Grid Impacts of Uncoordinated Fast Charging of Electric Ferry
Abstract
1. Introduction
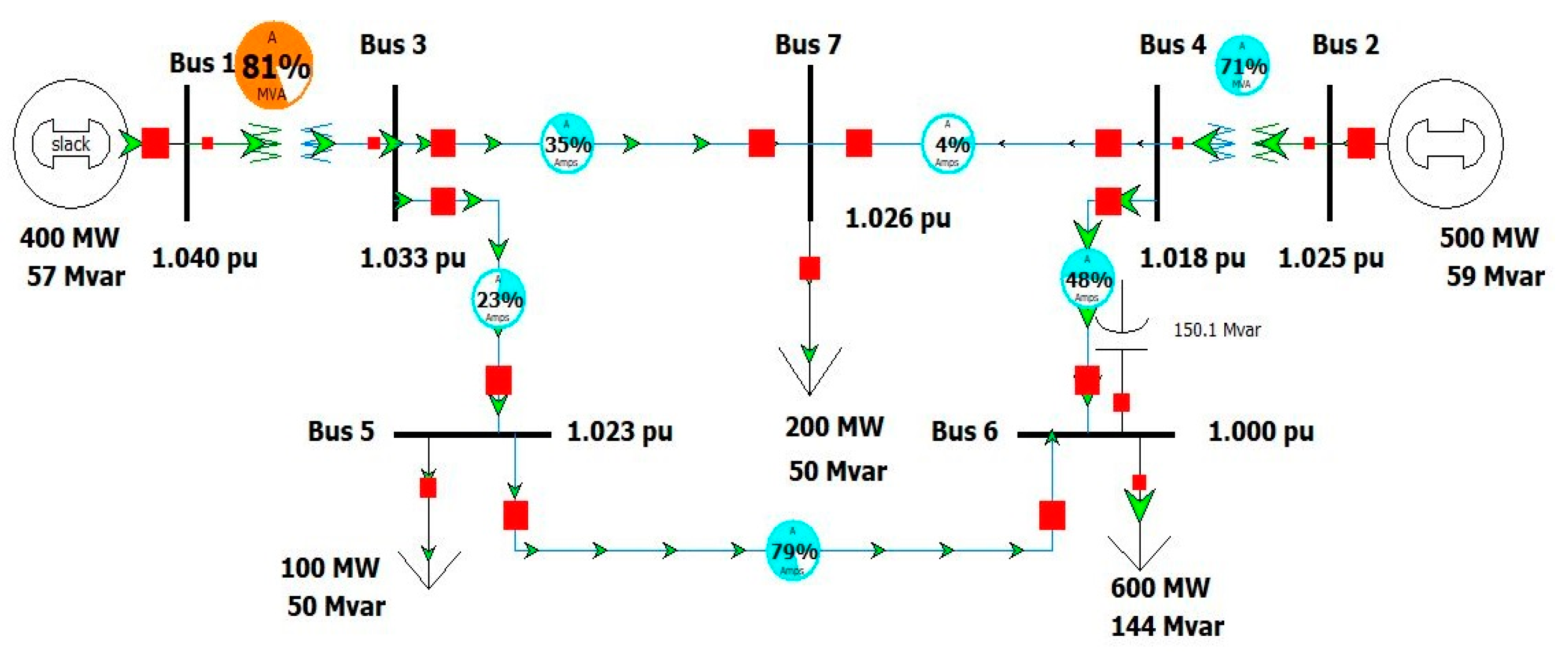
2. Simulation Results on Impacts of System Stability
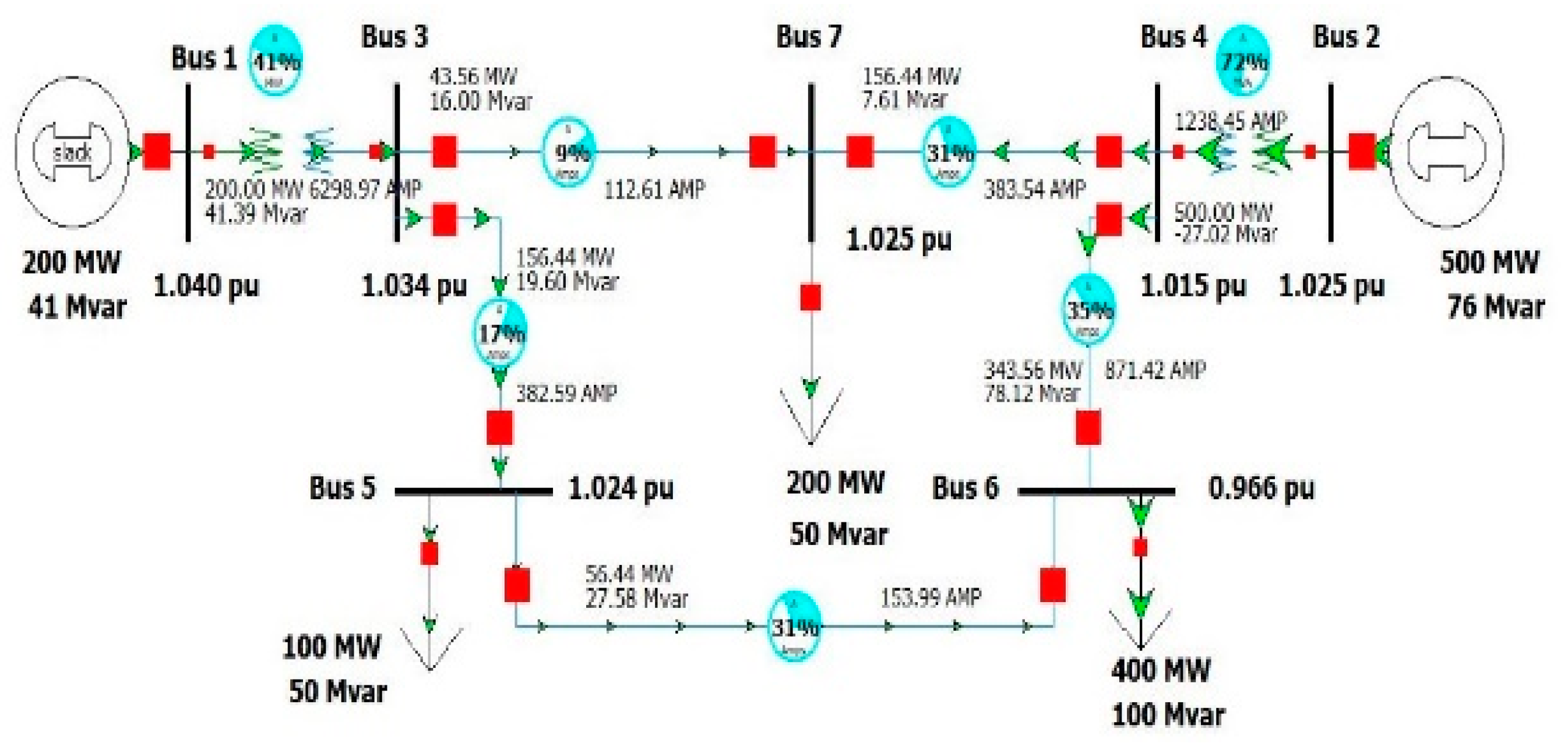
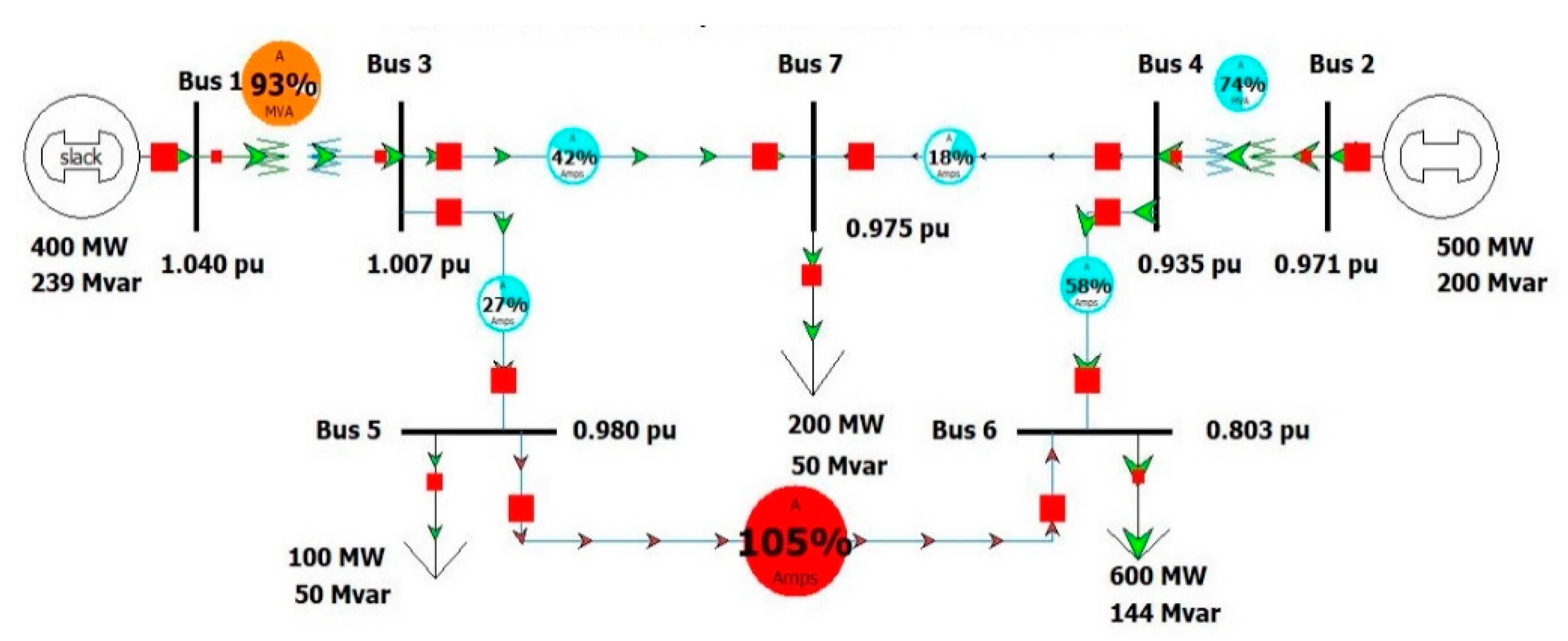
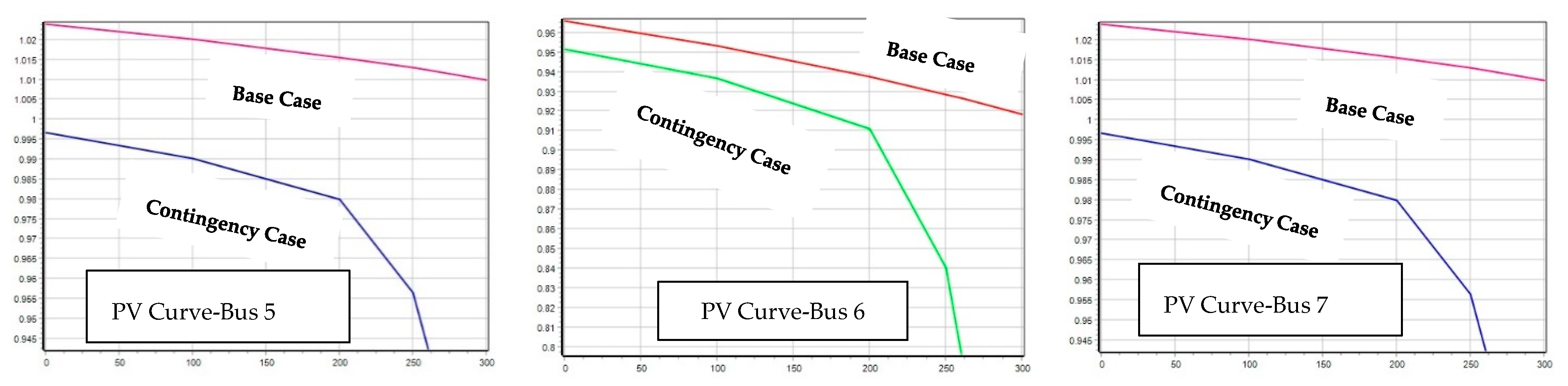
2.1. Impacts on Voltage Stability
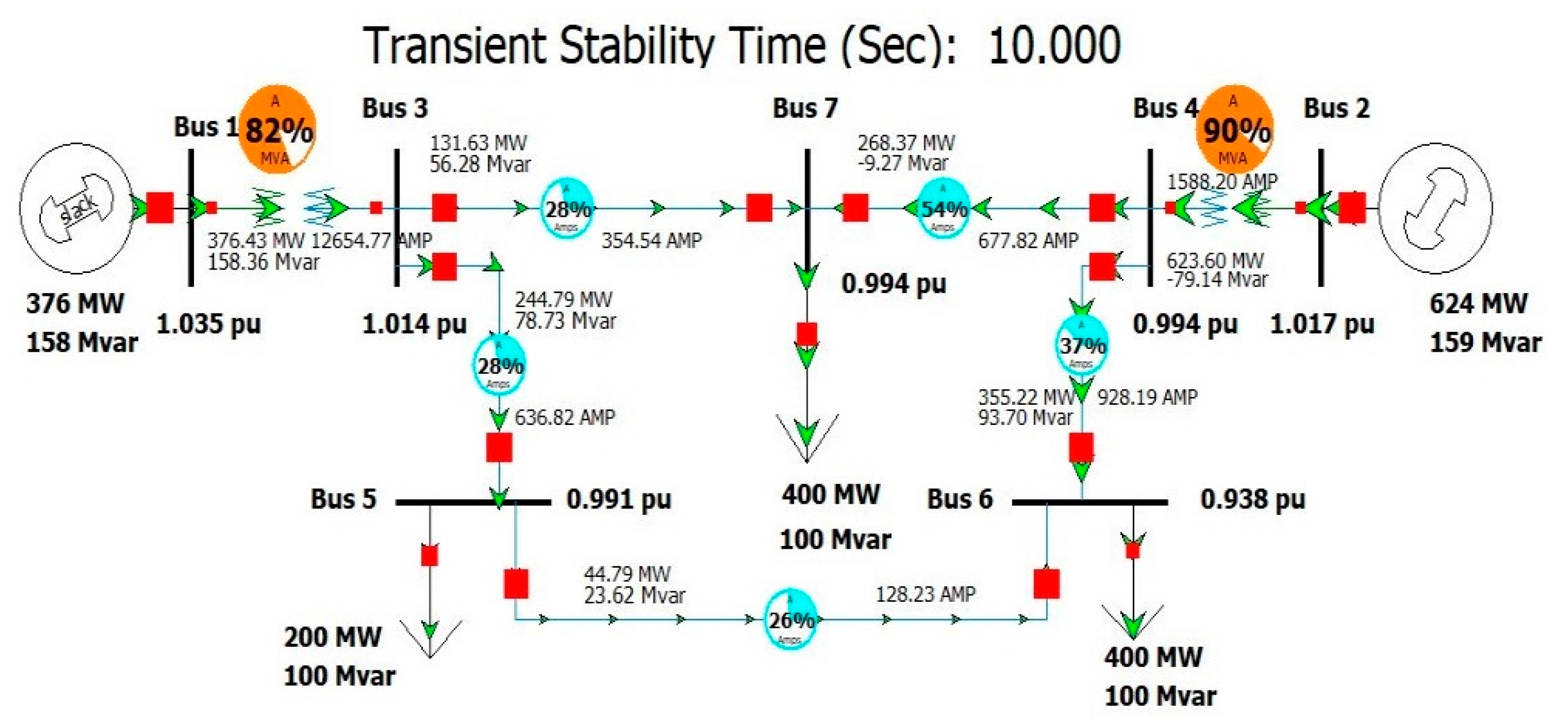
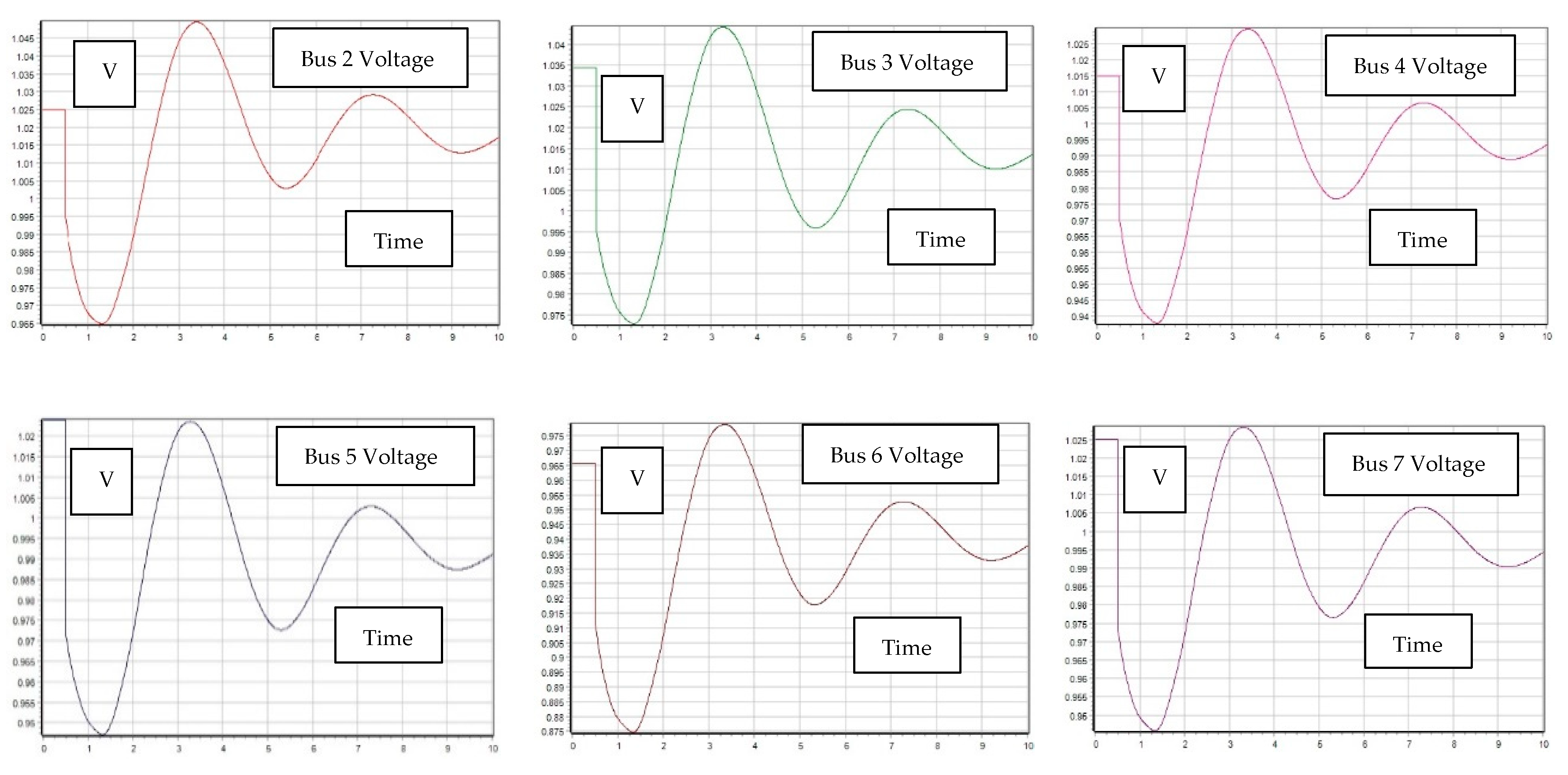
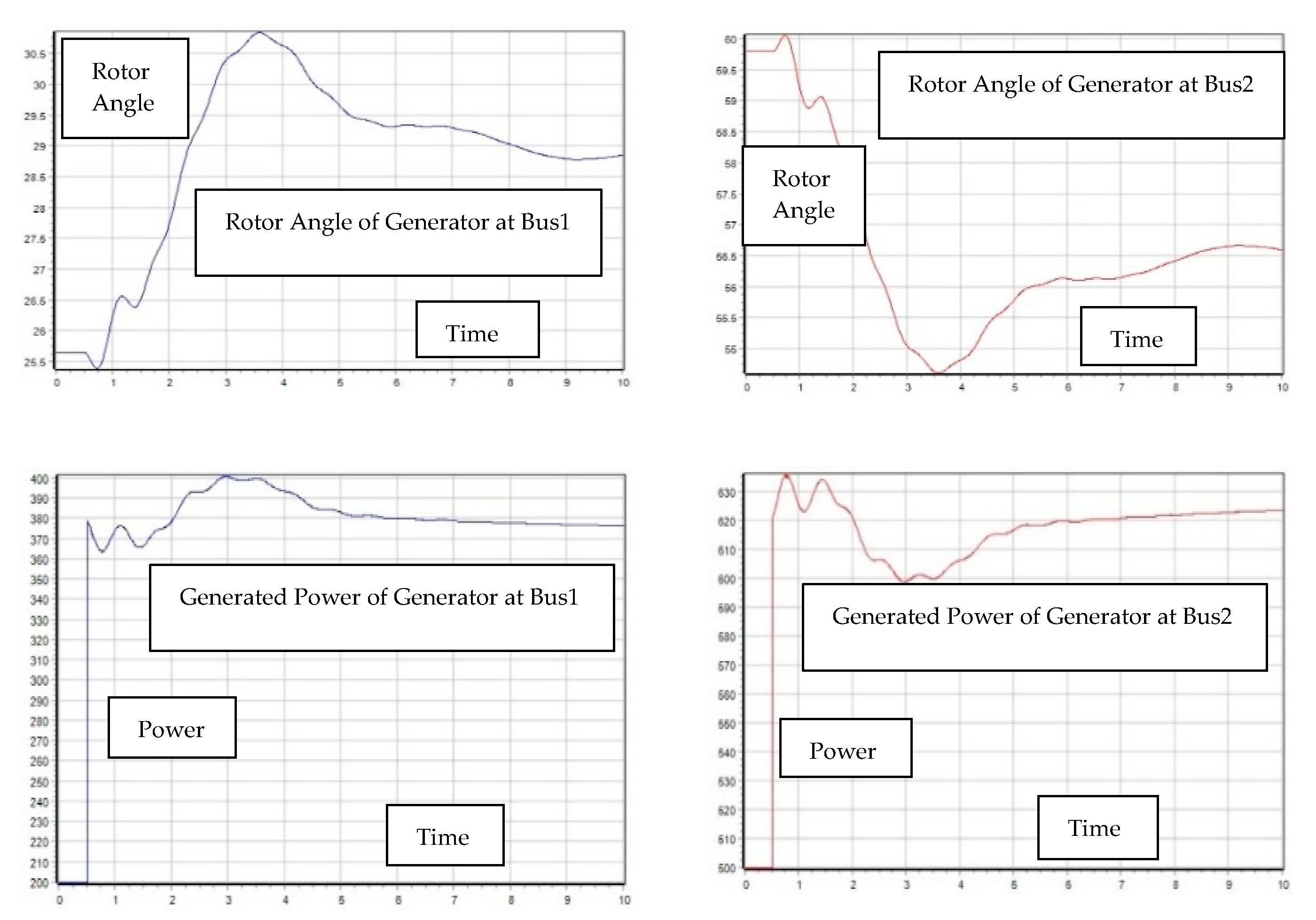
2.2. Transient Stability, V-P and V-Q Sensitivity Analysis
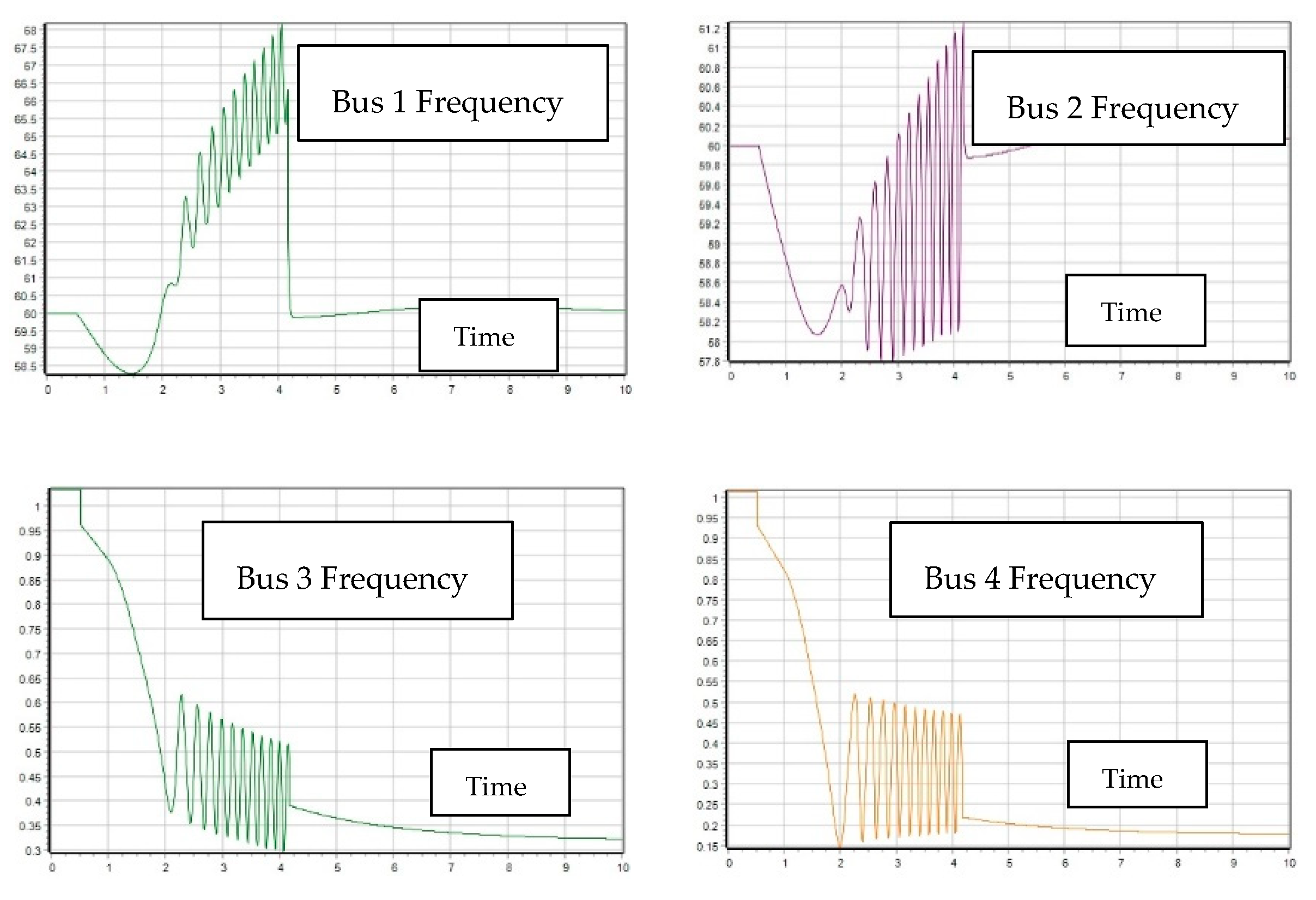
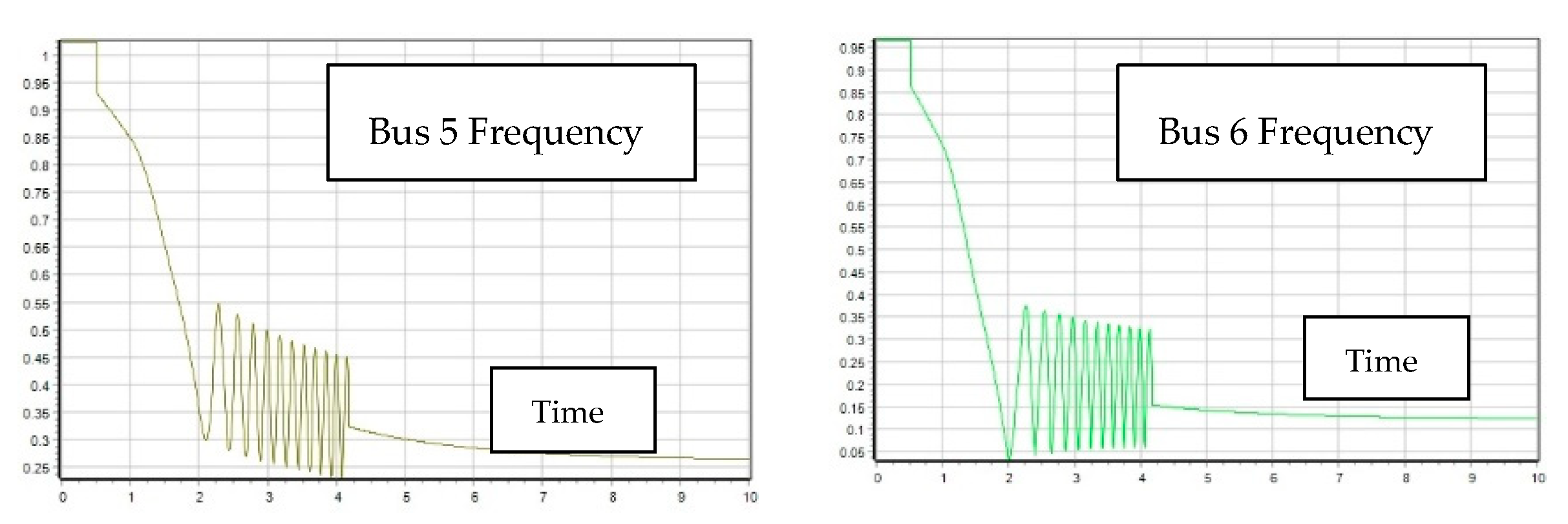
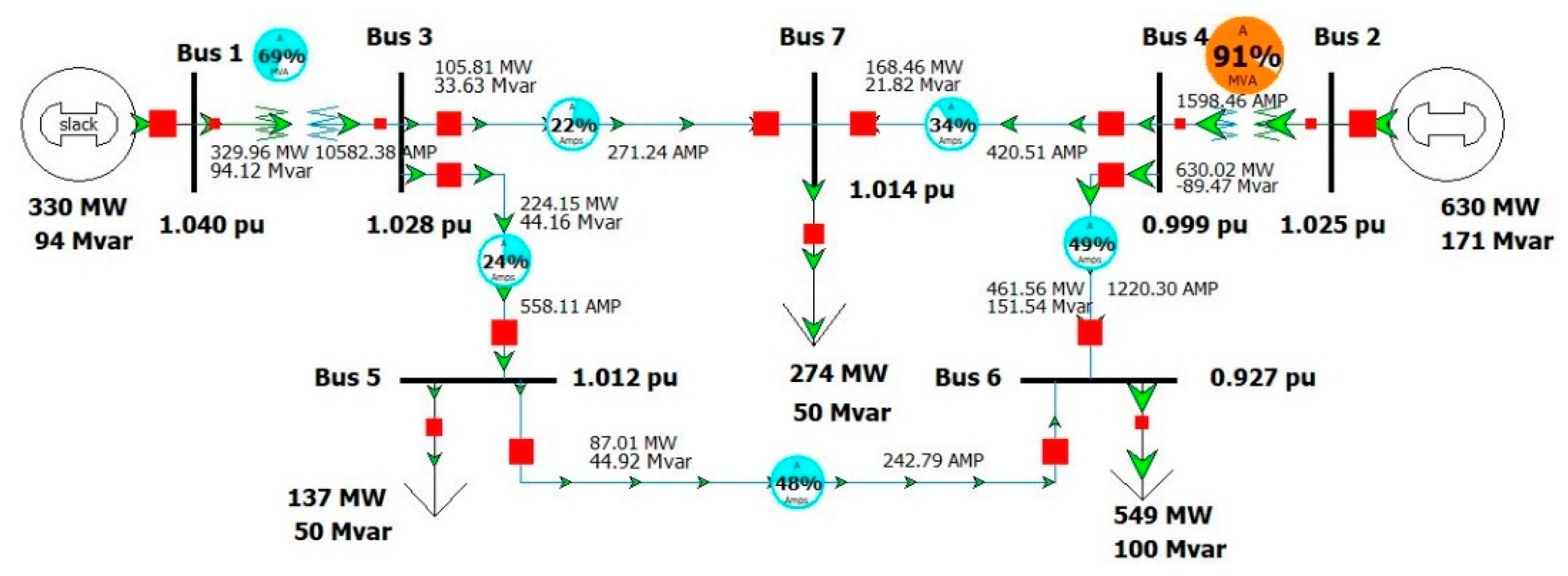
2.2.1. First Contingency Scenario: Increment of 100% Load at Buses 5 and 7
2.2.2. Second Contingency Scenario: Increment of 150% Load for Buses 5 and 7
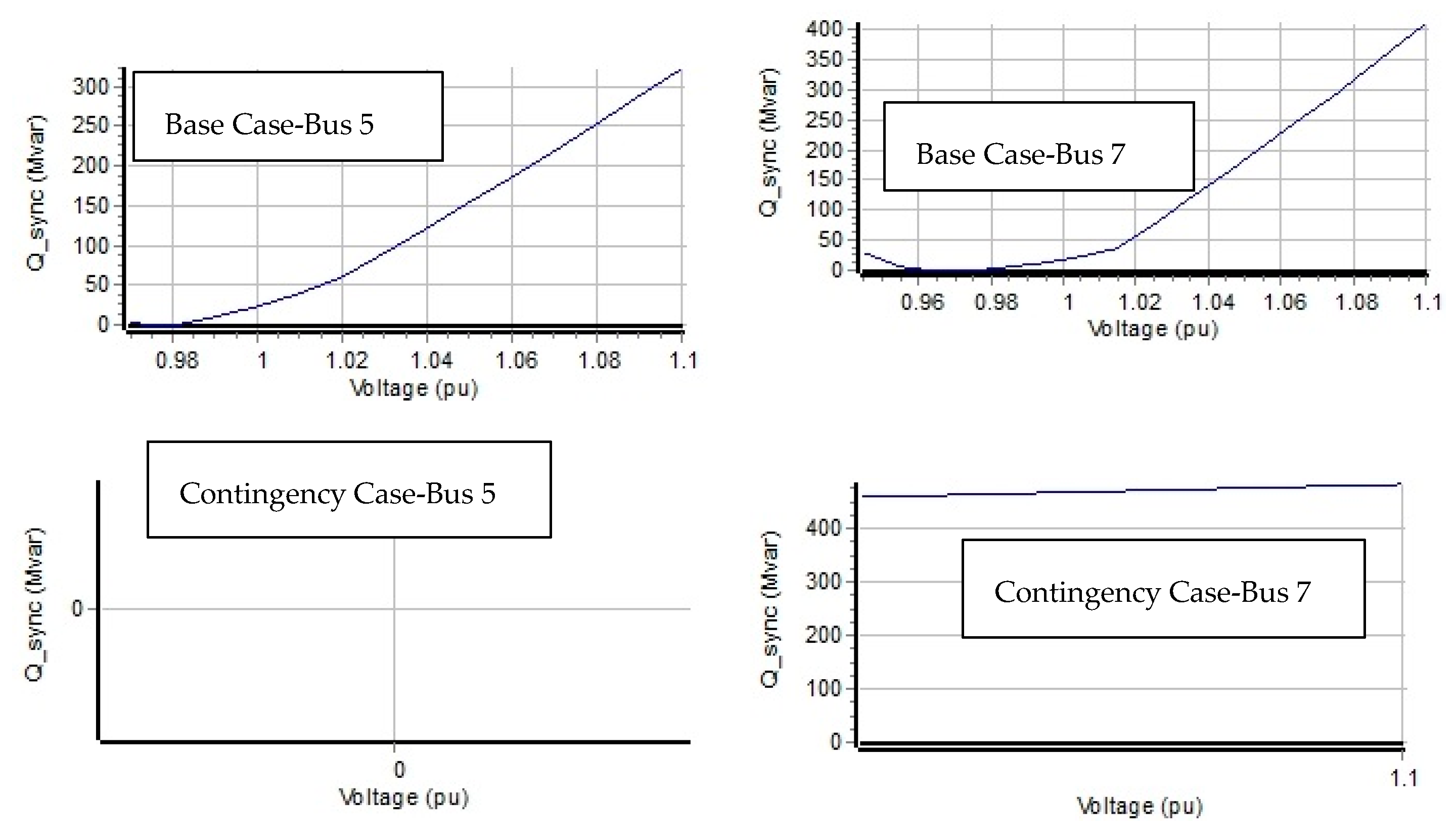
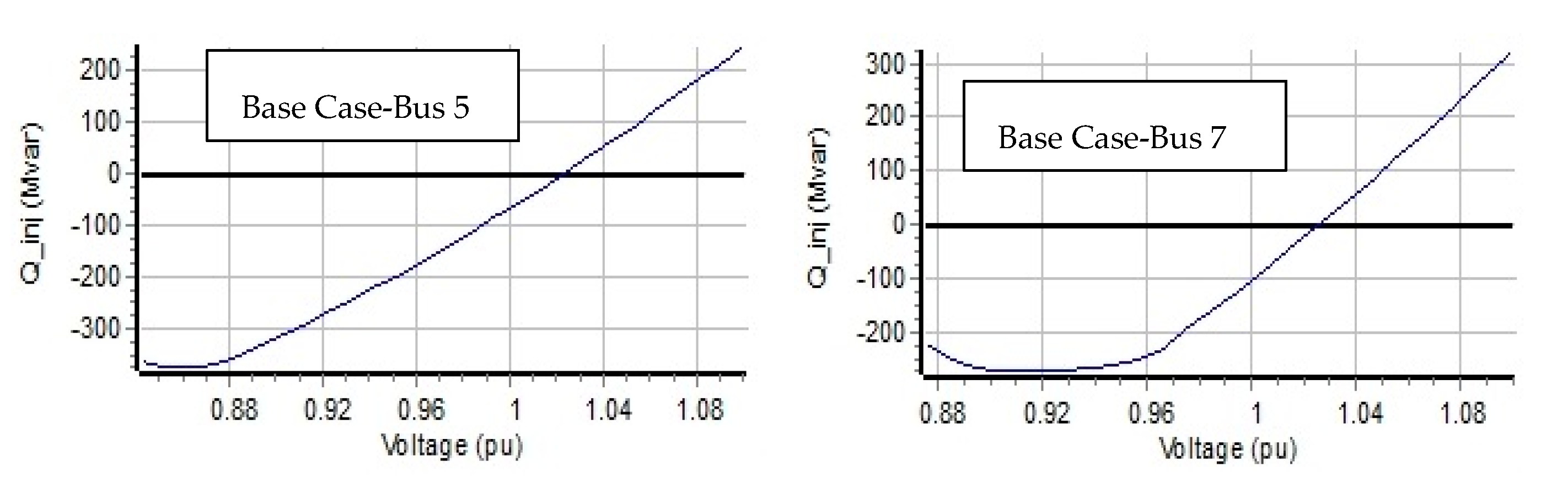
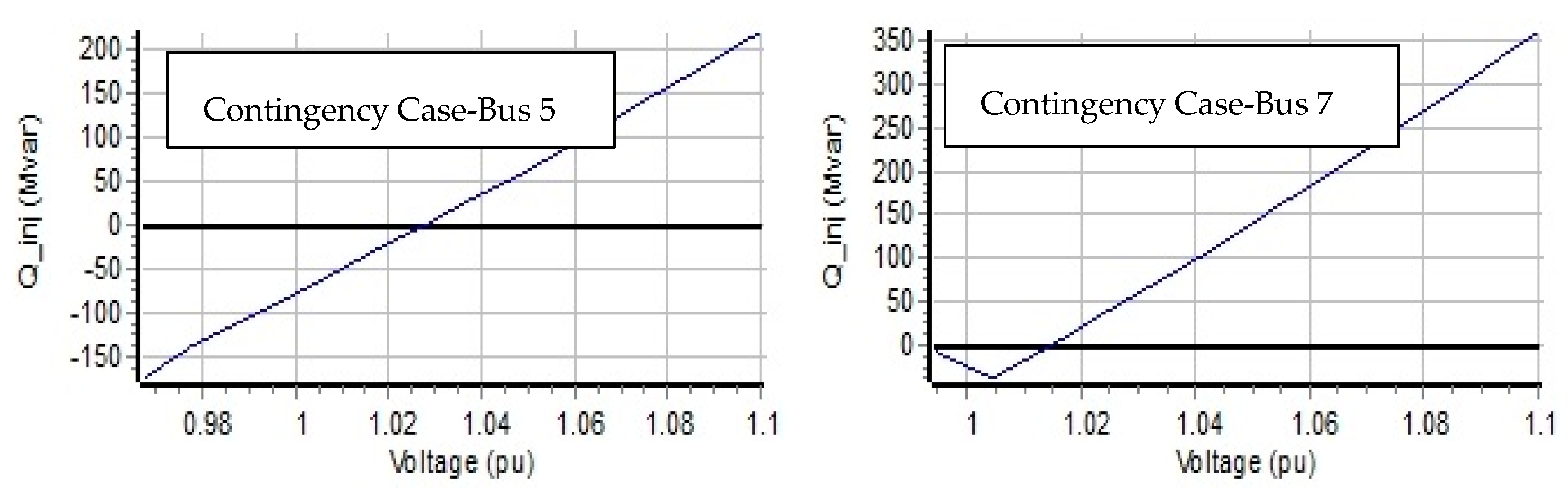
2.2.3. V-Q Sensitivity Analysis
2.2.4. V-P Sensitivity Analysis
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | Ampere |
| AC | Alternating Current |
| BESS | Battery Energy Storage System |
| CC | Constant Current |
| CV | Constant Voltage |
| CC-CV | Constant current Constant voltage |
| DC | Direct Current |
| EF | Electric Fleet |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| F2G | Ferry to Grid |
| G2F | Grid to Ferry |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| Hz | Hertz |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization |
| kW | Kilo Watt |
| kV | Kilo Volt |
| MJ/km | Megajoule per Kilometer |
| MVA | Mega Volt Ampere |
| MW | Mega Watt |
| Mvar | Mega Var |
| PQ | Real Power Reactive Power |
| P-V | Real power Voltage |
| pu | Per Unit |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| Q | Reactive Power |
| Q-V | Reactive Power Voltage |
| V | Volt |
| V2G | Vehicle to Grid |
| V-P | Voltage Real Power |
| V-Q | Voltage Reactive Power |
| SOC | State of Charging |
| THD | Total Harmonic Distortion |
References
- IEA. World Energy Statistics 2017; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.W.P.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Anderson, B.A.; Corbett, J.J.; Faber, J.; Hanayama, S.; O’Keeffe, E.; Parker, S.; Johansson, L.; Aldous, L.; et al. Third IMO GHG Study 2014; International Maritime Organization: London, UK; Micropress Printers: Suffolk, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Buhaug, Ø.; Corbett, J.J.; Endresen, Ø.; Eyring, V.; Faber, J.; Hanayama, S.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, D.; Lindstad, H.; Markowska, A.Z.; et al. Second IMO GHG Study 2009; International Maritime Organization: London, UK; CPI Books Limited: Reading, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zavoda, F.; Puertas, R.R.; Dupre, J.L. Impacts of fast charging stations on grid quality. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Electricity Distribution, CIRED, Madrid, Spain, 3–6 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, R. Quantification of bottlenecks to fast charging of lithium ion-insertion cells for electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2014, 271, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, A.; Kar, K.; Gupta, A. Decentralized Charging of Plug-in Electric Vehicles with Distribution Feeder Overload Control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2016, 61, 3527–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skugor, B.; Deur, J. A novel model of electric vehicle fleet aggregate battery for energy planning studies. Energy 2015, 92, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Su, W.; Hu, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. A hierarchical framework for coordinated charging of plug-in electric vehicles in China. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Østergaard, P.A.; Connolly, D.; Ridjan, I.; Mathiesen, B.V.; Hvelplund, F.; Thellufsen, J.Z.; Sorknæs, P. Energy storage and smart energy systems. Int. J. Sustain. Energy Plan. Manag. March 2016, 11, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kempton, W.; Tomic, J. Vehicle-to-Grid Power Implementation: From Stabilizing the Grid to Supporting Largescale Renewable Energy. J. Power Sources 2005, 144, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Houghton, T.; Cruden, A.; Infield, D. Modeling the benefits of vehicle-togrid technology to a power system. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skugor, B.; Deur, J. A techno-economic analysis of an isolated energy system including electric delivery vehicle fleet and renewable energy sources. In Proceedings of the 10th Conference on Sustainable Development of Energy, Water and Environment Systems (SDEWES), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 27 September–2 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, S.; Kamran, M.; Rashid, U. Impact analysis of vehicle to grid technology and charging strategies of electric vehicles on distribution networks—A review. J. Power Sources 2015, 277, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifeng, H.; Venkatesh, B.; Guan, L. Optimal scheduling for charging and discharging of electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, K.; Denholm, P.; Markel, T. Costs and Emissions Associated with Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle Charging in the Xcel Energy Colorado Service Territory; Tech. Rep. NREL/TP-640-41410; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Boulder, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, A.; Ilg, J.; Van Dinther, C. Benchmarking Electric Vehicle Charging Control Strategies. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT), Berlin, Germany, 14–17 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, M.; Oda, T.; Ito, M. Battery Assisted Charging System for Simultaneous Charging of Electric Vehicles. Energy 2016, 100, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Padhy, N.P. Resilient scheduling portfolio of residential device sand plug-in electric vehicle by minimizing conditional value at risk. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2019, 15, 1566–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabaggio, P.; Carli, R.; Cavone, G.; Dotoli, M. Smart Control Strategies for Primary Frequency Regulation through Electric Vehicles: A Battery Degradation Perspective. Energies 2020, 13, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Werner, S.; Wiltshire, R.; Svendsen, S.; Thorsen, J.E.; Hvelplund, F.; Mathiesen, B.V. 4th Generation District Heating (4GDH): Integrating smart thermal grids into future sustainable energy systems. Energy 2014, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, R.; Dotoli, M.; Jantzen, J.; Kristensen, M.; Othman, B.S. Energy Scheduling of a Smart Microgrid with shared Photovoltaic Panels and Storage: The case of the Bllen Marina in Samsø. Energy 2020, 198, 117188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, C.; Sun, J.; Zheng, P.; Lin, X.; Bo, Z. Impacts of electric vehicles on the transient voltage stability of distribution network and the study of improvement measures. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Hong Kong, China, 7–10 December 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmakeerthi, C.H.; Mithulananthan, N.; Saha, T.K. Impact of electric vehicle fast charging on power system voltage stability. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 57, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmakeerthi, C.H.; Mithulananthan, N.; Saha, T.K. Overview of the impacts of plug-in electric vehicles on the power grid. In Proceedings of the Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT) Asia Conference, Perth, Australia, 13–16 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Clement-Nyns, K.; Haesen, E.; Driesen, J. The impact of charging plug-in hybrid electric vehicles on a residential distribution grid. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, A.; Paterakis, N.G.; Santarelli, M.; Gibescu, M. Optimizing the operation of energy storage using non-linear lithium-ion battery degradation model. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, P.; Manyage, M. Definitions of voltage unbalance. IEEE Power Eng. Rev. 2001, 5, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
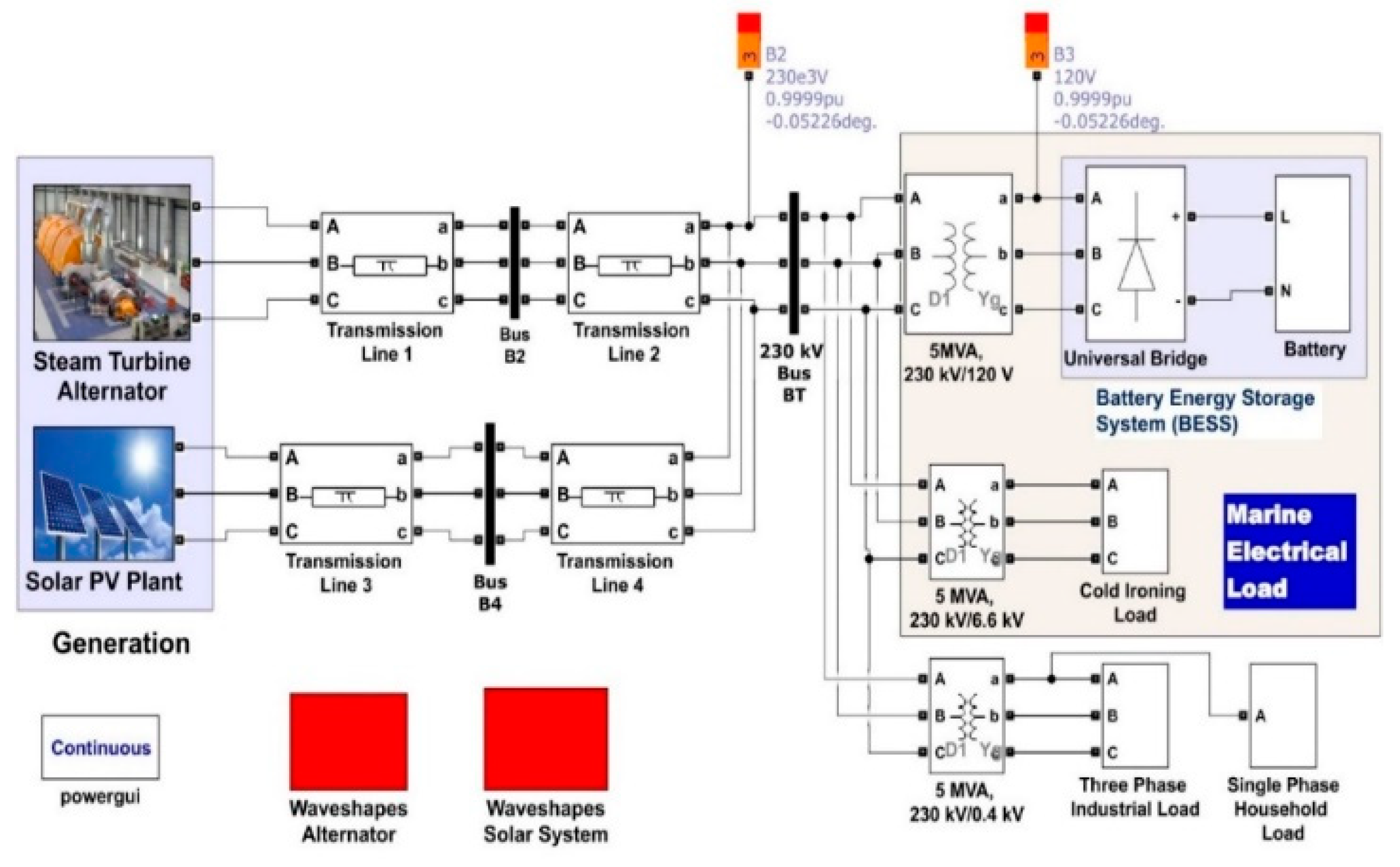
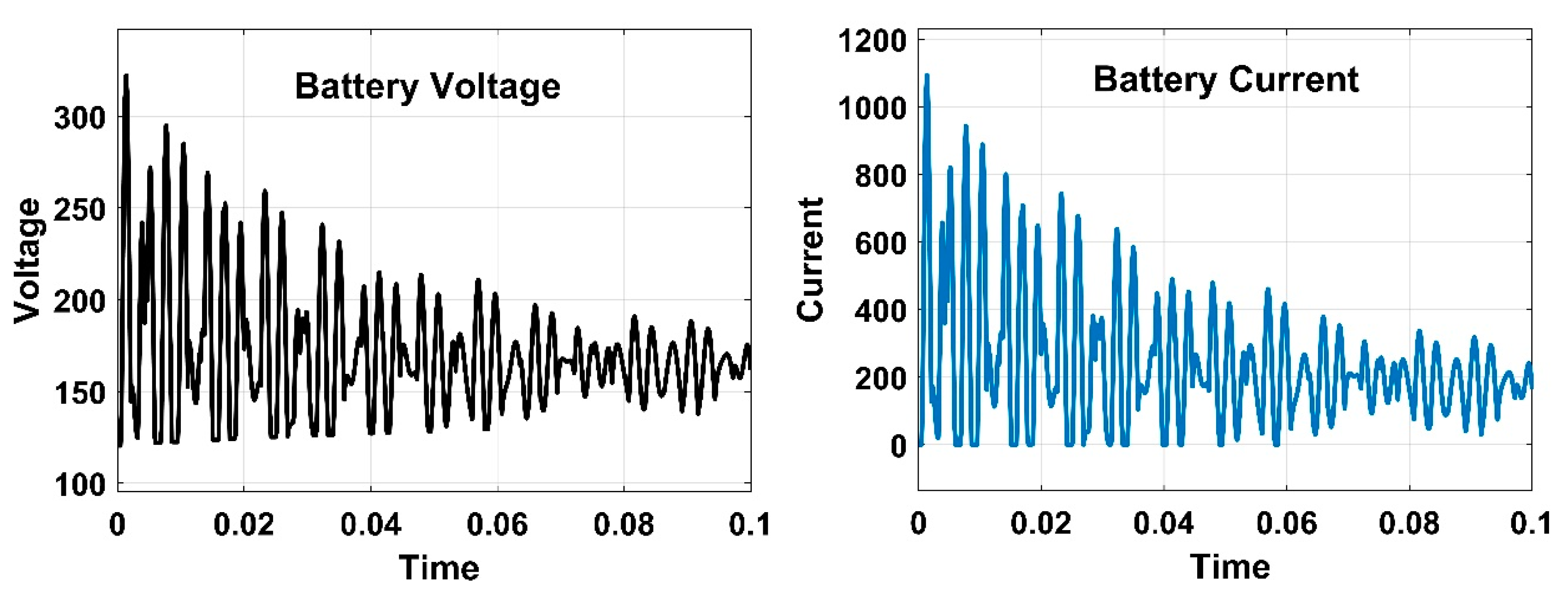

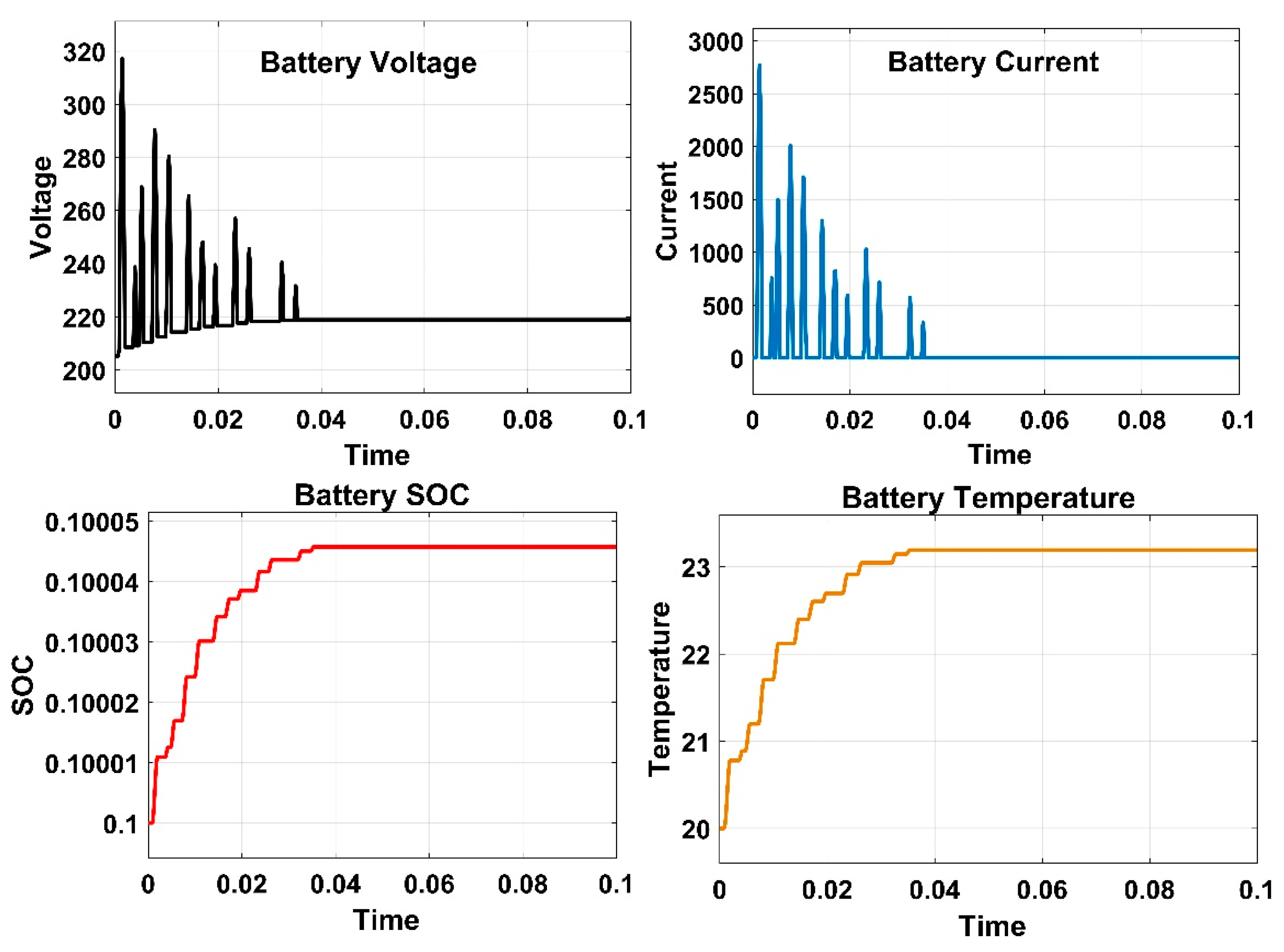
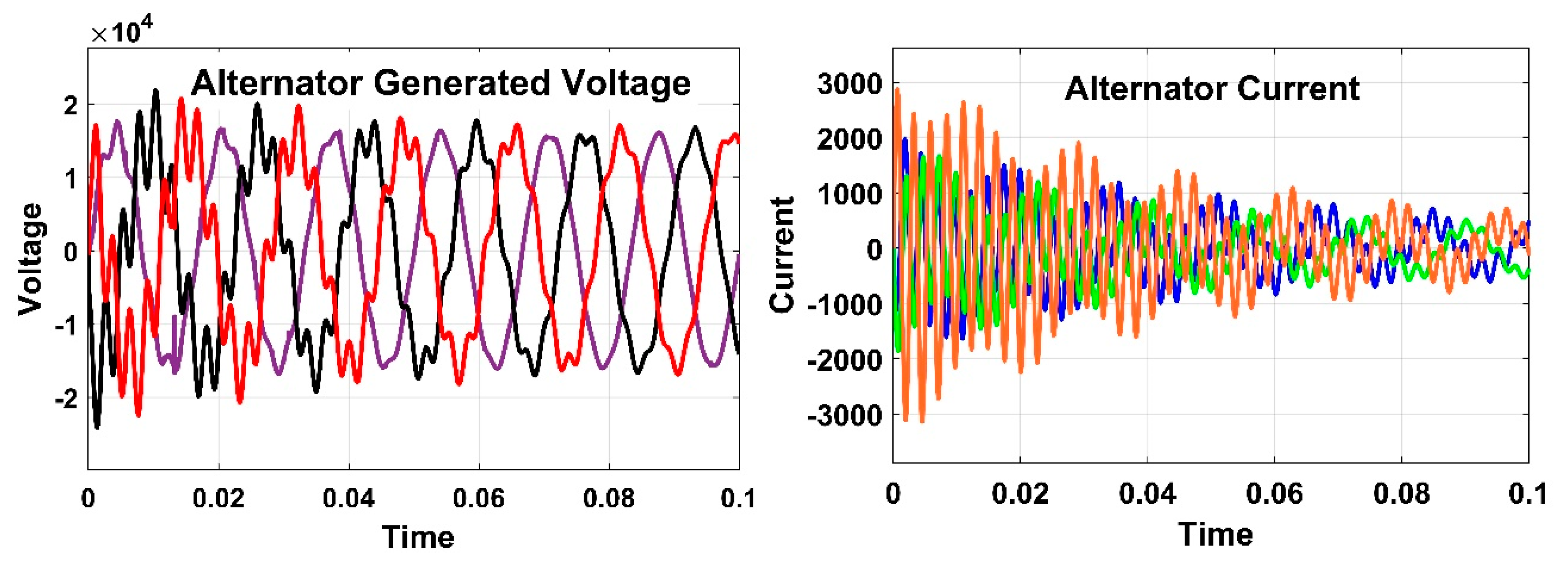
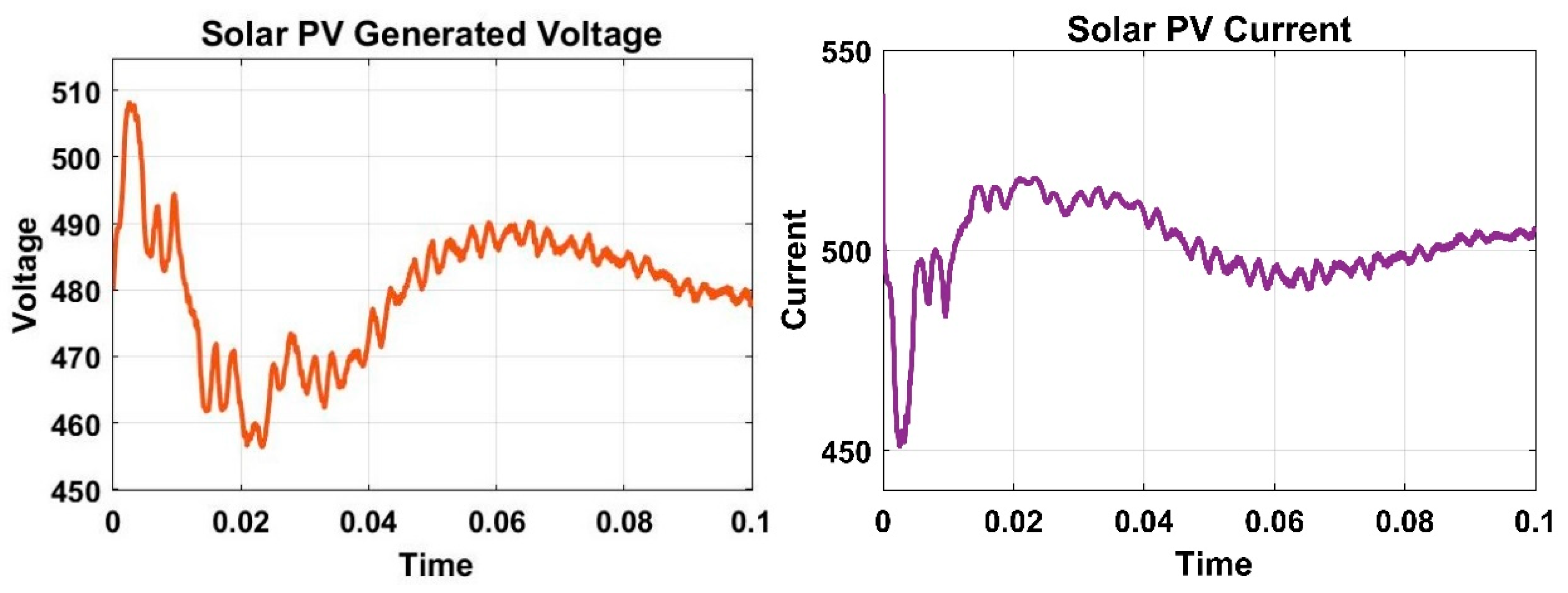
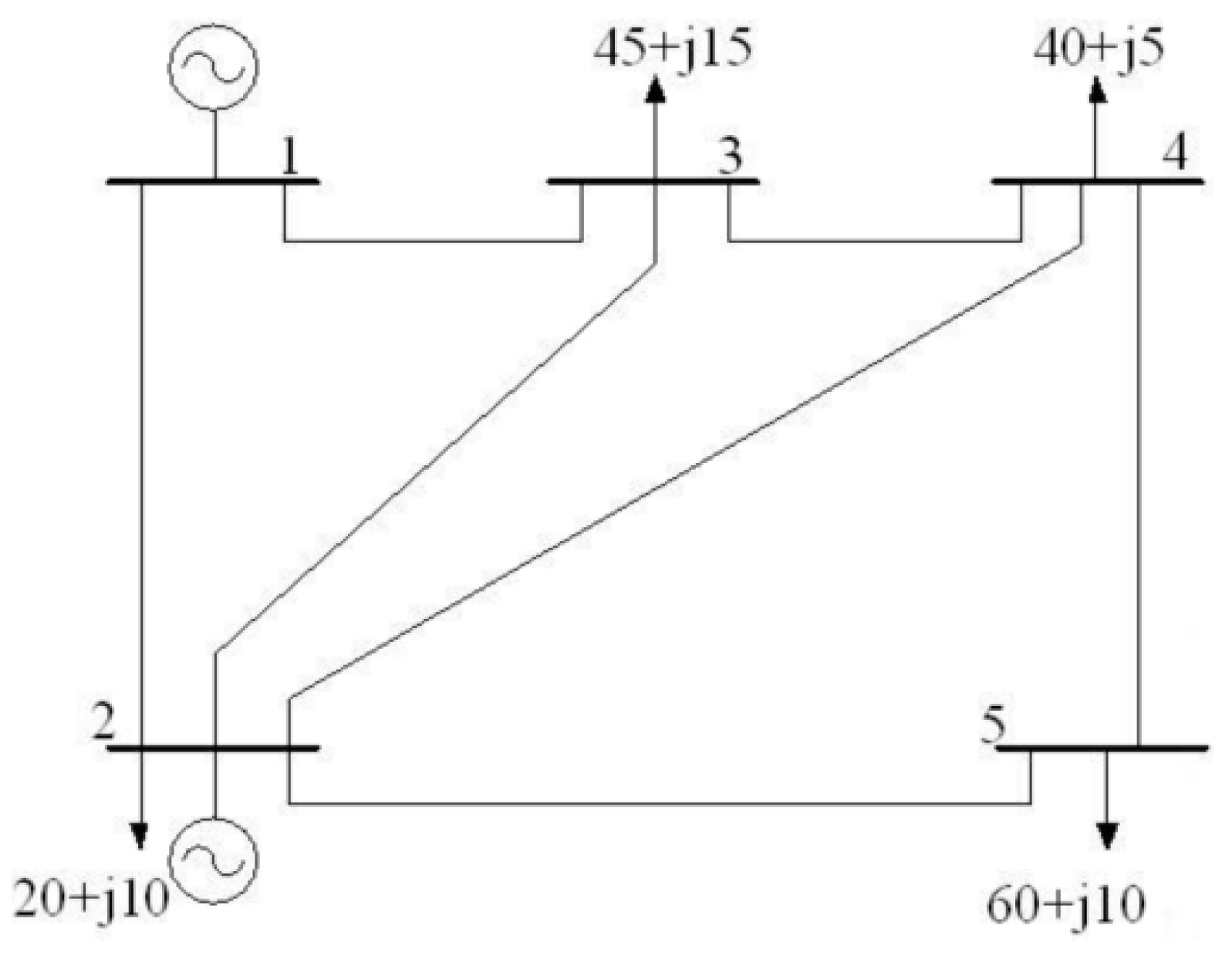
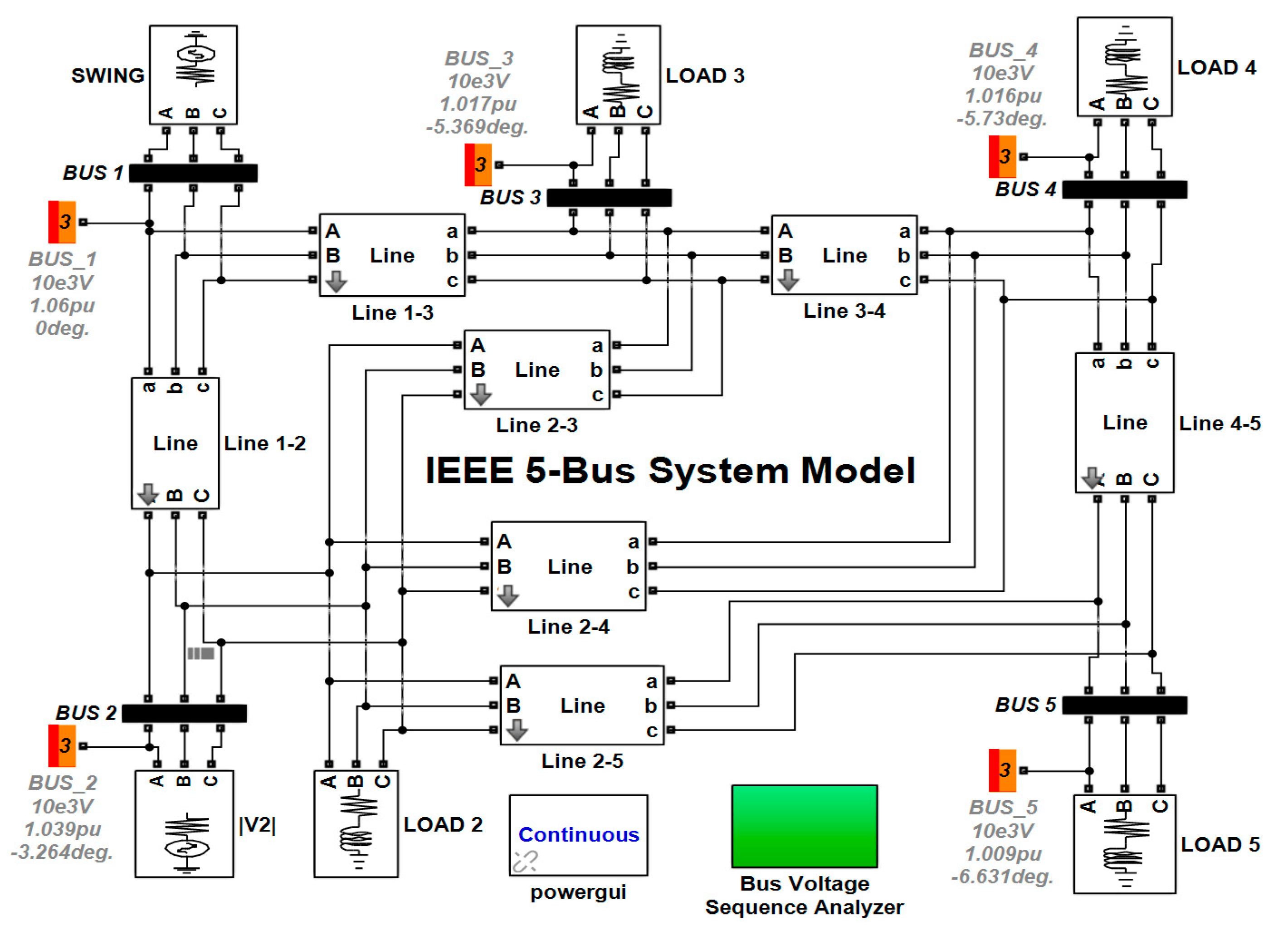
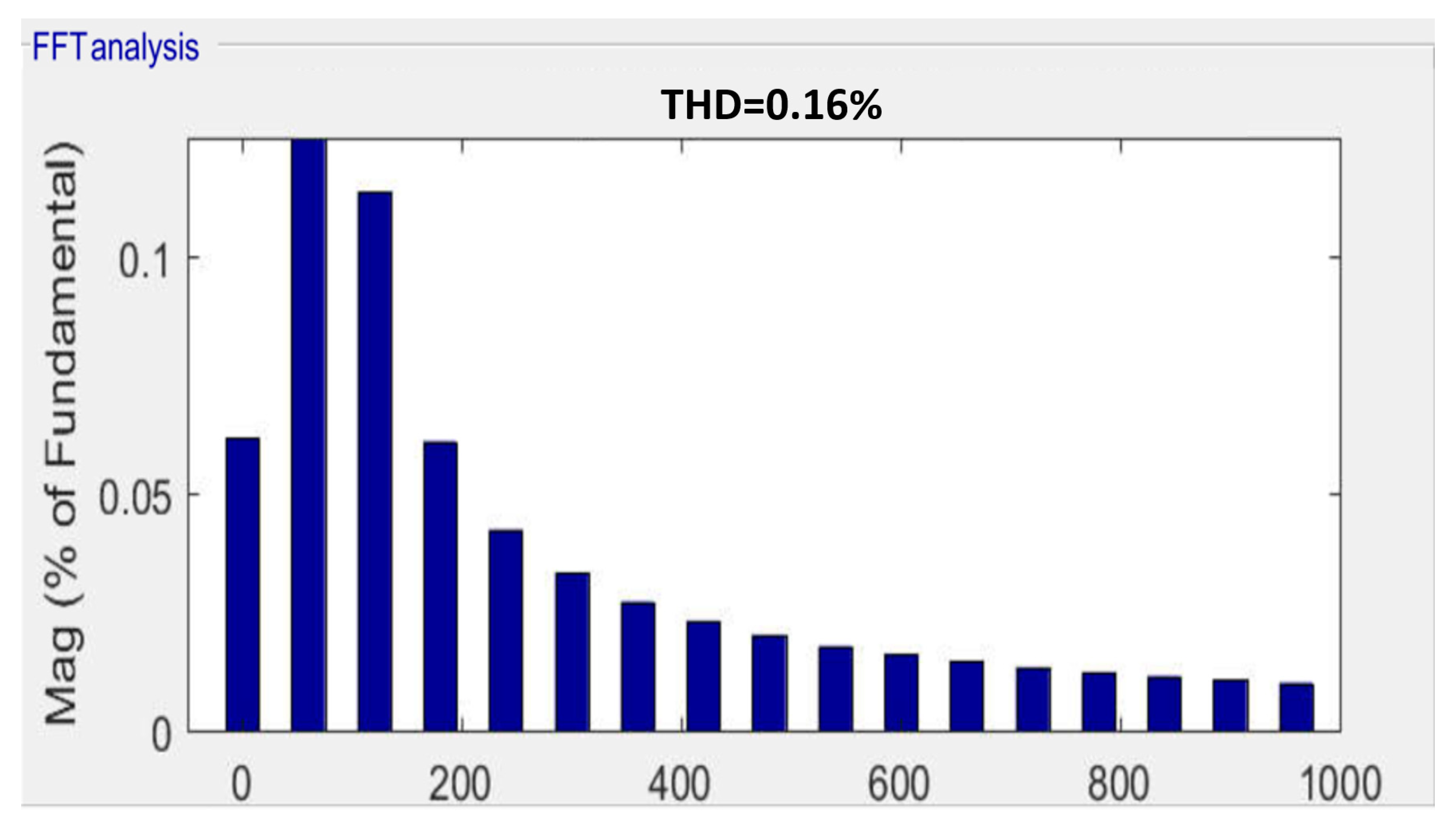

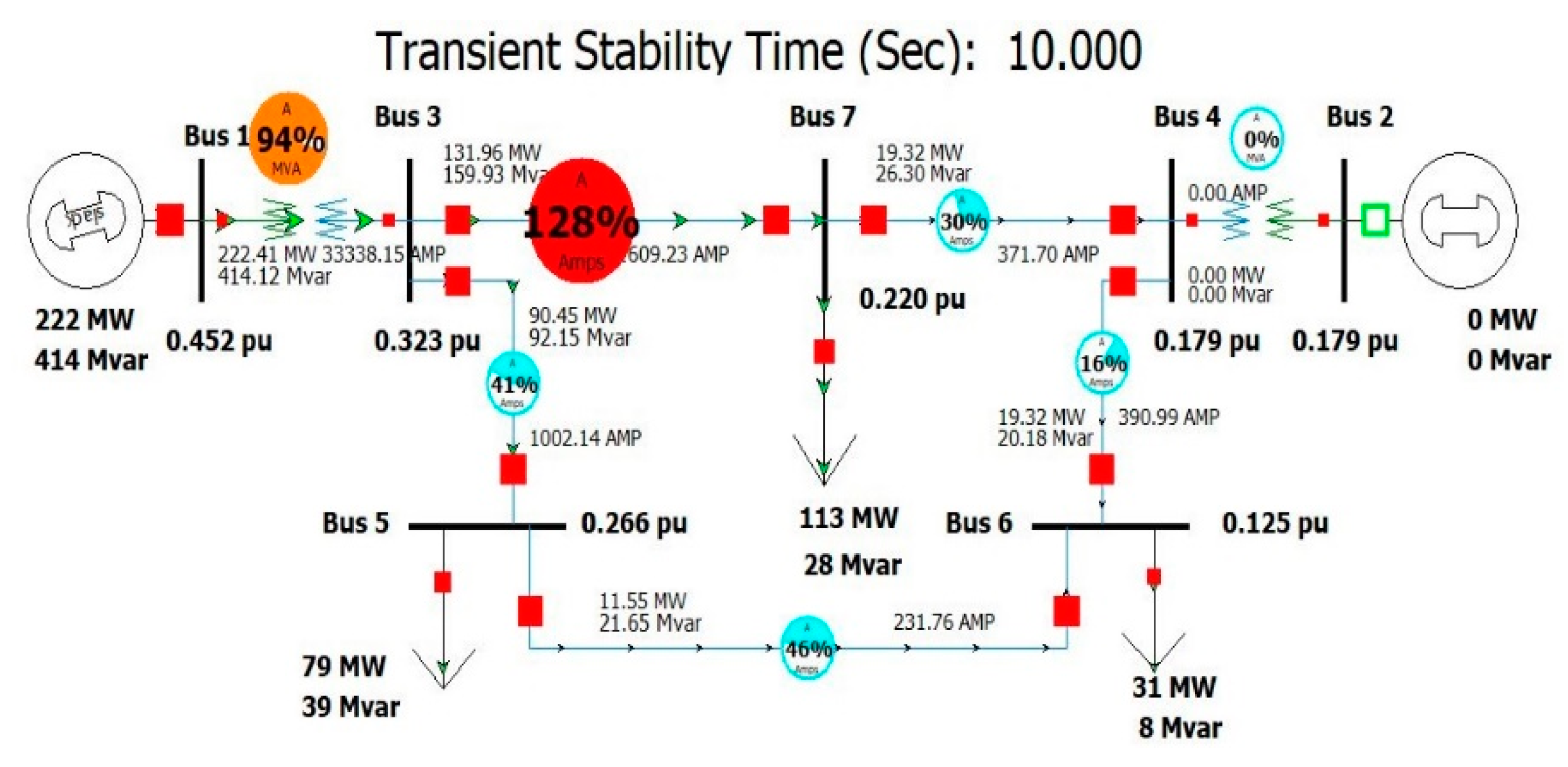
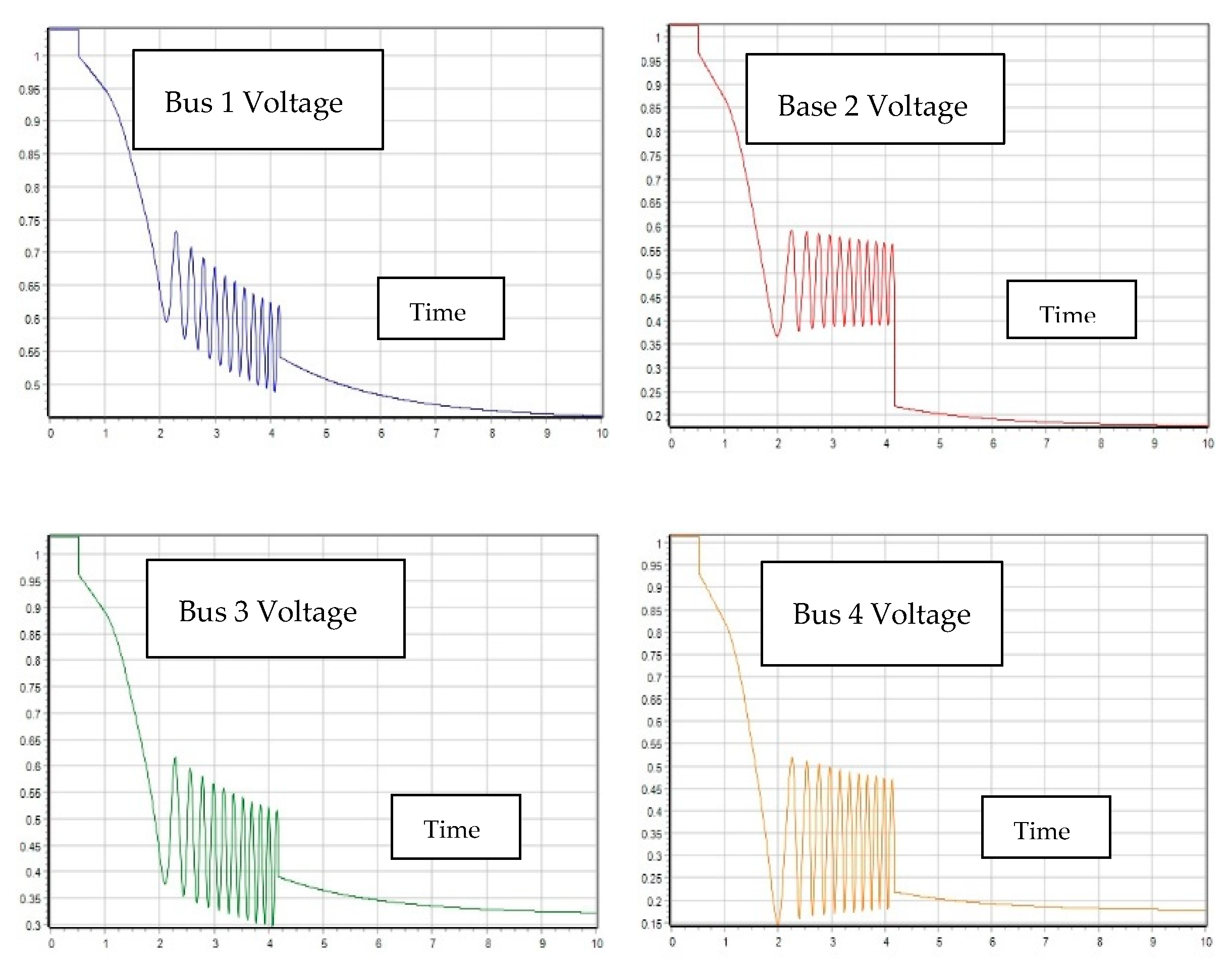
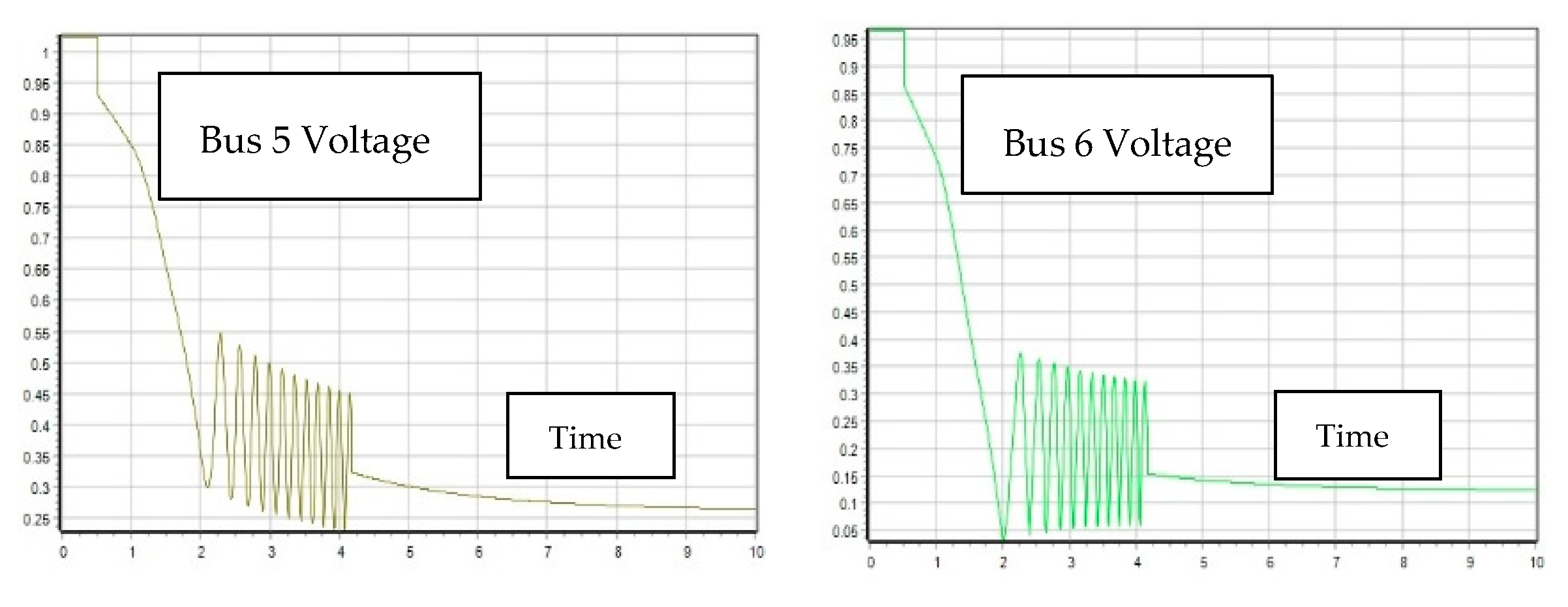
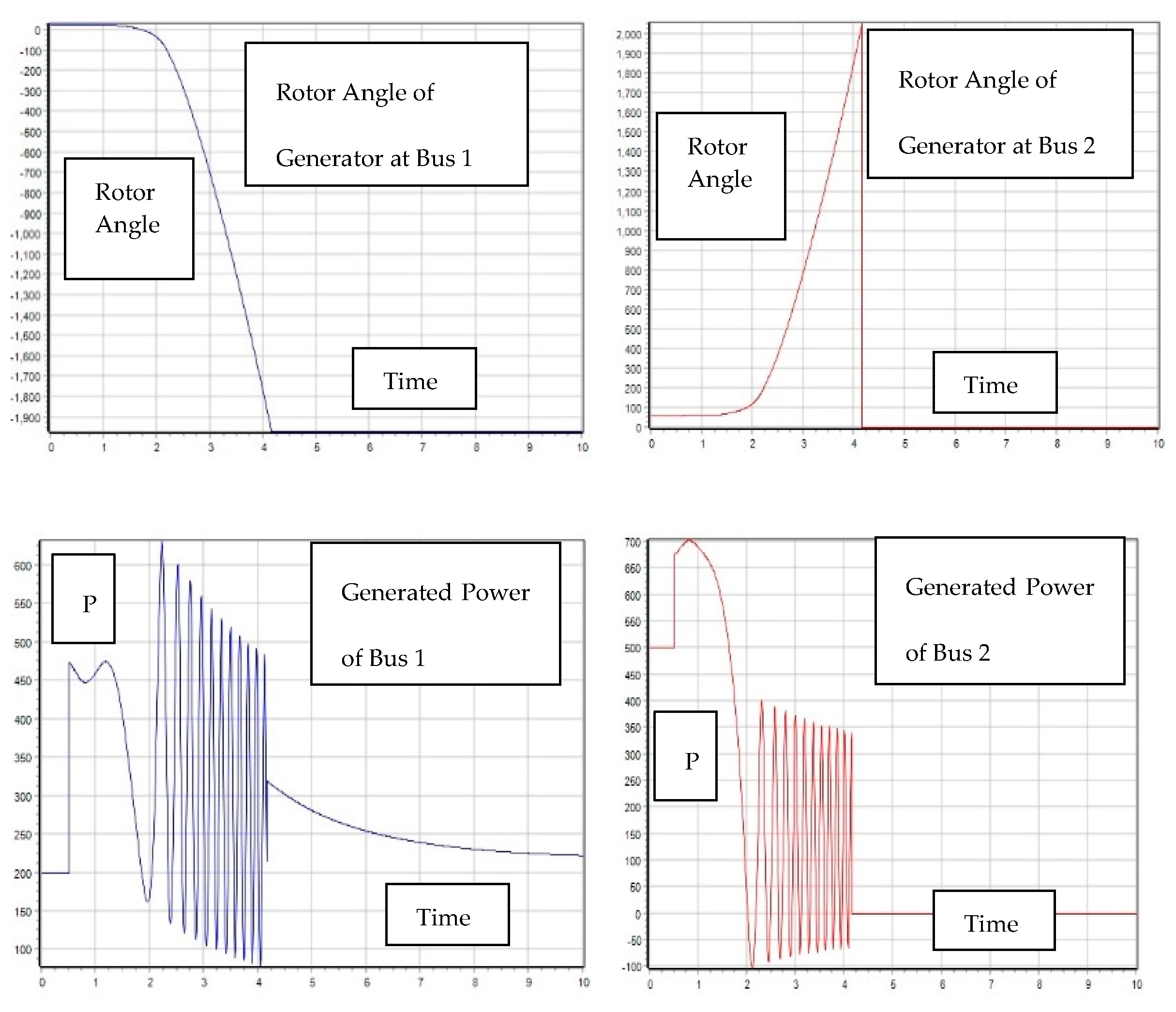
| Bus No. | Generation | Load Demand | Bus Voltage | Total Generation | Total Load | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar | Voltage (pu) | Angle (degree) | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar |
| 1 | 129.59 | −7.42 | 0 | 0 | 1.06 | 0 | 169.59 | 22.58 | 165 | 40 |
| 2 | 40 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 1.0474 | −2.8063 | ||||
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 45 | 15 | 1.0242 | −4.997 | ||||
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 5 | 1.0236 | −5.3291 | ||||
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 10 | 1.0179 | −6.1503 | ||||
| Bus No. | Generation | Load Demand | Bus Voltage | Total Generation | Total Load | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar | Voltage (pu) | Angle (degree) | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar |
| 1 | 173.87 | 12.50 | 0 | 0 | 1.06 | 0 | 213.87 | 42.50 | 206 | 50 |
| 2 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 12.5 | 1.0341 | −3.71 | ||||
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 55 | 17.5 | 1.0049 | −6.41 | ||||
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 51.26 | 7.5 | 1.0032 | −6.84 | ||||
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 12.5 | 0.9965 | −7.75 | ||||
| Bus No. | Generation | Load Demand | Bus Voltage | Total Generation | Total Load | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar | Voltage (pu) | Angle (degree) | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar |
| 1 | 219.20 | 35.67 | 0 | 0 | 1.06 | 0 | 259.20 | 65.67 | 247.5 | 60 |
| 2 | 40 | 30 | 40 | 15 | 1.0196 | −4.64 | ||||
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 65 | 20 | 0.9839 | −7.88 | ||||
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 62.5 | 10 | 0.9811 | −8.44 | ||||
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 15 | 0.9732 | −9.44 | ||||
| Bus No. | Generation | Load Demand | Bus Voltage | Total Generation | Total Load | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar | Voltage (pu) | Angle (degree) | MW | Mvar | MW | Mvar |
| 1 | 265.79 | 62.66 | 0 | 0 | 1.06 | 0 | 305.79 | 92.66 | 288.75 | 70 |
| 2 | 40 | 30 | 50 | 17.5 | 1.0037 | −5.60 | ||||
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 75 | 22.5 | 0.9610 | −9.45 | ||||
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 73.75 | 12.5 | 0.9569 | −10.13 | ||||
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 17.5 | 0.9477 | −11.25 | ||||
| Bus Voltage, V | Total Harmonic Distortion |
|---|---|
| V <= 10 kV | 8% |
| 10 kV < V <= 69 kV | 5% |
| 69 kV < V <= 161 kV | 2.5% |
| 161 kV < V | 1.5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, R.B.; Alahakoon, S.; Arachchillage, S.J. Grid Impacts of Uncoordinated Fast Charging of Electric Ferry. Batteries 2021, 7, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7010013
Roy RB, Alahakoon S, Arachchillage SJ. Grid Impacts of Uncoordinated Fast Charging of Electric Ferry. Batteries. 2021; 7(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Rajib Baran, Sanath Alahakoon, and Shantha Jayasinghe Arachchillage. 2021. "Grid Impacts of Uncoordinated Fast Charging of Electric Ferry" Batteries 7, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7010013
APA StyleRoy, R. B., Alahakoon, S., & Arachchillage, S. J. (2021). Grid Impacts of Uncoordinated Fast Charging of Electric Ferry. Batteries, 7(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7010013




