Modelling Li-V2O5 Batteries Using Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: Towards Final Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Galvanostatic Charge/Discharge Curves
2.2. Estimation of State of Charge (SoC)
2.3. Battery Modeling Considerations
2.4. Modeling Techniques
2.4.1. Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique (GITT)
2.4.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
2.5. Identification and Estimation of Parameters
2.5.1. Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique (GITT)
2.5.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thevenin Models and Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique
3.2. Thevenin Models and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, S.M.; Nayar, C.V.; Abu-Siada, A.; Hasan, M.M. Power Electronics for Renewable Energy Sources. In Power Electronics Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 783–827. [Google Scholar]
- Schipper, F.; Aurbach, D. A Brief Review: Past, Present and Future of Lithium Ion Batteries 1. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2016, 52, 1229–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, M.; O’Neill, L.; Zhang, T.; Purkayastha, R.; Minton, G.; Marinescu, M.; Offer, G.J. Lithium Sulfur Batteries, a Mechanistic Review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3477–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skundin, A.M.; Kulova, T.L.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Sodium-Ion Batteries (a Review). Russ. J. Electrochem. 2018, 54, 131–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liang, H. Micro- and Nano-Structured Vanadium Pentoxide (V2O5) for Electrodes of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Nisula, M.; Dhara, A.; Henderick, L.; Mattelaer, F.; Dendooven, J.; Detavernier, C. Atomic Layer Deposition of Indium-Tin-Oxide as Multifunctional Coatings on V2O5 Thin-Film Model Electrode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2001022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.K.; Gupta, P.S.; Rahaman, H. Doped Vanadium Oxides as Host Materials for Lithium Intercalation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 98, 1355. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, R.; El Sayed, M.; Arasaratnam, I.; Tjong, J.; Habibi, S. Reduced-Order Electrochemical Model Parameters Identification and SOC Estimation for Healthy and Aged Li-Ion Batteries Part I: Parameterization Model Development for Healthy Batteries. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 659–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtola, T.A.; Zahedi, A. Electric Vehicle Battery Cell Cycle Aging in Vehicle to Grid Operations: A Review. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitesh, K.A.; Ravichandra. A Study on Battery Controller Design for the Estimation of State of Charge (SoC) in Battery Management System for Electric Vehicle (EV)/Hybrid EV (HEV). SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulmrharj, S.; Ouladsine, R.; NaitMalek, Y.; Bakhouya, M.; Zine-dine, K.; Khaidar, M.; Siniti, M. Online Battery State-of-Charge Estimation Methods in Micro-Grid Systems. J. Energy Storage 2020, 30, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degla, A.; Chikh, M.; Mahrane, A.; Hadj Arab, A. Improved Lithium-Ion Battery Model for Photovoltaic Applications Based on Comparative Analysis and Experimental Tests. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 10965–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.Ö.; Zajonz, F.; Günther, T.; Dermenci, K.B.; Berecibar, M.; Urrutia, L. Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturing: Industrial View on Processing Challenges, Possible Solutions and Recent Advances. Batteries 2023, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Qiu, X.; Hou, G.; Liaw, B.Y.; Zhang, C. State of Health Estimation for Lithium Ion Batteries Based on Charging Curves. J. Power Sources 2014, 249, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.; Multiscale Modelling, C.; Zaghib, K.; Song, S.-W.; Ali, M.A.; Da Silva, C.M.; Amon, C.H. Multiscale Modelling Methodologies of Lithium-Ion Battery Aging: A Review of Most Recent Developments. Batteries 2023, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocciantelli, J.M.; Ménétrier, M.; Delmas, C.; Doumerc, J.P.; Pouchard, M.; Broussely, M.; Labat, J. On the δ → γ Irreversible Transformation in Li//V2O5 Secondary Batteries. Solid State Ion. 1995, 78, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lai, X.; Li, B.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, M.; Weng, J.; Zheng, Y. State Estimation Models of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Battery Management System: Status, Challenges, and Future Trends. Batteries 2023, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zuo, W.; Zhou, K.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, G. State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery Based on Second Order Resistor-Capacitance Circuit-PSO-TCN Model. Energy 2024, 289, 130025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yu, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Shen, W. State of Charge Estimation for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Cross-Domain Transfer Learning with Feedback Mechanism. J. Energy Storage 2023, 70, 108037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, H. One-Shot Parameter Identification of the Thevenin’s Model for Batteries: Methods and Validation. J. Energy Storage 2020, 29, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, J.; Jiang, R.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y. Parameters Identification of Thevenin Model for Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Self-Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization Differential Evolution Algorithm to Estimate State of Charge. J. Energy Storage 2021, 44, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroe, D.I.; Swierczynski, M.; Stan, A.I.; Knap, V.; Teodorescu, R.; Andreasen, S.J. Diagnosis of Lithium-Ion Batteries State-of-Health Based on Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Technique. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, ECCE 2014, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 4576–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröer, P.; Khoshbakht, E.; Nemeth, T.; Kuipers, M.; Zappen, H.; Sauer, D.U. Adaptive Modeling in the Frequency and Time Domain of High-Power Lithium Titanate Oxide Cells in Battery Management Systems. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, U.; Kroker, T.; Kurbach, K.; Kurrat, M. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Based Estimation of the State of Charge of Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Energy Storage 2016, 8, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z. A Framework for States Co-Estimation of Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Fractional-Order Theory. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, T.; Lyu, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, W.; Jiang, L.; Cai, G. Improved LSTM Based State of Health Estimation Using Random Segments of the Charging Curves for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 74, 109370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, O.; Dessaint, L.A. Experimental Validation of a Battery Dynamic Model for EV Applications. World Electr. Veh. J. 2009, 2, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.H.; Batarseh, I. An Overview of Generic Battery Models. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Detroit, MI, USA, 24–28 July 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.S.; Moo, C.S.; Chen, Y.P.; Hsieh, Y.C. Enhanced Coulomb Counting Method for Estimating State-of-Charge and State-of-Health of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Guo, D. An Improved Coulomb Counting Approach Based on Numerical Iteration for SOC Estimation with Real-Time Error Correction Ability. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 74274–74282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathoni, G.; Widayat, S.A.; Topan, P.A.; Jalil, A.; Cahyadi, A.I.; Wahyunggoro, O. Comparison of State-of-Charge (SOC) Estimation Performance Based on Three Popular Methods: Coulomb Counting, Open Circuit Voltage, and Kalman Filter. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Automation, Cognitive Science, Optics, Micro Electro—Mechanical System, and Information Technology (ICACOMIT), Jakarta, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2017; pp. 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Gazzarri, J.; Onori, S.; Habibi, S.; Jackey, R.; Rzemien, K.; Tjong, J.; Lesage, J. Model-Based Parameter Identification of Healthy and Aged Li-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicle Applications. SAE Int. J. Altern. Powertrains 2015, 4, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; He, L. A Novel Algorithm for SOC Using Simple Iteration and Coulomb Counting Method. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Student Conference on Electric Machines and Systems, Huzhou, China, 14–16 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, H.; Miniguano, M. Modelado e Identificación de Baterías de Ion-Litio y Supercondensadores Para. Su Aplicación al Vehículo Eléctrico. 2019. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10016/31517 (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Miniguano, H.; Barrado, A.; Lazaro, A.; Zumel, P.; Fernandez, C. General Parameter Identification Procedure and Comparative Study of Li-Ion Battery Models. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniguano, H.; Raga, C.; Barrado, A.; Lazaro, A.; Zumel, P.; Olias, E. A Comparative Study and Parameterization of Electrical Battery Models Applied to Hybrid Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Toulouse, France, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Patricia, S.; Solís, C. Modelado y Caracterización Funcional En Régimen Dinámico de Sistemas Electroquímicos de Almacenamiento de Energía: Aplicación a Supercondensadores y Baterías de Iones de Litio; Universidad Carlos III de Madrid: Madrid, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Deleebeeck, L.; Veltzé, S. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study of Commercial Li-Ion Phosphate Batteries: A Metrology Perspective. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 7158–7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Hori, N.; Kumagai, S. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy on the Performance Degradation of LiFePO4/Graphite Lithium-Ion Battery Due to Charge-Discharge Cycling under Different C-Rates. Energies 2019, 12, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.Y. Conversion of a Constant Phase Element to an Equivalent Capacitor. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Appleby, A.J.; Little, F.E. Low-Temperature Characterization of Lithium-Ion Carbon Anodes via Microperturbation Measurement. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantelme, F.; Mantoux, A.; Groult, H.; Lincot, D. Electrochemical Study of Phase Transition Processes in Lithium Insertion in V2O5 Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cui, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Song, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Quasi-Solid-State All-V2O5 Battery. Small 2023, 2304786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.; Wang, R.; Fu, Y.; Mi, C. Accurate and Reliable State of Charge Estimation of Lithium Ion Batteries Using Time-Delayed Recurrent Neural Networks through the Identification of Overexcited Neurons. Appl. Energy 2022, 305, 117962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, D.; Behi, H.; Van Mierlo, J.; Berecibar, M. Equivalent Circuit Model for High-Power Lithium-Ion Batteries under High Current Rates, Wide Temperature Range, and Various State of Charges. Batteries 2023, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suti, A.; Di Rito, G.; Mattei, G. Development and Experimental Validation of Novel Thevenin-Based Hysteretic Models for Li-Po Battery Packs Employed in Fixed-Wing UAVs. Energies 2022, 15, 9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Uthaichana, K.; Decarlo, R.A.; Tsoukalas, L.H. Development and Validation of a Battery Model Useful for Discharging and Charging Power Control and Lifetime Estimation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Storage Research and Development 2013 Progress Report, Sections 4–6|Department of Energy. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/vehicles/articles/energy-storage-research-and-development-2013-progress-report-sections-4-6 (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Martínez-Cisneros, C.S.; Pandit, B.; Antonelli, C.; Sanchez, J.Y.; Levenfeld, B.; Varez, A. Development of Sodium Hybrid Quasi-Solid Electrolytes Based on Porous NASICON and Ionic Liquids. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 7723–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Balseca, J.M.; Martínez-Cisneros, C.S.; Pandit, B.; Várez, A. High Performance NASICON Ceramic Electrolytes Produced by Tape-Casting and Low Temperature Hot-Pressing: Towards Sustainable All-Solid-State Sodium Batteries Operating at Room Temperature. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 43, 4826–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, B.; Johansen, M.; Andersen, B.P.; Martínez-Cisneros, C.S.; Levenfeld, B.; Ravnsbæk, D.B.; Varez, A. All-Solid-State Sodium-Ion Batteries Operating at Room Temperature Based on NASICON-Type NaTi2(PO4)3 Cathode and Ceramic NASICON Solid Electrolyte: A Complete in Situ Synchrotron X-ray Study. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 144509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
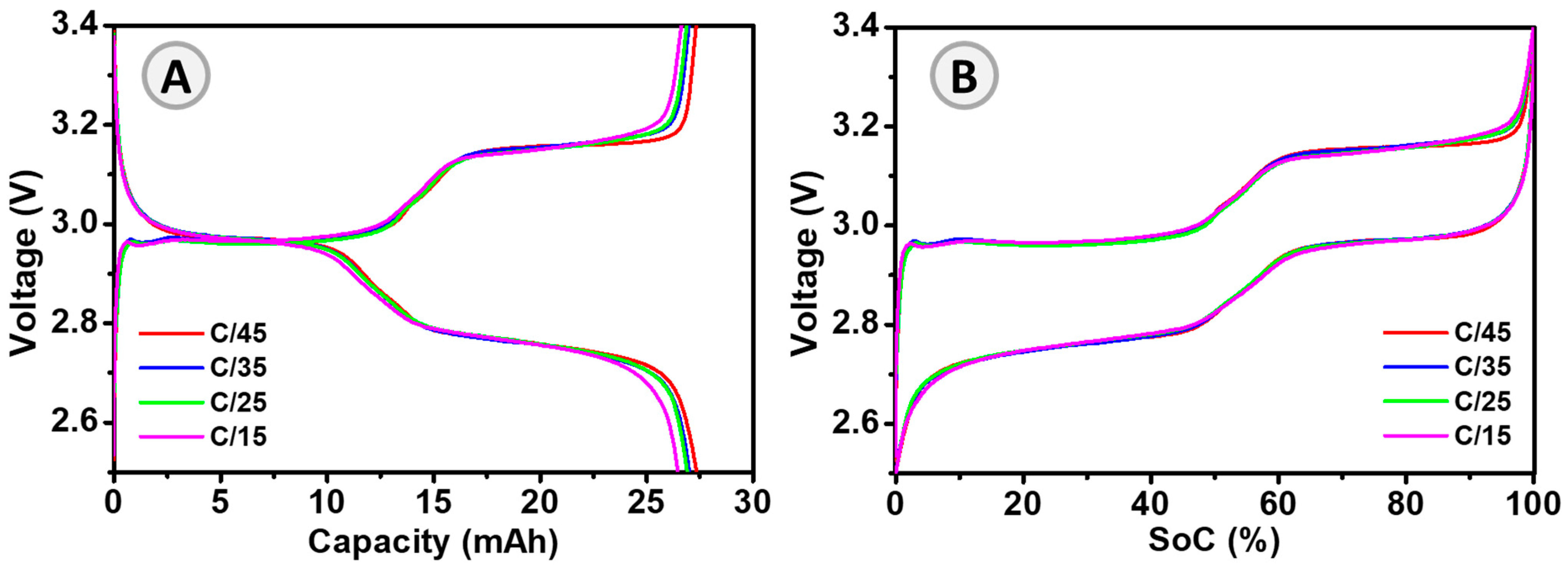

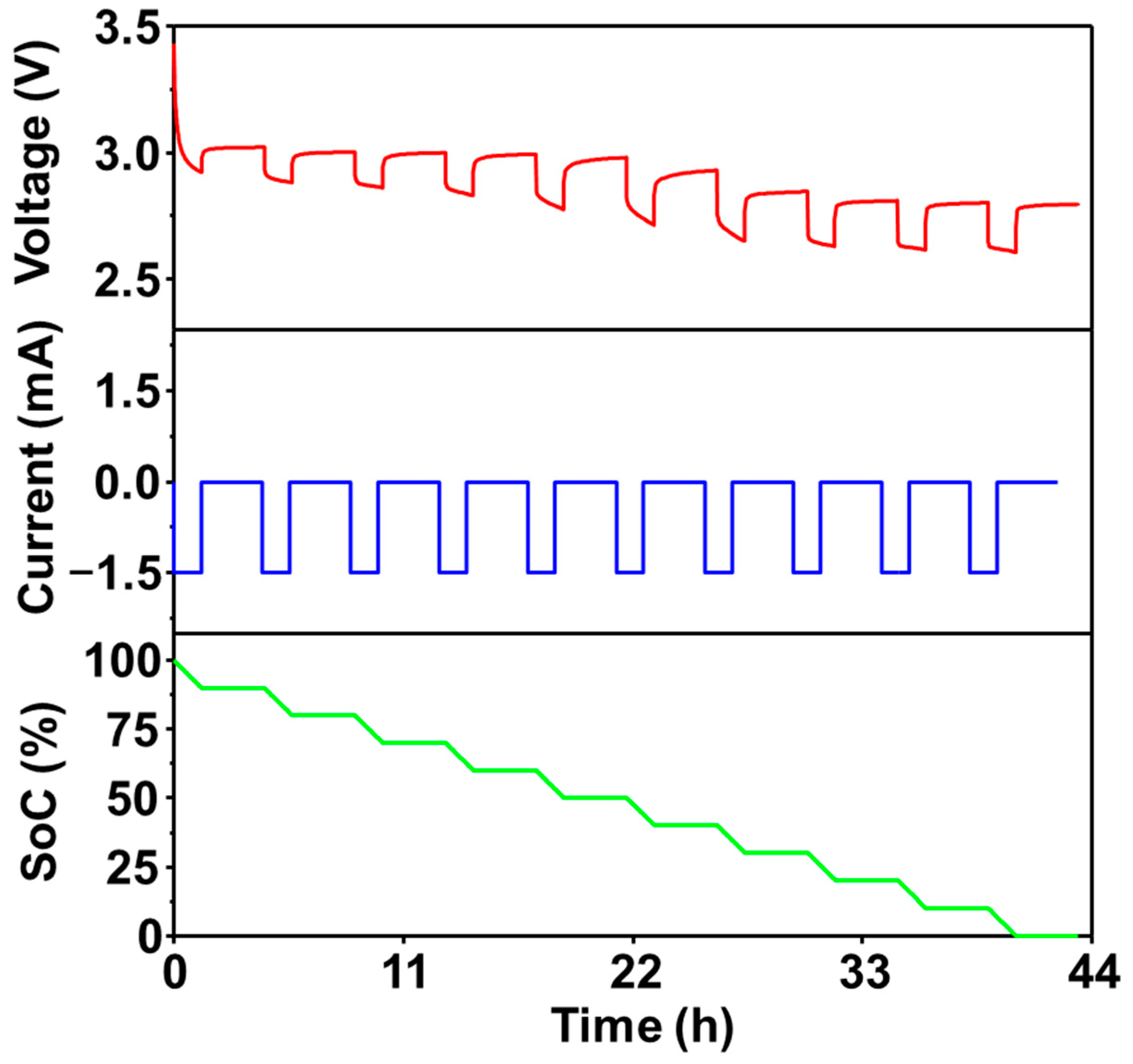
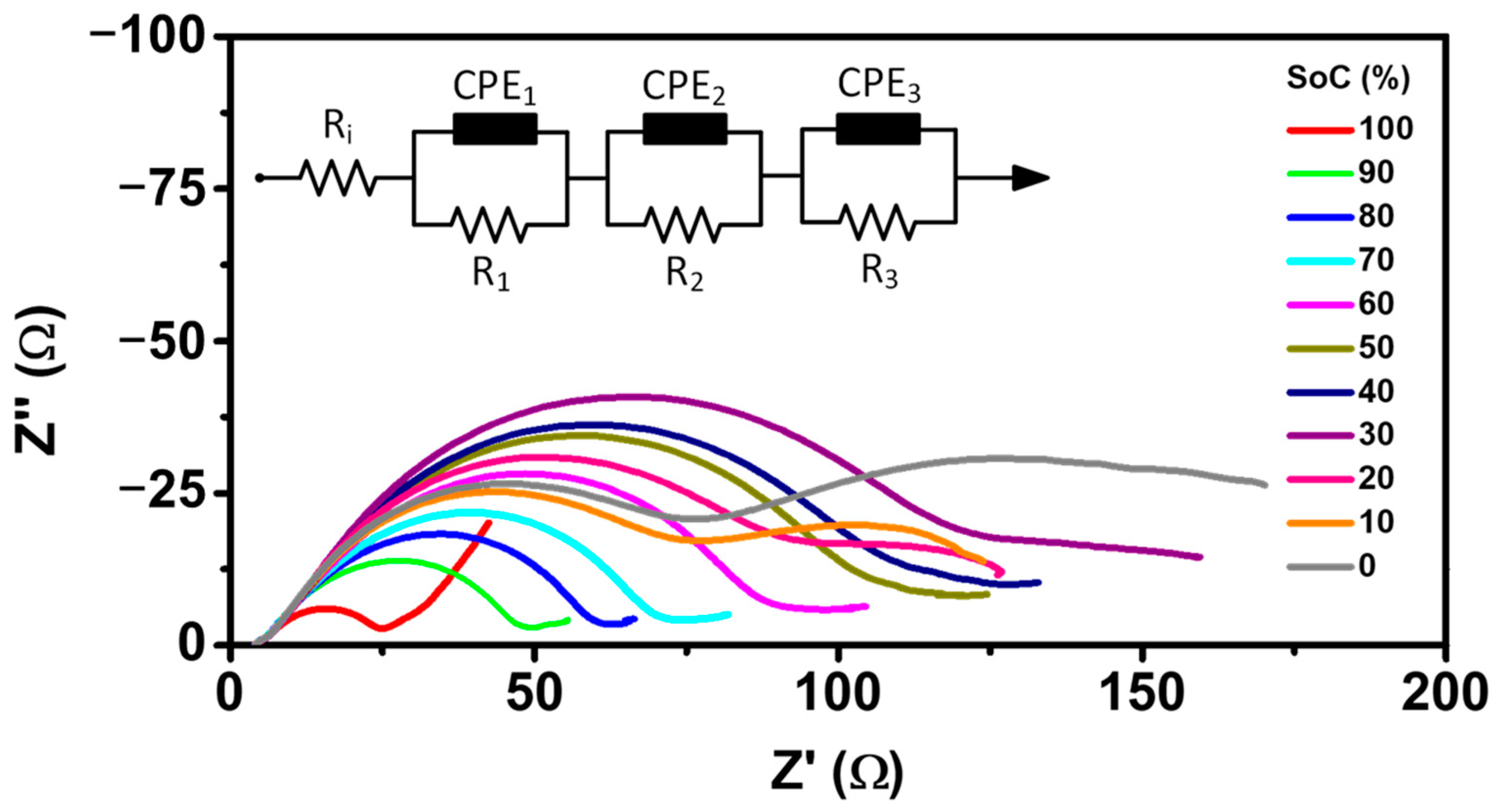

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nominal Capacity | 20~22.5 mAh |
| Nominal Voltage | 3 V |
| Open Circuit Voltage (OCV) | 2.95 V to 3.55 V |
| Maximum Voltage | 3.4 V ± 0.15 V |
| Cut-off Voltage | 2.5 V |
| Current Charge to 3 V | Maximum 1.5 mA (C/13) |
| Parameters | Conventional | SoC-Dependent Model | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 10% | 20% | 30% | 40% | 50% | 60% | 70% | 80% | 90% | 100% | ||
| Ri (Ω) | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.1 |
| R1 (Ω) C1 (mF) | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
| 0.2 | 0.047 | 0.052 | 0.046 | 0.073 | 0.045 | 0.286 | 0.046 | 0.070 | 0.448 | 0.427 | 0.103 | |
| R2 (kΩ) C2 (mF) | 33.3 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.027 | 0.033 | 0.030 | 0.250 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.105 | 0.254 | 0.346 |
| 0.2 | 0.346 | 0.254 | 0.105 | 0.067 | 0.067 | 0.255 | 0.030 | 0.033 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.027 | |
| R3 (kΩ) C3 (mF) | 62.2 | 0.075 | 0.072 | 0.069 | 0.086 | 0.090 | 0.086 | 0.070 | 0.053 | 0.051 | 0.056 | 0.098 |
| 12.8 | 13.1 | 13.9 | 14.4 | 9.8 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 13.0 | 17.3 | 16.1 | 16.8 | 10.0 | |
| Parameters | Conventional | SoC-Dependent Model | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 10% | 20% | 30% | 40% | 50% | 60% | 70% | 80% | 90% | 100% | ||
| Ri (Ω) | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.1 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.9 |
| R1 (Ω) C1 (mF) | 2.2 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| 13.4 | 11.6 | 12.9 | 97.7 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 16.7 | 15.5 | 15.5 | 13.9 | 12.5 | |
| R2 (kΩ) C2 (mF) | 70.4 | 80 | 62 | 78 | 106 | 100 | 92 | 83 | 61 | 51 | 42 | 19 |
| 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| R3 (kΩ) C3 (mF) | 158.5 | 82.0 | 80 | 65 | 95 | 48 | 50 | 74 | 55 | 55 | 164 | 492 |
| 38.8 | 0.3 | 13.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 12.4 | 58.6 | 58.6 | 258.2 | 24.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naranjo-Balseca, J.; Martínez-Cisneros, C.; Várez, A. Modelling Li-V2O5 Batteries Using Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: Towards Final Applications. Batteries 2024, 10, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060172
Naranjo-Balseca J, Martínez-Cisneros C, Várez A. Modelling Li-V2O5 Batteries Using Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: Towards Final Applications. Batteries. 2024; 10(6):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060172
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaranjo-Balseca, Johanna, Cynthia Martínez-Cisneros, and Alejandro Várez. 2024. "Modelling Li-V2O5 Batteries Using Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: Towards Final Applications" Batteries 10, no. 6: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060172
APA StyleNaranjo-Balseca, J., Martínez-Cisneros, C., & Várez, A. (2024). Modelling Li-V2O5 Batteries Using Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: Towards Final Applications. Batteries, 10(6), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10060172







