Development of a Highly Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Incorporated with Flocculation of Carbon Particles for Rapid On-Site Diagnosis of Blood Disease Bacterium Banana
Abstract
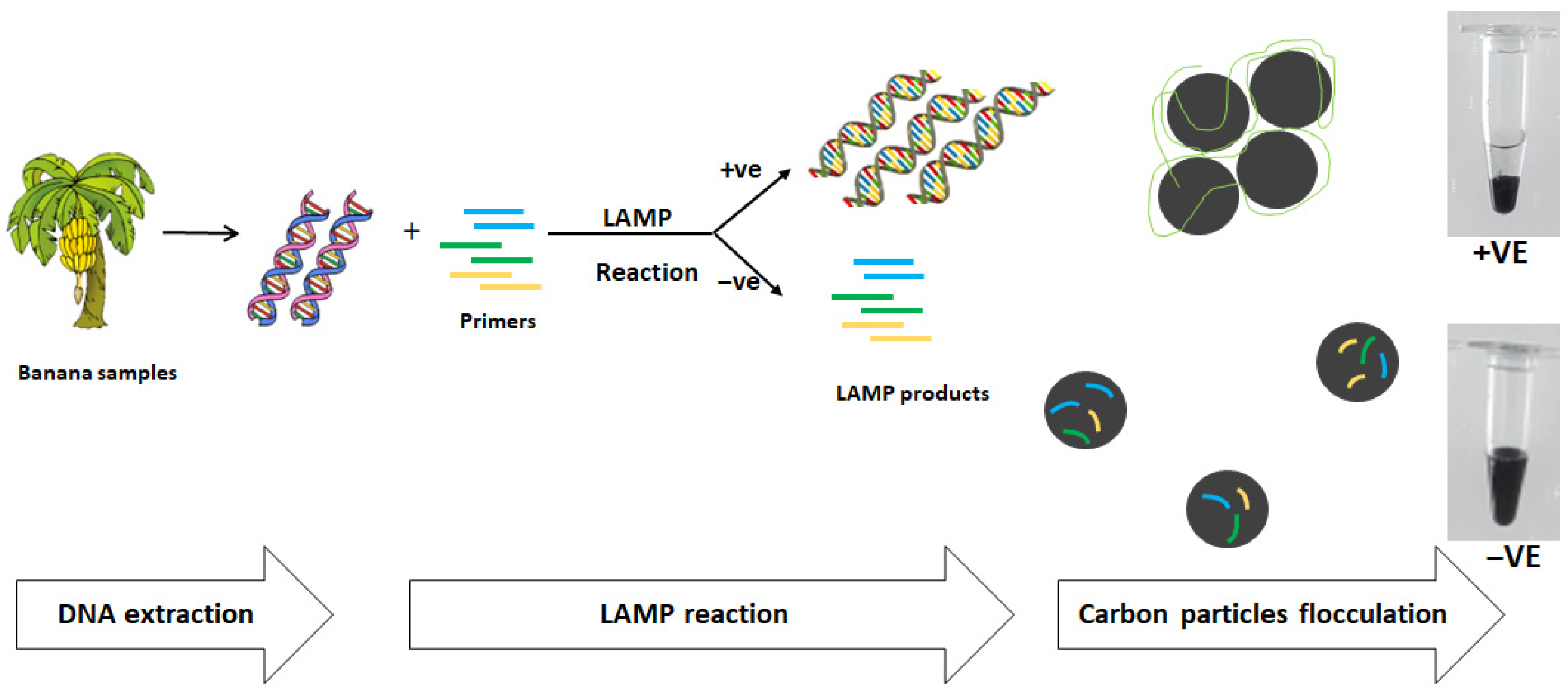
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pathogen Collection and Culture Conditions
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Design of LAMP Primer
2.4. LAMP Reaction
2.5. Analysis of LAMP Product Using Carbon Particles Flocculation
2.6. Inoculation Test
2.7. Field Test
2.8. Validation
3. Results
3.1. LAMP Assay Sensitivity
3.2. Specificity
3.3. Inoculation Test of BDB
3.4. Field Trial
3.5. Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahbandeh, M. World Production of Bananas in 2020, by Region. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/264003/production-of-bananas-worldwide-by-region/ (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Ploetz, R.C.; Kema, G.H.J.; Ma, L.J. Impact of Diseases on Export and Smallholder Production of Banana. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomme, G.; Dita, M.; Jacobsen, K.S.; Vicente, L.P.; Molina, A.; Ocimati, W.; Poussier, S.; Prior, P. Bacterial Diseases of Bananas and Enset: Current State of Knowledge and Integrated Approaches toward Sustainable Management. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden-Green, S.J. Diversity of Pseudomonas solanacearum and Related Bacteria in South Asia: New Direction of Moko Disease. In Bacterial Disease and its Causative Agent Pseudomonas solanacearum; Hayward, A.C., Hartman, G.L., Eds.; CAB International: Wellington, New Zealand, 1994; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gäumann, E. Onderzoekingen over de Bloedziekte Der Bananen Op Celebes, I. Meded. Inst. Plantenziekten 1921, 50, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Stover, R.H.; Espinoza, A. Blood Disease of Bananas in Sulawesi. Fruits 1992, 47, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Thwaites, R.; Eden-Green, S.J.; Black, R. Diseases Caused by Bacteria. In Diseases of Banana, Abacá and Enset; Jones, D.R., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, New Zealand, 2000; pp. 213–239. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, S.K.; Aziz, N.A.A.; Mustafa, M.; Laboh, R.; Ismail, I.S.; Sulaiman, S.R.; Azizan, A.A.; Devi, S. The Occurrence of Blood Disease of Banana in Selangor, Malaysia. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddenhagen, I. Blood Bacterial Wilt of Banana: History, Field Biology and Solution. Acta Hortic. 2009, 828, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, M.; Hayward, C.; Sly, L.I.; Fegan, M. Analysis of the Phylogenetic Relationships of Strains of Burkholderia Solanacearum, Pseudomonas Syzygii, and the Blood Disease Bacterium of Banana Based on 16S RRNA Gene Sequences. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remenant, B.; de Cambiaire, J.C.; Cellier, G.; Jacobs, J.M.; Mangenot, S.; Barbe, V.; Lajus, A.; Vallenet, D.; Medigue, C.; Fegan, M.; et al. Ralstonia Syzygii, the Blood Disease Bacterium and Some Asian, R. Solanacearum Strains Form a Single Genomic Species despite Divergent Lifestyles. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahetapy, B.; Maryana, N.; Manuwoto, S.; Mutaqin, K.H.; Latumahina, F. Test of Blood Disease Bacterium (Bdb) Transmission By Potential Insect Vectors. J. Hama Dan Penyakit Tumbuh. Trop. 2020, 20, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Safenkova, I.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. The Potential Use of Isothermal Amplification Assays for In-Field Diagnostics of Plant Pathogens. Plants 2021, 10, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruehrwein, R.A.; Ward, D.W. Mechanism of Clay Aggregation by Polyelectrolytes. Soil Sci. 1952, 73, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, T.W.; La Mer, V.K. The Energetics of Flocculation and Redispersion by Polymers. J. Colloid Sci. 1964, 19, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, A. The Relationship of Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas Solanacearum to Colony Appearance in a Tetrazolium Medium. Phytopathology 1954, 44, 693–695. [Google Scholar]
- Rohland, N.; Reich, D. Cost-effective, High-throughput DNA Sequencing Libraries for Multiplexed Target Capture. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deangelis, M.M.; Wang, D.G.; Hawkins, T.L. Solid-Phase Reversible Immobilization for the Isolation of PCR Products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4742–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Turechek, W.W. A Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay and Sample Preparation Procedure for Sensitive Detection of Xanthomonas Fragariae in Strawberry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, M.K.; Buela Parivallal, P.; Manjunatha, C.; Mahesh, H.B.; Pramesh, D.; Narayan, K.S.; Gopal, V.B.; Priyanka, K.; Puneeth, M.E.; Rangaswamy, K.T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Pre-Symptomatic Stage Detection of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae Infection in Pomegranate. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2020, 49, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, N.; Salacinas, M.; Mendes, O.; Seidi, M.F.; Meijer, H.J.G.; Schoen, C.D.; Kema, G.H.J. A Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification LAMP Assay Based on Unique Markers Derived from Genotyping by Sequencing Data for Rapid in Planta Diagnosis of Panama Disease caused by Tropical Race 4 in Banana. Plant Pathol. 2019, 68, 1682–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, M.G.; Botella, J.R. A Simple, Robust and Equipment-Free DNA Amplification Readout in Less than 30 Seconds. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 24440–24450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentini, P.; Fiammengo, R.; Sabella, S.; Gariboldi, M.; Maiorano, G.; Cingolani, R.; Pompa, P.P. Gold-Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Discrimination of Cancer-Related Point Mutations with Picomolar Sensitivity. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5530–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, C.Y. Sensitive Detection of Transcription Factors by Isothermal Exponential Amplification-Based Colorimetric Assay. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9544–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomean, S.; Wangmaung, N.; Sritongkham, P.; Promptmas, C.; Ittarat, W. Genotyping of α-Thalassemias by the Colorimetric Nanogold Probes. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 437, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomean, S.; Wangmaung, N.; Sritongkham, P.; Promptmas, C.; Mas-oodi, S.; Tanyong, D.; Ittarat, W. Molecular Diagnosis of α-Thalassemias by the Colorimetric Nanogold. Analyst 2014, 139, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Wang, W.; Mulchandani, A.; Shi, C. A Simple Colorimetric DNA Detection by Target-Induced Hybridization Chain Reaction for Isothermal Signal Amplification. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 457, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangchuen, A.; Chaumpluk, P.; Suriyasomboon, A.; Ekgasit, S. Colorimetric Detection of Ehrlichia Canis via Nucleic Acid Hybridization in Gold Nano-Colloids. Sensors 2014, 14, 14472–14487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Njiru, Z.K.; Mikosza, A.S.J.; Armstrong, T.; Enyaru, J.C.; Ndung’u, J.M.; Thompson, A.R.C. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method for Rapid Detection of Trypanosoma Brucei Rhodesiense. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Zha, L.; Fu, W.; Zou, M.; Li, W.; Xu, D. A Modified Visual Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for Diagnosis and Differentiation of Main Pathogens from Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Pu, J.; Qi, Y.; Yu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Peng, J. Development of a Real-Time Fluorescence Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Fusarium Oxysporum f. sp. Cubense Tropical Race 4 in Soil. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischbach, J.; Xander, N.C.; Frohme, M.; Glökler, J.F. Shining a Light on LAMP Assays- a Comparison of LAMP Visualization Methods Including the Novel Use of Berberine. Biotechniques 2015, 58, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leslie, D.C.; Li, J.; Strachan, B.C.; Begley, M.R.; Finkler, D.; Bazydlo, L.A.L.; Barker, N.S.; Haverstick, D.M.; Utz, M.; Landers, J.P. New Detection Modality for Label-Free Quantification of DNA in Biological Samples via Superparamagnetic Bead Aggregation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5689–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yao, B.; Fang, Q. Naked-Eye Detection of Nucleic Acids through Rolling Circle Amplification and Magnetic Particle Mediated Aggregation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, E.J.H.; Lau, H.Y.; Botella, J.R.; Trau, M. Re-Purposing Bridging Flocculation for on-Site, Rapid, Qualitative DNA Detection in Resource-Poor Settings. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5828–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Primer | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| F3 | AACTGGAGTGCTTGAAGC |
| B3 | CTCTGTGGCGATTGTCTAC |
| FIP | GGACCTGTCACTCGAACCATGCTGCGGACTCCACATTAC |
| BIP | GCTCGTCCGTCTCGTTGAGGGTTGCTTACCTTAGAGACTC |
| LF | GGCGTTACACCACATCCA |
| LB | GGTAATAGCCTCGCTCCG |
| PCR Fwd | GTCGCCGTCAACTCACTTTCC |
| PCR Rev | GTCGCCGTCAGCAATGCGGAATCG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azizi, M.M.F.; Lau, H.Y.; Abu Bakar, N.; Romeli, S.; Mohd Yusof, M.F.; Badrun, R.; Jaffar, N.S. Development of a Highly Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Incorporated with Flocculation of Carbon Particles for Rapid On-Site Diagnosis of Blood Disease Bacterium Banana. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050406
Azizi MMF, Lau HY, Abu Bakar N, Romeli S, Mohd Yusof MF, Badrun R, Jaffar NS. Development of a Highly Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Incorporated with Flocculation of Carbon Particles for Rapid On-Site Diagnosis of Blood Disease Bacterium Banana. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(5):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050406
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzizi, Mohammad Malek Faizal, Han Yih Lau, Norliza Abu Bakar, Sohana Romeli, Muhammad Fairuz Mohd Yusof, Rafidah Badrun, and Nur Sulastri Jaffar. 2022. "Development of a Highly Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Incorporated with Flocculation of Carbon Particles for Rapid On-Site Diagnosis of Blood Disease Bacterium Banana" Horticulturae 8, no. 5: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050406
APA StyleAzizi, M. M. F., Lau, H. Y., Abu Bakar, N., Romeli, S., Mohd Yusof, M. F., Badrun, R., & Jaffar, N. S. (2022). Development of a Highly Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Incorporated with Flocculation of Carbon Particles for Rapid On-Site Diagnosis of Blood Disease Bacterium Banana. Horticulturae, 8(5), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8050406





