Binding Energy Referencing for XPS in Alkali Metal-Based Battery Materials Research (II): Application to Complex Composite Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
- (i)
- Our work is as mentioned already not focused to study the detailed changes in chemical states in the samples, but should be a practical guide for the experimentalist to find the right way for BE referencing in such battery materials. Thus, we are not focusing on a quantification of amounts of chemical species in the samples.
- (ii)
- Many of the investigated surfaces are covered with mixtures of several species, which makes their identification really complex.
- (iii)
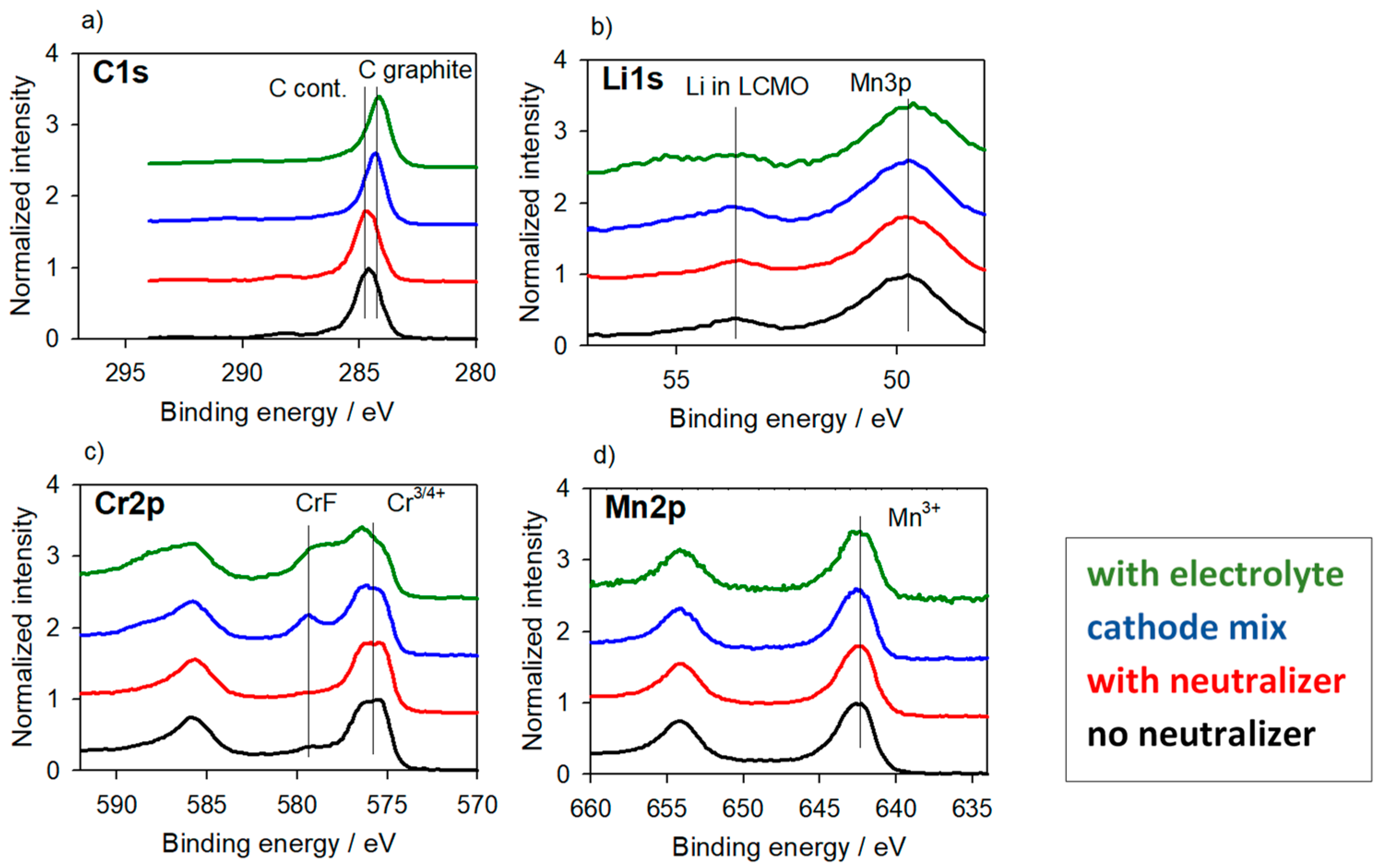
- As also discussed in previous works [19,21], the absolute values of the BE shift from the “alkaline effect” obviously depend on the near-surface Li-concentration and -distribution, which varies in our examples from case to case. In addition, the exact determination of the shifts is not really beneficial.
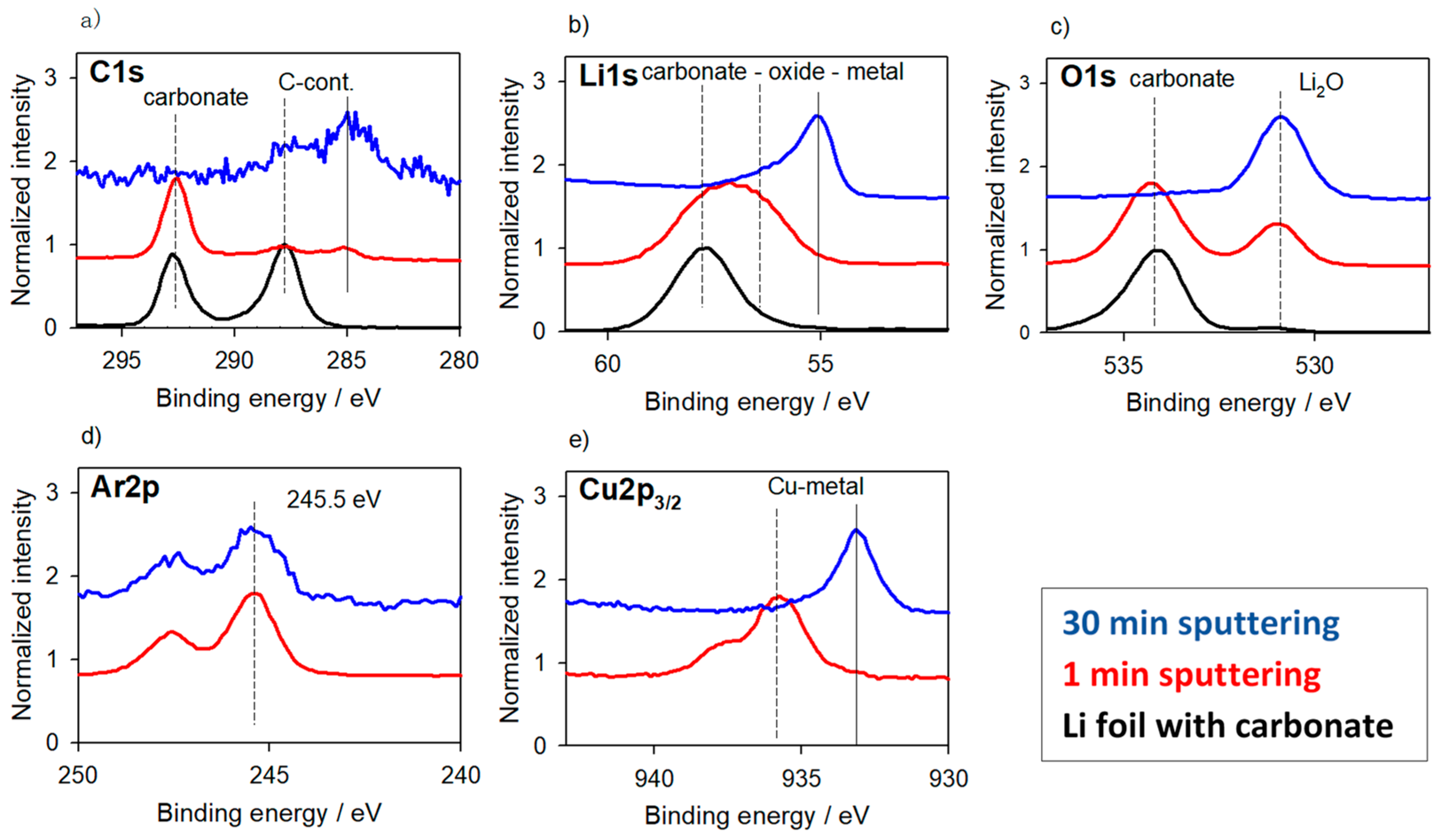
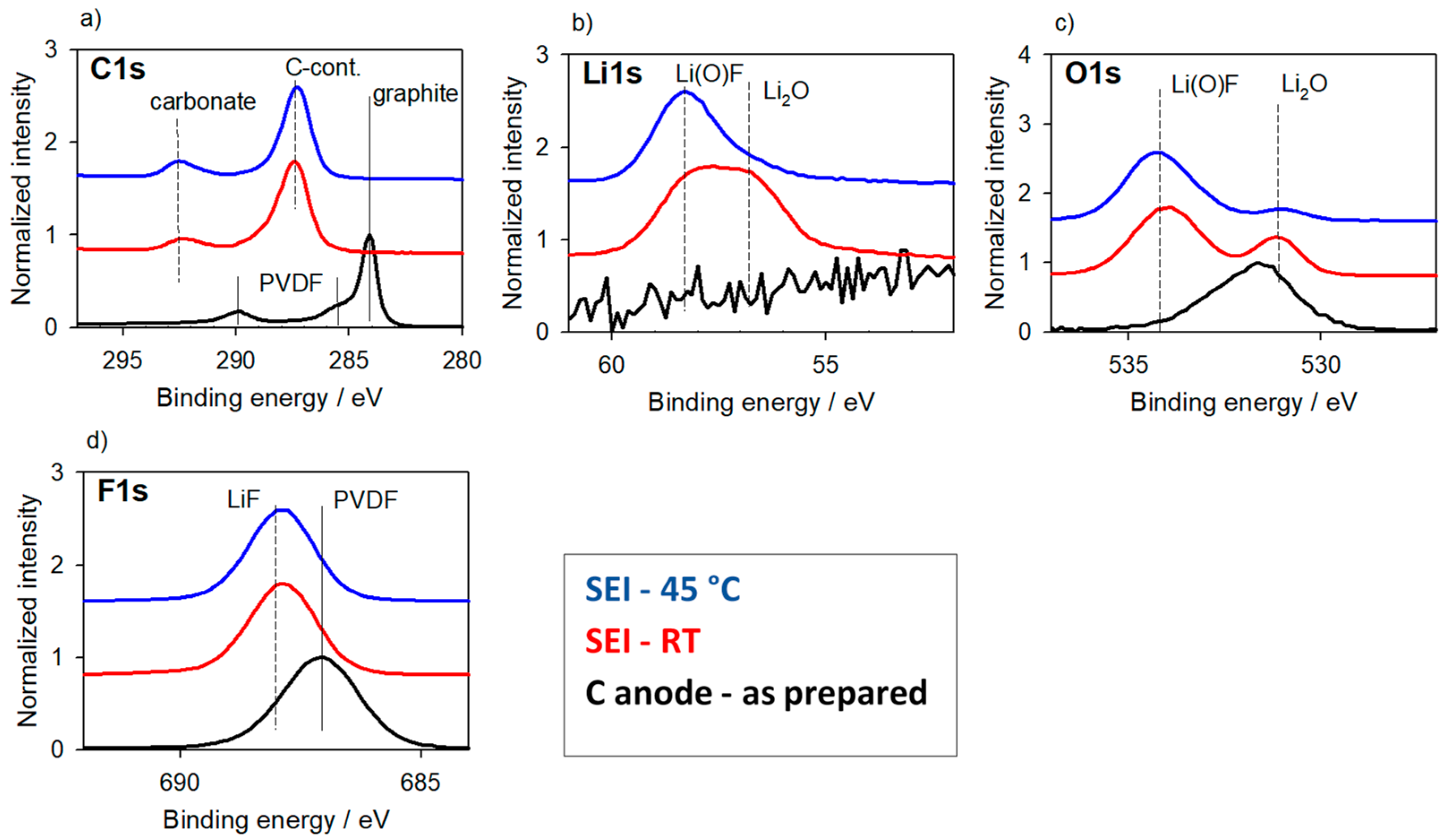
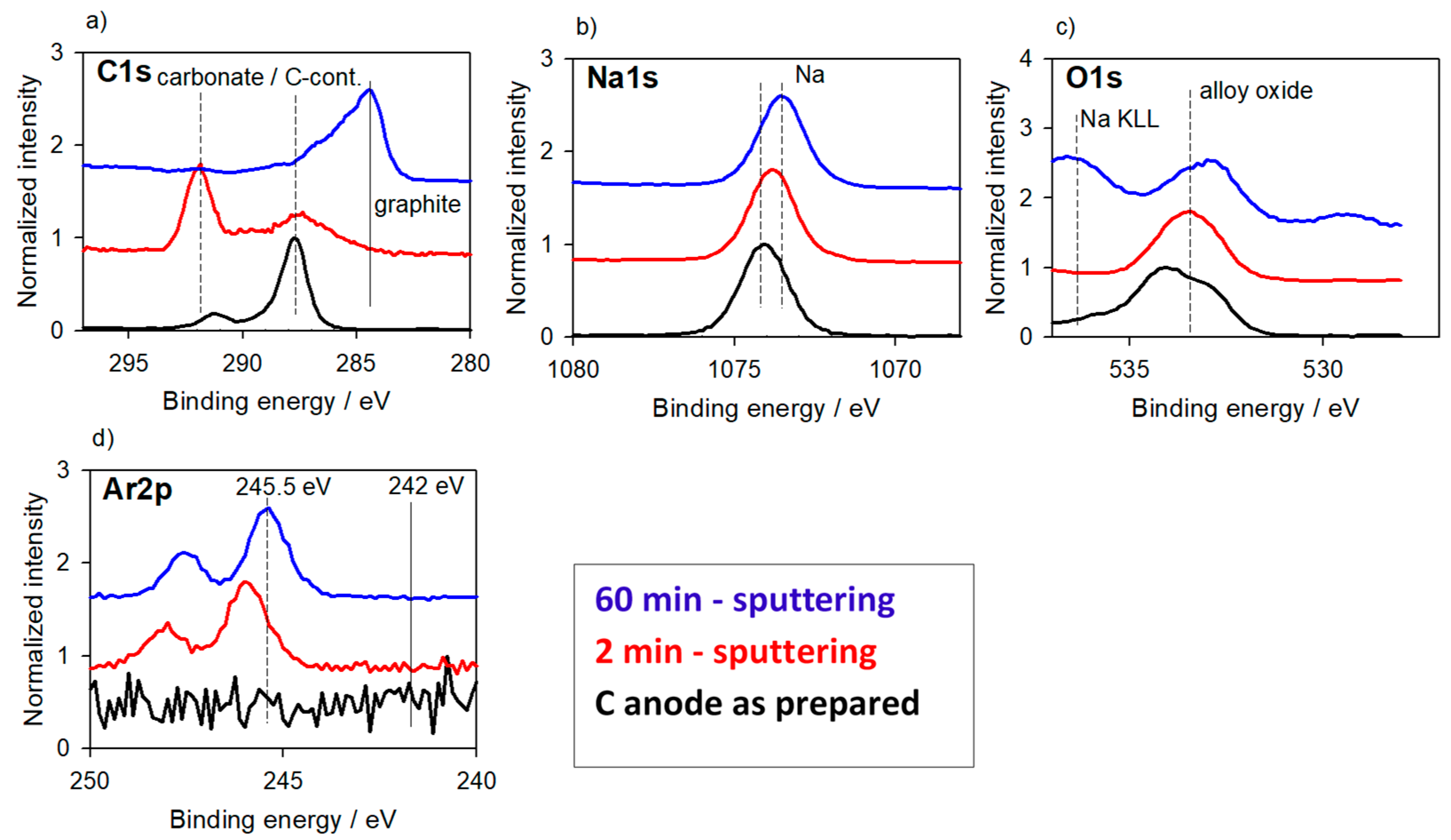
3.1. Reaction Layers—Without Surface Charging
3.1.1. Li-Metal Foil
3.1.2. Carbon-Based Anode Materials
3.1.3. Cathode Material
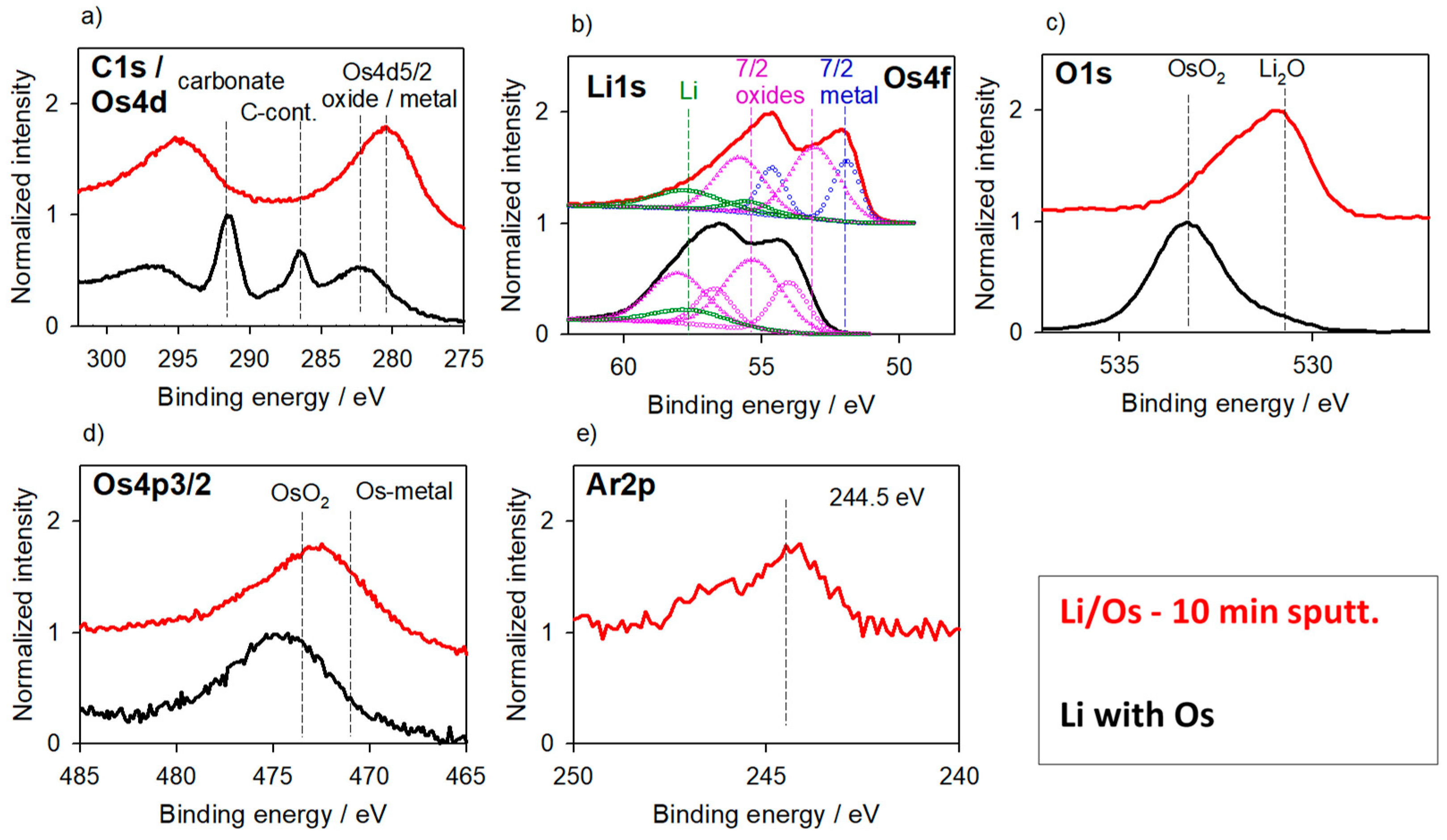
3.2. Reaction Layers—With Surface Charging
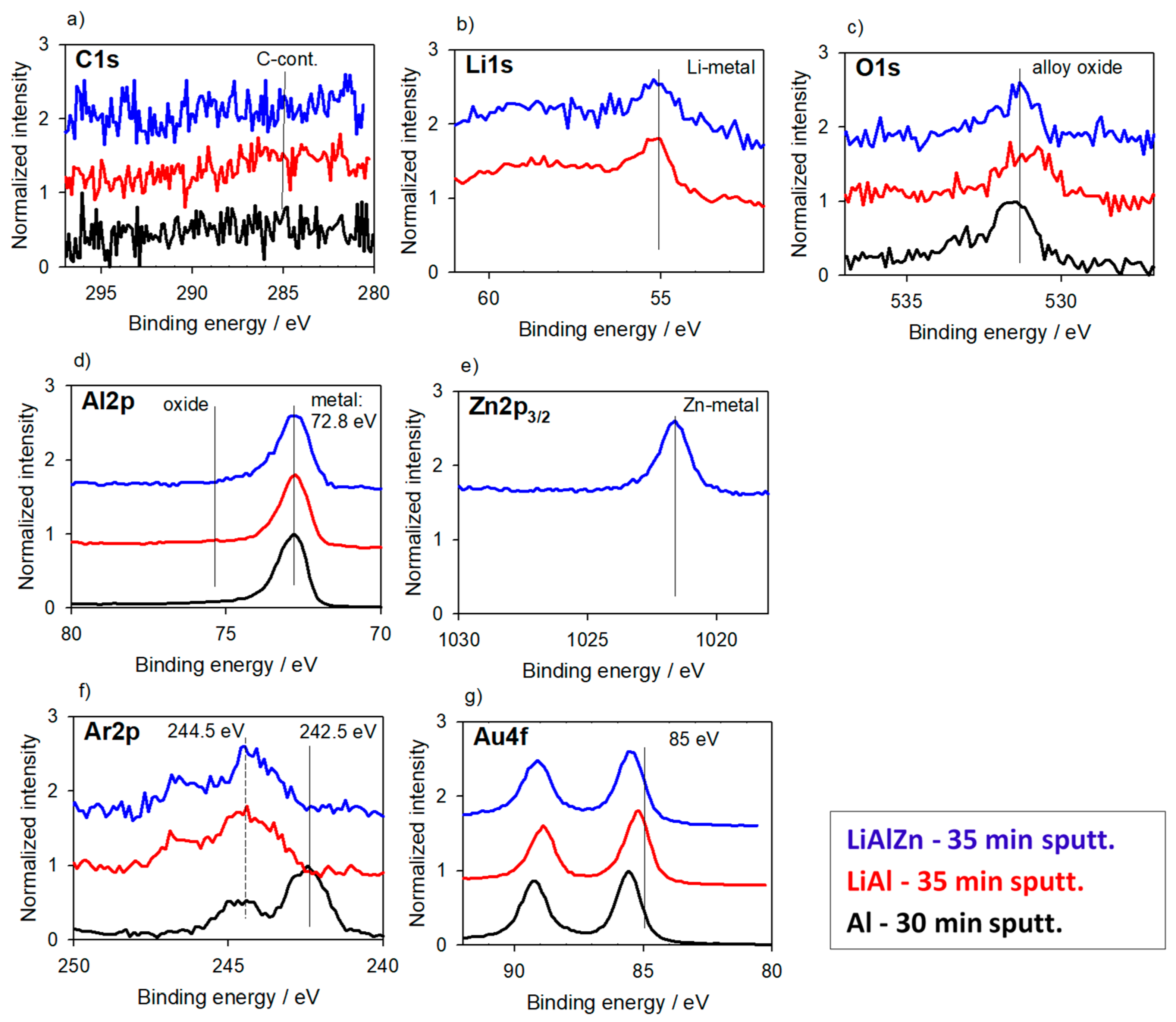
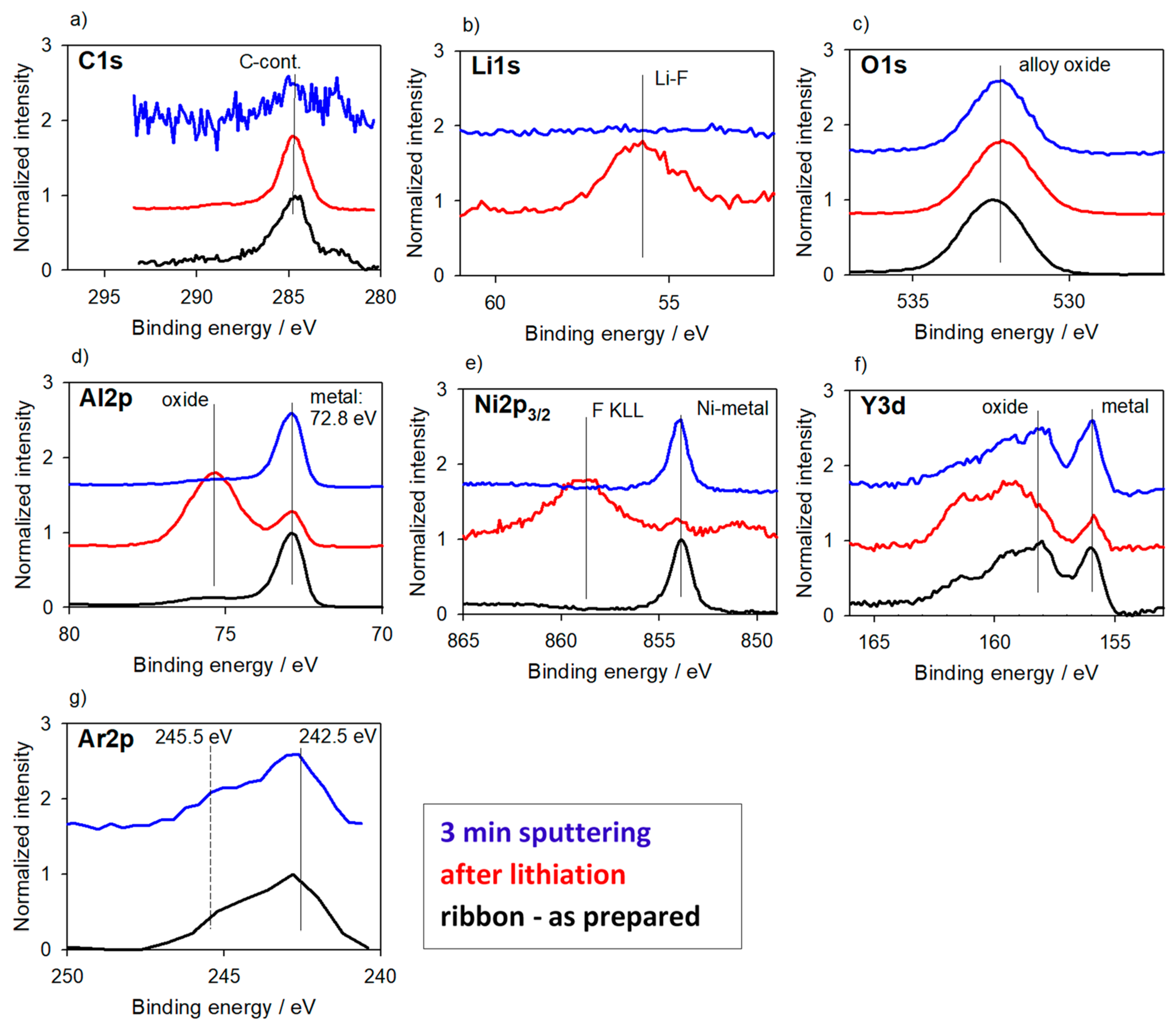
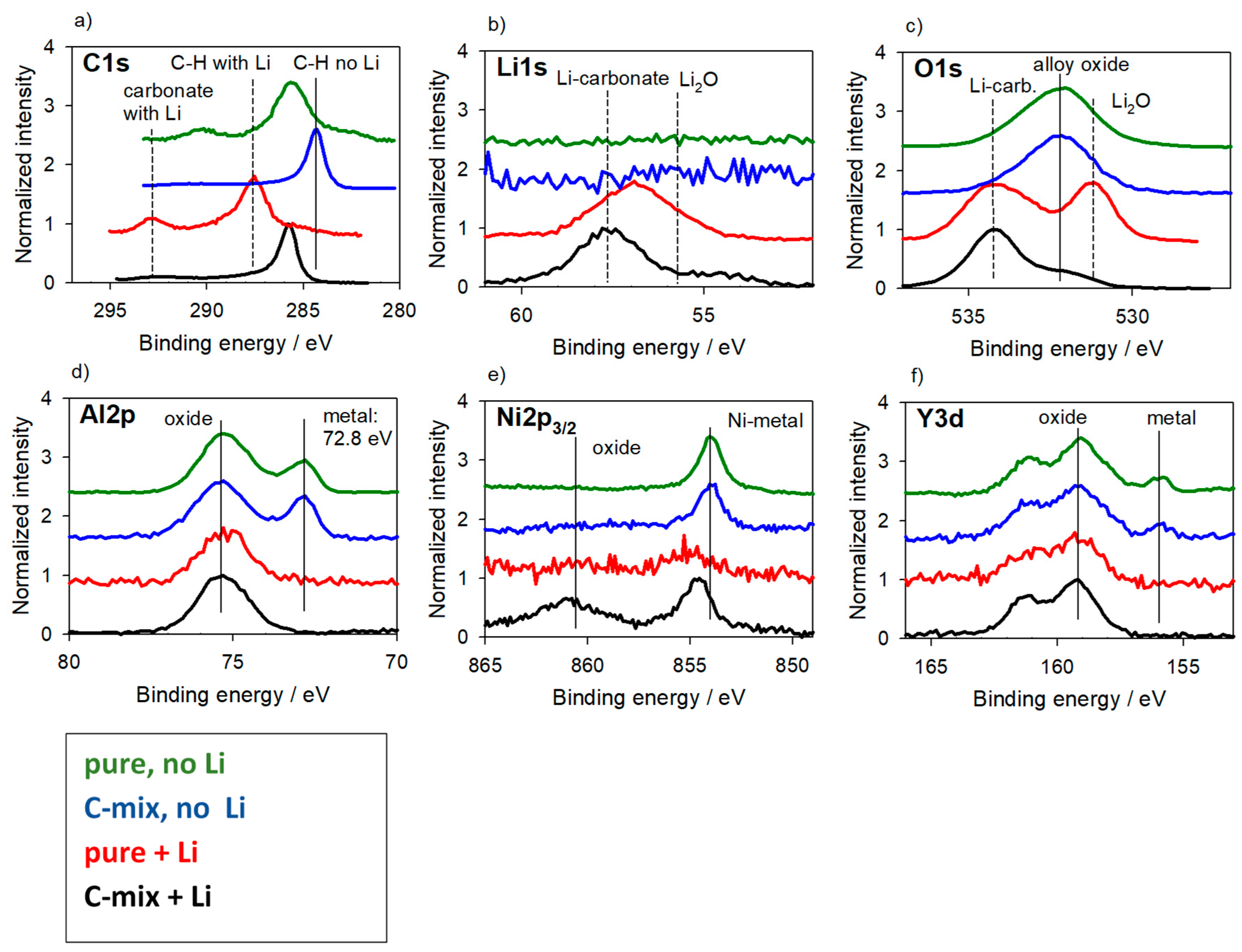
3.2.1. Alloys for Anodes
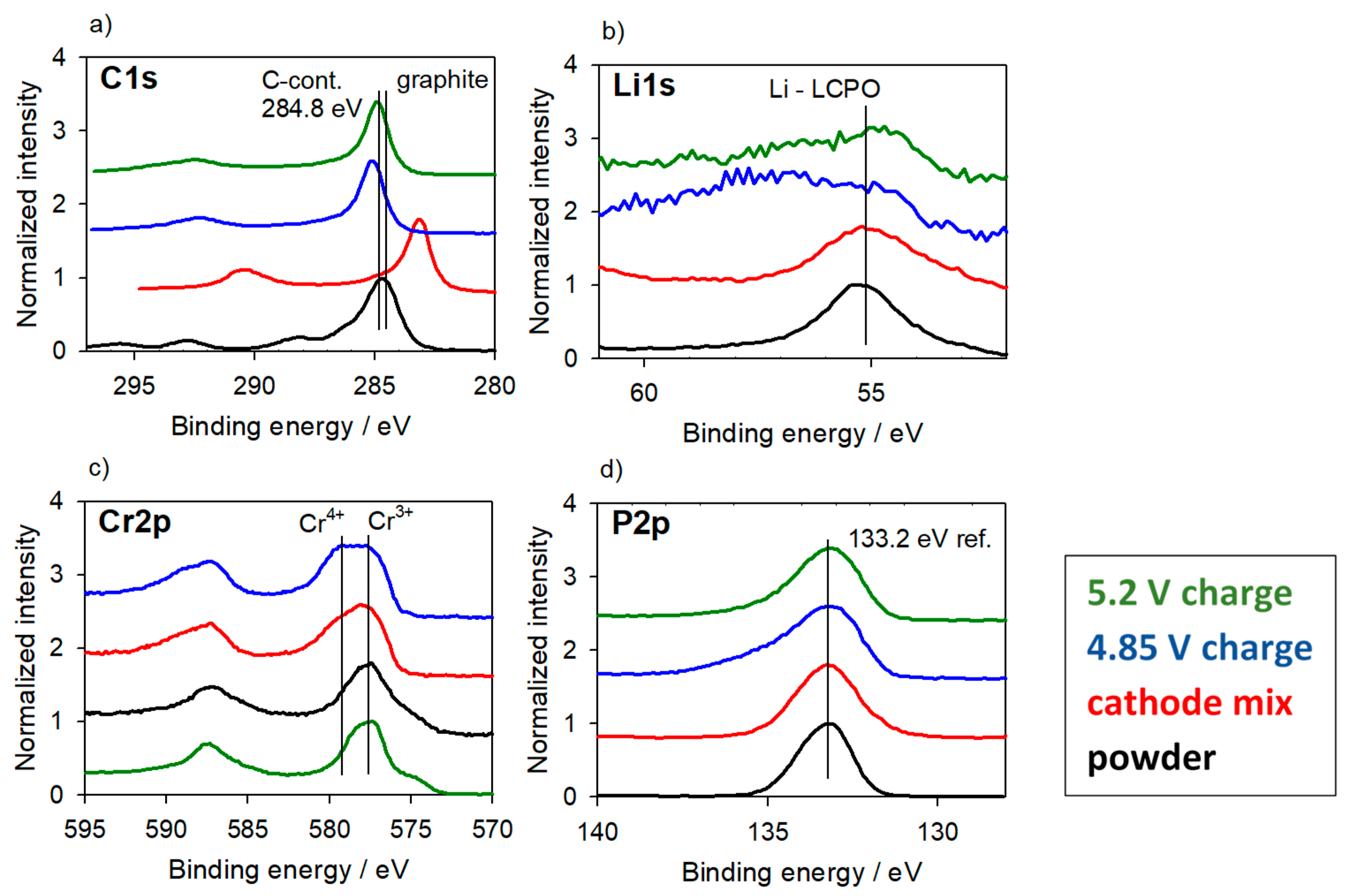
3.2.2. Cathode Material
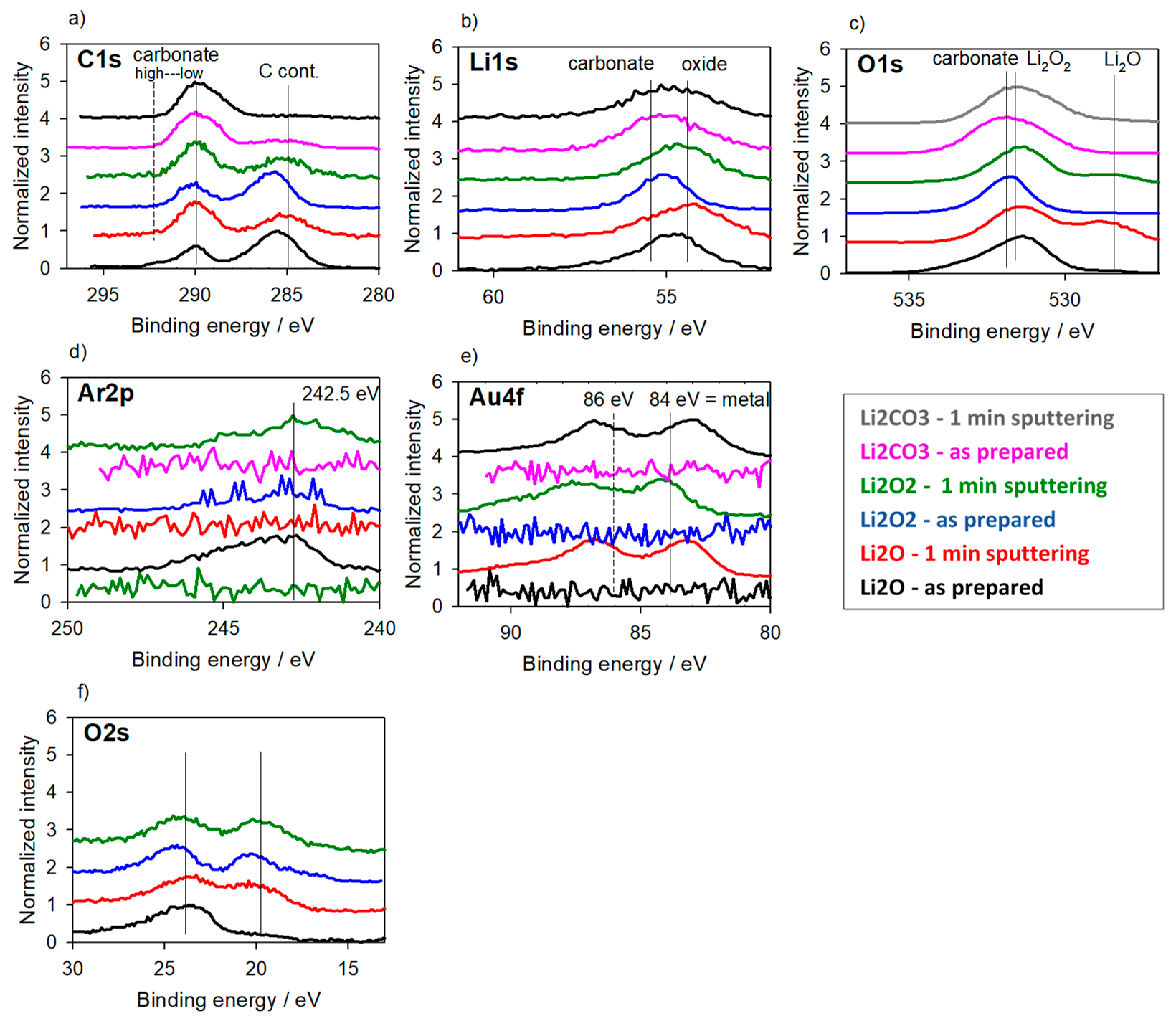
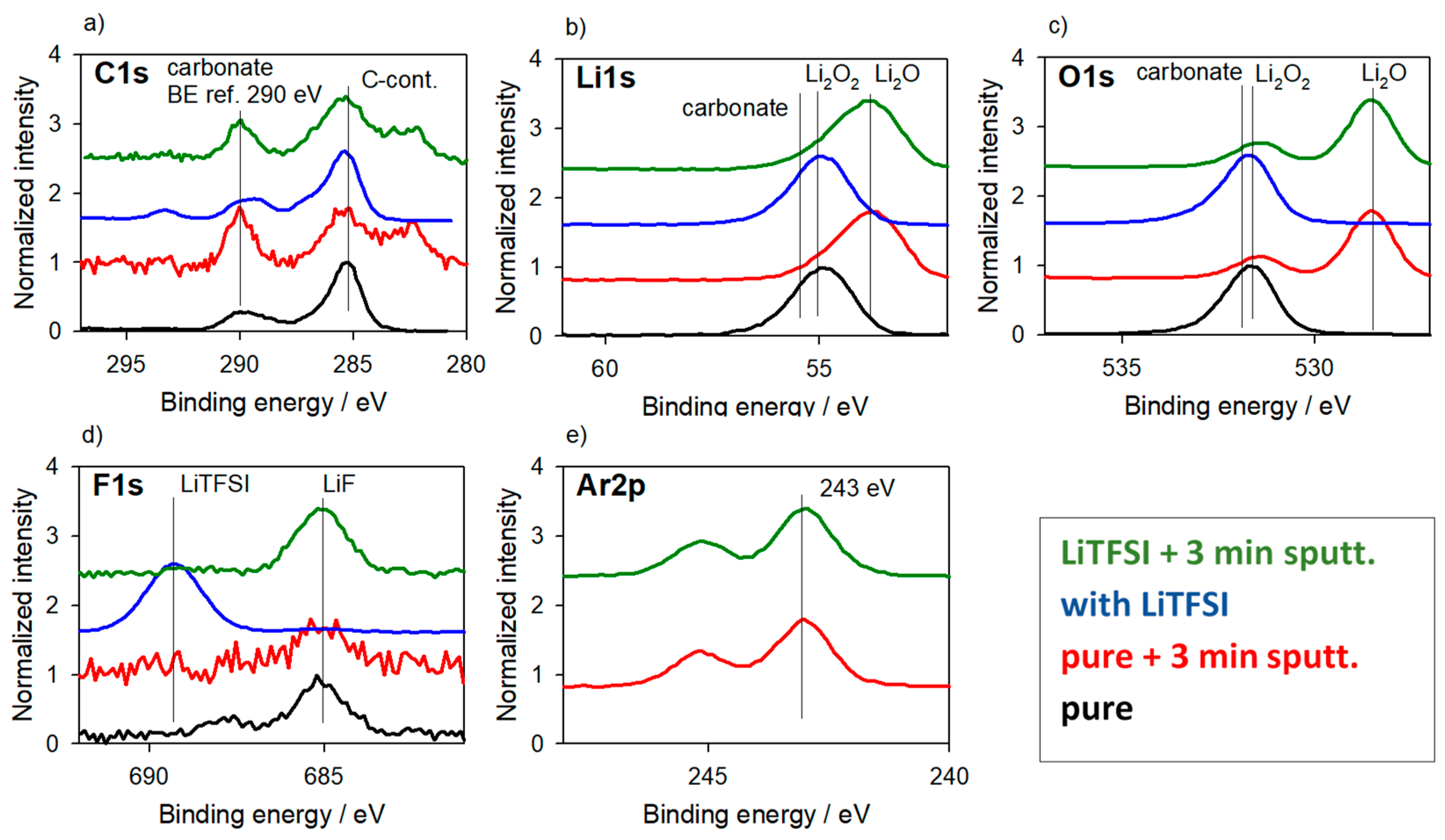
3.3. Reference Samples—With Charging
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, C.; Besenhard, J.O. (Eds.) Handbook of Battery Materials, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; ISBN 978-3-527-32695-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yabuuchi, N.; Kubota, K.; Dahbi, M.; Komaba, S. Research development on sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11636–11682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Maire, P.; Novák, P. A review of the features and analyses of the solid electrolyte interphase in Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6332–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, E.; Menkin, S. Review—SEI: Past, present and future. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A1703–A1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-G.; Xu, W.; Henderson, W.A. Lithium Metal Anodes and Rechargeable Lithium Metal Batteries; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-44054-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki, M.; Shaw, L.L. Advances and challenges of sodium ion batteries as post lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53129–53154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iermakova, D.I.; Dugas, R.; Palacín, M.R.; Ponrouch, A. On the comparative stability of Li and Na metal anode interfaces. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A706–A7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren, S.; Ciosek, K.; Hahlin, M.; Gustafsson, T.; Gorgoi, M.; Rensmo, H.; Edström, K. Comparing anode and cathode electrode/electrolyte interface composition and morphology using soft and hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 97, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, M.; Carney, T.J.; Grimaud, A.; Giordano, L.; Pour, N.; Chang, H.-H.; Fenning, D.P.; Lux, S.F.; Paschos, O.; Bauer, C.; et al. Electrode-electrolyte interface in Li-ion batteries: Current understanding and new insights. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4653–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Dolocan, A.; Oh, P.; Celio, H.; Park, S.; Cho, J.; Manthiram, A. Dynamic behaviour of interphases and its implication on high-energy-density cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, S.; Kloepsch, R.; Li, J.; Nowak, S.; Passerini, S.; Winter, M. How do reactions at the anode/electrolyte interface determine the cathode performance in lithium-ion batteries? J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A542–A548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edström, K.; Gustafsson, T.; Thomas, J.O. The cathode–electrolyte interface in the Li-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupré, N.; Cuisinier, M.; Martin, J.F.; Guyomard, D. Interphase evolution at two promising electrode materials for Li-ion batteries: LiFePO4 and LiNi1/2Mn1/2O2. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2014, 15, 1922–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, T.; Andersson, A.M.; Bishop, A.G.; Gejke, C.; Gustafsson, T.; Thomas, J.O. Surface analysis of LiMn2O4 electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A69–A78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbuena, P.B.; Wang, Y. Lithium-Ion Batteries—Solid-Electrolyte Interphase; Imperial College: London, UK, 2004; ISBN 978-1-86094-362-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, H.; Kubota, T.; Kita, A.; Kawashima, A. Investigation of the Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formed by Fluoroethylene Carbonate on Si Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A798–A801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Xie, K.; Diao, Y.; Hong, X. Properties of surface film on lithium anode with LiNO3 as lithium salt in electrolyte solution for lithium–sulfur batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 83, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Verbrugge, M.W. Toward High Cycle Efficiency of Silicon-Based Negative Electrodes by Designing the Solid Electrolyte Interphase. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1401398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, S. Binding energy referencing for XPS in alkali metal-based battery materials research (I): Basic model investigations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, S.; Hoffmann, M.; Zier, M. Peak position differences observed during XPS sputter depth profiling of the SEI on lithiated and delithiated carbon-based anode material for Li-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 401, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maibach, J.; Lindgren, F.; Eriksson, H.; Edström, K.; Hahlin, M. Electric Potential Gradient at the Buried Interface between Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes and the SEI Observed Using Photoelectron Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Physical Electronics Inc.: Chanhassen, MN, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-0-96481-241-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Reviving the lithium metal anode for high-energy batteries. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-B.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, C.-Z.; Zhang, Q. Toward safe lithium metal anode in rechargeable batteries: A review. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10403–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Lee, G.-H.; Park, M.; Li, W.; Kang, Y.-M. Recent Developments of the Lithium Metal Anode for Rechargeable Non-Aqueous Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1600811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthiram, A.; Fu, Y.; Chung, S.-H.; Zu, C.; Su, Y.-S. Rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11751–11787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenman, A.; Markevich, E.; Salitra, G.; Aurbach, D.; Garsuch, A.; Chesneau, F.F. Review on Li-sulfur battery systems: An integral perspective. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzola, J.J.; Russell, L.D. Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists, 2nd ed.; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Sudbury, MA, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-76370-192-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zier, M.; Scheiba, F.; Oswald, S.; Thomas, J.; Goers, D.; Scherer, T.; Klose, M.; Ehrenberg, H.; Eckert, J. Lithium dendrite and solid electrolyte interphase investigation using OsO4. J. Power Sources 2004, 266, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Leong, W.K.; Zhong, Z. Metallic osmium and ruthenium nanoparticles for CO oxidation. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 2315–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Novák, P. Formation of artificial solid electrolyte interphase by grafting for improving Li-ion intercalation and preventing exfoliation of graphite. Carbon 2012, 50, 2599–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwake, H.; Kuwabara, A.; Fisher, C.A.J.; Ikuhara, Y. Why is sodium-intercalated graphite unstable? RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36550–36554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jache, B.; Adelhelm, P. Use of graphite as a highly reversible electrode with superior cycle life for sodium-ion batteries by making use of co-intercalation phenomena. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10169–10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Yoon, G.; Kim, H.; Park, K.-Y.; Park, M.-S.; Yoon, W.-S.; Kang, K. Sodium intercalation chemistry in graphite. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irisarri, E.; Ponrouch, A.; Palacín, M.R. Review—Hard carbon negative electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A2476–A2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahn, J.R.; Zheng, T.; Liu, Y.; Xue, J.S. Mechanisms of lithium insertion in carbonaceous materials. Science 1995, 270, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, F.; Hintennach, A.; LaCroix, A.; Thiemig, D.; Oswald, S.; Scheiba, F.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Ehrenberg, H. Influence of temperature and upper cut-off voltage on the formation of lithium-ion cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 264, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, M. Neue Materialien und Konzepte für Lithium- und Natrium-Schwefel Batterien. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Lukaszewicz, J.P. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy studies of sodium modified carbon films suitable for use in humidity sensors. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 6063–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, S.; Nikolowski, K.; Ehrenberg, H. Quasi in situ XPS investigations on intercalation mechanisms in Li-ion battery materials. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, S.; Nikolowski, K.; Ehrenberg, H. XPS investigations of valence changes during cycling of LiCrMnO4-based cathodes in Li-ion batteries. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensling, D.; Thissen, A.; Gassenbauer, Y.; Klein, A.; Jaegermann, W. In-situ preparation and analysis of functional oxides. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2005, 7, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdier, S.; El Ouatani, L.; Dedryvère, R.; Bonhomme, F.; Biensan, P.; Gonbeau, D. XPS Study on Al2O3- and AlPO4-coated LiCoO2 cathode material for high-capacity Li ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A1088–A1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoss, F.; Giebeler, L.; Oswald, S.; Ehrenberg, H.; Eckert, J. Study on the reversible Li-insertion of amorphous and partially crystalline Al86Ni8La6 and Al86Ni8Y6 alloys as anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 60, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumak, I.; Dmytriv, G.; Pavlyuk, V.; Oswald, S.; Eckert, J.; Trill, H.; Eckert, H.; Pauly, H.; Ehrenberg, H. Li(Al1-zZnz) alloys as anode materials for rechargeable Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoss, F. Amorphe, Al-basierte Anodenmaterialien für Li-Ionen-Batterien. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thoss, F.; Giebeler, L.; Thomas, J.; Oswald, S.; Potzger, K.; Reuther, H.; Ehrenberg, H.; Eckert, J. Amorphous Li-Al-based compounds: A novel approach for designing high performance electrode materials for Li-Ion batteries. Inorganics 2013, 1, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herklotz, M.; Scheiba, F.; Glaum, R.; Mosymow, E.; Oswald, S.; Eckert, J.; Ehrenberg, H. Electrochemical oxidation of trivalent chromium in a phosphate matrix: Li3Cr2(PO4)3 as cathode material for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 139, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, O. Introduction. In The Lithium Air Battery: Fundamentals; Imanishi, N., Luntz, A.C., Bruce, P.G., Eds.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–22. ISBN 978-1-4899-8061-8. [Google Scholar]
- Oswald, S.; Mikhailova, D.; Scheiba, F.; Reichel, P.; Fiedler, A.; Ehrenberg, H. XPS investigations of electrolyte/electrode interactions for various Li-ion battery materials. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oswald, S.; Thoss, F.; Zier, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Jaumann, T.; Herklotz, M.; Nikolowski, K.; Scheiba, F.; Kohl, M.; Giebeler, L.; et al. Binding Energy Referencing for XPS in Alkali Metal-Based Battery Materials Research (II): Application to Complex Composite Electrodes. Batteries 2018, 4, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4030036
Oswald S, Thoss F, Zier M, Hoffmann M, Jaumann T, Herklotz M, Nikolowski K, Scheiba F, Kohl M, Giebeler L, et al. Binding Energy Referencing for XPS in Alkali Metal-Based Battery Materials Research (II): Application to Complex Composite Electrodes. Batteries. 2018; 4(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleOswald, Steffen, Franziska Thoss, Martin Zier, Martin Hoffmann, Tony Jaumann, Markus Herklotz, Kristian Nikolowski, Frieder Scheiba, Michael Kohl, Lars Giebeler, and et al. 2018. "Binding Energy Referencing for XPS in Alkali Metal-Based Battery Materials Research (II): Application to Complex Composite Electrodes" Batteries 4, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4030036
APA StyleOswald, S., Thoss, F., Zier, M., Hoffmann, M., Jaumann, T., Herklotz, M., Nikolowski, K., Scheiba, F., Kohl, M., Giebeler, L., Mikhailova, D., & Ehrenberg, H. (2018). Binding Energy Referencing for XPS in Alkali Metal-Based Battery Materials Research (II): Application to Complex Composite Electrodes. Batteries, 4(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4030036




