Production of Triploid Germplasm by Inducing 2n Pollen in Longan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
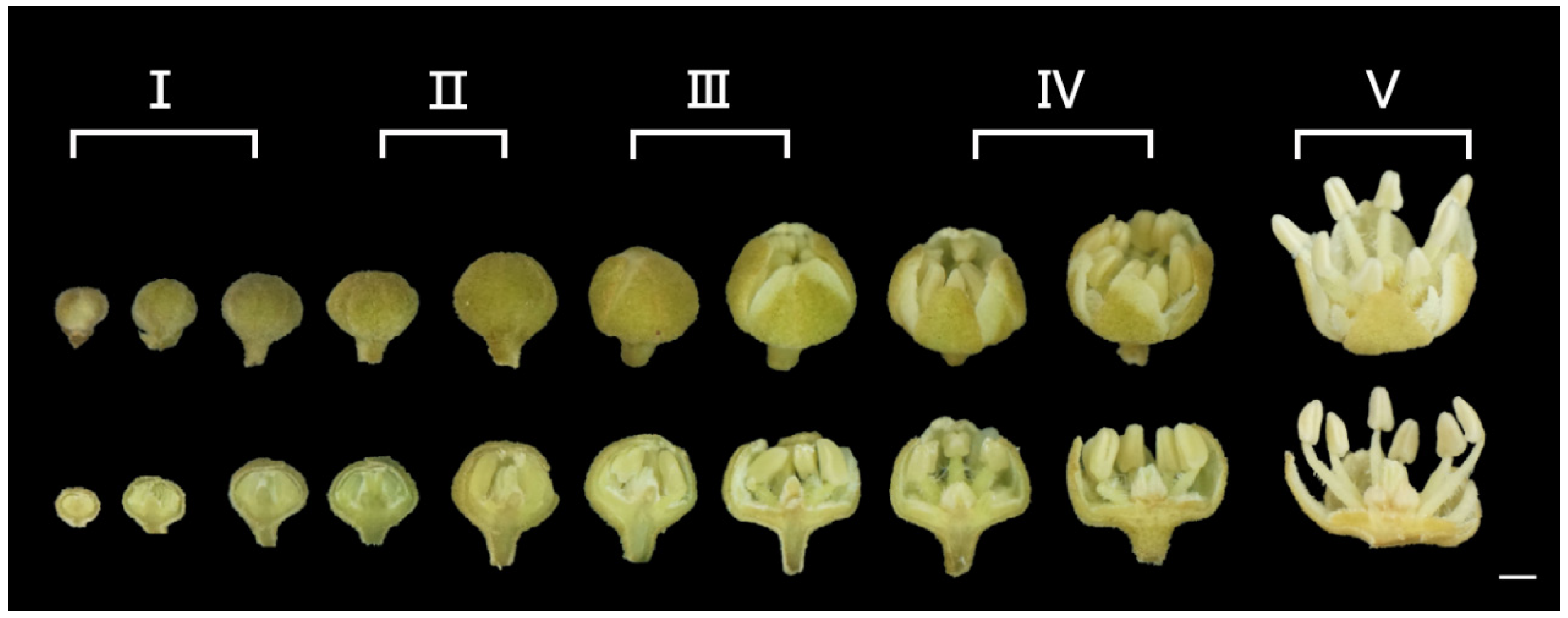
2.2. Male Flower Development and the Microspore Meiotic Process
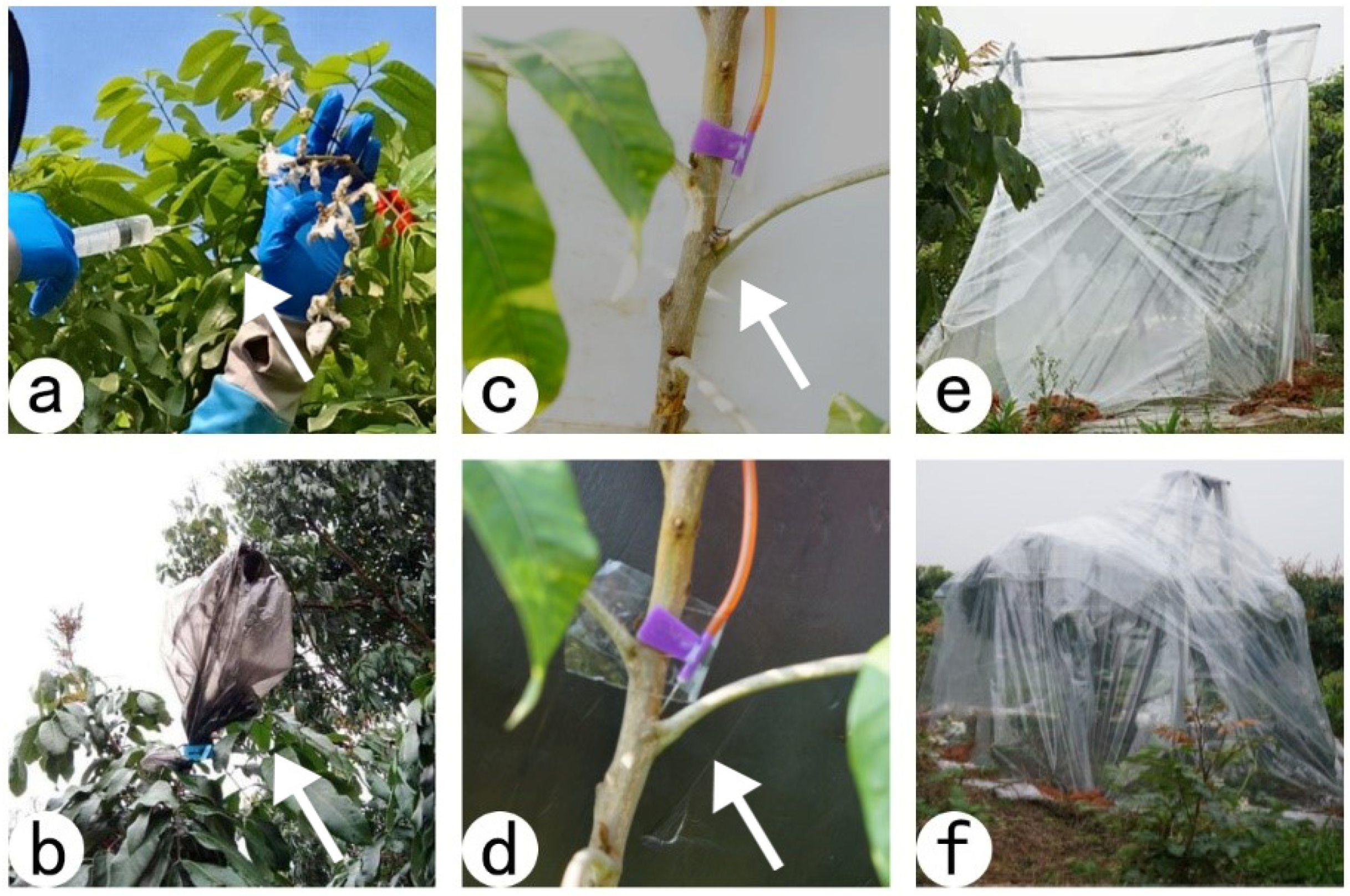
2.3. 2n Pollen Induction
2.4. Estimation of the Frequency of 2n Pollen
2.5. Artificial Pollination Using 2n Pollen
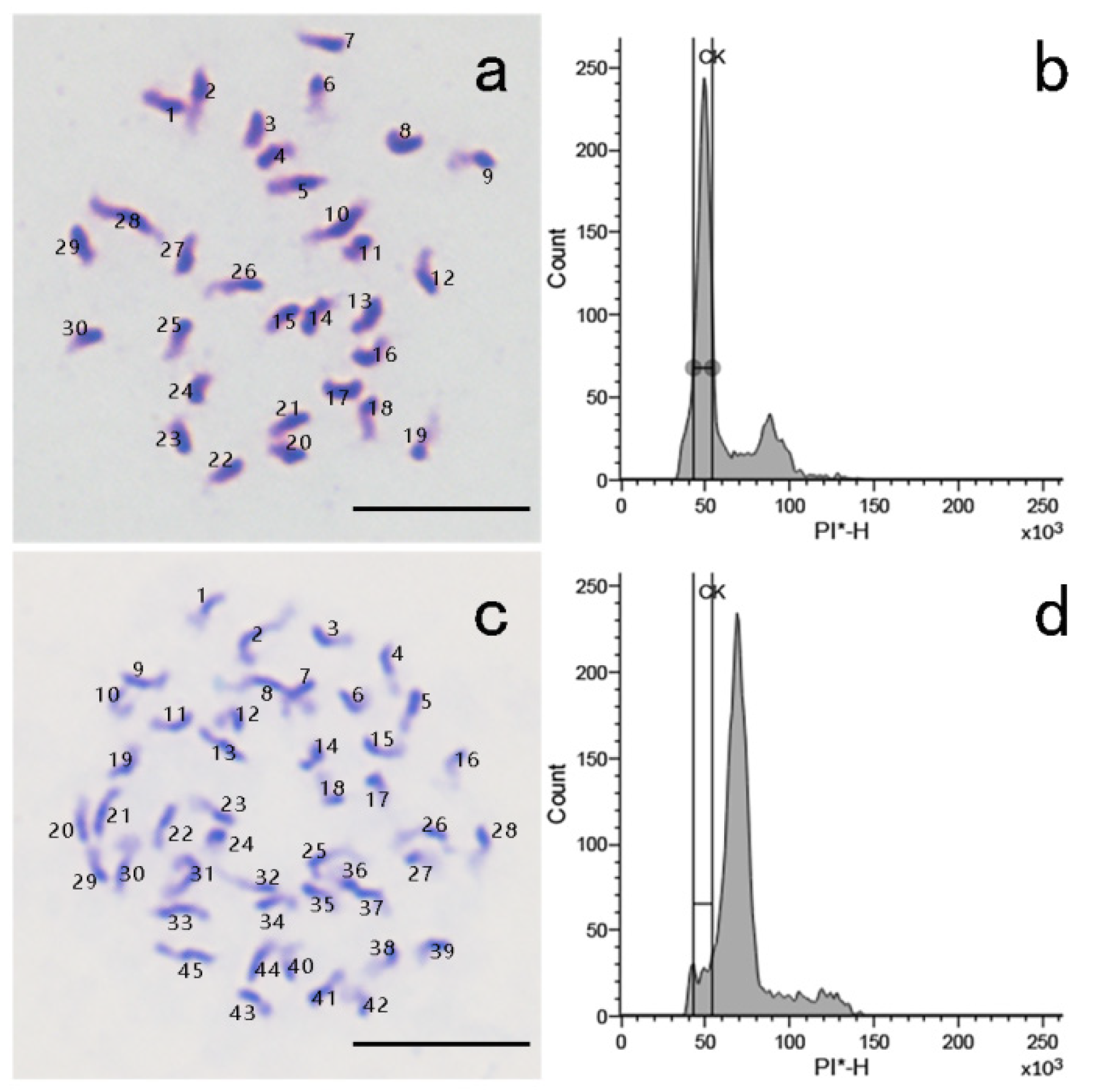
2.6. Ploidy Analysis by Chromosome Counting and Flow Cytometry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Relating the Meiotic Process of Microspore Mother Cells to the Morphological Changes of Male Flower Buds
3.2. 2n Pollen Induction and Identification
3.3. Triploid Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lai, Z.; Chen, C.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Z. Somatic embryogenesis in longan [Dimocarpus longan Lour.]. In Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants; Jain, S.M., Gupta, P.K., Newton, R.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 6, pp. 415–431. ISBN 978-94-017-3030-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kreiner, J.M.; Kron, P.; Husband, B.C. Frequency and maintenance of unreduced gametes in natural plant populations: Associations with reproductive mode, life history and genome size. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, T.T.; Shuai, L.; Han, D.M.; Lai, Z.Y.; Du, X.X.; Guo, X.M.; Hu, W.S.; Wu, Z.X.; Luo, T. Comparative metabolomics reveals differences in primary and secondary metabolites between “Shixia” and “Chuliang” longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) pulp. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5785–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.S.; Xu, X.D.; Zheng, S.Q.; Xu, J.H. Selection for aborted-seeded longan cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2001, 558, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Joyce, D.; Lin, H. Longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.). In Postharvest Biology and Technology of Tropical and Subtropical Fruits; Yahia, E.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; Volume 16, pp. 408–423. ISBN 978-1-84569-735-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.C.; Hu, G.; Huang, H.B.; Li, J.G.; Pan, X.W. Effects of panicle thinning and application of growth regulators on fruit sizes and quality of ‘Shixia’ longan. Acta Hortic. 2005, 665, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, J.; Schemske, D. Pathways, mechanisms, and rates of polyploid formation in flowering plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998, 29, 467–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, D.Y.; Dilkes, B.; Luo, H.B.; Douglas, A.; Yakubova, E.; Lahner, B.; Salt, D.E. Polyploids Exhibit Higher Potassium Uptake and Salinity Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Science 2013, 341, 658–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, H.; Fait, A.; Tel Zur, N. Morphological, cytological and metabolic consequences of autopolyploidization in Hylocereus (Cactaceae) species. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comai, L. The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollitrault, P.; Froelicher, Y.; Dambier, D.; Luro, F.; Yamamoto, M. Seedlessness and ploidy manipulations. In Citrus Genetics, Breeding and Biotechnology; Khan, I.A., Ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2007; Volume 8, p. 197. ISBN 9780851990194. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Khan, I. Growth, morphology and fruit comparison of diploid and tetraploid kinnow mandarin. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2002, 39, 126–128. [Google Scholar]
- Corneillie, S.; De Storme, N.; Van Acker, R.; Fangel, J.U.; De Bruyne, M.; De Rycke, R.; Geelen, D.; Willats, W.G.T.; Vanholme, B.; Boerjan, W. Polyploidy Affects Plant Growth and Alters Cell Wall Composition. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosellini, D.F.N.; Allegrucci, S.; Capomaccio, S.; Zago, E.D.; Leonetti, P.; Balech, B.; Aversano, R.; Carputo, D.; Reale, L.; Veronesi, F. Sexual Polyploidization in Medicago sativa L.: Impact on the Phenotype, Gene Transcription, and Genome Methylation. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzoor, A.; Ahmad, T.; Bashir, M.A.; Hafiz, I.A.; Silvestri, C. Studies on Colchicine Induced Chromosome Doubling for Enhancement of Quality Traits in Ornamental Plants. Plants 2019, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robertson, A.; Rich, T.; Allen, A.; Houston, L.; Roberts, C.; Bridle, J.; Harris, S.; Hiscock, S. Hybridization and polyploidy as drivers of continuing evolution and speciation in Sorbus. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendiburu, A.O.; Peloquin, S.J. Bilateral sexual polyploidization in potatoes. Euphytica 1977, 26, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Hwang, Y.J.; Lim, K.B. Exploitation of induced 2n-gametes for plant breeding. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Shang, F.; Kang, X. High temperature-induced production of unreduced pollen and its cytological effects in Populus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Hao, J. Pollen Chromosome Doubling Induced by High Temperature Exposure to Produce Hybrid Triploids in Populus canescens. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2018, 54, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Li, H.; Suo, Y.; Fu, J.; Sun, P.; Han, W.; Diao, S.; Li, F. High temperature treatment generates unreduced pollen in persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.). Sci. Hortic. 2019, 258, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespel, L.; Le Bras, C.; Relion, D.; Roman, H.; Morel, P. Effect of high temperature on the production of 2n pollen grains in diploid roses and obtaining tetraploids via unilateral polyploidization. Plant Breed. 2015, 134, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, X.J.; Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Guo, L.Q.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, B. Induction of 2n pollen by colchicine in Populus × popularis and its triploids breeding. Silvae Genet. 2011, 60, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Pengqiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Mo, J.; Wang, J.; Kang, X. Induction of 2n pollen with colchicine during microsporogenesis in Eucalyptus. Euphytica 2016, 210, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Hu, L.; Wang, L.H.; Liu, P.; Liu, M.J. Meiosis and 2n pollen formation of Ziziphus jujuba ‘Wuhefeng’ after treated with colchicine. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2017, 44, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Ke, G.W. Studies on Morphologic Differentiation of Flower Buds in Longan. J. Fujian Acad. Agric. Sci. 1992, 1, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Z.; Zhu, J.H.; Xu, N.; Li, G.W.; Wei, L.H.; Ren, H.; Peng, H.X. Study on the flowering and fruit setting characteristics of longan of Stone Kip. Fujian Fruits 2006, 4, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Sung, W.C.; Li, H.L. A new method for preparing mitotic plant chromosomes. Acta Bot. Sin. 1979, 21, 297–298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, J.; Sang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M. Effects of Colchicine on Populus canescens Ectexine Structure and 2n Pollen Production. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Xue, Z.H.; Li, J.; Peng, B.; Wang, J.R.; Dai, L.; Li, X.S.; Liu, M.J. Establishment of a 2n pollen induction method based on minimum invasion in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.). Acta Hortic. 2016, 1116, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Liu, P.; Liu, M. Cytological mechanism of 2n pollen formation in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill. ‘Linglingzao’). Euphytica 2011, 182, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; Wang, Y.; Pan, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C. The chromosomes observation of several rare germplasm in litchi and longan. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2010, 37, 1991–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, B.; Wu, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, C.; Feng, Q.; Ye, Z.; Hu, G.; Wang, H. Nuclear isolation buffer optimization and the determination of ploidy level and genome size of litchi using flow cytometry. J. Fruit Sci. 2019, 36, 939–946. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, P.; Kang, X. Induction of 2n female gametes in Populus adenopoda Maxim by high temperature exposure during female gametophyte development. Breed. Sci. 2013, 63, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.-m.; Yang, M.-h.; Zhang, F.; Fan, L.-J.; Zhou, Y. The strong competitive role of 2n pollen in several polyploidy hybridizations in Rosa hybrida. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orjeda, G.; Freyre, R.; Iwanaga, M. Production of 2n Pollen in Diploid Ipomoea trifida, a Putative Wild Ancestor of Sweet Potato. J. Hered. 1990, 81, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conicella, C.; Genualdo, G.; Errico, A.; Frusciante, L.; Monti, L. Meiotic restitution mechanisms and 2n pollen formation in a Solanum tuberosum dihaploid and in dihaploid × wild species hybrids. Plant Breed. 1996, 115, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, H. Study on the effective treating period for pollen chromosome doubling of Populus tomentosa × P. bolleana. Sci. Silvae Sin. 1999, 35, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Guo, Q.G.; Xiang, S.Q.; Li, X.L.; Liang, G.L. Study on the effect of hot-shock treatment on the occurrence frequency of 2n pollen of Loquat Trees. J. Fruit Sci. 2003, 4, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singhal, V. Erratic Male Meiosis Resulting in 2n Pollen Grain Formation in a 4x Cytotype (2n=28) of Ranunculus laetus Wall. ex Royle. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 691545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crespel, L.; Sébastien, R.; Gudin, S. The production of 2n pollen in rose. Euphytica 2006, 151, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.; Nijs, A. A statistical mixture model for estimating the proportion of unreduced pollen grains in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) via the size of pollen grains. Euphytica 1993, 70, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bretagnolle, F.; Thompson, J. Tansley Review No. 78. Gametes with the somatic chromosome number: Mechanisms of their formation and role in the evolution of autopolyploid plants. New Phytol. 2006, 129, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.; Pagliarini, M.; Carraro, I. Abnormal Spindles in Second Meiosis in Canola (Brassica napus and Brassica campestris). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 1999, 42, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariani, A.; Campanoni, P.; Gianì, S.; Breviario, D. Meiotic mutants of Medicago sativa show altered levels of alpha- and beta-tubulin. Genome 2000, 43, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Meiotic Phases | Different Developmental Stages of Male Flower Buds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | ||
| Prophase I | Leptotene | 28.7% a (173 b) | 1.6% (8) | |||
| Zygotene | 11.9% (72) | 1.0% (5) | ||||
| Pachytene | 13.6% (82) | 2.6% (13) | ||||
| Diplotene | 27.7% (167) | 2.6% (13) | ||||
| Diakinesis | 14.1% (85) | 9.0% (45) | ||||
| Metaphase I | 3.7% (22) | 14.4% (72) | ||||
| Anaphase I | 0.3% (2) | 8.2% (41) | ||||
| Telophase I | 6.2% (31) | |||||
| Prophase II | 8.2% (41) | |||||
| Metaphase II | 3.6% (18) | |||||
| Anaphase II | 6.6% (33) | |||||
| Telophase II | 5.8% (29) | |||||
| Tetrad | 12.6% (63) | 4.5% (9) | ||||
| Microspore cells | 17.6% (88) | 95.5% (191) | 100.0% (100) | —— | ||
| Treatment No. | Treatment | Treatment Time/Volume | Average Diameter of Pollen (μm) | Pollen Diameter Range (μm) | 2n Pollen Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | control | - | 21.2 ± 0.3 c | 15.3~27.9 | 0.4 ± 0.0 e |
| 2 | soaking with colchicine 5% | 5 d | 21.7 ± 0.1 bc | 16.0~29.2 | 4.2 ± 0.3 b |
| 3 | soaking with colchicine 7% | 5 d | 21.8 ± 0.1 bc | 15.9~28.9 | 2.4 ± 0.1 d |
| 4 | injection with colchicine 5% | 120 mL | 23.6 ± 0.2 a | 15.5~30.1 | 3.1 ± 0.2 c |
| 5 | injection with colchicines 7% | 120 mL | 22.6 ± 0.1 b | 16.3~30.9 | 3.3 ± 0.3 c |
| 6 | high temperature (38 ± 2 °C) | 10 d | 23.8 ± 0.1 a | 16.6~33.2 | 5.7 ± 0.2 a |
| Treatment No. | Split Rate (%) | 2n Pollen Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyad | Triad | Tetrad | ||
| 1 | 0 | 2.0 ± 0.1 d | 98.0 ± 0.1 a | 0.5 ± 0.0 e |
| 2 | 1.4 ± 0.2 b | 14.2 ± 0.6 a | 84.4 ± 0.8 d | 4.4 ± 0.2 b |
| 3 | 1.0 ± 0.2 b | 8.6 ± 0.4 c | 90.4 ± 0.4 b | 2.7 ± 0.1 d |
| 4 | 1.4 ± 0.1 b | 11.3 ± 0.9 b | 87.3 ± 0.96 c | 3.7 ± 0.3 c |
| 5 | 1.4 ± 0.1 b | 10.0 ± 0.6 bc | 88.6 ± 0.6 bc | 3.3 ± 0.1 cd |
| 6 | 2.4 ± 0.4 a | 15.9 ± 0.8 a | 81.7 ± 1.1 d | 5.5 ± 0.4 a |
| Female Gamete Type | Male Gamete Type | Pollinated Female Flower Number | Seed Number | Fruit Set Rate (%) | Seedling Number | Germination Rate (%) | Triploid Number | Triploid Production Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SX (n) | SX (n) | 1500 | 1070 | 71.3 | 950 | 88.1 | 2 | 0.2 |
| SX (2n) | 1500 | 884 | 58.9 | 629 | 71.2 | 4 | 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Gan, J.; Xiong, H.; Mao, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Liu, C.; Fu, J. Production of Triploid Germplasm by Inducing 2n Pollen in Longan. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050437
Li H, Gan J, Xiong H, Mao X, Li S, Zhang H, Hu G, Liu C, Fu J. Production of Triploid Germplasm by Inducing 2n Pollen in Longan. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(5):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050437
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huimin, Jichang Gan, Hai Xiong, Xiaodan Mao, Shuwei Li, Huiyun Zhang, Guibing Hu, Chengming Liu, and Jiaxin Fu. 2022. "Production of Triploid Germplasm by Inducing 2n Pollen in Longan" Horticulturae 8, no. 5: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050437
APA StyleLi, H., Gan, J., Xiong, H., Mao, X., Li, S., Zhang, H., Hu, G., Liu, C., & Fu, J. (2022). Production of Triploid Germplasm by Inducing 2n Pollen in Longan. Horticulturae, 8(5), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050437





