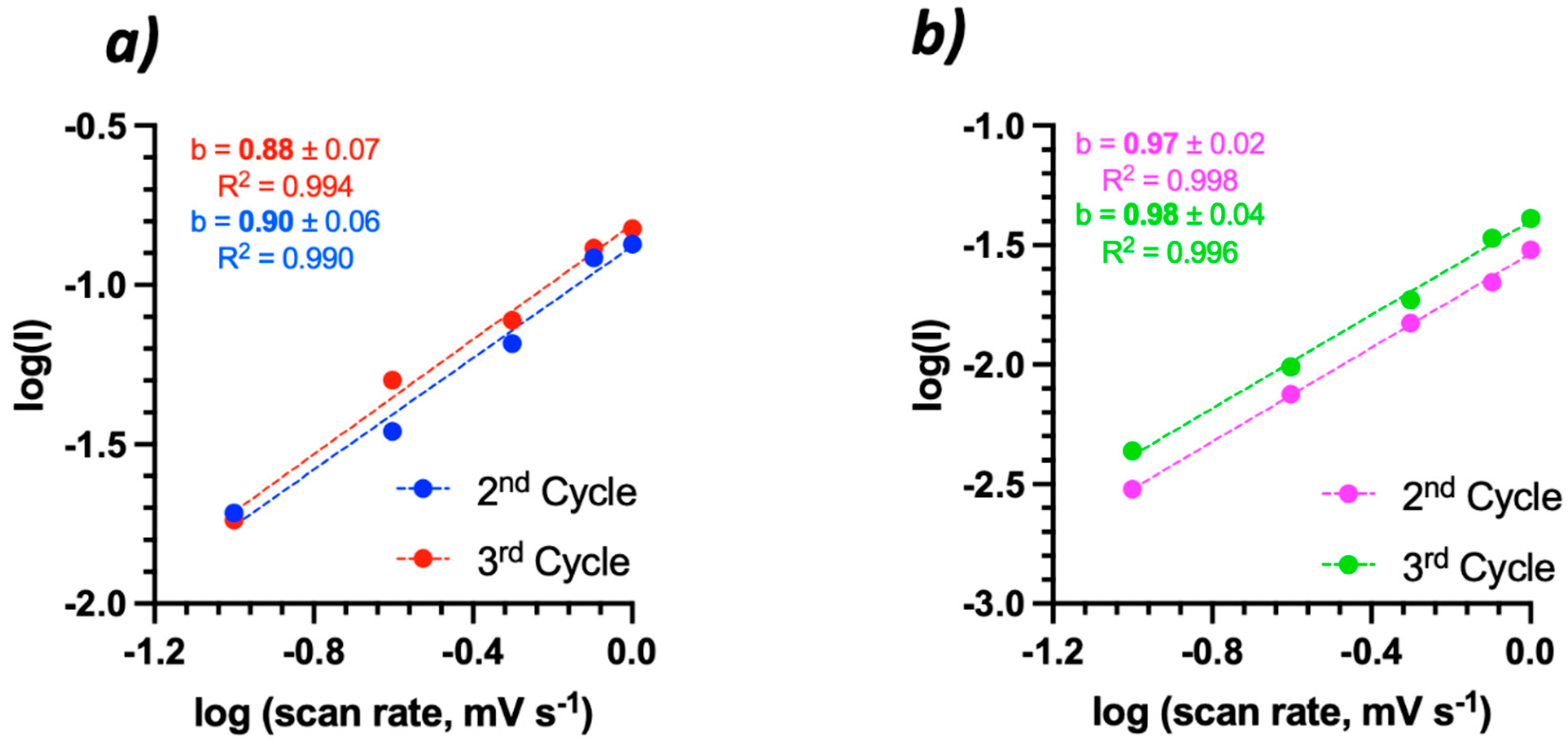
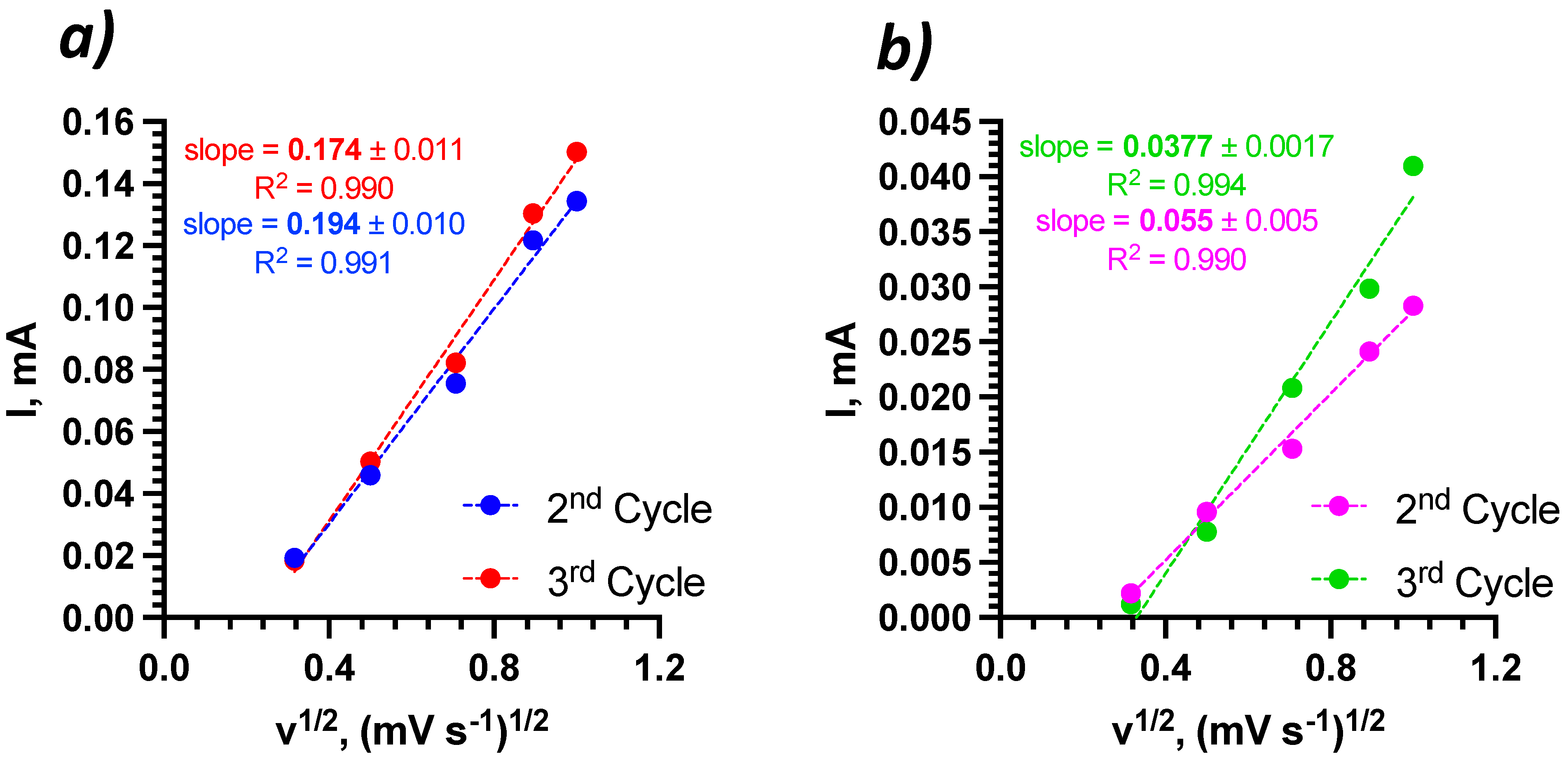
3.2. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olabi, A.G.; Onumaegbu, C.; Wilberforce, T.; Ramadan, M.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Alami, A.H.A. Critical review of energy storage systems. Energy 2021, 214, 118987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthiram, A. Materials Challenges and Opportunities of Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Yao, Y.-X.; Zhu, G.-L.; Yan, C.; Jiang, L.-L.; He, C.; Huang, J.-Q.; Zhang, Q. A review on energy chemistry of fast-charging anodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3806–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicki, M.; Shaw, L.L. Advances and challenges of sodium ion batteries as post lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53129–53154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, E.P.; Orendorff, C.J. How electrolytes influence battery safety. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2012, 21, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresce, A.; Xu, K. Aqueous lithium-ion batteries. Carbon Energy 2021, 3, 721–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhi, C. Voltage issue of aqueous rechargeable metal-ion batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 180–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, K. Aqueous Rechargeable Li and Na Ion Batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11788–11827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Sarkar, S.; Shi, S.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Yan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Recent Progress in Advanced Organic Electrode Materials for Sodium-Ion Batteries: Synthesis, Mechanisms, Challenges and Perspectives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Ming, F.; Alshareef, H.N. Sodium-ion battery anodes: Status and future trends. Energy Chem. 2019, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Bi, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, J. Bismuth chalcogenide compounds Bi2×3 (X=O, S, Se): Applications in electrochemical energy storage. Nano Energy 2017, 34, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Li, M.; Oh, J.A.S.; Zeng, K.; Lu, L. Recent advances of bismuth based anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Mater. Technol. 2018, 33, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chou, S.-L.; Dou, S.-X. Advances and Challenges in Metal Sulfides/Selenides for Next-Generation Rechargeable Sodium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lukas, K.C.; McEnaney, K.; Lee, S.; Zhang, Q.; Opeil, C.P.; Chen, G.; Ren, Z. Studies on the Bi2Te3–Bi2Se3–Bi2S3 system for mid-temperature thermoelectric energy conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhou, H.; Chi, X.; Chen, H.; Li, A.X.; Yao, Y.; Chen, S. Bi2Se3/C Nanocomposite as a New Sodium-Ion Battery Anode Material. Nano-Micro Lett. 2018, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chae, S.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, N.; Sung, J.; Cho, J. Integration of Graphite and Silicon Anodes for the Commercialization of High-Energy Lithium-Ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 110–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andzane, J.; Buks, K.; Strakova, M.N.; Zubkins, M.; Bechelany, M.; Marnauza, M.; Baitimirova, M.; Erts, D. Structure and Doping Determined Thermoelectric Properties of Bi2Se3 Thin Films Deposited by Vapour-Solid Technique. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2019, 18, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarini, F. Redetermination of the structure of bismuth(III) nitrate pentahydrate, Bi(NO3)3·5H2O. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1985, 41, 1144–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Qi, S.; He, P.; Ma, J. Antimony- and Bismuth-Based Chalcogenides for Sodium-Ion Batteries. Chem. An Asian J. 2019, 14, 2925–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Ito, K.; Dutta, A.; Kubo, Y. Dendrite-Free Epitaxial Growth of Lithium Metal during Charging in Li–O 2 Batteries. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 13390–13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.J.; Chang, D.; Kim, J.; Moon, S.; Oh, K.; Park, K.Y.; Seong, W.M.; Park, H.; Kwon, G.; et al. Toward a low-cost high-voltage sodium aqueous rechargeable battery. Mater. Today 2019, 29, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, M.; Rajendran, V. A comprehensive model for cyclic voltammetric study of intercalation/de-intercalation process incorporating charge transfer, ion transport and thin layer phenomena. J. Power Sources 2000, 88, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jung, Y.; Park, J.; Hong, M.; Byon, H.R. Sodium fluoride-rich solid electrolyte interphase for sodium–metal and sodium–oxygen batteries. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2021, 42, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Ji, X.; Wang, P.F.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, L.; Cui, C.; Deng, T.; Liu, S.; et al. High-Energy Aqueous Sodium-Ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 11943–11948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B. Intercalated water in aqueous batteries. Carbon Energy 2020, 2, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, T.S.; Kurra, N.; Wang, X.; Pinto, D.; Simon, P.; Gogotsi, Y. Energy Storage Data Reporting in Perspective—Guidelines for Interpreting the Performance of Electrochemical Energy Storage Systems. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1902007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, M. Bismuth selenide nanocrystalline array electrodes for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, J.P.; Amine, K.; Chen, Z. Revealing the Rate-Limiting Li-Ion Diffusion Pathway in Ultrathick Electrodes for Li-Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 5100–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Before Cycling | After 5 Cycles | After 30 Cycles | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | mass % | atomic % | 3σ, mass % | mass % | atomic % | 3σ, mass % | mass % | atomic % | 3σ, mass % |
| Bismuth | 58.53 | 27.03 | 5.29 | 45.71 | 10.19 | 3.44 | 29.51 | 4.31 | 2.24 |
| Selenium | 33.61 | 41.08 | 2.99 | 15.91 | 9.39 | 1.74 | 11.27 | 4.36 | 1.26 |
| Oxygen | 0.72 | 4.37 | 0.58 | 10.23 | 29.81 | 2.57 | 20.66 | 39.44 | 5.29 |
| Nitrogen | 0.70 | 4.84 | 0.67 | 1.73 | 5.76 | 0.61 | 5.84 | 12.74 | 1.89 |
| Carbon | 0.39 | 3.09 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Silicon | 2.73 | 9.37 | 0.41 | 10.00 | 16.60 | 0.96 | 2.51 | 2.73 | 0.31 |
| Sodium | 0.63 | 2.65 | 0.21 | 9.02 | 18.29 | 1.27 | 22.42 | 29.78 | 3.00 |
| Magnesium | 0.79 | 3.14 | 0.21 | 1.00 | 1.91 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.16 |
| Potassium | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 2.25 | 2.68 | 0.23 | 3.10 | 2.42 | 0.30 |
| Calcium | 1.82 | 4.38 | 0.25 | 2.20 | 2.56 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.12 |
| Chlorine | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.85 | 2.43 | 0.21 | 3.78 | 3.26 | 0.36 |
| Fresh Sample | After the 1st Cycle | After the 5th Cycle | After the 10th Cycle | After the 20th Cycle | After the 30th Cycle | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rel, Ω∙cm2 | 36 | 41 | 41 | 39 | 43 | 41 |
| RSEI, Ω∙cm2 | - | 273 | 157 | 96 | 58 | 40 |
| CPESEI, Ω−1 s−n | - | 365 | 379 | 111 | 126 | 71 |
| Rct, Ω∙cm2 | 1596 | 900 | 1010 | 1155 | 1178 | 1221 |
| CPEct, Ω−1 s−n | 4 | 553 | 398 | 272 | 95 | 57 |
| W, Ω·s−1/2 | 16 | 756 | 809 | 785 | 759 | 896 |
| Electrode | Thickness | Electrolyte | Intercalation | Deintercalation | Cycle | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi2Se3 thin film | 500 nm | 1 M NaNO3 | 1.1 × 10−11 1.4 × 10−11 | 5.1 × 10−13 1.1 × 10−12 | 2nd 3rd | This work |
| Bi2Se3/CC a | 1–20 µm * | 1 M NaClO4 EC/PC (1:1) | 2.2 × 10−13—9.7 × 10−12 | 1st | [27] | |
| Bi2Se3 microspheres | 1–20 µm * | 1 M NaClO4 EC/PC (1:1) | 9.3 × 10−13 | 5.7 × 10−15 | 1st | [27] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meija, R.; Lazarenko, V.; Skrastina, A.; Rublova, Y.; Andzane, J.; Voikiva, V.; Viksna, A.; Erts, D. The Electrochemical Characterization of Nanostructured Bi2Se3 Thin Films in an Aqueous Na Electrolyte. Batteries 2022, 8, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8030025
Meija R, Lazarenko V, Skrastina A, Rublova Y, Andzane J, Voikiva V, Viksna A, Erts D. The Electrochemical Characterization of Nanostructured Bi2Se3 Thin Films in an Aqueous Na Electrolyte. Batteries. 2022; 8(3):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeija, Raimonds, Vitalijs Lazarenko, Anna Skrastina, Yelyzaveta Rublova, Jana Andzane, Vanda Voikiva, Arturs Viksna, and Donats Erts. 2022. "The Electrochemical Characterization of Nanostructured Bi2Se3 Thin Films in an Aqueous Na Electrolyte" Batteries 8, no. 3: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8030025
APA StyleMeija, R., Lazarenko, V., Skrastina, A., Rublova, Y., Andzane, J., Voikiva, V., Viksna, A., & Erts, D. (2022). The Electrochemical Characterization of Nanostructured Bi2Se3 Thin Films in an Aqueous Na Electrolyte. Batteries, 8(3), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries8030025







